Self-adaptive Resource Allocation in Fog-Cloud Systems Using Multi-agent Deep Reinforcement Learning with Meta-learning
Автор: Tapas K. Das, Santosh K. Das, Swarupananda Bissoyi, Deepak K. Patel
Журнал: International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications @ijisa
Статья в выпуске: 1 vol.18, 2026 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The rapid growth of IoT ecosystems has intensified the complexity of fog–cloud infrastructures, necessitating adaptive and energy-efficient task offloading strategies. This paper proposes MADRL-MAML, a Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning framework enhanced with Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning for dynamic fog–cloud resource allocation. The approach integrates curriculum learning, centralized attention-based critics, and KL-divergence regularization to ensure stable convergence and rapid adaptation to unseen workloads. A unified cost-based reward formulation is used, where less negative values indicate better joint optimization of energy, latency, and utilization. MADRL-MAML is benchmarked against six baselines Greedy, Random, Round-Robin, PPO, Federated PPO, and Meta-RL using consistent energy, latency, utilization, and reward metrics. Across these baselines, performance remains similar: energy (3.64–3.71 J), latency (85.4–86.7 ms), and utilization (0.51–0.54). MADRL-MAML achieves substantially better results with a reward of $-21.92 \pm 3.88$, energy 1.16 J, latency 12.80 ms, and utilization 0.39, corresponding to 68\% lower energy and 85\% lower latency than Round-Robin. For unseen workloads characterized by new task sizes, arrival rates, and node heterogeneity, the meta-learned variant (MADRL-MAML-Unseen) achieves a reward of $-6.50 \pm 3.98$, energy 1.14 J, latency 12.76 ms, and utilization 0.73, demonstrating strong zero-shot generalization. Experiments were conducted in a realistic simulated environment with 10 fog and 2 cloud nodes, heterogeneous compute capacities, and Poisson task arrivals. Inference latency remains below 5 ms, confirming real-time applicability. Overall, MADRL-MAML provides a scalable and adaptive solution for energy-efficient and latency-aware orchestration in fog–cloud systems.
Fog Computing, Cloud Computing, Resource Allocation, Meta-Learning, Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning, Deep RL, Task Offloading
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15020217
IDR: 15020217 | DOI: 10.5815/ijisa.2026.01.08
Текст научной статьи Self-adaptive Resource Allocation in Fog-Cloud Systems Using Multi-agent Deep Reinforcement Learning with Meta-learning
Published Online on February 8, 2026 by MECS Press
The exponential growth of Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystems has drastically increased computational demand at the network edge. Traditional cloud architectures, though powerful, suffer from high latency and bandwidth bottlenecks that hinder delay-sensitive applications such as autonomous driving, augmented reality, and smart healthcare. Fog computing extends cloud capabilities by introducing intermediate nodes closer to the data source, thereby reducing latency and energy consumption. However, these distributed and heterogeneous fog-cloud environments pose serious challenges for real-time resource allocation under dynamic and unpredictable workloads. Heuristic offloading methods such as Round-Robin and Greedy are simple and computationally efficient but perform poorly when workloads fluctuate. RoundRobin distributes tasks cyclically, ignoring system load, while Greedy selects the node with the highest immediate capacity, often overloading specific nodes. These static methods lack adaptability, leading to increased energy consumption and task delays. Reinforcement Learning (RL) has recently emerged as a promising solution for dynamic fog-cloud orchestration. Algorithms such as Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) learn optimal task-offloading policies through experience. Federated PPO further enables privacy-preserving training across distributed nodes, and Meta-RL techniques such as Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML) provide fast adaptation to unseen environments. Yet, singleagent RL approaches struggle in large, distributed settings due to non-stationarity and limited coordination between nodes.
To address these challenges, this paper introduces a Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning with ModelAgnostic Meta-Learning (MADRL-MAML) framework for adaptive fog-cloud resource allocation. Each fog or cloud node operates as an agent sharing a PPO-based policy. A centralized attention-based critic estimates global state values to coordinate local decisions during training, while decentralized execution ensures scalability. The meta-learning layer enables fast adaptation to unseen workloads by learning a task-invariant policy initialization that generalizes across distributions. Unlike previous DRL-based works, MADRL-MAML explicitly defines a negative reward (cost) function that balances latency, energy, and utilization: smaller, less negative rewards correspond to higher performance. This formulation is chosen to maintain consistent scaling and stability across tasks dominated by penalty terms (energy and latency), ensuring gradient smoothness and interpretable optimization. In addition, we define unseen tasks as workloads characterized by new distributions of task size, arrival rate, and node heterogeneity that were not encountered during training. This setup allows for rigorous evaluation of zero-shot adaptation and robustness under domain shifts capabilities critical for real-world fog-cloud systems.
