Рост и урожайность сои (Glycine max L.) под влиянием разных доз инокулята Bradyrhizobium japonicum в засушливой зоне побережья Аравийского моря (провинция Balochistan, Пакистан)
Автор: Ali L., Waseem M., Anwar S., Ali Q., Sarfaraz Q., Abbas H.T., Khaliq G.
Журнал: Сельскохозяйственная биология @agrobiology
Рубрика: Продуктивность, качество и технологии
Статья в выпуске: 5 т.58, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Соевые бобы ( Glycine max L.) - важный источник масла и белка для большой части населения Азии и Америки. Известно, что у сои формирование арбскулярной микоризы и корневых клубеньков приводит к увеличению сырой массы, сухой массы и массы семян по сравнению с контролем. Однако в Пакистане, и особенно в провинции Balochistan, эффект обработки семян сои инокулятами крайне мало изучен. Мы провели свое исследование с целью оценить пригодность ризобии для инокуляции разных сортов сои в условиях региона (особенности рельефа почвы и окружающей среды). Эксперименты проводили на агрономической экспериментальной ферме Lasbela University of Agriculture, Water and Marine Sciences (Balochistan) в течение зимнего сезона 2018 года. Использовалась рандомизированная конструкция полного блока (RCBD) с факторным расположением и размером тестового участка 4,5×3,0 м (13,5 м2) в трех повторностях. Изучали два сорта сои (NARC I и NARC II) и три дозы Bradyrhizobium japonicum (200 г/акр, 400 г/акр и 600 г/акр). Результаты опыта показали, что наибольшие показатели (высота растения - 35,4 см, число стручков на растении - 24,7, длина стручка - 4,5 см, число клубеньков на растении - 64,5, длина корня - 13,2 см, семенной индекс - 31,8 г, содержание масла - 34,5 %, протеина - 37,7 %, урожайность семян - 1160,0 кг/га, биологическая урожайность - 2019,7 кг/га) имел сорт NARC II. Взаимодействие сорт×доза инокулята проявилось в максимальных показателях в варианте NARC I×600 г/акр (высота растения 41,3 см, 31,3 стручка на растении, длина стручка 4,8 см, 83,6 клубенька на растении, длина корня 15,3 см, индекс семян 40,2 г, содержание масла 38,0 %, протеина - 43,0 %, урожайность семян 1333,8 кг/га, биологическая урожайность 2325,0 кг/га и уборочный индекс 1,3 %), а минимальные показатели отмечали для варианта NARC I×200 г/акр дозы инокулята (высота растения 22,6 см, 15,0 стручков на растении, длина стручка 3,1 см, 42,3 клубенька на растении, длина корня 7,5 см, семенной индекс 18,5 г, содержание масла 29,8 %, белка - 30,5 %, урожайность семян 876,3 кг/га, биологическая урожайность 1448,3 кг/га и индекс урожая 1,1 %). Полученные результаты указывают на неодинаковое влияние разных доз инокулята на сорта сои в условиях опыта. Сорт сои NARC II давал максимальный урожай семян при дозе инокулята 600 г/акр, максимальное образование клубеньков также наблюдалось при дозе инокулята 600 г/акр.
Glycine max l, соя, bradyrhizobium japonicum, инокулят, рост растений, элементы структуры урожая, побережье аравийского моря
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142239857
IDR: 142239857 | УДК: 635.655:579.262:581.1 | DOI: 10.15389/agrobiology.2023.5.875rus
Текст научной статьи Рост и урожайность сои (Glycine max L.) под влиянием разных доз инокулята Bradyrhizobium japonicum в засушливой зоне побережья Аравийского моря (провинция Balochistan, Пакистан)
Соя ( Glycine max L., семейство Fabaceae , подсемейство Faboidae ) — важнейшая масличная культура в мире. Из сои производят различные продукты (порошок для приготовления каш, пищевое масло, соевое мясо, соевое молоко и соевый кофе). Соевые бобы являются важным источником жира и белка для большой части населения Азии и Америки (1).
Морфологически соя принадлежит к семейству Fabaceae , растения имеют стержневую корневую систему до 1,5 м в длину, с боковыми ответвлениями (0-30 см по горизонтали). Характер роста сои бывает детерминант-ным и индетерминантным. Растения детерминантного типа сначала завершают вегетативный рост, а затем вступают в репродуктивную фазу. У инде-терминантного типа вегетативное и репродуктивное развитие может происходить одновременно. Цветение сои длится около 15-20 сут в зависимости от длины дня, температуры и особенностей роста, индетерминантная соя начинает цвести раньше, чем детерминантная. Соя возникла в Китае, где упоминание об этой культуре датируется 2838 годом до нашей эры. В Пакистан соя была завезена в начале 1960-х годов из США в экспериментальных целях. В Пакистане соя с черными семенами (Mothi) выращивается в северных холмистых районах (2).
Соевые бобы возделывают в основном в США, Бразилии, Аргентине и Китае. При коммерческом выращивании сои одна из главных проблем — период вегетации, достаточный для созревания (3). В начале XXI века обширные территории Южной Америки были превращены в сельскохозяйственные поля для соевых бобов. Соевые бобы — древняя культура, возделываемая с самого начала развития земледелия (4). Благодаря высокому содержанию макро- и микроэлементов соевые бобы признаны ценным пищевым продуктом для человека, также они испльзуются в животноводствое, в качестве промышленного сырья и в медицинских целях (5). Соевые бобы считаются здоровой пищей, поскольку они богаты незаменимыми аминокислотами (6).
В 2016 году в мире соей было засеяно 120,48 млн га, на которых было произведено 351,48 млн т семян. Крупнейший производитель сои — США (117,20 млн т). Министерство сельского хозяйства США прогнозировало производство 347,7 млн т сои в мире еще в 2017-2018 годах. В Пакистане производство соевого масла в 2016 году составило 240 т, а в 2017 году выросло до 260 т (7). Соя является важным источником ненасыщенных жирных кислот, минералов, таких как Ca и P, витаминов A, B и D, а также белка (8). В симбиозе с ризобиями Bradyrhizobium japonicum , формирующими клубеньки на корнях, соя фиксирует свободный азот из атмосферы. Включение сои в севообороты повышает плодородие и продуктивность почвы (9).
