Роль тучных клеток в прогрессировании контрактуры Дюпюитрена
Автор: Щудло Наталья Анатольевна, Ступина Татьяна Анатольевна, Варсегова Татьяна Николаевна, Останина Дарья Андреевна
Журнал: Гений ортопедии @geniy-ortopedii
Рубрика: Оригинальные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.29, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Данные мировой литературы свидетельствуют об участии тучных клеток в патогенезе болезни Дюпюитрена. Сведения о содержании тучных клеток в патологически изменённой ладонной фасции пациентов в зависимости от степени контрактуры отсутствуют. Цель. Изучить изменения численности, локализации и дегрануляционной активности тучных клеток в ладонном апоневрозе при контрактуре Дюпюитрена разной степени выраженности. Материалы и методы. Патогистологическое исследование операционного материала от 52 пациентов (49 мужчин и 3 женщины) с контрактурой Дюпюитрена (возраст 35-78 лет, средний возраст - 59,12 ± 1,25 года) с применением гистоморфометрии эпоксидных полутонких срезов, окрашенных метиленовым синим - основным фуксином. Пациенты распределены на две группы: 1 - с 1-2 (n = 16), 2 - с 3-4 (n = 36) степенью контрактуры. Результаты. В группе 2 чаще, чем в группе 1 регистрировали расположение тучных клеток среди контрактильно изменённых коллагеновых волокон плотной соединительной ткани. В группе 2 по сравнению с группой 1 статистически значимо увеличены медиана численной плотности тучных клеток на 33,79 % (p = 0,0508), медиана площади тучных клеток - на 48,40 % (p = 0,0008) и индекс дегрануляции тучных клеток - на 94,68 % (p = 0,00000001). Дискуссия. Наряду с изменением типичной локализации тучных клеток получены объективные доказательства увеличения их численности, активации и дегрануляции у пациентов с контрактурами тяжёлой степени. Выводы. Полученные результаты свидетельствуют о роли тучных клеток в прогрессировании контрактуры Дюпюитрена и расширяют представления о потенциальных терапевтических мишенях.
Ладонный фасциальный фиброматоз, контрактура дюпюитрена, гистология, морфометрия, тучные клетки
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142238194
IDR: 142238194 | УДК: 616.757.7-007.681: | DOI: 10.18019/1028-4427-2023-29-3-265-269
Текст научной статьи Роль тучных клеток в прогрессировании контрактуры Дюпюитрена
Контрактура Дюпюитрена (ладонный фасциальный фиброматоз) относится к фибропролиферативным заболеваниям, которое поражает не только ладонный апоневроз, но и все виды соединительных тканей ладони [1]. Формирование фиброматозных узлов и хорд [2] вызывает ограничение разгибательных движений, а затем и стойкие сгибательные контрактуры суставов пальцев, затрудняющие тонкую работу и социальную активность пациентов [3].
На протяжении сотен лет заболевание хорошо знакомо хирургам, предложены многочисленные методики его лечения, каждая из которых имеет сильные и слабые стороны [4, 5]. Однако не решены
проблемы рецидивов [6, 7] и прогнозирования течения заболевания у разных категорий пациентов [8] с целью адекватного выбора стратегии лечения. Несмотря на многочисленные исследования генетической предрасположенности [9, 10] и эпигенетических факторов [11, 12], этиопатогенез фиброматоза раскрыт не в полной мере вплоть до настоящего времени [13].
На сегодняшний день общепризнана концепция фасциального фиброматоза как миофибробластного заболевания [14, 15], но миофибробласты не являются специфичными для него [16]. Хотя инициирующий фактор наблюдающейся при фиброматозе аномальной
пролиферации фибробластов и их трансдифференцировки в миофибробласты неизвестен, современные исследования сосредоточены на TGF- β , IL-1 β и VEGF как потенциальных терапевтических мишенях в лечении болезни Дюпюитрена [17, 18]. Признавая ведущую роль TGF- β , другие авторы продемонстрировали усиленную пролиферацию миофибробластов в культурах тканей от пациентов с болезнью Дюпюитрена, стимулированную секрецией тучными клетками фактора IL-13 [19]. Между тем сведения о содержании тучных клеток в ладонной фасции пациентов с контрактурой Дюпюитрена скудны и противоречивы. При сравнении 10 тканевых образцов ладонной фасции от пациентов с идиопатическим карпальным синдромом с 20 аналогичными образцами от пациентов с контрактурой Дю-
пюитрена установлено 12-кратное повышение численности тучных клеток в ладонной фасции при болезни Дюпюитрена [20]. Однако при исследовании операционного материала от 100 пациентов с болезнью Дюпюитрена тучные клетки были описаны как спорадически встречающиеся вблизи кровеносных сосудов [21]. При этом в доступной литературе мы не встретили данных о содержании и морфофункциональном статусе тучных клеток в патологически изменённой ладонной фасции пациентов в зависимости от степени контрактуры Дюпюитрена.
