Signal morphological criteria for cardiotoxicity in breast cancer chemotherapy
Автор: Shikhlyarova Alla I., Frantsiyants Elena M., Vladimirova Lyubov Y., Storozhakova Anna E., Vashchenko Larisa N., Kechedzhieva Emma E., Zhukova Galina V., Sheyko Elena A.
Журнал: Cardiometry @cardiometry
Рубрика: Original research
Статья в выпуске: 16, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Aims A high incidence of breast cancer is observed in all countries throughout the world, and this dictates the use of aggressive antitumor drugs. The toxogenic effect of anthracycline drugs on the cardiovascular system under conditions of oncological pathology determines the need to expand the diagnostic capabilities for detecting cardiotoxicity, including searching for signal morphological markers in blood serum. The aim of this work is to study the structure of solid-state films of blood serum in patients with breast cancer at the stages of their chemotherapeutic treatment to identify signal criteria for cardiotoxicity. Materials and methods Studies were conducted in 25 patients with primary breast cancer (BC) with an extent of spread of the tumor process corresponding to T2-4N0-1M0. Polychemotherapy (PCT) was carried out in a neoadjuvant regimen, which included doxorubicin (60 mg/m2) and cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m2) supported by echocardiography examinations and ECG monitoring. Morphological testing of solid-state blood serum samples was carried out using the Shatokhina-Shabalin method of wedge-shaped dehydration both before PCT and in the course thereof. Samples were visualized with the Leica DMLS2 microscope with a magnification from x20 to x90. Results Before starting the PCT course, in the serum facias, in 55% of the cases detected has been the loss of the radial symmetry system and the formation of pathological types, including the “double” facias that is a criterion of systemic intoxication. Local markers of comorbid states with a detection rate of up to 40% of intoxication21.05.2020impaired vascular elasticity, sclerosis, hypertension and ischemia have been identified. After 3 courses of PCT including anthracyclines, the occurrence rate of formation of these pathological criteria increased by 1.7 times; the occurrence rate of myocardial trophic disorder markers was found to be higher. At stages 5-6 of the treatment course, in 80% of the cases, some signal signs of the cumulative effect of anthracyclines associated with impaired cardiac rhythmogenesis were detected in the facias structure. Conclusions Inhibition of tumor growth under PCT including anthracyclines is accompanied by structural deformation of the systemic and local self-organization of blood serum. An intensification of crystallogenesis of inflammation pathological proteins, sclerosis, intoxication, hypertension, stagnation angiospasm and cardiac arrhythmias makes it possible to assess the intensity of drug cardiotoxicity using the identifying markers, predict long-term effects of PCT and a possibility of their prevention.
Breast cancer, anthracycline, cardiotoxicity, blood serum morphology
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148311465
IDR: 148311465 | DOI: 10.12710/cardiometry.2020.16.6773
Текст научной статьи Signal morphological criteria for cardiotoxicity in breast cancer chemotherapy
Alla I. Shikhlyarova, Elena M. Frantsiyants, Lyubov Y. Vladimirova, Anna E. Storozhakova, Larisa N. Vashchenko, Emma E. Kechedzhieva, Galina V. Zhukova, Elena A. Sheyko. Signal morphological criteria for cardiotoxicity in breast cancer chemotherapy. Cardiometry; Issue 16; May 2020; р.67-73; DOI: 10.12710/cardiometry.2020.16.6773; Available from:
A significant occurrence rate of breast cancer (BC) and a high mortality rate in females make the issues of the BC treatment and diagnostics of patients topical [1]. Chemotherapy is known to be one of the leading methods of treating breast cancer, and the most effective drugs for the therapy are anthracyclines, tax-anes, alkylating agents, fluoropyrimidines and trastuzumab [2]. With extending growth of medication options, the risk of cardiovascular complications also increases. Antitumor agents of various classes may produce a pathogenic effect on the cardiac muscle and contribute to the development of functional disorders, including cardiac arrhythmias, myocarditis, pericarditis, infarction, acute or congestive heart fail ure. Within the range of various complications of the anthracycline antitumor therapy, cardiotoxicity is of particular danger [3, 4]. This spectrum of events may occur either immediately or years upon the CT completion, therefore, it is so important to identify eligible operational prognostic criteria for cardiotoxicity, indicating the need for correction of cardiovascular pathology [5, 6, 7].