На практике для инокуляции применяют обработку семян культурой B. japonicum . При недостаточном количестве B. japonicum в почве инокуляцию считают необходимой (10). Соевые бобы — одна из основных масличных культур в мире (11). О влиянии инокуляции B. japonicum на образование клубеньков сои и фиксацию азота сообщали многие исследователи (12). Положительный эффект от инокулятов B. japonicum сопровождался повышением урожайности семян сои (13). Сочетание везикулярно-арбускуляр-ной микоризы (ВАМ, Glomus macrocarpum ) с инфицированием В. japonicum усиливало развитие ВАМ и образование клубеньков по сравнению с контролем. Также наблюдалось увеличение сырой массы, сухой массы и массы семян по сравнению с контролем (14).
В Пакистане соевые бобы выращивают по всей стране, особенно в холмистых районах. Это тропическая зернобобовая культура (15). Для ее произрастания лучше всего подходят районы с умеренным, тропическим и субтропическим климатом, а Восточная Азия считается родиной этой культуры (16). В Китае соя была зарегистрирована как основная культура еще в XI веке, позже она была завезена в Америку и изучена на предмет питательной ценности и оптимальных условий роста (17). В Африку ее завезли в 1903 году, где затем выращивали как основную продовольственную культуру (18).
Известно, что бобовые преобразуют атмосферный азот в аммиачный, который используется растениями. Для усиления процесса азотфик-сации в почву вносят ризобии (19). Отношения между ризобиями и бобовыми являются симбиотическими. Фиксация азота происходит в корневых клубеньках. Бактерии проникают в корневые волоски и, колонизируя клетки корня, формируют клубеньки, в которых происходит азотфиксация (20). Поддержание плодородия почвы, обеспечивающего образование клубеньков и симбиотическую фиксацию азота, имеет большое значение для получения максимальной урожайности у бобовых (21). Фосфор и калий оказывают значимое влияние на образование клубеньков и последующую фиксацию азота. Молибден — еще один микроэлемент, важный для фиксации азота (22).
R.M. Morshed с соавт. (23) провели эксперимент на факультете биологии в Gulnagar University, Dhaka, в течение 2004-2005 годов в сезон раби с использованием сорта G2 (бангладешская соя). Нормы азота составляли N 1 10,58; N 2 15,87; N 3 21,16; N 4 26,45; N 5 31,74 и N 6 37,03 кг/га. Перед посевом семена инокулировали Bradyrhizobium . При норме азота 26,45 кг/га была достигнута самая высокая урожайность — 685 кг/га. O. Herliana с со-авт. (24) с мая по октябрь 2018 года изучали эффекты разных доз биоудобрений и азота на сельскохозяйственном факультете Gendarmes Dilman University. Дизайн эксперимента — полная рандомизация (FCRD) по двум факторам. Основными элементами были Rhizobium (R) — R. radiobacter , R. pusenses , R. nepotum , вторым фактором были дозы азотного удобрения (N) — 0, 25 %, 50 %, 75 % и 100 % (рекомендуемая доза 120 кг). Были обнаружены изменения в верхней части растений, типе и расположении листьев, диаметре стебля, сухой массе корня, массе семени, массе 100 семян, массе стручка и растения. Результаты подтвердили, что использование изолята R. neoptum дало наилучшие результаты по площади листьев, массе стручка, типу стручка, а доза 25 % азотного удобрения приводила к образованию стеблей с разной морфологией. Взаимодействия между типом изо-лята и дозой азотного удобрения не наблюдалось.
A.Z. Khan с соавт. (25) обнаружили, что дата и густота посадки оказали существенное влияние на содержание белка и масла у сортов сои. Содержание белка в поздних посевах было выше, чем в ранних, тогда как по содержанию масла наблюдалась обратная связь. L.M. Jaureguy с соавт. (26) отметили, что ранние и поздние сроки посева неодинаково влияли на восемь селекционных линий сои, выращиваемых в течение 2 лет в двух разных местах в Арканзасе, США, с формированием разного состава семян (высокое содержание белка, масла, олеиновой кислоты, неорганического фосфора, низкое содержание линоленовой кислоты, насыщенных жирных кислот, стахиозы).
E.A. Obidiebube с соавт. (27) изучили адаптацию десяти сортов сои в полевых экспериментах, проведенных в двух районах тропических лесов (Асаба и Окпе-Исоко — Asaba, Okpe-Isoko). Испытуемые сорта — TGX1904-6F, TGX1910-11F, TGX1910-15F, TGX1910-10F, TGX1905-2F, TGX1910-1F, TGX1910-8F, TGX1910-6F и TGX1905-5F. Результаты выявили существенные различия между сортами по некоторым из оцениваемых параметров (р ≤ 0,05). У TGX1910-8F, TGX1905-2F и TGX1904-6F было наибольшее число цветков и стручков — 68,3 и 26,3 и самый большой период до созревания — 106,6 сут. По сухой массе семян на гектар (2,90 т/га) TGX1910-8F превосходил TGX1910-15F (2,89 т/га). TGX 1910-8F, TGX1905-2F и TGX1904-6F обеспечили максимальные средние значения сухой массы. Следовательно, в этом агроэкологическом регионе рекомендуется выращивать более урожайные сорта TGX1910-8F и TGX1910-15F.
M. Rehman с соавт. (28) провели полевые исследования в агроэкологических условиях округа Faisalabad, провинция Punjab, для оптимизации сроков посева различных сортов сои. В эксперименте использовалась схема RCBD с тремя повторностями, при этом на участках одной делянки с единой датой посева размещали разные сорта. Согласно полученным данным, при посеве 28 января соевые бобы сорта Faisal дали больше стручков и семян на растение. У этого сорта зафиксирована самая высокая урожайность семян — 1647,10 и 1440,23 кг/га при посеве соответственно 28 января и 21 января. В итоге 28 января рассматривается как идеальная дата при посеве яровой сои для получения высокого урожая. В условиях округа Faisalabad сорт Faisal показал преимущество над двумя другими сортами.
G.E. Nwofia с соавт. (29) оценили четыре генотипа сои по урожайности семян, росту и другим факторам в 2012 и 2013 годах. Сроки посева — начало июня, конец июня, начало июля, конец июля, начало августа, конец августа. Делянки различались по датам посева, участки каждой делянки — по генотипам сои. Было показано, что урожайность сои, посеянной в июле, выше — 1320,07 и 860,20 кг/га соответственно в 2012 и 2013 годах. Соя с генотипом TGx1485-1D показала лучшую урожайность — 980,74 кг/га в 2012 году и 520,58 кг/га в 2013 году.
