Селинексор у больных с рецидивами/рефрактерными формами множественной миеломы
Автор: Бессмельцев С.С.
Журнал: Вестник гематологии @bulletin-of-hematology
Рубрика: Передовая статья
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.20, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Выживаемость пациентов с множественной миеломой значительно улучшилась в последние годы благодаря внедрению различных классов новых препаратов, таких как ингибиторы протеасом, иммуномодулирующие агенты и моноклональные антитела. Однако у подавляющего большинства больных множественной миеломой наблюдается рецидив с более агрессивным течением заболевания из-за приобретения дальнейших генетических изменений, которые могут вызывать устойчивость к текущим методам терапии. Лечение таких пациентов, часто с тройной (или даже более) рефрактерностью остается сложной задачей, и для преодоления этой устойчивости требуются альтернативные подходы. Недавно были разработаны и в настоящее время изучаются иммунотерапия новыми моноклональными, лекарственно-конъюгированными или биспецифическими антителами, а также использование химерных антигенных рецепторов Т-клеток. Однако неиммунологические терапевтические схемы на основе мелфлуфлена, венетоклакса или селинексора с новым механизмом действия также показали многообещающие результаты в условиях рецидивирующей/рефрактерной миеломы. Селинексор - первый в своем классе, пероральный, медленно обратимый, высокоспецифичный ингибитор экспортина-1 (XPO-1), который является важным ядерным экспортером для более чем 200 белков, включая многие белки-супрессоры опухолей. В настоящем обзоре мы сообщаем самые последние литературные данные относительно селинексора, уделяя особое внимание его эффективности и безопасности при множественной миеломе.
Множественная миелома, рецидив/рефрактерное заболевание, селинексор, эффективность, безопасность, выживаемость
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170207418
IDR: 170207418
Текст научной статьи Селинексор у больных с рецидивами/рефрактерными формами множественной миеломы
Введение. За последние 20 лет выживаемость пациентов с множественной миеломой (ММ) значительно улучшилась благодаря внедрению новых лекарственных препаратов. В частности, бортезо-миб, карфилзомиб и иксазомиб (ингибиторы про- теасом), талидомид, леналидомид и помалидомид (иммуномодулирующие агенты) произвели революцию в лечении ММ. Разработаны и активно изучаются иммунотерапевтические опции, включающие моноклональные, конъюгированные с лекарствен- ными средствами или биспецифические антитела, все большее применение находит CAR-T клеточная терапия. Кроме того, ингибитор гистондеацетилазы панобиностат и пегилированный липосомальный доксорубицин были одобрены в комбинации с бортезомибом, а пероральный ингибитор протеа-сом иксазомиб и моноклональное антитело против SLAMF7 элотузумаб были рекомендованы в комбинации с леналидомидом [1-7].
В настоящее время сочетание этих и других препаратов в виде триплетов является стандартной практикой, основанной на данных клинических исследований, показывающих, что триплеты могут вызывать глубокие и длительные ремиссии. Однако ни одна из этих лечебных опций не является излечивающей, практически у всех пациентов развивается рецидив заболевания либо резистентность к нескольким препаратам. Все большее число пациентов страдают тройной рефрактерностью, которая определяется как заболевание, резистентное к ингибиторам протеасом, иммуномодулирующим препаратам и моноклональным антителам. Большинство пациентов получают лечение пятью препаратами, которые наиболее часто используются в настоящее время (карфилзомиб, бортезомиб, леналидомид, помалидомид и даратумумаб). У пациентов, не восприимчивых к двум ингибиторам, двум иммуномодулирующим препаратам и анти-CD38 моноклональным антителам, устанавливают пента-рефрактерность. Общая выживаемость пациентов с миеломой, резистентной к этим классам лекарственных препаратов, невелика; при резистентности к даратумумабу медиана общей выживаемости колеблется от 1,7 до 3,0 месяцев [8, 9]. Наибольшее количество больных, не доживших до следующей линии терапии, – высокий риск, ослабленные и пожилые пациенты. Так, установлено, что к очередной линии терапии в целом теряется от 15 до 35% пациентов и до 50% пациентов пожилого возраста, а также пациентов, не являющихся кандидатами на аутологичную трансплантацию гемопоэтических стволовых клеток (АутоТГСК), пациентов, отягощенных сердечно-сосудистыми расстройствами, нарушениями легочного кровообращения и патологией почек [3]. Прогрессирование миеломы сопровождается сложными цитогенетическими и эпигенетическими изменениями, которые включают избыточную экспрессию онкобелков и мутацию или функциональную инактивацию белков-супрессоров опухоли [10]. В настоящее время у этих пациентов нет вариантов лечения с доказанной клинической пользой [11]. Все это требует разработки новых лекарственных препаратов и методов лечения и оценки их эффективности [12, 13].
Между тем разработаны неиммунологические терапевтические схемы на основе мелфлуфлена, венетоклакса или селинексора с новыми механизмами действия, которые показали многообеща- ющие результаты в условиях рецидивирующей/ рефрактерной множественной миеломы (РРММ). Эти препараты могут иметь возможное преимущество, заключающееся в избежание некоторых специфических побочных эффектов, связанных с иммунологическими подходами (например, синдрома высвобождения цитокинов, реакций, связанных с инфузией, осложнений со стороны центральной нервной системы или необычных инфекций), что позволяет оценивать их как возможные альтернативные варианты или, что еще лучше, как партнеров для новых комбинаций.
Цель настоящей работы. Обзор основных клинических исследований по оценке эффективности и безопасности применения селинексора, преимущественно в комбинированных схемах терапии, при рецидивах/рефрактерных формах множественной миеломы (РРММ).
Материалы и методы. Для достижения поставленной цели нами проанализированы основные научные публикации, посвященные применению селинексора в комбинации с десаметазоном, ингибиторами протеасомы, иммуномодулирующими агентами и моноклональными антителами. Для изучения отобраны 55 работ, опубликованных в преобладающем большинстве в течение последние 10 лет. Включение более ранних работ допускалось в связи с высокоинформативными материалами либо, если это были первоисточники.
Результаты . Система ядерного экспорта является привлекательной мишенью для противоопухолевой терапии. Из восьми известных белков млекопитающих, которые опосредуют перенос макромолекул из ядра в цитоплазму, экспортин-1 (XPO1, также известный как CRM1) является единственным, который способствует транспорту белков-супрессоров опухолей (TSPs, например, p53, IκB and FOXO3a), глюкокортикоидных рецепторов и РНК-мессенджеров онкобелков (мРНК, например, c-Myc, Bcl-xL, MDM2 и cyclin D1) из ядра в цитоплазму [14, 15]. XPO1 с высокой плотностью экспрессируется на клетках больных ММ, что напрямую коррелирует со снижением их выживаемости и увеличением числа поражений костей скелета [16].
Селинексор, также известный как KPT-330, представляет собой пероральный низкомолекулярный препарат, избирательно ингибирующий ядер-ный экспорт (SINE – Selective Inhibition of Nuclear Transport). Причем следует отметит, что он является первым в своем классе, биодоступным при пероральном приеме, селективным ингибитором ядерного экспорта, который медленно обратимым ковалентным образом связывает и инактивирует экспортин-1 (XPO1), жизненно необходимый белок для экспорта более 200 белков-супрессоров опухоли из ядра. В доклинических исследованиях сели-нексор обратимо ингибировал ядерный экспорт белков-супрессоров опухолей, регуляторов роста и мРНК онкогенных белков, блокируя XPO1. Ингибирование экспортина-1 с помощью селинексора приводит к накоплению белков-супрессоров опухолей в ядре, снижению некоторых онкопротеинов, таких как c-MYC, и cyclin D1, остановке клеточного цикла и апоптозу опухолевых клеток, в том числе миеломных, но не нормальных клеток [17]. Повышенная экспрессия XPO1 в клетках миеломы, как и в большинстве раковых клеток, делает селинексор многообещающей таргетной терапией для пациентов с ММ [16]. Противоопухолевая активность селинек-сора не зависит от мутации p53 [14] и синергично увеличивается при сочетании с другими терапевтическими средствами [18]; сочетание с глюкокортикоидами также усиливает противомиеломную активность селинексора [19]. Более того, селинексор, ингибируя NF-kB, снижает в микросреде цитокины, которые жизненно важны для выживания клеток MM, такие как IL-6, IL-10 и уровень сосудистого эндотелиального фактора роста (VEGF) [14]. Установлено также, что он ослабляет действие рецептора-активатора ядерного фактора каппа-В-лиганда (RANK-L), опосредующего дифференцировку остеокластов, что потенциально смягчает тяжесть поражения костей скелета [20]. Причем селинексор продемонстрировал in vitro проапоптотическую активность в клеточных линиях множественной миеломы и в образцах опухолей пациентов, а также в моделях мышиных ксенотрансплантатов.
В ходе исследования первой фазы селинексор сам по себе или в комбинации с низкими дозами дексаметазона проявил широкую активность при гематологических злокачественных новообразований [21]. Данные о применении селинексора у пациентов с множественной миеломой, включенных в исследование I фазы по изучению безопасности, фармакокинетики и фармакодинамики различных доз, были представлены на ежегодной конференции ASH в декабре 2014 года. Селинексор в комбинации с низкими дозами дексаметазона (каждый из которых вводится дважды в неделю в дозе 45 мг/ м2 и 20 мг соответственно) у девяти пациентов, которым ранее проводилось интенсивное лечение и которые были рефрактерными к предшествующей терапии, продемонстрировал высокие показатели стойкого ответа, включая 67% общего ответа (частичный ответ или выше) и 89% клинического эффекта (минимальный ответ или выше). Медиана продолжительности ответа составила приблизительно 7 месяцев. Наиболее частыми побочными эффектами 1/2 степени тяжести были тошнота, утомляемость, анорексия и рвота.
В 2018 г. были опубликованы результаты многоцентрового клинического исследования I фазы (NCT01607892), в котором оценивалась безопасность и эффективность различных дозировок перорального селинексора [22]. В исследование вошли тяжело предлеченные пациенты с РРММ и макро- глобулинемией Вальденстрема. На этапе увеличения дозы 25 пациентам с тяжелой формой ММ (22 больных) или макроглобулинемией Вальденстрема (3 больных) назначали селинексор по 3-60 мг/м2 (8 или 10 доз в течение 28-дневного цикла). В другой группе, состоящей из 59 пациентов с ММ, на этапе увеличения дозы селинексор давали по 45 или 60 мг/м2 с 20 мг дексаметазона два раза в неделю 28-дневными циклами или селинексор в фиксированной дозе (40 или 60 мг) без кортикостероидов 21-дневными циклами.
Выяснилось, что наиболее частыми негематологическими нежелательными явлениями (НЯ) были тошнота (75%), утомляемость (70%), анорексия (64%), рвота (43%), потеря массы тела (32%) и диарея (32%), но в основном они были 1 или 2 степени тяжести. Наиболее распространенными НЯ 3-й или 4-й степени тяжести были гематологические, в частности тромбоцитопения (45%). Комбинация селинексор+дексаметазон продемонстрировала снижение степени тяжести тошноты и незначительную потерю веса по сравнению с приемом только селинексора.
При назначении селинексора в монорежиме частота общего ответа (ЧОО) составила 4%, а клинический ответ – 21%. Напротив, добавление дексаметазона увеличило ЧОО, при этом в группе пациентов, принимавших селинексор в дозе 45 мг/м2 плюс дексаметазон в дозе 20 мг два раза в неделю, ЧОО выросла до 50%, (в основном ≥частичный ответ). Кроме того, у 46% пациентов наблюдалось снижение уровня большинства маркеров ММ по сравнению с исходным уровнем [22]. Основываясь на этих результатах, авторы пришли к выводу, что селинексор в комбинации с дексаметазоном более эффективен в сравнении с монорежимом у больных ММ, получавших ранее интенсивную терапию, а рекомендуемая доза его равна 45 мг/м2 (80 мг) плюс дексаметазон в дозе 20 мг, которые назначаются два раза в неделю.