Цель – изучить изменения численности, локализации и дегрануляционной активности тучных клеток в ладонном апоневрозе при контрактуре Дюпюитрена разной степени выраженности.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
Выполнено патогистологическое исследование операционного материала – ладонный апоневроз 52 пациентов (49 мужчин и 3 женщины) с контрактурой Дюпюитрена (возраст 35-78 лет, средний возраст – 59,12 ± 1,25 года).
Критерии включения – контрактура Дюпюитрена 1-2 степени (группа 1, n = 16) и 3-4 степени (группа 2, n = 36) по классификации R. Tubiana [22] с гистологически подтверждённым диагнозом фасциального фиброматоза. Критерии исключения – повреждения кисти, политравма в анамнезе.
Исследование выполнено в соответствии с этическими нормами Хельсинкской декларации (пересмотренной в октябре 2013 года), одобрено комитетом по этике (протокол № 4 (68) от 11.11.2020). От всех пациентов получено добровольное информированное согласие на публикацию результатов исследования без раскрытия личности.
Операционный материал – фрагменты патологически изменённого ладонного апоневроза фиксировали в смеси растворов глутарового альдегида и параформальдегида на фосфатном буфере с добавлением пикриновой кислоты, постфиксировали в 1 % растворе оксида осмия (VIII) и заливали в аралдит, полутонкие срезы изготавливали на ультратоме "Nova" LKB (Швеция). Учитывая полианионные свойства молекулы гепарина связываться с катионными красителями, для визуализации тучных клеток полутонкие срезы окрашивали полихромным красителем – метиленовым синим и ос-
новным фуксином [23]. Светооптическое исследование и оцифровку микропрепаратов осуществляли с помощью микроскопа «AxioScope.A1» и цифровой камеры «AxioCam» (Carl Zeiss MicroImaging GmbH, Германия). Количественные данные получены с использованием программного обеспечения «Zenblue» (Carl Zeiss MicroImaging GmbH, Германия). В полноцветных изображениях полутонких срезов при увеличении 1000× определяли численную плотность тучных клеток (N) в поле зрения и их площадь (S, мкм2), анализировали в среднем 20 полей зрения от каждого случая. Дегрануляцию (секреторную активность) тучных клеток определяли полуколичественным методом, предложенным Д.П. Линднер с соавторами (1980), путем расчета индекса дегрануляции (ИДГ):
ИДГ = A × 0 + Б × 1 + В × 2 + Г × 3/n , где А – неактивные клетки; Б – слабо дегранулирующие клетки; В – клетки с умеренной дегрануляцией; Г – клетки с сильной дегрануляцией; n – общее число клеток [24].
Статистическую обработку данных выполняли в компьютерной программе Attestat, версия 9.3.1 (сертификат о регистрации в Роспатенте № 2002611109). Количественные данные представляли в виде медиан и квартилей (Me (Р25-Р75)), так как для некоторых выборок гипотеза о нормальности была отклонена. Для проверки статистических гипотез о различиях при попарном сравнении групп между собой применяли критерий Манна – Уитни.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
При светооптическом исследовании полутонких срезов тучные клетки в обеих группах наблюдались преимущественно в рыхлой соединительной ткани вблизи сосудов, а также нервных фасцикул прилежащей к ладонной фасции фиброзно изменённой гиподермы (рис. 1 и 2, а, б).
В группе 2 чаще, чем в группе 1 регистрировали расположение тучных клеток вдали от кровеносных
сосудов в межклеточном веществе среди контрактиль-но изменённых коллагеновых волокон плотной соединительной ткани (рис. 2, в и г).
Гистоморфометрическое исследование (табл. 1) выявило, что в группе 2 по сравнению с группой 1 увеличены медиана численной плотности тучных клеток на 33,79 %, медиана площади тучных клеток – на 48,40 % и индекс дегрануляции тучных клеток – на 94,68 %.
