Scientific and practical aspects of organizing week-end routes in the natural environment using technologies of active tourism
Автор: Anokhin Alexey Yu., Kropinova Elena G.
Журнал: Современные проблемы сервиса и туризма @spst
Рубрика: Региональные проблемы развития туристского сервиса
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.14, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article reveals modern trends in the development of tourism both in Russia and abroad. The authors first of all provide an overview of trends emerging in the pre-coronavirus period and associated with a shift from mass-tourism to its sustainable forms. The study as well underlines the problems that emerged during the COVID-19 pandemic, both in consumer demand and by tourism providers. Particular attention is paid to the types of domestic tourism, which, according to experts, will receive an additional impulse for development in the post-coronavirus period. The practical aspects of organizing weekend itineraries as a promising type of domestic tourism are considered on the example of the internal regions of the Kaliningrad region of Russia located on the mainland adjacent to the Curonian lagoon. According to the results of the study, an integrative model of the formation of a recreational effect by active tourism technologies was developed taking into account the concept of sustainable development in post-coronavirus conditions. Field studies were carried out as part of the implementation of the international project of the Lithuania-Russia Cross-Border Cooperation Programme 2014-2020 ““Сommon Heritage of Curonian lagoon: from Extraordinary to Familiar - CROSS-HERITAGE».
Туризм после соvid-19, domestic tourism, outdoor activities, recreation, weekend tour, family holidays, differentiation of tourist services, tourist clusters, small accommodation facilities, sustainable development, ecological tourism / ecotourism, international cooperation, tourism after соvid-19
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140249878
IDR: 140249878 | УДК: 338.48(911:33+332.1) | DOI: 10.24411/1995-0411-2020-10205
Текст научной статьи Scientific and practical aspects of organizing week-end routes in the natural environment using technologies of active tourism
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY-SA 4.0). To view a copy of this license, visit https://creativecommons.
Introduction. In the aftermath of the coronavirus pandemic, there is a transition from mass services in tourism to a more differentiated, customer-oriented one. There is an interest in a deeper touch with tourist resources located in the immediate vicinity of the place of permanent residence, which is an additional incentive in the development of domestic tourism. The intensive development of small accommodation facilities, accompanied by the synchronous development of recreation facilities, increases the attractiveness of underdeveloped territories and creates a stable local tourist flow (in the conditions of the Kaliningrad region it is also cross-border). A system of interaction of identified, systematized and included in the tourist use the recreational resources with objects of the tourism industry makes it possible to create a unique and differentiated tourism product. In this case, the integration between the subjects of the tourism business is built on the technology of the cluster approach, in which the close location and the built technological interconnections facilitate to bring manufacturability, efficiency, attractiveness and product promotion to a qualitatively new level. In the Kaliningrad region, such a subarea are territories adjacent to the Curonian lagoon. Thus, there is the possibility of forming a tourist product for local consumption and, in part, inbound tourism due to the cross-border nature of these territories. The described components are a dispersed managed subsystem of the cluster structure of the formation of a tourist product. The managing (integrating) subsystem is the information systems that formulate the promotion of this product on the regional and interregional tourist market: local administrations and their electronic resources, tourist information centers, stand systems with visual information, tour operator and travel agencies of the region (and in post-corona-virus conditions, apparently, the consumers themselves). In this study the authors developed the routes and described the travel industry infrastructure along them. They could be recommended as weekend tours for tour operators as well as for individual tourists.
Methods and Methodology. In the heart of our approach is the principle of the integrity and continuity of the production and con sumption of tourism services. This approach was put into the base of the model of the formation a tourist product, which was constructed using outdoor activities and recreation on the base of small accommodation facilities in a low-urban (countryside) area. In accordance with the principle of emergence, while constructingthe model, we have included into it the system-forming components, selected on the basis of standard data collection techniques. To collect information on the project development area, we used standard literary and expeditionary (field) research methods; to analyze the consumer demand, we introduced the questionnaire method; to display the results, we applied cartographic method.
Strengthening "green trends" in consumer demand for tourism services
The development of society is reflected in the development of consumer demand, not only for new tourist destinations, but also for new forms of tourism. Already in the pre-coronavirus era, there were cleartrends in increasing the share of "green tourism". There is a special section "Tourism and Sustainable development in the Baltic Sea region" in the Encyclopedia of UN Sustainable development goals devoted to the sustainable tourism [17].
For instance, in his work "Demand for Sustainable Tourism" (2019), F. Weber carried out a review of works confirming lifestyle changes and related attitudes toward proximity to nature, or the search for authenticity and self-realization, emphasizing the increasing demand for sustainable tourism [21].
However, a survey of 4800 respondents in Switzerland conducted by the Institute of Tourism of the Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts, cited by Weber [20], indicated that consumers want to book a sustainable tour product, but their desire to pay extra for "sustainability" is very limited. Most of the respondents indicated that they were ready to pay only 1.5% more [21, 22]. Therefore, while developing environmental tours, one should make them inexpensive.
In particular, F. Weber (2019) concluded that the understanding of sustainability among tourists varies greatly, and its perception is often quite selective, especially during the holidays. And since "sustainability"
remains a fairly abstract concept for many people, it must be made tangible for guests. Such "tangibility" can be, for example, an emphasis on health, comfort, clean air or a regional product [21, P. 278]. And here, it is very important that the designed tourist product meets the expectations of consumers!
It is noteworthy that Russians are among the three leading countries whose respondents indicated sustainability criteria as one the 3 main factors when planning vacation (21.9% of respondents), ahead of Germany (16.8%) and Sweden (15.4%) [21, P. 269].
