Simple linear econometric modeling in the field of marketing
Автор: Tairova F.F.
Журнал: Теория и практика современной науки @modern-j
Рубрика: Основной раздел
Статья в выпуске: 1 (91), 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The investigative learning style of English language learners is at the center of this study. The purpose of the paperwork is to examine the educational content given to pupils and determine whether or not it corresponds with their learning preferences. The research tool utilized to gather data from the students was a questionnaire. Teaching young students, a foreign language is challenging unless the teacher does not have enough background knowledge about students’ learning processes and styles. Teachers must be able to consider a variety of factors relating to young students in order to deliver the required subject in the classroom effectively. In light of all of this, the purpose of this paperwork has been to make foreign language teachers aware of the knowledge they require in order to conduct a successful lesson. It goes without saying that having knowledge in the relevant sector is usually very beneficial for both teachers and students.
Learning styles, designing activities, teachers, students, learners
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140297166
IDR: 140297166
Текст научной статьи Simple linear econometric modeling in the field of marketing
1.I ntroduction
The often-conscious acts or behaviors that language learners employ to improve their acquisition, storage, retention, retrieval, and use of new information are known as language learning methods (R. L. Oxford, 1990; Rigney, J. W., 1978). Strategies can be evaluated using a variety of techniques such as diary, thought, observation, and research. Studies in and outside linguistics (Brown, A.L. и др., 1983) and language learners(R. Oxford & Crookall, 1989; R. L. Oxford, 1990; Skehan, 1991) show that most successful students use learning techniques that are suitable for the subject matter. One of the main learning theories that take into account individual differences and emphasizes individual differences in learning, depending on the material, the task at hand, the goals, the needs and the level of learning, is the cognitive approach. This paradigm recognizes the importance of individual learning differences(Loo *, 2004).
There is overwhelming evidence that discrepancies between student learning preferences and teachers' teaching methods can adversely affect student learning (Almasa Mulalic и др., 2009; Felder & Henriques, 1995). Through experience, people develop learning preferences and methods through certain idiosyncrasies and other abilities (Seif, A., 2001). The following research supports and argues that it is beneficial to consider learning styles when designing training and materials (Dunn и др., 2009; Hayes & Allinson, 1993, 1996; Riding & Grimley, 1999; Schmeck, 1988).
This analysis suggests that content creators and material developers should focus on learning goals when creating materials. Research shows that teaching and practicing honest communication enhances learning.
2. Literature review
Learning style is essentially a subfield of educational psychology. The process of teaching and learning can be enhanced by studying and exploring the idea of learning style. It can also help students become more socially adept. Interpersonal knowledge is the individual's understanding of their memory, thinking style, and learning style (Brown, A. L., 1984). The student becomes aware of his learning style as a result of this awareness, and conscious analysis of it will help to improve the learner's learning style and process.
Lindsay (1999) discovered that students performed better in school and were more satisfied with their education when their learning and teaching styles were in sync. The majority of studies emphasize that individual preferences of teachers and educational planners should be based on the learning styles of their students when presenting topics, as learning styles can influence the effectiveness of educational materials, models, and methods (Goold & Rimmer, 2000;
There are a variety of learning styles, as mentioned earlier. Based on (Memletics-learning-styles-inventory, б. д.), the seven-style classification is one of these new classifications. From this perspective, people may have the following learning styles:
Visual space ): These people like to use images, figures and spatial awareness. Hearing (auditory music) : These people like to use sounds and music.
(linguistic) Verbal : They favor involving words in expressing and composing. Kinetic (physical) : They prefer to use their hands, body, and sense of touch. Mathematical logic : They like to use systems, logic, and reasoning.
Interpersonal (social) : They prefer to learn in groups or with others. Lone Wolf (interpersonal ): They prefer to work alone and are self-readers.
Black or white, present or absent, learning styles are not binary. Typically, learning styles operate on a continuum or multiple, interconnected continua. A person may, for instance, be more extroverted than introverted, more closure-oriented than open, or equally interested in the visual and auditory worlds but less so in the kinesthetic and tactile worlds. According to (Ehrman, 1996), very few people fall into any of these categories at all.
