Сексуальная активность и болезнь Альцгеймера: инструменты и технологии нейроэндокринной реабилитации
Автор: Булгакова Светлана Викторовна, Романчук Наталья Петровна
Журнал: Бюллетень науки и практики @bulletennauki
Рубрика: Медицинские науки
Статья в выпуске: 7 т.8, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Болезнь Альцгеймера - это эволюционная, генетическая и эпигенетическая маршрутизация Homo sapiens , с внедрением реабилитационной программы «БАЯМ-365/22/77» (Alzheimer’s disease & nuclear medicine) и медико-социальными нейрокоммуникациями и сопровождениями. Геронтология и гериатрия, гинекология/андрология и нейроэндокринология, нейрофизиология и нейросоциология маршрутизируют H. sapiens в активное / здоровое / качественное / религиозное / нравственное / сексуальное / нейрокоммуникативное долголетие . Огромный прирост научных данных, полученных как в доклинических, так и в клинических исследованиях, сокращает большой пробел в знаниях о специфических для пола особенностях течения многих заболеваний (нейродегенеративных, психических, аутоиммунных, онкологических, сердечно-сосудистых, инфекционных). Тем не менее, остаются до конца не изучены факторы, определяющие половые различия в эпидемиологии, патофизиологии, клинической картине, исходах ряда патологий. В настоящем обзоре литературе представлен анализ современных исследований, посвященных роли гормональной регуляции в гендерной медицине и гендерным особенностям в ключевых клинических областях. Половые различия в иммунном ответе, сердечно-сосудистых заболеваниях, неврологических расстройствах, COVID-19 описаны в данной статье. Показано, что в настоящее время созрели все предпосылки для формирования персонализированных подходов в клинической медицине и общественном здравоохранении для улучшения качества жизни пациентов и здоровья населения в целом.
Болезнь альцгеймера, генетика, гендерная медицина, эстрогены, когнитивное здоровье
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14124448
IDR: 14124448 | УДК: 616.83/.85:616.43/57 | DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/80/21
Текст обзорной статьи Сексуальная активность и болезнь Альцгеймера: инструменты и технологии нейроэндокринной реабилитации
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice
УДК 616.83/.85:616.43/57
Население мира стареет. Ожидаемая продолжительность жизни при рождении увеличилась на 6 лет во всем мире за последние 3 десятилетия, а в 2050 году доля пожилых людей старше 60 лет, по оценкам, достигнет 22% во всем мире. Такое увеличение имеет прямое следствие: рост заболеваемости возрастными заболеваниями, в частности нейродегенерацией. По данным различных организаций, таких как Всемирная организация здравоохранения (ВОЗ), нейродегенеративные расстройства, наряду с сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями, являются основными причинами смерти в западных странах. Более 20% взрослых в возрасте 60 лет и старше развивают неврологические расстройства, наиболее распространенным из которых является деменция. По оценкам ВОЗ, около 47 млн человек страдают этим расстройством, причем почти 10 миллионов новых случаев заболевания ежегодно. Таким образом, по оценкам, общее число людей с деменцией увеличится почти до 75 млн в 2030 г. и 132 млн к 2050 г. во всем мире. Болезнь Альцгеймера является наиболее распространенной причиной деменции, способствуя 60–70% случаев. Хотя сообщалось о взаимосвязи между развитием когнитивных нарушений и факторами риска, связанными со стилем жизни, такими как ожирение, употребление табака и алкоголя, возраст по-прежнему остается самым сильным фактором риска развития деменции и других нейродегенеративных заболеваний (World Health Statistics).
Осознанное осмысление гендерных различий в доклинических и клинических исследованиях было начато лишь в последние несколько десятилетий, хотя историческое утверждение о половых различиях в проявлении болезней и реакции на лечение было высказано еще Гиппократом более 2000 лет назад. Современные научные исследования, сравнивая группы мужчин и женщин, изучают половые различия в проявлениях заболеваний, эффективности медикаментозной и немедикаментозной терапии и т. д. Однако расовая и культурная специфичность, а также психосоциальный и экономический статус являются ограничивающими факторами, которые ведут к тому, что женщины гораздо реже участвуют в экспериментальных исследованиях. Разработка клинических испытаний с одинаково скорректированным набором участников по половому признаку является довольно сложной задачей, особенно в связи с репродуктивной активностью, периодами беременности и лактации у женщин, что значительно ограничивает их участие в исследованиях лекарственных препаратов. Напротив, изучение неврологических или аутоиммунных заболеваний из-за их преобладания у женщин представляет определенную проблему. Также следует учитывать суточные колебания уровня гормонов (например, тестостерона), чему уделяется ограниченное внимание в экспериментальных исследованиях, не связанных с гормональной терапией.
Кроме того, важно подчеркнуть расходящуюся терминологию пола и гендера, которые традиционно ошибочно используются как синонимы. Пол относится к биологическим и генетическим особенностям людей, тогда как гендер рассматривается как социальная особенность людей в отношении самовыражения, поведения и социальных ролей. Последнее считается личным выбором и может порождать небинарный диапазон гендерных идентичностей. Хотя некоторая взаимосвязь между гормональной и генетической средой и выбором половой идентичности может существовать, точные механизмы до сих пор неизвестны. Это явление довольно сложно исследовать из-за того, что люди обладают сознанием, черта, которая все еще неясна, по крайней мере, для животных, и исследования в этой области ограничены [1] .
Специфические для пола биологические различия в настоящее время регистрируются во многих областях клинической практики, влияющих на физиологию, патофизиологию, клинические проявления, естественное течение, заболеваемость, распространенность, ответ на лечение и показатели смертности от ключевых заболеваний. Точно так же гендернозависимые социокультурные проблемы также влияют на эпидемиологию и течение заболеваний, например, в случае нездорового из-за вредных привычек образа жизни или ограниченного доступа к медицинским услугам. Данный обзор литературы посвящен роли гормональной регуляции в гендерной медицине и гендерным особенностям в ключевых клинических областях.
Половые различия в физиологии: роль половых стероидных гормонов Синтез и роль половых гормонов
Половые стероидные гормоны отвечают за поведение и половую дифференцировку, а также играют ключевую роль в нормальном функционировании различных органов и систем, включая головной мозг. Основные половые стероидные гормоны включают в себя эстрогены (эстрон (Е1), эстрадиол (Е2) и эстриол (Е3)); прогестагены (прогестерон); андрогены, наиболее важным из которых является тестостерон. Последний отвечает за регуляцию работы репродуктивных органов мужчин, а также за вторичные половые признаки, развитие мышечной массы, рост костной ткани. Тестостерон вырабатывается надпочечниками, яичками из его предшественника холестерина [2] и существенно меняется с возрастом. Выброс половых гормонов регулируется гипоталамо-гипофизарно-гонадной системой по принципу отрицательной обратной связи. Гонадотропин-рилизинг-гормон (ГнРГ), вырабатываемый гипоталамусом, стимулирует секрецию лютеинизирующего (ЛГ) и фолликулостимулирующего (ФСГ) гормонов гипофизом, которые способствуют секреции половых гормонов гонадами [3]. В частности, тестикулярный стероидогенез происходит в клетках Лейдига, где ЛГ стимулирует ферменты, необходимые для биосинтеза половых гормонов [4]. В частности, стероидогенный острый регуляторный белок (StAR) способствует превращению холестерина внутри митохондрий в прегненолон. Фермент P450c17 гидроксилирует прегненолон в 17-ОН прегненолон с помощью 17α-гидроксилазы и далее превращает его в дегидроэпиандростерон (ДГЭА) с помощью 17/20-лиазы. Фермент 17α-гидроксилаза также отвечает за превращение прогестерона в 17-ОН-прогестерон, тогда как 17/20-лиаза далее превращает его в андростендион. Дополнительные ферменты, включая 3β-и 17β-гидроксистероиддегидрогеназу, необходимы для превращения ДГЭА в андростендион и его последующего метаболизма в тестостерон. Тестостерон окончательно превращается 5α- редуктазой в дигидротестостерон и 17β-эстрадиол под действием ароматазы. Процесс ароматизации тестостерона происходит у мужчин в небольших объемах и в основном на периферии [5].
Напротив, у женщин тека-клетки яичников совместно с ЛГ ответственны за синтез половых гормонов. Активация ароматизации высокими уровнями ЛГ во время фолликулярной фазы эстрального цикла приводит к повышенным уровням эстрогенов, особенно Е2. В последующей лютеиновой фазе снижение уровня ЛГ и ароматизация приводят к снижению уровня эстрогенов и повышению уровня прогестерона [4] . Следовательно, женские половые гормоны демонстрируют значительные колебания во время менструального цикла, что, порой, препятствует включению женщин в клинические исследования, но, несомненно, это следует учитывать, поскольку цикличная выработка гормонов отвечает за значительные половые различия в патофизиологии и лечении различных заболеваний. Был проведен ряд исследований для определения точных фаз менструального и эстрального циклов и связанных с ними концентраций гормонов в сыворотке [6] . Так же у мужчин были обнаружены колебания уровня тестостерона. Уровни гормона пропорциональны солнечному свету и продолжительности сна с пиком в утренние часы и снижением во второй половине дня. Снижение, по-видимому, сокращается с возрастом [4, 7, 8] .
У женщин также продуцируется небольшое количество тестостерона надпочечниками и яичниками. Женские половые гормоны эстрогены и прогестерон имеют решающее значение для определения вторичных половых признаков у женщин, включая рост молочных желез и оволосение по гиноидному типу [2] . Кроме того, половые гормоны в основном присутствуют в разных участках мозга, где они способствуют нормальной неврологической функции и синаптической пластичности. Они производятся не только гонадами. Многочисленные исследования показали, что примерно 2% свободных половых гормонов плазмы, синтезируемых на периферии, проникают через гематоэнцефалический барьер, возможен их синтез в головном мозге [9] . Стероидогенез в головном мозге приводит к образованию нейростероидов, которые могут действовать как ингибирующие или возбуждающие нейромодуляторы при прямом взаимодействии со стероидными нейрорецепторами или посредством аллостерической регуляции ионных каналов [10] . Аллопрегнанолон, андростендиол и тетрагидродезоксикортикостерон (THDOC) являются одними из наиболее важных нейростероидов [11] .
Как упоминалось выше, половая дифференцировка также связана с ранней выработкой половых гормонов. В частности, в то время как генетический пол эмбриона приобретается при оплодотворении путем наследования пары хромосом XY для мужчин или XX для женщин, половая дифференцировка включает в себя прогрессивное развитие гонад и гениталий в по мужскому или женскому типу. В первом случае высвобождение антимюллерова гормона (АМГ) и андрогенов, особенно тестостерона, продуцируемого клетками Лейдига, способствует развитию мужских гениталий, подавляя женскую морфологию. Наоборот, женский фенотип развивается в отсутствии мужских гормонов. Хотя ранее считалось, что только ген SRY, присутствующий на Y-хромосоме, отвечает за дифференцировку гонад [1, 12] . Таким образом, высвобождение или отсутствие тестикулярных половых гормонов также имеет решающее значение для развития мозга, происходящего во второй половине беременности, и сексуального поведения путем маскулинизации или феминизации мозга соответственно.
Однако, в исследованиях на млекопитающих и птицах было обнаружено, что специфическая экспрессия или репрессия генов в половых хромосомах изменяет путь половой дифференцировки мозга независимо от гонадных гормонов [13, 14] . Поскольку развитие мозга не происходит одновременно с дифференцировкой половых органов, гендерная идентичность и сексуальная ориентация человека могут не соответствовать его или ее хромосомной паре. Дальнейшие исследования воздействия половых гормонов на мозг в пренатальном периоде или воздействия эндокринологических модуляторов во время беременности необходимы для лучшего понимания их потенциального влияния на гендерные различия [15] .
О роли половых стероидных гормонов и их рецепторов
Половые гормоны взаимодействуют со специфическими рецепторами, расположенными в цитоплазме, ядре клеток-мишеней или на клеточной мембране [9] . Рецепторы эстрогена состоят из ядерных (ER) и неядерных рецепторов эстрогена, включая альфа-рецептор эстрогена (ERα) и бета-рецептор эстрогена (ERβ), а также рецепторы эстрогена, связанные с G-белком (GPER), мембранные рецепторы, которые расположены в эндоплазматическом ретикулуме многих клеток [16] . Активация рецепторов начинается, когда эстрогены связываются с цитоплазматическими ER, которые затем перемещаются в ядро.
Комплекс лиганд-рецептор связывается с элементом гормонального ответа, особым контролирующим сегментом ДНК в промоторной области генов, что приводит к модуляции транскрипции и модификации мРНК [17] . Исследования показали, что, помимо типичного геномного взаимодействия эстрогенов с их рецепторами, связывание неядерных ER может запускать быстрые сигнальные пути, участвующие в различных клеточных функциях, в том числе, в различных гистотипах, включая клетки нервной системы и лимфоциты [9, 17, 18, 19] .
Классические ядерные ER могут функционировать как факторы транскрипции и регулировать экспрессию генов в медленном временном диапазоне. Эти факты озадачили ученых, так как они не могли объяснить наблюдаемые быстрые изменения в неврологической или иммунной системах, связывая с наличием другого типа ER. Первоначально эту гипотезу проработали исследователи, которые поняли, что наличие эстрадиола в тканях полости матки приводит к быстрому увеличению цАМФ, что связано с взаимодействием эстрадиола с рецепторами гормонов клеточной мембраны. Позднее эта концепция была подтверждена дополнительными исследованиями, в которых также наблюдалось быстрое усиление фосфорилирования транскрипционного фактора цАМФ-чувствительного элемента-связывающего белка (CREB) при повышенных концентрациях эстрадиола, опосредованное через систему MAPK/ERK [20, 21] .
Дополнительная, до сих пор неизученная функция ER связана с их экспрессией на митохондриях. В доклинических исследованиях установлено наличие комплексов ER-эстроген в митохондриях первичных культур нейронов, а также в митохондриях пресинаптических и постсинаптических нейронов гиппокампа грызунов. Однако на данный момент информация о механизмах работы этих рецепторов ограничена, необходимы дальнейшие исследования. Однако, есть предположения, что эта регуляция митохондрий наряду с потенциальными мутациями мтДНК, которые могут накапливаться с течением времени, связана со старением мозга и другими нейродегенеративными расстройствами [22] .
Половые различия в патологии
Половые различия при неврологических заболеваниях
Как упоминалось выше, половые гормоны играют роль в развитии ряда неврологических и психических заболеваниях. Этот факт в основном обусловлен их регулирующей ролью в проведении нейронных сигналов и, таким образом, в работе головного мозга. Ряд исследований на животных был посвящен выяснению роли половых различий, наблюдаемых при неврологических расстройствах, но эти работы не всегда могут согласовываться с исследованиями на людях, что еще больше усложняет картину. Например, у самцов грызунов ароматаза превращает тестостерон в эстрадиол в развивающемся мозге плода, избыточные уровни эстрадиола сдерживаются альфа-фетопротеином, что нельзя сказать о людях [15, 23] . В целом, существующие знания подчеркивают влияние половых гормонов на некоторые из наиболее характерных неврологических расстройств, таких как болезнь Альцгеймера, болезнь Паркинсона, эпилепсию, а также депрессию и шизофрению.
