Scope of Big Data analytics in green supply chain management: a review
Автор: Singh S., Gandhi M.K., Kumar A.
Журнал: Cardiometry @cardiometry
Рубрика: Original research
Статья в выпуске: 22, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In the modern era, the specialists working in the supply chain arenas are engulfed with enormous amounts of data, which has made them think out of the box and probe more into the sources of the data and techniques of analyzing and organizing the unstructured data. The new bud scholars and professionals have endorsed big Data Analytics (BDA) lately as a decisive green supply chain management facilitator. Research in this particular area is still to be explored to the fullest. The findings of the research are still in the introductory stages. Our study comprises an organized literature review of 42 significant papers published in the previous 18 years, which performs thorough reasoning and outlines three types of GSCM field: green product innovation, reverse logistics, and green procurement. The study presents the scope of BDA in these respective areas of GSCM. The study helps to portray the extent of usage of BDA tools in distinct GSCM fields. The literature review also sheds light on certain gaps in the research work. It caters to the directions for future work in the dedicated field.
Big data analytics, reverse logistics, green procurement, green supply chain management, green product innovation
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148324610
IDR: 148324610 | DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2022.22.306312
Текст научной статьи Scope of Big Data analytics in green supply chain management: a review
Shubham Singh, Madhup Kantilal Gandhi, Ankush Kumar. Scope of big data analytics in green supply chain management: a review. Cardiometry; Issue 22; May 2022; p. 306-312; DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2022.22.306312; Available from: analytics
The term sustainability was first combined with the Earth Summit at Rio in 1992. The United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP) was established to look into the matters related to the environment and manage the business linked with it. After the establishment of UNEP, several steps were taken to promote the idea of sustainability. According to Rao P, Environmental Management System, Cleaner Production, Responsible Manufacturing, and green supply chain management were emphasized and managed to entice all stakeholders [1].
Green Supply Chain Management (GrSCM) encompasses several important subunits. Four niche fields work by being dependent on each other and help in achieving the company’s goals. According to Venu, GrSCM is an aggregate of Reverse Logistics, Green Distribution, and Green Manufacturing/mate-rial management in Figure 1.
Green Supply Chain has directly connected both Supply Chain Management (SCM) and environmental management. The inclusion of the term ‘Green’ in supply chains has helped the industries monitor the supply chain links and environment. The introduction of GrSCM is driving the companies’ operation towards the idea of sustainability [2]. This concept has made industries adopt green initiatives, which are the need of the hour for the present world.
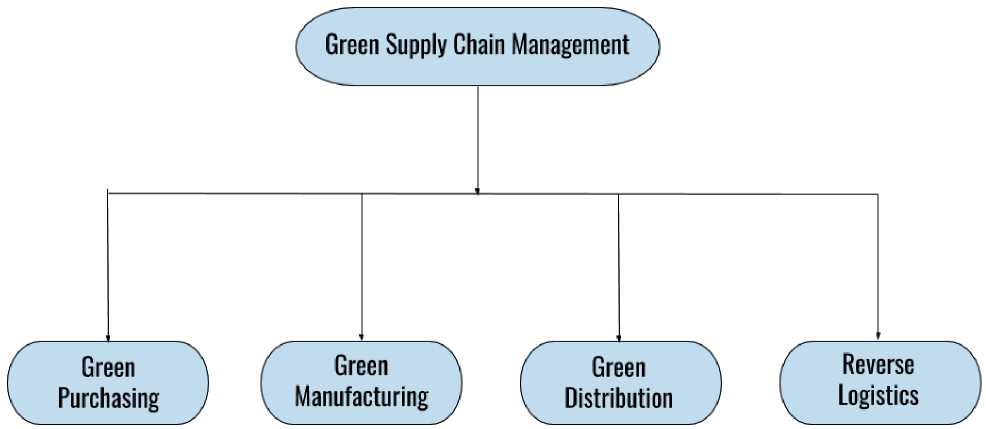
Fig. 1. Four fields of GrSCM
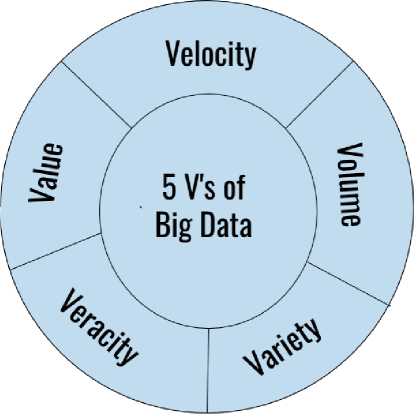
Fig. 2. 5 V’s of big data
The IoT and Big Data have displayed immense potential to be deemed a future technology that will affect people’s lives in the evolving world. The operations executive associations have begun their probe to filter out the needful insights and prospects, as researched by Accenture.