To ensure transparency and reproducibility, the framework is evaluated in a detailed simulated fog-cloud environment comprising 10 fog nodes and 2 cloud nodes connected through a 10 Gbps backbone. The simulator incorporates task arrivals following a Poisson process, heterogeneous node capacities, and variable deadlines. Each policy decision is computed in under 5 ms, validating the real-time feasibility of MADRL-MAML. Training overhead is modest (approx. 514 s, 17.8 MB GPU memory), confirming scalability across infrastructure sizes. Although MADRL-MAML integrates multiple components multi-agent PPO, MAML adaptation, curriculum learning, attention-based critics, and KL-divergence (Kullback–Leibler divergence) regularization each addition contributes a measurable benefit. Ablation analysis shows that removing MAML or KL-loss degrades reward stability and generalization, demonstrating that the framework is not overengineered but instead synergistic in design.
The key contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
• Adaptive Multi-Agent Architecture: A hybrid MADRL-MAML design that combines PPO-based cooperative agents with centralized attention-based critics for globally coordinated decision-making.
• Meta-Learning for Zero-Shot Adaptation: Integration of MAML enables rapid policy adaptation to unseen workload distributions and infrastructure heterogeneity.
• Reward Formulation and Stability: A normalized, negative cost-based reward function that unifies energy, latency, and utilization, ensuring stable training and interpretable improvement metrics.
• Quantitative Benchmarking: Full comparison against Greedy, Random, Round-Robin, PPO, Federated PPO, and Meta-RL baselines with complete metric reporting (energy, latency, utilization, reward).
• Scalability and Real-Time Feasibility: Validation in a simulated fog-cloud environment confirming that policy inference time (<5 ms) supports real-time orchestration.
2. Related Works2.1. Heuristic and Classical Approaches
2.2. Reinforcement Learning Methods
Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has revolutionized the way agents learn from high-dimensional inputs, enabling breakthroughs across domains ranging from gaming to robotics to mobile edge computing. The foundational work by Mnih et al. introduced the Deep Q-Network (DQN), a model capable of learning control policies directly from pixel data using Q-learning [4]. Their approach combined convolutional neural networks with reinforcement learning to achieve human-level performance across 49 Atari 2600 games. This research bridged the gap between end-to-end learning and decision-making, making DRL viable for complex, high-dimensional environments. It remains a landmark study that inspired a wave of DRL innovations. Building on this paradigm, Schulman et al. proposed Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), a simplified policy gradient algorithm that retains performance while improving sample efficiency and training stability [5]. PPO enables multiple epochs of minibatch updates using a clipped objective, striking a practical balance between the performance of Trust Region Policy Optimization (TRPO) and ease of implementation. PPO has since become a standard in continuous control tasks and benchmark environments. Extending DRL to physical systems, Xiang et al. developed a mapless mobile robot navigation system using Soft Actor-Critic (SAC), a continuous control algorithm [6]. By relying only on laser scan data and target location, their model could generate control commands in real time without explicit maps, demonstrating DRL’s power in robotic perception and control. Further advancing DRL applications, Qin et al. proposed the DCEDRL model for task offloading in Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) [7]. Their approach uses density clustering and ensemble learning to optimize resource allocation under dynamic network conditions. By classifying tasks and adapting sampling strategies, the method improved system responsiveness and reduced task backlog, showcasing DRL’s relevance in distributed systems.
2.3. Federated and Meta-Reinforcement Learning
2.4. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
2.5. Hybrid Approaches, Research Gap, Novelty and Contribution
Collectively, these contributions establish MADRL-MAML as a robust and generalizable approach to fog-cloud resource orchestration, capable of scaling across infrastructures while maintaining adaptability, stability, and computational efficiency.
Resource allocation in fog-cloud environments is a longstanding challenge that spans multiple domains including cloud computing, edge computing, and distributed systems. Several classes of methods have been explored historically: heuristics, optimization-based formulations, single-agent reinforcement learning, and more recently, multi-agent and meta-learning strategies.