Болезнь Альцгеймера
Болезнь Альцгеймера (БА) представляет собой прогрессирующее нейродегенеративное заболевание головного мозга, которое включает широкий спектр проявлений, в том числе спутанность сознания, языковые трудности, зрительно-пространственную дисгнозию, снижение памяти, нарушение мышления, когнитивные нарушения различной степени тяжести, от легких до развития выраженной деменции. БА страдают, как мужчины, так и женщины, однако наблюдается заметный диморфизм. Женщины демонстрируют более высокую распространенность БА. Женское долголетие может частично объяснить эту закономерность, но, тем не менее, половые гормоны должны являются вероятными факторами риска наряду с возрастом. По мере старения у женщин более высокий риск заболеть БА с частотой встречаемости 0,7% в возрасте 65–69 лет, тогда как у мужчин риск составляет 0,6% в той же возрастной группе [24] . Многочисленные европейские исследования выявили более высокую вероятность диагностики деменции у женщин с БА, что не соответствует исследованиям, проведенным в США или других странах. Это несоответствие может указывать на то, что, помимо пола, географический регион, ограниченный доступ к образованию также могут являться факторами риска деменции при БА [25, 26] . Исследования, касающиеся БА и нейропсихиатрических симптомов деменции, влияющих на поведение, показали сравнительно более высокую вероятность развития депрессии и тревоги у женщин, в то время как возбуждение и враждебное поведение чаще отмечались у мужчин [26] .
В развитии БА помимо социально-психологических факторов риска, несомненно, участвуют биологические особенности, такие как структура мозга, половые гормоны и генотипические различия. Был проведен ряд исследований, сравнивающих женский и мужской головной мозг, чтобы проверить или опровергнуть версию, связанную с нейросексизмом [27]. Определено, что существуют некоторые межполовые различия в структуре и функциях мозга, хотя эти данные не подтверждены предыдущими исследованиями. Было высказано предположение, что мужской мозг обычно больше по объему, а у женщин пропорционально большее количество серого вещества по сравнению с белым веществом в различных отделах мозга [28]. Различия в функциях головного мозга также могут указывать на вклад в снижение когнитивных функций, поскольку у женщин повышается активность в сенсорной ассоциативной коре теменной доли, а у мужчин — в моторной и зрительной коре [29]. Хотя, согласно данным современной литературы, наличие бляшек амилоида-β (Aβ), биомаркера БА, не показывает каких-либо четких половых различий в распределении в областях мозга, тем не менее, наблюдалась корреляция количества бляшек со скоростью нейродегенерации. В частности, даже у пациентов с легкими когнитивными нарушениями (MCI) женский мозг демонстрирует более выраженную атрофию гиппокампа с более быстрым наступлением когнитивных нарушений, чем у мужчин. В связи с этим были изучены уровни другого биомаркера БА – образование тау-клубков – с порой, противоречивыми результатами. Так, наблюдалась более высокая агрегация тау в определенных сегментах коры головного мозга у женщин с БА и общая повышенная концентрация тау у пациентов с MCI [30].]. Дальнейшие исследования, анализирующие токсичность Aβ, подчеркивают роль окислительного повреждения. Сообщалось, что пептиды Аβ способны связываться с гемовой группой субстратов, участвующих в дыхательной цепи митохондрий, и приводить к повышенному высвобождению активных форм кислорода, в связи с чем происходила активация защитных антиоксидантных функций женских половых гормонов у молодых людей, снижающихся с возрастом [31].
В настоящее время раскрыта роль половых гормонов в сохранении памяти и развитии когнитивных нарушений через дофаминергическую систему и в снижении накопления Aβ при БА. У женщин быстрое снижение уровня эстрогенов во время менопаузы способствует распространению атопического дерматита. Анализ аутопсии у пациентов с БА показал снижение уровней эстрогенов и андрогенов в головном мозге у женщин и мужчин, соответственно, что свидетельствует об изменении синтеза гормонов в головном мозге у пациентов с БА [15, 32] . На самом деле, более низкие уровни свободного эстрадиола и более высокие уровни ГСПГ связаны с более быстро развивающимся снижением когнитивных функций [33] .
В связи с этим данные предлагают использовать гормональную терапию в качестве стратегии защиты от когнитивных нарушений у женщин только тогда, когда она начинается в перименопаузе или после хирургической овариоэктомии [34] .
Кроме того, известно, что половые гормоны влияют на гены, предрасполагающими к БА, например, аллели гена ApoE. Исследования показали, что женщины, являющиеся носителями аллеля ApoE4, имеют значительно более быстрое снижение когнитивных функций по сравнению с пациентами мужского пола с аналогичными генотипами, но также имеют повышенную экспрессию фермента, расщепляющего АРР (BACE1) в β-сайте, который имеет решающее значение для производства Aβ. Объяснение этого факта может быть найдено в модуляторной роли ER в регуляции гена ApoE, участиb ERα в усилении экспрессии гена ApoE и противоположной роли, которую играет ERβ. Объяснения этих механизмов отражены в исследованиях, посвященных специфической гормональной терапии in vitro, и в доклинических исследованиях [35] . В заключение, понимание точных диморфных механизмов этого нейродегенеративного заболевания может привести к многообещающим методам лечения, например, через связь с рецептором кортикотропин-рилизинг-гормона (CRF) [36] .
Болезнь Паркинсона
Болезнь Паркинсона (БП) — еще одно нейродегенеративное заболевание, характеризующееся накоплением телец Леви (из-за агрегации α-синуклеина) и истощением дофаминергических (ДАергических) нейронных цепей в нигростриарной системе. Отмечены половые различия в частоте и распространенности заболевания, а также в его клинических проявлениях. Эпидемиологические исследования показали, что мужчины более предрасположены к развитию БП, при этом соотношение мужчин и женщин составляет 1,6:1. У мужчин также быстрее развиваются симптомы, которые включают гиперсаливацию, сексуальную дисфункцию и чрезмерную сонливость в дневное время, а также более тяжелые нейропсихиатрические и двигательные симптомы, такие как ригидность, расстройство поведения во сне с быстрым движением глаз (REM) и деменция по сравнению с женщинами [37].
Нейропротективная роль женских половых гормонов была поставлена под сомнение в патогенезе, прогрессировании и ответе на лечение при БП. Исследования подтвердили, что у женщин молодого возраста или женщин, получающих заместительную гормональную терапию, обнаруживаются высокие уровни ДА-ергической системы в нигростриарном пути и моноаминоксидазы (МАО). Кроме того, у женщин, даже пожилых, обнаружена высокая активность переносчиков дофамина (DAT) в стриатуме головного мозга по сравнению с мужчинам [38] . Исследования у дрозофил, грызунов и людей продемонстрировали регуляторную взаимосвязь между везикулярным переносчиком глутамата (VGLUT), участвующим в патогенезе БП, и возрастной потерей нейронов в головном мозге. Результаты показывают, что более высокая экспрессия VGLUT, которая увеличивается с возрастом, характерна для женщин, что вполне объяснимо их устойчивостью к ранней DA-эргической нейродегенерации и их меньшей двигательной симптоматикой по сравнению с мужчинами [39] . Посмертные исследования выявили различия в экспрессии генов биомаркеров БП, таких как α-синуклеин и PINK1, которые, по-видимому, демонстрируют более высокую частоту мутаций у мужчин, что делает их более восприимчивыми к дегенерации нейронов и окислительному повреждению.
Мутации ER также изучались в поисках корреляции между мутациями гена ERβ и началом БП, но результаты все еще неоднозначны [40] . Серия мутаций в гене, кодирующем киназу 2 с богатыми лейцином повторами (LRRK2), выявила диморфный паттерн, особенно в связи с уровнями уратов, обеспечивающими защиту. Женщины и здоровые мужчины имеют более высокие уровни уратов и обнаруживают меньше паттернов мутаций LRRK2 по сравнению с мужчинами с БП [41] .
Таким образом, симптоматическое лечение БП как при двигательных, так и при немоторных проявлениях должно быть разработано с учетом гендерных признаков. Симптомы моторной БП купируются леводопой. Однако длительное применение леводопы с достижением им высоких уровней концентрации в плазме крови связано с развитием циклических колебаний и дискинезии. Предполагается, что самая высокая и быстрая биодоступность леводопы характерна для женщин, что сокращает промежуток времени между началом лечения и появлением леводопа-индуцированной дискинезии: так, средний временной интервал составляет 4 года по сравнению с 6 годами у мужчин [41, 42] .
Эпилепсия
Половые различия проявляются и при различных типах эпилептических синдромов. Социокультурные половые различия (например, из-за культурных привычек, часто недооценивающих психические заболевания) наряду с биологическими факторами, как правило, влияют на заболеваемость и распространенность эпилептического спектра, но также мешают подходам к лечению, поскольку они могут снижать адекватность и безопасность лекарств [43]. Исследования, проведенные в развивающихся странах, показывают, что эпилептические припадки, как спровоцированные, так и неспровоцированные, чаще встречаются у мужчин (50,7 случая на 100 000), чем у женщин (46,2 на 100 000) [44].
Симптоматические парциальные припадки также преобладают у мужчин, в то время как идиопатическая генерализованная эпилепсия (ИГЭ), ювенильная миоклоническая эпилепсия (ЮМЭ), височная эпилепсия (ВЭЛ) и идиопатические генерализованные тоникоклонические припадки чаще встречаются у женщин [45, 46] . В частности, было обнаружено, что распространенность ИГЭ выше у молодых женщин и снижается с возрастом, что предполагает роль половых гормонов в дебюте заболевания. В связи с этим многочисленные исследователи пришли к выводу, что циркулирующие половые гормоны и нейростероиды влияют на тормозные ГАМКергические синапсы и возбуждающую глутаматергическую передачу, которые в значительной степени участвуют в развитии припадков.
Аналитически считается, что женский половой гормон прогестерон обладает противосудорожными свойствами, отрицательно модулируя глутаматергический сигнальный путь и помогая ферментативному превращению нейростероида аллопрегнанолона, который затем может положительно регулировать передачу ГАМК путем аллостерической активации ГАМК А рецепторов. Продукты метаболизма прогестерона также оказывают противоэпилептическое действие.
Эстрогены, напротив, особенно эстрадиол, имеют тенденцию повышать частоту приступов, но исследования их проконвульсивного действия противоречивы: в то время как ряд исследований на крысах отмечают эпилептическую роль, другие предполагают защитную функцию эстрадиола.
Наконец, андрогены также оказывают двойное действие на предрасположенность к судорогам. Метаболизм тестостерона в эстрогены оказывает проконвульсивное действие, но сам тестостерон при метаболизме в андростендиол обладает свойствами, сходными с аллопрегнанолоном [47, 48] .
Что касается использования противоэпилептических препаратов, в большинстве исследований не отмечается существенного изменения уровня половых гормонов в начале лечения; однако у пациентов, получавших вальпроат, наблюдались более низкие показатели тестостерона, ЛГ и ФСГ, что, по-видимому, также связано с эндокринными нарушениями, включая аменорею, поликистоз яичников и снижение либидо. Следовательно, следует соблюдать осторожность при выборе противосудорожных препаратов при планировании зачатия [49, 50] .
Депрессия
Большинство психических расстройств, по-видимому, связаны с половыми гормонами. Депрессивные расстройства, в том числе большое депрессивное расстройство и другие депрессивно-подобные состояния, имеют разную частоту возникновения, клинические проявления и тактику лечения у мужчин и женщин, что свидетельствует о сильном патофизиологическом влиянии половых гормонов [51] . Исследования подтверждают, что женщины более склонны к развитию депрессивных симптомов в подростковом возрасте [52] .
Колебания женских половых гормонов во время менструального цикла, по-видимому, провоцируют изменение выраженности депрессивных симптомов. Результаты клинических исследований показывают, что женщины с более низким уровнем прогестерона во время лютеиновой фазы цикла испытывают более выраженные изменения настроения по сравнению с фолликулиновой фазой. Такие же результаты были получены при исследовании женщин, принимавших противозачаточные препараты: у них были нарушения сна и симптомы депрессии [53].
Половые гормоны, по-видимому, также влияют на гипоталамо-гипофизарно-надпочечниковую ось (ГГН), которая гиперактивна у пациентов с депрессией, при этом кортикотропин-рилизинг-фактор (КРФ) гиперэкскретируется из гипоталамуса, индуцируя высвобождение адренокортикотропного гормона (АКТГ), что приводит к повышенной секреции кортизола. Исследования, анализирующие уровни кортизола как у людей с депрессией, так и здоровых, показали повышенную концентрацию кортизола у депрессивных женщин по сравнению с мужчинами в депрессии и здоровыми добровольцами [54] .
Предменструальный синдром, беременность, послеродовой период и менопауза — события жизни женщины, в которых половые гормоны играют огромную роль [55] . Эстрогены были исследованы на предмет их роли в серотонинергической, дофаминергической, глутаматергической и ГАМКергической системах через ERα, ERβ и GPER, и считается, что их действие в значительной степени сравнимо с действием антидепрессантов и атипичных антипсихотических препаратов. Было показано, что они являются положительными регуляторами триптофангидроксилазы (TPH) (фермент-предшественник 5-HT), модуляторами специфических рецепторов 5-HT и ингибиторами метаболических катализаторов, таких как МАО. Они специфически блокируют ауторецептор 5-HT1A и повышают концентрацию 5-HT в синаптической цепи, а также пресинаптически блокируют обратный захват 5-HT [56] . При лечении депрессивных симптомов антидепрессантами лучший эффект отмечен при их комбинации с половыми гормонами: так, у женщин в постменопаузе показаны лучшие результаты в комбинации с эстрадиолом [57] .
Половые гормоны и иммунная система
Выявлены большие различия при сравнении иммунной системы мужчин и женщин. Иммунологические ответы различаются между полами в ответ как на эндогенные, так и на экзогенные антигены, создавая различия в частоте и тяжести как инфекционных, так и аутоиммунных заболеваний.
Данные из доступной литературы указывают на относительно более сильную активацию и производительность иммунной системы у женщин. Этим объясняется их большая способность к лучшему ответу на инфекционные агенты и более частое возникновение аутоиммунных заболеваний по сравнению с мужчинами. Понимание задействованных молекулярных механизмов поддерживает персонализированный подход к предотвращению распространения инфекционных заболеваний и борьбе с неинфекционными заболеваниями с сильным иммунологическим компонентом [58, 59] .
Гормональная модуляция иммунитета
Половые гормоны, в том числе эстроген, тестостерон и их рецепторы, или другие генетические факторы являются биологическими переменными, также компонентами в модификации сигнальных путей иммунной системы, как во врожденных, так и в адаптивных [58] . Точнее, в первой линии защитной системы (врожденный ответ) мужские половые гормоны, в первую очередь тестостерон, оказывают подавляющее действие на выработку и активность многочисленных иммуноассоциированных клеток.
