Self-compacting concrete for monolithic constructions with highly dispersed silica-based additives
Автор: Urkhanova L.A., Lkhasaranov S.A., Danzanov D.V., Bituev A.V.
Журнал: Nanotechnologies in Construction: A Scientific Internet-Journal @nanobuild-en
Рубрика: Construction materials science
Статья в выпуске: 6 Vol.17, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. Self-compacting concrete offers broad potential in construction due to its operational reliability and durability. However, the high cost of self-compacting concrete and the technological complexity of its production require the development of new concrete mix designs and improved placement technologies. When selecting concrete mix designs for self-compacting concrete, chemical additives can be used to reduce cement consumption and improve the concrete's properties. Materials and methods. To ensure the rheological and technological properties of the concrete mix, fly ash, a dry polycarboxylate-based superplasticizer, and ultrafine additives were used. The ultrafine additives were produced by hydrolysis, using pure Portland cement as a precursor, with the concentration in the solution varying from 1 to 5%. The cement hydrolysis reaction results in the formation of a multicomponent sol containing silicic acid, aluminum hydroxide, iron hydroxide and calcium hydroxide. Results and discussion. Experiments were conducted to modify self-compacting concrete with an ultrafine additive obtained using sol-gel technology. An optimal composition of modified cement containing an ultrafine additive with an average particle size of up to 100–150 nm was developed. The use of the ultrafine additive accelerated the cement hardening kinetics and improved the physical and mechanical properties of cement stone by 1.4–1.8 times compared to cement without the additive due to water accumulation, an increase in the volume of cement gel, and a decrease in capillary porosity. Based on an assessment of the technological and rheological properties of concrete mixtures containing fly ash as a microfiller and a modifying additive, compositions corresponding to strength classes B40–B60 were established, containing 7.5–44% fly ash and an additive in an amount of 0.1% of the cement weight on a dry matter basis. It has been established that the introduction of ultrafine fly ash and fly ash into the concrete mix reduces segregation by 17–19%, increases viscosity by 13% to 20%, and reduces flowability only slightly by 5–10%. It has been established that self-compacting concrete with the combined use of fly ash with medium pozzolanic activity, a chemically active ultrafine additive, and a polycarboxylate-based superplasticizer is characterized by intensive strength gain within 1–3 days of curing and an increase in strength by 15–17% within the design curing period. Conclusion. As a result of the research, a low-temperature method for producing a modifying additive using sol-gel technology was developed. This method is simple to synthesize, does not require complex process equipment, and can be added along with mixing water and uniformly distributed throughout the concrete mix. Concrete mix formulations for self-compacting concrete of strength classes B40–B60 were developed using an ultrafine additive, which improves the process properties, quality indicators, and physical and mechanical properties of the concrete.
Self-compacting concrete, ultra-dispersed additive, fly ash, superplasticizer, hydrolysis of Portland cement, sol-gel technology, technological and rheological properties, concrete mixture, compressive strength, dense structure
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142246524
IDR: 142246524 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2025-17-6-666-676
Текст научной статьи Self-compacting concrete for monolithic constructions with highly dispersed silica-based additives
Original article
Урханова Л.А., Лхасаранов С.А., Данзанов Д.В., Битуев А.В. Самоуплотняющиеся бетоны для монолитных конструкций с высокодисперсными добавками на основе кремнезема. Нанотехнологии в строительстве. 2025;17(6):666–676. https://doi. org/10.15828/2075-8545-2025-17-6-666-676. – EDN: SDLVWE.
One of the trends in the construction industry is increasing the operational reliability and durability of building structures, including through the use of high-strength multi-component concretes. These concretes include high-strength self-compacting concrete (SCC), known in international scientific and technical literature as SelfCompacting Concrete (SCC), whose composition and production technology differ from traditional concrete [1, 2].
Globally, SCC has been widely used for the production of monolithic and precast reinforced concrete structures since the mid-1990s [3, 4]. The undoubted advantages of SCC include high flowability of the mixture, even in densely reinforced and thin-walled structures, and the elimination of vibration during concreting. However, the main limiting factor to the widespread use of SCC, both internationally and in Russia, is its high cost [3]. Therefore, the search for rational SCC compositions that meet both technical and economic requirements continues [3, 5].