Эффективность применения селинексора в сочетании с низкими дозами дексаметазона у пациентов с ММ была хорошо документирована в многоцентровом открытом исследовании фазы 2b STORM (NCT02336815), проходившем с мая 2015 по март 2018 г. в 60 центрах США и Европы. Больные, вошедшие в исследование, ранее получали леналидомид, помалидомид, бортезомиб, карфилзомиб и дара-тумумаб. Перед включением в исследование у них установлена рефрактерность к предшествующему лечению бортезомибом, карфилзомибом, леналидомидом и помалидомидом (четверная рефрак-терность – квадро-рефрактерность: quad-refractory disease) или дополнительно к этому резистентность к терапии моноклональными антителами к CD38 [пента-рефрактерность (рефрактерность к пяти препаратам) - penta-refractory disease]. То есть в исследование были включены тяжело предле- ченные больные с накопленной медикаментозной токсичностью, с ограниченными резервами костномозгового кроветворения и часто декомпенсированные сопутствующими заболеваниями.
Именно, основываясь на результатах клинического исследования STORM, Управление по контролю за продуктами и лекарствами США (US FDA) в июле 2019 г. одобрило применение селинексора в сочетании с дексаметазоном у пациентов с РРММ, которые получили не менее четырех предшествующих линий терапии и рефрактерных к не менее чем двум ингибиторам протеасомы (ИП), не менее чем двум иммуномодуляторам (IMiD) и анти-CD38 моноклональным антителам (пента-рефрактер-ность) [23]. Аналогичны рекомендации европейского медицинского агентства (EMA) – селинексор в комбинации с дексаметазоном показан взрослым пациентам с ММ, получившим минимум 4 предшествующих линии терапии, с прогрессированием заболевания и имеющим рефрактерное заболевание, включающее по крайней мере 2 ингибитора про-теасомы, 2 иммуномодулятора и моноклональные антитела к CD38 [24].
В связи с этим, разберем результаты этого исследования более подробно.
Исследование STORM (Selinexor Treatment of Refractory Myeloma) состояло из двух частей: в 1 часть исследования были рекрутированы 79 больных ММ. Пациенты, вошедшие в исследование (Ме возраста – 63 года), ранее проходили лечение по крайней мере тремя противомиеломными препаратами, включая алкилирующие препараты, глюкокортикоиды, бортезомиб, карфилзомиб, леналидомид и помалидомид [19]. Пациенты должны были иметь рефрактерность (определяемую как менее чем 25%-ный ответ на терапию или прогрессирование заболевания в ходе лечения или в течение 60 дней после завершения терапии) к последней линии терапии и быть рефрактерными к бортезоми-бу, карфилзомибу, леналидомиду и помалидомиду по отдельности или к их комбинации. Кроме того, была включена подгруппа пациентов с заболеванием, резистентным к моноклональным антителам против CD38 (даратумумаб – 15 больных, изатукси-маб – 10 больных).
Пациенты ранее получили 7 линий (Ме: медиана) терапии (диапазон 3-17) и были резистентными к последней линии терапии. Все пациенты получали терапию глюкокортикоидами, 97% – алкилирующими агентами, 41% – антрациклинами и 77% больных находились в рецидиве после выполненной Ау-тоТГСК. Из 79 больных, включенных в исследование, у 48 установлена квадро-, а у 31 – пента-рефрактер-ность. У трех пациентов была выявлена резистентность только к леналидомиду или помалидомиду, у шести пациентов – к карфилзомибу или бортезоми-бу и у четырех пациентов – к карфилзомибу или бор-тезомибу и леналидомиду или помалидомиду.
Основной целью исследования была оценка общей частоты ответа на лечение (ЧОО). Вторичными точками были продолжительность ответа, выживаемость, свободная от прогрессии (PFS), общая выживаемость (OS) и профиль безопасности.
Селинексор назначался перорально в дозе 80 мг два раза в неделю в дни 1, 3, 8, 10, 15 и 17 (шесть доз) каждого 28-дневного цикла, а дексаметазон перорально по 20 мг в день приема селинексора. Доза и режим приема были выбраны на основе данных исследования I фазы. После того, как первые 23 пациента начали лечение, было отмечено, что многие из них соответствовали клиническим и лабораторным критериям, позволяющим продолжить прием препарата до 4-й недель в 1-м цикле. Поэтому протокол был изменен таким образом, чтобы обеспечить непрерывный прием селинексора и дексаметазона два раза в неделю в дни 1, 3, 8, 10, 15, 17, 22 и 24 каждого 28-дневного цикла (восемь доз). Для пациентов, по крайней мере со стабильным течением заболевания и хорошей переносимостью лечения, дозу селинексора увеличивали до 100 мг два раза в неделю. Все пациенты должны были получать 8 мг ондансетрона (или его эквивалента) перед первой дозой исследуемого препарата и два или три раза в день при необходимости. Пациентам также разрешалось назначать другие противорвотные средства, стимуляторы аппетита, гемопоэтические факторы роста, агонисты рецепторов тромбопоэти-на (элтромбопаг или ромиплостим) и добавки хлорида натрия по мере необходимости.
ЧОО составила 21% (95% доверительный интервал – CI: 13-31), в том числе у 5% пациентов достигнут очень хороший частичный ответ (охЧО) и у 15% частичный ответ (ЧО), еще у 13% пациентов зарегистрирован минимальный ответ (МО). Стабилизация наблюдалось у 35% пациентов, при этом медиана продолжительности стабильного течения заболевания составила 2,0 мес. (диапазон 0,9-7,6). Следует отметить, что ответная реакция на лечение была быстрой: 22 (85%) из 26 пациентов достигли ≥МО в течение первого цикла лечения. Медиана продолжительности ответа у пациентов с ЧО или выше составила 5 мес., при этом по крайней мере один ответ продолжался 8,4 мес. Обращала на себя внимание величина ЧОО у пациентов с квадро- и пента-реф-рактерностью – 21% и 20%, то есть сходные значения. ЧОО у 17 пациентов с цитогенетическими аномалиями высокого риска составила 35%, а среди 12 пациентов с делецией 17p был получен один охЧО и два ЧО (ЧОО= 25%).
Медиана беспрогрессивной и OS составили 2,3 и 9,3 мес. соответственно (рис. 1). Пациенты, достигшие ЧО или хотя бы МО, имели значительно лучшую общую выживаемость, чем пациенты со стабильным или прогрессирующим течением заболевания (медиана не достигнута vs 7,2 мес. соответственно; P = 0,01).
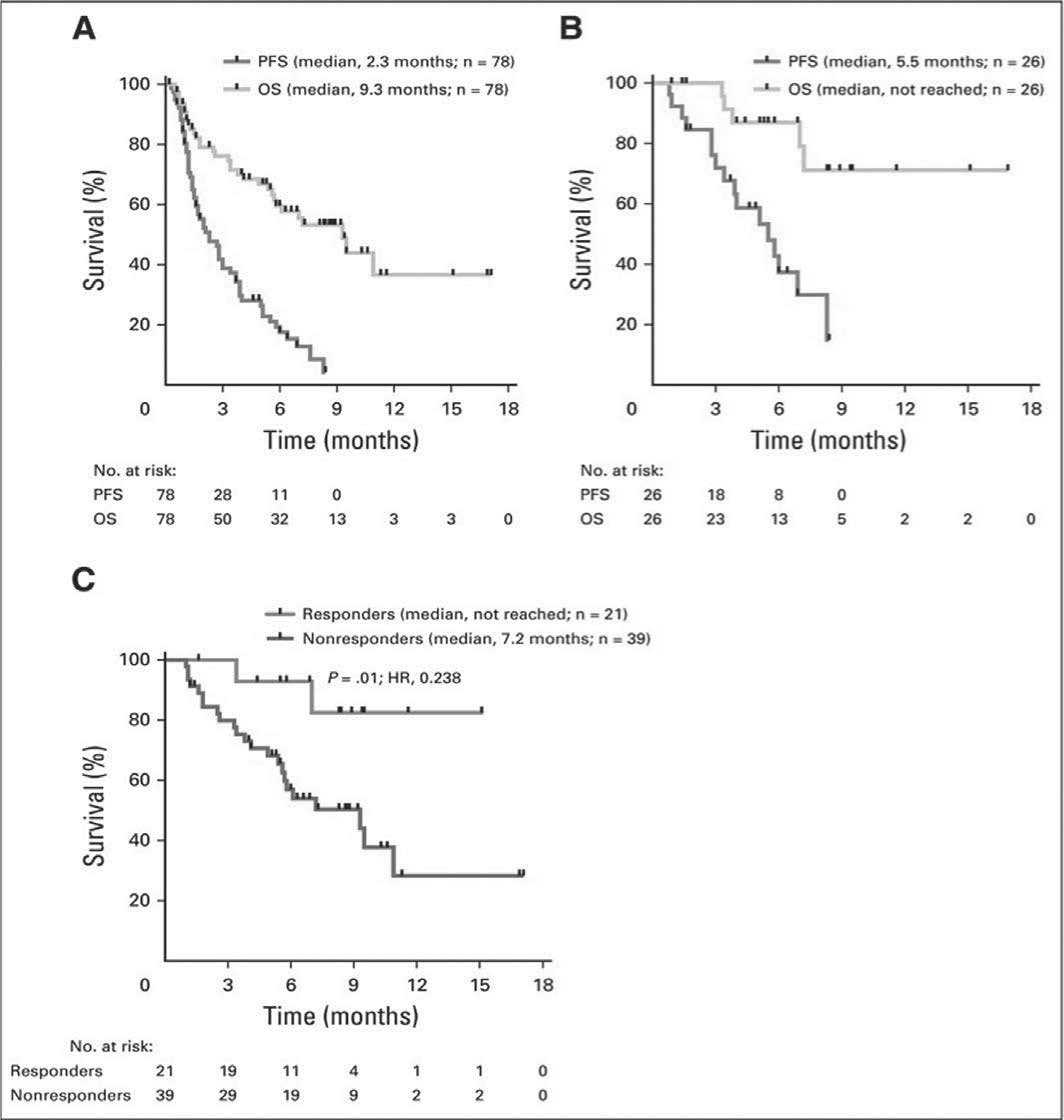
Рисунок 1. Анализ беспрогрессивной (PFS) и общей выживаемости (OS) для (A) всех больных и (B) больных, достигших хотя бы минимального ответа. (C) сравнительный анализ OS между пациентами с минимальным ответом или лучше и без него, которые были живы и поддавались оценке на предмет ответа через 1 месяц.
Примечание . PFS – беспрогрессивная выживаемость, OS – общая выживаемость, Responders – ответившие, Nonresponders – не ответившие
Установлено, что частыми негематологическими НЯ, связанными с лечением, были тошнота (73%), анорексия (49%), повышенная утомляемость (63%), рвота (44%) и диарея (43%), но, как и в исследовании I фазы, главным образом, они были представлены 1-й или 2-й степенью тяжести. Гораздо реже встречалась 3-й и 4-й степень тяжести: повышенная утомляемость (15%), тошнота (8%) и диарея (5%). Гипонатриемия 3-й степени отмечалась у 22% пациентов, но, как правило, протекала бессимптомно и была обратимой. Среди наиболее частых гематологических НЯ 3-й или 4-й степени были тромбоцитопения (59%), анемия (28%) и нейтропения (23%). Кровоточивость ≥ 3-й степени наблюдалась лишь у двух пациентов (3%). Фебрильная нейтропения выявлена у одного пациента, а инфекция ≥ 3 степени тяжести – у 14 пациентов. Не найдено значимых различий в токсических проявлениях у пациентов, получивших шесть или восемь доз селинексора за цикл лечения.
В связи с нежелательными явлениями 41 пациенту (52%) потребовались перерывы в приеме соответствующей дозы препарата, а снижение дозы произошло у 29 пациентов (37%). Лечение прекратили 14 пациентов (18%). Обращало на себя внимание, что все же большему числу пациентов в группе, получавшей восемь доз селинексора, потребовалось снижение дозы или перерывы в 1-м цикле (71%), чем пациентам в группе, получившей шесть доз (43%). Три пациента, у которых после первого цикла состояние по крайней мере стабилизировалось и не было побочных эффектов, ограничивающих дозу, получали увеличенную дозу селинексора до 100 мг два раза в неделю. Однако более высокая доза неизменно сопровождалась усилением побочных эффектов, и всем трем пациентам потребовалось прервать прием или уменьшить дозу.