Результаты большинства исследований in vivo и in vitro доказывают усиливающее воздействие тестостерона на чувствительность иммунной системы. Однако последние экспериментальные данные свидетельствуют о том, что фактическая роль тестостерона заключается в иммуномодулирующей, а не исключительно супрессивной [60]. Например, моноциты, которые представляют собой цитокин-продуцирующие клетки, способные дифференцироваться в макрофаги, некогерентно регулируются тестостероном, который усиливает высвобождение IL-12 и IL-1 и, таким образом, опосредует дифференцировку CD4+ хелперных Т-клеток и типы адаптивных ответов [61]. Доклинические исследования на гонадэктомированных мышах, получавших тестостерон, показали снижение экспрессии определенного типа молекулы распознавания образов (PRM), толл-подобного рецептора 4 (TLR4) на поверхности клеток макрофагов, по сравнению с кастрированными мышами, что отражает супрессивное действие циркулирующего тестостерона [62].
Кроме того, тестостерон влияет на экспрессию TNF-α, IL-1β и IL-6 и, как видно из исследований in vivo на мужчинах, получающих заместительную терапию тестостероном, у них вырабатываются ограниченные провоспалительные биомаркеры [63] . Широкое влияние тестостерона на иммунный ответ также было обнаружено в ходе клинического исследования на мужчинах цимане (коренные жители низменной Боливии), получавших селективный Т-клеточный митоген фитогемагглютинин (ФГА) и В-клеточные и моноцитарные митогенные липополисахариды (ЛПС). Результаты показывают большее иммунодепрессивное действие тестостерона на продукцию цитокинов Т-клетками при использовании ФГА, в то время как его действие после стимуляции ЛПС незначительно [64] .
С другой стороны, женские половые гормоны, включая эстроген и прогестерон и их рецепторы, являются гормональными медиаторами, которые способствуют усилению иммунных реакций, воздействуя на различные иммунные клетки.
Различные доклинические эксперименты и анализ клинических данных свидетельствуют о связи женских половых гормонов с концентрацией и активностью нейтрофилов, лейкоцитов, продуцирующих хемотаксические мессенджеры и распознающих инородные тела по экспрессии молекул распознавания гуморальных паттернов (PRM).
Точнее, было доказано, что концентрация нейтрофилов повышена в крови беременных и у женщин во время лютеиновой фазы менструального цикла, что подчеркивает усиливающееся влияние эстрогена и прогестерона на иммунный ответ [65] . Моноциты, напротив, по-видимому, подавляются высокими уровнями эстрогенов, которые стимулируют другие провоспалительные реакции макрофагов, включая дифференцировку Т-хелперов CD4+, регулирующих различные типы реакций адаптивного иммунитета. Известно, что цитокины IL-1 и IL-6, происходящие из Th17 CD4+ хелперных Т-клеток, повышены в ответ на эстрогены, в то время как IL-17, IL-22 и IL-23 имеют противоположную модуляцию. Дендритные клетки также были связаны с концентрацией эстрогена, так как Т-хелперы 2 типа цитокинов IL-4, IL-10 и IL-13, которые также опосредуют экспрессию MHC II и запускают выработку антител B-клетками. Индуцированное эстрогеном подавляющее действие проявляется особенно в естественных клетках-киллерах, ответственных за выработку цитокинов Th1, IL-2 и IFN- γ, которые участвуют в мобилизации макрофагов и цитотоксических Т-лимфоцитов [61, 66] .
Следовательно, клетки, участвующие в адаптивном иммунном ответе, также модулируются циркулирующими женскими половыми гормонами. Усиление гуморального ответа и ответа типа 2 в присутствии эстрогена указывает на усиленную дифференцировку В-клеток и выработку антител у женщин. Этот паттерн обеспечивает большую безопасность в случае инфекции, но повышает восприимчивость к аутоиммунным заболеваниям [67, 68] .
Аутоиммунные заболевания
Гиперактивная иммунная система женщин ответственна за более высокую частоту аутоиммунных заболеваний по сравнению с мужчинами: фактически женщины составляют примерно 85% пациентов с аутоиммунными заболеваниями [69] . При аутоиммунных заболеваниях нарушения в иммунной системе вызывают повреждение здоровых клеток. На этот сбой влияют эндокринологические изменения, которые происходят с женщинами в течение жизни (например, в период полового созревания, беременности и менопаузы, когда резко изменяются концентрации женских половых гормонов) [70] . В частности, аутоиммунные заболевания, включая системную красную волчанку (СКВ), рассеянный склероз (РС) и ревматоидный артрит (РА), известны своим эллиптическим течением в разные этапы репродуктивного пути женщины. Например, СКВ может усиливаться во время беременности, когда ранее преобладавший иммунный ответ Th1 заменяется Th2, о чем свидетельствуют наблюдения за соотношением TH1/TH2 у беременных [71] . Наоборот, РС и РА представляют собой уменьшение проявлений симптомов во время беременности, поскольку они зависят от иммунитета Th1-типа [69] .
Экспериментально доказано, что SLS связан с эстрадиолом, действующим через ERα, в то время как ERβ, как полагают, обладает незначительными иммунозащитными свойствами в отношении образования аутоантител B-клетками. Кроме того, клинические взаимоотношения между уровнями эстрадиола и SLS обнаруживаются у женщин, принимающих противозачаточные таблетки и получающих гормональную терапию.
Известно, что в первом случае риск SLS определенно повышен, в то время как во втором — данные противоречивы [72] . При РС у пациентов присутствуют аутоантигены, такие как структурные компоненты миелина, которые вызывают аутовоспалительные реакции, ведущие к нейродегенерации. Эстрогены, прогестерон и пролактин с их защитными действиями в центральной нервной системе, по-видимому, способны влиять на прогрессирование заболевания [73] .
Связь между концентрацией женских гормонов и риском РА также была подтверждена последними данными, полученными после первого триместра после родов. Так, обострение заболевания коррелирует с более низкими уровнями эстрогенов, прогестерона и гуморального иммунного ответа, а также с более высокими уровнями TNF-α и IFN- γ [74] .
Инфекционные заболевания и воспалительные реакции
Различные закономерности, наблюдаемые в специфических механизмах иммунитета, соответствуют диморфному фенотипу распространенности, прогрессирования и лечения инфекционных заболеваний у полов. Например, репликации вируса зависит от воспалительных механизмов индивидуума, которые, как упоминалось выше, имеют большие половые различия и находятся под сильным влиянием половых гормонов. Гормональные факторы, влияющие на эти различия, изучались в экспериментальных исследованиях инфекционных заболеваний.
Однако данные уровня смертности от инфекционных агентов подчеркивают необходимость более тщательного изучения связанных с полом различий [75] . Инфекции мочевыводящих путей (ИМП), например, чаще встречаются у женщин, но имеют более тяжелую форму у мужчин.
Сообщалось, что эстрогены, благодаря их влиянию на воспалительные реакции, оказывают положительное влияние на инфекции ИМП, как показано в доклинических исследованиях с участием мышей после овариэктомии, которые показали снижение резистентности хозяина к инфекции E. coli, и в клинических моделях на женщинах в постменопаузе, получавших заместительную гормональную терапию [76].
Исследования, анализирующие грипп, вирус иммунодефицита человека (ВИЧ) и вирус гепатита С (ВГС), например, показали более высокую уязвимость беременных женщин к развитию тяжелой гриппозной инфекции, а также лучшее лечение прогрессирования ВГС и ВИЧ-1 у женщин в сравнение с мужчинами [77] .
Согласно оценке статистического анализа австралийского населения, было установлено, что большее количество подтвержденных случаев гриппа А наблюдалось у взрослых женщин по сравнению с мужчинами [78] . Это также верно для случаев ВИЧ, у женщин распространенность инфекции в 1,62 раза выше [79] .
Напротив, согласно исследованиям, проведенным среди населения Европы и США, инфицирование ВГС значительно выше у мужчин по сравнению с женщинами [80] .
Половые гормоны и COVID-19
Известно о значительных различиях между мужчинами и женщинами в эпидемиологии коронавирусной инфекции 2019 (COVID-19), вызванной коронавирусом тяжелого острого респираторного синдрома 2 типа (SARS-CoV-2). Метаанализ, проведенный на 57 различных эпидемиологических отчетах, показал, что общая распространенность риска заражения COVID-19 у мужчин составляет 55,00 по сравнению с 45,00 у женщин, с разной восприимчивостью в зависимости от возраста [81] .
Тем не менее, случаи COVID-19 во всем мире существенно не различаются между полами, тогда как показатели смертности от этого заболевания значительно выше у мужчин. Например, согласно данным, полученным из Итальянского национального института здравоохранения, на мужчин приходилось 60% всех смертей, вызванных SARS-CoV-2, зарегистрированных в Италии до 20 мая 2021 года, независимо от возрастного диапазона [82] . Данные из разных географических регионов сообщают об аналогичных различиях. Это несоответствие возникает, по-видимому, в силу как половых (биологических), так и гендерных (социокультурных) причин. Например, сообщалось, что курение, которое усиливает экспрессию ангиотензинпревращающего фермента 2 типа (ACE-2) и связывание с ним SARS-CoV-2, увеличивает риск тяжелых симптомов COVID-19 в 1,4 раза по сравнению с некурящими [81] . Поскольку привычка курить чаще встречается у мужчин, это может отражать соответствующую гендерную предрасположенность. Что касается биологических факторов, то в настоящее время проводится ряд исследований. Например, половые гормоны и рецепторы половых гормонов следует оценивать при рассмотрении репликации вируса и воспалительного ответа при COVID-19. Обсуждаемые выше противовоспалительные эффекты эстрогенов могут играть защитный эффект при прогрессировании COVID-19. Было показано, что за счет усиления передачи сигналов TLR и продукции цитокинов, включая IFN-α, эстрогены коррелируют с менее тяжелыми случаями, как это наблюдалось в исследованиях с участием женщин в пременопаузе и мужчин того же возраста. Тем не менее, существуют противоречивые сообщения о действии эстрогенов на экспрессию ACE-2 и его возможной активности в снижении доступных сайтов связывания для SARS-CoV-2 [83] .
Механизмы регуляции рецепторов ACE-2 эстрогенами изучаются также в качестве адъювантной терапии заболевания [84]. Многие исследования на животных подтверждают защитную роль эстрогенов, наблюдая худшие результаты COVID-19 у инфицированных самок мышей, перенесших овариэктомию или получавших ингибиторы рецепторов эстрогена [85]. Улучшение или ухудшение течения заболевания, а также восприимчивость к инфекциям приписываются уровням женских гормонов, присутствующим в течение жизни, даже если этот процесс еще не полностью выяснен. Например, у беременных женщин наблюдается снижение числа CD4+ Т-хелперов и CD8+ Т-клеток, а также повышение экспрессии ACE-2, что может указывать на то, что они более уязвимы к инфекциям и дальнейшим осложнениям. Напротив, сниженный уровень циркулирующих и локально вырабатываемых эстрогенов у женщин в менопаузе наряду с выработкой высоких уровней IgG-антител в начале инфекции, по-видимому, сохраняет существенный защитный ответ по сравнению с мужчинами того же возраста [86]. Модуляция андрогенов в иммунологическом ответе на COVID-19, по-видимому, также находится в противоречии. Исследования на инфицированных самцах мышей показали более высокую вирусную нагрузку и большее количество воспалительных моноцитов и макрофагов [85]. Эти результаты потенциально могут соответствовать картине так называемого «цитокинового шторма», присутствующего в наиболее тяжелых случаях COVID-19, когда гиперактивность иммунной системы приводит к повышенным концентрациям IL-6, IL-1, TNF-α, IFN- γ и других провоспалительных цитокинов [87].
Дальнейшие научные исследования на животных и людях мужского пола привели к предположению, что тестостерон связан со смертностью от COVID-19, но его роль все еще обсуждается. Научные предположения раскрывают положительные модулирующие эффекты тестостерона на рецепторы ACE-2 и на трансмембранную протеазу серин 2 (TMPRSS2), действие которой заключается в активации спайковых белков SARS-CoV-2 [88] . Как повышенный уровень тестостерона усугубляет естественное течение болезни, было установлено контрольными исследованиями на больных раком простаты. Хотя пациенты с ослабленным иммунитетом переносят COVID-19 более тяжело, пациенты с раком предстательной железы, получающие блокаторы андрогенов и, следовательно, TMPRSS2, менее подвержены риску заболевания [89] . Последние исследования, предполагающие связь между повышенным риском тяжелого течения COVID-19 и концентрацией андрогенов, выявили более высокий риск госпитализации у мужчин с андрогенетической алопецией, распространенным дерматологическим заболеванием, которое характеризуется гиперандрогенностью и гиперактивностью генов рецепторов андрогенов [90] . Более короткая длина тринуклеотидного повтора CAG в первом экзоне генов AR, изменение, которое часто встречается у мужчин с этим типом расстройства, было связано с более тяжелыми и фатальными случаями COVID-19 [90] .
Другой заметный ключ к эффекту тестостерона был обнаружен в исследовании госпитализированных пациентов с легкой и тяжелой формой COVID-19, где у тяжелобольных пациентов мужского пола отмечены более низкие концентрации тестостерона [91] . Низкий уровень тестостерона также был связан с дисрегуляцией эндотелиальных клеток и продукцией активных форм кислорода, поскольку SARS-CoV-2 конкурирует с ангиотензином II за связывание с рецепторами ACE-2, вызывая повышение уровня ангиотензина II и снижение уровня ангиотензина-1, важного вазопротектора ренин-ангиотензиновой системы [81, 92] .
Полученные таким образом данные могут способствовать использованию тестостерона у пациентов мужского пола за счет ослабления провоспалительного состояния, присутствующего у мужчин, лишенных тестостерона, не препятствуя основным иммунным реакциям, а также положительно влияя на дыхательную систему [93]. Тем не менее, влияние половых гормонов на COVID-19 бесспорно, но еще не до конца изучено. Осведомленность о том, как они влияют на течение заболевания, может помочь в реализации новых стратегий лечения, о чем свидетельствует повышенный интерес к половым различиям в возможном целевом лечении, недавно продемонстрированный исследователями, участвовавшими в разработке лекарств от COVID-19 [94].
Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания
Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания (ССЗ) относятся к тем заболеваниям, для которых характерны значительные половые различия. Половой диморфизм был признан в отношении риска, прогрессирования, исхода и лечения различных патологий сердца и кровеносных сосудов, включая сердечную недостаточность, атеросклероз, гипертонию и инсульт. Опять же, генетические факторы (например, частичная инактивация женской Х-хромосомы, концентрация половых гормонов и расположение их рецепторов), по-видимому, играют важную роль в диморфизме.
Инсульт
Инсульт является ургентным состоянием, которое требует экстренной терапии. Бывает в виде двух клинических вариантов: ишемический инсульт вследствие образования тромба (чаще у женщин) или геморрагический. Инсульт часто может приводить к прогрессирующей нейродегенерации, коррелирующей со степенью повреждения ткани [95] .