When selecting the composition of concrete mixtures for SCC, it is possible to use chemical additives, for example, a viscosity modifier, the use of which allows for the complete elimination of microfiller, solution separation and sedimentation of coarse aggregate [3]; the use of industrial waste, for example, fly ash as a microfiller to increase the water-holding capacity of the concrete mixture and compaction of the structure [6]. When obtaining SCC, the efficiency of cement systems can be improved by increasing the degree of hydration, increasing density, strength and creating a less defective structure at the nano- and microlevels through the use of various types of modifying additives. There are a number of studies proving the effectiveness of nanometer-sized additives for modifying SCC, the use of which improves the physical and mechanical properties of concrete by compacting its structure [7, 8].
Among the variety of nanodispersed components used as concrete modifiers, silicon dioxide should be highlighted as the basis for the pozzolanic reaction. One promising method for obtaining it is the sol-gel method, which has several advantages: synthesis can be carried out at low temperatures; the pH can be varied to obtain high-purity ultradispersed additive particles; the kinetics of the process can be regulated by changing the composition of the reaction mixture [9].
The sol-gel method for producing nanosilica, as noted by many authors [9-11], has several advantages, such as the homogeneity of the raw materials upon mixing, the relatively low synthesis temperature, the uniformity of the resulting particles and the stability of their properties, and the possibility of obtaining the substance in large quantities.
The development of high-strength concrete compositions, including self-compacting concrete (SCC), is relevant for the construction industry in the Republic of Buryatia, where high-rise construction, residential infrastructure, housing and utilities systems, and transportation hubs with dense reinforcement are developing. Experience in constructing such projects suggests the use of self-compacting concrete.
The aim of this study is to develop a self-compacting concrete composition of various compressive strength classes using raw materials from the Republic of Buryatia and a modifying additive in the form of a colloidal additive obtained by the sol-gel method. Experiments were conducted to determine the process parameters of the modified mixtures and the physical and mechanical properties of the hardened concrete.
When developing the composition of the SCC, a number of features of the composition of the self-compacting concrete mixture were taken into account in comparison with the selection of the composition of traditional concrete: a specific approach to the ratio and granulometry of the filler (approximately the same ratio of fine and coarse filler, maintaining the continuity of the granulometry of the fillers to achieve the most cohesive structure of the concrete mixture), the mandatory presence of fillers and superplasticizers and increased cement consumption [2, 6].
Fly ash was used as a finely dispersed filler to save cement and improve the water-holding capacity and technological properties of concrete mixes. Experience has been gained in using both acidic [6, 10, 12, 13] fly ash with a CaO content of less than 10% and basic fly ash with a CaO content of more than 10% in various SCC formulations [14].
MATERIALS AND RESEARCH METHODS
To produce concrete mixtures for the SCC, materials traditionally used in the construction industry of the Republic of Buryatia were used:
– Portland cement CEM I 42.5 N, compliant with Russian national standards 30108-2020 (PC);
– Microfiller: acidic fly ash from field IV of the electrostatic precipitator of the Gusinoozerskaya State District Power Plant, a branch of InterRAO, complying with grade ZU KUK-A-1 according to Russian national standards 25818-2017. The pozzolanic activity of the fly ash was 32.5 mg/g of absorbed CaO, which corresponds to an active mineral additive with average pozzolanic properties according to GOST 25592-2018. The specific surface area of the ash was 540 m2/kg;
– Class I quartz-feldspar sand with a fineness modulus of Mk = 2.1, complying with Russian national standards 8736-2014;
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
– Crushed granite of 5–20 mm fraction with a density of 2.6 g/сm3 and a crushability grade of 1200, complying with Russian national standards 8267-93;
– Sika ViscoCrete 20 Gold superplasticizer based on polycarboxylates – an effective superplasticizing and super-water-reducing admixture with rapid early strength gain, designed for the manufacture of high-performance reinforced concrete products in factory production conditions. The superplasticizer dosage was determined experimentally and amounted to 2% of the cement mass in the concrete mix;
– A multicomponent sol – an ultrafine additive (UFA) obtained by hydrolysis of Portland cement – was used as a modifying additive. Three series of concrete mix compositions were prepared, with PC content varying from 375 to 500 kg/m3, microfiller content from 40 to 165 kg/m3, and water-cement ratios from 0.36 to 0.48. The concrete mix was used to form 10×10×10 cm specimens, which were cured under normal conditions. Strength determinations were performed according to standard methods outlined in Russian national standards 10180-2012. Samples were tested after 3, 7, and 28 days of curing.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Within the framework of this study, aimed at expanding the potential applications of self-compacting concretes in construction, the influence of ultrafine additives on the material’s properties was investigated. The ultrafine additive was produced via hydrolysis, using plain Portland cement as a precursor. The concentration of the cement in the suspension (colloidal solution, hereinafter referred to as the solution) was varied from 1% to 5%.