3. Preferences for particular senses
Sensory preferences can be grouped primarily into four areas:
Visual, auditory, kinesthetic (motion-oriented), and tactile (touch-oriented). Sensory preferences refer to the physical and perceptual learning channels with which students are most comfortable. Visual students enjoy reading and benefit greatly from visual stimulation. Lectures, conversations, and verbal instructions can be very confusing without visual support. In contrast, hearing students enjoy and benefit from no-frills lectures, conversations, and verbal instructions because they feel comfortable without visual input. They are enthusiastic about classroom interaction with role-plays and similar activities. However, they sometimes struggle with written work. Kinesthetic and tactile students enjoy a lot of movement and enjoy working with physical objects, collages, and index cards. Sitting at a desk for long hours is not for her. They take frequent breaks and like to move around the room.
Scientist (Reid, 1987) showed that the sensory preferences of ESL students differed greatly, with individuals from particular cultures favoring the three main learning modalities differently. For instance, students from Asian cultures tended to be very visual, with Koreans being the most so. Hispanic learners are frequently auditory, according to numerous types of research, including Reid's. Reid discovered how nonauditory the Japanese are. ESL learners from various cultural backgrounds preferred tactile and kinesthetic senses.
4. Personality types
Desired Degree of Generality
This section contrasts the learner who is more concerned with the big picture or the main idea with the learner who is more concerned with the specifics. Students who are holistic or global prefer socially interactive and communicative events where they can focus on the main idea and not on grammatical nuances. Even when they don't have all the information, they feel at ease and can make guesses based on the situation. Analytic students frequently steer clear of more free-flowing communicative activities because they tend to focus on grammatical details. Analytic learners typically do not take the risks required to guess from the context unless they are fairly certain of their guesses' accuracy because they are concerned about precision. Both the analytical student and the global student can benefit greatly from one another. For L2 learning, a balance between specificity and generality is very helpful.
Biological differences
Contrasts in L2 learning style can likewise be connected with natural variables, for example, biorhythms, food, and area. Biorhythms indicate when students perform best and feel their best during the day. Some L2 students prefer to study in the morning, while others prefer to wait until the afternoon to begin their studies. Still, others are creatures of the night and happily "pull an all-nighter" when necessary. The requirement for food or drink while learning is referred to as sustenance. A lot of L2 students don't like learning when they can't have a candy bar, a cup of coffee, or a soda with them, and others are distracted from studying by food and drink. The environment is a factor in a location: temperature, sound, lighting, and even how firm the chairs are. The students in L2 have very different perspectives on these external factors. The biological aspects of the L2 learning style are frequently overlooked, but observant educators can frequently make adjustments and concessions when necessary.
Beyond the stylistic comfort zone
It is clear that L2 learners need to make the most of their style preferences. However, sometimes you need to extend beyond your stylistic preferences. By offering a wide range of classroom activities to suit different learning styles, teachers can help L2 students grow beyond their comfort zones determined by their natural style preferences. The key is to systematically deliver different activities within a learner-centered communication approach.
5. Selecting and designing activities
It is important to point out that teachers of young students have a lot of responsibilities in the classroom, from designing the materials to putting them into use in the right way. According to (Klein, K., 1993), the teacher must be creative in selecting engaging activities and provide a wide range of them because it is nearly impossible to cater to the interests of about 25 students.
With all of this in mind, teachers of foreign languages should concentrate on the fact that both teachers and young students need to be motivated to learn.
According to (Moon, 2000), young learners learn a foreign language
In addition to the aforementioned tenets, engaging young learners with a variety of activities, games, songs, and technological tools would speed up and make learning more enjoyable.
It is common knowledge that visual imagery is an older form of world knowledge than linguistic symbolism. In terms of language learning, the majority of students, except young learners, enjoy learning visually and spatially. Teachers believe that teaching any subject should be supported visually; through large, colorful pictures, posters, drawings, flashcards, puppets, real objects, mime, facial expressions, and gestures, among other means. There are numerous advantages to using visuals in the classroom.
It would appear that every learner of a mother tongue or a foreign language appreciates context-based learning. Learning any subject is made easier by contextualized activities, which require students to decipher the meanings of unfamiliar language from a situation or context. As a result, contextualizing the unknown language gives it more meaning than simply presenting it in a single sentence with no explanation to help understand its meaning. Retention would be extended if the classroom contexts and introduced language were accompanied by visuals.
"Games in foreign language teaching help students to see learning English as enjoyable and rewarding," states (Phillips, 2001). The ability to cooperate, compete without aggression, and be a good loser is all enhanced by classroom games. Naturally, there are a lot of everyday games and puzzles that can be used to learn a foreign language that students are already familiar with. They will find that playing these games comes easily to them, and it will give them the impression that they are in a secure setting where they can venture out and take risks. In addition, games can be extremely beneficial to students if used appropriately and with the appropriate challenges or clues. There is always some kind of language gain, regardless of the type or how straightforward it is. Children may not even be aware that some languages are being memorized as part of a fun activity. As a result, children may be encouraged to establish their own rules through enjoyable, informal activities. Structure games, vocabulary games, spelling games, and so on are examples of types of games that can be used in the classroom.