Распространенность инсульта и смертность от него выше у женщин. Причем более высокая частота инсульта у пожилых женщин и ниже в молодом возрасте [96] . Прогноз после инсульта у женщин также оказался довольно неблагоприятным, в основном из-за проблем восстановления сонных артерий, связанных с половыми гормонами, а именно их влияния на образование атеросклеротических бляшек, а также анатомическими различиями, в том числе меньший диаметр сосудов у женщин [97] . Экспериментальные работы были проведены с целью выяснения биологических факторов риска, связанных с основными видами инсульта (ишемическим и геморрагическим).
Исследования на мышах показали, что повреждение головного мозга после ишемии преобладает у молодых самцов, а не у самок, и эта тенденция меняется после 15-месячного возраста.
Это открытие говорит о том, что возможным объяснением может быть прогрессирующая с возрастом потеря эстрадиола, но, тем не менее, низкие уровни гормона, наблюдаемые до полового созревания, затрудняют четкое представление о точном гормональном влиянии.
Одно из возможных объяснений заключается в том, что гормоны оказывают регулирующее действие на устойчивые повреждения головного мозга, вызванные инсультом [98] .
Результаты исследований на животных также показали, что специфичные для пола ишемические изменения не могут быть связаны с генетикой (ни с дополнительной женской Х-хромосомой, ни со специфическими генами на Y-хромосоме).
Что касается тестостерона, исследования у молодых мужчин указывают на повышенный риск развития сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний. Орхиэктомированные самцы крыс, получавшие тестостерон, подтвердили предрасполагающие эффекты тестостерона. У пациентов с ишемическим инсультом также был обнаружен низкий уровень тестостерона. Это может быть связано с превращением тестостерона в эстроген (т. е. с внутренними защитными механизмами ароматизации тестостерона) [99] .
Ожирение
Ожирение является одним из основных факторов риска развития ССЗ как у мужчин, так и у женщин. Состав тела при ожирении, характеризующийся избыточной жировой массой и дефицитом тощей, может провоцировать развитие сердечной недостаточности и ишемической болезни сердца, а также изменять нормальную анатомию миокарда, приводя к кардиомиопатии. Основные механизмы, приводящие к этим сопутствующим заболеваниям, зависят от продукции жировой тканью провоспалительных цитокинов и способствуют образованию атеросклеротических бляшек [100 –102] .
Уровни половых гормонов могут влиять на патофизиологию фенотипа ожирения и, следовательно, на регуляторные пути, ведущие к сердечно-сосудистым заболеваниям. Стоит отметить, что так называемый «парадокс ожирения» гласит, что статус ожирения, особенно у пожилых людей, смягчает исход уже существующей далеко зашедшей формы сердечной недостаточности, а это означает, что повышенный индекс массы тела может минимизировать уровень смертности и у женщин, и у мужчин.
Тем не менее проведено недостаточное количество исследований, изучающих этот парадокс у обоих полов [103] . В целом, ожирение представляет собой вяло текущее воспаление с метаболически активными процессами, включающее избыточную висцеральную жировую ткань, секрецию адипокинов, инсулинорезистентность, повышенную секрецию инсулина и липопротеинов очень низкой плотности по сравнению с людьми с нормальной массой тела.
В ряде исследований подчеркивается связь эстрогенов с этими процессами. Например, у женщин в постменопаузе наблюдается избыток адипокинов и усиленное образование иммунных медиаторов, что приводит к более высокому риску кардиометаболических заболеваний.
Сам по себе этот синдром включает инсулинорезистентность, дислипидемию и гипертонию в качестве клинических симптомов, увеличивающих риск заболеваний коронарных артерий, инсульта [104] . Тем не менее, статистические данные из разных европейских стран указывают на более высокую распространенность избыточного веса и ожирения среди взрослых мужчин по сравнению с женщинами тех же возрастных групп, хотя данные, по-видимому, различаются в зависимости от географического положения и социальных особенностей людей [105] .
С биологической точки зрения, благодаря способности жировой ткани секретировать адипокины, такие как провоспалительный лептин и противовоспалительные адипонектин и резистин, ее можно считать органом с эндокринными функциями, которые могут способствовать развитию сердечно-сосудистых и онкологических заболеваний [106, 107] .
Сообщалось также о половых различиях в приверженности пациентов к программам по снижению веса, что необходимо учитывать для правильного выбора метода терапии [108] .
Атеросклероз
Атеросклероз — это, состояние хронического воспаления, характеризующееся образованием атеросклеротических бляшек в различных артериальных сосудах, препятствующих притоку крови к тканям и приводящим к ишемическим состояниям. Со временем бляшки могут кальцифицироваться, сузив диаметр артерий, или даже потерять целостность в результате образования тромба.
Атеросклероз является основной причиной заболеваемости и смертности среди представителей обоих полов, в основном из-за инфаркта миокарда (ИМ), сердечной недостаточности и инсульта. В литературе отмечается более бурное проявление и неблагоприятный исход атеросклероза у мужчин. Исследования на животных подтверждает эту тенденцию, а также выдвигают на первый план вывод о том, что атеросклеротическое воспаление связано с худшими исходами и прогнозом, а не с объемом бляшек [109].
Эпидемиологические источники, как уже упоминалось, продемонстрировали более высокий риск развития ССЗ у мужчин молодого возраста, чем у женщин, что также относится к эволюции атеросклероза. Это может быть частично объяснено поведенческими привычками, включающими курение и употребление алкоголя, которые более распространены среди мужчин, а также предполагаемыми защитными механизмами эстрогенов у молодых женщин, что также подтверждено исследованиями на животных. Что весьма спорно, так это безопасность гормонального лечения у мужчин и женщин в пожилом возрасте.
Хотя эстроген и тестостерон в адекватных дозах снижают риск развития атеросклероза, потенциальное лечение пожилых людей может иметь негативные последствия [110] . Процесс образования атеросклеротических бляшек на фоне состояния хронического воспаления, их состав были тщательно изучены, однако без анализа вопроса половых различий. Кроме того, были предложены варианты морфологического строения бляшек: более толстая фиброзная оболочка в стабилизированных бляшках у молодых женщин и большее некротическое ядро у пожилых. Определен больший риск разрыва бляшки из-за высокого уровня общего холестерина по сравнению с эрозией бляшки, которая присутствует в более широких, менее кальцифицированных артериях молодых женщин [111] .
Половые различия отмечены не только в элементах состава атеросклеротических бляшек, но и в системе воспаления. Точнее, согласно источнику, изучающему этапы воспаления при миокардите, тестостерон может быть ответственным за запуск тучных клеток и активацию макрофагов, усиление макрофагов TLR-типа и агрегацию пенистых клеток в бляшках, вызывая структурные перестройки и последующий тромботический ИМ. И наоборот, эстрогены связаны с повышенным количеством антител и аутоантител, наряду с антителами против окисленного ЛПНП, которые оседают на стенках узких кровеносных сосудов, вызывая тромбоз и ИМ [112] .
Таким образом, были обнаружены половые различия в риске развития атеросклероза и в морфофизиологических элементах бляшек.
Гипертония
Артериальная гипертензия является основным фактором риска сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, для нее характерны гендерные и половые особенности. Исследования говорят о более высокой распространенности артериальной гипертензии у мужчин с изменением этой тенденции у лиц старческого возраста и долгожителей. Опять же, менопаузальные гормональные изменения у женщин, по-видимому, связаны с повышенным уровнем артериальной гипертензии у пожилых женщин [113] .
Исследования по мониторингу изменения артериального давления (АД) во время менструального цикла с помощью холтеровского мониторирования давления как у больных АГ, так и у здоровых лиц продемонстрировали заметные различия между полами. Женщины, по-видимому, имели более высокое АД во время менструации и в фолликулиновую фазу менструального цикла, а не в лютеиновую [114] . Несмотря на то, что клинические симптомы у мужчин и женщин различаются, рекомендации по контролю АД не зависят от пола.
Необходимы дальнейшие исследования с привлечением большего количества представителей обоих полов для изучения мониторинга АД и отработки схем антигипертензивной терапии с учетом гендерного диморфизма [115] .
Сердечная недостаточность
Сердечная недостаточность (СН) представляет собой одно из наиболее распространенных ССЗ, поражающих как мужчин, так и женщин во всем мире.
Гендерное различие относится к факторам риска, влияющим на заболеваемость и фенотипический спектр проявлений. Хроническое вялотекущее воспаление, ригидность артериальных сосудов, приводящая к сосудистой жесткости, эпизоды гипертензии во время беременности, эмоциональный стресс и терапия рака молочной железы являются факторов риска развития СН, характерными для женщин [116] .
Отличительные признаки СН в зависимости от пола включают в себя: сниженная (HFrEF) или средняя (HFmrEF) фракция выброса у мужчин, сохранная фракция выброса (HFpEF) у женщин. Женщины, по-видимому, страдают от большего количества сопутствующих заболеваний, но имеют более благоприятный прогноз и низкий уровень смертности, чем мужчины [117] .
Различные комбинации сопутствующих заболеваний связаны с отдельными фенотипами HFpEF. Так, один из вариантов характеризуется снижением ремоделирования сердца и снижением высвобождения натрийуретического пептидного гормона с клиническими проявлениями ожирения, что чаще встречается у женщин; другой, более тяжелый, связан с хронической почечной недостаточностью, ремоделированием левого желудочка, и менее благоприятным прогнозом, чаще наблюдаемый у мужчин [116] . СН, в целом, приводит к более низкому качеству жизни у женщин, несмотря на более оптимистичные прогнозы, тогда как на мужчин более сильно влияют психофизические факторы [118] .
Таким образом, поведенческие характеристики наряду с другими социальноэкономическими факторами (например, повышенное внимание женщин к своему здоровью и связанное с ним раннее обращение к врачам) привели к сходной частоте госпитализаций у мужчин и женщин, несмотря на наиболее тяжелый фенотип СНнФВ у мужчин [119] .
Лечение СН выявило высокую частоту побочных эффектов, особенно у женщин. Тем не менее, терапию СН и других ССЗ можно модернизировать, применяя в исследованиях четкий гендерный подход [120] .
Планирование исследований лекарственной терапии с учетом пола и гендера, кажется ключевым для разработки персонализированного подхода в медицине. Следует модифицировать экспериментальные (т.е. доклинические) и клинические исследования с учетом пола. В реалиях, самок практически не включают в доклинические исследования на животных (обычно работы проводятся на самцах грызунов) и в интервенционные или наблюдательные биомедицинские исследования.
По-видимому, это связано с тем, что у женского пола явно проявляются циклические гормональные изменения, которые затрудняют интерпретацию результатов. Тем не менее, для разработки новых, прогрессивных схем терапии необходимо учитывать широкое влияние половых гормонов на различные органы и системы организма, а также их участие в патогенезе ряда заболеваний.
Персонализированная и ориентированная на пол медицина может привести к революционным клиническим и терапевтическим методам воздействия на организм, символизирующим улучшение качества оказания медицинской помощи. Воплощение в протоколах биомедицинских исследований нетрадиционных, нестереотипных руководящих принципов, пропагандирующих половое и гендерное равенство, могло бы стать отличной отправной точкой для достижения апогея последующих научных открытий.
Кроме того, необходимо признать, что гендерное неравенство не ограничивается только медициной, но в значительной степени представляет собой важный социальный вопрос.
Сексуальная активность и болезнь Альцгеймера: медико-социальное сопровождение Стратегии и прогнозы
Геронтология и гериатрия, гинекология и нейроэндокринология, нейрофизиология и нейросоциология маршрутизируют H. sapiens в активное / здоровое / качественное / религиозное / нравственное/сексуальное / нейрокоммуникативное долголетие .
Бюро переписи населения США прогнозирует, что к 2030 году один из каждых пяти жителей США будет пенсионного возраста, а число пожилых людей впервые в истории США превысит число детей. Это означает, что к 2035 году будет 78 миллионов человек 65 лет и старше по сравнению с 76,7 миллионами в возрасте до 18 лет. Теперь добавьте к этому знание о том, что активная сексуальная жизнь связана с улучшением физического и психического здоровья, более высоким качеством жизни и более низкими показателями одиночества, и имеет смысл, что ученые фокусируются на сексе у пожилых людей. Исследователи геронтологии и гинекологии считают, что сексуальная активность является важным аспектом человеческой функции на протяжении всей жизни и что уважительная забота о пожилых людях, включая людей с когнитивными нарушениями, требует понимания сексуальных норм и проблем.
Используя данные Национального проекта по социальной жизни, здоровью и старению (NSHAP), исследователи намеревались узнать больше о взаимосвязи не только между сексуальным поведением и функциями среди пожилых людей, но и об их способности думать и принимать решения о сексе. Они обнаружили, что пожилые мужчины и женщины, в том числе с деменцией, занимаются сексом, и хотя уровень проблем с сексуальной функцией высок, большинство людей, включая мужчин и женщин с более низким уровнем познания, считают сексуальность важной частью жизни и хотят ее больше. Исследовано, 1550 женщин и 1455 мужчин, в возрасте от 57 до 85 лет, было показало, что около половины мужчин и женщин сообщили по крайней мере об одной сексуальной проблеме и что мужчины и женщины с плохим здоровьем менее склонны к сексуальной активности. Наиболее распространенными сексуальными проблемами среди женщин были низкое желание, трудности с вагинальной смазкой и неспособность достичь кульминации. Среди мужчин наиболее распространенными сексуальными проблемами были трудности с эрекцией, и многие использовали лекарства или добавки для их лечения.
Исследователи заявили, что нынешнее исследование является первым, которое установило национальные репрезентативные данные о сексуальности в отношении когнитивной функции для пожилых людей, проживающих дома, в Соединенных Штатах. Сегодня около 3,2 миллиона человек, живущих дома, страдают болезнью Альцгеймера. Ожидается, что к 2050 году это число вырастет до более чем 8 миллионов. И эксперты согласны с тем, что мы очень мало знаем о сексуальности среди людей с когнитивными проблемами. Таким образом, вопрос для этих исследователей становится: «Всегда ли пожилые люди имеют возможность согласиться на сексуальную активность? Они надеются, что их результаты будут направлять профессиональных, а также семейных опекунов в этическом обращении с пожилыми людьми в ближайшие годы. Более трети мужчин и одна из 10 женщин в группе деменции сообщили о сексуальных проблемах, особенно об отсутствии интереса к сексу, отметили авторы, но большинство людей, включая мужчин и женщин с более низким уровнем познания, считали сексуальность важной частью жизни и сообщали о сексе реже, чем им хотелось бы.
Тем не менее, не все результаты должны заставить молодых людей бояться своей будущей сексуальной жизни. Более 40 процентов мужчин и женщин в возрасте от 80 до 91 года, живущих с деменцией, все еще были сексуально активны. И исследователи отметили, что трудности с эрекцией были ниже у мужчин с худшими когнитивными функциями, включая мужчин, которые не были сексуально активны с партнером. «Это открытие может относиться к центральным растормаживающим эффектам или другим физиологическим механизмам деменции или лекарствам, обычно используемым в этой популяции, и требует дальнейшего изучения», - пишут авторы исследования. «Мы обнаружили, что, хотя скорректированные по возрасту показатели индивидуальной и партнерской сексуальной активности ниже у людей с худшими когнитивными функциями, большинство пожилых мужчин и женщин, имеющих положительный результат скрининга на деменцию, сексуально активны, в том числе 40% партнеров в возрасте от 80 до 91 года».