Таким образом, данные исследования показывают, что комбинация селинексора с низкими дозами дексаметазона эффективна у пациентов с ММ, тяжело предлеченных, резистентных ко всем наиболее часто используемым терапевтическим средствам. В это проспективное исследование 2b фазы были включены пациенты с медианой предшествующих линий терапии 7, резистентные как к ингибиторам протеасом, так и к иммуномодуляторам, а также к алкилирующим препаратам и кортикостероидам. Относительно короткий период с момента постановки диагноза в сочетании с квадро- и пента-рефрактерным статусом позволяет предположить, что у этой популяции больных была особенно агрессивная миелома. Важным с практической точки зрения является то, что селинексор проявлял сходную активность независимо от предшествующего лечения (в том числе антителами к CD38) и цитогенетического риска. Ответная реакция на селинексор и низкие дозы дексаметазона была клинически значимой и ассоциировалась с улучшением общей выживаемости по сравнению с историческим контролем.
Селинексор является первым противомиелом-ным препаратом, который продемонстрировал явную активность при пента-рефрактерной миеломе – группе пациентов с высокой неудовлетворенной потребностью в медицинской помощи. Хотя наблюдаемый общий уровень ответа в 21% не был статистически значимо выше, чем установленный в исследовании порог в 15%, этого доказательства эффективности достаточно для проведения дальнейших исследований. Оглядываясь назад, можно сказать, что пороговый уровень ответа в 10% был бы более подходящим. И, тем не менее, наблюдаемая частота ответа выгодно отличалась от более низкой частоты ответа на однократное применение дексаметазона или анти-CD38 моноклонального антитела даратумумаба в подгруппе пациентов с квадро-рефрактерной миеломой в исследовании 2 фазы [25]. Приведенные выше данные бесспорно свидетельствуют о том, что дуплет селинексор+дексаметазон становится новым методом лечения пациентов с рефрактерной миеломой.
Комбинация селинексора с дексаметазоном имеет патогенетическое обоснование и связана с более высокой частотой ответа по сравнению с монотерапией селинексором. Ингибируя XPO1, селинексор усиливает удержание в ядрах и функциональную активацию важнейших белков-супрессоров опухолей и ограничивает трансляцию мРНК онкобелков, что приводит к апоптозу злокачественных клеток. Оправдалось предположение о том, что этот новый механизм действия будет основой для дополнения селинексором существующих методов лечения миеломы, а также других новообразований. Селинексор усиливает опосредованную глюкокортикоидами активацию глюкокортикоидного рецептора, что приводит к усилению опосредованной глюкокортикоидами транскрипции и индукции апоптоза в клетках миеломы, в том числе в клетках, ранее резистентных к глюкокортикоидам [26]. В исследовании I фазы, в котором участвовали пациенты с миеломой, получавшие интенсивное предварительное лечение, добавление дексаметазона увеличило частоту ответа на селинексор (в различных дозах) с 4% до 50% [22]. Эффективность однократного применения дексаметазона при миеломе, предварительно подвергнутой интенсивному лечебному воздействию, низкая; при однократном применении дексаметазона в трехкратно большей дозе (40 мг/сут в дни с 1 по 4, с 9 по 12 и с 17 по 20 дни 28-дневного цикла) у тяжело предлеченных больных ММ, не получавших помалидомид, частота ответа составила 10%, а в подгруппе пациентов, рефрактерных как к бортезомибу, так и к леналидомиду, только 6% [7]. Таким образом, маловероятно, что наблюдаемые в исследовании STORM ответные реакции являются результатом применения только дексаметазона.
Профиль побочных эффектов схемы селинексор+дексаметазон включает тошноту, анорексию, повышенную утомляемость, тромбоцитопению, гипонатриемию и анемию. Эти побочные эффекты аналогичны тем, которые наблюдались при терапии селинексором у пациентов с другими гематологическими злокачественными новообразованиями, ранее подвергавшимися интенсивному лечению, хотя цитопения менее распространена у пациентов с солидными опухолями [27,28]. Более половины пациентов, участвовавших в исследовании, нуждались в прерывании лечения или снижении дозы из-за токсичности. Тем не менее, поддерживающая терапия была прекращена из-за токсичности лишь у 18% пациентов. Эффективная сопроводительная терапия, рекомендуемая пациентам, получающим селинексор, включает профилактические дозы противорвотных средств и, при необходимости, добавки хлорида натрия и гемопоэтические факторы роста. Не наблюдалось увеличения токсичности при применении восьми доз селинексора в течение каждого 28-дневного цикла по сравнению с шестью дозами, поэтому расширенный режим дозирования обеспечивает надлежащий баланс между максимальной интенсивностью дозирования, возможностью индивидуального прерывания приема препарата и уменьшения его дозы по мере необходимости.
На основании сформулированных выводов части 1 исследования STORM, режим селинексор 80 мг и дексаметазоном 20 мг 1, 3, 8, 10, 15, 17, 22 и 24 день каждого 28-дневного цикла был рекомендован для продолжения исследования.
Во 2 части исследования STORM была изучена активность селинексора в более однородной популяции больных [29]. Пациенты, вошедшие в исследование, как и в 1 части исследования, ранее получали лечение бортезомибом, карфилзомибом, леналидомидом, помалидомидом, даратумумабом (предшествующее воздействие пятью препаратами (penta-exposed), а также глюкокортикоидами и алкилирующими препаратами. Медиана числа предшествующих линий терапии составила 7 (диапазон 3-18); 86 (70%) пациентов ранее получали даратумумаб в комбинации с другими препаратами, 102 (84%) перенесли АутоТГСК и 2 (2%) получали Т-клетки с химерным антигенным рецептором (CAR-T терапию). У всех пациентов была верифицирована ММ, резистентная по крайней мере к одному иммуномодулирующему препарату, одному из ингибиторов протеасомы, даратумумабу, глюкокортикоидам, а также рефрактерность к трем классам препаратов (triple-class refractory myeloma – тройная рефрактерность). В общей сложности у 83 пациентов (68%) была диагностирована пента-реф-рактерность. Примечательно, что у 96% пациентов была миелома, резистентная к наиболее мощным препаратам каждого класса: карфилзомибу, пома-лидомиду и даратумумабу.
Рефрактерное заболевание, также как и в 1 части исследования, определялось как прогрессирование во время лечения или в течение 60 дней после завершения терапии, или как ответ на терапию менее чем на 25%. Селинексор назначался по 80 мг в комбинации с дексаметазоном (20 мг) в 1-й и 3-й дни, еженедельно, 4-недельными циклами до прогрессирования заболевания, летального исхода или прекращения лечения. Модификация дозы препаратов выполнялась с целью контроля НЯ. Медиана продолжительности лечения селинексором в сочетании с дексаметазоном составила 9,0 недель (диапазоне 1-60).
Всего было рекрутировано 123 пациента, но один пациент не соответствовал всем критериям включения (ранее не получал карфилзомиб); таким образом, 122 пациента вошли в измененную выборку пациентов, планирующих лечение. Медиана (Ме) возраста составила 65,2 года, а Ме продолжительности ММ – 6,6 года; 53% пациентов имели цитогенетические аномалии высокого риска (del17p, t(4;14), t(14;16), 1q21). Клиренс креатинина менее 60 мл в минуту выявлен у 39 пациентов (32%) и менее 40 мл в минуту – у 14 пациентов (11%).
По результатам исследования, частичный ответ или лучше наблюдался у 26% пациентов (95%CI: 19-35), в том числе 2 полных ответа (2%), 6 – охЧО (5%) и 24 – ЧО (20%). Даже у обоих пациентов с рецидивом после CAR-T терапии был получен частичный ответ. Минимальный ответ наблюдался у 16 пациентов (13%), а у 48 пациентов (39%) заболевание расценивалось как стабильное, в то же время у 26 (21%) миелома прогрессировала или не поддавалась оценке на предмет ответа. Медиана времени до достижения ЧО или клинического улучшения составила 4,1 недели (диапазон 1–14). Минимальный ответ или выше наблюдался у 39% пациентов (95%CI: 3-49). Медиана продолжительности достигнутого ответа составила 4,4 мес. (95% CI: 3,7-10,8). Медиана PFS равнялась 3,7 мес. (95% CI: 3,0-5,3), а медиана OS (mOS) – 8,6 мес. (95% CI: 6,2-11,3) (рис. 2А и 2B). У пациентов, у которых был получен ≥ЧО или ≥МО, медиана общей выживаемости составила 15,6 месяцев (рис. 2С).
Наиболее частыми НЯ, возникшими во время лечения, были тромбоцитопения (73%), повышенная утомляемость (73%), тошнота (72%) и анемия (67%). НЯ 3 или 4 степени тяжести характеризовались развитием тромбоцитопении (59%), анемии (44%), гипонатриемии (22%) и нейтропении (21%). Тромбоцитопения чаще возникала у пациентов, у которых она выявлялась исходно, чем у тех, у кого ее не было. У шести пациентов с тромбоцитопенией 3-й степени и выше было сопутствующее кровотечение. Большинство негематологических НЯ были ограничены 1-й или 2-й степенью тяжести и только
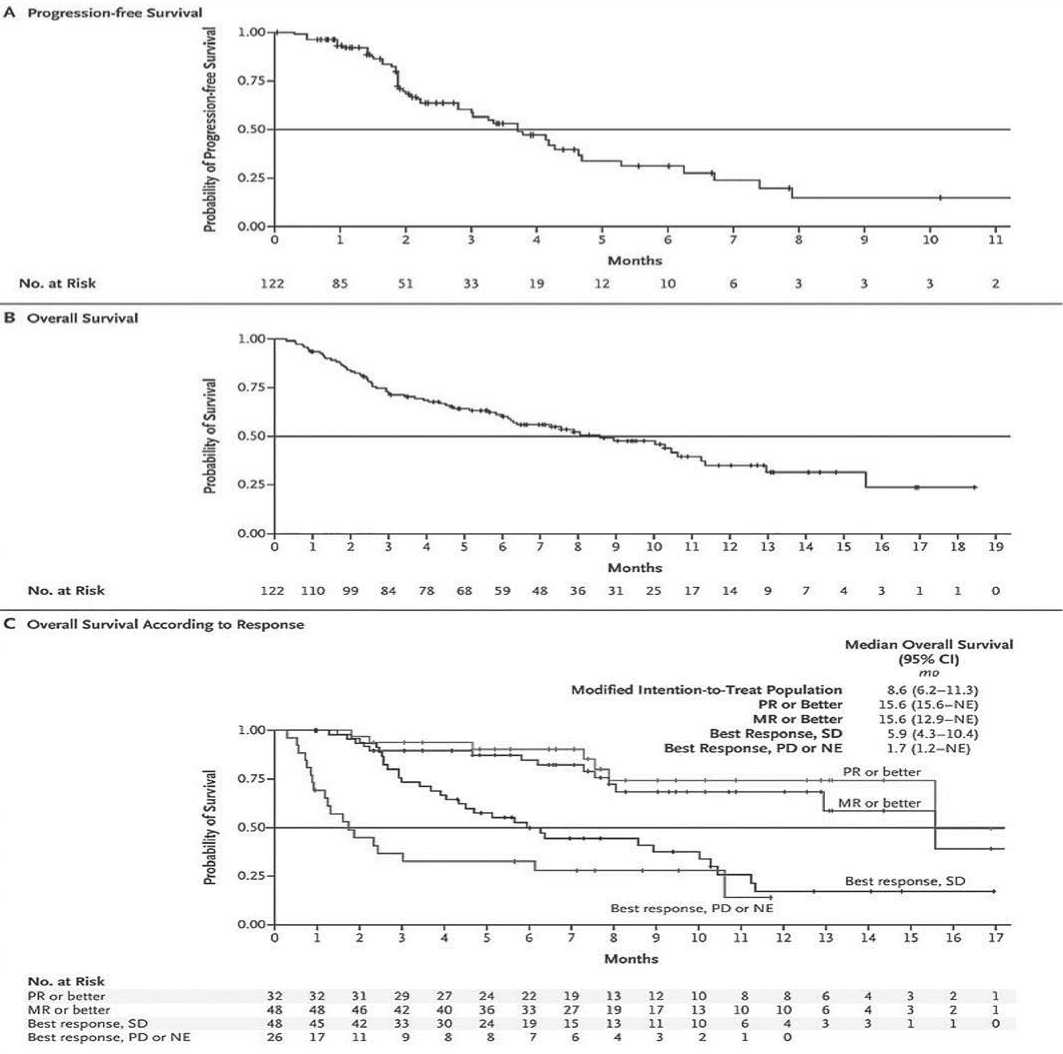
Рисунок 2. Беспрогрессивная выживаемость (А), общая выживаемость (В) и общая выживаемость с учетом глубины достигнутого ответа (С) (Progression-free Survival, Overall Survival, and Overall Survival According to Response).