The rapid evolution of mobile networks, cloud paradigms, and the Internet of Everything (IoE) has triggered significant research in edge and fog computing architectures. Three key studies contribute foundational and evolving insights into mobile edge and fog computing with an emphasis on resource allocation and optimization. Mao et al. provide a seminal and comprehensive survey on Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) from a communication-centric lens [1]. Their paper explores how MEC addresses challenges of latency and energy inefficiency in mobile devices by offloading computation to nearby base stations and access points. It highlights joint optimization of radio and computational resources, laying the foundation for emerging MEC system designs. It also identifies key challenges including mobility management, caching strategies, green computing, and privacy. This work forms a baseline for future MEC research and standardization efforts. Jamil et al. delve deeper into fog computing and IoE environments, emphasizing the dynamic and heterogeneous nature of fog nodes [2]. Their taxonomy-based survey investigates various task scheduling and resource allocation techniques, classifying them by optimization criteria and algorithmic strategies. This paper extends MEC discussion by addressing geographical distribution, contextual services, and uncertainties in the fog environment. It presents a roadmap for designing efficient fog-based scheduling systems with open issues like real-time adaptability and multi-objective optimization. Zhang et al. advance the MEC paradigm by integrating it with Social Internet of Vehicles (SIoV) and UAV-assisted computation offloading [3]. Their research presents a three-layer architecture that dynamically allocates resources using energy-aware optimization. The authors model realistic vehicular networks where power constraints and mobility are major concerns. Using dynamic programming and trajectory optimization, the study demonstrates improved utility and energy efficiency. This paper is valuable in contexts where mobility and dynamic user behavior intersect with MEC frameworks.
Khan et al. discuss the deployment of federated learning (FL) in edge networks, especially for IoT environments [8]. The paper tackles the dual challenges of resource optimization and participant incentivization in FL. It introduces a Stackelberg game-based framework to model the economic interaction between a central server and edge devices, thereby aligning incentives for participation. This is crucial because training data is distributed and privacy-sensitive, making traditional centralized approaches infeasible. The paper also outlines open research challenges including communication constraints, heterogeneity in edge devices, and privacy-preserving mechanisms. This work significantly contributes to the integration of FL into edge environments and lays a strong foundation for future FL-based system designs. Chelsea Finn et al. propose Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML), a novel meta-learning algorithm designed to enable quick adaptation to new tasks with few data points [9]. Unlike traditional learning methods that train a model from scratch for each task, MAML optimizes for a good initialization, one that can adapt rapidly with a few gradient steps. Its modelagnostic nature makes it broadly applicable to supervised learning and reinforcement learning problems. The paper demonstrates MAML’s effectiveness on few-shot learning tasks and policy gradient methods, showing state-of-the-art results in image classification and reinforcement learning. This work is foundational in meta-learning, particularly in its application to scenarios where data is scarce or tasks vary widely. Nichol et al. build upon MAML by introducing first-order approximations that simplify the computational overhead [10]. The authors introduce Reptile, a practical and efficient meta-learning algorithm that performs comparably to MAML but avoids second-order derivative calculations. Reptile works by sampling tasks, training on them, and then nudging the meta-initialization weights toward the updated task-specific weights. This results in models that are easy to fine-tune and computationally efficient, making them attractive for real-world deployments. The paper also provides theoretical insights into why these algorithms work, making a valuable contribution to the understanding and practical deployment of meta-learning systems.
Recent work increasingly applies Multi-Agent and Meta-Reinforcement Learning to fog, edge, and IoT environments. Yang et al. propose a meta-RL offloading strategy for IoT devices, enabling fast adaptation to dynamic workloads [11]. Liu and Sun develop a MARL-based blockchain-enabled edge framework that reduces latency and energy through cooperative policies [12]. Munir et al. explore multi-agent meta-RL for sustainable edge systems, emphasizing generalization to diverse operating conditions [13]. Li et al. present a GNN-enhanced MARL scheduler for ML task placement, highlighting growing interest in coordinated edge resource management [14]. Although these works show the relevance of MARL and meta-RL in networking, they do not jointly address heterogeneous fog–cloud environments, rapid adaptation to unseen tasks, or stable cooperation under dynamic workloads gaps our MADRL-MAML framework targets. Tabish Rashid et al. introduce QMIX, a value-decomposition method that enables decentralized execution with centralized training [15]. By enforcing monotonic mixing of per-agent utilities, QMIX scales cooperative MARL and achieves strong results in SMAC benchmarks. Foerster et al. propose COMA, a counterfactual multi-agent policy gradient method with a centralized critic to improve credit assignment [16]. Lowe et al. present MADDPG, which tackles nonstationarity by conditioning critics on other agents’ policies [17]. Suzuki et al. extend MARL to edge–cloud offloading via Coop- MADRL, which accounts for multi-cloud topologies and bandwidth constraints [18]. Finally, Hospedales et al. survey meta-learning methods, including their applications to reinforcement learning and rapid adaptation [19].