During cement hydration, the hydrolysis of the main minerals of Portland cement clinker–tricalcium silicate (C3S) and dicalcium silicate (C2S)–occurs in four distinct stages [15]. Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2, is formed at each stage. The intermediate products of the first three stages are calcium hydroorthosilicates with varying degrees of substitution: Ca3[HSiO4]2, CaH2SiO4, and Ca(H2SiO4)2, formed sequentially. At the fourth stage, complete hydrolysis concludes with the decomposition of the original compounds into their constituent prod-ucts–Ca(OH)₂ and orthosilicic acid, H4SiO₄.
In our view, when the Portland cement concentration in the solution ranges from 1% to 5%, the hydrolysis of the main cement minerals proceeds to completion, yielding the corresponding hydroxides and acids in a colloidal state. Under these conditions, the likelihood of forming intermediate hydroxysalts of the respective metals is reduced. As a result of cement hydrolysis, a multicomponent sol is formed, containing simultaneously silicic acid, aluminum hydroxide, iron hydroxide, and calcium hydroxide. Hydroxides of multivalent metals typically form colloidal systems in which micelles are stabilized by an extensive hydration shell, thereby preventing particle aggregation.
It is well established that the extent of hydrolysis depends on temperature and the concentrations of the substances involved: the degree of hydrolysis increases with rising temperature and solution dilution (i.e., with higher water concentration) [16]. The experimental results demonstrate that the concentration of the initial precursor significantly affects the physical and mechanical properties of the hydrated cement paste incorporating the ultrafine additive (see Table 1). As the concentration of the initial solution used to produce the additive increases, the amount of calcium hydroxide formed also increases. The Ca(OH)2 content was determined by titration in accordance with Russian national standards 22688–2018.
The optimal concentration of the precursor solution for producing the ultrafine additive (UFA), as demonstrated by the compressive strength results of the cement paste, is a 2% solution. As the concentration of the initial precursor solution increases up to 2%, the compressive strength of the cement paste rises significantly compared to plain (additive-free) cement–by approximately 25– 50% after 3 days of curing and by 44–84% after 28 days of curing.
Table 1. Physical and mechanical properties of Portland cement with the addition of ultrafine additive (UFA) obtained by hydrolysis of cement at various solution concentrations (additive dosage: 0.4% by mass of cement)
|
Concentration of the initial precursor used to produce the ultrafine additive (UFA) |
Compressive strength of cement paste, MPa, after curing, days |
||
|
3 |
7 |
28 |
|
|
Without additive |
32.5 |
44.5 |
54.1 |
|
1% solution |
41 |
59 |
78 |
|
2% solution |
50.2 |
77.6 |
99.7 |
|
3% solution |
36 |
51 |
63 |
|
4% solution |
33.5 |
50 |
55 |
|
5% solution |
33.1 |
49 |
54.6 |
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
Despite the increased calcium hydroxide content– which influences the pH of the reaction system and the morphology of the formed particles–further increasing the precursor concentration beyond 2% for UFA synthesis leads to a diminished effectiveness of the additive in modifying the cement matrix. Higher solution concentrations result in larger aggregates of colloidal particles and reduced overall dispersity of the compounds.
Laser diffraction analysis of the particle size distribution of the 2% UFA solution, performed using a Shimadzu SALD-7500 particle size analyzer, revealed a poly-modal size distribution in the range of 100 to 1000 nm, with a peak maximum at approximately 300 nm (Fig. 1). It is evident that the measured size corresponds not to individual dispersed particles but rather to their aggregates.
When the 2% UFA solution was incorporated into cement paste at a dosage of 0.4% by mass of cement and a water-to-cement ratio (w/c) of 0.26–sufficient to achieve standard consistency–the resulting particle size in the hardened matrix was reduced by a factor of 2.5–3. The higher the degree of hydration of colloidal particles in the form of micelles, the fewer impurities from the original compounds they contain, resulting in smaller particle size and greater dispersity.
