Role of Crystalline Silica (SiO2) in Assessing the Fame and Quality of Quarries and Work Hazards in Roman Times
Автор: Bouazza H., Kelouaz Kh., Bouazza A., Bouazza L.
Журнал: Science, Education and Innovations in the Context of Modern Problems @imcra
Статья в выпуске: 7 vol.8, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This study aims to shed light on the occupational diseases that affected quarry workers during the Roman period, particularly silicosis caused by inhaling crystalline silica dust. While physical injuries like fractures were common, the focus here is on respiratory diseases previously overlooked. The study introduces a new methodology to assess the impact of Roman quarries on workers' health, and the quality and uses of the extracted stones. It involves petrographic examination, XRD (X-ray Diffraction), and XRF (X-ray Fluorescence) analysis to measure the content of various types of crystalline silica in ancient quarries. The study analyzes archaeological evidence and skeletal remains from sites like Pompeii and Herculaneum and reviews ancient historians like Pliny the Elder and Strabo. This research offers a deeper understanding of the health risks associated with harsh working conditions in Roman quarries, particularly focusing on the prevalence of silicosis among workers.
Silicosis, Roman quarries, Occupational diseases, Crystalline silica, Analysis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/16010884
IDR: 16010884 | DOI: 10.56334/sei/8.7.61
Текст научной статьи Role of Crystalline Silica (SiO2) in Assessing the Fame and Quality of Quarries and Work Hazards in Roman Times
RESEARCH ARTICLE Role of Crystalline Silica (SiO2) in Assessing the Fame and Quality of Quarries and Work Hazards in Roman Times Haithem Bouazza / / / / / \ \ \ Doctor Laboratory of Community and Local Development Issues in Algeria, University of Hassiba Ben Bouali, Department of Archeology, Ouled fares Chlef, Algeria Email: Khaled Kelouaz Doctor Laboratory of Community and Local Development Issues in Algeria, University of Hassiba Ben Bouali, Department of Archeology, Ouled fares Chlef, Algeria Email: Ali Bouazza / Doctor University of Mostaganem, Provincial Directorate of University Services Mostaganem, Algeria Email: Leila Bouazza / Doctor Ministry of Culture and Arts, Public National Museum Nasreddine Dinet, Msila Boussaada, Algeria Email: X Doi Serial / Keywords Silicosis, Roman quarries, Occupational diseases, Crystalline silica, Analysis. Abstract This study aims to shed light on the occupational diseases that affected quarry workers during the Roman period, particularly silicosis caused by inhaling crystalline silica dust. While physical injuries like fractures were common, the focus here is on respiratory diseases previously overlooked. The study introduces a new methodology to assess the impact of Roman quarries on workers' health, and the quality and uses of the extracted stones. It involves petrographic examination, XRD (X-ray Diffraction), and XRF (X-ray Fluorescence) analysis to measure the content of various types of crystalline silica in ancient quarries. The study analyzes archaeological evidence and skeletal remains from sites like Pompeii and Herculaneum and reviews ancient historians like Pliny the Elder and Strabo. This research offers a deeper understanding of the health risks associated with harsh working conditions in Roman quarries, particularly focusing on the prevalence of silicosis among workers. Declarations: Conflict of Interest There are no conflicts of interest related to this paper. Citation Bouazza H, Kelouaz Kh., Bouazza A., Bouazza L. (2025). Role of Crystalline Silica (SiO2) in Assessing the Fame and Quality of Quarries and Work Hazards in Roman Times. Science, Education and Innovations in the Context of Modern Problems, 8(7), 581-595; doi:10.56352/sei/8.7.61. \ Licensed X © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Science, Education and Innovations in the context of modern problems (SEI) by
IMCRA - International Meetings and Journals Research Association (Azerbaijan). This is an open access article under the CC BY license .
Beyond the physical injuries such as wounds and fractures commonly suffered by quarry workers in ancient times, especially during the Roman period, archaeological studies of skeletal remains from sites like Pompeii and Herculaneum, as well as limestone quarries in ancient Egypt, provide clear evidence of frequent workplace accidents. In Pompeii, skeletal remains of miners display signs of poorly healed fractures in long bones, indicating frequent accidents(Roberts & Buikstra, 2003, pp. 120-130). In Egyptian limestone quarries, patterns of fractures in ribs and long bones suggest injuries from falls or heavy stone handling (David, 1999, pp. 98-110). In Herculaneum, repeated fractures in the spine and limbs point to recurrent accidents and inadequate medical care (D'Anastasio & Capasso, 2001, pp. 143-155). Similar evidence from Roman Britain, such as at Lydney Port, shows that miners frequently suffered rib and limb fractures, with varying stages of healing, indicating insufficient recovery periods after injuries (Roberts & Buikstra, 2003, pp. 156-168). Further evidence from mines in Rio Tinto, Spain, and other sites like Jerash in Jordan and Breda in Germany shows that workers endured injuries due to harsh working conditions and chronic exposure to mineral dust (Domergue, 1990, pp. 213-220) (Weisgerbe, 2000, pp. 87-95) (Jackson, 1988, pp. 145-150) (Fiema, 2002, pp. 45-52). The archaeological analysis of these fractures provides a deeper understanding of the nature of work and the health risks faced by workers in ancient times .