Исследователи также обнаружили, что почти половина всех мужчин с деменцией были сексуально активны, как и 18 процентов женщин. Они сообщили, что, хотя около 83 процентов мужчин и 57 процентов женщин имели интимного партнера, чем больше человек был ослаблен в мышлении и принятии решений, тем меньше вероятность того, что у них будет интимный партнер. Женщины с более низкими когнитивными оценками реже, чем мужчины с более низкими когнитивными оценками, имели интимных партнеров. И среди людей с интимным партнером большинство — 59% мужчин и 51% женщин — были сексуально активны. Исследователи также обнаружили, что один из 10 партнеров чувствовал угрозу или страх со стороны партнера, что является фактором, вызывающим беспокойство у пожилых людей. Однако, напротив, «хотя большинство сексуально активных людей в разных группах были удовлетворены своей сексуальной жизнью, люди с деменцией чаще других сообщали об обязательном сексе и сексе без чувства возбуждения и находили физические прикосновения непривлекательными». Установлено, что люди с более низким уровнем познания, особенно женщины, также реже говорили с партнером или врачом о сексуальных проблемах, может частично объяснить эти результаты.
В исследовании не рассматривалась распространенность сексуального насилия или изнасилования со стороны партнера, хотя люди с более серьезными когнитивными нарушениями подвергаются более высокому риску сексуальной виктимизации. Эта озабоченность привела к ограничительной политике и даже судебным искам против супругов людей с деменцией. Эксперты и руководящие принципы призывают врачей выявлять жестокое обращение с пожилыми людьми, включая сексуальное насилие, но определения жестокого обращения и стандарты согласия на секс сильно различаются, и их может быть трудно реализовать на практике. Исследование добавляет новые доказательства для использования при изучении улучшения этих стандартов.
NSHAP широко признаны действительными и были использованы в других крупных популяционных исследованиях старения, которые оценивали сексуальность. Они отмечают, что, хотя существует мало доказательств того, что ответы на вопросы о сексуальности менее надежны, чем в других областях, надежность этих ответов может снижаться с ухудшением когнитивных функций и что в двух небольших исследованиях людей (в основном мужчин) с болезнью Альцгеймера меньшинство сообщило о более высокой частоте сексуальности их супруги. Еще одним возможным ограничением, по словам Ландау, было то, что исследование было в значительной степени сосредоточено на изучении женатых людей и что результаты исследования не дают представления об однополых партнерствах.
По оценкам исследователей, «в домашнем населении Соединенных Штатов в возрасте 62 лет и старше, по крайней мере, 1,8 миллиона мужчин и 1,4 миллиона женщин с вероятной деменцией сексуально активны, и это число более чем удвоится к 2050 году». Отмечено, что врачи редко консультируют этих людей, особенно женщин, о сексуальных изменениях, которые могут возникнуть в результате деменции или других заболеваний. Результаты о сексуальности пожилых людей в контексте когнитивных нарушений должны помочь в подходе к предварительным директивам, консультированию, лечению и личностно‐ ориентированному принятию решений врачами и другими лицами, ответственными за этическую и гуманную заботу о пожилых людях [12 1].
Estrogen therapy, SERMs
? Loss of estrogen, progesterone
• increased p-amyloid
• increased tau phosphorylation
• increased neuron death
• decreased spine density
• impaired cognition
Environmental, Genetic factors
Normal aging
Alzheimer’s disease
Testosterone therapy, SARMs
Loss of testosterone
• increased p-amyloid
• increased tau phosphorylation
• increased neuron death
• decreased spine density
• impaired cognition
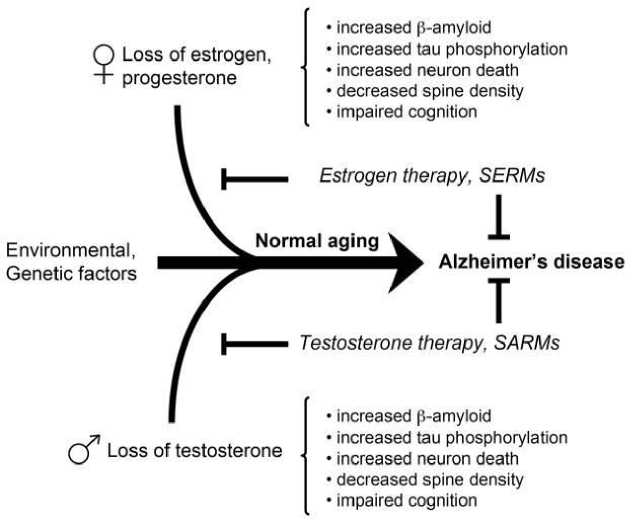
Рисунок 1. Возрастная потеря половых гормонов и болезнь Альцгеймера [12 1]
Взаимодействие между возрастной потерей половых гормонов и риском развития болезни Альцгеймера
Патогенез болезни Альцгеймера является многофакторным процессом. Пожизненное воздействие комбинации выявленных генетических и экологических факторов риска взаимодействует с многочисленными нормальными возрастными изменениями, способствуя развитию болезни Альцгеймера. Одним из важных нормальных возрастных изменений, связанных с дисфункцией и заболеванием во многих тканях, является потеря половых гормонов, эстрогенов у женщин и тестостерона у мужчин. Возрастное истощение эстрогенов и тестостерона может быть особенно значительным для развития болезни Альцгеймера, поскольку эти половые гормоны являются установленными регуляторами нескольких событий, связанных с заболеванием, включая накопление бета-амилоида, фосфорилирование тау, гибель нейронов и снижение плотности позвоночника. Раннее вмешательство с использованием терапии на основе эстрогена и тестостерона или синтетических гормональных миметиков, называемых модуляторами рецепторов эстрогена (SERMs) и модуляторами рецепторов андрогенов (SARMs), может восстановить утраченные защитные функции и предотвратить болезнь Альцгеймера [121].
Понимание того, как старение способствует процессу заболевания, представляет собой потенциально мощный подход для разработки стратегий задержки и, возможно, предотвращения заболевания. В этом контексте нормальные возрастные потери половых стероидных гормонов у мужчин и женщин представляются значительными событиями. На самом деле, многочисленные данные свидетельствуют о том, что низкие уровни половых гормонов, эстрогенов у женщин и тестостерона у мужчин, являются факторами риска развития болезни Альцгеймера. Фундаментальные исследования выявили и механистически охарактеризовали многочисленные защитные действия половых гормонов, которые улучшают нервное функционирование и устойчивость и могут противодействовать патогенезу болезни Альцгеймера. Мало того, что половые гормоны увеличивают нейронную пластичность и улучшают аспекты познания, они также защищают нейроны от гибели клеток, вызванной рядом токсических воздействий. Самое главное, что половые гормоны являются эндогенными негативными регуляторами, накопление которых инициирует и управляет каскадами болезни Альцгеймера в нейроэндокринных механизмах взаимодействия эстрогенов и андрогенов (HT). Вместе эти линии доказательств утверждают, что эстроген у женщин и тестостерон HT у мужчин должны эффективно снижать риск болезни Альцгеймера и способствовать здоровью нервной системы [12 1].
Хотя теория о том, что половые гормоны могут защитить от болезни Альцгеймера, является убедительной, клиническая демонстрация эффективности HT показала только смешанный успех. Во-первых, похоже, что потенциальные преимущества HTS на основе эстрогена и тестостерона в значительной степени ограничены профилактикой, а не лечением болезни Альцгеймера. Новые исследования показывают, что существует несколько переменных, которые, вероятно, влияют на эффективность HT. Например, для достижения оптимальных результатов может потребоваться, чтобы гормоны доставлялись трансдермально, а не традиционным оральным путем. Кроме того, можно ожидать, что HT будет иметь различные эффекты в зависимости от того, доставляется ли он непрерывно или циклически. Хотя уровни инкрети секса естественно колебаются, тестостерон поднимая и падая в суточном ритме и E2 и P4 через ежемесячный овариальный цикл, отказ HT соответствовать естественной цикличности уровней инкрети может подорвать свою способность восстановить нормальные действия инкрети. Кроме того, в случае эстрогена HT роль прогестагенов требует дополнительного определения. Новые данные показывают, что природные P4 и синтетические прогестагены могут ослаблять или усиливать защитные действия E2 в зависимости от их доставки [12 1].
Возможно, самым сложным препятствием для преодоления при оценке терапевтического потенциала половых гормонов является роль старения. Ключевой переменной в отрицательном результате нескольких исследований HT, по-видимому, является пожилой возраст, в котором была начата HT. Недавние исследования показывают, что стареющие мужские и женские мозги изменились, как правило, уменьшили чувствительность к половым гормонам, которая не улучшается гормональным лечением в пожилом возрасте.
Таким образом, эффективный HT может потребовать инициации в среднем возрасте, когда истощение половых гормонов является значительным, и все же мозг сохраняет гормональную отзывчивость. Однако для окончательного клинического доказательства того, что начало HT в среднем возрасте снижает риск болезни Альцгеймера в пожилом возрасте, потребуется много лет. Даже в этом случае необходимо решить важные вопросы. Как долго должен поддерживаться HT, чтобы реализовать преимущества, пять лет, десять лет, больше?
Поскольку длительное использование HT кажется вероятным, необходимо учитывать побочные эффекты половых гормонов. Хотя половые гормоны имеют многочисленные преимущества для здоровья, они также связаны с рисками, включая развитие рака в репродуктивных тканях. Этот риск может быть сведен к минимуму путем дальнейшего совершенствования нового поколения SERMs и SARMS, миметиков половых гормонов, которые оказывают тканеспецифические агонистические эффекты. Продолжение исследований в течение следующих нескольких лет должно дать значительное представление об этих проблемах и определить полезность HT для защиты от болезни Альцгеймера [12 1].
После преклонного возраста женский пол является основным фактором риска развития болезни Альцгеймера с поздним началом, наиболее распространенной причиной деменции, поражающей более 24 миллионов человек во всем мире [12 2]. Распространенность болезни Альцгеймера выше у женщин, чем у мужчин, причем женщины в постменопаузе составляют более 60% всех пострадавших. Хотя большинство исследований было сосредоточено на гендерном риске, новые данные указывают на половые и гендерные различия в патофизиологии, начале и прогрессировании болезни Альцгеймера, что может помочь объяснить более высокую распространенность у женщин. Примечательно, что связанные с болезнью Альцгеймера изменения мозга развиваются в течение 10-20-летней продромальной фазы, происходящей в среднем возрасте, таким образом, в непосредственной близости от гормональных переходов эндокринного старения, характерных для перехода менопаузы у женщин. Доклинические данные о нейропротекторных эффектах гонадных половых стероидных гормонов, особенно 17β-эстрадиола, убедительно доказывают связь между женской фертильностью, репродуктивным анамнезом и риском болезни Альцгеймера. Уровень гонадных гормонов, которым подвергается женский мозг, значительно меняется на протяжении всей жизни, что имеет отношение к риску болезни Альцгеймера. Однако нейробиологические последствия гормональных колебаний, а также гормональной терапии еще предстоит полностью понять. Эпидемиологические исследования дали контрастные результаты защитных, вредных и нулевых эффектов воздействия эстрогена на риск деменции. Напротив, исследования визуализации мозга дают обнадеживающие доказательства положительной связи между большим кумулятивным воздействием эстрогена в течение всей жизни и более низким риском болезни Альцгеймера у женщин, тогда как лишение эстрогена связано с негативными последствиями для структуры, функции и биохимии мозга. Здесь мы рассматриваем существующую литературу и оцениваем силу наблюдаемых ассоциаций между специфическими для женщин факторами репродуктивного здоровья и риском болезни Альцгеймера у женщин, уделяя особое внимание роли эндогенного и экзогенного воздействия эстрогена как ключевого основного механизма. Главными среди этих переменных являются репродуктивная продолжительность жизни, статус менопаузы, тип менопаузы (спонтанная или индуцированная), количество беременностей и воздействие гормональной терапии, включая гормональные контрацептивы, гормональную терапию менопаузы и антиэстрогенное лечение. Поскольку старение является самым большим фактором риска для болезни Альцгеймера, за которым следует женский пол, понимание специфических для пола биологических путей, через которые репродуктивная история модулирует старение мозга, имеет решающее значение для информирования о профилактических и терапевтических стратегиях болезни Альцгеймера [12 2].
В целом, половые стероидные гормоны являются давно упущенным, но важным фактором когнитивного старения. Хотя нейробиологические последствия репродуктивного анамнеза и гормональных изменений для старения мозга и риска болезни Альцгеймера только начали пониматься, сходящиеся данные подтверждают роль кумулятивного воздействия эстрогена в снижении риска болезни Альцгеймера и деменции в более позднем возрасте. Это убедительно доказывает необходимость дальнейшего изучения половых гормонов и факторов репродуктивного анамнеза в стратегиях профилактики болезни Альцгеймера у женщин. Существует острая необходимость в проспективных эпидемиологических, клинических и биомаркерных исследованиях с данными, полученными в нескольких временных точках, начиная с среднего возраста, которые изучают связи между кумулятивным воздействием эстрогена и когнитивной функцией в более позднем возрасте. Понимание динамического взаимодействия между полом, хронологическим старением, эндокринным старением и дополнительными факторами риска имеет решающее значение для информирования и обоснования стратегий первичной профилактики, нацеленных на специфические для женщин факторы риска, лежащие в основе увеличения распространенности болезни Альцгеймера у женщин, и для разработки будущей персонализированной профилактической помощи [12 2].
Многие доказательства выяснили соответствующие механизмы действия эстрогена, прогестерона и тестостерона на познание, включая процессы обучения и памяти, как на животных моделях, так и на людях Это влияние может зависеть от их модуляторной роли в нескольких нейромедиаторных системах и обширного присутствия их рецепторов в областях головного мозга, участвующих в когнитивных функциях, включая миндалину, формирование гиппокампа и кору головного мозга. В частности, после введения, иллюстрирующего общие механизмы модуляции половых гормонов на процессы памяти, специфическая роль эстрогена, прогестерона и тестостерона в памяти описывается в трех различных разделах. Помимо влияния на репродуктивное поведение, предполагается, что гонадные гормоны также влияют на многие функции мозга (Рисунок 2) [12 2]. Помимо обобщения наиболее актуальных действий половых стероидных гормонов в модуляции обучения и памяти, также подчеркивается, что многие аспекты и механизмы до сих пор не полностью поняты, и для их выяснения необходимы обширные будущие исследования.