For young language learners, songs, rhymes, chants, and musical activities are excellent teaching tools (Abdulvahit Cakir, 1999). Such activities have the potential to teach them indirectly. They like imitating the voices of the actors and playing out situations from a sketch or dialogue. It is evident from their delivery that they pronounce words in a manner that closely resembles the characters they have seen or heard. Thus, one of the objectives of teaching English to young learners is to enable them to quickly and unconsciously pick up highly significant concepts.
6 .MethodologyParticipants
Schoolers were asked to participate in this survey. All the respondents were seniors from 9, 10 and 11 grades, as they were the most experienced students and had the most refined sense of their preferred learning modes. There were 45 students in total, and 15 respondents from each grade were chosen. Furthermore, English is the second learning language for those respondents, so they were selected as they are the students with the greatest levels of confidence.
Materials
The instrument to survey the preference of learners’ learning styles in this research was questionaries consisting of 10 quizzes. There were questions with provided options that participants chose to answer.
The learning materials that were given to them were examined to determine whether the chosen learning style and the structure of the material and edition matched up, and suggestions for improving the material and methodology were made. Results were analyzed, counted, and inserted into the computer. The materials were analyzed according to ( Memletics-learning-styles-inventory , б. д.) proposed for classification to find a match between the learner's preferred style and the composition and structure of the material for second language learners.
7 .Results and Discussion
The survey was done to find out the student’s learning preferences. The results show that most participants agreed on social learning style, meaning learners prefer studying in a group. Social style helps them to learn fast and easily. When the reason was asked, they said that while working on some kind of class work together, they exchange ideas and thoughts. As a result, it helps them to bring a solution or any kind of decision faster. Only less than 5 pupils disagreed about social style preference. It was said by those participants that they cannot interact easily with other students. They find it difficult and are shy to express their ideas and thoughts on something among other people.
The logical style was chosen by 34 pupils who said they understand if they learn the lesson step by step and first theory and then practice. But others said it is best to mix theory and practice together as they may forget what they had in the previous lesson if they do not boost it with other skills like reading, listening, etc.
-
39 participants were happy if they participant in a lesson where there is a role play or exercise which requires physical involvement. This type of learner memorizes best if they work with their body. They cannot sit in one place and do practical tasks or listen to the teacher’s explanation. On the other hand, 6 out of 45 pupils said once more that they are shy or it does not help them in their learning process and showed resistance against the Kinesthetic learning style.
It can be seen that many of the participants were against verbal style. This style is about the aspect of spoken interaction. They showed their shyness and were hesitant to communicate in another language as they were afraid to make grammar mistakes. But a small number of participants (13) preferred verbal style which illustrates they are ready to include a conversation with others while learning the language.
The auditory-style question was about movies, videos, podcasts and other oral activities. 42 pupils said they like it if there would be involvement in auditory activities as they provide real-life language usage and it helps to bring them into their native language environment. But only 3 of the participants said disagreed because even if they study well the language and know more vocabulary, they still cannot understand the real native language conversation. They find it challenging for them. Still, in total all of the participants agree that these activities make them aware of social-cultural conversation when it comes to language usage.