This study aims to address a previously overlooked disease, known as silicosis, a chronic lung disease caused by inhaling crystalline silica dust. Although there is no evidence that Roman physicians specifically identified this disease, they were aware of the health problems caused by dust inhalation. This awareness is documented in the works of ancient historians like Pliny the Elder and Strabo, as mentioned earlier. Silica, present in materials like sandstone, limestone, and granite, was a significant component of Roman quarries. Vitruvius noted the prevalent use of limestone by the Romans(Vitruvius, 1931-1934, p. 75) , which was commonly used in North African buildings. The study analyzes the incidence of silicosis among Roman quarry workers based on the materials they extracted.
-
1. Mechanism of Silicosis:
-
2. Amount of Silica in Sandstone, Limestone, Granite, and Marble:
Silicosis occurs when crystalline silica dust, inhaled from sources such as sandstone, limestone, granite, and marble(Silicosis, 2024), reaches the alveoli in the lungs, where the body cannot effectively remove it(Silicosis, 2024). The immune system's macrophages attempt to engulf and destroy the silica particles, but silica resists digestion, leading to the destruction of macrophages. This process releases enzymes that cause inflammation and tissue damage(Silicosis, 2024). The resulting scarring reduces lung elasticity and impairs breathing over time, with symptoms worsening progressively(American Lung Association, 2024). Chronic exposure can lead to persistent cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, unintended weight loss, and, in severe cases, respiratory failure and death(Symptoms and Medical Monitoring, 2024).
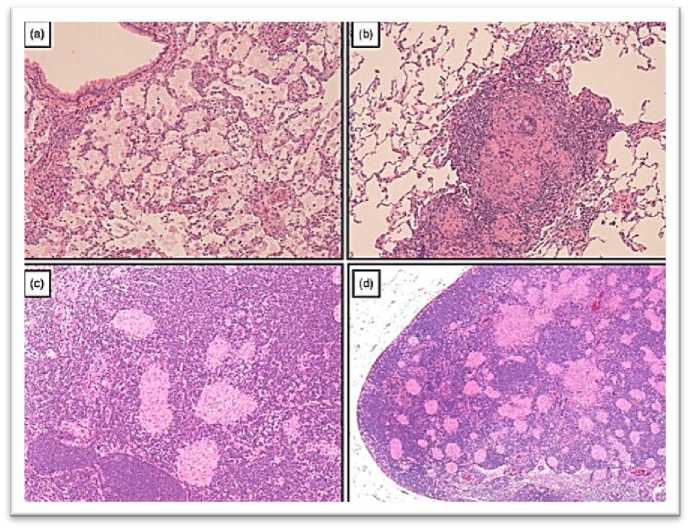
Fig.1 The light microscopy images show lung tissue from rats exposed to crystalline silica particles for 6 months. Observations include the disintegration of macrophages and the infiltration of foamy macrophages in the alveoli, along with the activation of alveolar surfactant proteins (Panel A). Granuloma formations are visible in the interstitial tissue (Panel B). Multiple granulomas are observed in intrapulmonary lymph nodes (Panel C) and peribronchial lymph nodes (Panel D).Source:(Gernand & al, 2010)
Sandstone contains a high percentage of silica, primarily composed of quartz, a form of crystalline silica. The silica content in sandstone ranges from 25% to 75%(Cleveland Clinic, 2024). In contrast, limestone has a lower silica content compared to sandstone, primarily consisting of calcium carbonate, but it can contain small amounts of silica, ranging from 10% to 30%(American Lung Association, 2024). Granite has a moderate silica content ranging from 20% to 60%, composed of silica minerals such as quartz, feldspar, and mica(Verywell Health, 2024). Marble, primarily composed of calcium carbonate like limestone, contains small amounts of silica, ranging from 1% to 5%. The concentration of silica in marble is much lower than in sandstone and granite (Symptoms and Medical Monitoring, 2024).