Another trend, which is quite popular among Europeans and which the Scandinavian tour operators have successfully applied to marketing of their travel product, is "slow adventure" [18]. This kind of travel is possible not the only in conditions of the wild northern nature, but also is quite feasible in peripheral areas with rich natural resources suitable for tourist use. The theoretical foundations of "slow tourism" are discussed in details in the work of de Salvo et al. "The value of Time: Slowness, a Positive Way of Performing tourism" [15]. In this work, the authors cite the cornerstones of this concept proposed by Lamsdon and McGrath [19], namely, the slowness and value of time, the destination and on-site activities, the means of transport and the voyage experience and the environmental ethics. At the same time, there is undoubtedly a clear link between "slow tourism", sustainable development, the number of participants in the tour, the features of the services provided and the availability of territory provided with natural (and cultural-historical) resources. As long as entire regions (Scandinavian countries) offer such a product to foreign markets, then our, Russian domestic resources, are unlimited in this case.
At the same time, promoting the ideas of outdoor recreation, even with the small num-berof groups, there is always a threat to biodiversity. Especially when it comes to organizing tours in unique corners of nature; moreover, as a rule, the more unique nature is, the more vulnerable it is. Therefore, ecological tours should be considered as the optimal type of weekend tours when it comes to outdoor recreation. The most comprehensive definition of ecotourism is proposed in the Encyclope dia of Tourism as "a subsidiary of sustainable tourism, which relies on nature-based attractions; employs best practice environmental management; contributes to conservation; involves local communities; offers effective interpretation; and generally, though not exclusively, favors smaller scale operation" [14]. However, pretty fast this type of tourism became so popular that some public parks currently receive more than ten million visitors a year, which is far more than many urban tourism destinations do. And ecotourism itself has become an integral part of the general spectrum of tourist attractions, activities, quality of service, products and price ranges [14]. Ecotourism in the post-coronavirus era is destined, in our opinion, to return to its original form and again become an alternative to mass tourism. At the same time, as the above mentioned components designated by R. Buckley became to be an integral part of ec-otours, they will remain in the future as well.
We have already begun to observe this shift in connection with the introduction a number of restrictions on visiting national parks. For example, the administration of the Lithuanian national park of the Curonian Spit in December 2019 announced plan to double the ecological fee for entrance starting from the summer of 2020 in order to reduce the flow of tourists), similar measures are in plans of the administration of the national park "Kurshskaya Kosa" ("Curonian Spit", Russia), where there are over 600 thousand visitors annually. The involvement in tourism use of alternative territories with a lower environmental status (or without it at all), but with favorable natural conditions will reduce the load on popular tourism centers and ensure individuality (which is identical to the "distancing" that became popular during the COVID-19). By that, it is important that such approach will follow the five main criteria for sustainable development, outlined in the work of Freud (2019) with reference to Muller (1994), namely: environmental protection, preservation of local culture and traditions, the general welfare of the local population, economic well-being, optimal satisfaction of the needs of guests (tourists) [16,20]. This means that the development of eco-tourism allows us to move the virtual border separat- ing "unstable" tourism from "sustainable" to the latter.
At the same time, the formation of consumer demand is similar to the formation of taste - the demand (taste) for nature-oriented tourism must be formed from childhood. It is family travel (in particular, weekend tours), that can lay the foundation for a lifetime and instill a love for such travels.
New trends in the development of a tourist product
Currently, there are new trends in the development of the tourism product. The main one concerns travel motivation. From the S-S-S (Sea - Sun - Sand) paradigm that dominated in the second half of the 20th century, the modern tourism and travel industry is shifting to the L-L-L (Lore - Landscape - Leisure) paradigm. In our opinion, this is a manifestation of a deeper trend - the differentiation of the tourism product. Each tourist has his own unique socio-psychological pattern, from which follows a deeply individualized structure of recreational needs. For a long time (following the SSS paradigm), the tourism industry, developing the main economic growth areas (the construction of large coastal hotels, the development of passenger aircraft, the formation of tour operator and travel agencies, and, subsequently, reservation systems), to some extent ignored individual needs, offering slightly differentiated mass product. A partial inevitable differentiation of the tourism product was soon reflected in the classification of tourism by types of tourist activity. Such types were highlighted as follows: entertaining (including beach), cognitive, business, health, sports, event and rural tourism. Over time, this classification has developed dynamically in the direction of differentiation. For example, event tourism generated festival tourism, trips to sporting events, gastronomic tours.
Currently, we can talk about the "transition of quantity into quality". That is, about the advent of the era in tourism, in which the formation of tourist products is increasingly carried out by the client independently on the basis of booking or purchasing certain tourism industry services (accommodation, food, entertainment). The other option is travel agency, which could provide this assistance, performing similar actions on behalf of the client (on a direct client order). We consider this trend to be a long-term and deterministic due to the creation of a global information space. In our opinion reinforced by the opinion of other experts, this trend will undoubtedly increase in the post-coronavirus era. Thus, the Minister for Culture and Tourism of the Kaliningrad region is confident that the structure of tourism consumption will fundamentally change, namely, "the emphasis will be on individual tours, this is completely obvious. The largest groups will be families, that is, there will be mostly family trips", he also noted that there will be "a roll towards ecological travel, of some kind of contemplative recreation, with the maximum social distance"1.