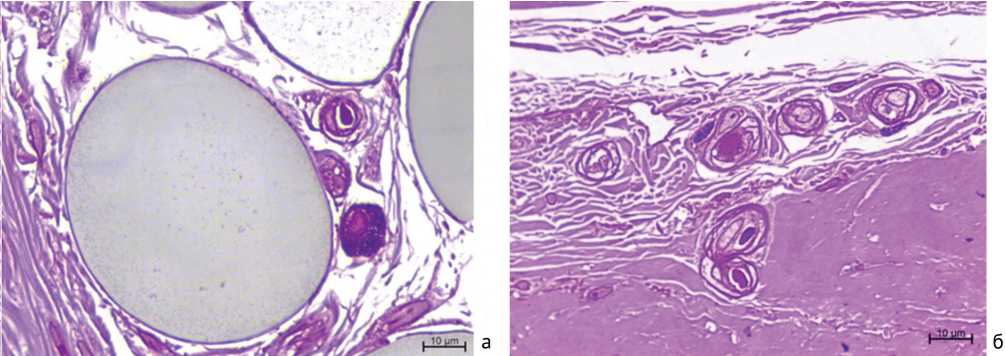
Рис. 1. Фрагменты полутонких срезов тканевых образцов от пациентов с 1-2 степенью контрактуры Дюпюитрена. Локализация тучных клеток в рыхлой соединительной ткани вблизи сосудов. Окраска метиленовый синий – основной фуксин. Увеличение – ×1000
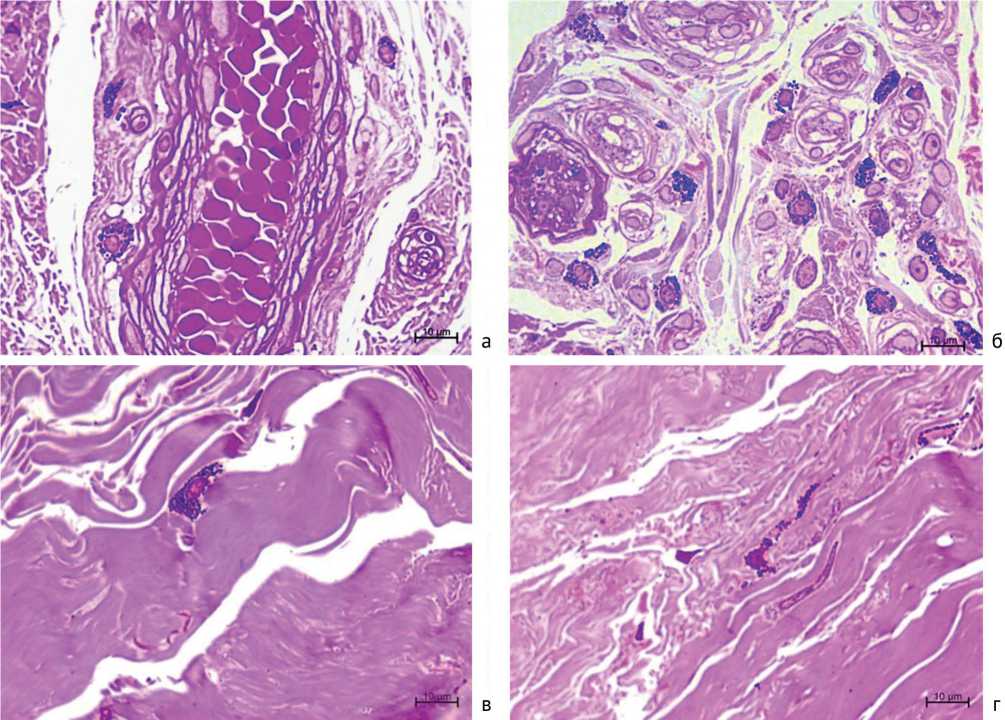
Рис. 2. Фрагменты полутонких срезов тканевых образцов от пациентов с 3-4 степенью контрактуры Дюпюитрена. Расположение тучных клеток в рыхлой соединительной ткани вблизи сосудов и нервных фасцикул (а, б), среди контрактильно изменённых коллагеновых волокон плотной соединительной ткани (в, г). Окраска метиленовый синий – основной фуксин. Увеличение – ×1000
Таблица 1
Морфометрические характеристики тучных клеток в ладонном апоневрозе при контрактуре Дюпюитрена
|
Параметр |
Группа 1 (n = 16) Группа 2 (n = 36) |
U, р |
|
|
Me (Р25-Р75) |
|||
|
Численная плотность (N, mm-2) |
1,45 (1,25-2,16) |
1,95 (1,5-2,57) |
U = 386,5; p = 0,05 |
|
Площадь (S, мкм2) |
28,16 (19,57-35,52) |
41,79 (31,28-50,94) |
U = 456; p = 8 × 10-4 |
|
Индекс дегрануляции (ИДГ) |
0,94 (0,63-1,16) |
1,83 (1,64-2,15) |
U = 571,5; p = 1 × 10-8 |
Примечание: Me – медиана; Р25-Р75 – процентили; U – значения критерия Манна – Уитни, различия значимы при р ≤ 0,05.