A. Nsengiyumva с соавт. (30) провели эксперимент в секторе Nyarubaka округа Kamonyi (Руанда) по изучению реакции двух сортов сои (Peka6 и SB24) на инокуляцию ризобиями без ограничения фосфорного питания. Сорт Peka6 оказался чувствительнее к инокуляции, чем SB24. T. Shah с соавт. (31) выполнили полевые опыты по проверке сроков посева у разных сортов сои в округе Charsadda, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Использовали четыре периода посадки для двух сортов. Результаты показали, что сорт Williams 82, посаженный 21 марта, дал большое количество стручков и семян с одного растения.
Y. Kawasaki с соавт. (32) выявили влияние позднего посева на урожайность семян сои в течение двух лет подряд (2016-2017 годы) в Японии. Сообщалось, что отсроченный посев семян сои вызвал значительное увеличение индекса урожая HI с 0,464-0,571 в 2016 году до 0,524-0,585 в 2017 году, но плотность посадки не оказала значительного влияния (p > 0,05). R.C. Um-buranas с соавт. (33) провели полевые исследования в течение двух вегетационных сезонов, чтобы выяснить, как сроки посева и норма высева семян влияют на урожайность сои и ее характеристики. Установлено, что поздний посев снижает урожайность из-за уменьшения биомассы побегов. Более высокие нормы высева снижали биомассу побегов, уменьшали площадь листьев, число стручков и семян на растении.
G. Toum с соавт. (34) определяли урожайность и качество урожая — высоту до первого стручка, число стручков на одно растение, массу 100 семян, индекс урожая, продуктивность соломы, урожайность семян, содержание белка и жира в зерне. Было обнаружено, что высота до первого стручка, масса 100 семян, индекс урожая, урожайность зерна и содержание белка в зерне значительно колеблются в зависимости от даты посева. Посев 1 июля по сравнению с более поздними сроками в том же сезоне (15 июля) привел к увеличению урожайности зерна на 72 %. По сравнению с более поздними сроками посева (15 июля) ранние (15 июня) и средние (1 июля) сроки привели к увеличению содержания белка в зерне на 5 %.
На рост растений сои и производство зерна, а также на его качество может влиять дата посева (35), и выход конечного продукта часто снижается, если сою высаживали после 1 мая (36). Это отмечали в северо-центральной части США и в штатах Среднего Запада (37, 38). Согласно анализу (39), сельскохозяйственные культуры, скорее всего, были посажены в середине апреля или начале мая на юге, что снизило урожайность. Когда в середине июня соевые бобы высевали на северо-востоке США, получили мало стручков и снижение урожайности (40).
При слишком ранней посадке на растения часто влияет прохладная погода. Из-за влажности и низкой температуры почвы прорастание семян сои может задержаться, что, как следствие, замедлит формирования стеблестоя и уменьшит урожайность зерна. Тем не менее урожайность зерна сои обычно выше при смещении даты посева на более ранние сроки (41), так как при этом увеличивается продолжительность вегетативной и генеративной стадии развития (42). Еще один способ — использование рядов с расстоянием менее 30 дюймов, что позволяет максимизировать урожайность за счет оптимального использования земли и ресурсов (в Пакистане фермеры в основном сажают растения широкими рядами, что считается малоэффективным приемом) (38).
В Пакистане, особенно в провинции Balochistan, почти не проводилось исследований по обработке семян сои инокулятом ризобий как технологическому приему повышения урожайности сои. В нашем исследовании представлены первые данные по эффективности ризобий при инокуляции сортов сои в засушливой зоне побережья Аравийского моря.
Цель исследования — оценить влияние разных доз инокулята ризо-бий на рост и урожайность растений сои в агроклиматических условиях округа Lasbela.
Методика . Полевой эксперимент проводили в Lasbela University of Agriculture, Water and Marine Sciences (LUAWMS), Uthal, Lasbela (провинция Balochistan, 25,8700 ° с.ш., 66,7129 ° в.д.) в 2018 году. Округ Lasbela характеризуется суглинистыми почвами и сухим тропическим климатом со среднегодовым количеством осадков 178 мм.
До и после посева с опытного поля случайным образом для каждого варианта обработки отбирали по пять образцов почвы с глубины 30 см с помощью шнека. Физико-химические свойства образцов почвы анализировали в Почвенной лаборатории Agriculture Research Institute (ARI), Quetta. Почву высушивали в печи при температуре 105 ° С в течение 24 ч. Почва участков имела супесчаную текстуру с содержанием песка около 91-94 %, pH в пределах 7-7,5, электропроводность 10,24 dSm - 1; содержание азота и органического вещества в почве — около 0,020 и 0,40 %, обеспеченность фосфором и калием — соответственно 2,08 и 124 мг/кг.
Использовали два сорта сои (NARC I и NARC II) и три дозы инокулята (200 г/акр, 400 г/акр и 600 г/акр). Эксперимент выполняли в трех повторностях, применяя схему полностью рандомизированных блоков (RCBD) с факторным расположением. Использовали рекомендуемую норму высева семян 40 кг/акр (100 кг/га) (43). Всего в эксперименте использовали 18 площадок. Размер участка составил 4,5½3,0 м (13,5 м2). Растения прореживали на стадии 4-6 листьев. В течение вегетационного периода использовались все общепринятые агротехнические практики.
Bradyrhizobium japonicum был получен из Национального центра сельскохозяйственных исследований (National Agricultural Research Center — NARC, г. Исламабад). При подготовке к инокуляции 1 кг сахара растворяли в 1 л воды и смачивали 40 кг семян для лучшего прилипания бактерий, также растворенный сахар служит исходным питательным субстратом для бактерий. Инокулят распределяли по сухим семенам вручную равномерным перемешиванием. Инокуляцию проводили по стандартным процедурам в затененном месте непосредственно перед посевом (контроль — без инокуляции).
Посев проводили весной 2018 года с помощью инструмента Dibbler. Перед посевом семена обрабатывали разными дозами инокулята. Опытный участок выравнивали, вспахивали ротаватором (лучшее приспособление для обработки почвы под сою), поливали; окончательно готовили почву к посеву с помощью культиватора. При выращивании сои применяли рекомендуемую норму удобрений (NPK 25-60-50 кг/га). Азотные удобрения применяли в виде мочевины в разделенных дозах на вегетативных и репродуктивных стадиях. Все фосфорные (P) и калийные (K) удобрения вносились во время посева в форме соответственно диаммонийфосфата (DAP) и сульфата калия (SOP).