The recreational paradigm in considering the formation of a tour product involves an assessment of the recreational effect. Of course, due to the differentiation of the tourist product, it is necessary to recognize the multimodality of the recreational effect. One can distinguish such modalities as relaxation, cognition, healing, physical activity, mastery of skills, communication and others. The limited total time of rest in the weekend tour (as well as in one-day routes) suggests a rather high tourist activity. For example, relaxation in its pure form, health and cure tourism for a sufficient effect most often requires a longer time, but cognitive activity, physical activity, mastery of skills and communication can very well be effective even in a short period of time. Of course, and we will proof that below, the combination of several recreational modalities in one form of activity will significantly increase its recreational effect. From the above it follows that effective weekend recreation is optimal if it includes outdoor activities or is full of cognitive and communicative components. Along with the consideration of the recreational paradigm, it is important to remember that rest is a change of activity and a change of scenery. That is, certain requirements are also imposed on the recreational space. For most city dwellers, a change of scenery implies a natural environment or attractive low-urban settlements. In this context, given the small distance from the place of permanent residence, a good option for a weekend break would be a vacation in the countryside. Based on the above mentioned, the main content of tourists' activities can be active recreation routes (hiking, cycling, kayaking, horseback riding, quad biking), acquaintance with the historical, cultural and natural sights of the territory, traditions, crafts, and local cuisine.
Cluster approach to forming a weekend tour
Russia has a large number of low-urban areas, which are a natural resource for the development of domestic tourism. The content of the weekend is largely determined by the resources of the territory, the mentality of the population, and the technological capabilities of organizing leisure. As said above, an active recreation is one of the most effective extensions of the content of tourism in countryside. From this point of view, it is likely that one can talk about developing a recreation model that meets the principles of sus tainable tourism. This model includes a set of components identified in R.Bukley's work [14] which are typical for ecological tourism and contain many attractions, including physical activity. First of all, this applies to the weekend formats of tourism, as well as to the consumption of outdoor activities in a one-day format (kayaking, horse riding and hiking). In this context, a weekend tour provides recreational opportunities for those who cannot afford anothertypes of tourism due to financial or other reasons. Some authors directly point to this trend as the connection of outdoor activities and accommodation in rural areas [4], [11], [12]. It is equally important to highlight the effectiveness of this type of recreation. To our opinion, one can talk about the following areas of impact: physiological (increase in basic health indicators); psychological (the effect of practicing the favorite type of activity); communicative (communication with friends during the holidays); social (socialization, inclusion in a social group, acquisition of an appropriate status in it). The other authors detail individual aspects of the recreational impact of outdoor activities. For example, the influence of schoolchildren's hiking on the level of skills and physical fitness [13], the development of important social qualities during hikes [10], a positive emotional attitude, harmonization of family relations with joint active recreation by the whole family [2]. Research in the field of outdoor activities for students highlights factors that positively affect the quality of life: namely, a change of scenery; optimal physical activity; stimulation of the immune system [6].
To achieve high economic efficiency, there is need for a high density of tourism industry objects and technological interaction between them. Thus, one can talk about using a cluster approach to create a model for the development of a weekend holiday segment. This problem has already been highlighted in the works of Russian and foreign authors. For instance, 0. Afanasyev (2016) writes that the provision of tourist services in individual tourist centers ideally seeks to form a tourist and recreational cluster that brings together producers of the tourist product, their counterparties and consumers. By that, the cluster approach itself is considered as a sys- tem-forming in the formation of tourist flows in domestic and, in part, in inbound tourism [3]. A. Alexandrova (2007) considers the economic nature of the cluster and focuses on the value accumulation system in the tourism cluster: from suppliers who are the "previous subsystem" to suppliers of tourism services (accommodation, meals, transportation, attractions, souvenirs, etc.) to aggregation chains and sales of services (individually or as a complex) to consumer chains [1] . According to the UN WTO, with a week-long stay of a tourist in a remote tourist center, from 10 to 20 chains operate, with involvement of 30-50 economic entities [1].
Organization of weekend routes in the mainland of the Curonian Lagoon (Kaliningrad Region of the Russian Federation)
The study covered the area east of the Curonian lagoon (Polessky and Slavsky municipality of the Kaliningrad region). The bay is divided between the Republic of Lithuania and the Russian Federation. The water area mainly belongs to Russia (1.2 th. km2 of 1.6 th. km2). The bay is shallow with an average depth of about 3.7 m. The bay is a freshwater body since the Neman (annual flow 21 km3) flowing into it. The Neman is located in the northern part, forming a stable outgoing stream through the strait. The bay has vast fish resources. The ichthyofauna of the lagoon includes 53 species of fish from 18 families, which makes the lagoon and adjacent rivers suitable for amateur fishing.
With westerly and northerly winds, waves up to 0.8 m high are frequent in the bay. It is to some extent is an obstacle for kayaking. The eastern coast of the lagoon represents a lowland and polder lands, pierced by a large number of full-flowing rivers, canals, as well as small drainage ditches.
One of the areas of research in our previous studies was the development of shipping on inland waterways. The main water route of the Kaliningrad region "Kaliningrad Gulf - Kaliningrad - the river Pregol, the river Deima -Curonian Lagoon" is a part of the international European route E-70. The Neman is part of route E-41. It is important to include Rybachy settlement (small village on the Curonian Spit) to route E-70 [8]. In 2011, there were amend ments made to the Code for Inland Water Transport of Russia, which allowed now to sail on the inland waterways of the Russian Federation for sports and pleasure boats flying a foreign flag, with a total capacity of up to 18 people. In 2015, the construction of a marina was completed in the estuary of the river Trostyanka at the confluence of the river into the Curonian lagoon in Zelenogradsky municipality of the Kaliningrad region3.
Figure 1 shows the rivers and canals of the region suitable for navigation of small vessels. It demonstrates that a significant part of these sites is concentrated in the territorial framework of our study.