ДИСКУССИЯ
Многочисленные исследования на животных и людях показали, что тучные клетки промотируют формирование рубцов; в фетальных тканях численность и активация тучных клеток снижена – соответственно раны заживают без образования рубца [25, 26]. При моделировании посттравматических контрактур у экспериментальных животных установлено значительное повышение содержания миофибробластов, тучных клеток и нейропептидов в суставной капсуле [27]. Подобно заживлению кожных ран, такие заболевания соединительной ткани, как болезнь Дюпюитрена или болезнь Пейрони, могут быть затронуты воспалением [28, 29], однако вклад тучных клеток в процесс дегенерации соединительной ткани при этих заболеваниях практически не изучен.
T.E. Schubert с соавторами [20] обнаружили 12-кратное увеличение количества тучных клеток при контрактуре Дюпюитрена по сравнению с нормальной тканью фасции, отмечена их ассоциация со спраутин-гом ноцицептивных волокон, однако C. Mayerl et al. в материале от 100 пациентов [21] выявили спорадические тучные клетки вблизи кровеносных сосудов.
В нашем исследовании впервые на достаточном клиническом материале установлены существенные качественные и количественные отличия тучных клеток в зависимости от степени контрактуры Дюпюитрена. Типичная локализация тучных клеток вблизи кровеносных сосудов отражает их участие в регуляции сосудистого гомеостаза и ангиогенеза в норме [30] и определяет вазогенные факторы патогенеза ладонного фасциального фиброматоза [31]. Для пациентов с тяжёлой (3-4) степенью контрактуры Дюпюитрена помимо паравазального расположения тучных клеток
характерна их локализация вдали от нервов гиподермы и кровеносных сосудов в межклеточном веществе плотной соединительной ткани среди контрактильно изменённых коллагеновых волокон, что указывает на их участие в ремоделировании внеклеточного матрикса, при этом численная плотность, площадь и индекс дегрануляции тучных клеток значительно повышены по сравнению с аналогичными гистоморфометриче-скими параметрами группы пациентов с 1-2 степенью контрактуры. Таким образом, наряду с изменением типичной локализации тучных клеток у пациентов с контрактурами тяжёлой степени получены объективные доказательства увеличения их численности, активации и дегрануляции.
Известно, что активация и дегрануляция тучных клеток промотирует экспериментальный почечный фиброз [32], клинически выявлена корреляция численности тучных клеток с выраженностью лёгочного фиброза [33], установлена их роль в патогенезе фиброза печени [34].
Доклинические исследования выявили благоприятное дозозависимое влияние стабилизатора мембран тучных клеток кетотифена на выраженность фиброза суставной капсулы и биомеханические параметры посттравматической контрактуры, опосредование снижением содержания миофибробластов, тучных клеток и P-реактивных нервных волокон в суставной капсуле [35, 36]. Поскольку данный препарат более 40 лет применяется в лечении аллергических заболеваний, перспективны клинические исследования его влияния на течение контрактуры Дюпюитрена у пациентов с сопутствующими аллергическими заболеваниями.
ВЫВОДЫ
Полученные результаты свидетельствуют о роли пюитрена и расширяют представления о потенциаль-тучных клеток в прогрессировании контрактуры Дю- ных терапевтических мишенях.