Примечание . PR or Better - частичный ответ или лучше, MR or Better – минимальный ответ или лучше, SD – стабилизация, PD - прогрессия
у 10% пациентов наблюдалась тошнота 3-й степени и у 3% – рвота 3-й степени тяжести.
Побочные эффекты, приведшие к изменению дозы или прерыванию приема препарата, наблюдались у 80% пациентов, причем большинство из них приходилось на первые два цикла. Наиболее частыми НЯ, приводившими к снижению дозы или ее отмене, были тромбоцитопения (у 43% пациентов), утомляемость (у 16%) и нейтропения (у 11%). Сопроводительная терапия, включающая гранулоцитарный колониестимулирующий фактор, агонисты рецепторов тромбопоэтина, соответствующее потребление жидкости и калорий, стимуляторы аппетита, психостимуляторы и дополнительные противосудорожные средства, обычно уменьшала интенсивность или продолжительность побочных эффектов. Все побочные эффекты были обратимыми, без признаков токсического воздействия на основные органы (связанная с лечением сердечная, легочная, печеночная или почечная дисфункция 3-й степени или выше) или кумулятивных токсических эффектов, лишь у одного пациента (1%) было зарегистрировано необратимое острое повреждение почек.
Наиболее распространенными серьезными побочными эффектами были пневмония (11%) и сепсис (9%). В ходе исследования в общей сложности 28 пациентов умерли (16 от прогрессирования заболевания и 12 от нежелательных явлений). Среди 12 пациентов с этими нежелательными явлениями, 2 события были оценены исследователем как связанные с лечением (пневмония с сопутствующим прогрессированием заболевания [у 1 пациента] и сепсис [у 1 пациента]).
Результаты исследования STORM примечательны по нескольким причинам. Исследование носило разрешительный характер и позволяло регистрироваться пациентам со сниженной функцией почек, тромбоцитопенией и нейтропенией. Это пациенты после нескольких циклов интенсивного предшествующего лечения (Ме 7), включающего в целом 10 (Ме) уникальных противомиеломных препаратов. У пациентов на момент начала терапии было верифицировано быстро прогрессирующее течение ММ, а за 12 дней от скрининга до начала терапии тяжесть заболевания увеличилась на 22%.
Такие характеристики согласуются с ежедневной клинической практикой. В настоящее время наблюдается отчетливый рост числа пациентов с ММ, у которых исчерпаны все доступные методы лечения, но эти пациенты все еще хотят продолжать терапию. Учитывая быстрое прогрессирование рефрактерной миеломы с предшествующим применением 5 препаратов и тройную рефрактер-ность, шансы предотвратить дальнейшее развитие заболевания и летальный исход невелики. Поэтому в исследовании STORM для достижения быстрого контроля над заболеванием была начата терапия высокими дозами селинексора. Поскольку большинство пациентов, участвовавших в исследовании, были пожилыми и слабыми, с ограниченным резервом функций конечных органов и повышенным риском развития побочных эффектов, предполагалось изменение дозы при необходимости наряду с обязательной сопроводительной терапией. Побочные эффекты, которые наблюдались в ходе исследования, зависели от дозы, режима приема и исходных клинических характеристик (например, цитопении). Тромбоцитопения, которая частично обусловлена ингибированием селинексором передачи сигналов тромбопоэтина на ранних стадиях мегакариопоэза, была обратимой и купировалась снижением дозы и применением агонистов рецепторов тромбопоэтина.
Очевидные преимущества двойной комбинации селинексор+дексаметазон над стандартной терапией продемонстрированы в ретроспективном исследовании "Моноклональные антитела при множественной миеломе: результаты после неудачной терапии" (MAMMOTH). Это исследование было разработано для изучения течения и исходов ММ у пациентов с РРММ после того, как они стали невосприимчивы к анти-CD38 моноклональным антителам, и включало подгруппу пациентов с тройной рефрактерностью; пациенты проходили лечение в академических центрах, получали стандартную терапию, но не получали комбинация селинексор+дексаметазон. В настоящем анализе массив данных MAMMOTH был использован для создания когорты пациентов, похожих по основным характеристикам на пациентов в исследовании STORM. Цель исследования – сравнить показатели OS и ЧОО у пациентов, получавших стандартное лечение в исследовании MAMMOTH и двойную комбинацию селинексор+дексаметазон в исследовании STORM [30]. Отобрано 128 из 275 пациентов, которые соответствовали критериям включения в STORM. У пациентов, вошедших в исследование STORM, было больше времени между постановкой диагноза ММ и назначением терапии, а также большая доля пациентов, резистентных к карфилзоми-бу и в целом ко всем методам лечения, содержащих карфилзомиб, помалидомид и даратумумаб. В исследовании STORM после прекращения терапии пациенты продолжали наблюдаться для расчета в последующем OS. При косвенном сравнении основных результатов в этих двух исследованиях, получено следующее. У пациентов в исследовании STORM общая выживаемость была лучше, чем у пациентов в исследовании MAMMOTH; медиана 10,4 мес. (95%CI: 7,9 – не поддается оценке) против 6,9 мес. (95% CI: 5,3-8,6); P = 0,043 (рисунок 3).
При многофакторном анализе пациенты в исследовании STORM имели более низкий риск смерти по сравнению с пациентами в исследовании MAMMOTH [скорректированное отношение рисков = 0,55; Р = 0,009]. ЧОО составила 32,8% (21 из 64 пациентов) в STORM по сравнению с 25,0% (32 из 128 пациентов) в MAMMOTH (P = 0,078). У пациентов с высоким цитогенетическим риском (включая p53, del17p, t[4;14], t[14;16], del 13) показатель ЧОО составил 21,9% (7/32 пациентов) в группе STORM и 24,6% (16/65 пациентов) в группе MAMMOTH (Р = 0,96). Для пациентов, рефрактерных к карфилзо-мибу, помалидомиду и даратумумабу, ЧОО по результатам STORM была выше, чем в исследовании MAMMOTH и составила 33,3% (20/60 пациентов) и 26,0% (27/104 пациентов) соответственно. Традиционными стратегиями повторного лечения в MAMMOTH были препараты, которые пациенты
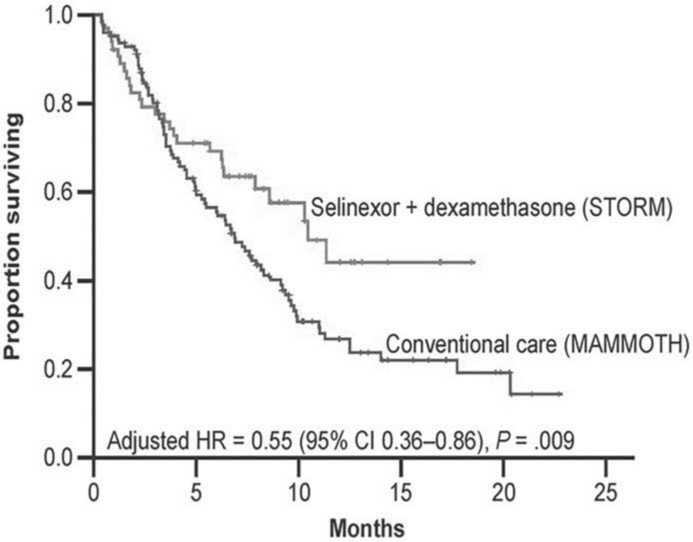
Рисунок 3. Общая выживаемость больных ММ с тройной рефрактерностью, получавших селинексор+дексаметазон в исследовании STORM vs стандартная терапия в исследовании MAMMOTH.
Примечание . CI – доверительный интервал; HR – отношение рисков
получали ранее; во многих случаях была подтверждена резистентность к этим препаратам. Между тем, результаты исследования STORM свидетельствуют о том, что схема селинексор+дексаметазон представляет собой терапию без перекрестной резистентности, которую можно использовать до прогрессии заболевания. Растущая частота развития мультирезистентной ММ у пациентов, связанная с ранним началом лечения несколькими классами препаратов, включая новые препараты, такие как даратумумаб и другие моноклональные антитела, подчеркивает важность выбора подходящего метода лечения на ранних стадиях ММ [3,12,31,32].
Аналогичный анализ с сопоставимой популяцией реальных пациентов, получавших доступную терапию (кроме комбинации селинексор+дексаметазон) (аналитическая база данных Flatiron Health (FHAD; n = 37)), показал, что если mOS в группах больных исследования STORM составила 10,4 мес., то по данным анализа FHAD – 5,2 мес., т.е. в 2 раза меньше (P = 0,024) [33]. Эти данные вполне сопоставимы с анализом в исследовании MAMMOTH. Возможными причинами улучшения выживаемости, наблюдаемого при применении селинексора, являются использование поддерживающей терапии (терапия проводилась до прогрессии), короткий период полувыведения селинексора и снижение степени и частоты НЯ, возникающих при лечении, после прекращения лечения.
По результатам китайского исследования MARCH (2 фаза), эффективность применения селинексора и дексаметазона у пациентов с РРММ в Китае была сопоставима с таковой исследования STORM, а именно: ЧОО – 26,7%, медиана продолжительности достигнутого ответа – 4,6 мес., медиана PFS – 3,7 мес., а медиана OS не достигнута. Показатель 9-месячной выживаемости 68,5% [34]. Исследование MARCH продемонстрировало значимую клиническую пользу селинексора в сочетании с низкими дозами дексаметазона среди китайских пациентов с РРММ, в том числе у пациентов с тройной рефрактерностью и, таким образом, подтвердило результаты исследования STORM. Наблюдаемые НЯ были ожидаемыми и поддавались лечению при сопроводительной терапии и изменении дозы селинексора.
Таким образом, вышеизложенные данные убедительно свидетельствуют о доказанной противомие-ломной эффективности селинексора в сочетании с дексаметазоном, у тяжело предлеченных пациентов с рефрактерностью к ингибиторам протеасомы, иммуномодулирующим агентам и анти-CD38 моноклональным антителам. Преимущество данного дуплета над стандартными методами лечения подтверждено результатами из реальной клинической практики.
В настоящее время все большее внимание обращается на триплеты, которые как показывает растущее число исследований, в большинстве сво- ем обладают преимуществом. Доклинические исследования селинексора выявили его синергизм с ингибиторами протеасом, аддитивность к иммуномодулирующим препаратам и сенсибилизацию клеток миеломы к моноклональным антителам против CD38 Полученные результаты стали основанием для проведения клинических исследований, оценивающих эффективность и безопасность се-линексора в комбинированных схемах (триплетах), содержащих указанные препараты.
STOMP (Selinexor and Backbone Treatments of Multiple Myeloma Patients) — это исследование фазы 1b/2, в котором оценивалась эффективность и безопасность селинексора и низких доз дексаметазона в комбинации с одним из нескольких одобренных ранее препаратов (бортезомиб, помалидомид, леналидомид, карфилзомиб, даратумумаб и др.) у пациентов с РРММ. Кроме того, в 2018 году в это исследование было добавлено новое направление – изучение комбинации селинексора и леналидомида у впервые выявленных пациентов с множественной миеломой.