Урожай сои собирали вручную серпом, когда 90-95 % стручков пожелтели, скошенные растения сушили в течение 5-6 сут, затем обмолачивали. Семена сои считаются физиологически созревшими, если семенная кожура полностью желтая, независимо от цвета стручков.
Оценивали всхожесть семян (%), высоту растения в зрелом состоянии (см), число стручков на одно растение, длину стручка (см), выход семян (кг/га), биологическую урожайность (кг/га), индекс урожая (%), число клубеньков на одно растение, длину корня (см), содержание (%) белка и масла.
Статистическую обработку полученных данных проводили с использованием методов дисперсионного анализа с F -критерием Фишера (ANOVA); для оценки достоверности различий между вариантами использовали наименьшую существенную разность при уровне значимости 5 % НСР 05 (LSD 05 ) (44).
Результаты . Климатические данные (рис., А-Г) получали из метеорологической обсерватории LUAWMS в течение 2018 года.
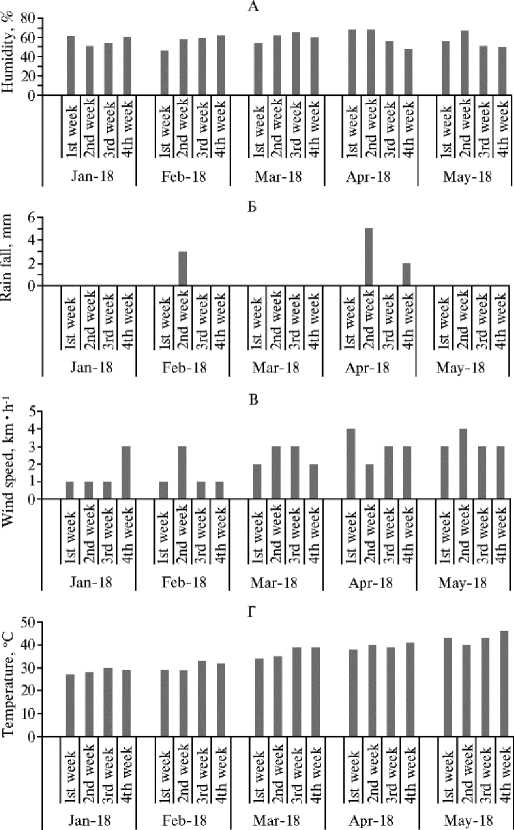
Months
Еженедельные значения относительной влажности (А) , количества осадков (Б) , относительной скорости ветра (В) и теммпературы воздуха (Г) с января по май 2018 года в месте проведения эксперимента по инокуляции сортов сои ( Glycine max L.) бактериями Bradyrhizobium japonicum (Lasbela University of Agriculture, Water and Marine Sciences, Uthal, Lasbela, провинция Balochistan, 25,8700 ° с.ш., 66,7129 ° в.д.; данные метеостанции LUAWMS).
Всхожесть семян (%). Процент всхожих семян играет ключевую роль в достижении необходимого производства семян сои. Всхожесть семян (%) у сортов сои при разных дозах инокулята различалась незначительно (табл. 1). Результат показал, что всхожесть имеет недостоверные
(р > 0,05) вариации по обоим факторам. Взаимодействие V½I (сорта½дозы инокулятов) давало незначительный эффект (p > 0,05).
-
1. Всхожесть семян сои ( Glycine max L.) в зависимости от сорта и дозы инокулята Bradyrhizobium japonicum (Lasbela University of Agriculture, Water and Marine Sciences, Uthal, Lasbela, провинция Balochistan, 25,8700° с.ш.,
66,7129° в.д., 2018 год)
-
2. Длина стручка и семенная продуктивность у сои ( Glycine max L.) в зависимости от сорта и дозы инокулята Bradyrhizobium japonicum (Lasbela University of Agriculture, Water and Marine Sciences, Uthal, Lasbela, провинция Balochistan, 25,8700° с.ш., 66,7129° в.д., 2018 год)
Длина стручка, см
Урожайность семян, кг/га
M
M
A — сорт (V):
V 1 = NARC I
4,5
1033,3 b
V 2 = NARC II
3,6
1160,0 a
SE
0,1432
25,937
НСР 05
0,3192 NS
57,791**
B — доза инокулята (I):
I 1 = 200 г/акр
3,6
917,8 c
I 2 = 400 г/акр
4,3
1122,3 b
I 3 = 600 г/акр
4,3
1249,7 a
SE
0,1754
31,766
НСР 05
0,3909 NS
70,779**
C — взаимодействие сорт½доза инокулята
(V½I):
V 1 ½I 1
3,1
876,3 d
V 1 ½I 2
3,9
1057,9 c
V 1 ½I 3
3,9
1165,7 b
V 2 ½I 1
4,1
959,4 cd
V 2 ½I 2
4,7
1186,7 b
V 2 ½I 3
4,8
1333,8 a
SE
0,2481
44,924
НСР 05
0,5528NS
100,10**
Пр и м еч ани е. Сравниваемые средние значения в столбце, которые не отмечены одинаковыми буквами, различаются статистически значимо при р = 0,05; ** — высокий уровень значимости, NS — отсутствие статистической значимости.
Урожайность семян (кг/га). Урожайность семян линейно влияет на коммерческое производство сои. Полученные нами данные по урожайности семян у изученных сортов сои в зависимости от доз инокулята и их взаимодействия представлены в таблице 2. Дисперсионный анализ выявил статистически значимые (р < 0,05) различия для сортов, доз инокулята и их взаимодействия. У сорта NARC II урожайность семян (1160,0 кг/га) была выше, чем у сорта NARC I (1033,3 кг/га). При дозе 600 г/акр была зафиксирована наибольшая урожайность семян (1249,7 кг/га), при 400 г/акр она была ниже (1122,3 кг/га), при 200 г/акр урожайность семян была
минимальной (917,8 кг/га). Взаимодействие I 3 ½V 2 обеспечивало максимальную урожайность семян (1333,8 кг/га), I 1 ½V 1 — минимальную урожайность (876,3 кг/га).