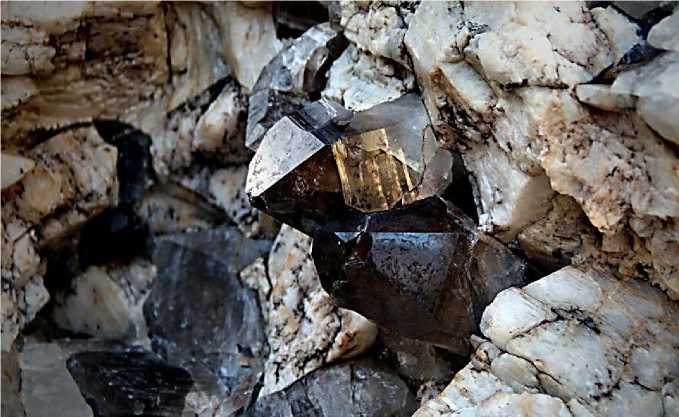

Fig.2 Hexagonal quartz crystals found in granite, a type of silica. Source:(Anna, 2024)
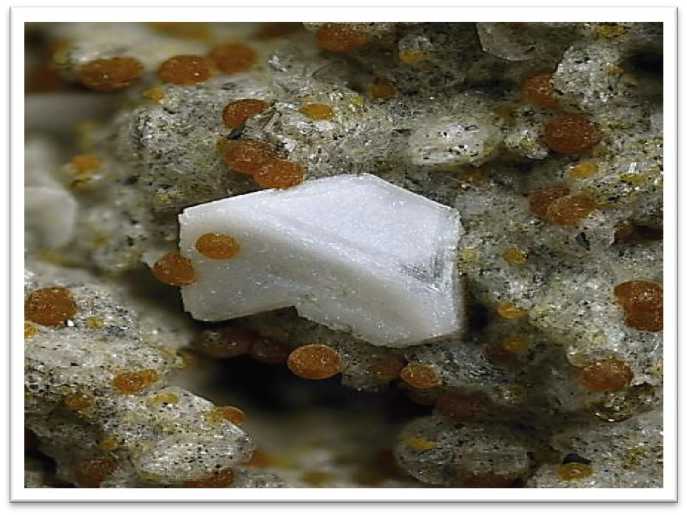

Fig.3 Cristobalite crystals, a type of silica found in volcanic rocks. Source: (Mindat, 2024)

Fig.4 Left: Scanning electron microscope image of a bipyramidal quartz crystal, with slightly rounded edges and tips. Right: Thin section of volcanic quartz from the same deposits, showing fractures resulting from the section preparation process. Both grains are approximately 0.3 mm in width. Source:(Asiasellet, 2024) /
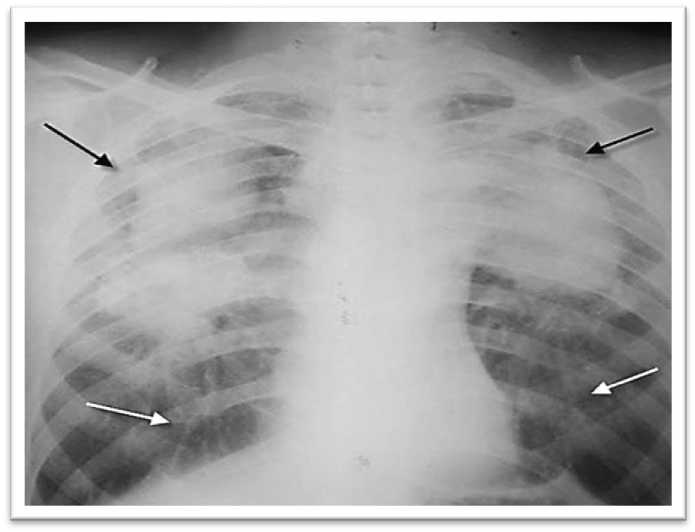
Fig.5 X-ray image of a lung from an individual with advanced silicosis, showing densities in the soft lung tissue in both upper lobes (black arrows) with linear scarring extending from the lower lobes (white arrows). Source: (Learning Radiology, 2024).