The appearance of functional and structural changes in the heart and blood vessels is reflected in the circulating blood composition. It is known that blood transports toxic substances (tissue destruction products, incomplete protein-, lipid- and mineral exchange-related metabolism products), therefore, the presence of toxins in blood, i.e. toxemia, is a pathological state that can be detected in blood testing. Along with the earliest biochemical criteria for intoxication, there is an important condition that indicates that the non-cellular component of blood (plasma, blood serum), in addition to the detectable biochemical (dynamic) changes, can serve as an important source of information about the formative (static) characteristics of the fluid phase, when the blood fluid is transformed into its solid state. This unique approach to the diagnostics of pathological states was developed by Russian scientists, Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS) Shabalin V.N. and Corresponding Member of RAS Shatokhina S.N. They created the methodological basis for biological fluid morphology [9-10]. The methods proposed by the above researchers for the diagnostics of the morphological structure of blood serum and other biological fluids are supported by the description of the criteria for identifying pathological states and their structural features, which have found applications in assessing effects made by different therapeutic factors [10-13].
The aim of this research work is to study the structure of solid-state films of blood serum in patients with breast cancer (BC) at the stages of their chemotherapeutic treatment for identifying signal criteria for cardiotoxicity and determining their prognostic value.
Materials and methods
The study included 25 patients aged under 50 (49.8 ± 0.5) with primary breast cancer (PBC). The extent of spread of the tumor process has been found in 90.5% of patients to correspond to T2-4N0-1M0. Polychemotherapy (PCT) was carried out in a neoadjuvant regi- 68 | Cardiometry | Issue 16. May 2020
Results
The study of morphology of the solid-state blood serum samples in the BC patients before PCT including anthracyclines revealed initial disorders in the systemic self-organization thereof. This was evidenced by the absence of the full radial symmetry of the cracks, the appearance of zigzag-pattern beads and ridges along the circumference line in the boundary and intermediate zones of the facias. In 45% of the cases a partially radial morphotype of the facia has been detected, in 35% of the cases an irradial morphotype

а) b)
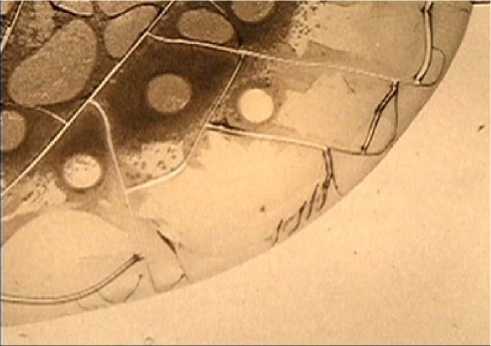
Figure 1. Fragments of the blood serum facias in patients with BC before PCT: a) departure from the radial symmetry of the cracks, appearance of beads in the facia boundary zone; b) the “double” facia morphotype; the ‘wrinkling” structure and toxic plaques along the edge of the lower facia. Magn. x 40.
thereof has been identified, and in 20% of the tests the formation of an extremely unfavorable morpho-type, the so-called “double” facia has been discovered that marks a highly toxic state of biofluid (see Figure 1 herein).
The pronounced invariance of the pathological serum morphotypes before PCT indicated the influence of the malignant process on the organism and made it possible to identify paraspecific signs of the tumor growth (see Figure 2 herein). The paraspecific signs primarily included such structures as “wrinkling” and “toxic plaques”, representing markers of intoxication and toxin products of the liquid medium, which were detected with an occurrence rate up to 35-40%. Before the treatment, in a quarter of the examined patients with initial cardiac arrhythmias, a signal marker of extrasystole, a “finger-shaped structure”, was found. In 25% of the cases, markers of chronic inflammatory processes were recorded, which were shaped like regional fields of some crystallized inflammatory proteins building structures of the split Arnold tongue type and the Sierpinski carpet type. The occurrence rate of impaired vascular elasticity markers, namely, the structures like “silver cracks”, as well as sclerotic processes in blood vessels, i.e. the “leaf”-type structure, increased to a level of 40%.