Положительное влияние эстрогена на различные клеточные процессы, такие как производство активных форм кислорода (АФК) и антиоксидантная защита, сердечнососудистая защита, иммунная компетентность и поддержание теломер, было хорошо признано, по крайней мере частично, для увеличения продолжительности жизни женщин [12 3, 124] может показаться парадоксальным, что женщины все еще живут дольше мужчин после гормональной потери из-за менопаузы и, следовательно, долго после того, как извлекли выгоду из защитных эффектов эстрогенов. Интересно, что недавно сообщалось о положительной корреляции между более поздним возрастом в менопаузе или более длительной репродуктивной жизнью с долголетием [12 5]. Это говорит о том, что пожизненное кумулятивное воздействие эстрогенной стимуляции на протяжении всей фертильной жизни может оказывать длительные эффекты и объяснять такой половой диморфизм в долголетии. Это воздействие также повлияет на старение мозга и нейродегенеративные процессы. В целом, вышеупомянутые половые различия предполагают, что учет пола в качестве биологической переменной может иметь решающее значение при подходе к терапии для лечения нейроденегеративных заболеваний или задержки старения мозга [12 6].
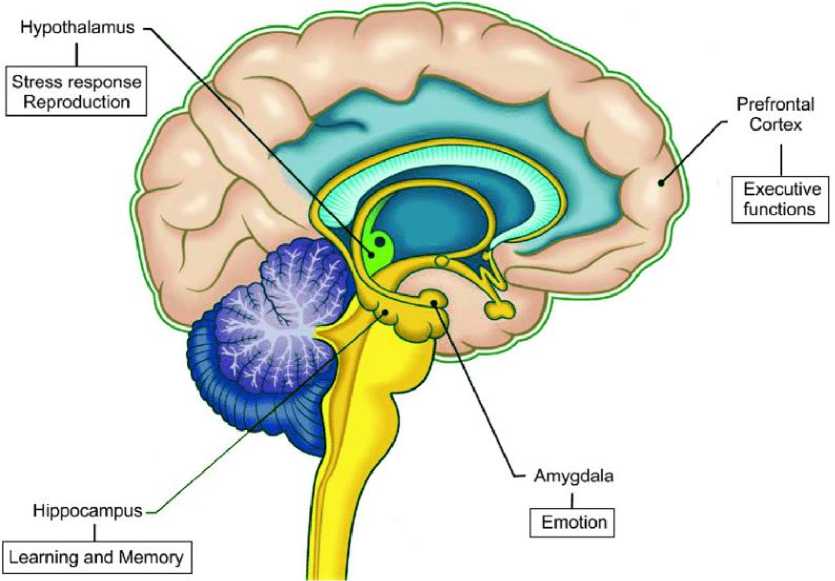
Рисунок 2. Влияние половых гормонов на различные области мозга [12 2].
Старение — неизбежный физиологический процесс, организованный множеством молекулярных механизмов, которые взаимодействуют для изменения гомеостаза организма, в конечном итоге приводя к функциональному снижению организма и заболеваниям. Хотя в течение многих лет мозг не считался органом, реагирующим на половые гормоны, за исключением гипоталамуса для регуляции репродуктивной функции, в настоящее время хорошо признано, что весь мозг является как мишенью, так и источником половых гормонов [12 7, 128]. Половые гормоны оказывают многочисленные защитные и антиоксидантные действия в мозге взрослого человека, повышая нервную функцию и устойчивость и способствуя выживанию нейронов. По мере старения организма происходит относительно быстрая потеря гормонов яичников у женщин после менопаузы и постепенное, но действительно значительное снижение тестостерона у мужчин. Таким образом, неудивительно, что репродуктивное старение как у мужчин, так и у женщин оказывает негативное влияние на нервную функцию и представляет собой значительный возрастной фактор риска нейродегенеративных заболеваний, таких как болезнь Альцгеймера [129].
Таким образом, старение — неизбежный биологический процесс, характеризующийся прогрессирующим снижением физиологических функций и повышенной восприимчивостью к болезням. Пагубные последствия старения наблюдаются во всех тканях, мозг является наиболее важным из-за его основной роли в гомеостазе организма. Поскольку наши знания о основных механизмах старения мозга увеличиваются, потенциальные подходы к сохранению функции мозга значительно возрастают. Накопленные данные свидетельствуют о том, что потеря геномного обслуживания может способствовать старению, особенно в центральной нервной системе из-за ее низкой способности к репарации ДНК. Половые гормоны, особенно эстрогены, обладают мощными антиоксидантными свойствами и играют важную роль в поддержании нормальных репродуктивных и не репродуктивных функций. Они оказывают нейропротекторное действие, и их потеря во время старения и естественной или хирургической менопаузы связана с митохондриальной дисфункцией, нейровоспалением, синаптическим снижением, когнитивными нарушениями и повышенным риском возрастных расстройств. Кроме того, было предложено, чтобы потеря половых гормонов способствовала ускоренному старению фенотипа, что в конечном итоге приводит к развитию гипометаболизма мозга, что часто наблюдается у женщин в менопаузе и продромальной болезни Альцгеймера. Хотя данные о связи между половыми гормонами и механизмами репарации ДНК в мозге все еще ограничены, различные исследования связывают уровни половых гормонов с различными ферментами репарации ДНК. Исследованы [22], антивозрастные и нейропротекторные механизмы эстрогена, которые в настоящее время являются областью интенсивного изучения, а также влияние, которое они могут оказывать на способность репарации ДНК в мозге.
Исследование подразумевает половое созревание как дальнейший критический период для половой дифференциации регуляции генов и обеспечивает архетип для изучения действия рецепторов гормонов на разных этапах жизни, в различных областях мозга [130].
Половые гормоны играют важную роль в формировании поведения человека, и их влияние начинается рано. Гормональные всплески в раннем возрасте помогают формировать развивающийся мозг, создавая нейрокоммуникации, которые будут влиять на поведение в течение всей жизни. Сотни генов в мозге попадают под контроль эстрогена. Колеблющиеся уровни гормона вызывают сдвиги в настроении, энергетическом балансе и поведении на протяжении всей жизни, через нейрокоммуникации нейронных цепей [130].
Поэтому объединение результатов исследований МРТ с различными методами, такими как позитронно-эмиссионная томография или эпигенетический анализ, было бы полезно для развития более широких знаний о гормональных механизмах [131]. Кроме того, несколько исследований не смогли предоставить координаты мозга значимых результатов и использовали различные статистические контрасты и подходы (анализ всего мозга против области интересов), что делает метаанализ невозможным в данный момент. В целом, для того, чтобы сделать дальнейшие выводы, необходимы дополнительные исследования, систематически исследующие роль гормональных колебаний в структуре мозга [131].
Социально-когнитивная парадигма мозга человека
Психоделическая инструментализация в социокогнитивной нише человека
Человеческая ниша включает в себя личные взаимодействия внутри социальных групп, взаимодействия между социальными группами и сложную социальную динамику, как на групповом, так и на более крупном уровне сообщества (Рисунок 3). Использование психоделиков увеличивало участие в формирующейся нише, в которой социальные переживания, такие как игра и смех, пение и танцы, фантазия и рассказывание историй и участие в религиозных ритуалах, стали обычными действиями. Коллективное использование психоделиков, возможно, таким образом обогатило социальную жизнь и укрепило герменевтическую и риторическую деятельность, улучшив управление групповой напряженностью (через эмоциональный катарсис) и укрепив социальные связи (путем запуска эндорфиновой системы), в конечном счете облегчив сложную социальность и коммуникацию во все больших человеческих группах. Коэволюционные процессы построения ниши и генной культуры объясняют, как диетическое и социальное включение психоделиков могло стать эволюционно значимым [132].
Вхождение в социально-когнитивную нишу включало увеличение познания, социальности, коммуникации и социального обучения. Рисунок 3 обобщает модель того, как эти основные аспекты формирующегося адаптивного комплекса человека были потенциально усилены случайным приемом психоделиков и периодической психоделической инструментализацией. Модель предполагает, что псилоцибин усилил бы необходимые способности для все более сложного социального взаимодействия и набор когнитивных способностей, поддерживающих социально-когнитивную нишу, включая аспекты творчества, невербального и лингвистического выражения и внушаемости (левая сторона рисунка 3). Эти эффекты могли способствовать общему решению проблем, совместному добыванию пищи, ритуальному исцелению, традиционному представлению и символике (включая формирование мифа и идентичности) и практике инкультурации (например, обряды перехода) [132].
SOCIO-COGNITIVE NICHE
Рисунок 3. Эволюционная модель и социально-когнитивная парадигма мозга человека [132]
Модель инструментализации психоделиков ранними людьми и эволюционных последствий ее повторения из поколения в поколение. Левая сторона представляет процесс инструментализации, который может повторяться на протяжении жизни поколения гомининов. Правая сторона представляет процесс конструирования ниши, поддерживающей коэволюцию генной культуры между поколениями, поскольку популяции конструируют и наследуют трансформированные экологические и социальные среды, которые оказывают избирательное влияние на последующие поколения. Левая часть диаграммы изображает потенциальные селективные преимущества, предоставляемые использованием психоделиков в социально-экологических условиях, в которых эволюционировали наши предки. Правая сторона иллюстрирует процесс селективной обратной связи благодаря чему психоделическая инструментализация могла бы способствовать созданию и эволюции человеческой социально-когнитивной ниши. Четыре цветных прямоугольника слева представляют основные аспекты формирующегося адаптивного комплекса человека, создавшего социально-когнитивную нишу; они включают навыки и процессы, потенциально усиленные психоделической инструментализацией, с двунаправленными стрелками между прямоугольниками, представляющими взаимосвязь этих областей компетенции, которые совместно развивались в создании нашего уникального режима адаптации. Появление и сохранение этого адаптивного комплекса на протяжении всей эволюции человека позволило постепенно создавать социально модифицированные среды (представленные зеленым квадратом в правой части диаграммы), которые, в свою очередь, выбирались для улучшения тех же основных человеческих склонностей и возможностей (представленных стрелками со знаком плюс [+]), в которых устойчивая социально-когнитивная ниша [132].
Следующие разделы объединяют современное понимание социально-когнитивной ниши с недавними психоделическими исследованиями (в основном контролируемыми экспериментальными исследованиями на людях, как в клинических популяциях, так и на здоровых добровольцах), чтобы проиллюстрировать, как психоделики могли адаптивно использоваться нашими предками. Исследователи [132] фокусируется на четырех взаимосвязанных целях психоделической инструментализации: управление психологическим стрессом и лечение проблем со здоровьем; улучшение социального взаимодействия и межличностных отношений; содействие коллективной ритуальной и религиозной деятельности; и улучшение группового принятия решений.
Болезнь Альцгеймера и ядерная медицина
На клеточном и молекулярном уровнях – детерминанты старения для контроля начала и прогрессирования старения, включают потерю полезных компонентов и накопление вредных факторов. Эпигенетический прогресс в области выявление различных факторов, влияющих на процесс старения и долголетия, делают акцент, как эти детерминанты влияют на продолжительность жизни H. sapiens , являются современным медико-социальным инструментом, а также мультимодальным ключом междисциплинарного и межведомственного взаимодействия [133]. Более глубокое понимание индивидуальных вариаций траекторий жизни, даже среди генетически идентичных особей, и того, как эпигеномные изменения могут способствовать этим различным траекториям, будет иметь решающее значение для нашего понимания тайн старения и здорового долголетия (Рисунок 4) [133].
Все этапы, связанные с медико-биологическим направлением нейронаук и технологий — диагностика, терапия, реабилитация и профилактика неврологических и психических расстройств — имеют свои сложности, что ведет к недостаточно эффективной помощи больным. Поэтому критически важной задачей является дальнейшее развитие технологий и методик в этих областях, наряду с прорывами в накоплении фундаментальных знаний о возникновении и развитии данных заболеваний. В исследовании [134] были сделаны следующие выводы:
-Нейропластичность, нейрокоммуникации и инструменты нейрореабилитации взаимосвязаны с религиозностью H. sapiens.
-Наноматериалы и новые высокоэффективные нанорадиопротекторы с максимизацией лекарственной эффективности воздействия на мозг H. sapiens, работа гиппокампа с «винчестерами» памяти и состояние духовного мира человека, синхронизированы.

Рисунок 4. Активное долголетие: биофизика генома, нутригеномика, ревитализация [133]
нутригенетика,
Десятилетний авторский опыт внедрения результатов исследований (алгоритмы/инструменты/изобретения) позволили проведению успешной медицинской реабилитации когнитивных нарушений и увеличению (здоровой / качественной / культурной
/ религиозной) продолжительности жизнедеятельности.
L АКТШОЕ ДОЛГОЛЕТИЕ:
' БИОФИЗИКА ГЕНОМА,-1 . НУТРИГЕНОМИКА, : 1УТРИГЕ1ЕТШ, .РЕБИТАЛИЗАЦИЯ
ПРОГРАММА ПРОФИЛАКТИКИ КОГНИ ТИВНЫХ НАРУШЕНИЙ «БАЯМ -565/22/77»
Выработка половых гормонов у Мужчины и Женщины
5. Лечение и профилактика хронической инсомнии:
5.1. Мелатонин по схеме.
5.2. Циркадин по схеме.
5.3. Велсон по схеме.
5.4. Сомлел ('юпиклон 7,5 мг) пли имован / поддал по схеме.
ч. 1. Лк аг ин ол-мема ниш по схеме, №365.
2. Церебролизин 5-10-15 мл в/в струйно №5, затем 20 мл в/в струйно №5.
Ж 3. ЦеретОн (холина альфосцерат) 1000 мг в/в кап утром и в обед №7, зат ем Цсрстон 400 мг во время еды 3 р/д №30.
по п. 2 и 3 длительность терапии 47 дней.
терапию Церебролилиюм и Церетоном повторить через 6 месяцев.
4. При поведенческих расстройствах рекомендовано:
4.1. Кветиапин 2 5 мг на ночь. _ - aj?‘ £ S^k
4.2. Г ало перидол 5 кап на ночь. - . :■ .. X -. \
Примечание: выполнение программы профилактики когнитивных нарушений проводится пой постоянным систематическим контролем структурной и функциональной иейровизуализацин, нейришнзхачигическиго тестирования, 5Р Медицины и 5G технологий.
б.Днета для головного мозга: биоэлементология и нутрициология (функционально-сбалансированная).
7.Ко1'нитивпыс грсиишм в (кабинетах иамяги/ОСР КЦСОЬКДУ).
8.Физическая активность (индивидуально, с учетом коморбидиости).
9. Восстановление микробиома и ЗДОРОВОЙ МИКРОБИОТЫ.
16. НИИ НЕЙРОНАУК (применение/внедрение/тиражированне):
10. I. реабилитация с помощью нейротренажеров (пациент-ориентированных ).
10.2. циркадианного воздействия очков BLUE SKY Pro
10.3 виртуальной и дополненной реальности.
10.4. алгоритмов нсйросоииальиых технологий.
11.5Р Medicine and SG technology.
12. Nuclear Medicine: radioprotective pharmaceuticals and nutriciology.
Рисунок 5. Программа лечения и профилактики когнитивных нарушений и когнитивных расстройств «Болезнь Альцгеймера и ядерная медицина «БАЯМ- 365 /22 / 77» [135]
Культурная парадигма здоровья мозга H. sapiens в десятилетнем исследовании «Активное долголетие: биофизика генома, нутригеномика, нутригенетика, ревитализация» активизирует проникновение эволюционных и социально-когнитивных нейрокоммуникаций мозга человека в современные нейротехнологии ядерной медицины, новую 5P медицину и 5G технологию. Комбинированная медикаментозная платформа и обогащенная биоэлементология и нутрициология (мозга / микробиоты и генома / эпигенома), гибридная нейровизуализация и нейротехнологии ядерной медицины работают как превентивно, так и в долгосрочных программах медицинской реабилитации.