Список литературы Роль тучных клеток в прогрессировании контрактуры Дюпюитрена
- Mareallum P., Hueston J.T. The pathology of Dupuytren's contracture. Aust NZ J Surg. 1962;31:241-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1962.tb03271.x
- Reilly RM, Stern PJ, Goldfarb CA. A retrospective review of the management of Dupuytren's nodules. J Hand Surg Am. 2005;30(5):1014-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2005.03.005
- Boe C, Blazar P, Iannuzzi N. Dupuytren Contractures: An Update of Recent Literature. J Hand Surg Am. 2021;46(10):896-906. doi: 10.1016/j. jhsa.2021.07.005
- Denkler KA, Park KM, Alser O. Treatment Options for Dupuytren's Disease: Tips and Tricks. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022;10(1):e4046. doi: 10.1097/G0X.0000000000004046
- Шевцов В.И., Исмайлов Г.Р., Козьмина Т.Е., Знаменская М.Г., Данилкин М.Ю. Возможности чрескостного остеосинтеза при лечении больных с приобретенной патологией кисти. Гений Ортопедии. 2002;(1):19-23.
- Kan HJ, Verrijp FW, Hovius SER, van Nieuwenhoven CA; Dupuytren Delphi Group; Selles RW. Recurrence of Dupuytren's contracture: A consensus-based definition. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0164849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164849
- Könneker S, Broelsch GF, Krezdorn N, Dastagir K, Kuhbier JW, Paprottka FJ, Vogt PM. Multiple Recurrences in Aggressive Forms of Dupuytren's Disease-Can Patients Benefit from Repeated Selective Fasciectomy? Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2017 23;5(2):e1247. doi: 10.1097/G0X.0000000000001247
- Broekstra DC, Lanting R, Werker PMN, van den Heuvel ER. Disease Course of Primary Dupuytren Disease: 5-Year Results of a Prospective Cohort Study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022;149(6):1371-1378. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000009115
- Becker K, Tinschert S, Lienert A, Bleuler PE, Staub F, Meinel A, Rößler J, Wach W, Hoffmann R, Kühnel F, Damert HG, Nick HE, Spicher R, Lenze W, Langer M, Nürnberg P, Hennies HC. The importance of genetic susceptibility in Dupuytren's disease. Clin Genet. 2015;87(5):483-7. doi: 10.1111/cge.12410
- Michou L, Lermusiaux JL, Teyssedou JP, Bardin T, Beaudreuil J, Petit-Teixeira E. Genetics of Dupuytren's disease. Joint Bone Spine. 2012;79(1):7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.05.027
- Alencar FHU, Perini JA, Monteiro AV, Duarte MEL, Motta GDR, Guimaräes JAM. Epidemiology of Dupuytren disease and Patients Undergoing Selective Fasciectomy. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2021;56(4):478-484. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1721839
- Hahn P. Epidemiologie des Morbus Dupuytren [Epidemiology of Dupuytren's disease]. Orthopade. 2017;46(4):298-302. (In German) doi: 10.1007/ s00132-017-3384-8
- Samulenas G, Insodaite R, Kunceviciene E, Poceviciute R, Masionyte L, Zitkeviciute U, Pilipaityte L, SmalinskieneA. The Role of Functional Polymorphisms in the Extracellular Matrix Modulation-Related Genes on Dupuytren's Contracture. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(5):743. doi: 10.3390/genes13050743
- Musumeci M, Vadala G, Russo F, Pelacchi F, Lanotte A, Denaro V. Dupuytren's disease therapy: targeting the vicious cycle of myofibroblasts? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015;19(12):1677-87. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2015.1068758
- Walthall J, Anand P, Rehman UH. Dupuytren Contracture. 2022 Oct 31. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-.
- Tai Y, Woods EL, Dally J, Kong D, Steadman R, Moseley R, Midgley AC. Myofibroblasts: Function, Formation, and Scope of Molecular Therapies for Skin Fibrosis. Biomolecules. 2021;11(8):1095. doi: 10.3390/biom11081095
- Bianchi E, Taurone S, Bardella L, Signore A, Pompili E, Sessa V, Chiappetta C, Fumagalli L, Di Gioia C, Pastore FS, Scarpa S, Artico M. Involvement of pro-inflammatory cytokines and growth factors in the pathogenesis of Dupuytren's contracture: a novel target for a possible future therapeutic strategy? Clin Sci (Lond). 2015;129(8):711-20. doi: 10.1042/CS20150088
- Zhou C, Zeldin Y, Baratz ME, Kathju S, Satish L. Investigating the effects of Pirfenidone on TGF-ß1 stimulated non-SMAD signaling pathways in Dupuytren's disease -derived fibroblasts. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-2486-3
- Akbar M, Garcia-Melchor E, Chilaka S, Little KJ, Sood S, Reilly JH, Liew FY, McInnes IB, Millar NL. Attenuation of Dupuytren's fibrosis via targeting of the STAT1 modulated IL-13Ra1 response. Sci Adv. 2020;6(28):eaaz8272. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz8272
- Schubert TE, Weidler C, Borisch N, Schubert C, Hofstädter F, Straub RH. Dupuytren's contracture is associated with sprouting of substance P positive nerve fibres and infiltration by mast cells. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(3):414-5. doi: 10.1136/ard.2005.044016
- Mayerl C, Del Frari B, Parson W, Boeck G, Piza-Katzer H, Wick G, Wolfram D. Characterisation of the inflammatory response in Dupuytren's disease. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2016;50(3):171-9. doi: 10.3109/2000656X.2016.1140054
- Tubiana R. Dupuytren's disease of the radial side of the hand. Hand Clin. 1999 Feb;15(1):149-159.