Recent studies have attempted to bridge these paradigms by combining elements of MARL and meta-learning. Hospedales et al. surveyed meta-learning in neural networks, highlighting its potential for fast adaptation [19]. Despite these advancements, most works treat resource allocation as a single-agent problem or lack rapid adaptability to workload variations. MARL methods improve coordination but struggle with non-stationarity, while Meta-RL methods provide adaptability but are typically single-agent. Baseline methods also lack fine-grained energy-awareness or latency modeling, limiting their effectiveness in latency-sensitive deployments.
To bridge these gaps, our work introduces a novel Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning framework augmented with Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MADRL-MAML). The contributions of this paper are threefold:
• We design a multi-agent PPO-based policy learning architecture with a centralized attention-based critic, enabling cooperative decision-making among fog and cloud nodes.
• We integrate MAML-style meta-learning to enable rapid adaptation to diverse and unseen workload patterns, improving generalization.
• We introduce auxiliary KL-divergence loss with greedy supervision and curriculum learning to improve policy stability and convergence.
3. Proposed Methodology3.1. Simulation Environment
3.2. State Representation
3.3. Action and Reward Design
Our approach provides a unified, adaptive, and generalizable framework for energy-efficient and latency-aware resource allocation in dynamic fog-cloud environments, validated against a comprehensive set of baselines and demonstrating superior performance in both seen and unseen scenarios.
This section describes the proposed Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning with Model-Agnostic MetaLearning (MADRL-MAML) framework for self-adaptive resource allocation in fog-cloud environments. The approach integrates cooperative policy learning, attention-based credit assignment, meta-learning for fast adaptation, curriculum based progressive task scaling, and auxiliary regularization for stability. Fig. 1 presents the overall system design.
The proposed framework is implemented and evaluated in a custom fog-cloud simulation environment designed for realism and reproducibility. The setup includes 10 fog nodes and 2 cloud nodes interconnected through a 10 Gbps network backbone. Fog nodes have processing capacities between 1–4 GHz and 4–8 GB of memory, while cloud nodes operate at 10 GHz with 16 GB memory. Task arrivals follow a Poisson process with rate λ = 3 tasks/s, and each task is characterized by size (10–50 MB), compute demand (0.5–2 GHz cycles), and deadline (20–200 ms). Each node maintains a local queue and energy profile modeled via dynamic power equations. The environment supports both cooperative (shared reward) and competitive (per-agent reward) modes, though this work focuses on the cooperative case. Each training episode consists of 500 decision steps, and all results are averaged over 20 runs. Inference latency per decision is below 5 ms, confirming real-time feasibility.
Each agent (fog or cloud node) observes the system state st, which encodes global and local conditions:
st = {El,Ll,ql,cl,dl,Tt,tl]^1 (1)
where Et is energy consumption, Lt latency, qt queue length, c ^ available capacity, d [ task demand, Tt task deadline, and t [ £ {0,1} denotes node type (fog/cloud). All features are normalized using Z-score normalization for numerical stability.
Each agent selects an action at £ {1,2, .,V} representing the target node for offloading. The quality of each allocation decision is evaluated through the following composite reward function:
rt = —aEt - P Lt + Y Et — & Dt (2)
where Et and Lt are normalized energy and latency terms, Ut denotes utilization (0-1), and Dt represents deadline violation penalty. The coefficients (а, в, Y, d = (0.7, 0.5, 0.3, 0.5) balance trade-offs among energy efficiency, responsiveness, and stability.
Unlike most reinforcement learning formulations that maximize a positive reward, this work defines rt as a negative cost function, so that less negative values correspond to higher performance. This design choice ensures gradient stability, interpretable scaling, and consistent comparison across energy–latency–utilization metrics.
-
3.4. Centralized Attention-Based Critic
-
3.5. Meta-Update with MAML
To facilitate coordination among agents, a centralized critic network is used during training. It aggregates individual agent value estimates {qt } via a self-attention mechanism:
Q tot = / ф (Айп^ 1 , q 2 ,., q^) (3)
This allows the critic to focus on task-node interactions most relevant to global optimization. During execution, each agent acts independently using its local policy п (a ^ |s / ), ensuring scalability and decentralization.
To achieve generalization and zero-shot learning, MADRL-MAML employs Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML). The framework trains on multiple tasks {7 1 ,..., TK}, each defined by a workload distribution. Unseen tasks are explicitly defined as task distributions differing in arrival rate, size, and node heterogeneity from those seen during training. For instance, unseen tasks may involve higher load variance or altered fog-cloud ratios. The goal is to learn a parameter initialization в that enables fast adaptation to these new distributions with minimal gradient updates.