Thus, the initial picture of the solid-state blood serum samples in the above mentioned cohort of the BC patients indicated that, against the background of systemic disorders in the self-organization in biological fluid, the revealed paraspecific signs did not differ from those revealed with the conventional equipment and instrumentation used for diagnostics of cardiac and vascular pathology in the patients before their drug treatment. It is no doubt that the tumor itself makes a vast contribution to the development of the above disorders under the localized malignant process conditions. Of considerable interest was our analysis of the initial morphotypes with samples obtained after the first three courses of PCT, which limited the pathogenic effect produced by the tumor, but provoked at the same time the side effect of enriching the internal environment with aggressive drugs and their metabolites.
The completion of 3 courses of antitumor PCT with anthracyclines included significantly affected the structure of the serum facias. First, the partially radial morphotype of the facias, which is closest to the normotype of the radial symmetry, was completely lost. The pathologically stable morphotypes, namely the ir-radial and the circular types with a pronounced asymmetry and a chaotic distribution of cracks, which indicated a systemic disorganization of the facia structure, were dominant. Second, some morphological signs of chronic insufficiency of cerebral and cardiac circulation of the hypertonic and atherosclerotic genesis were revealed in the form of a circular arrangement of band-type cracks against the background of the three-ray ones (see Figure 3 herein). The above suggestion was confirmed by the presence of structures like "silver cracks", which made us possible to identify disorders in the blood vessel elasticity and hypertension. The most frequently found marker of hypertension and angiospasm was a cluster of the “scallop struc-

а)
b)
d)
c)
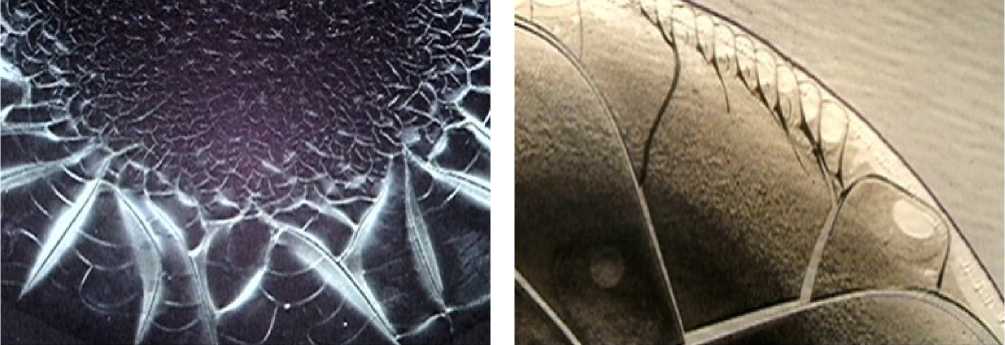
Figure 2. Fragments of serum facias in BC patients before PCT:
a) a cluster of pathological markers of intoxication and inflamma-
tion: “wrinkling” of toxic proteins in the boundary zone and signs of the Arnold tongue types in the intermediate zone; b) a cluster of markers of inflammation: markers of the Arnold tongue types, markers of angiospasm and hypertension: “scallop” structures; c) sclerosing markers: the “leaf” structure visible using the polarized light; d) “scallop” structures and “silver cracks”. Magn.х 20,х 40.
tures” in the boundary zone of the facias, at the base of which there were lines of dash-type cracks. During the systematic use of hypotensive drugs by BC patients, the structure of “the scallops” was transformed into broken lines, and the presence of “the dash-type cracks” demonstrated the possibility of a compensatory development of the microcirculatory network to restore the blood supply in those areas of the brain or the heart tissues affected by hypoxia or ischemia, that was observed in 50% of the cases.
In addition, in 60% of the cases, detected were the markers, which manifested a myocardial trophism disorder and which contained the "spike” type structures of various sizes in large and small cracks of the facias. At the considered stage of the treatment, an increase in the occurrence rate and enlargement of local structures of the “toxic plaques” and “wrinkling” structures built by toxic proteins, toxins and incomplete metabolism products, was observed, that determined a high level of general intoxication and was directly related to cardiotoxicity.