- Григорьев И.П., Коржевский Д.Э. ^временные технологии визуализации тучных клеток для биологии и медицины (обзор). Современные технологии в медицине. 2021;13(4):93-107. doi: 10.17691/stm2021.13.4.10
- Линднер Д.П., Поберин И.А., Розкин М.Я., Ефимов В.С. Морфометрический анализ популяции тучных клеток. Архив патологии. 1980;6:60-64.
- Ud-Din S, Wilgus TA, Bayat A. Mast Cells in Skin Scarring: A Review of Animal and Human Research. Front Immunol. 2020;11:552205. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.552205
- Wilgus TA, Ud-Din S, Bayat A. A Review of the Evidence for and against a Role for Mast Cells in Cutaneous Scarring and Fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9673. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249673
- Hildebrand KA, Zhang M, Salo PT, Hart DA. Joint capsule mast cells and neuropeptides are increased within four weeks of injury and remain elevated in chronic stages of posttraumatic contractures. J Orthop Res. 2008;26(10):1313-9. doi: 10.1002/jor.20652
- Karkampouna S, Kreulen M, Obdeijn MC, Kloen P, Dorjee AL, Rivellese F, Chojnowski A, Clark I, Kruithof-de Julio M. Connective Tissue Degeneration: Mechanisms of Palmar Fascia Degeneration (Dupuytren's Disease). Curr Mol Biol Rep. 2016;2(3):133-140. doi: 10.1007/s40610-016-0045-3
- Patel DP, Christensen MB, Hotaling JM, Pastuszak AW. A review of inflammation and fibrosis: implications for the pathogenesis of Peyronie's disease. World J Urol. 2020;38(2):253-261. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02815-6
- Krystel-Whittemore M, Dileepan KN, Wood JG. Mast Cell: A Multi-Functional Master Cell. Front Immunol. 2016;6:620. doi: 10.3389/ fimmu.2015.00620
- Щудло Н.А., Варсегова Т.Н., Ступина Т.А., Щудло М.М. Типы и стадии сосудистого ремоделирования при контрактуре Дюпюитрена (анализ 506 артерий в операционном материале 111 пациентов). Гений ортопедии. 2020;26(2):179-184. doi: 10.18019/1028-4427-2020-26-2-179-184
- Summers SA, Gan PY, Dewage L, Ma FT, Ooi JD, O'Sullivan KM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Kitching AR, Holdsworth SR. Mast cell activation and degranulation promotes renal fibrosis in experimental unilateral ureteric obstruction. Kidney Int. 2012;82(6):676-85. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.211
- Overed-Sayer C, Rapley L, Mustelin T, Clarke DL. Are mast cells instrumental for fibrotic diseases? Front Pharmacol. 2014;4:174. doi: 10.3389/ fphar.2013.00174
- Weiskirchen R, Meurer SK, Liedtke C, Huber M. Mast Cells in Liver Fibrogenesis. Cells. 2019;8(11):1429. doi: 10.3390/cells8111429
- Monument MJ, Hart DA, Befus AD, Salo PT, Zhang M, Hildebrand KA. The mast cell stabilizer ketotifen reduces joint capsule fibrosis in a rabbit model of post-traumatic joint contractures. Inflamm Res. 2012;61(4):285-92. doi: 10.1007/s00011-011-0409-3
- Schneider PS, Johal H, Befus AD, Salo PT, Hart DA, Hildebrand KA. The Dose-Response Effect of the Mast Cell Stabilizer Ketotifen Fumarate on Posttraumatic Joint Contracture: An in Vivo Study in a Rabbit Model. JB JS Open Access. 2021;6(1):e20.00057. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.0A.20.00057