В одном из направлений исследования STOMP (NCT02343042) изучался триплет SPd (селинексор/ помалидомид/дексаметазон). Целями исследования было определение максимально переносимой дозы селинексора и рекомендуемой дозы в этом триплете для 2-й фазы (RP2D), а также оценка безопасности и активности режима SPd, в том числе у пациентов, получающих RP2D. Селинексор назначали в дозе 60, 80 или 100 мг внутрь или 60 или 80 мг два раза в неделю в сочетании с Pd (помалидомид/ дексаметазон). Шестьдесят пять пациентов с РРММ (Ме возраста 64 года; диапазон 37-85 лет) были включены в исследование после 3-х (диапазон 1-10) предыдущих линий терапии [35].
В исследовании RP2D для селинексора установлена на уровне 60 мг, помалидомид назначался в дозе 4 мг и дексаметазон 40 мг. Наиболее частые гематологические НЯ, связанные с лечением (при использовании различных доз препарата), включали (все степени тяжести, степень ≥3) нейтропению (63%, 55%), анемию (58%, 32%) и тромбоцитопению (54%, 31%). Среди негематологических НЯ исследователи отметили тошноту (62%, 2%), усталость (55%, 11%) и снижение аппетита (45%, 2%). В группе помалидомид-наивных или не рефрактерных (n = 44) пациентов ЧОО составила 57% (1 – сПО: строгий полный ответ, 1 – ПО, 8 – охЧО, 15 – ЧО); медиана беспрогрессивной выживаемости (mPFS) составила 12,2 мес. У пациентов, получавших RP2D (n = 20), показатель ЧОО был сходным и равнялся 65% (1 – сПО, 5 – охЧО, 7 – ЧО); mPFS не была достигнута при медиане наблюдения 3,9 мес. У пациентов с резистентностью к помалидомиду и пациентов с предшествующей терапией даратумумабом ЧОО составила 44% (7/16) и 60% (9/15) соответственно. Новых признаков НЯ выявлено не было.
По мнению исследователей, полностью пероральная комбинация селинксор+Pd обладает высокой активностью с ЧОО равной 65% при RP2D (по сравнению с ожидаемым ЧОО≤30% при применении дуплета Pd) и обеспечивает длительный положительный эффект с общей продолжительностью ответа 12,2 месяца.
Двадцать четыре пациента с РРММ были включены в исследование STOMP (NCT02343042) для получения селинексора, дексаметазона и леналидомида [36]. Медиана количества предшествующих линий терапии составила 1,5 (диапазон 1-8). Показатель RP2D был установлен на уровне 60 мг селинексора, 40 мг дексаметазона и 25 мг леналидомида. Что касается исходов, то среди пациентов, не получавших леналидомид (n = 12), ЧОО составила 92%, включая один сПО, четыре охЧО и шесть ЧО. PFS не была достигнута, при этом медиана наблюдения составила 7,8 месяцев. Между тем, у пациентов, ранее получавших леналидомид (n = 8), ЧОО была ниже (13%), что свидетельствует о том, что триплет селинексор– леналидомид-дексаметазон показан пациентам с РРММ, которые ранее не получали леналидомид.
В рамках исследования STOMP (NCT02343042) была проведена оценка применения еще одного триплета – селинексор в комбинации с даратуму-мабом и дексаметазоном (SDd). Рекрутированы 34 пациента с РРММ, которые ранее получили три или более линий терапии (диапазон 2-10), включая ингибиторы протеасом (85%) и иммуномодуляторы (76%), или у которых ММ была резистентна и к ингибиторам протеасом, и к иммуномодуляторам (74%), и у 6% выявлена резистентность к дарату-мумабу [37]. На этапе увеличения дозы селинексора пациенты были распределены на две группы по схеме 3+3, в которых пациенты последовательно распределялись блоками по три человека. После того, как три пациента вошли в группу, получавшую сели-нексор один раз в неделю, следующие три пациента были включены в группу, получавшую селинексор два раза в неделю. Пациенты получали либо сели-нексор 100 мг перорально один раз в неделю в сочетании с дексаметазоном в дозе 40 мг внутривенно (в/в) или внутрь в виде однократной или разделенной дозы в течение 28-дневных циклов, либо сели-нексор 60 мг перорально с дексаметазоном в дозе 40 мг (в/в или перорально) 28-дневными циклами. RP2D для селинексора составила 100 мг еженедельно, даратумумаб 16 мг/кг (еженедельно в течение 1-8 недели, каждые 2 недели в течение 9–24 недели, а затем каждые 4 недели в течение ≥25 недель) и дексаметазон 40 мг еженедельно.
Среди пациентов, у которых оценивался ответ (n = 32), у 11 (34%) был достигнут охЧО, еще у 11 (34%) – ЧО. У четырех (13%) пациентов удалось добиться МО, что в целом привело к повышению объективного ответа до 87% у пациентов, не получавших да-ратумумаб. Необходимо акцентировать внимание на том, что ответная реакция была быстрой: все 25 (100%) пациентов, достигших минимального ответа или более высокого уровня, ответили на лечение в течение первого цикла. Так, из 11 пациентов, достигших охЧО, у четырех (36%) из них ответ наблюдался уже после первого курса лечения. Ме продолжительности наблюдения в этой группе пациентов, эффективность которой можно было оценить (n = 32), составила 12,5 месяцев. В подгруппе из 25 пациентов, получавших селинексор 100 мг и дексаметазон 40 мг еженедельно в сочетании с даратуму-мабом по 16 мг/кг, ЧОО составила 75% (18/24), что превышает установленный минимальный показатель ответа в 60%, требуемый для данной комбинации. У двух пациентов с ММ выявлена рефрактер-ность к даратумумабу. У одного пациента, который был включен в исследование в связи с прогрессией в течение первых 4 недель терапии даратумума-бом, помалидомидом и дексаметазоном, примерно через 1 месяц после первого цикла SDd наступило прогрессирование. Другой пациент, который получал даратумумаб и дексаметазон за 10,9 мес. до включения в исследование, достиг стабилизации заболевания с максимальным снижением уровня M-протеина на 20,6%. Продолжительность ответа составила 11,4 месяца. Медиана PFS у пациентов, не получавших даратумумаб (n = 30), составила 12,5 месяцев. Уровень парапротеина снизился у 29 пациентов (91%), при этом у 22 пациентов (69%) снижение ≥50%, а у 11 (34%) – ≥90%.
Таким образом, комбинация селинексора по 100 мг перорально, дексаметазона по 40 мг и даратуму-маба по 16 мг/кг внутривенно обеспечила глубокий и стойкий эффект у тяжело предлеченных пациентов с РРММ, у 74% из которых была ММ, рефрактерная к ингибиторам протеасомы и иммуномодуляторам.
На следующем этапе в исследование STOMP (NCT02343042) было набрано 32 пациента с РРММ, которым назначен триплет селинексор+карфилзом иб+дексаметазон [38]. В исследование вошли больные с рецидивом/рефрактерностью (но не рефрактерные к карфилзомибу). У 38% больных установлена тройная рефрактерность и у 53% пациентов высокий цитогенетический риск [del(17p), t(4;14), t(14;16) и/или gain 1q]. Максимально переносимая доза (МПД) и доза, рекомендуемая (RPD2D) для се-линексора, составила 80 или 100 мг, карфилзомиба 56 или 70 мг/м2 и дексаметазона 40 мг 1 раз в неделю. На этапе оценки начальная доза селинексора в исследовании составила 100 мг в сутки, карфил-зомиба – 20/56 мг/м2 в сутки и дексаметазона – 40 мг в сутки. Поскольку противоопухолевые эффекты селинексора и карфилзомиба синергичны, а сели-нексор обычно применяют в дозах 60, 80 или 100 мг/сут, а карфилзомиб – в дозах 45-70 мг/м2 еженедельно, оптимизация дозы в комбинации требует модуляции обоих препаратов. Правила оценки уровня дозы и ее снижения соответствовали стандартным правилам 3+3: 1-я группа – три пациента в группе селинексор 100 мг, карфилзомиб 56 мг/м2, 3 пациента в группе селинексор 80 мг, карфилзомиб 70 мг/м2, 18 пациентов в группе селинексор 80 мг, карфилзомиб 56 мг/м2, 3 пациента в группе сели-нексор 60 мг в сочетании с карфилзомибом в дозе 70 мг/м2, и 2-я и 3-я группы – селинексор в дозе 60 мг в сочетании с карфилзомибом в дозе 56 или 70 мг/м2 соответственно, в которых селинексор назначался в 1, 8 и 15-й дни, но не на 22-й день 4-недельного цикла
Частота общего ответа, по результатам исследования, составила 78%, включая 44% ≥охЧО: 2 (6,3%) – сПО, 3 (9,4%) – ПО, 9 (28,1%) – охЧО и 11 (34,4%) – ЧО. В целом медиана беспрогрессивной выживаемости составила 15 мес. (Ме наблюдения 8,0 мес.), медиана продолжительности ответа – 22,7 мес., а mOS не была достигнута (Ме наблюдения – 15,1 мес.). У девяти пациентов, ранее получавших менее 2-х линий терапии, ЧОО составила 88,9%.
У пациентов с тройной рефрактерностью (n = 12) ЧОО составила 66,7% (8/12), медиана PFS – 23,7 мес., медиана продолжительности ответа – 22,7 мес., а mOS – 20,4 мес. Наличие генетических факторов высокого риска при первоначальной диагностике не повлияло на эффективность лечения: у 17 пациентов с цитогенетическими факторами высокого риска ЧОО составила 82,4% (14/17), медиана PFS – 15,0 мес., медиана продолжительности ответа – 22,7 мес., а mOS не была достигнута.
Были протестированы два уровня доз: селинек-сор в дозе 100 мг с карфилзомибом в дозе 56 мг/м2 и селинексор в дозе 80 мг с карфилзомибом в дозе 70 мг/м2, оба с дексаметазоном в дозе 40 мг. Однако следующий более низкий уровень – селинексор в дозе 80 мг, карфилзомиб в дозе 56 мг/м2 и дексаметазон в дозе 40 мг – был идентифицирован как максимально переносимая доза и определен в качестве RP2D.
По заключению авторов, комбинация селинек-сора 80 мг перорально, дексаметазона 40 мг и кар-филзомиба 56 мг/м2 внутривенно обеспечила более глубокий и стойкий эффект у пациентов с РРММ, ранее получавших интенсивную терапию, у 37,5% которых была тройная рефрактерность, а у 53,1% – высокий цитогенетический риск.
У двух из первых трех пациентов, включенных в группу селинексора в дозе 100 мг и карфилзомиба в дозе 56 мг/м2, развилась тромбоцитопения 3-й степени и рвота 3-й степени. Аналогичным образом, у двух из первых трех пациентов, включенных в группу селинексора в дозе 80 мг и карфилзомиба в дозе 70 мг/м2, развилась тромбоцитопения 4 степени + пневмония). У первых трех пациентов, получавших селинексор в дозе 80 мг в сочетании с карфилзоми-бом в дозе 56 мг/м2 и дексаметазоном в дозе 40 мг, не наблюдалось побочных эффектов; еще три паци- ента были включены в эту группу для подтверждения переносимости, и никаких побочных эффектов не наблюдалось; таким образом, этот уровень дозы и график приема были определены как максимально переносимая доза и RP2D для пациентов расширенной фазы.
Еще в одном исследовании 21 пациент с РРММ после 4 предшествующих линий терапии получал селинексор, карфилзомиб, дексаметазон, при этом 95% ранее получали карфилзомиб, а 81% были резистентны к иммуномодуляторам и ингибиторам протеасомы и ранее получали бортезомиб, карфил-зомиб, леналидомид и помалидомид [39]. Показатель RP2D был установлен на уровне 60 мг селинек-сора, карфилзомиба – 20/27 мг/м2 и дексаметазона – 20 мг. ЧОО составила 48%, контроль над опухолевым процессом получен у 71% больных. Показатели ≥ МО, ≥ ЧО и охЧО составили 71%, 48% и 14% соответственно; аналогичные результаты наблюдались у пациентов с двойной рефрактерностью (n = 17) и пациентов, рефрактерных к карфилзомибу в последней линии терапии (n = 13). Медиана выживаемости без прогрессирования заболевания составила 3,7 мес., а общая выживаемость в общей популяции больных – 22,4 мес.
Теперь снова вернемся к очередному этапу исследования STOMP (NCT02343042), в которое были включены 42 пациента с РРММ; все получали сели-нексор, дексаметазон и бортезомиб [40]. Медиана числа предшествующих линий терапии – 3 (диапазон 1-11). 50% пациентов были резистентны к предыдущему лечению ингибиторами протеасомы (бортезомиб, карфилзомиб или иксазомиб), а 45% – как к ингибиторам протеасомы, так и к иммуномодуляторам (леналидомид, помалидомид или талидомид). Больным назначен селинексор 100 мг, бортезомиб 1,3 мг /м2 и дексаметазон 40 мг. В целом по группе больных ЧОО составила 63%. На что обращается внимание в этом исследовании. Ответ зарегистрирован у 84% больных нерефактерных к ингибиторам протесом и у 43% рефрактерных к ним. Медиана PFS в целом по группе составила 9,0 мес.; 17,8 мес. у пациентов нерефактерных к ингибиторам протесомы и 6,1 мес. у рефрактертных.
Гематологические НЯ ≥3 включали тромбоцитопению (50%), нейтропению (26%) и анемию (19%). Клинические последствия этих гематологических осложнений были незначительными, так как кровотечения (5%, оба случая 1 степени тяжести) и фебрильная нейтропения (5%) были редкостью. Негематологические НЯ 3-й степени включали повышенную утомляемость (14%), диарею (7%), тошноту (5%), гипонатриемию (5%), снижение аппетита (2%), спутанность сознания (2%) и рвоту (2%). Не было зарегистрировано случаев реактивации herpes zoster. Во время исследования у шести пациентов была пневмония. Все случаи пневмонии раз- решились после госпитализации. Из 8 пациентов, прервавших лечение из-за НЯ, 5 (12%) были вызваны желудочно-кишечными или конституциональными побочными эффектами (тошнота, анорексия, рвота, повышенная утомляемость), 2 (5%) – сердечными приступами. Периферическая нейропатия зарегистрирована лишь у 4 пациентов (10%): в 2-х случаях 1-й степени и в 2-х случаях 2-й степени. У двух из 4 пациентов при скрининге была выявлена ранее существовавшая нейропатия, связанная с предшествующим применением бортезомиба. Медиана времени до появления симптомов периферической нейропатии составила 12 недель (диапазон 5 – 37). Снижение дозы бортезомиба потребовалось у 2 из этих 4 пациентов.
Полученные явно позитивные результаты 2 фазы исследования применения селинексора при РРММ, явились основанием для проведения 3 фазы клинических исследований.
BOSTON (Bortezomib, Selinexor and dexamethasone, NCT03110562) – это ключевое международное, рандомизированное исследование 3 фазы, посвященное применению селинексора в комбинации с бортезомибом и низкими дозами дексаметазона в сравнении с бортезомибом и низкими дозами дексаметазона у пациентов с множественной миеломой, которые ранее получили от одной до трех линий терапии. В исследование вошли 402 пациента с РРММ, которые были случайным образом распределены для получения бортезомиба, дексаметазона (Vd) +/- селинексор (S) (SVd: 195 пациентов; Vd: 207 пациентов) [41]. Рандомизация была проведена с использованием технологии интерактивного взаимодействия и стратифицирована в зависимости от предшествующего воздействия ингибиторами протеасомы (да vs нет), линий терапии (1 vs 2-3) и стадии ММ (R-ISS; I–II vs III). Больным проводилось лечение по схеме SVd: селинексор один раз в неделю плюс бортезомиб один раз в неделю и 40 мг дексаметазона в сравнении со стандартным приемом бортезомиба два раза в неделю и дексаметазона в умеренных дозах (80 мг/нед) (схема Vd) у пациентов с ММ (соотношение 1:1). Важно отметить, что в группе исследования как селинексор, так и борте-зомиб назначались один раз в неделю, в то время как в контрольной группе бортезомиб вводился по текущей схеме дважды в неделю. Допускался переход на SVd при прогрессировании заболевания на Vd. Медиана числа предшествующих линий терапии составила 2 (диапазон 1-3).
После медианы периода наблюдения, равного 13,2 мес., в группе больных, получавших SVd и 16,5 мес. Vd, медиана PFS оказалась значительно больше в группе SVd (13,93 мес.), чем в группе Vd (9,46 мес.). ЧОО в группе SVd составила 76,4% (против 62,3% в группе Vd) и включала 19 случаев сПО, 14 случаев ПО, 54 случая охЧО и 62 случая ЧО (таблица 1).
Эффективность в группах больных ММ , получавших SVd и VD.
Таблица 1
|
Ответ |
SVd (n=195) |
Vd (n=207) |
p-значение |
|
Частота общего ответа |
|||
|
Число ответивших |
149 |
129 |
|
|
Показатель, % (95% CI) |
76,4 (69,8, 82,2) |
62,3 (55,3, 68,9) |
0,0012* |
|
Ответы, n (%) |
|||
|
Строгий полный ответ |
19 (10) |
13 (6) |
|
|
Полный ответ |
14 (7) |
9 (4) |
|
|
Очень хороший частичный ответ |
54 (28) |
45 (22) |
|
|
Частичный ответ |
62 (32) |
62 (30) |
|
|
Минимальный ответ |
16 (8) |
20 (10) |
|
|
Стабилизация заболевания |
25 (13) |
40 (19) |
|
|
Прогрессия заболевания |
1 (1) |
10 (5) |
|
|
Ответ не может быть оценен |
4 (2) |
8 (4) |
|
|
Отрицательный статус минимальной остаточной болезни† |
9 (5) |
8 (4) |
Примечание . *Рассчитано с использованием теста Кокрана-Мантеля-Хензеля. †Минимальная остаточная болезнь оценивалась у пациентов с строгим полным ответом или полным ответом. Отрицательный статус минимальной остаточной болезни определялся как отсутствие злокачественных клонов на 100000 лейкоцитов.
Медиана длительности достигнутого ответа была более длительной при SVd и составила 20,3 мес., в то время как при применении Vd – 12,9 мес. Кроме того, медиана времени до следующей линии терапии было гораздо больше в группе SVd (16,1 мес.), чем в группе Vd (10,8 мес.). В течение исследования было зарегистрировано 109 смертей (27%), из них 47 в группе SVd (mOS не достигнута) и 62 в группе Vd (mOS составила 25 мес.).
Эффективность была одинаковой в различных подгруппах пациентов, включая пациентов с цитогенетическими аномалиями высокого риска. Так ЧОО была выше для пациентов из группы SVd, чем для Vd, как при высоком (78,6% против 57,7%, Р = 0,0041), так и стандартном риске (75,2% против 64,7%; Р = 0,0329). В подгруппе высокого риска доля пациентов, достигших ≥охЧО, почти в два раза выше для SVd, чем для Vd (30,0% против 18,3%). У пациентов, получавших SVd, как в группах стандартного, так и высокого риска, были более низкие показатели прогрессирования заболевания, чем среди пациентов, получавших Vd (высокий риск, SVd – 0% против Vd – 7,0%; стандартный риск, SVd – 0,8% против Vd – 3,7%).
Результаты у пациентов с del(17p) продемонстрировали значительное увеличение PFS при лечении SVd (12,22 против 5,91 мес.; отношение рисков (HR) 0,38; 95%CI 0,16–086; Р = 0,0080). У пациентов с del(17p), получавших SVd в сравнении с Vd, наблюдалась тенденция к улучшению длительности ответа (14,75 против 6,82 мес.; HR 0,43, 95%
CI 0,13-1,40; Р = 0,08). Интересно, что у пациентов с del (17p) отмечалось улучшение OS при терапии SVd: HR = 0,43 (95% CI 0,16-1,16; Р = 0,04), хотя медианы были сходными. В целом, терапия SVd приводила к улучшению PFS и ЧОО по сравнению с Vd в подгруппах пациентов, определяемых по статусу цитогенетического риска, за исключением t(14;16) и исходных характеристик заболевания, включая количество предшествующих линий терапии, предшествующее лечение леналидомидом (67,5% vs 53,2%) и низкий клиренс креатинина (30–60 мл/мин – 79,2% vs 56,7%). Примечательно, что SVd была значительно эффективнее, чем Vd для пациентов с R-ISS I-II ст.
На конгрессе ASCO 2021 года был представлен последующий анализ этого исследования, в котором сравнивались преимущества в выживаемости у пациентов в возрасте ≥65 лет и <65 лет; у пациентов старше 65 лет mOS не была достигнута при SVd, в то время как при Vd она составила 28,6 мес.; у пациентов моложе 65 лет не было различий в показателях OS [42]. В другом последующем анализе [43] сообщалось об улучшении показателей ЧОО, PFS и времени до следующего лечения в группе с SVd по сравнению с Vd, независимо от документально подтвержденного статуса рефрактерности к леналидомиду или любым другим иммуномодуляторам.
Результаты клинического исследование 3-й фазы BOSTON, привели к одобрению Европейскими и Американскими регулирующими органами триплета SVd для лечения больных с РРММ, которые получили 1-3 линий предшествующей терапии, в качестве второй линии терапии после даратуму-маб- и леналидомид-содержащих режимов. Комбинация «Селинексор/бортезомиб/дексаметазон» еженедельно (категория 1) рекомендована экспертами NCCN [44] и международной рабочей группой по лечению ММ [45].
Существует быстро растущее число активных вариантов лечения, доступных для лечения пациентов с рецидивирующей и/или рефрактерной множественной миеломой. В то же время, недопредставленность пожилых пациентов, пациентов с распространенными сопутствующими заболеваниями и пониженным соматическим статусом, пациентов, получивших множество циклов предшествующей терапии, включающей, по сути, все используемые на сегодняшний день лекарственные препараты, в рандомизированных клинических исследованиях может привести к заметным пробелам в реальной клинической практике [46,47]. Например, данные, полученные из реестра CONNECT, свидетельствуют о том, что примерно 40% реальных пациентов с ММ не будут иметь права на участие в клинических испытаниях 3 фазы на основе стандартного включе-ния/критерии исключения и, в частности, того, что у этих пациентов более низкая 3-летняя выживаемость по сравнению с пациентами, которые имели бы право на участие в клинических испытаниях (63% против 70%, Р = 0,0392) [48]. Однако среди различных исследовательских групп растет понимание того, что «реальная» популяция пациентов с РРММ в сообществе не полностью представлена популяциями пациентов, включенных в клинические исследования 3 фазы и что «разрыв» между клиническими испытаниями и условиями реального мира может привести к различным результатам. Учитывая эти результаты, врачам важно понимать различия между популяциями, участвующими в реальных и клинических испытаниях, и то, как они могут повлиять на перевод результатов клинических испытаний в их реальную практику. Таким образом, данные о схемах лечения РРММ в реальных условиях представляют собой важный компонент принятия терапевтических решений в этой среде.
В этой связи мы хотим обратить внимание на результаты исследования эффективности и безопасности селинексора из реальной жизни. В одном из отчетов об опыте из реальной клинической практики было описано 8 тяжело предлеченных пациентов с РРММ, с медианой предшествующих линий терапии равной 11 (диапазон 6–18). Им было назначено лечение по схеме SVd, используемой в исследовании BOSTON [49]. Несмотря на крайне тяжелую предлеченность больных, полученные результаты весьма оптимистичны. Авторам удалось достичь одного ПО, одного охЧО, двух ЧО. Еще у трех пациентов наблюдалась стабилизация опухолевого процесса и только у одного – прогрессия заболевания. Медиана беспрогрессивной выживаемости составила 91 день (диапазон 58-350), в то время как OS была выше и составила 300 дней (диапазон 68-376). Побочные эффекты, связанные с лечением, включали повышенную утомляемость, тромбоцитопению и нейтропению, которые устранялись с помощью коррекции дозы селинексора и сопроводительной терапии.