-
3. Биологическая продуктивность, индекс урожая, образование клубеньков и длина корня у сои ( Glycine max L.) в зависимости от сорта и дозы инокулята Bradyrhizobium japonicum (Lasbela University of Agriculture, Water and Marine Sciences, Uthal, Lasbela, провинция Balochistan, 25,8700° с.ш., 66,7129° в.д., 2018 год)
Вариант опыта
Биологическая продуктивность, кг/га
Индекс урожая, %
Число клубеньков на растении
Длина корня, см
M
M
Me
M
A — сорт (V):
V 1 = NARC I
1785,9 b
1,2
54,5 b
20,2 b
V 2 = NARC II
2019,7 a
1,2
64,3 a
23,5 a
SE
34,898
0,0419
0,9950
0,3225
НСР 05
77,757**
0,0935NS
2,2171**
0,7185**
B — доза инокулята (I):
I 1 = 200 г/акр
1607,3 c
1,1
45,1 c
15,1 c
I 2 = 400 г/акр
1887,2 b
1,3
57,0 b
21,1 b
I 3 = 600 г/акр
2213,8 a
1,3
76,1 a
29,4 a
SE
42,741
0,0514
1,2187
0,3949
НСР 05
95,232**
0,1145NS
2,7154**
0,8799**
C — взаимодействие сорт½доза инокулята (V½I):
V 1 ½I 1
1448,3 e
1,1
42,3 f
13,7 f
V 1 ½I 2
1806,7 d
1,2
52,6 d
16,5 e
V 1 ½I 3
2102,7 b
1,3
68,6 b
27,9 b
V 2 ½I 1
1766,3 d
1,1
48,0 e
19,1 d
V 2 ½I 2
1967,7 c
1,3
61,3 c
23,0 c
V 2 ½I 3
2325,0 a
1,3
83,6 a
30,9 a
SE
60,445
0,0726
1,7235
0,5585
НСР 05
134,68**
0,1619NS
3,8401**
1,2444**
Примечани е. Сравниваемые средние значения в столбце, которые не отмечены одинаковыми буквами,
различаются статистически значимо при р =
0,05; ** — высокий уровень значимости,
NS — отсутствие
статистической значимости.
Дисперсионный анализ выявил достоверные различия (р < 0,05) для сортов, доз инокулята и их взаимодействия. Биологическая продуктивность сорта NARC II была выше (2019,7 кг/га), чем у сорта NARC I (1785,9 кг/га).
-
4. Содержание (%) белка и масла у сои ( Glycine max L.) в зависимости от сорта и дозы инокулята Bradyrhizobium japonicum (Lasbela University of Agriculture, Water and Marine Sciences, Uthal, Lasbela, провинция Balochistan, 25,8700° с.ш., 66,7129° в.д., 2018 год)
Вариант опыта
Содержание белка
Содержание масла
M
M
A — сорт (V):
V 1 = NARC I
34.8 b
32.4 b
V 2 = NARC II
37.7 a
34.5 a
SE
0.4734
0.3497
НСР 05
1.0548**
0.7792**
B — доза инокулята (I): I 1 = 200 г/акр
31.2 c
30.4 c
I 2 = 400 г/акр
36.1 b
33.4 b
I 3 = 600 г/акр
41.4 a
36.5 a
SE
0.5798
0.4283
НСР 05
1.2919**
0.9543**
C — взаимодействие сорт½доза инокулята (V½I):
V 1 ½I 1
30.5d
29.8 d
V 1 ½I 2
34.0 c
32.3 c
V 1 ½I 3
39.9 b
35.1 b
V 2 ½I 1
32.0 d
31.1 cd
V 2 ½I 2
38.1 b
34.5 b
V 2 ½I 3
43.0 a
38.0 a
SE
0.8200
0.6057
НСР 05
1.8270**
1.3496**
Пр им еч ан и е. Сравниваемые средние значения в столбце, которые не отмечены одинаковыми буквами,
различаются статистически значимо при р =
0,05; ** — высокий уровень значимости, NS — отсутствие
статистической значимости.
|
Всхожесть семян, % |
Высота растения, см |
Число стручков на растении |
|
|
M |
M |
M |
|
|
A — сорт (V): |
|||
|
V 1 = NARC I |
67,2 |
25,4 b |
14,7 b |
|
V 2 = NARC II |
61,3 |
35,8 a |
24,7 a |
|
SE |
6,8192 |
0,6939 |
0,9571 |
|
НСР 05 |
15,194NS |
1,5461** |
2,1326** |
|
B — доза инокулята (I): |
|||
|
I 1 = 200 г/акр |
68,8 |
26,8 c |
13,8 c |
|
I 2 = 400 г/акр |
58,0 |
30,5 b |
21,0 b |
|
I 3 = 600 г/акр |
66,0 |
34,6 a |
24,5 a |
|
SE |
8,3518 |
0,8498 |
1,1722 |
|
НСР 05 |
18,609NS |
1,8936** |
2,6118** |
|
C — взаимодействие сорт½ |
доза инокулята (V½I |
): |
|
|
V 1 ½I 1 |
74,3 |
22,6 e |
16,0 c |
|
V 1 ½I 2 |
65,0 |
25,6 d |
27,0 b |
|
V 1 ½I 3 |
62,3 |
28,0 d |
31,3 a |
|
V 2 ½I 1 |
63,3 |
31,0 c |
11,6 d |
|
V 2 ½I 2 |
51,0 |
35,3 b |
15,0 cd |
|
V 2 ½I 3 |
69,6 |
41,3 a |
17,6 c |
|
SE |
11,811 |
1,2019 |
1,6578 |
|
НСР 05 |
26,317NS |
2,6779** |
3,6937** |
|
Примечани е. Сравниваемые средние значения в столбце, которые не отмечены одинаковыми буквами, различаются статистически значимо при р = 0,05; ** — высокий уровень значимости, NS — отсутствие статистической значимости. |
|||
Всхожесть семян у сорта NARC I (67,2 %) была выше, чем у сорта NARC II (61,3 %). Максимальную всхожесть семян (68,8 %) зафиксировали при обработке дозой инокулята I 1 (200 г/акр), при дозе I 3 (600 г/акр) показатель был ниже (66,0 %), а минимальную всхожесть семян (58,0 %) отмечали при дозе инокулята I 2 (400 г/акр). Взаимодействие I 1 ½V 1 приводило к максимальной всхожести семян (74,3 %), взаимодействии I 2 ½V 2 — к минимальной (51,0 %).