-
40 out of 45 participants said yes if they learn a foreign language through images, real-life objects and reading. They can easily make the connection between these things and the words they are reading or saying. A small number of pupils showed resistance against this style interpreting their reason as they are not good at visual memory or do not always understand what they are reading as they easily lose concentration while reading. (fig.1)
8.Conclusion
learners' styles
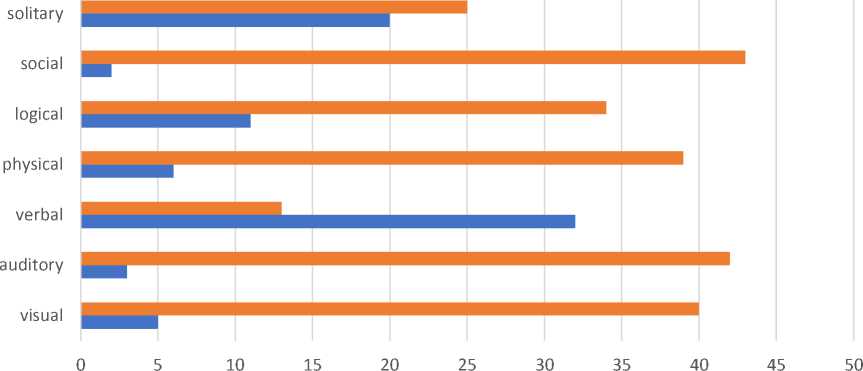
■ agree ■ disagree
Figure.1 Learners styles
It can be concluded from the above survey that most of the participants are active and positive about any kind of learning preferences. This survey’s results can be used for effectively conducting the lesson. So, while making a lesson plan and designing, and selecting activities, teachers should take into consideration of their student’s preferences and styles in learning the language. To make the lesson more interesting, the teacher can mix a variety of activities where all learners’ learning styles would be included. Otherwise, the entire teaching environment will be confusing and ineffective if the teacher is unfamiliar with the preferred learning styles of her students. The teacher must concentrate on a few key elements from activity design to application. First and foremost, it's crucial to make activities engaging for young learners when developing them. Any activity intended to teach a particular concept would not necessarily be appropriate for them unless it was difficult, deliberate, and involved the use of genuine language along with images, objects, noises, mime, motions, etc. The result of the activity is crucial when presenting activities to students. Additionally, students will be inspired to feel content with the result of their study. It should be remembered that young students will learn more effectively when they feel safe and content and when the activity provides a fun learning environment in the classroom.
Список литературы Simple linear econometric modeling in the field of marketing
- Abdulvahit Cakir. (1999). Musical Activities for Young Learners of EFL. The Internet TESL Journal. http://www.aitech.ac.jp/.
- Almasa Mulalic, Parilah M. Shah, & Fauziah Ahmad. (2009). Perceptual learning-style preference of ESL students. European Journal of Social Sciences, 1(2), 101–113.
- Anderson, T., & Fathi Elloumi (Ред.). (2004). Theory and Practice of Online Learning. Athabasca Univ.
- Banner, G., & Rayner, S. (1997). Teaching in style: Are you making a difference in the classroom? Support for Learning, 12(1), 15–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9604.1997.tb00492.x
- Belanger, F., & Jordan, D. H. (2000). Evaluation and Implementation of Distance Learning: Technologies, Tools and Techniques. IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-878289-63-6
- Brown, A. L. (1984). Metakognition, Handlungskontrolle, Selbststeuerung und andere noch geheimnisvollere Mechanismen. Kohlhammer.
- Brown, A.L., Bransford, J.D., Ferrara, R., & Campione, J.C. (1983). Learning, remembering, and understanding.: Т. Flavell&E. M. Markham (Eds.),Carmichael’s manual of child psychology. New York, NY: Wiley.
- Çakır, İ. (2003). Designing Supplementary Activities for the Sixth Grade English Course Through the Multiple Intelligences Theory. (сс. 101–112) [Unpublished PhD. Dissertation.]. Kırıkkale Üniversitesi Fen-Edebiyat Fakültesi, Kırıkkale.
- Carson, J. G., & Longhini, A. (2000). Focusing on Learning Styles and Strategies: A Diary Study in an Immersion Setting. Language Learning, 52(2), 401–438. https://doi.org/10.1111/0023-8333.00188
- Celce-Murcia, M., & Hilles, S. (1988). Techniques and resources in teaching grammar. Oxford University Press.
- Cornett, C. E. (1983). What you should know about teaching and learning styles. Phi Delta Kappa Educational Foundation.