В продолжающемся исследовании (Рисунок 5) [134] следующих стратегических научно-практических направлений, установлено следующее:
Программа лечения и профилактики когнитивных нарушений и когнитивных расстройств «Болезнь Альцгеймера и ядерная медицина (БАЯМ-365 /22 / 77)» обеспечивает работу квалифицированного разума , сопровождает создание и совершенствование не только когнитивного потенциала мозга , но и управление когнитивной реабилитацией при болезни Альцгеймера.
Эффективность стратегических мероприятий когнитивной реабилитации напрямую зависит от биоплатформы здоровой микробиоты и синхронизации работы «висцерального и когнитивного мозга». Нейросоциологическое и нейроэкономическое сопровождение новой когнитивной реабилитации при болезни Альцгеймера потребует реинкарнации информационного взаимодействия современного человека в процессе всей жизнедеятельности.
Выводы
Болезнь Альцгеймера — это эволюционная, генетическая и эпигенетическая маршрутизация H. sapiens , с внедрением реабилитационной программы «БАЯМ-365/22/77» (Alzheimer’s disease & nuclear medicine (ADNM)) и медико-социальными нейрокоммуникациями и сопровождениями.
Геронтология и гериатрия, гинекология/андрология и нейроэндокринология, нейрофизиология и нейросоциология маршрутизируют H. sapiens в активное/ здоровое/ качественное/религиозное/нравственное/сексуальное/нейрокоммуникативное долголетие.
Роль половых гормонов выходит за рамки регуляции и развития только репродуктивных функций, половые гормоны (эстрогены, андрогены, лютеинизирующий гормон, тестостерон) играют важную роль в поддержании здорового функционирования нейронов головного мозга, в развитии нейрональных сетей и когнитивных процессов.
Доказана роль кортизола, эстрогена, тестостерона и окситоцина - в возрастных изменениях функции головного мозга, в частности, в контексте когнитивного и социальноэмоционального старения.
Нейродегенеративные и возраст-ассоциированные хронические заболевания, при которых имеют место такие патофизиологические проявления как нестабильность генома и эпигенома, окислительный стресс, хроническое воспаление, укорочение теломер, утрата протеостазиса, митохондриальные дисфункции, клеточное старение, истощение стволовых клеток и нарушение межклеточной коммуникации преимущественно инициируются несбалансированным питанием и дисбалансом симбиотической кишечной микробиоты, уровнем и возрастным соотношением женских и мужских половых гормонов.
Список литературы Сексуальная активность и болезнь Альцгеймера: инструменты и технологии нейроэндокринной реабилитации
- Bhargava A. Considering sex as a biological variable in basic and clinical studies: an endocrine society scientific statement // Endocrine reviews. 2021. V. 42. №3. P. 219 258. https://doi.org/10.1210/endrev/bnaa034
- Булгакова С. В., Романчук Н. П., Волобуев А. Н. Новая личность и нейрокоммуникации: нейрогенетика и нейросети, психонейроиммуноэндокринология, 5P медицина и 5G технологии // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2021. Т. 7. №8. С. 202 240. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414 2948/69/26
- Tokatli M. R. Hormones and sex specific medicine in human physiopathology // Biomolecules. 2022. V. 12. №3. P. 413.
- Волобуев А. Н., Романчук Н. П., Булгакова С. В. Нейрогенетика мозга: сон и долголетие человека // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2021. Т. 7. №3. С. 93 135. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414 2948/64/12
- Hiort O., Paul Martin H. The molecular basis of male sexual differentiation // European journal of endocrinology. 2000. V. 142. №2. P. 101 110.
- Veldhuijzen D. S. The role of circulating sex hormones in menstrual cycle dependent modulation of pain related brain activation // Pain. 2013. V. 154. №4. P. 548 559.
- Булгакова С. В. Эндокринная система и старение организма человека // Клиническая геронтология. 2020. Т. 26. №7 8. С. 51 56.
- Wittert G. The relationship between sleep disorders and testosterone in men // Asian journal of andrology. 2014. V. 16. №2. P. 262. https://doi.org/10.4103%2F1008 682X.122586
- Schipper H. M. The impact of gonadal hormones on the expression of human neurological disorders // Neuroendocrinology. 2016. V. 103. №5. P. 417 431. https://doi.org/10.1159/000440620
- Пятин В. Ф., Романчук Н. П., Булгакова С. В., Романов Д. В., Сиротко И. И., Давыдкин И. Л., Волобуев А. Н. Циркадианный стресс Homo sapiens: новые нейрофизиологические, нейроэндокринные и психонейроиммунные механизмы // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2020. Т. 6. №6. С. 115 135. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414 2948/55/16
- Reddy D. S., Bakshi K. Neurosteroids: Biosynthesis, molecular mechanisms, and neurophysiological functions in the human brain // Hormonal Signaling in Biology and Medicine. Academic Press, 2020. P. 69 82. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978 0 12 813814 4.00004 3
- Rey R., Josso N., Racine C. Sexual differentiation // Endotext [Internet]. 2020.
- Maekawa F. The mechanisms underlying sexual differentiation of behavior and physiology in mammals and birds: relative contributions of sex steroids and sex chromosomes // Frontiers in neuroscience. 2014. V. 8. P. 242. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2014.00242
- Arnold A. P. Sex chromosomes and brain gender // Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2004. V. 5. №9. P. 701 708. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1494
- Булгакова С. В., Романчук Н. П. Половые гормоны и когнитивные функции: современные данные // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2020. Т. 6. №3. С. 69 95. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414 2948/52/09
- Warfvinge K. Estrogen receptors α, β and GPER in the CNS and trigeminal system molecular and functional aspects // The Journal of Headache and Pain. 2020. V. 21. №1. P. 1 16.
- Delchev S., Georgieva K. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of the effects of sex hormones on the nervous system // Sex Hormones in Neurodegenerative Processes and Diseases. 2018. P. 1 19.
- Xu S. G protein coupled estrogen receptor: a potential therapeutic target in cancer // Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2019. V. 10. P. 725.
- Notas G., Kampa M., Castanas E. G protein coupled estrogen receptor in immune cells and its role in immune related diseases // Frontiers in endocrinology. 2020. V. 11. P. 579420. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00725
- Eisinger K. R. T. Interactions between estrogen receptors and metabotropic glutamate receptors and their impact on drug addiction in females // Hormones and behavior. 2018. V. 104. P. 130 137.
- Mishra K. N., Moftah B. A., Alsbeih G. A. Appraisal of mechanisms of radioprotection and therapeutic approaches of radiation countermeasures // Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2018. V. 106. P. 610 617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.150
- Obrador E., Salvador R., Villaescusa J. I., Soriano J. M., Estrela J. M., Montoro A. Radioprotection and radiomitigation: from the bench to clinical practice // Biomedicines. 2020. V. 8. №11. P. 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8110461
- Романчук Н. П., Булгакова С. В., Тренева Е. В., Волобуев А. Н., Кузнецов П. К. Нейрофизиология, нейроэндокринология и ядерная медицина: маршрутизация долголетия Homo sapiens // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2022. Т. 8. №4. С. 251 299. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414 2948/77/31
- Smith T. A., Kirkpatrick D. R., Smith S., Smith T. K., Pearson T., Kailasam A., Agrawal D. K. Radioprotective agents to prevent cellular damage due to ionizing radiation // Journal of translational medicine. 2017. V. 15. №1. P. 1 18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967 017 1338 x
- Belfiore A. et al. Insulin receptor isoforms in physiology and disease: an updated view // Endocrine reviews. 2017. V. 38. №5. P. 379 431. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2017 00073
- Belfiore A. et al. Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease // Endocrine reviews. 2009. V. 30. №6. P. 586 623. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2008 0047
- Hölscher C. New drug treatments show neuroprotective effects in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases // Neural regeneration research. 2014. V. 9. №21. P. 1870. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673 5374.145342
- Akintola A. A., van Heemst D. Insulin, aging, and the brain: mechanisms and implications // Frontiers in endocrinology. 2015. V. 6. P. 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2015.00013
- Numan S., Russell D. S. Discrete expression of insulin receptor substrate 4 mRNA in adult rat brain // Molecular brain research. 1999. V. 72. №1. P. 97 102. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169 328X(99)00160 6
- Araki E. et al. Signalling in mice with targeted disruption // Nature. 1994. V. 372. №1. P. 186 90.
- Schubert M. Insulin receptor substrate 2 deficiency impairs brain growth and promotes tau phosphorylation // Journal of Neuroscience. 2003. V. 23. №18. P. 7084 7092. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23 18 07084.2003
- Taguchi A., Wartschow L. M., White M. F. Brain IRS2 signaling coordinates life span and nutrient homeostasis // Science. 2007. V. 317. №5836. P. 369 372. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1142179
- Sadagurski M. et al. Irs2 and Irs4 synergize in non LepRb neurons to control energy balance and glucose homeostasis // Molecular metabolism. 2014. V. 3. №1. P. 55 63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2013.10.004
- Brüning J. C. et al. Role of brain insulin receptor in control of body weight and reproduction // Science. 2000. V. 289. №5487. P. 2122 2125. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.289.5487.2122
- Bomfim T. R. et al. An anti diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer’s disease associated Aβ oligomers // The Journal of clinical investigation. 2012. V. 122. №4. P. 1339 1353. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI57256
- Talbot K. et al. Demonstrated brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease patients is associated with IGF 1 resistance, IRS 1 dysregulation, and cognitive decline // The Journal of clinical investigation. 2012. V. 122. №4. P. 1316 1338. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI59903
- Denver P., English A., McClean P. L. Inflammation, insulin signaling and cognitive function in aged APP/PS1 mice // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2018. V. 70. P. 423 434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2018.03.032
- Boucher J., Kleinridders A., Kahn C. R. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin resistant states // Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology. 2014. V. 6. №1. P. a009191. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a009191
- Cho N. H. et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045 // Diabetes research and clinical practice. 2018. V. 138. P. 271 281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2018.02.023
- Pugazhenthi S., Qin L., Reddy P. H. Common neurodegenerative pathways in obesity, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease // Biochimica et Biophysica Acta ( Molecular Basis of Disease. 2017. V. 1863. №5. P. 1037 1045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.04.017
- Reitz C., Mayeux R. Alzheimer disease: epidemiology, diagnostic criteria, risk factors and biomarkers // Biochemical pharmacology. 2014. V. 88. №4. P. 640 651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.12.024
- Anor C. J. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer disease, vascular dementia, and mixed dementia // Neurodegenerative Diseases. 2017. V. 17. №4 5. P. 127 134. https://doi.org/10.1159/000455127
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G. The amyloid cascade inflammatory hypothesis of Alzheimer disease: implications for therapy // Acta neuropathologica. 2013. V. 126. №4. P. 479 497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401 013 1177 7
- Wright A. L. Neuroinflammation and neuronal loss precede Aβ plaque deposition in the hAPP J20 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease // PloS one. 2013. V. 8. №4. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059586
- Li J. Effects of diabetes mellitus on cognitive decline in patients with Alzheimer disease: a systematic review // Canadian journal of diabetes. 2017. V. 41. №1. P. 114 119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcjd.2016.07.003
- Denver P., McClean P. L. Distinguishing normal brain aging from the development of Alzheimer's disease: inflammation, insulin signaling and cognition // Neural regeneration research. 2018. V. 13. №10. P. 1719. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673 5374.238608
- Frölich L. Brain insulin and insulin receptors in aging and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease // Journal of neural transmission. 1998. V. 105. №4 5. P. 423 438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050068
- Ratzmann K. P., Hampel R. Glucose and insulin concentration patterns in cerebrospinal fluid following intravenous glucose injection in humans // Endokrinologie. 1980. V. 76. №2. P. 185-188. PMID: 7004864
- Querfurth H. W., LaFerla F. M. Mechanisms of disease // N Engl J Med. 2010. V. 362. №4. P. 329 344.
- Suzanne M. Insulin resistance and neurodegeneration: progress towards the development of new therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease // Drugs. 2017. V. 77. №1. P. 47 65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265 016 0674 0
- Gabuzda D. Inhibition of energy metabolism alters the processing of amyloid precursor protein and induces a potentially amyloidogenic derivative // Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1994. V. 269. №18. P. 13623 13628.
- Романчук Н. П., Пятин В. Ф., Волобуев А. Н., Булгакова С. В., Тренева Е. В., Романов Д. В. Мозг, депрессия, эпигенетика: новые данные // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2020. Т. 6. №5. С. 163 183. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414 2948/54/21
- Zimbone S. Amyloid Beta monomers regulate cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein functions by activating type‐1 insulin‐like growth factor receptors in neuronal cells // Aging cell. 2018. V. 17. №1. P. e12684. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12684
- Тренева Е. В., Булгакова С. В., Курмаев Д. П., Нестеренко С. А., Ленкин С. Г. Анализ циркадных ритмов секреции кортизола у мужчин с признаками ускоренного старения и их клинико организационное значение // Современные проблемы здравоохранения и медицинской статистики. 2022. №1. С. 213 224.