Высота растения (см). Важный фактор, определяющий урожайность соломы и семян, — высота растения, поскольку она влияет на фотосинтез и перемещение веществ снизу вверх по растению. Морфологию растений обычно рассматривают как генетический признак, наследуемый от родительского материала сортов; однако на размер растения могут влиять несколько факторов, связанных с применением ресурсов и технологий
Мы зафиксировали значительную высоту растений у сортов сои при разных дозах инокулята (см. твбл. 1). У сорта NARC II растения были выше (35,8 см), чем у NARC I (25,4 см). Высоту 34,6 см отмечали при обработке инокулятом в дозе I 3 (600 г/акр), 30,5 см — в варианте I 2 (400 г/акр). Минимальная высота растений (26,8 см) наблюдалась при дозе инокулята I 1 (200 г/акр). Статистический анализ данных показал, что существует достоверная (p < 0,05) разница в высоте растений между сортами сои и в зависимости от доз инокулята и взаимодействия этих факторов. Взаимодействие I 3 ½V 2 обеспечивало максимальную высоту растения (41,3 см), а минимальная высота растения (22,6 см) была зафиксирована при взаимодействии I 1 ½V 1 (см. табл. 1).
Число стручков на растении. Урожайность сои в основном связана с числом стручков в расчете на одно растение, что также отражает эффективность обработок. Этот показатель оказался весьма значительным (см. табл. 1). Сорт сои NARC II по числу стручков на растении превосходил сорт NARC I (24,7 против 14,7).
Максимальное число стручков на растении — 24,5 мы обнаружили в посевах сои, обработанной инокулятом в дозе I 3 (600 г/акр), при дозе инокулята I 2 (400 г/акр) число стручков на растении составило 21,0, в варианте I 1 (200 г/акр) оно было меньше — 13,8. Статистический анализ данных выявил значимые различия (p < 0,001) по числу стручков на растении между сортами сои. Взаимодействие I 3 ½V 2 приводило к максимальному числу стручков на растении (31,3), а I 1 ½V 2 — к минимальному (11,6).
Длина стручка (см). У сои размер стручка наследуется от родителей; но управление посевами также влияет на этот признак. У изученных сортов сои наблюдались различия по этому показателю (табл. 2). Статистический анализ выявил различия на высоком уровне значимости (p < 0,001).
У сорта сои NARC I стручки были длиннее, чем у сорта NARC II — 4,5 см против 3,6 см. При инокуляции в дозах I 3 (600 г/акр) и I 2 (400 г/акр) длина стручка (4,3 см) была выше, чем в варианте I 1 (200 г/акр) (3,6 см). Взаимодействие I 3 ½V 2 приводило к максимальной длине стручка (4,8 см), а I 1 ½V 1 — к минимальной (3,1 см).
Биологическая урожайность (кг/га). Биомасса растения, как пракило, связана с его высотой и числом ветвей или листьев. Обычно сорта оказывают доминирующее влияние на этот признак, но применение агротехнологий и управление развитием культуры, включая время посева, также изменяют этот параметр. Результаты выполненной нами оценки биологической урожайности изученных сортов сои в зависимости от использованных доз инокулята и взаимодействия этих факторов представлены в таблице 3.
Результат применения различных доз инокулята показывает, что при дозе инокулята 600 г/акр оцениваемый показатель был самым высоким (2213,8 кг/га), при 400 г/акр — средним (1887,2 кг/га), а при 200 г/акр — минимальным (1607,3 кг/га). При взаимодействии V 2 ½I 3 биологическая продуктивность была максимальной (2325,0 кг/га), а в варианте V 1 ½I 1 — минимальной (1448,3 кг/га) (см. табл. 3).
Индекс урожая (%). Индекс урожая — один из основных показателей, которые учитываются при создании сорта сельскохозяйственной культуры или разработке агротехнологии. Индекс урожая также определяет, сколько продуктов фотосинтеза преобразуется в экономический урожай. В случае сои индекс урожая характеризует процент семян в общей биомассе.
Результаты оценки индекса урожая в нашем опыте для сортов, доз инокулята и их взаимодействия представлены в таблице 3. Дисперсионный анализ выявил достоверные различия (р < 0,05) в зависимости от варианта опыта. В среднем у обоих сортов (NARC I и NARC II) индекс урожая равнялся 1,2 %.
При дозах инокулята 600 г/акр и 400 г/акр индекс урожая составил 1,3 %, при 200 г/акр он снижался до 1,1 % (см. табл. 3). В варианте V 2 ½I 3 индекс урожая был максимальным (1,3 %), в варианте V 1 ½I 1 — минимальным (1,1 %).
Число клубеньков на растении. Растения сои способны формировать симбиотическую ассоциацию с азотфиксирующими ризоби-ями с образованием корневых клубеньков. У быстро развивающихся растений сои образование клубеньков начинается сразу после появления всходов. Если растение имеет высоту 6 дюймов (15 см) с развернутым первым или вторым тройчатым листом, клубеньки начинают активно фиксировать N 2 атмосферы в доступный для растения азот. Увеличение числа клубеньков продолжается до начала формирования семян, а иногда продолжается немного дольше указанной стадии. Полученные нами результаты оценки этого признака представлены в таблице 3. У сорта сои NARC II число клубеньков на одно растение было выше, чем у сорта NARC I — 64,3 против 54,5. Максимальное значение показателя — 76,1 клубенька на одно растение зарегистрировали при обработке инокулятом в дозе I 3 (600 г/акр), для I 2 (400 г/акр) и I 1 (200 г/акр) показатель снижался соответственно до 57,0 и 45,1 клубенька. Между эффектом сорта, доз инокулята и их взаимодействием выявлены статистически значимые (р < 0,05) различия по числу клубеньков на одно растение. Взаимодействие V 2 ½I 3 приводило к максимальному числу клубеньков на одно растение (83,6), V 1 ½I 1 — к минимальному (42,3).
Длина корня (см). Изучение этого признака (см. табл. 3) показало, что для сорта сои NARC II характерна большая длина корней (23,5 см) по сравнению с NARC I (20,2 см). Максимальную длину корня (29,4 см) мы зарегистрировали при обработке инокулятом в дозе I 3 (600 г/акр), в варианте I 2 (400 г/акр) этот показатель составил 21,1 см, а для I 1 (200 г/акр) он был минимальным — 15,1 см. Взаимодействие V 2 ½I 3 привело к максимальной длине корня (30,9 см), I 1 ½V 1 — к минимальной (13,7 см). Статистический анализ выявил статистически значимые (р < 0,05) различия по вариантам опыта (см. табл. 3).