At the subsequent stages of the treatment, especially by the time of the completion of courses 5-6 of antitumor PCT in the BC patients, the further cumulative effect produced by anthracyclines had negative consequences associated with cardiac arrhythmias. In parallel with the clinical recording of these abnormalities, in solid samples of patients' blood serum, specific inclusions typical to atrial fibrillation were revealed. The inclusions represented small dual structures of triangles located within the doubled Arnold tongue type regions and the Sierpinski carpets (see Figure 4 herein).
It should be noted that before PCT including an-thracyclines this sort of structural markers was not detected. A significant increase in the occurrence rate of the "spikes” structure (up to 80% of the cases) at large cracks also confirmed the presence of disorder- а)
c


b)
d)


Figure 3. Fragments of serum facias in BC patients upon completion of the 3rd course of PCT with anthracyclines included: markers of chronic insufficiency of peripheral (a) and central (b) blood circulation: the circular arrangement of band-type cracks; c) markers of myocardial trophic disturbance: "spikes” structure; d) fractures and alignments of the "scallop" structures as markers of angio-
spasm and hypertension in accompanying therapy. Magn. Х 40.
ing in cardiac rhythmogenesis. An identification of “finger-shaped structures”, demonstrating their high specificity for the processes of rhythm disturbances and extrasystoles, deserved a particular attention in the context of the morphological analysis of solid-state blood serum sample structuring. Upon the completion of the anthracycline treatment, the above demonstrative marker of cardiac abnormalities was detected in 43% of the patients.
Conclusions
As evident from the completed monitoring of the blood serum facias in the BC patients at the stages of antitumor PCT including anthracycline drugs, the processes of structural self-organization of the biofluid undergo pronounced transformations both at the systemic and local levels. Prior to starting the drug therapy, detected were clear morphological signs of the pathogenic effect produced by a malignant tumor on the organism, reflecting the loss of normotypes of the radial symmetry and the formation of the “double” facia, the marker of intoxication. At the same time, the processes of the cancer-related intoxication were complicated by comorbid conditions, which manifested themselves at the level of local crystallogenesis of pathological proteins of inflammation, sclerosis due to intoxication, hypertension, angiospasm of congestive events, cardiac arrhythmias in the form of identifying paraspecific markers. Thus, before the treatment, the level of the damaging effect produced by the tumor on the internal environment state was adequately assessed.
As the tumor growth was inhibited, the markers did not disappear: on the contrary, they became a reflection of the side effects made by doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide. Our study of the facias, especially at the final stages of PCT, has demonstrated cumulative effects, which aggravate the systemic self-organi-
Issue 16. May 2020 | Cardiometry | 71
а)
c)
e)

b)
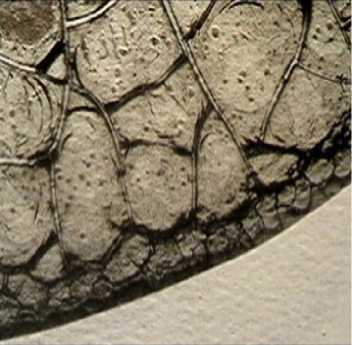

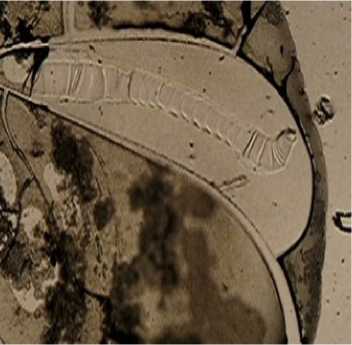
Figure 4. Fragments of serum facias in BC patients upon the completion of 5–6 courses of PCT with anthracyclines included: a, b) markers of atrial fibrillation: the structures of triangles in the double Arnold tongue regions c) the “spikes” structure at large cracks of the facias in case of heart rhythm disorders; d, e, f) markers of extrasystole: the “finger-shaped” structures. Magn. х 40, х 90.