The given research work hovers around certain specific areas related to Green SCM. It undertakes the following questions: 1) What are the multiple regions of Green SCM, which are legitimized by the BDA tools and attributes. 2) What is the present status of BDA tools that are being incorporated in Green SCM.
2 Research methodologies
To deliver a comprehensive Literature Review for the research papers, presenting the purview of Big Data Analytics in the GSCM, we managed to gather the data from the sources like “Web of Science,” “Scopus,” “Science Direct,” and “Research Gate.” There are a few distinct keywords, which were at the center of at- tention, such as “Green Supply Chain linked with Big Data,” “Big Data Analytics with the Sustainable Supply Chain,” “Big Data integrated with logistics,” “Big Data and the Green Purchasing.” Our work was inclined with the 42 published research papers within the span of 2002 to 2020 [6]. We have gone through the research procedure and the Literature Review of the segregated 42 papers. The insights were displayed from the paper we referred to with proper explanations. At the very last of our analysis, we ended with the conclusions and future scopes to bridge current research gaps. Figure 3 shows the research methodology.
3 Literature review 3.1 Overview of green supply chain management
GrSCM has its underlying foundations in both Supply Chain and environmental management. Including the ‘green’ segment gracefully to supply-chain management tends to impact and connect the supply chain and the indigenous habitat. The idea of SCM is reliant on the objective of the specialist.
3.2 Big data analytics
The outset of digital technologies and tools has helped to consider the data and its analysis. The emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT) and other auto-
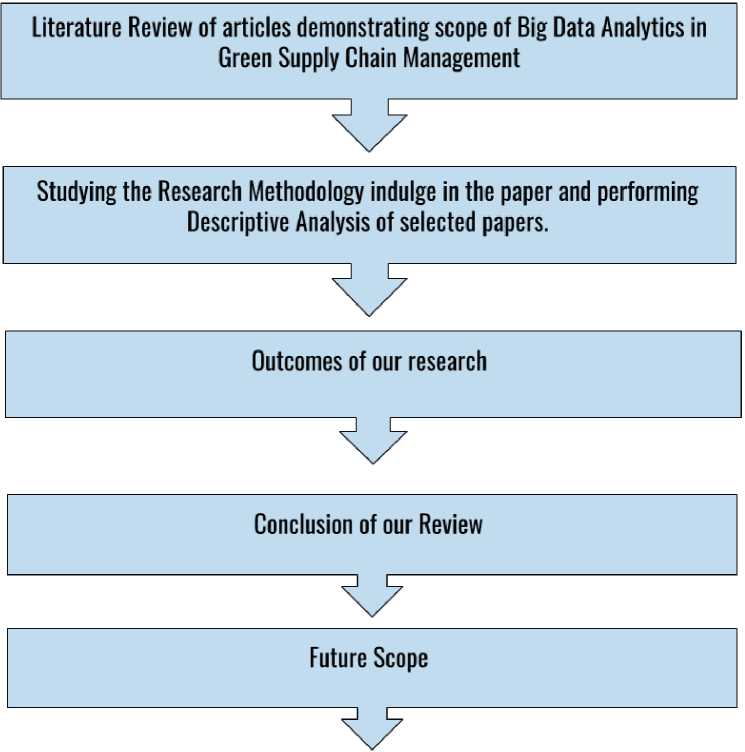
Fig. 3. Research methodology
mated tools and Web 2.0 with the Industry 4.0 have made the visualizations of Big Data quite easy, as observed by Hui & Silvana. This research has enormous scope and is very popular among upcoming scholars. Gigantic unstructured data are now gathered from various origins. The sources include ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), scattered production surroundings, orders, and freight logistics, patterns of buying preferred by customers, social media records, the lifespan of articles and their operations, and high-tech data directed sources like GPS (Global Positioning System), RFID (Radio Frequency based Identifications) spotting, vigilance data and many more. The industries currently are negotiating with the data files, which fall under the scope of 4Vs; volume, veracity, variety, and velocity [9]. The bigger datasets of these criteria become very challenging to work with, and visualizing them to hand over fruitful results.