Содержание белка (%). Белок — это макронутриент, необходимый для наращивания мышечной массы, и он обычно содержится в продуктах на основе мяса, но хорошо известны и другие источники белка — в основном орехи и бобовые. Дисперсионный анализ содержания белка у изученных сортов сои в зависимости от доз инокулята и взаимодействия этих факторов (табл. 4) выявил статистически значимые (р < 0,05) различия. У сорта NARC II содержание белка было выше (37,7 %), чем у сорта NARC I (34,8 %). Доза инокулята 600 г/акр обеспечивала максимальное накопление белка (41,4 %), при дозе 400 г/акр показатель имел промежуточное значение (36,1 %), при 200 г/акр — был минимальным (31,2 %). Взаимодействие V 2 ½I 3 обеспечивало максимальное содержание белка (43,0 %), а V 2 ½I 1 — минимальное (30,5 %).
Содержание масла (%). В состав соевого масла входят четыре основные жирные кислоты — линолевая (55 %), пальмитиновая (10 %), олеиновая (18 %) и стеариновая (4 %). Статистический анализ полученных нами данных выявил значимые (р < 0,05) различия по содержанию масла между сортами сои, дозами инокулята и взаимодействием этих АКТОРОВ (см. табл. 4).
У сорта сои NARC II содержание масла было выше (34,5 %), чем у сорта NARC I (32,4 %). Доза инокулята I3 обеспечивала максимальное содержание масла (36,5 %), при дозе I2 отмечали промежуточное значение этого показателя (33,4 %) и для I1 оно было наименьшим (30,4 %). В варианте V2½I3 содержание масла было максимальным (38,0 %), а в случае I1½V1 — минимальным (29,8 %).
Таким образом, наш эксперимент, проведенный в засушливой зоне побережья Аравийского моря (провинция Balochistan, Пакистан) показал, что применение разных доз инокулята Bradyrhizobium japonicum существенно влияет на ростовые характеристики сои. Сорт сои NARC II в нашем эксперименте давал максимальный урожай семян и проявлял лучшие ростовые показатели при дозе инокулята 600 г/акр, максимальное образование клубеньков также наблюдалось при дозе инокулята 600 г/акр.
Список литературы Рост и урожайность сои (Glycine max L.) под влиянием разных доз инокулята Bradyrhizobium japonicum в засушливой зоне побережья Аравийского моря (провинция Balochistan, Пакистан)
- The state of agricultural commodity markets: High food prices and the food crisis, experiences and lessons learned. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2009.
- Nazir M.S., Robyn E.B. Crop production. National Book Foundation, Islamabad, Pakistan, 1994.
- Bloom A.J. Energetics of nitrogen acquisition. Annual Plant Reviews, 2011, 42: 63-81 (doi: 10.1002/9781444328608.ch3).
- Jandong M.A., Siddiqua A., Chowdhury M.A.H., Prodhan M.Y. Nodulation, yield and quality of soybean as influenced by integrated nutrient management. Journal Bangladesh Agriculture University, 2009, 7(2): 229-234.
- Akparobi S.O. Evaluation of six cultivars of soybean under the soil of rainforest agro-ecological zones of Nigeria. Middle East Journal of Scientific Research, 2009, 4(1): 6-9.
- Jensen E.S., Peoples M.B., Boddey R.M., Gresshoff P.M., Hauggaard-Nielsen H., Alves B.J., Morrison M.J. Legumes for mitigation of climate change and the provision of feedstock for biofuels and bio refineries. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2011, 32(2): 329-364 (doi: 10.1007/s13593-011-0056-7).
- Situation and Outlook Report, Economic Research Service 17th. USDA, USA, 2017.
- Mrkovacki N., Marinkovi J., Acimovic R. Effect of N fertilizer application on growth and yield of inoculated soybean. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca, 2008, 36(1): 48-51 (doi: 10.15835/nbha36190).
- Hatim M., Nazir S., Bashir E., Bantel R., Mian H.R. Oilseed crops. Journal of Crop Production, 2014, 14(1): 330-331.
- Albareda M., Rodriguez-Navarro D.N., Camacho M., Temprano F.J. Alternatives to peat as a carrier for rhizobia inoculants: solid and liquid formulations. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2009, 40(11): 2771-2779 (doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.07.021).
- Shahid M.Q., Saleem M.F., Khan H.Z., Anjum S.A. Performance of soybean (Glycine max L.) under different phosphorus levels and inoculation. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2009), 46(4): 237-241.
- Bai Y., Pan B., Charles T.C., Smith D.L. Co-inoculation dose and root zone temperature for plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on soybean [Glycine max L.) Merr] grown in soil-less media. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2002, 34: 1953-1957 (doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00173-6).
- Mabood F., Souleimanov A., Khan W., Smith D.L. Jasmonates induce nod factor production by Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2006, 44: 759-765 (doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2006.10.025).
- Jalaluddin M. Effect of inoculation with vamfungi and bradyrhizobium on growth and yield of soybean in Sindh. Pakistan Journal of Botony, 2005, 37: 169-173.
- Khurshid H., Baig D., Jan S.A. Miracle crop: the present and future of soybean production in Pakistan. MOJ Biol. Med., 2017, 2 (1): 189-191 (doi: 10.15406/mojbm.2017.02.00042).
- Tian C.F., Zhou Y.J., Zhang Y.M., Li Q.Q., Zhang Y.Z., Li D.F., Chen W.X. Comparative genomics of rhizobia nodulating soybean suggests extensive recruitment of lineage-specific genes in adaptations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012, 109(22): 8629-8634 (doi: 10.1073/pnas.1120436109).
- Zhang Y.M., Li Y. Jr., Chen W.F., Wang E.T., Tian C.F., Li Q.Q., Zhang Y.Z., Sui X.H., Chen W.X. Biodiversity and biogeography of rhizobia associated with soybean plants grown in the North China Plain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2011, 77(18): 6331-6342 (doi: 10.1128/AEM.00542-11).
- Soyabeans — production guidelines. Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry, Pretoria, 2010.
- Schulz T.J., Thelen K.D. Soybean seed inoculant and fungicidal seed treatment effects on soybean. Crop Science, 2008, 48: 1975-1983 (doi: 10.2135/cropsci2008.02.0108).
- Shu-Jie M.I.A.O., Yun-Fa Q.I.A.O., Xiao-Zeng H.A.N., An M. Nodule formation and development in soybeans (Glycine max L.) in response to phosphorus supply in solution culture. Pedosphere, 2007, 17(1): 36-43 (doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60005-8).