The mainland of the Curonian lagoon has a rich historical and cultural heritage, which is important not only for domestic but also for inbound cross-border tourism. Polessky and Slavsky municipalities of the Kaliningrad region are known for their great historical potential. Polessk is located on the border of two historical regions of ancient Prussia: Sam-bia (the left bank of the Deima) and Nadrovia (the right bank of the Deima). The city of Polessk itself has a rich history. Forthe first time, this locality was mentioned in historical documents in 1249 as Labiau /Labegove. The modern Slavsky municipality (Slavsk until 1945 was called Heinrichswalde) is located on parts of the territories of two historical regions of ancient Prussia: Nadrovia (south of the municipality) and Skalovia (north of the municipality). In Slavsky municipality there are 3 archaeological sites: the Rzhevskoye burial ground, which dates from the 1st - 13th centuries AD.; Oktyabrskoye settlement- dated back approximately to V — X centuries and the village "Rzhevskoe", which refers to the IX-XIV centuries.
Potential water routes along the rivers and canals of Polessky and Slavsky municipalities of the Kaliningrad region have their own historical and cultural potential. The drawbridge in Polessk (Eagle Bridge) is one of the main attractions of the city. The bridge
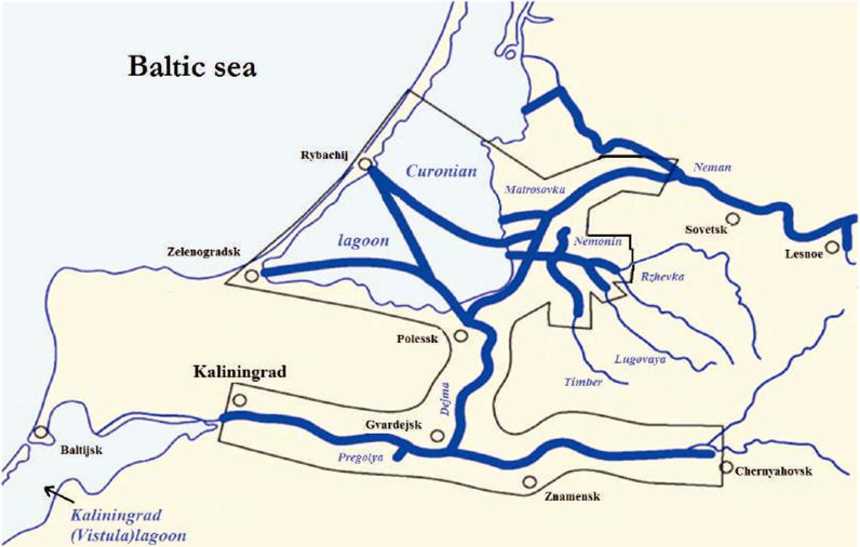
Fig. 1-Map of the waterways of the Kaliningrad region
was built in 1922 and reconstructed in 2002. In Slavsky municipality, near the village Gro-movo, there is a unique drawbridge across the river Rzhevka. It looks like typical Dutch bridges that were built through land reclamation facilities. At 6 kilometers from the village Zapovednoye, the ruins of a drawbridge across the Nemoninsky Canal is an interesting tourist attraction. Not far from the village Len-inskoye (before 1945 it was called Weidenau) in Slavsky municipality, structural elements of the old lock system are partially preserved. The former gateway is located on the bypass channel of the river Matrosovka and today does not function, but it is an attraction for kayaking routes.
The system of rivers and canals itself is unique in that it is actually man-made. The reclamation network began in the mid-17th century. By 1939, 889.4 thousand hectares were drained in the north of the East Prussia, of which 420.5 were with closed drainage and 468.9 were with open drainage. The area of polder lands reached 91.7 thousand hectares. 600 km of dams were erected, about 30 thousand kilometers of canals were laid, 116 pumping stations were built with a total flow of 102.7 cubic meters per second.
One of the main ethno-cultural phenomena of this territory is the organization of fishing in the lagoon. The fishing vessels were Kurenas type, which were used until the second half of the 19th century. Since 1884 on the main mast of Kurenas was a colored wooden weathercock (serving as pennant). The weathercock of Kurenas is an object of intangible cultural heritage. The surviving pennants and their replicas are objects of display in regional museums of the Kaliningrad region (for instance, in Visit Center of the national park "Kurshskaya kosa") and in Lithuanian museums (for instance, in VydQnas Cultural Centre in the village of Kintai).
The accommodation industry in the studied area is represented by 9 small accommodation facilities, of which 1 in Polessk and 8 in rural areas. There are 2 of them are of 3-star category (both of which are located in rural areas). The total number of rooms of all categories is 131 and it varies from 4 to 36. Moreover, 3-star properties have 33 and 36 rooms, respectively, and in starless accommodation facilities there are from 4 up to 14 rooms. The average value for starless facilities is 8.85 rooms / property. The average price for a double-bed standard room is 2000 rubles and it varies from 1700 to 2500 rubles. The price for the guesthouse standing apart is about 800 rubles per day per room. Meal is provided by 5 out of 9 accommodation facilities. For the others there was not such information available. These accommodation facilities offer standard services as follows: transfer to / from the airport, parking, laundry, safe, banquet room, barbecue area, bathhouse, sauna and pool, children's playground, billiards, SPA
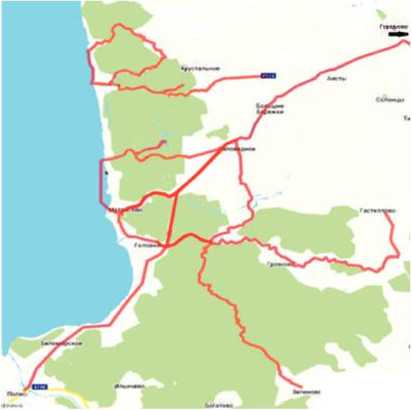
Fig. 2 -Kayaking routes in Polessky andSlavsky municipalities of the Kaliningrad region complex, petting zoo. Outdoor activities are also offered, such as fishing and gear rental, bike rental, boat and boat trips, boat, kayak, catamaran rental, hunting, ATV rental. Due to the fact that this territory is practically not used for agriculture, all of these facilities are for tourist use. Moreover, the concentration of tourism industry objects per unit area is significantly lower than on the other side of the lagoon - on the Curonian Spit (the national park, which is an object of UNESCO). There are over 39 objects of different star categories on the Curonian Spit.