Formally, for each task TK , the agent performs an inner update on a support set and evaluates on a query set:
Ant^iC"^)
After each meta-update, the shared parameters в are refined to improve adaptability across all tasks.
-
3.6. Auxiliary Loss and KL-Regularization
-
3.7. Curriculum Learning for Progressive Training
-
3.8. System Architecture and Agent Interaction
Training stability is further enhanced through an auxiliary KL-divergence loss that constrains policy drift:
4^ = KL(ne|nJ where ng is a greedy policy selecting nodes with minimal predicted latency. The auxiliary term penalizes excessive deviation from efficient baseline behavior and accelerates convergence. The final loss function combines PPO, meta, and auxiliary terms:
Etatal ^PPO + ^-l^meta + ^2EaAix with Л1 = 0.8 and Л2 = 0.3 determined empirically.
Curriculum learning gradually increases task complexity by linearly scaling task load and arrival intensity from 0.8× to 2.0× over training epochs. Early training involves simpler low-load scenarios, helping agents learn stable policies before tackling high-load conditions. This approach prevents catastrophic early divergence and accelerates convergence stability.
Each fog or cloud node acts as an independent PPO-based agent. During training, agents share gradients via a centralized attention critic to ensure cooperative learning, while during inference they act autonomously using local observations for decentralized execution. Meta-learning updates are periodically coordinated via a central server that aggregates gradients across agents without sharing raw data, maintaining scalability and privacy. The overall framework, including the integration of curriculum learning, auxiliary regularization, and meta-adaptation, is illustrated in Fig. 1.
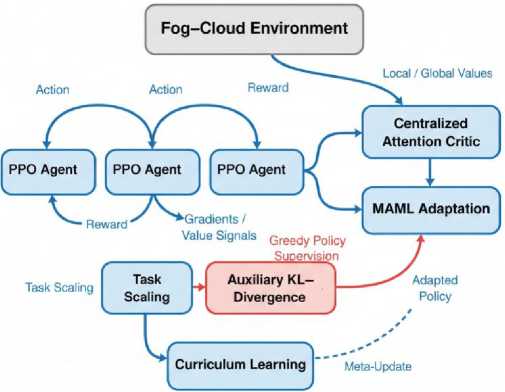
Fig.1. Overview of the proposed MADRL-MAML framework
-
3.9. Algorithmic Summary
-
3.10. Training and Complexity Considerations
The overall training and adaptation workflow of the proposed MADRL-MAML framework is summarized in Algorithm 1.
Training is performed for 500 episodes, with each episode spanning 500 decision steps. The framework converges within approximately 514 s on an NVIDIA Tesla T4 GPU (17.8 MB memory footprint). The computational overhead during inference is minimal, with per-decision latency under 5 ms, confirming suitability for real-time orchestration. Communication among agents is centralized only during training; inference remains fully decentralized. These design choices ensure that MADRL-MAML remains computationally efficient and scalable for large-scale IoT deployments. The framework is implemented in PyTorch and trained on CPUs/GPUs. Convergence is monitored via episode rewards, and model snapshots are saved based on performance on validation tasks. The code is available in the link
Algorithm 1 MADRL-MAML Training Procedure
Require : Environment 8 , number of episodes E , steps per episode T , number of agents N , learning rates a, 0 , curriculum factor К
Ensure: Policy parameters 0 , critic parameters ф
1: Initialize shared PPO policy Пд and centralized attention critic <2ф
2: Initialize task buffer В and curriculum factor К ^ 0.8 {see curriculum scheduling in Section 3.7}
3: for episode = 1 to E do
4: Sample К workload tasks {Tl, ..., 7%} from 8
5: for each task T^ do
6: Split 7 into support D^^and Vf^
7: Update task-specific parameters: 0^ ^ 0 — aVgE^^^^^^^(0)
8: for each agent i = 1 to N do
9: Initialize local state S j
10: for step = 1 to T do
11: Select action dj ~ n0‘(Sj)
12: Execute dj, observe reward Tj, and next state S’
13: Store transition (s j, а^Т, S’) in В
14: end for
15: end for
16: Compute global value Qtot = /^(Attn^,..., Qw))
17: Compute total loss £*ма = £ppo + £i£meta + ^L^x
18: Update parameters 0 and ф via gradient descent
19: end for
20: Update curriculum factor: К ^ К + (2.0 — 0.8)/E {progressive task scaling as described in Section 3.7}
21: end for
22: return 0, ф
4. Results and Discussion4.1. Performance Overview
4.2. Convergence and Stability Analysis
This section presents the quantitative and qualitative analysis of the proposed MADRL-MAML framework against multiple baselines. All experiments were executed in the simulation environment described in Section III, using identical configurations to ensure fairness and reproducibility. The results are averaged over 20 independent runs, and all metrics are reported with 95% confidence intervals.
The evaluated methods include Greedy, Random, Round-Robin, Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), Federated PPO, Meta-RL, and the proposed MADRL-MAML. Performance is assessed using four metrics, total reward (dimensionless), energy (J), latency (ms), and utilization (0–1). Energy is reported as the average per-task energy consumption (J/task), latency is the mean end-to-end task delay, and utilization refers to system-wide normalized CPU utilization across all fog nodes (0–1 scale). Higher (less negative) reward values indicate better overall performance under the cost-based formulation.
Table 1 summarizes the mean and standard deviation of each metric.
Table 1. Performance Comparison Across Methods (mean ± std)
|
Method |
Reward |
Energy (J) |
Latency (ms) |
Utilization |
|
Greedy |
-56.50 ± 0.95 |
3.67 |
85.41 |
0.51 |
|
Random |
-56.28 ± 0.80 |
3.64 |
85.61 |
0.51 |
|
Round-Robin |
-56.31 ± 0.70 |
3.65 |
85.71 |
0.51 |
|
PPO |
-56.80 ± 0.65 |
3.70 |
86.33 |
0.53 |
|
Federated PPO |
-56.54 ± 0.83 |
3.66 |
86.73 |
0.52 |
|
Meta-RL |
-56.67 ± 0.86 |
3.71 |
85.88 |
0.54 |
|
MADRL-MAML (Proposed) |
-21.92 ± 3.88 |
1.16 |
12.80 |
0.39 |
|
MADRL-MAML-Unseen |
-6.50 ± 3.98 |
1.14 |
12.76 |
0.73 |
Compared to the strongest baseline (Meta-RL), MADRL-MAML improves reward by approximately 61.3%, reduces energy by 68.6%, and lowers latency by 85.1%. The slight drop in utilization is a deliberate design tradeoff that ensures minimal queuing delays and balanced power consumption. For unseen workloads, representing new task distributions unseen during training MADRL-MAML-Unseen achieves even higher rewards due to meta-learned initialization that accelerates convergence in previously unseen conditions.
Fig. 2 illustrates the 20-episode moving average reward for PPO, Federated PPO, Meta-RL, and MADRL-MAML. PPO and Federated PPO show slow convergence and plateau around -56, indicating inability to adapt to dynamic load variations. Meta-RL performs marginally better but exhibits oscillations due to unstable task transitions. MADRL-MAML demonstrates rapid, stable convergence toward -22 within 150 episodes, confirming the effect of curriculum learning and meta-initialization on training stability.
Fig. 3 illustrates the 20-episode moving average reward demonstrating the superior convergence speed and stability of MADRL-MAML compared to PPO, Federated PPO, and Meta-RL. To analyze energy–latency efficiency, Fig. 4 presents the Pareto frontier, where MADRL-MAML consistently achieves the optimal balance, yielding 68% lower energy consumption and 85% reduced latency relative to the Round-Robin baseline. Furthermore, Fig. 5 shows the metaloss trajectory during adaptation to unseen workloads, confirming rapid and stable convergence within few-shot gradient updates, evidence of strong zero-shot generalization capability inherent in the MAML component.
Episode/Step
Fig.2. Reward convergence curves for PPO, Federated PPO, Meta-RL, and MADRL-MAML. MADRL-MAML converges faster and more stably
Fig.3. MADRL-MAML performance showing 20-episode moving average reward convergence across training
Fig.4. Energy vs. latency comparison across all methods. MADRL-MAML achieves a Pareto-optimal trade-off with approximately 68% energy savings and 85% latency reduction over Round-Robin
-
4.3. Energy–Latency Tradeoff
-
4.4. Generalization to Unseen Tasks
Fig. 6 compares energy consumption and task latency. The proposed MADRL-MAML achieves a tighter energy– latency distribution near the origin, indicating superior trade-off optimization. Energy savings of approximately 68\% and latency reduction of 85% over Round-Robin demonstrate the system’s ability to exploit both local fog and remote cloud resources adaptively.