Другой реальный опыт основан на лечении 13 пациентов с РРММ, имевших 7 (медиана) предшествующих линий терапии (диапазон 4–10); пациенты получали селинексор (40–80 мг), дексаметазон (20–40 мг) и бортезомиб (1,3 мг/м2) один раз в неделю [50]. В целом результаты практически аналогичны предыдущему опыту. Так, ЧОО составила 23% (ответы включали три охЧО, один МО, пять стабилизаций и четыре прогрессии). Неблагоприятные события соответствовали известному профилю безопасности каждого из компонентов.
Несмотря на небольшое число пациентов в этих 2-х представленных работах, можно согласиться с тем, что триплет SVd в популяции тяжело предле-ченных больных продемонстрировал клиническую активность в реальных условиях, и эти результаты могут послужить руководством для будущих исследований с увеличением числа пациентов. Применение селинексора перорально один раз в неделю в комбинации с ингибиторами протеасомы (а возможно и с иммуномодуляторами и анти-CD38 моноклональными антителами) может быть многообещающим вариантом лечения, удовлетворяющим неудовлетворенную потребность в реальной жизни пациентов с прогрессирующей и рефрактерной ММ.
Грани возможности селинксора расширяются, появляются исследования по оценке его эффективности в комбинации с другими лекарственными препаратами. Так, в рамках открытого исследования I фазы (NCT02831686) [51] cелинексор был назначен в комбинации с иксазомибом и дексаметазоном 18 пациентам с тяжело предлеченной ММ. Медиана предшествующих линий терапии составила 5, при этом 83% больных, вошедших в это исследование, были рефрактерны к ингибиторам протеасомы. Выделено 2 группы больных: группа А получала селинексор в двух дозах (40 и 60 мг) раз в две недели; группа В получала еженедельно сели-нексор в двух дозах (80 и 100 мг). ЧОО составила 22%, а максимальная продолжительность ответа достигла 14 месяцев. Обращается внимание на то, что из-за лучшей переносимости было предпочтительно назначать селинексор один раз в неделю, а максимально переносимая доза селинексора составляла 80 мг.
Еще в одном многоцентровом открытом клиническом исследовании 1/2 фазы (NCT02186834) селинексор применялся в комбинации с доксорубицином и дексаметазоном у 27 пациентов с РРММ
[52]. Среднее количество линий предшествующего лечения составило 6 (диапазон 2-10). Рекомендуемые и используемые в настоящем исследовании дозы препаратов были следующими: селинексор 80 мг, доксорубицин 20 мг/м2 и дексаметазон 40 мг. Результаты выглядят не столь оптимистично, чем те, которые были представлены выше, т.е. при сочетании селинексора с ингибиторами протеасо-мы, иммуномодулирующими препаратами, моноклональными антителами. ЧОО составила 15%, а контроль над опухолевым процессом был получен у 26% больных.
Среди других исследований эффективности се-линексора, вызывающих интерес, следует обратить внимание на исследование, в которое было включено семь пациентов с прогрессией ММ после терапии CAR-Т клетками. Одному пациенту назначен дуплет селинексор-дексаметазон, еще одному – триплет селинексор–бортезомиб–дексаметазон и пять пациентов получали селинексор–карфил-зомиб–дексаметазон [53]. Все пациенты тяжело предлечены различными лекарственными препаратами, медиана числа линий предшествующей терапии составила 10; у четырех пациентов установлена пента-рефрактерность и быстро прогрессирующее течение болезни. Несмотря на высокую предлеченность, результаты лечения привлекают: один пациент достиг сПО, три – охЧО, два – ЧО и у одного больного зарегистрирован минимальный ответ, т.е. объективный ответ достиг 100%. Хотя эти данные и предварительные, они свидетельствуют об эффективности режима на основе сели-нексора даже после терапии CAR-Т-клетками.
Что касается роли селинексора в лечении больных с впервые выявленной множественной миеломой, то на сегодняшний день имеются ограниченные данные, как и данные о любом потенциальном воздействии новых препаратов на сбор гемопоэтических стволовых клеток. Тем не менее, такие работы появляются все чаще. Например, в исследовании STOMP (NCT02343042) была сформирована группа из семи пациентов с впервые выявленной миеломой. Всем была назначения комбинация, включающая селинексор (60 мг один раз в неделю), леналидомид (25 мг, в дни 1-21 каждого 28-дневного цикла) и дексаметазон (40 мг) [54]. Все пациенты достигли ответа (100%), включая 1 ПО, 4 охЧО и 2 ПО. При среднем периоде наблюдения 10,2 мес. медиана PFS не была достигнута. Нежелательные явления ≥3 степени не отличались от описанных при лечении РРММ: тромбоцитопения (38%), нейтропения (75%), усталость (50%), и снижение аппетита (13%).
Еще одно важное направление, которое разрабатывается, это применение селинексора в поддерживающей терапии – идущее рандомизированное исследование фазы 3 SeaLAND (ALLG MM23). Цель исследования сравнить стандартную поддержку леналидомидом и в сочетании с низкой дозой сели-нексора после выполнения больным ММ АутоТГСК, чтобы понять если какие-либо преимущества с точки зрения удержания полного ответа, негативного статуса минимальной остаточной болезни и пролонгирования беспрогрессивной выживаемости. Больным был назначен селинексор по 40 мг в неделю и леналидомид по 10-15 мг с 1 по 21 день 28-дневного цикла [55]. Набор участников в исследование продолжается. По предварительным данным, профиль безопасности соответствовал каждому из препаратов, применяемых в отдельности. При этом исследователи отмечают, что биодоступность селинексора при пероральном приеме и еженедельный режим приема делают его подходящим для поддерживающей терапии в сочетании с леналидомидом.
Заключение
Селинексор является многообещающим препаратом, проявившим высокую эффективность при лечении больных с рецидивами/рефрактерными формами множественной миеломы. Результаты исследования STORM показали, что прием селинексо-ра с дексаметазоном вызывал ответную реакцию у 26% тяжело предлеченных пациентов (от 3 до 17 линий предшествующей терапии) с рефрактерно-стью к бортезомибу, карфилзомибу, леналидомиду, помалидомиду, даратумумабу, с квадро- и пента-рефрактерностью и резистентностью к последней линии терапии. Удивительно, но ответили больные не только с рецидивом после АутоТГСК, но и после CAR-T терапии. Ответная реакция на селинексор и низкие дозы дексаметазона была клинически значимой и ассоциировалась с улучшением общей выживаемости по сравнению с историческим контролем. Выводы исследования STORM бесспорно свидетельствуют о том, что дуплет селинексор в сочетании с дексаметазоном становится новым методом лечения пациентов с рефрактерной миеломой. Причем, схема селинексор+дексаметазон может рассматриваться в качестве метода выбора в тех случаях, когда все доступные методы лечения исчерпаны.
Результаты, наблюдаемые при приеме трех препаратов на основе селинексора, выше, чем при приеме двух препаратов, что убедительно продемонстрировано в клиническом исследовании STOMP, в котором оценивалась эффективность и безопасность селинексора и дексаметазона в комбинации с ингибиторами протеасомы (бортезомиб, кар-филзомиб), иммуномодулирующими препаратами (леналидомид, помалидомид), анти-CD38 моноклональными антителами (даратумумаб) у тяжело предлеченных пациентов с РРММ. Пероральный селинексор один раз в неделю в комбинации с ингибиторами протеасомы, иммуномодуляторами и анти-CD38 моноклональными антителами может стать одним из важных вариантов лечения, удов- летворяющим неудовлетворенную потребность пациентов с прогрессирующей и рефрактерной ММ в реальной практике врача-гематолога.
В этом плане весьма примечательны результаты международного, рандомизированного исследования третьей фазы BOSTON, посвященного применению селинексора в комбинации с бортезомибом и низкими дозами дексаметазона (SPd) в сравнении с бортезомибом и низкими дозами дексаметазона (Vd) у пациентов с множественной миеломой, которые ранее получили от одной до трех линий терапии. Преимущества SVd перед Vd выявлены как в целом по группам, так и в выделенных подгруппах, включая возраст, цитогенетический риск, стадии R-ISS, количество предшествующих линий терапии, предшествующее лечение леналидомидом и низкий клиренс креатинина.
Следует отметить еще один важный момент: результаты исследования BOSTON подтверждены опытом из реальной клинической практики. Пока опыт небольшой, но он четко продемонстрировал высокую эффективность и вполне удовлетворительную переносимость триплета SVd среди чрезвычайно тяжело предлеченных больных (до 18 линий предшествующей терапии).
Важным с практической точки зрения является то, что селинексор проявлял сходную активность независимо от предшествующего лечения и у пациентов с высоким цитогенетическим риском. Сели-нексор показал явную активность при пента-рефрактерной миеломе – группе пациентов с высокой неудовлетворенной потребностью в медицинской помощи, что открывает новые возможности для пациентов, которые исчерпали другие терапевтические возможности. Эта особая роль подчеркивает важность понимания уникального механизма действия селинексора, его терапевтического потенциала и необходимости точных критериев отбора пациентов для оптимизации результатов лечения и является ориентиром для дальнейших исследований.
Необходимы хорошо спланированные, ключевые клинические испытания для дальнейшего изучения селинексора, предпочтительно в комбинации и, возможно, на более ранних этапах лечения, где этот препарат мог бы принести большую пользу. И такие исследования уже начались. Если это так, то станет очевидным его точное место в терапевтическом цикле лечения пациентов с ММ.
Что касается побочных эффектов селинексора, то, как правило, они обратимы при применении модификации дозы и соответствующей сопроводительной терапии для снижения их частоты и максимального повышения эффективности терапии.
В любом случае, полностью или даже частично пероральные комбинации, в том числе содержащие пероральный селинексор (селинексор/декса-метазон, селинексор/помалидомид/дексаметазон, селинексор/леналидомид/дексаметазон, (сели-нексор/карфилзомиб/дексаметазон, селинексор/ бортезомиб/дексаметазон) у пациентов с PPMM — начало новой эры в лечении этого заболевания. Такие комбинации можно рассматриваться в качестве одного из предпочтительных вариантов по сравнению со схемами, включающими только парентерально вводимые агенты (особенно в виде длительных внутривенных инфузий) для пациентов, которым необходимо преодолевать большие расстояния, чтобы посетить клинику, для которых бремя повторных посещений для внутривенных инъекций могут ограничить целесообразность длительной терапии.
Список литературы Селинексор у больных с рецидивами/рефрактерными формами множественной миеломы
- Mateos M-V., Ludwig H., Bazarbachi A. et al. Insights on multiple myeloma treatment strategies. // Hemasphere. – 2019. – Vol. 3. – P. e163.
- Dimopoulos M.A, Oriol A., Nahi H. et al. Daratumumab, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma. // N Engl J Med. – 2016. – Vol. 375. – P. 1319-1331.
- Федеральное руководство по гематологии. Т. 2 / [Бессмельцев С.С. и др.]; под ред. С.С. Бессмельцева и С.В. Сидоркевича. – М.: СИМК, 2024. – 572 с.
- Palumbo A., Chanan-Khan A., Weisel K. et al. Daratumumab, bortezomib, and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma. // N Engl J Med. – 2016. – Vol. 375. – P. 754-766.
- Shah J.J., Stadtmauer E.A., Abonour R. et al. Carfilzomib, pomalidomide, and dexamethasone for relapsed or refractory myeloma. // Blood. – 2015. – Vol. 126. – P. 2284-2290.
- Бессмельцев С.С., Карягина Е.В., Илюшкина Е.Ю., Столыпина Ж.Л., Мифтахова Р.Р., Кострома И.И., Шелковская Т.Л. Клиническая эффективность даратумумаба в монотерапии рецидивов и рефрактерных форм множественной миеломы//Клиническая онкогематология. – 2020. – Т. 23, №1. – С. 25-32.