The particles formed in the colloidal solution exhibit high surface energy and act as nucleation sites for the crystallization of binding phases [17].
The change in the phase composition of the cement stone upon the introduction of the additive is confirmed by IR spectral analysis performed using an IRAffinity-1 FTIR spectrometer (Fig. 2).
Analysis of IR spectra shows a change in the intensity of peaks at 1647.21cm–1 and 1653.00 cm–1, indicating a reduction in the amount of free water and intensification of calcium hydrosilicate formation processes. Furthermore, a shift and change in intensity are observed for peaks cor- responding to siloxane group vibrations –O–Si–O–: in the control sample, the maximum appears at 977.91 cm–1, whereas in the sample with the ultrafine additive, it shifts to 985.62 cm–1. This shift is characteristic of the formation of low-basicity calcium hydrosilicates, which possess higher density and structural ordering. These processes contribute to densification of the cement matrix structure and, consequently, enhance its strength properties when fly ash is used in combination with an ultrafine additive.
In subsequent studies, a multicomponent sol was used to modify self-compacting concrete (SCC). The sol was applied as a 2% aqueous solution with a density of 1.004 g/cm3 and introduced into the concrete mixture together with the mixing water at a dosage of 5% by mass of cement. The admixture consumption, recalculated to dry matter, amounted to 0.1% of cement mass, allowing it to be considered as a micro-dosage that effectively influences the main properties of concrete.
The compositions of concrete mixtures prepared using the above-mentioned components are presented in Table 2. Based on laboratory trials, formulations for self-compacting concrete mixtures were developed for concrete strength classes B45, B50, and B55 under compression.
In designing the concrete mix composition, appropriate selection of coarse and fine aggregates was carried out to ensure continuous particle size distribution and, consequently, a cohesive mixture structure.
Optimization of fine and coarse aggregate contents in the self-compacting concrete mix was performed according to the methodology described in [18], under the condition of achieving maximum bulk density of the dry aggregate blend at various sand volume fractions (r) ranging from 0.40 to 0.60 (Fig. 3).
Based on the obtained dependency, the optimal gradation of the aggregate blend was achieved with a sand