- Булгакова С. В., Романчук Н. П. Сон и старение: эндокринные и эпигенетические аспекты // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2020. Т. 6. No8. С. 65 96. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414 2948/57/08
- Zhao W. Q. et al. Amyloid beta oligomers induce impairment of neuronal insulin receptors // The FASEB Journal. 2008. V. 22. №1. P. 246 260. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.06 7703com
- Ma Q. L. et al. β amyloid oligomers induce phosphorylation of tau and inactivation of insulin receptor substrate via c Jun N terminal kinase signaling: suppression by omega 3 fatty acids and curcumin // Journal of Neuroscience. 2009. V. 29. №28. P. 9078 9089. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1071 09.2009
- Schubert M. et al. Role for neuronal insulin resistance in neurodegenerative diseases // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2004. V. 101. №9. P. 3100 3105. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0308724101
- Vandal M. et al. Insulin reverses the high fat diet induced increase in brain Aβ and improves memory in an animal model of Alzheimer disease // Diabetes. 2014. V. 63. №12. P. 4291-4301. https://doi.org/10.2337/db14 0375
- Farris W. et al. Insulin degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid β protein, and the β amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2003. V. 100. №7. P. 4162 4167. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0230450100
- Ittner L. M. et al. Dendritic function of tau mediates amyloid β toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models // Cell. 2010. V. 142. №3. P. 387 397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.036
- Hong M., Lee V. M. Y. Insulin and insulin like growth factor 1 regulate tau phosphorylation in cultured human neurons // Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997. V. 272. №31. P. 19547 19553. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.40.25326
- Bhat R. et al. Structural insights and biological effects of glycogen synthase kinase 3 specific inhibitor AR A014418 // Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2003. V. 278. №46. P. 45937-45945. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M306268200
- Freude S. et al. Peripheral hyperinsulinemia promotes tau phosphorylation in vivo // Diabetes. 2005. V. 54. №12. P. 3343 3348. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.54.12.3343
- Cheng C. M. et al. Tau is hyperphosphorylated in the insulin like growth factor I null brain // Endocrinology. 2005. V. 146. №12. P. 5086 5091. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2005 0063
- Phiel C. J. et al. GSK 3α regulates production of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid β peptides // Nature. 2003. V. 423. №6938. P. 435 439. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01640
- Sims Robinson C. et al. How does diabetes accelerate Alzheimer disease pathology? // Nature Reviews Neurology. 2010. V. 6. №10. P. 551. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2010.130
- De la Monte S. M. et al. Neuronal thread protein regulation and interaction with microtubule associated proteins in SH Sy5y neuronal cells // Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences CMLS. 2003. V. 60. №12. P. 2679 2691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018 003 3305 3
- Bedse G. et al. Aberrant insulin signaling in Alzheimer’s disease: current knowledge // Frontiers in neuroscience. 2015. V. 9. P. 204. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2015.00204
- Zlokovic B. V. Neurovascular pathways to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and other disorders // Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2011. V. 12. №12. P. 723 738. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3114
- Kahn A. M. et al. Insulin Acutely Inhibits Cultured Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Contraction by a Nitric Oxide Synthase Dependent Pathway // Hypertension. 1997. V. 30. №4. P. 928 933. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.30.4.928
- Bhamra M. S., Ashton N. J. Finding a pathological diagnosis for A lzheimer’s disease: Are inflammatory molecules the answer? // Electrophoresis. 2012. V. 33. №24. P. 3598 3607. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201200161
- Mushtaq G. et al. Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes via chronic inflammatory mechanisms // Saudi journal of biological sciences. 2015. V. 22. №1. P. 4 13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2014.05.003
- Fishel M. A. et al. Hyperinsulinemia provokes synchronous increases in central inflammation and β amyloid in normal adults // Archives of neurology. 2005. V. 62. №10. P. 1539-1544. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.62.10.noc50112
- Sokolova A. et al. Monocyte chemoattractant protein‐1 plays a dominant role in the chronic inflammation observed in Alzheimer’s disease // Brain pathology. 2009. V. 19. №3. P. 392-398. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750 3639.2008.00188.x
- Nakamura M., Watanabe N. Ubiquitin like protein MNSFβ/endophilin II complex regulates Dectin 1 mediated phagocytosis and inflammatory responses in macrophages // Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2010. V. 401. №2. P. 257 261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.09.045
- Akash M. S. H., Rehman K., Chen S. Role of inflammatory mechanisms in pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus // Journal of cellular biochemistry. 2013. V. 114. №3. P. 525 531. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24402
- Erickson M. A., Hansen K., Banks W. A. Inflammation induced dysfunction of the low density lipoprotein receptor related protein 1 at the blood brain barrier: protection by the antioxidant N acetylcysteine // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2012. V. 26. №7. P. 1085 1094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2012.07.003
- Matrone C. et al. Inflammatory risk factors and pathologies promoting Alzheimer’s disease progression: is RAGE the key // Histology and histopathology. 2015. V. 30. №2. P. 125 139.
- Münch G. et al. Alzheimer’s disease synergistic effects of glucose deficit, oxidative stress and advanced glycation endproducts // Journal of neural transmission. 1998. V. 105. №4 5. P. 439-461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050069
- Булгакова С. В., Тренева Е. В., Захарова Н. О. Бета коронавирусы и эндокринная система человека: новые данные (обзор литературы) // Клиническая лабораторная диагностика. 2022. Т. 67. №3. С. 140 146. https://doi.org/10.51620/0869 2084 2022 67 3 140-146
- Chiang M. C. et al. Metformin activation of AMPK dependent pathways is neuroprotective in human neural stem cells against Amyloid beta induced mitochondrial dysfunction // Experimental cell research. 2016. V. 347. №2. P. 322 331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.08.013
- Chung M. M. et al. The neuroprotective role of metformin in advanced glycation end product treated human neural stem cells is AMPK dependent // Biochimica et Biophysica Acta ( Molecular Basis of Disease. 2015. V. 1852. №5. P. 720 731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.01.006
- Gupta A., Bisht B., Dey C. S. Peripheral insulin sensitizer drug metformin ameliorates neuronal insulin resistance and Alzheimer’s like changes // Neuropharmacology. 2011. V. 60. №6. P. 910 920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.01.033
- Kickstein E. et al. Biguanide metformin acts on tau phosphorylation via mTOR/protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) signaling // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2010. V. 107. №50. P. 21830 21835. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0912793107
- Li J. et al. Metformin attenuates Alzheimer’s disease like neuropathology in obese, leptin resistant mice // Pharmacology biochemistry and behavior. 2012. V. 101. №4. P. 564 574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2012.03.002
- Chen Y. et al. Antidiabetic drug metformin (GlucophageR) increases biogenesis of Alzheimer's amyloid peptides via up regulating BACE1 transcription // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2009. V. 106. №10. P. 3907 3912. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0807991106
- Ng T. P. et al. Long term metformin usage and cognitive function among older adults with diabetes // Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2014. V. 41. №1. P. 61 68. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD131901
- Guo M. et al. Metformin may produce antidepressant effects through improvement of cognitive function among depressed patients with diabetes mellitus // Clinical and experimental pharmacology and physiology. 2014. V. 41. №9. P. 650 656. https://doi.org/10.1111/14401681.12265
- Herath P. M. et al. The effect of diabetes medication on cognitive function: evidence from the PATH through life study // BioMed research international. 2016. V. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7208429
- Moore E. M. et al. Increased risk of cognitive impairment in patients with diabetes is associated with metformin // Diabetes care. 2013. V. 36. №10. P. 2981 2987. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc13 0229
- Osborne C. et al. Glimepiride protects neurons against amyloid β induced synapse damage // Neuropharmacology. 2016. V. 101. P. 225 236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.09.030
- Alp H. et al. Protective effects of beta glucan and gliclazide on brain tissue and sciatic nerve of diabetic rats induced by streptozosin // Experimental diabetes research. 2012. V. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/230342
- Esmaeili M. H., Bahari B., Salari A. A. ATP sensitive potassium channel inhibitor glibenclamide attenuates HPA axis hyperactivity, depression and anxiety related symptoms in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease // Brain research bulletin. 2018. V. 137. P. 265 276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.01.001
- Hsu C. C. et al. Incidence of dementia is increased in type 2 diabetes and reduced by the use of sulfonylureas and metformin // Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2011. V. 24. №3. P. 485 493. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD 2011 101524
- Landreth G. Therapeutic use of agonists of the nuclear receptor PPARγ in Alzheimer’s disease // Current Alzheimer Research. 2007. V. 4. №2. P. 159 164. https://doi.org/10.2174/156720507780362092
- Heneka M. T. et al. Acute treatment with the PPARγ agonist pioglitazone and ibuprofen reduces glial inflammation and Aβ1 42 levels in APPV717I transgenic mice // Brain. 2005. V. 128. №6. P. 1442 1453. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awh452
- Yu Y. et al. Insulin sensitizers improve learning and attenuate tau hyperphosphorylation and neuroinflammation in 3xTg AD mice // Journal of neural transmission. 2015. V. 122. №4. P. 593 606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702 014 1294 z
- Fernandez Martos C. M. et al. Combination treatment with leptin and pioglitazone in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease // Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions. 2017. V. 3. №1. P. 92 106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2016.11.002
- Sato T. et al. Efficacy of PPAR γ agonist pioglitazone in mild Alzheimer disease // Neurobiology of aging. 2011. V. 32. №9. P. 1626 1633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.10.009
- Cheng H. et al. The peroxisome proliferators activated receptor gamma agonists as therapeutics for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: a meta analysis // International Journal of Neuroscience. 2016. V. 126. №4. P. 299 307. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207454.2015.1015722
- Hölscher C. The role of GLP 1 in neuronal activity and neurodegeneration // Vitamins & Hormones. Academic Press, 2010. V. 84. P. 331 354. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978 0 12 381517 0.00013 8
- Hunter K., Hölscher C. Drugs developed to treat diabetes, liraglutide and lixisenatide, cross the blood brain barrier and enhance neurogenesis // BMC neuroscience. 2012. V. 13. №1. P. 33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471 2202 13 33
- McClean P. L., Hölscher C. Liraglutide can reverse memory impairment, synaptic loss and reduce plaque load in aged APP/PS1 mice, a model of Alzheimer’s disease // Neuropharmacology. 2014. V. 76. P. 57 67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.08.005
- Hansen H. H. et al. The GLP 1 receptor agonist liraglutide reduces pathology specific tau phosphorylation and improves motor function in a transgenic hTauP301L mouse model of tauopathy // Brain research. 2016. V. 1634. P. 158 170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2015.12.052
- Gejl M. et al. In Alzheimer’s disease, 6 month treatment with GLP 1 analog prevents decline of brain glucose metabolism: randomized, placebo controlled, double blind clinical trial // Frontiers in aging neuroscience. 2016. V. 8. P. 108. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2016.00108
- Kosaraju J. et al. Saxagliptin: a dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor ameliorates streptozotocin induced Alzheimer’s disease // Neuropharmacology. 2013. V. 72. P. 291 300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.008
- Kosaraju J. et al. Vildagliptin: an anti‐diabetes agent ameliorates cognitive deficits and pathology observed in streptozotocin‐induced Alzheimer’s disease // Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 2013. V. 65. №12. P. 1773 1784. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12148
- Kornelius E. et al. DPP‐4 inhibitor linagliptin attenuates Aβ‐induced cytotoxicity through activation of AMPK in neuronal cells // CNS neuroscience & therapeutics. 2015. V. 21. №7. P. 549-557. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12404
- Rizzo M. R. et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors have protective effect on cognitive impairment in aged diabetic patients with mild cognitive impairment // Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biomedical Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2014. V. 69. №9. P. 1122 1131. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glu032
- Kern W. et al. Improving influence of insulin on cognitive functions in humans // Neuroendocrinology. 2001. V. 74. №4. P. 270 280. https://doi.org/10.1159/000054694
- Freiherr J. et al. Intranasal insulin as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease: a review of basic research and clinical evidence // CNS drugs. 2013. V. 27. №7. P. 505 514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263 013 0076 8
- Пятин В. Ф., Маслова О. А., Романчук Н. П., Булгакова С. В., Волобуев А. Н. Гемостаз и когнитивный мозг: 5П медицина и хронотерапия артериальной гипертонии // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2021. Т. 7. №5. С. 127 183. (in Russian). https://doi.org/10.33619/2414 2948/66/16
- Craft S. et al. Effects of regular and long acting insulin on cognition and Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers: a pilot clinical trial // Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2017. V. 57. №4. P. 1325-1334. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD 161256
- Łabuzek K. et al. Quantification of metformin by the HPLC method in brain regions, cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of rats treated with lipopolysaccharide // Pharmacological Reports. 2010. V. 62. №5. P. 956 965. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1734 1140(10)70357 1
- Cheng C. et al. Type 2 diabetes and antidiabetic medications in relation to dementia diagnosis // Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biomedical Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2014. V. 69. №10. P. 1299 1305. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glu073
- Luchsinger J. A. et al. Metformin in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: results of a pilot randomized placebo controlled clinical trial // Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2016. V. 51. №2. P. 501 514. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD 150493
- Luchsinger J. A. et al. Metformin, lifestyle intervention, and cognition in the diabetes prevention program outcomes study // Diabetes care. 2017. V. 40. №7. P. 958 965. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc16 2376
- Valencia W. M. et al. Metformin and ageing: improving ageing outcomes beyond glycaemic control // Diabetologia. 2017. V. 60. №9. P. 1630 1638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125017 4349 5
- Imfeld P. et al. Metformin, other antidiabetic drugs, and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: a population‐based case control study // Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2012. V. 60. №5. P. 916 921. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532 5415.2012.03916.x
- Geldmacher D. S. et al. A randomized pilot clinical trial of the safety of pioglitazone in treatment of patients with Alzheimer disease // Archives of neurology. 2011. V. 68. №1. P. 45 50. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2010.229
- Femminella G. D. et al. Antidiabetic drugs in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanisms of action and future perspectives // Journal of diabetes research. 2017. V. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7420796
- Nauck M. A. Glucagon like peptide 1 (GLP 1) in the treatment of diabetes // Hormone and metabolic research. 2004. V. 36. №11/12. P. 852 858. https://doi.org/10.1055/s 2004 826175
- Drucker D. J. et al. Incretin based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: evaluation of the risks and benefits // Diabetes care. 2010. V. 33. №2. P. 428 433. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09 1499
- Cork S. C. et al. Distribution and characterization of Glucagon like peptide 1 receptor expressing cells in the mouse brain // Molecular metabolism. 2015. V. 4. №10. P. 718 731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2015.07.008
- Liu X. Y. et al. Liraglutide prevents beta amyloid induced neurotoxicity in SH SY5Y cells via a PI3K dependent signaling pathway // Neurological research. 2016. V. 38. №4. P. 313-319. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2016.1145914
- Cai H. Y. et al. Lixisenatide attenuates the detrimental effects of amyloid β protein on spatial working memory and hippocampal neurons in rats // Behavioural brain research. 2017. V. 318. P. 28 35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.10.033
- Isik A. T. et al. The effects of sitagliptin, a DPP 4 inhibitor, on cognitive functions in elderly diabetic patients with or without Alzheimer’s disease // Diabetes research and clinical practice. 2017. V. 123. P. 192 198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2016.12.010
- Shingo A. S. et al. Intracerebroventricular administration of an insulin analogue recovers STZ induced cognitive decline in rats // Behavioural brain research. 2013. V. 241. P. 105 111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2012.12.005
- Gegenhuber B. et al. Gene regulation by gonadal hormone receptors underlies brain sex differences // Nature. 2022. V. 606. №7912. P. 153 159. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586 022 04686
- Пятин В. Ф., Маслова О. А., Романчук Н. П., Волобуев А. Н., Булгакова С. В., Романов Д. В., Сиротко И. И. Нейровизуализация: структурная, функциональная, фармакологическая, биоэлементологии и нутрициологии // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2021. Т. 7. №10. С. 145 184. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414 2948/71/18
- Arce J. M. R., Winkelman M. J. Psychedelics, Sociality, and Human Evolution // Frontiers in Psychology. 2021. V. 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.729425
- Романчук П. И. Активное долголетие: биофизика генома, нутригеномика, нутригенетика, ревитализация.Самара, 2013.
- Романов Д. В., Романчук Н. П. Болезнь Альцгеймера и ядерная медицина: циркадианный стресс и нейровоспаление, нейрокоммуникации и нейрореабилитация // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2022. Т. 8. №5. С. 256 312. https://doi.org/10.33619/24142948/78/35
- Волобуев А. Н., Романчук Н. П., Маслова О. А., Пятин В. Ф., Романов Д. В. Проблемы ядерной медицины и когнитивной реабилитации // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2022. Т. 8. №6. С. 308 350. https://doi.org/10.33619/2414 2948/79/33