- Miguel J.S., Weisel K., Moreau P. et al. Pomalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone versus high-dose dexamethasone alone for patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma (MM-003): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. // Lancet Oncol. – 2013. – Vol. 14. – P. 1055-1066.
- Kumar S.K., Dimopoulos M.A., Kastritis E. et al. Natural history of relapsed myeloma, refractory to immunomodulatory drugs and proteasome inhibitors: a multicenter IMWG study. // Leukemia. – 2017. – Vol. 31. – P. 2443-2448.
- Pick M., Vainstein V., Goldschmidt N. et al. Daratumumab resistance is frequent in advanced-stage multiple myeloma patients irrespective of CD38 expression and is related to dismal prognosis. // Eur J Haematol. – 2018. – Vol. 100. – P. 494-501.
- Abdi J., Chen G., Chang H. Drug resistance in multiple myeloma: Latest findings and new concepts on molecular mechanisms. // Oncotarget. – 2013. – Vol. 4. – P. 2186-2207.
- Pick M., Vainstein V., Goldschmidt N. et al. Daratumumab resistance is frequent in advanced-stage multiple myeloma patients irrespective of CD38 expression and is related to dismal prognosis. // Eur J Haematol. – 2018. – Vol. 100. – P. 494-501.
- Бессмельцев С.С., Абдулкадыров К.М. Множественная миелома: рук. для врачей. – М.: МК, 2016. – 504 с.
- Dimopoulos M-A., Richardson P., Lonial S. Treatment options for patients with heavily pretreated relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma// Clinical Lymphoma Myeloma and Leukemia. - Available online 10 January 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2022.01.005Get rights and content.
- Tai Y.T., Landesman Y., Acharya C., Calle Y. et al. CRM1 inhibition induces tumor cell cytotoxicity and impairs osteoclastogenesis in multiple myeloma: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. // Leukemia. – 2014. – Vol. 28. – P. 155–165.
- Fung HoY.J., Chook Y.M. Atomic basis of CRM1-cargo recognition, release and inhibition. // Semin Cancer Biol. – 2014. – Vol. 27. – P. 52-61.
- Schmidt J., Braggio E., Kortuem K.M. et al. Genome-wide studies in multiple myeloma identify XPO1/CRM1 as a critical target validated using the selective nuclear export inhibitor KPT-276. // Leukemia. – 2013. – Vol. 27. – P. 2357-2365.
- Golomb L., Bublik D.R., Wilder S. et al. Importin 7 and exportin 1 link c-Myc and p53 to regulation of ribosomal biogenesis. // Mol Cell. – Vol. 2012. – Vol. 45. – P. 222-2232.
- Allegra A., Innao V., Allegra A.G., Leanza R., Musolino C. Selective Inhibitors of Nuclear Export in the Treatment of Hematologic Malignancies. // Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. – 2019. – Vol. 19, N 11. – P. 689–698.
- Vogl D.T., Dingli D., Cornell R.F. et al. Selective Inhibition of Nuclear Export With Oral Selinexor for Treatment of Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. // J Clin Oncol. – 2018. – Vol. 36, N 9. - 859–866.
- Turner J.G., Dawson J.L., Cubitt C. al. Inhibition of CRM1-dependent nuclear export sensitizes malignant cells to cytotoxic and targeted agents. // Semin Cancer Biol. – 2014. – Vol. 27. – P. 62–73.
- Chen C., Garzon R., Gutierrez M. et al. Safety, efficacy, and determination of the recommended phase 2 dose of the oral selective inhibitor of nuclear export (SINE) selinexor (KPT-330). // Blood. – 2015. – Vol. 126. – P. 285.
- Chen C., Siegel D., Gutierrez M. et al. Safety and Efficacy of Selinexor in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma and Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia. // Blood. – 2018. – Vol. 131, N 8. – P. 855–863.
- XPOVIOTM (selinexor). Prescribing Information. Reference ID: 4457635—US FDA.
- Nexpovio-Union Register of medicinal products - Public health - European Commission. Available from: https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h1537.htm. Accessed May 20, 2021.
- Lonial S., Weiss B.M., Usmani S.Z. et al. Daratumumab monotherapy in patients with treatment-refractory multiple myeloma (SIRIUS): An open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. // Lancet. – 2016. – Vol. 387. – P. 1551-1560.
- Kashyap T., Klebanov B., Lee M.S. et al. Selinexor, a selective inhibitor of nuclear export (SINE) compound, shows synergistic anti-tumor activity in combination with dexamethasone characterized by specific pattern of gene expression in multiple myeloma (MM). // Blood. – 2015. – Vol. 126. – P. 3683.
- Abdul Razak A.R., Mau-Soerensen M., Gabrail N.Y. et al. First-in-class, first-in-human phase I study of selinexor, a selective inhibitor of nuclear export, in patients with advanced solid tumors. // J Clin Oncol. – 2016. – Vol. 34. – P. 4142-4150.
- Gounder M.M., Zer A., Tap W.D. et al. Phase IB study of selinexor, a first-in-class inhibitor of nuclear export, in patients with advanced refractory bone or soft tissue sarcoma. // J Clin Oncol. – 2016. – Vol. 34. – P. 3166-3174.
- Chari A., Vogl D.T., Gavriatopoulou M. et al. Oral Selinexor–Dexamethasone for Triple-Class Refractory Multiple Myeloma // N Engl J Med. – 2019. – Vol. 381. – P. 727-738.
- Cornell R., Hari P., Tang S., Biran N., Callander N., Chari A. et al. Overall Survival of Patients With Triple-Class Refractory Multiple Myeloma Treated With Selinexor Plus Dexamethasone vs Standard of Care in MAMMOTH. // Am J Hematol. – 2021. – Vol. 96, N 1. – P. E5–8.
- Schmidt J., Braggio E., Kortuem K.M., et al. Genome-wide studies in multiple myeloma identify XPO1/CRM1 as a critical target validated using the selective nuclear export inhibitor KPT-276. // Leukemia. – 2013. – Vol. 27. – P. 2357–2365.
- Gandhi U.H., Cornell R.F., Lakshman A. et al. Outcomes of patients with multiple myeloma refractory to CD38-targeted monoclonal antibody therapy. // Leukemia. – 2019. – Vol. 27, N 12. – P. 2357-2365.
- Richardson P.G., Jagannath S., Chari A. et al. Overall survival (OS) with oral selinexor plus low dose dexamethasone (Sd) in patients with triple class refractory-multiple myeloma (TCR-MM). // J Clin Oncol. – 2019. – Vol. 37. – P. 8014.
- Fu W., Xia Z., Fu C., Chen W., An G., Cai Z. et al. Results of the Phase 2 MARCH Study: Oral ATG-010 (Selinexor) Plus Low Dose Dexamethasone in Chinese Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM) Previously Treated With an Immunomodulatory Agent (IMiD) and a Proteasome Inhibitor (PI). // J Clin Oncol. – 2021, Vol. 39, Suppl 15. - Abstr e20002.
- White D., Chen C., Baljevic M. et al. Oral Selinexor, Pomalidomide, and Dexamethasone (XPd) at Recommended Phase 2 Dose in Relapsed Refractory Multiple Myeloma (MM). // J Clin Oncol. – 2021. – Vol. 39, Suppl 15: abstr 8018.
- White D.J., LeBlanc R., Baljevic M. et al. Selinexor, Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone (SRd) for Patients With Relapsed/Refractory and Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma. // Blood. – 2020. – Vol. 136, Suppl 1. – P. 45–46.
- Gasparetto C., Schiller G.J., Tuchman S. et al. Selinexor, Daratumumab, and Dexamethasone in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. eJHaem. – 2020. – Vol. 2, N 1. – P. 56–75.
- Gasparetto C., Schiller Gary J, Tuchmanet Sascha A al. Once Weekly Selinexor, Carfilzomib, and Dexamethasone (XKd) in Carfilzomib Nonrefractory Multiple Myeloma (MM) Patients. // Br J Cancer. – 2022. – Vol. 126, N 5. – P. 718-725.
- Jakubowiak A.J., Jasielec J.K., Rosenbaum C.A. et al. Phase 1 Study of Selinexor Plus Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. // Br J Haematol. – 2019. – Vol. 186, N 4. – P. 549–560.
- Bahlis N.J., Sutherland H., White D., Sebag M. et al. Selinexor Plus Low-Dose Bortezomib and Dexamethasone for Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. // Blood. – 2018. – Vol. 132, N 24. – P. 2546–2554.
- Grosicki S., Simonova M., Spicka I. et al. Once-Per-Week Selinexor, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone Versus Twice-Per-Week Bortezomib and Dexamethasone in Patients With Multiple Myeloma (BOSTON): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. // Lancet. – 2020. – Vol. 396, Vol. 10262. – P. 1563–1573.
- Facon T., Auner H.W., Gavriatopoulou M. et al. Survival Among Older Patients With Previously Treated Multiple Myeloma Treated With Selinexor, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone (XVd) in the BOSTON Study. // J Clin Oncol. – 2021. – Vol. 39, Suppl 15: Abstr 8019.
- Leleu X., Mateos M.V., Jagannath S., Delimpasi S et al. Effects of Refractory Status to Lenalidomide on Safety and Efficacy of Selinexor, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone (XVd) Versus Bortezomib and Dexamethasone (Vd) in Patients With Previously Treated Multiple Myeloma. //J Clin Oncol. – 2021. – Vol. 39, Suppl 15. - Abstr 8024.
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Multiple Myeloma. Version 4.2022 — December 14, 2021.
- Philippe Moreau, Shaji K Kumar, Jesús San Miguel et al. Treatment of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma: recommendations from the International Myeloma Working Group// Lancet Oncol. – 2021. – Vol. 22. – P. e105–e118.
- Richardson P.G., San Miguel J.F., Moreau P. et al. Interpreting clinical trial data in multiple myeloma: translating findings to the real-world setting. //Blood Cancer J. – Vol. 2018. – Vol. 8. – P. 109.
- Голенков А.К., Бессмельцев С.С. Концепция клинических исследований в гематологии, интегрированных в реальную клиническую практику// Вестник гематологии. – 2020. – Т.XVI, №1. – С. 6-14.
- Shah J.J., Abonour R., Gasparetto C. et al. Analysis of common eligibility criteria of randomized controlled trials in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients and extrapolating outcomes. // Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. – 2017. – Vol. 17, N 9. – P. 575–583.
- Mouhieddine T.H., Parekh S., Cho H.J. et al. Selinexor, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone (SVD) in Heavily Treated Relapsed Refractory Multiple Myeloma. // Ann Hematol. - 2021. – Vol. 100, N 12. – P. 3057-3060.
- Magen H., Geva M., Volchik Y., Avigdor A., Nagler A. Selinexor, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone for Heavily Pretreated Multiple Myeloma: A Case Series. // Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. – 2020. – Vol. 20, N 12). – P. e947–955.
- XPOVIOTM (selinexor). Prescribing Information. Reference ID: 4457635—US FDA.
- Baz R., Zonder J.A., Shain K.H., Alsina M. et al. Phase I/II Study of Liposomal Doxorubicin (DOX) in Combination With Selinexor (SEL) and Dexamethasone (Dex) for Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM). // Blood. – 2017. – Vol. 130, Suppl. 1. – P. 3095.
- Malandrakis P., Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I., Gavriatopoulou M., Terpos E. Clinical Utility of Selinexor/ Dexamethasone in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma: A Review of Current Evidence and Patient Selection. // Onco Targets Ther. – 2020. – Vol. 13. – P. 6405–6416.
- White D.J., LeBlanc R., Baljevic M. et al. Selinexor, Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone (SRd) for Patients With Relapsed/Refractory and Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma. // Blood. – 2020. – Vol. 136, Suppl 1. – P. 45–46.
- Quach H., Lasica M., Routledge D. et al. A Randomized, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study of Low-Dose Selinexor and Lenalidomide (Len) Versus Len Maintenance Post Autologous Stem Cell Transplant (ASCT) for Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma (NDMM): ALLG MM23, Sealand. // J Clin Oncol. – Vol. 2021. – Vol. 39, Suppl 15. - Abstr TPS8055.