In addition to the accommodation industry, in Polessky and Slavsky municipalities there are also specialized enterprises organizing weekend water routes and for renting kayaks. The renting service provides delivery of kayaks to the place of the beginning of the alloy by road or water vehicle.
As part of the study, we conducted a survey of Kaliningrad consumers of the eco logical tourism product. The most popular answers to the question "Who do you prefer to travel with" were: with family (38%) and with friends (36%). Such answer confirms the relevance of small formats for organizing tourist activities. It is such a product that small accommodation facilities are ready to provide. The key parameters of the attractiveness of the ecological tour were as follows: the favorable ecological situation (76%), the ability to see the untouched nature (68%), the ability to see animals in the natural environment (60%) (several options for the answer were allowed). In the question "What activities, in your opinion, should be included in the ecot-our?" the most common answer was: active types, including alloys, cycling, etc. - 70%; then - visit to ecological museums - 66% and hiking along ecological trails - 64%. This study allows to simulate the image of a weekend tour in this territory as a family or a small group of friends, with the presence of active types of recreation, including the possibility of excursions of a natural or historical-cultural orientation.
In Polessky municipality there are 2 large facilities providing kayaking routes and kayaking rental services. They are guest house Fishdorf and a kayaking station in the village Golovkino. We have developed a network of kayak routes based on these facilities (taking into account the possible delivery of kayaks to the starting point of the rafting by special transport). Graphically, Figure 2 demonstrates the routes. Table 1 presents more detailed information about the routes.
All routes are focused on a balanced acquaintance with natural attractions (rivers, lakes, forests, rare species of plants and animals), historical and cultural attractions (churches, bridges, floodgates, dams, water pumping stations), dosed physical activity. All described routes suggest moderate- intensity or high level of physical activity. As long as there is a need for its reduction, partial or radial passage of routes is possible. Another possibility for the development of the route network is the formation of two-day routes with overnight stays in tents in beautiful places (Lake Tav, Mary Lake).
Table 1 - Planned kayaking routes
|
Route link |
Intensity of physical activity |
Aim/Purpose of travel |
|
Gorodkovo settlement - the river Matrosovka r -Matrosovo settlement n. Городково - p. Матросовка - п. Матросово |
High |
Visiting of the floodgate, dams, church in Zapovednoye. Visiting of rare species of aquatic vegetation |
|
Prichaly settlement - Curonian lagoon - Rybnoe settlement -the river Bicheva - Prichaly settlement n. Причалы - Куршский залив - p. Рыбная - p. Бичева -п. Причалы, 1 день |
Moderate |
Visiting of forests on polder lands Visiting of rare species of aquatic vegetation Exit to the Curonian lagoon |
|
Vishnevka settlement - the river Shljuzovaja - the river Rogozhinka - pr.Gribov (rad) - the river Bicheva - Prichaly settlement n. Вишневка - p. Шлюзовая - p. Рогожинка - пр. Грибов (рад.) - р. Бичева - п. Причалы |
Moderate |
Visiting of forests on polder lands Visiting of rare species of aquatic vegetation Visiting of water pumping stations and bridges |
|
Matrosovo settlement - Curonian lagoon - the river Tava -the river Matrosovka - Matrosovo settlement п. Матросово - Куршский залив - p. Тава - Тавские озера (рад.) - р. Тава - р. Матросовка - п. Матросово |
High |
Visiting of forests on polder lands Visiting of rare species of aquatic vegetation Visiting the Tav Lakes. Exit to the Curonian lagoon |
|
Zelenovosettlement-the river Zalesinka-Golovkinsky canal (Timber)-the riverNemonin- Primorsky canal- the river Matrosovka -Matrosovo settlement п. Зеленово - p. Залесинка - Головкинский канал (Тимбер)- р. Немонин - Приморский канал - р. Матросовка - п. Матросово |
High |
Visiting of forests on polder lands Visiting of rare species of aquatic vegetation Visitingofreclamationfacilities |
|
Matrosovo settlement-channel (protoka)-the river Nemonin -Nemoninsky canal - Zapovednoe settlement -the river Matrosovka -Matrosovo settlement n. Матросово - протока - p. Немонин - Немонинский канал - п. Заповедное - р. Матросовка - п. Матросово |
High |
Visiting of the floodgate, dams, church in Zapovednoye. Visiting of rare species of aquatic vegetation |
|
Gastellovo settlement- Mokry cannal - the river the river Rzhvka - the river Nemonin - Primorsky canal- the river Matrosovka -Matrosovo settlement п. Гастеллово - канал Мокрый - p. Ржевка - p. Немонин - Приморский канал - р. Матросовка - п. Матросово |
High |
Visiting of forests on polder lands Visiting of rare species of aquatic vegetation Visitingofreclamationfacilities |
|
Golovkino settlement -the river Nemonin -Polessky canal (in one side) п. Головкино - p. Немонин - Полесский канал (в одну сторону) |
Moderate |
Visiting of reclamation facilities Water arrival to Polessk |
Table 2-Planned cycling routes
|
Route link |
Intensity of physical activity |
Aim/Purpose of travel |
|
Polessk-Golovkino settlement г. Полесск- п. Головкино |
Moderate |
Visiting of the Polessk Canal, arrival from Polessk by active means |
|
Golovkino settlement -Zapovednoje (farm) n. Головкино - хутор Заповедное |
Moderate |
Visiting of forests on polder lands Visiting of the Primorsky Canal |
|
Polessk- Saranskoe settlement - Golovkinsky canal -Golovkino (marina) г. Полесск - п. Саранское - Головкинский канал -пристань Головкино |
High |
Visiting of forests on polder lands Visiting of rare species of aquatic vegetation Exploring Lauken Castle |
|
Slavsk - Gastellovo settlement - Zapovednoje settlement - Zapovednoje (farm) г. Славск- п. Гастеллово - п. Заповедное - хутор Заповедное |
High |
Visiting of forests on polder lands Visiting of the floodgate, dams, church in Zapovednoye. |
|
Route link |
Intensity of physical activity |
Aim/Purpose of travel |
|
Gastellovo settlement - Nemoninka River - Ne-moninsky canal п. Гастеллово - река Немонинка - канал Немонинский |
Moderate |
Visiting of forests on polder lands Visitingofreclamationfacilities |
|
Sovetsk - Prigorodnoe settlement - Slavsk road-Gastellovo г. Советск - п. Пригородное - шоссе Славск- Гастеллово |
High |
Visiting of picturesque forest landscapes Arrival in Sovetsk |
|
Slavsk - Jasnoe settlement - Prichaly settlement г. Славск - п. Ясное - п. Причалы |
High |
Visiting of forests on polder lands Visiting of the church in the city of Slavsk, in the village of Yasnoe |
|
Prichaly settlement - Prokhladnoe settlement - the river Shljuzovaja п. Причалы - п. Прохладное - p. Шлюзовая |
Moderate |
Visiting of forests on polder lands Visiting of reclamation facilities Visiting of bridges, dams |
|
Saranskoe settlement - Sosnovka settlement -Bol-shakovo settlement-Gastellovo settlement n. Сараноское - n. Сосновка - п. Большакове - n. Гастеллово |
High |
Visiting of the church, Lauken castle, narrow gauge railway Fast moving around the area from the south |
|
Jasnoje settlement - Vishnevka settlement - the river Shljuzovaja- Khrustalny settlement n. Ясное - п. Вишневка - река Шлюзовая - п. Хрустальный |
High |
Visiting of forests on polder lands Visiting of reclamation facilities Visiting of bridges, dams |
|
The river Shljuzovaja - Kljuchvoy canal - the river Matrosovka - the river StarajaTava -Marijskoe lake -the river Shljuzovaja p. Шлюзовая - канал Ключевой - p. Матросовка -река СтараяТава - оз. Марийское - р. Шлюзовая |
High |
Visiting of forests on polder lands Visiting of reclamation facilities Visiting of bridges, dams |
The developed cycling routes are for acquaintance with the sights of the area and provide the necessary physical activity. The route network represents individual segments (route links) that can be designed by tourists in any combination. The network of routes is
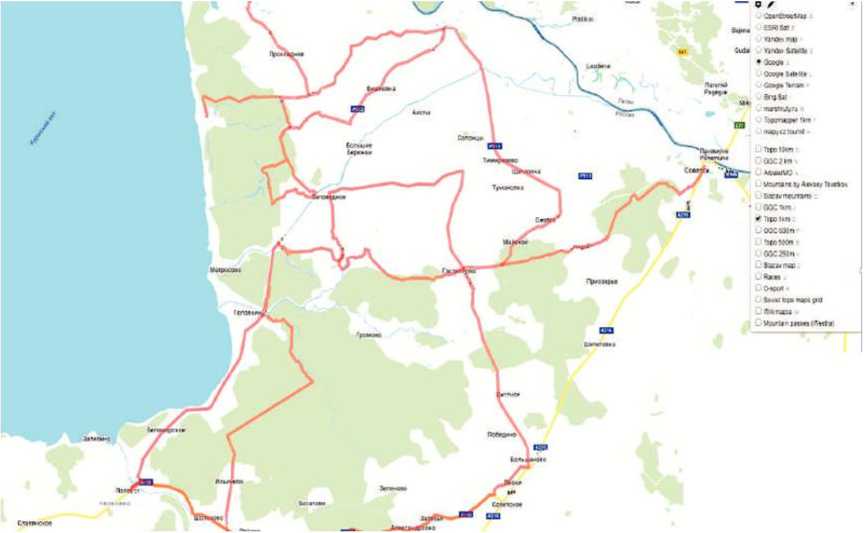
Fig. 3-Cycling routes in the Polessky andSlavsky districts of the Kaliningrad region
presented in Fig. 3. The detailed information is provided in Table 3. The length of the routes varies from 5 to 45 km. The Intensity of physical activity is indicated taking into account the length of the route and coating of the road. Due to the dominance in the area of waterways, in one of the points (Golovkino marina), bicycle routes are connected by boat crossing. The imposition of networks of kayaking and cycling routes implies the possibility of combined multimodal weekend routes, provided that appropriate logistics is organized.
Discussion. Tourism experts repeatedly carried out zoning of the territory of the Kaliningrad region according to the level of tourism development, the prospects of various regions of the region, the stages of their development and inclusion in tourist activities; Poles and growth points, peripheral areas, etc. The coastal territories of Polessky and Slavsky municipalities of the Kaliningrad region considered in our study, until recently, in most cases fell either in the periphery zone, and in the best cases, were assigned to promising areas with a low degree of development [5,7,9]. At the same time, all researchers noted the richness and diversity of tourist resources associated with the uniqueness of the Curonian Lagoon biota, the rich historical and cultural heritage of various eras, and the presence of man-made engineering structures - polders. Fishing and hunting and rural tourism were pointed among the promising types (and since the 2000s, along with the development of its popularity, ecotourism). The geographical proximity to the regional center - Kaliningrad - has been an additional factor contributing to the development of this territory. All these resources, undoubtedly, allowed this part of the region to receive accelerated development and ensure the sustainable development of tourism in the Kaliningrad region. Despite this, right up to the COVID-19 pandemic, this territory remained quite backward compared to the intensive development of other areas, for example, resorts of federal meaning at the Kaliningrad region coastal zone of the Baltic Sea. However, in the spring of 2020, the factor COVID-19 was added to the factors already identified by us. It increased the element of uncertainty in the forecasts of development of this remote part of the region. As noted in his address related to Earth Day celebrated in April, UN Secretary-General, Antonio Guterres: "We can go back to the world as it was before or deal decisively with those issues that make us all unnecessarily vulnerable to the crises". In this regard, the question arises: can the peripheral territory of the Kaliningrad region, which has rich tourism potential, in the new post-coronavirus situation receive a new impetus in development and become a new center of attraction for tourists? Will it be able to develop in accordance with the principles of sustainable development (namely, the protection of nature, the preservation of natural and cultural heritage, economic efficiency, the general well-being of the local population), while optimally meeting the needs of the modern consumer?
Results of the research. Thus, we have constructed the integrative model based on the analysis of theoretical aspects and its application for the development of specific weekend routes in the natural environment with application of active recreation technologies (Fig. 4). The case is for the Russian part of the continental regions adjacent to the Curonian lagoon.
The model proposed in Figure 4 is a structure that reflects the essential, substantial, technological and organizational relationships of the following components: 1) basis (the natural and landscape potential of the territory, its historical and cultural heritage), 2) the managed subsystem (the provision of basic tourist services, the organization and provision of outdoor activities), and 3) the managing/integrat-ing subsystem (which includes the activities of tour operator and travel agencies, public and non-profit organizations, as well as the activities of state bodies of tourism management and regulation). The central category of the model is the recreational effect. The basic services, providing the recreational effect are as follows: the very fact of visiting an ecologically clean and attractive landscape, comfortable accommodation, healthy meals, additional services in an accommodation facility), as well as technologies for organizing outdoor activities. Either separate or integrated component in active leisure activities may be museum and sightseeing services on routes. At the same time, an important substantive idea of this model is the integrating effect of the
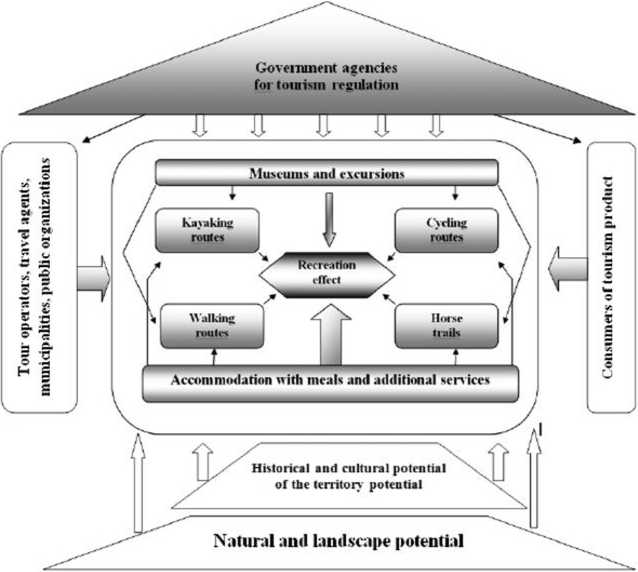
Fig. 4-An integrative model of the formation of a recreational effect by active tourism technologies, taking into account the concept of sustainable development in post-COVID-19 conditions
management subsystem. Such effect provides, at a minimum, the formation of a tourism product from disparate services. This allows business entities in accordance with a systematic approach (principle of emergence), to provide more services and increase added value. This is important for consumers, as it allows them to receive services of a qualitatively new level. In the maximum development, this leads to the formation of an integrated system of interaction, in which the "edges" between individual business entities are "erased" and the consumer "travels" between them, undergoing a constant change of interiors, landscapes, and mode of activity. This will allow the consumers to get the maximum recreational effect, and to the service providers to get the maximum profit and the realization of their capabilities. From the point of view of marketing, this facilitates the promotion on the market of little-known means of accommodation or the provision of other services. At the same time, the creation of a comprehensive tourism product does not require each subject of the tourism industry to possess the entire arsenal of equipment, inventory and competencies. Along with the activities of tour operators, the management subsystem includes a promotion system.
This system ranges from classic travel agencies to regional tourist information centers, information resources of international programs and projects. For example, cross-border cooperation programs are a powerful information resource for promoting a tourism product. Moreover, taking into account the specifics of the Kaliningrad region, it can be noted that, due to the established traditions of consumer motivation, foreign markets (Poland, Lithuania, and Germany) are more targeted than the domestic one.
By itself, it is worth highlighting the regulatory, and, in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, even the restrictive influence of the state. On the one hand, tourism authorities are interested in the maximum development of tourism, and in this context, municipal funding is aimed at creating infrastructure used by both local residents and tourists. Also, municipalities participate in cross-border cooperation programs and can support business projects at the regional level. On the other hand, during a pandemic, the requirements for protecting public health imply a number of restrictive measures that seriously affect traditional mass recreation formats (in particular, the requirements of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare). However, these measures to a lesser extent limit small (family, etc.) formats, the contents of which are considered in this mod el. Our approach could be applied to develop weekend routes for other regions of Russia with the goal of developing and promoting domestic tourism in the post-coronavirus era.
Список литературы Scientific and practical aspects of organizing week-end routes in the natural environment using technologies of active tourism
- Aleksandrova, A. Yu. (2007). Turistskie klastery: soderzhanie, granitzy, mechanism funktzionirovanija [Tourist clusters: content, boundaries, mechanism of functioning]. Sovremennye problemy servisa i turizma [Service and Tourism: Current Challenges], 1, 51-61. (In Russ.).