3/ Diagnosing Silicosis from a Roman-Era Skeleton:
Diagnosing silicosis, or any lung disease caused by inhaling dust, from the skeletal remains of a person who lived during the Roman era is a complex task. However, certain indicators can help researchers identify this disease through skeletal remains. This process involves looking for indirect evidence that suggests the presence of a chronic lung disease. Several methods and steps can be employed, such as analyzing long bones, examining ribs and the spine, conducting chemical analysis, using microscopic examination, and studying the common markers of diseases. In long bone analysis, signs of fractures may appear due to osteoporosis caused by reduced physical activity from chronic shortness of breath, as well as the presence of chronic infections that may result from a decline in overall health and a weakened immune system (Roberts & Mancheste, 2007, pp. 154-163)When examining the ribs and spine , structural changes such as hypertrophy or erosion caused by long-term inflammation in the lungs can be observed (Prowse & al, 2004, p. 475) (Roberts & Mancheste, 2007, p. 165). Chemical analysis of bones, such as stable isotope analysis, can reveal dietary patterns and overall health status, indicating the presence of chronic diseases. The chemical analysis can also detect high levels of heavy metals, suggesting chronic exposure to silica dust (Prowse & al, 2004, p. 482). Microscopic analysis can also be used to examine the bones under a microscope to look for signs of chronic pulmonary fibrosis, such as the presence of small silica deposits (Prowse & al, 2004, p. 478).Finally, it is important to consider the presence of other symptoms concurrent with silicosis,such as pulmonary tuberculosis (TB), which was common in ancient times and can be exacerbated by lung diseases (Roberts & Mancheste, 2007, p. 177).Diagnosing silicosis through a Roman skeleton requires a multidisciplinary approachthat combines paleopathology, analytical chemistry, and microscopic analysis. This approach can help researchers detect signs of chronic respiratory diseases that affected ancient Roman workers due to exposure to silica dust.
4/The impact of working in Roman quarries on workers' health
At first glance, it may seem impossible to assess, but numerous attempts have led to the development of a method involving a series of physical and chemical analyses. This includes measuring the crystalline silica content and comparing it with the availability of water in the area. This method can help assess the health conditions within the quarry. The method's steps can be summarized as follows:
A/ Sample Collection: In the study of Roman quarries, collecting stone samples is a fundamental step to understand the characteristics of the quarry and the potential health impacts on workers. Between 3 to 10 stone samples, sized between 3
to 6 cm³, are selected from various locations within the quarry to ensure comprehensive geological representation. GPS technology is used to accurately document the geographical location of each sample, aiding in precise site analysis and identification of the geographical origins of the samples. Field conditions around each site, such as fractures, humidity, and temperature, are documented to provide a complete context for the sample analysis. This methodology ensures the reliable collection of data for studying the health risks associated with working in Roman quarries.