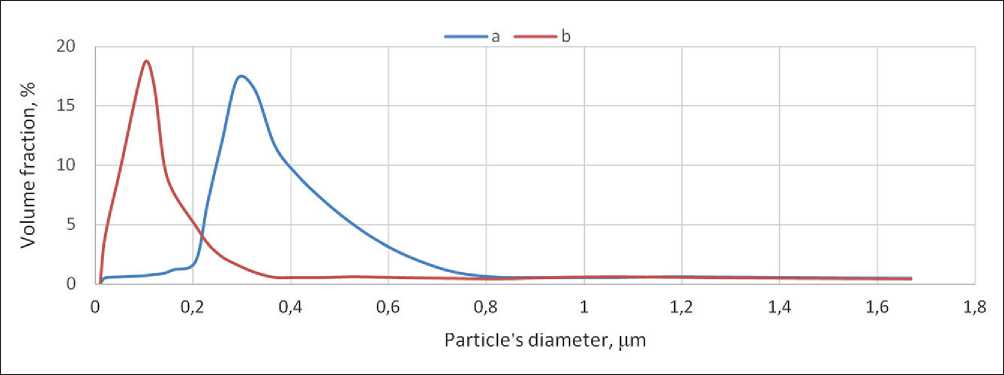
Fig. 1. Analysis of dispersion of the initial 2% solution of the additive (a) and the additive diluted with mixing water when introduced into the cement (b)
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
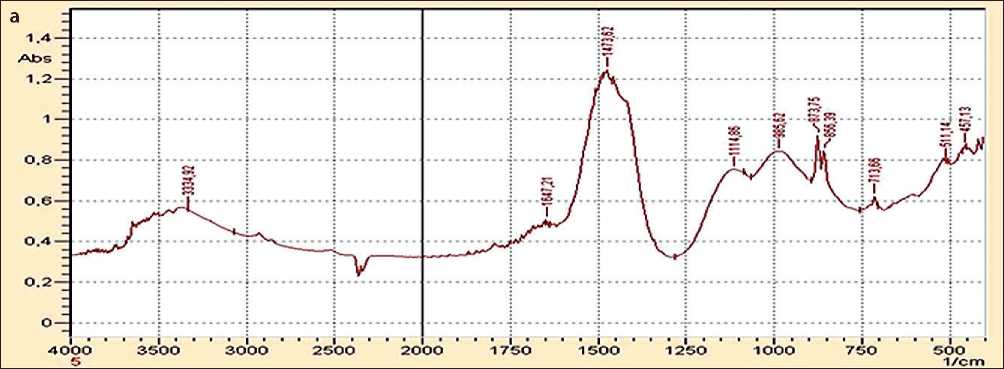
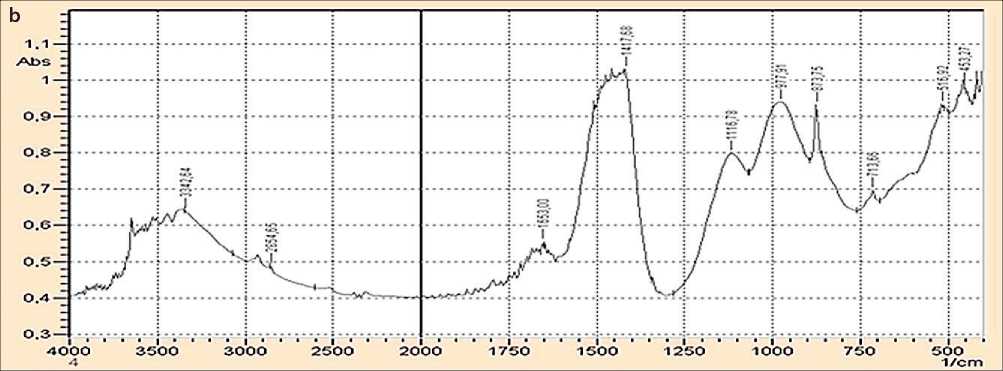
Fig. 2. IR spectra of Portland cement with fly ash without (a) and with ultrafine additive (b)
Table 2. Compositions of self-compacting concrete
For the investigated concrete mix designs, the following technological and rheological properties were monitored: concrete mix density, flow spread using the standard cone and the J-ring (SFJ), flow time of the standard cone to a diameter of 500 mm, passage through the
J-ring, efflux time through the V-funnel, and segregation resistance measured by bleed water content. The rheological properties of the investigated mixes were optimized to achieve self-consolidation and self-leveling behavior, and tested in accordance with Russian national standards R 59715-2012 (Table 3).
The self-compacting concrete mix compositions, selected experimentally in the laboratory, meet the required
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
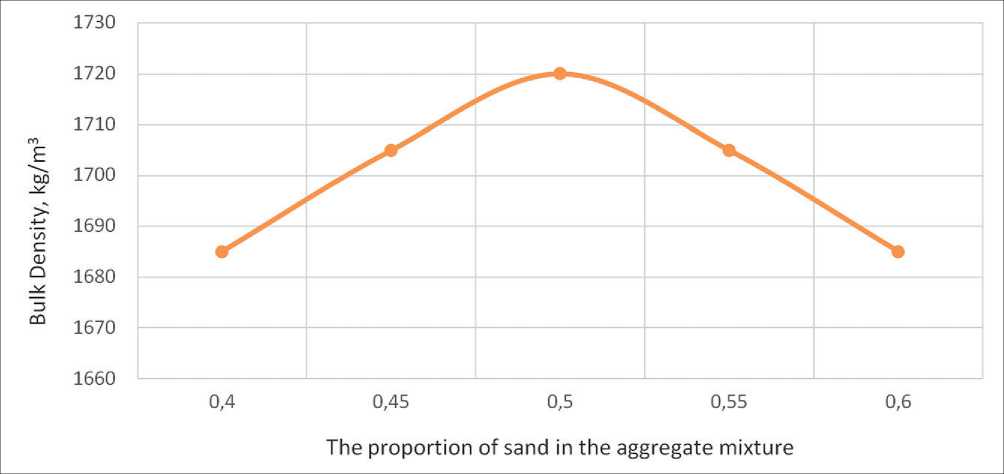
Fig. 3. Dependence of the bulk density of the aggregate mixture on the proportion of sand in the mixture
Table 3. Rheological characteristics of self-compacting concrete mixtures
A solution to the problem of wider application of SCC in construction, especially in regions with limited natural resources, is the development of a technology for producing self-compacting concrete using fly ash as a microfiller. The ash content, which ensures self-compacting of the concrete mix and the cost-effectiveness of the concrete produced, has been established within the range of 8–44% of the cement mass. The introduction of fly ash made it possible to obtain a concrete mixture with high mobility, fluidity and self-compacting effect. However, the low pozzolanic activity of the original ash does not provide the effect of increasing the strength of concrete due to the pozzolanic reaction and the increase in the number of new formations in the initial stages of hardening. To regulate the pozzolanic activity of the microfiller, the addition of ultrafine fly ash is necessary. The combined use of fly ash and ultrafine additives can not only optimize the particle size distribution and pozzolanic activity, but also increase the density and accelerate the strength gain of concrete.