- Antufiev, D. A., & Antufieva, S. L. (2012). Organizatzija sovmestnogo aktivnogo ondyha detej I roditelej na prirode [Organization of joint outdoor activities for children and parents in nature]. Primary School, 7, 49-53. (In Russ.).
- Afanasiev, O. E. (2016). Turistskije klastery i destinatzii: problem sozdanija i prodvizhenija [Tourist clusters and destinations: problems of creation and promotion]. Sovremennye problemy servisa i turizma [Service and Tourism: Current Challenges], 10(1), 5-6. (In Russ.).
- Gerasimova, M. I., & Tarasov, A. E. (2014). Sozdanie turistskoy bazy dlja organizatzii aktivnogo otdyha naselenija [Creating a tourist base for organizing outdoor activities]. The path of science, 1(9), 75-79. (In Russ.).
- Dragileva, I. I. (2006). Transgranichnoje sotrudnichestvo i razvitije turisma Jugo-Vostochnoj Baltiki [Cross-border cooperation in the development of tourism in the South-East Baltic]: PhD thesis. (In Russ.).
- Krivosheeva, T. M., & Kugusheva, A. N. (2013). Organizatzija turisma i aktivnogo otdyha dlja studentov [Organization of tourism and outdoor activities for students]. Vestnik Assotsiatsii vuzov turizma i servisa [Universities for Tourism and Service Association Bulletin], 1, 48-53. (In Russ.).
- Kropinova, E. G., & Zaitseva, N. A. (2015). Razrabotka stzenarijev razvitija turizma v Kaliningradskoj oblasti do 2030 goda [Development of tourism development scenarios in the Kaliningrad region until 2030]. Regional Studies, 4(50), 126-132. (In Russ.).
- Kropinova, E., & Anokhin, A. (2014). The development of new trans-border water routes in the South-East Baltic: methodology and practice. Baltic Region, 3(21), 145-162.
- DOI: 10.5922/2079-8555-2014-3-11
- Kropinova, E. G., & Mitrofanova, A. V. (2011). Regional'nyj turistskij klaster kak turistsko-rekreacionnaja sistema regional'nogo urovnja [Regional tourist cluster as a tourist-recreation system at the regional level]. Regional'nye issledovanija [Regional research], 1(31), 40-46. (In Russ.).
- Matveev, A. E. (2017). Peshekhodnyi turism kak forma aktivnogo otdyha [Hiking as a form of outdoor activities]. Almanac of world science, 3-3(18), 114-115. (In Russ.).
- Polynsky, A. S. (2017). Osnovnye napravlenija razvitija aktivnogo otdyha i aktivnogo turizma v Omskoj oblasti [The main directions of development of outdoor activities and active tourism in the Omsk region]. Sovremennye problemy servisa i turizma [Service and Tourism: Current Challenges], 3(11), 120-129. (In Russ.).
- Saibel, N. Yu., & Zubareva, D. D. (2018). Aktivny otdykh v Krasnodarskom kraje: sovremennoe sostojanije i perspektivy razvitija [Active recreation in the Krasnodar Territory: current status and development prospects]. In: Collection of articles of the XII International Scientific and Practical Competition, 89-93. (In Russ.).
- Sytin, A. P. (2016). Turizm kak aktivnaja forma otdyha detej [Tourism as an active form of recreation for children]. Out-of-school student, 2(170), 42-44. (In Russ.).
- Buckley, R. (2016). Ecotourism. In: Jafari J., Xiao H. (Eds.). Encyclopedia of Tourism. Springer, Cham.
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-01384-8
- de Salvo, P., Calzati, V., & Soglia, S. (2019). Value for Time: Slowness, a Positive Way of Performing Tourism. In: Campón-Cerro A., Hernández-Mogollón J., Folgado-Fernández J. (Eds.). Best Practices in Hospitality and Tourism Marketing and Management. Applying Quality of Life Research (Best Practices). Springer, Cham.
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-91692-7_16
- Freude, T. (2019). Ecotourism and Sustainable Development. In: Leal Filho W., Azul A., Brandli L., Özuyar P., Wall T. (Eds.). Decent Work and Economic Growth. Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Springer, Cham.
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-71058-7
- Kropinova, E. (2020). Tourism and the sustainable development of the Baltic Sea Region. In: Leal Filho W., Azul, A.M., Brandli, L., Lange Salvia, A., Wall, T. (Eds.). Decent Work and Economic Growth. Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Springer, Cham.
- Laven, D., Chekalina, T., Fuchs, M., Margaryan, L., Varley, P. & Taylor, S. (2019). Building the Slow Adventure Brand in the Northern Periphery. In: Cassinger, C., Lucarelli, A., & Gyimothy, Sz. (Eds.). The Nordic Wave in Place Branding. Edward Elgar Publishing.
- Lumsdon, L., & McGrath, P. (2011). Developing a conceptual framework for slow travel: A grounded theory approach. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 19(3), 265-279.
- Müller, H. (1994). The thorny path to sustainable tourism development. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 2(3), 131-136.
- DOI: 10.1080/09669589409510690
- Weber, F. (2019). Demand for Sustainable Tourism. In: Lund-Durlacher D., Dinica V., Reiser D., Fifka M. (Eds.). Corporate Sustainability and Responsibility in Tourism. CSR, Sustainability, Ethics & Governance. Springer, Cham.
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-15624-4_16
- Wehrli, R., Egli, H., Lutzenberger, M., Pfister, D., Schwarz, J., & Stettler, J. (2011). Is there demand for sustainable tourism? Study for the World Tourism Forum Lucerne 2011. ITW Working Paper Series Tourism 001/2011, short version, Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts, Lucerne.