The financial performance was analyzed by Feng et al. of a Chinese manufacturing company through “data-driven supply chain capabilities.” The proposed structural equation modelling for this study [10]. The results indicated that there is a positive relationship between supply chain responsiveness corresponding to the changes in the demand from markets or consumers that are buckled up with the organization’s financial performance.”
3.3 Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 was adopted to incorporate digital transformations, mainly in manufacturing or production organizations. It inducts various categories of high-tech and breakthrough concepts. At the same time, it paves the way for inculcating BDA in GrSCM, according to Jan Ola Strandhagen et al.
Some of the broadly used technologies in industrial manufacturing are:
i. The very first is the Identification tool. It is known as Auto ID, which helps elicit the characteristics of an object. It is also embedded with sensor technology that helps to gather the real-time data compilation from the appliances present in the workplace [12].
ii. Virtual Reality (VR) has directly helped the operators responsible for the functioning of machinery present in the manufacturing and assembly line.
iii. Big Data analytics helps to squeeze out the invaluable information present in the unstructured data, which are available in enormous quantities.
iv. Autonomous vehicles and robots for easy transportation along with saving fuel along with time.
v. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has enhanced the efficiency of the process by integrating automation in the simplest of procedures. It has influenced the decision-making and operations without the physical mediation of humans.
vi. Cloud computing, through which cloud manufacturing has become capable of interlinking the production sources, has directly optimized the internal and external logistics.
4.2 Green purchasing/procurement
4 Outcomes of literature review 4.1 Green product innovation
The basic idea of adopting the green model of the supply chain by the industries is to curb the carbon footprint and promote environmentally sustainable procurement. The measure of carbon generated from the side of suppliers should be monitored. Selection of suppliers must be done on these criteria. Therefore, to help this thought, certain sustainability benchmarks were included to assess the suppliers’ carbon footprint [16]. The few criteria like fuel efficiency, fuel used, packaging material used, the medium of transportation, and distance from the plant are considered, as re- 310 | Cardiometry | Issue 22. May 2022
Collaboration with the suppliers is regarded as another important step in Green purchasing. The sustainable goals and environmental criteria must be communicated with the vendors and suppliers to achieve the targeted, sustainable limits and business information. BDA aids in the proper sharing of the information with the suppliers and efficiently contributes to environmental collaboration, as Raut et al.
4.3 Reverse logistics
The products, which do not follow the predefined life cycle and exit from the supply chain because of the reasons mentioned above, the end-of-life of these products, can be assessed using Big Data Analytics. It helps in remanufacturing, reuse, recycle, inspection, and sorting of the products. Furthermore, big data helps gather real-time analytics of vehicles and materials and facilitates assessing the locations to find best-suited routes for the transportation of materials, as to Jan Ola Strandhagen et al.