Fly ash, as a conditionally inert microfiller, has an average particle size of 4.19 µm (Fig. 4), with a dispersion
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
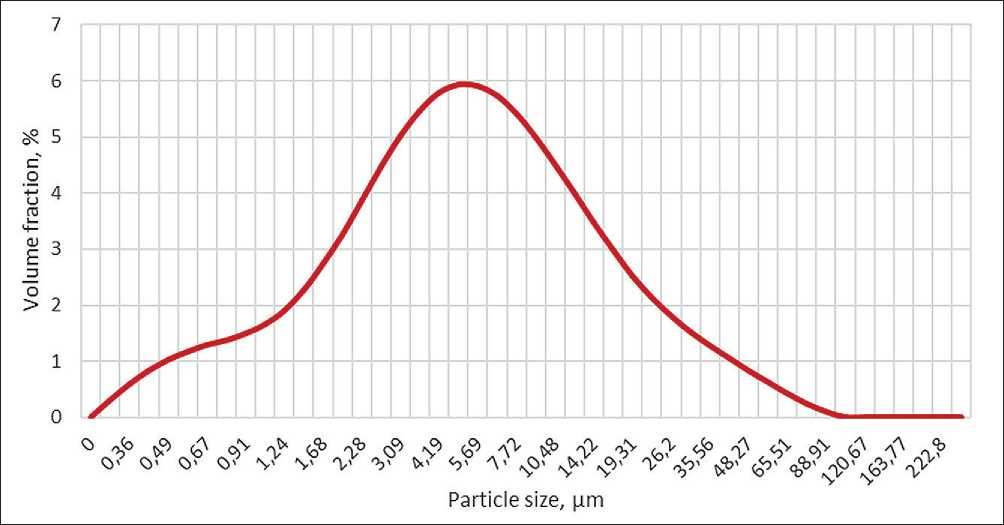
Fig. 4. Dispersion analysis of fly ash
almost twice as great as that of the original cement, and is located in the intergranular space of the original Portland cement. The ultrafine additive with an average particle size of 0.1 µm exhibits high chemical activity due to the high degree of dispersion of the formed nanoparticles and enhances the effect of using ash, especially in the presence of effective superplasticizers based on polycarboxylates. One of the main problems arising during the synthesis of additives by the sol-gel method is the aggregation and sedimentation instability of their aqueous solutions, which subsequently transform into a gel [9]. A surfactant in the form of a superplasticizer not only improves the rheological properties of the concrete mixture, but also ensures stabilization of the synthesized additive, extending the period of its practical application.
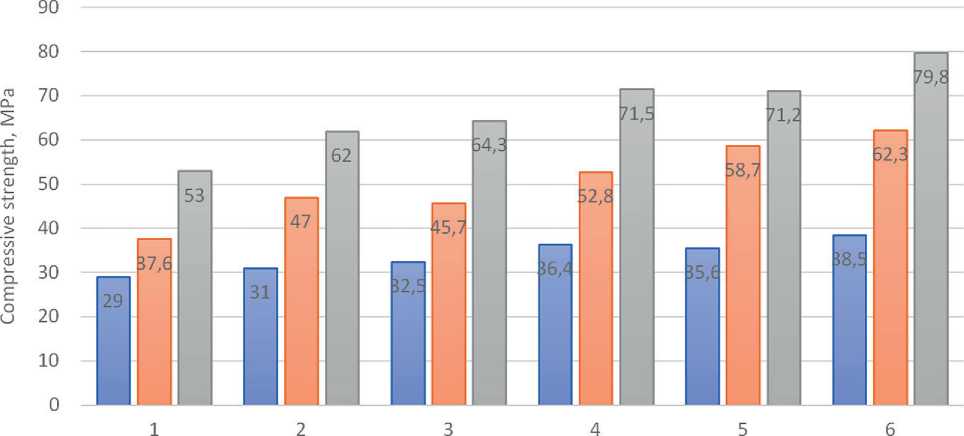
The physical and mechanical properties of selfcompacting concrete were determined for the developed compositions. The compressive strength of the control samples after 28 days of normal curing (Fig. 5) corresponds to the design class for all concrete compositions under consideration. The introduction of UFA increases the compressive strength of concrete by 27% compared to the control composition at the age of up to 7 days of hardening and by 17% at the design age.