B/ Transportation and Storage of Stone Samples: The containers used play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the samples and preventing damage or contamination. It is preferable to use sturdy containers, such as thick plastic or metal, to ensure they can withstand the heavy weight and protect the samples. The containers are lined with materials like foam or sponge to absorb shocks and prevent internal collisions. The containers are labeled with waterproof and durable labels to indicate essential information about the sample, such as sample number, collection date, geographic location, and any notes on the collection conditions. This helps in easily tracking the samples and prevents mix-ups. Although stone samples do not require stringent sterilization like biological samples, maintaining the cleanliness of containers is essential to avoid contamination with other materials that could affect the analysis results. The storage of samples involves securing the containers in a stable environmental location, away from extreme fluctuations in temperature and humidity. This precaution ensures that the properties of the samples remain unchanged due to environmental conditions, thereby enhancing the accuracy of analytical results. These measures ensure that the samples reach the laboratory in optimal condition, which in turn improves the precision of analyses and the validity of scientific conclusions.
C/ Sample Analysis: This involves a series of standard procedures in the analysis of geological samples, including preparing and evaluating the samples using various techniques to obtain accurate information about their mineral composition. Preparation begins with thoroughly cleaning the rock samples to remove any impurities or contaminants that might affect the analysis results. This typically includes washing the samples with distilled water and possibly using a brush to remove fine particles. After cleaning, the samples are dried and prepared for slicing into thin sections if necessary. Then, a series of analyses are conducted, including:
Petrographic Examination
XRD Analysis (X-ray Diffraction)
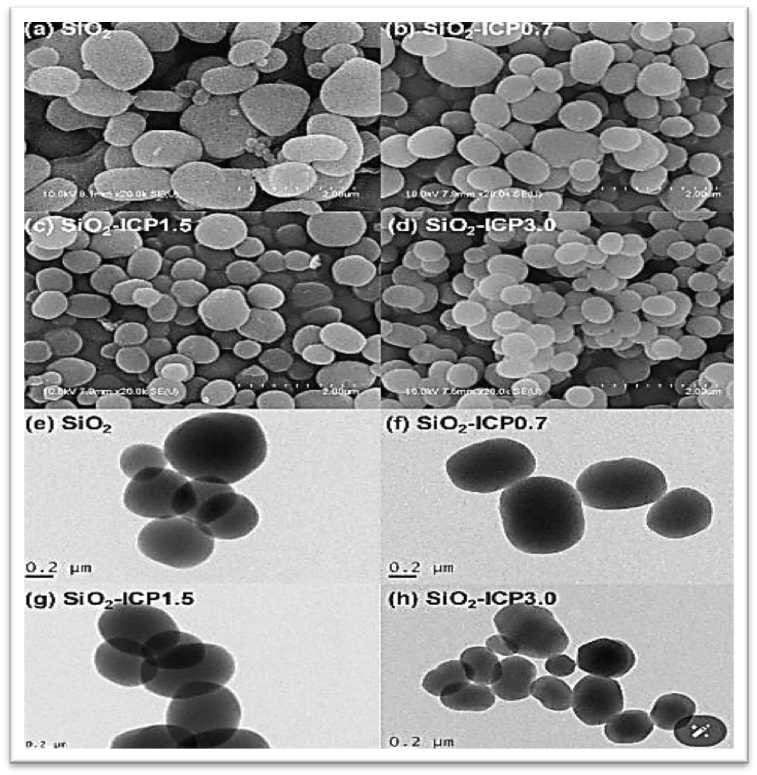
Fig.6 SEM and TEM images of SiO 2 nanoparticles according to ICP concentration. Source: (Cho, Mansoo, Choi, Jung, & Seon, 2020) * (Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): This technique uses electrons instead of light to create a detailed image of the surface. SEM reveals the surface details of a sample with high resolution, aiding in the assessment of surface structure and the composition of nanoparticles./ Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM): This technique also uses electrons, but they pass through the sample, providing higher-resolution images of the internal structure of materials. TEM is useful for observing the internal structure of nanoparticles, including shape, size, and internal distribution./ ICP Concentration: This usually refers to "Inductively Coupled Plasma" (ICP), a method used to analyze the chemical concentrations of elements in various samples. In the mentioned context, "ICP concentration" likely refers to determining the concentrations of specific elements within SiO 2 nanoparticles using this technique. In ICP analysis, the sample is converted into plasma by heating it to very high temperatures using an induction power source. This plasma excites the atoms in the sample, causing them to emit photons at specific wavelengths that can be measured to determine the quantitative concentrations of different elements within the sample. This technique is widely used in fields such as environmental chemistry, materials science, and geological research to accurately analyze chemical composition. For more details, see (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 2018)
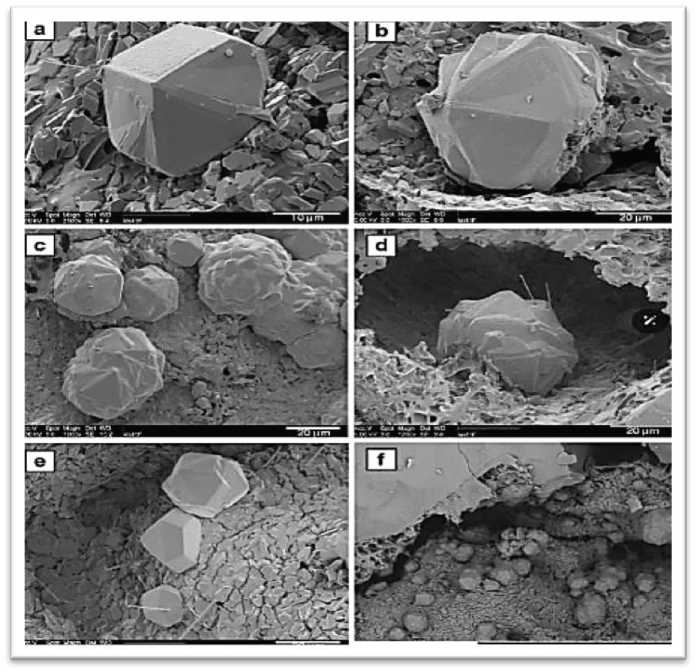
Fig.7 Scanning electron microscope micrographs of vertical cristobalite in rough rock fragments. Source:(Horwell, Williamson, Llewellin, & al, 2013).