d)
f)

zation of the facias and add to the complexity of the cardiopathology up to the appearance of atrial fibrillation markers. An increase in the occurrence rate of detecting the “finger-shaped” structure markers, linked with an increase in the Sierpinski carpet areas and the Arnold tongue type regions, associated with their texture of multiple triangles, which are possibly associated with degenerative changes in cardiomyocytes, may bear witness to a progression of the myocardial strain tension related to the rhythm-generating system. As shown by Shatokhina S.N. and Shabalin V.N., abnormal structures of the solid-state phase of blood serum are formed by pathological metabolites and can be found in a variety of their combinations with other structures. In other words, cardiotoxicity is targeted not only at the muscle system, but also at the nervous system of the heart, represented by structural elements highly sensitive to toxins.
It should be pointed out that medical monitoring of the cardiovascular system state and mandatory accompanying therapy for patients during the entire period of their treatment certainly produced a cardiotropic effect that made it possible to suppress the toxic attack of anthracyclines and provide the required completion of the PCT courses. At the same time, the possibility of additional testing and identification of the anthracyclines’ toxic effect markers may have a great prognostic value considering a reduction in the risk of delayed adverse effects made by anthracyclines, well-timed administration and completion of the required supportive cardiotropic therapy.
Statement on ethical issues
Research involving people and/or animals is in full compliance with current national and international ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author contributions
The authors read the ICMJE criteria for authorship and approved the final manuscript.
Список литературы Signal morphological criteria for cardiotoxicity in breast cancer chemotherapy
- Demidov VP, Ostrovtsev LD, Volkova MA. Breast Cancer. Combined and Comprehensive Treatment of Patients with Malignant Tumors: Guide for Physi¬cians. Мoscow: Meditsina; 1989.
- Moiseenko VM. Practical Recommendations for the Treatment of Malignant Tumors (RUSSCO). Мoscow: Russian Society of Clinical Oncology; 2017.
- Cardiovascular Toxicity Induced by Chemothera¬py and Targeted Drugs. Practical Recommendations. Мoscow: RUSSCO; 2013.
- Ewer MS, Ewer SM. Cardiotoxicity of antican¬cer treatments. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015(12):620. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.65. 4. 4. Ewer MS, Ewer SM. Cardiotoxicity of anticancer treatments. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015(12):620. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.65.
- Kononchuk NB, Mitkovskaya NP, Abramova ES, et al. Cardiotoxicity induced by chemotherapy for breast cancer: risk factors, pathogenesis. Medical Journal (Minsk). 2013;3(45):4-7.
- Semiglazova TY, Teletaeva NA, Kozyavin NA, Za¬gatina AV. Diagnosis and prevention of cardiotoxicity in patients with breast cancer from the perspective of oncologist and cardiologist. Tumors of the female re¬productive system. 2017;13(3):17-25.
- Yandieva RA, Saribekyan EK, Mamedov MN. Cardio¬toxicity in the treatment of cancer. International Journal of Heart and Vascular Diseases. 2018;6(17):3-11.
- Semenova AI. Cardio-neurotoxicity of antitumor drugs (pathogenesis, clinical features, prevention, treatment). Practical Oncology. 2009(10): 168-176.
- Shabalin VN, Shatokhina SN. Morphology of biological fluid in humans. Moscow: Chrysostom, 2001. 304 p.
- Shatokhina SN, Shabalin VN. Atlas of human non-cellular tissue structures in norm and patholo¬gy: in 3 volumes. Vol. II Morphological structures of blood serum. Мoscow-Tver: LLC Publishing house "Triada", 2013.-240p.: 862 ill.
- Shikhlyarova AI, et al. Methodological fundamen¬tals of experimental magneto-therapy of tumors (his-torical essay). Cardiometry.2015;7: 42-46.
- Kit OI, et al. Theory of health: successful transla¬tion into the real life. Cardiometry.2015;7: 11-17.
- Shikhlyarova AI, Sheiko EA, Kozel’ YY, Kurki¬na TA. Prognostic possibilities of the method of wedge-shaped dehydration in assessing the effective¬ness of treatment in infants with hemangiomas with LED radiation of the red spectrum. Laser Medicine. 2013;17(2):27-32.