The introduction of an ultrafine, chemically active mineral additive into the cement composition not only ensures the physical filling of intergranular voids but also intensifies the formation of hydration products, which act as additional structural elements and bind both free intergranular water and water adsorbed on the surface of filler particles. This process results in a reduction in the overall porosity of the cement stone and a significant improvement in the microstructure of the contact zone between the binder and filler (Fig. 6, JEOL-JSM-6510LV, Progress Center for Collective Use, ESSUTM). This creates a highly dense structure, changes the nature of porosity, and improves the physical and mechanical properties of the modified concrete.
When self-compacting concrete is modified with an ultra-dispersed additive, the morphology of the resulting calcium hydrosilicates changes. On the surface of the concrete chip with UFA, a greater number of needle-shaped crystals of low-basic calcium hydrosilicates are observed compared to the control composition.
CONCLUSION
As a result of the research, a low-temperature method for producing a modifying additive using sol-gel technology was developed. This method is characterized by its simplicity of synthesis, does not require complex process equipment, and can be added along with mixing water and uniformly distributed throughout the concrete mix. Concrete mix compositions have been developed that ensure self-compacting without signs of stratification or separation, while maintaining the properties of the mix for up to 2 hours from the start of mixing.
For compositions modified with an ultrafine additive in microdoses of 0.1% in terms of dry matter, an increase in compressive strength of 17–20% was established after 28 days of hardening, depending on the composition, compared to control samples, which is due to the poz-
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
□ 3 days □ 7 days □ 28 days
Compositions of concrete
Fig. 5. Compressive strength of self-compacting concrete
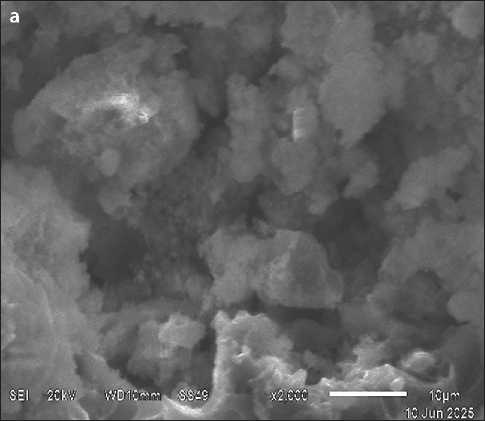
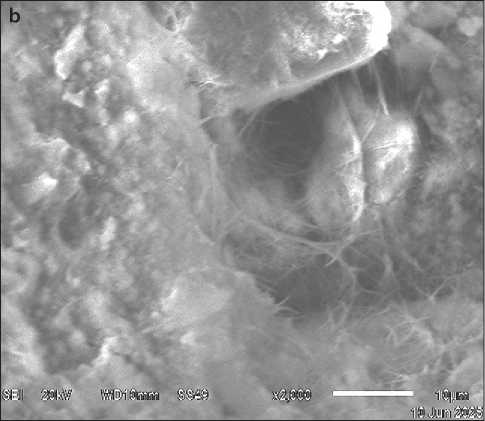


Fig. 6. Scanning electron microscopy of self-compacting concrete: a – control composition, b – composition with UDD
zolanic effect of fly ash and UFA and compaction of the concrete structure due to the introduction of finely dispersed particles.
With the increase in the number of stores in construction and the complexity of the forms of monolithic structures, self-compacting concrete mixtures will be widely used in construction [19, 20]. A series of laboratory experiments demonstrated the potential of producing selfcompacting concrete based on natural and man-made raw materials from the Republic of Buryatia, using modifying additives, and their application in monolithic construction.
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE