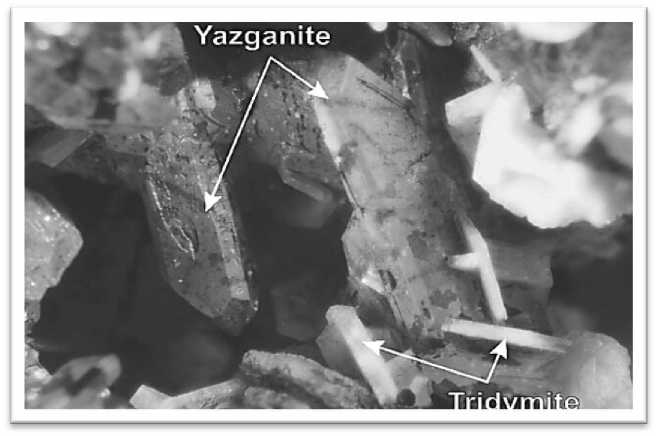
Fig.8 Yazganite and tridymite minerals under a binocular microscope. Source: (Karaman, Mehmet, & al, 2015)
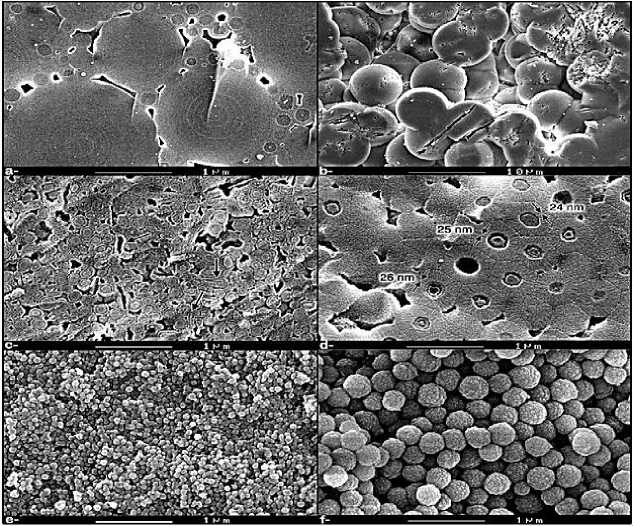
Fig.9 Scanning electron microscope images (30,000×) of opal samples. Source(Graetsch, Horst, & al., 2024)
Based on the analysis above, we can determine the hierarchy of stone types by the presence of different forms of crystalline silica. Sandstone is found to contain high levels of quartz, owing to its significant resistance to erosion and weathering. Opal can also be present as deposits in the interstices between grains. Granite, in addition to quartz, includes significant amounts of feldspar and mica. Cristobalite and tridymite may occur in metamorphosed granite under high-temperature conditions. Limestone and marble contain smaller amounts of quartz as secondary minerals or impurities. Cristobalite and tridymite are rarely found in these rocks due to their carbonate composition. Consequently, we conclude that the likelihood of respiratory diseases such as bronchitis, silicosis, and lung cancer varies depending on the type of rock quarried. This analysis ranks sandstone quarries as the most hazardous for workers, followed by granite quarries, and finally marble and limestone quarries. The relative risk in quarries, therefore, depends on the type of stone extracted, and when comparing quarries of the same stone type, the assessment should involve X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis.
X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) Analysis
We always resort to XRF analysis to determine the level of risk posed by quarries to workers' health. This method allows us to analyze the crystalline silica (SiO 2 ) content in samples, particularly from sandstone, which can vary due to several geological and environmental factors. One of the primary factors is the source of the deposits, as the silica content can vary based on the original source of the sediments. Sandstones derived from silica-rich rocks, such as granite or quartzite, have a higher silica content compared to those from silica-poor rocks (Folk & Robert, 1980, p. 102) (Boggs & Sam, 2014, p. 251). The process of deposition also plays a crucial role, as depositional environments (such as rivers, deserts, or seas) influence the silica content. Rapid sedimentation environments may retain higher crystalline silica concentrations (Blatt, Harvey, Robert, & Tracy, 2006, pp. 329-335). The age of the rock is another factor, as older rocks typically undergo more geological transformations, which can either increase or decrease the silica content (Tucke & Maurice, 2001, p. 178). Additionally, chemical and physical changes, including chemical interactions with groundwater during burial and lithification processes, can affect the silica content (Blatt, Harvey, Robert, & Tracy, 2006, p. 335).