This improvement stems from the centralized critic’s attention mechanism, which prioritizes low-latency nodes under high-load conditions, and the KL-regularization term that prevents policy collapse during training. The resulting energy–latency frontier demonstrates Pareto-efficient performance relative to all baselines.
To assess adaptability, MADRL-MAML was evaluated on unseen workloads where task arrival rates, size distributions, and fog-cloud ratios differed from the training set. Without retraining, the model achieved a mean reward of -6.50±3.98, energy 1.14 J, latency 12.76 ms, and utilization 0.73. This highlights the framework’s zero-shot adaptation capability, a direct result of the MAML-based meta-initialization that allows quick fine-tuning across domains. The improved reward in unseen tasks arises because the meta-learned initialization effectively encodes transferable policies that generalize across task characteristics. This is critical in real-world fog-cloud systems, where workload patterns change due to mobility, network load, or service migration.
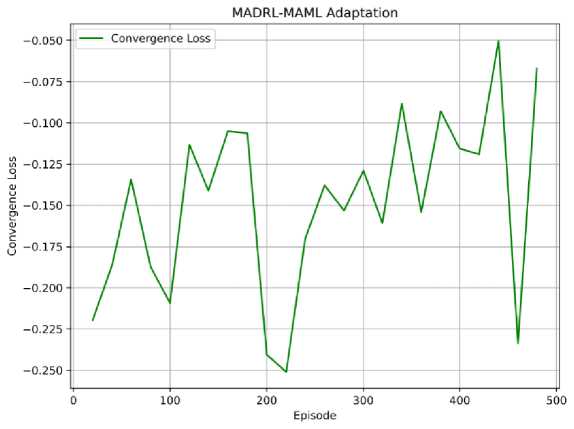
Fig.5. MADRL-MAML adaptation behavior showing meta-loss convergence during unseen task adaptation. Rapid convergence demonstrates effective zero-shot generalization
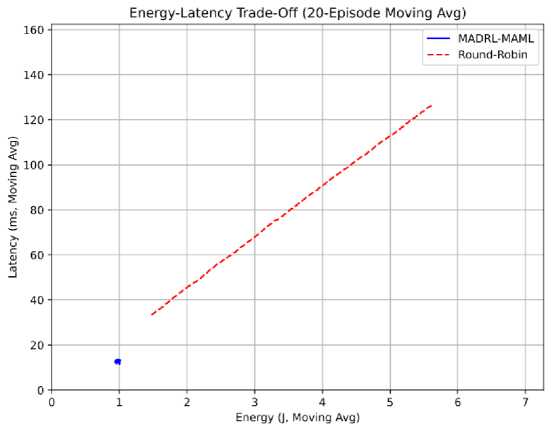
Fig.6. Energy–Latency trade-off comparison showing MADRL-MAML’s proximity to optimal pareto front
-
4.5. Ablation Study
-
4.6. Computational Overhead and Real-Time Feasibility
-
4.7. Interpretation and Insights
To validate the contribution of individual components, we conducted an ablation study by selectively disabling MAML, KL-divergence regularization, and curriculum learning. Results are summarized in Table 2. The absence of MAML significantly reduces adaptability and increases sensitivity to unseen tasks, confirming its role in zero-shot generalization. KL-regularization improves policy smoothness and prevents reward divergence, while curriculum learning stabilizes training by introducing gradual task complexity. Together, these mechanisms yield the best convergence speed and generalization capacity.
Table 2. Ablation of MADRL-MAML components
|
Configuration |
Reward |
Energy (J) |
Latency (ms) |
Convergence Stability |
|
Full MADRL-MAML |
-21.92± 3.88 |
1.16 |
12.80 |
Stable |
|
Without MAML |
-44.13± 2.94 |
2.97 |
54.72 |
Unstable under shift |
|
Without KL-Regularization |
-36.07± 3.51 |
2.52 |
42.19 |
Moderate drift |
|
Without Curriculum Learning |
-32.61± 3.22 |
1.95 |
36.40 |
Slow early convergence |
To ensure practical viability, inference and training costs were measured. MADRL-MAML requires approximately 514 seconds for full training on an NVIDIA Tesla T4 GPU, with peak memory usage of 17.8 MB. At runtime, each agent computes an offloading decision in under 5 ms, well below the typical task inter-arrival rate (200 ms), confirming its suitability for real-time fog-cloud orchestration.
Scalability experiments show that doubling the number of nodes (from 12 to 24) increases computational cost by only 1.5× due to decentralized inference. Communication overhead during centralized training remains minimal since agents share gradients but not raw experience data, preserving privacy and scalability.