- Dunn, R., & Griggs, S. A. (1988). Learning Styles: Quiet Revolution in American Secondary Schools. The Clearing House: A Journal of Educational Strategies, Issues and Ideas, 63(1), 40–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/00098655.1989.9955719
- Dunn, R., Honigsfeld, A., Doolan, L. S., Bostrom, L., Russo, K., Schiering, M. S., Suh, B., & Tenedero, H. (2009). Impact of Learning-Style Instructional Strategies on Students’ Achievement and Attitudes: Perceptions of Educators in Diverse Institutions. The Clearing House: A Journal of Educational Strategies, Issues and Ideas, 82(3), 135–140. https://doi.org/10.3200/TCHS.82.3.135-140
- Ehrman, M. (1996). Understanding Second Language Learning Difficulties. SAGE Publications, Inc. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781452243436
- Ehrman, M., & Oxford, R. (1989). Effects of Sex Differences, Career Choice, and Psychological Type on Adult Language Learning Strategies. The Modern Language Journal, 73(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-4781.1989.tb05302.x
- Ehrman, M., & Oxford, R. (1990). Adult Language Learning Styles and Strategies in an Intensive Training Setting. The Modern Language Journal, 74(3), 311–327. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-4781.1990.tb01069.x
- Felder, R. M., & Brent, R. (2005). Understanding Student Differences. Journal of Engineering Education, 94(1), 57–72. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2168-9830.2005.tb00829.x
- Felder, R. M., & Henriques, E. R. (1995). Learning and Teaching Styles In Foreign and Second Language Education. Foreign Language Annals, 28(1), 21–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1944-9720.1995.tb00767.x
- Galton, F. (1883). Mental imagery. В F. Galton, Inquiries into human faculty and its development. (сс. 83–114). MacMillan Co. https://doi.org/10.1037/14178-016
- Goold, A., & Rimmer, R. (2000). Factors affecting performance in first-year computing. ACM SIGCSE Bulletin, 32(2), 39–43. https://doi.org/10.1145/355354.355369
- Hawk, T. F., & Shah, A. J. (2007). Using Learning Style Instruments to Enhance Student Learning. Decision Sciences Journal of Innovative Education, 5(1), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-4609.2007.00125.x
- Hayes, J., & Allinson, C. W. (1993). Matching Learning Style and Instructional Strategy: An Application of the Person-Environment Interaction Paradigm. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 76(1), 63–79. https://doi.org/10.2466/pms.1993.76.1.63
- Hayes, J., & Allinson, C. W. (1996). The Implications of Learning Styles for Training and Development: A Discussion of the Matching Hypothesis. British Journal of Management, 7(1), 63–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8551.1996.tb00106.x
- James William. (1980). The principles of psychology. MacMillan Co.
- Keefe, James W., & Ferrell, Barbara G. (1990). Developing a Defensible Learning Style Paradigm. Educational Leadership, 48(2), 57–61.
- Klein, K. (1993). Teaching Young Learners. English Language Teaching Forum, 31(14).
- Kolb, D. A. (1984). Experiential learning: Experience as the source of learning and development. Prentice-Hall.
- Lindsay, E.K. (1999). An analysis of matches of teaching style and the uses of education technology. The American Journal of Distance Education, 13(2), 113–119.
- Loo *, R. (2004). Kolb’s learning styles and learning preferences: Is there a linkage? Educational Psychology, 24(1), 99–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144341032000146476
- Memletics-learning-styles-inventory. (б. д.). memletics. http://www.memletics.com/
- Moenikia, M., & Zahed-Babelan, el. (2010). The role of learning styles in second language learning among distance education students. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2(2), 1170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.03.167
- Montgomery, S., & Grout, L. (1998). Student learning styles and their implications for teaching. Michigan: Centre for Research on Learning and Teaching.
- Moon, J. (2000). Children learning english (1. publ., 3. pr). Macmillan Heinemann.
- Oxford, R., & Crookall, D. (1989). Research on Language Learning Strategies: Methods, Findings, and Instructional Issues. The Modern Language Journal, 73(4), 404–419. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-4781.1989.tb05321.x
- Oxford, R. L. (1990). Language learning strategies: What every teacher should know (Nachdr.). Heinle & Heinle.
- Paivio, A. (1986). Mental representations: A dual coding approach. Oxford University Press ; Clarendon Press.
- Peirce, C. S. (2000). Writings of Charles S. Peirce: A chronological ed. Indiana university press.
- Phillips, S. (2001). Young learners (Nachdr.). Oxford Univ. Press.
- Reid, J. M. (1987). The Learning Style Preferences of ESL Students. TESOL Quarterly, 21(1), 87–111. https://doi.org/10.2307/3586356
- Reid, J. M. (Ред.). (1995). Learning styles in the ESL/EFL Classroom. Heinle & Heinle.
- Riding, R., & Grimley, M. (1999). Cognitive style, gender and learning from multi‐media materials in 11‐year‐old children. British Journal of Educational Technology, 30(1), 43–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8535.00089
- Rigney, J. W. (1978). Learning strategies: A theoretical perspective. New York: Academic Press., 164–205.
- Schmeck, R. R. (1988). Strategies and Styles of Learning. В R. R. Schmeck (Ред.), Learning Strategies and Learning Styles (сс. 317–347). Springer US. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-2118-5_12
- Seif, A. (2001). Educational psychology: Learning and education. Tehran: Agah.
- Skehan, P. (1991). Individual Differences in Second Language Learning. Studies in Second Language Acquisition, 13(2), 275–298. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0272263100009979