Table.1 Classification of Limestone Quarries Based on Crystalline Silica Content
|
Category |
Crystalline Silica Percentage |
Description |
Risk Level with Water Spraying and Traditional Protective Clothing |
|
Low Risk |
Less than 10% |
Quarries have a very low percentage of crystalline silica, making them more susceptible to erosion and less hazardous to workers. |
Very low |
|
Moderate Risk |
10% - 20% |
Quarries have a moderate percentage of crystalline silica, providing a balance between hardness and erosion. |
Low |
|
High Risk |
20% - 30% |
Quarries have a high percentage of crystalline silica, making them more resistant to erosion and harder, increasing the risk to workers. |
Moderate |
|
Very High Risk |
More than 30% |
Quarries have a very high percentage of crystalline silica, making them among the most resistant and hardest types, significantly increasing the risk to workers. |
High |
Table.2 Classification of Sandstone Quarries Based on Crystalline Silica Content
|
Category |
Crystalline Silica Percentage |
Description |
Risk Level with Water Spraying and Traditional Protective Clothing |
|
Low Risk |
Less than 25% |
Quarries have a low percentage of crystalline silica, making them less hazardous to workers. |
Low |
|
Moderate Risk |
25% - 50% |
Quarries have a moderate percentage of crystalline silica, requiring moderate protective measures. |
Moderate |
|
High Risk |
50% - 75% |
Quarries have a high percentage of crystalline silica, making them hazardous and requiring strict protective measures. |
High |
|
Very High Risk |
More than 75% |
Quarries have a very high percentage of crystalline silica, making them extremely hazardous to workers. |
Very high |
Table.3 Classification of Granite Quarries Based on Crystalline Silica Content
|
Category |
Crystalline Silica Percentage |
Description |
Risk Level with Water Spraying and Traditional Protective Clothing |
|
Low Risk |
Less than 20% |
Quarries have a low percentage of crystalline silica, making them less hazardous to workers. |
Low |
|
Moderate Risk |
20% - 40% |
Quarries have a moderate percentage of crystalline silica, requiring moderate protective measures. |
Moderate |
|
High Risk |
40% - 60% |
Quarries have a high percentage of crystalline silica, making them hazardous and requiring strict protective measures. |
High |
|
Very High Risk |
More than 60% |
Quarries have a very high percentage of crystalline silica, making them extremely hazardous to workers. |
Very High |
Table.4 Classification of Marble Quarries Based on Crystalline Silica Content
|
Category |
Crystalline Silica Percentage |
Description |
Risk Level with Water Spraying and Traditional Protective Clothing |
|
Low Risk |
Less than 5% |
Quarries have a very low percentage of crystalline silica, making them less hazardous to workers. |
Very Low |
|
Moderate Risk |
5% - 15% |
Quarries have a moderate percentage of crystalline silica, requiring moderate protective measures. |
Low |
|
High Risk |
15% - 25% |
Quarries have a high percentage of crystalline silica, making them hazardous and requiring strict protective measures. |
Moderate |
|
Very High Risk |
More than 25% |
Quarries have a very high percentage of crystalline silica, making them extremely hazardous to workers. |
High |
So far, through the analysis of the crystalline silica content in various rocks, along with the availability of water for spraying and traditional protective measures, we can estimate the health risk levels and classify quarries based on silica content. The results show that sandstone quarries are the most hazardous, followed by granite quarries, then marble and limestone quarries. The availability of water for spraying and the use of protective fabrics help reduce the risk, but inadequate measures in the past have increased the suffering of workers. Therefore, these physical and chemical analyses are crucial for understanding health conditions and the prevalence of silicosis within quarries.
5/ The Fame of Quarries and the Quality of Stones Extracted and Their Uses
Table.5 Quality of sandstone based on crystalline silica content.
|
Crystalline Silica Percentage |
Quality |
Description |
|
< 25% |
Low Quality |
Low hardness, weak resistance to erosion, limited uses such as decoration and interior sculpture. |
|
25%-50% |
Medium Quality |
Medium hardness and resistance, good balance between durability and cost, suitable for moderate interior and exterior construction. |
|
50%-75% |
High Quality |
High hardness, excellent resistance to erosion, ideal for flooring, walls, and columns in large structures and public buildings. |
Table.06 Limestone based on crystalline silica content.
|
Crystalline Percentage |
Silica |
Quality |
Description |
|
< 10% |
Low Quality |
High fragility, weak resistance to erosion, limited uses such as decoration and interior sculpture. |
|
|
10%-20% |
Medium Quality |
Medium hardness and resistance, good balance between durability and cost, suitable for moderate interior and exterior construction. |
|
|
20%-30% |
High Quality |
Good hardness, reasonable resistance to erosion, ideal for flooring, walls, and columns in large structures. |
|
Conclusion and Discussion.