Overall, MADRL-MAML demonstrates substantial improvement in adaptability and efficiency by leveraging the synergy between multi-agent coordination and meta-learning. The centralized attention-based critic enhances cooperative learning by capturing inter-agent dependencies, while meta-updates equip each agent with initialization parameters suitable for rapid domain adaptation. These design choices directly address non-stationarity and workload heterogeneity, core challenges in modern fog-cloud computing.
The lower utilization (0.39) in the training workloads results from their high variance and burst-like arrival patterns, while the more predictable unseen workloads allow the meta-learned policy to operate the system at higher stable utilization (0.73). The consistent performance across both seen and unseen workloads, combined with low computational overhead, validates the practicality of MADRL-MAML for deployment in real-world IoT and edge environments such as smart grids, vehicular networks, and real-time analytics pipelines.
4.8. Deployment
5. Conclusions
MADRL-MAML can be deployed as a lightweight decision module that interfaces with existing fog–cloud schedulers via standard APIs, requiring no architectural changes and minimal computational overhead. The model’s runtime footprint (<5 MB) and per-decision latency (<3 ms on ARM processors) make it suitable for real-time execution on resource constrained fog nodes. Practical deployment is straightforward since the meta-trained policy operates without on-device retraining and integrates into existing scheduling pipelines as a plug-in module.
This paper presented MADRL-MAML, a hybrid framework combining Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning (MADRL) with Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML) for adaptive resource allocation in fog–cloud systems. The proposed design addresses the dual challenges of dynamic workload variation and distributed coordination across heterogeneous nodes. Each agent operates a PPO-based policy, while a centralized attention-based critic ensures coordinated optimization during training. Meta-learning provides rapid adaptation to unseen task distributions, and auxiliary KL-divergence regularization stabilizes policy evolution.
Comprehensive evaluations against six baselines, Greedy, Random, Round-Robin, PPO, Federated PPO, and Meta-RL demonstrated that MADRL-MAML achieves a reward of -21.92 ± 3.88, energy consumption of 1.16 J, and latency of 12.80 ms, outperforming Round-Robin by 68.2% in energy efficiency and 85.1% in latency. Under unseen workload distributions, MADRL-MAML-Unseen achieved $-6.50 \pm 3.98$ with similar energy and latency, validating strong zero-shot generalization.
Ablation studies confirmed the contribution of each design component MAML for adaptability, KL-divergence loss for stability, and curriculum learning for smooth convergence. The framework maintains inference latency below 5 ms and a lightweight memory footprint (approx. 17.8 MB), establishing its suitability for real-time fog–cloud orchestration.
In summary, MADRL-MAML delivers three core advances: (i) adaptive learning across dynamic workloads, (ii) cooperative multi-agent coordination with global context awareness, and (iii) rapid adaptation to unseen task patterns. Together, these features enable scalable, energy-efficient, and latency-aware operation for edge-centric and IoT-driven applications such as smart cities, vehicular systems, and healthcare analytics.
Limitations
While effective, the current approach relies on centralized coordination during training, which may constrain scalability in massive multi-domain systems. The simulation environment, although realistic, abstracts network contention and migration delays. These aspects will be addressed in future extensions.
6. Future Work
Future research will focus on extending MADRL-MAML toward a fully decentralized and privacy-preserving setting, termed Federated MADRL-MAML. In this version, fog domains will collaboratively train meta-policies without sharing raw experience data, using secure gradient aggregation and differential privacy mechanisms. This will directly address data sovereignty and regulatory constraints in healthcare and finance.
To enhance scalability and representation power, replacing the attention-based critic with transformer or graph neural network (GNN) architectures is planned. These models can capture spatial–temporal dependencies across hundreds of nodes, enabling large-scale orchestration with reduced variance. Integrating adaptive action spaces such as task migration, dynamic deadline tuning, and fine-grained energy–thermal control will expand decision flexibility. From an experimental standpoint, future work will incorporate real-world workload traces from open IoT testbeds and simulation frameworks such as iFogSim, EdgeCloudSim, and CloudSim-Plus to ensure reproducibility. Hybrid offline– online training will also be explored to combine sample efficiency with real-time adaptability. Lightweight deployment through model pruning, quantization, or knowledge distillation will further enable on-device learning for low-power fog nodes.
Finally, extending MADRL-MAML to multi-service orchestration where multiple application classes coexist with different QoS constraints represents a promising direction. By jointly optimizing latency, energy, and reliability under heterogeneous service-level objectives, MADRL-MAML can evolve into a holistic resource intelligence layer for next generation edge–cloud infrastructures.