- Afzal A., Bano A., Fatima M. Higher soybean yield by inoculation with N-fixing and P-solubilizing bacteria. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2010, 30(2): 487-495 (doi: 10.1051/agro/2009041).
- Faria M., Martinelli M., Rolim G.K. Immobilized molybdenum acetylacetonate complex on montmorillonite K-10 as catalyst for epoxidation of vegetable oils. Applied Catalysis Agriculture General, 2011, 403(1-2): 119-127 (doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2011.06.021).
- Morshed R.M., Rahman M.M., Rahman M.A. Effect of nitrogen on seed yield, protein content and nutrient uptake of soybean (Glycine max L.). Journal of Agriculture & Rural Development, 2008, 6(1): 13-17 (doi: 10.3329/jard.v6i1.1652).
- Herliana O., Harjoso T., Anwar A.H.S., Fauzi A. The effect of rhizobium and N fertilizer on growth and yield of black soybean [(Glycine max (L) Merril]. Earth Envirmental Sciences, 2019, 255: 12-15 (doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/255/1/012015).
- Khan A.Z., Akhtar M., Ahmad R., Ahmad N., Shah P. Planting date and plant density effects on protein and oil contents of soybean varieties under the environmental condition of Peshawar, Pakistan. Journal of Biological Sciences, 2001, 1(3): 126-128 (doi: 10.3923/jbs.2001.126.128).
- Jaureguy L.M., Ledesma Rodriguez F., Zhang L., Chen P., Brye K., Oosterhuis D., Mauromoustakos A., Clark J.R. Planting date and delayed harvest effects on soybean seed composition. Crop Science, 2013, 53, 2162-2175 (doi: 10.2135/cropsci2012.12.0683).
- Obidiebube E.A., Achebe U.A., Akparobi S.O. Evaluation of soybean varieties [Glycine max L. Merril.], for adaptation to two locations of rainforest zone of delta state. European Journal of Business and Innovation Research, 2013, 1(3): 69-73.
- Rehman M., Khaliq T., Ahmed A., Wajid S.A., Rasul F., Hussain J., Hussain S. Effect of planting time and cultivar on soybean performance in semi-arid Punjab, Pakistan. Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: Agriculture and Veterinary, 2014, 14(3-1): 41-45.
- Nwofia G.E., Edugbo R.E., Mbah E.U. Interaction of genotype½sowing date on yield and associated traits of soybean [Glycine max L. Merrill] over two cropping seasons in a humid agro-ecological zone of south-eastern Nigeria. Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 11(3): 164-177.
- Nsengiyumva A., Byamushana C.K., Rurangwa E. Evaluation of the response of two soybean varieties to rhizobia inoculation for improved biological nitrogen fixation. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 2017, 6: 109-112.
- Shah T., Nazia K.Z., Abrar A., Arshad J. Yield and quality traits of soybean cultivars response to different planting windows. International Journal of Statistics and Actuarial Science, 2017, 1(2): 55-59 (doi: 10.11648/j.ijsas.20170102.14).
- Kawasaki Y., Yamazaki R., Katayama K. Effects of late sowing on soybean yields and yield components in southwestern Japan. Plant Production Science, 2018, 21: 339-348 (doi: 10.1080/1343943X.2018.1511376).
- Umburanas R.C., Yokoyama A.H., Balena L., Dourado-Neto D., Teixeira W.F., Zito R.K., Kawakami J. Soybean yield in different sowing dates and seeding rates in a subtropical environment. International Journal of Plant Production, 2019, 13(2): 117-128 (doi: 10.1007/s42106-019-00040-0).
- Toum G., Khalifa N., Ahmed A.S. Idris H. Effect of planting date and sowing method on yield and grain quality of soybean (Glycine max L.) under North Sudan conditions. Crop Science, 2020, 53(5): 2162-2175.
- Rehaman M., Rahman M., Hampton J.G., Hil M.J. Soybean seed yieldas affected by time of sowingin a cool temperate environment. Journal of New Seeds, 2005, 7(4): 1-15 (doi: 10.1300/J153v07n04_01).
- Zhang Q.Y., Gao Q.L., Herbert S.J., Li Y.S., Hashemi A.M. Influence of sowing date on phenological stages, seed growth and marketable yield of four vegetable soybean cultivars in North-eastern USA. African Journals of Agricultural Research, 2010, 5(18): 2556-2562.
- Bastidas A.M., Setiyono T.D., Dobermann A., Cassman K.G., Elmore R.W., Graef G.L., Specht J.E. Soybean sowing date: the vegetative, reproductive, and agronomic impacts. Crop Science, 2008, 48(2): 727-740 (doi: 10.2135/cropsci2006.05.0292).
- De Bruin J.L., Pedersen P. Effect of row spacing and seeding rate on soybean yield. Agronomy Journal, 2008,100(3): 704-710 (doi: 10.2134/agronj2007.0106).
- Rahman M.M., Hampton J.G., Hill M.J. The effect of time of sowing on soybean seed quality. Seed Science and Technology, 2005. 33(3): 687-697 (doi: 10.15258/sst.2005.33.3.16).
- Cox W.J., Shields E., Cherney J.H. Planting date and seed treatment effects on soybean in the northeastern United States. Agronomy Journal, 2008, 100(6): 1662-1665 (doi: 10.2134/agronj2008.0015).
- Andales A.A., Batchelor W.D., Anderson C.E. Modification of a soybean model to improve soil temperature and emergence date reduction. Transactionsof the American Society of Agriculture Engineers (ASAE), 2002, 43(1): 121 (doi: 10.13031/2013.2693).
- Chen G., Watrak P. Soybean development and yield are influenced by planting date and environmental conditions in the southeastern coastal plain, United State. Agronomy Journal, 2010, 102(6), 1731-1737 (doi: 10.2134/agronj2010.0219).
- Aziz A., Asif M., Khan M., Javaid M.M., Nadeem M.A., Raza A., Babar B.H. Evaluation of soybean (Glycine max l.) cultivars productivity in relation to different sowing dates under semi-arid conditions. Journal of Agricultural Research, 2021, 59(2): 141-150.
- Steel R.G.D., Torrir J.H., Dicky D.A. Principle and procedure of statistics. A biometrical approach. McGrew Hill Book Co. Inc., NY, 1997: 400-428.