The analysis of the mechanism of silicosis reveals a strong connection between the inhalation of crystalline silica particles and the development of the disease. These particles, when inhaled, reach the alveoli in the lungs and resist digestion by macrophages. This resistance leads to inflammation and scarring of lung tissue, which reduces elasticity and causes symptoms such as persistent cough and shortness of breath. In advanced cases, the condition can worsen to respiratory failure and death. This mechanism clearly explains why silicosis is prevalent among workers frequently exposed to silica dust.The amount of silica in different types of rocks plays a crucial role in determining the risk of silicosis among quarry workers. Sandstone, which contains a high silica content ranging from 25% to 75%, is considered the most hazardous to workers' health. Studies indicate that the prevalence of silicosis among sandstone quarry workers can reach up to 72%. Granite, with a medium silica content ranging from 20% to 60%, also poses significant risks, with a silicosis prevalence rate of 32.7% among workers after five years of exposure. On the other hand, limestone contains lower amounts of silica, ranging from 10% to 30%, resulting in a lower risk of silicosis. However, the risk remains, especially under poor working conditions or lack of adequate personal protective equipment, as was often the case in ancient times.These findings indicate that the type of rock and the level of exposure to silica dust are the primary factors determining the risk of silicosis among Roman quarry workers. Diagnosing this condition in Roman skeletal remains requires specialized methodologies. Signs of the disease can be detected through the analysis of long bones, ribs, and the spine, revealing conditions such as bone fragility and fractures resulting from chronic respiratory distress and persistent infections. Additionally, chemical analysis of bones, including stable isotope analysis, can provide insights into dietary patterns and chronic illnesses. Microscopic examination can reveal small silica deposits, which serve as strong indicators of chronic lung fibrosis. It is also crucial to consider the presence of comorbid conditions, such as tuberculosis, which may have been exacerbated by respiratory issues.This interdisciplinary approach helps researchers understand the health conditions of Roman workers and the impact of quarrying on their health. The analysis of quarry samples is critical for assessing health risks. By collecting and analyzing samples using techniques like petrographic examination, XRD, and XRF analysis, researchers can determine the crystalline silica content in rocks. These analyses are instrumental in evaluating the dangers posed by different quarries to workers' health.The results indicate that sandstone quarries are the most hazardous for workers due to their high silica content, followed by granite, marble, and limestone quarries. Previous studies have shown that silica levels can vary even among rocks of the same type, indicating that quarries extracting the same kind of stone can differ in their health risks to workers. XRF analysis plays a crucial role in determining the chemical composition of samples and assessing their danger. This analysis helps accurately identify the crystalline silica content, enabling the assessment of a quarry's risk level. Quarries with high silica content require stringent protective measures for workers, while those with lower levels are considered less dangerous.Additionally, using water sprays and protective fabrics can reduce health risks, a measure often lacking in Roman quarries. The quality and reputation of stones from Roman quarries were mainly based on their physiological and physical properties. According to Vitruvius, selecting stones with high durability and resistance to environmental factors, such as erosion and harsh weather conditions, was essential to ensure the long-term sustainability of buildings and structures.Sandstone and limestone were the most commonly used stones due to their ability to withstand heavy loads and environmental factors, although limestone tends to crack when exposed to fire. Among other stones, Peperino stone was noted for its high quality and resistance to frost and fire, making it ideal for construction that requires long-lasting durability. The importance of the distance between the quarry and the construction site was significant, as it was preferable for quarries to be close to the building locations to facilitate transportation and use. However, the quality of the stones played a more critical role in the decision-making process. For example, Vitruvius mentioned that stones from certain quarries would have been preferred for construction in Rome if they were closer, indicating that the quality of the stones could outweigh distance considerations if the quality was excellent.The crystalline silica content plays a crucial role in determining the hardness and durability of stones. Quartz, one of the forms of crystalline silica, significantly contributes to the hardness and resistance of stones to erosion and weathering. Stones with high quartz content, such as sandstone, are more resistant to environmental factors. Similarly, cristobalite and tridymite also contribute to the hardness of stones, although they are less common than quartz.Thus, a high silica content provides stones with greater chemical resistance, making them less prone to reacting with acids and other chemicals. It also enhances the durability of stones, making them suitable for construction in harsh conditions. For example, stones used in Roman bridges and monuments, which require high strength, often contained high levels of silica.Therefore, quarries can be classified into various specializations based on the crystalline silica content, such as quarries for decoration and sculpture, interior and exterior construction, flooring, walls and columns, and specialized engineering structures. This classification helps guide the use of different stones according to their unique properties and the architectural and engineering needs of construction.In conclusion, crystalline silica plays a vital role in archaeological research to understand the social and economic conditions in ancient Roman times and other civilizations.
Acknowledgments : “I dedicate this work to the soul of my beloved brother, Bouazza Ali , who was present at every stage of this research, contributing his ideas and efforts to its various aspects and details. Although he passed away during the preparation of this study, his scientific and personal influence remains present on every page.
I also dedicate this work to the soul of my dear father, Bouazza Mohamed , whose financial and moral support was the foundation that enabled me to pursue and complete this research. I would also like to express my sincere gratitude to all the professors of the Department of Archaeology at Guelma University, May 8, 1945, for their valuable guidance and continuous academic support”.
Funding : No funding was received for the development of this project or the publication of this paper.
Declarations :
Conflict of Interest There are no conflicts of interest related to this paper.