5 Conclusions
The study has inspected 42 papers demonstrating the scope of integration of the BDA and GSCM. By conducting a literature review, we were able to scrutinize three aspects related to GSCM that are connected with the BDA. These fields were Green Product Innovation, Green Purchasing/Procurement, and Green Logistics. Big Data Analytics has presented the window of scope for enhancing the veracity of decision forming. It has become a potential tool for forecasting future trends by using the data linked with the processes.
The systematic study of the literature review has displayed two connotations. Firstly, we presented comprehensive insights into the research advancement made in one of the emerging fields, BDA integrated with GSCM. Our study reinforces the perception of BDA in GSCM and interprets the aspects of the BDA in distinct GSCM areas. To be precise, our detailed analysis objectifies that this field is premature and demands the considerations of the experts coming from contrasting backgrounds of education to probe the potential aspects of the field.
Moreover, the scope of green operations can be diversified. It can hop from internal environment handling to foreign GSCM ventures. For example, integrating their supplies, vendors, and customers with the GSCM will enhance environmental performances.
6 Future scopes
We tried to present the forthcoming opportunities that can be explored in the research field through our study. Foremost, the current analysis has only tried to highlight the capacity of BDA in particular GSCM operations. The influence of BDA in GSCM may help present the interrelation of various operational activities linked with GSCM. Therefore, forthcoming research perspectives can cater to a comprehensive structure on the utilization of the BDA in organizations’ long-term GSCM executions.
Big Data is still showcasing the potential of applications in the different sectors. The respective articles do not comprehensively reflect the new-fangled BDA knowhow and their scope in GSCM. Thus, the upcoming scholars should concede the utilization of the surfacing BDA capabilities and their impressions on GSCM.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author contributions
The authors read the ICMJE criteria for authorship and approved the final manuscript.
Список литературы Scope of Big Data analytics in green supply chain management: a review
- Accenture. The role of big data and analytics in the developing world, (2013).
- T. Arunachalam, Y. Palanichamy, Does the soft aspects of TQM influence job satisfaction and commitment? The TQM Journal (2017)..
- C. Bai, J. Sarkis, Integrating sustainability into supplier selection with grey system and rough set methodologies. Int J Prod Eco, 252-264, (2010).
- G. Cajaiba-Santana, Social innovation: moving the field forward. A conceptual framework. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 42-51, (2014).
- Y. Chen, S. Lai, C. Wen, The influence of green innovation performance on corporate advantage in Taiwan. Bus. Ethics, 331-339, (2006).
- F. Ciliberti, P. Pontrandolfo, B. Scozzi, Logistics social responsibility: standard adoption and practicesin Italian companies. Int J Prod Eco, 88-106, (2008).
- Forrester. The Forrester Wave™: Big Data Predictive Analytics Solutions. Forrester, (2013).
- A. Mark, L. Douglas, The Importance of ’ Big Data’: A Definition. Gartner, (2012).
- K. Mathiyazhagan, K. Govindan, A. NoorulHaq, Y. Geng, An ISM approach for the barrier analysis in implementing green supply chain management. Journal of Cleaner Production, (2013).
- H. Min, G. Zhou, Supply chain modeling: past, present, and future. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 231-249, (2002).
- A. Presley, L. Meade, J. Sarkis, A strategic sustainability justification methodology for organizational decisions: a reverse logistics illustration. Int J Prod Res, (2017).
- P. Rao, Greening the supply chain: a new initiative in South East Asia. International Journal of Operations & Production Management (2002).
- P. Rao, Green Supply Chain Management: A Study Based on SMEs in India. Journal of Supply Chain Management Systems, 15-24, (2019).
- A. Venu, A Review on Green Supply Chain Management. Mukt Shabd Journal, 30-36, (2020).
- M. White, Digital workplaces: vision and reality. . Business Information Review, 205-214, (2012).
- S. Zailani, M. Iranmanesh, M. Shaharudin, K. Govindan, Y. Chong, Green innovation adoption in the automotive supply chain: the Malaysian case. Clean. Prod., 1115-1122, (2015).


