Синаптические процессы в околоводопроводном сером веществе мозга на модели болезни Паркинсона с протекцией гидрокортизоном
Автор: Овсепян М.Э., Погосян М.В., Саркисян Р.Ш., Даниелян М.А., Карапетян К.В., Ваградян А.Г., Симонян Л.Г., Минасян А.Л., Карамян Г.Г., Саркисян Д.С.
Журнал: Психология. Психофизиология @jpps-susu
Рубрика: Психофизиология
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.17, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Обоснование: при нейродегенеративных болезнях, в особенности при болезни Паркинсона(БП), поражаются антиноцицептивные центры, что сопровождается хронической болью. Поэтому является актуальным изыскание фармакологических препаратов, приводящих к протекции развитияБП и возможного купирования боли, связанного с БП.
Активность одиночных нейронов, высокочастотная стимуляция, синаптические ответы, ротеноновая модель болезни паркинсона, ротенон, болезнь паркинсона, околоводопроводное серое вещество мозга, большое ядро шва, гидрокортизон
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147244044
IDR: 147244044 | УДК: 612.821 | DOI: 10.14529/jpps240208
Текст научной статьи Синаптические процессы в околоводопроводном сером веществе мозга на модели болезни Паркинсона с протекцией гидрокортизоном
Примерно у четверти пациентов с болезнью Паркинсона (БП) диагностируется умеренное когнитивное нарушение. Когнитивные нарушения значительно повышают риск развития деменции при БП по мере ее прогрессирования. Такие симптомы, как нарушение планирования, умственная отсталость и ухудшение памяти, вызванные деменцией при
БП, наносят серьезный вред здоровью пациентов.
Было показано, что у пациентов с БП наблюдаются аномальные изменения в определенных частотных диапазонах ЭЭГ [1]. Вследствие этого актуально проведение более подробных электрофизиологических исследований различных центров мозга, вовлеченных в патологию при БП.
Болевая система, включающая рецепторы, нервные пути и аналитические центры мозга, существует у многих видов животных. Существуют доказательства болевой системы у всех изученных позвоночных, и есть доказательства некоторых ее аспектов у беспозвоночных [2]. Это позволило провести прямое сравнение клеточных и молекулярных признаков, важных для ноцицепции и ноцицептивной пластичности у беспозвоночных и млекопитающих [3]. К тому же систематическая оценка боли с эволюционной точки зрения началась недавно и может оказаться важной для клиники [4]. И что особенно интересно, выбор действий болевых центров зависит от цепей, обеспечивающих петли прямой и обратной связи, которые модулируются пере дачей дофамина [5].
Дофамин известен как нейромедиатор, опосредующий вознаграждение и мотивацию, но он также может побуждать животных избегать неприятных ситуаций и раздражителей [6]. В последние годы у людей с БП боль из немоторных симптомов все чаще признается распространенной и беспокоящей, негативно влияющей на качество жизни [7–10]. Оптимизация лечения противопаркинсоническими препаратами должна быть первым фармакологическим шагом в лечении боли, связанной с БП. Для этого изучаются инновационные варианты лечения боли у этой группы пациентов [11]. Боль, связанная с БП, может быть вызвана моторными симптомами или нейротрансмиссией и восприятием [12–14]. Низкие уровни дофамина могут усиливать распространение сигналов болевых раздражителей, вызывая повышенную чувствительность к боли у пациентов с БП [15–16].
Из высших структур, участвующих в контроле боли, следует отметить околоводопроводное серое вещество мозга (Periaqueductal gray matter – PAG) и ядро шва магнус (Nucleus Raphe magnus – RMG) [17]. Благодаря своей роли в возбуждении и боли, PAG играет важную роль в хронических стрессовых состояниях, включающих тревогу, панику и депрессию [18]. Основное клиническое значение, касающееся PAG, включает не только его ан-тиноцицептивный эндогенный опиоидный, но и неопиоидный опосредованный контроль боли [18]. Точно так же воздействие RMG сильно изменяет восприятие боли, оказывая обезболивающее действие [19].
Наконец, представляет интерес роль гидрокортизона в качестве протектора при БП.
гидрокортизон рассматривается как потенциальный профилактический агент для повышения экспрессии гена паркина и придания устойчивости клеточным стрессам при БП [20].
В настоящем исследовании проведено изучение соотношения возбудительных и тормозных синаптических ответов одиночных нейронов PAG при стимуляции RMG с целью оценки механизмов поражения важных анти-ноцицептивных структур мозга на ротеноно-вой модели БП и успешности их протекции гидрокортизоном.
Материалы и методы
Проведены электрофизиологические исследования на 15 крысах линии Альбино (230 ± 30 г): интактных, на ротеноновой модели БП, индуцированной унилатеральным введением ротенона, и выдержанных до опыта 4 недели; и в условиях протекции формирования БП гидрокортизоном (по 14 инъекций через день в дозе 1,25 мг/кг, 0,1 %). Введение ротенона осуществляли в условиях нембута-лового наркоза (40 мг/кг, в/б) из расчета 12 μг в 0,5 μл димексида (со скоростью 1 μл/мин) в “medial forebrain bundle” по координатам стереотаксического атласа [21] (AP + 0,2; L ± 1,8; DV + 8 мм). Исследование проводилось в соответствии с принципами Базельской декларации и рекомендациями руководства ARRIVE [22]. В стереотаксическом аппарате производили трепанацию черепа от брегмы до лямбды и вскрывали твердую мозговую оболочку. Стеклянные микроэлектроды с диаметром кончика 1–2 µM, заполненные 2M NaCl, вводили в PAG согласно стереотаксическим координатам (AP–4,92; L ± 2,0; DV + 5,7 мм) для экстраклеточной регистрации спайковой активности одиночных нейронов. Согласно стереотаксическим координатам (AP–11,6; L ± 2,0; DV + 10,3 мм) осуществляли высокочастотную стимуляцию (ВЧС) RMG посредством прямоугольных толчков тока длительностью 0,05 мс, амплитудой 0,12–0,18 мВ, силой тока 0,32 мА и частотой 100 Гц в течение 1 секунды. Операции осуществляли на наркотизированных животных (уретан 1,2 г/кг в/б), зафиксированных в стереотаксическом аппарате.
Регистрацию нейрональной активности проводили с использованием компьютерной программы, позволяющей осуществлять селекцию спайков амплитудной дискриминацией. При этом для каждого зарегистрированного нейрона строились перистимульные гистограммы и оценивались средние частоты разрядов (в Гц) до, во время и после ВЧС RMG.
В зависимости от характера изменения частоты разрядов нейрона во время и после ВЧС по сравнению с частотой спайковых разрядов до ВЧС активность нейронов PAG проявлялась в виде тетанической депрессии (ТД) или тетанической потенциации (ТП) во время ВЧС RMG, а также посттетанической депрессией (ПТД) или посттетанической потен-циацией (ПТП) после ВЧС RMG. После суммации гистограмм с однотипным характером проявления нейрональных реакций расчитывались средние частоты разрядов до (F BE ), во время (F TT ) и после ВЧС RMG (F PE ) для всех зарегистрированных нейронов PAG.
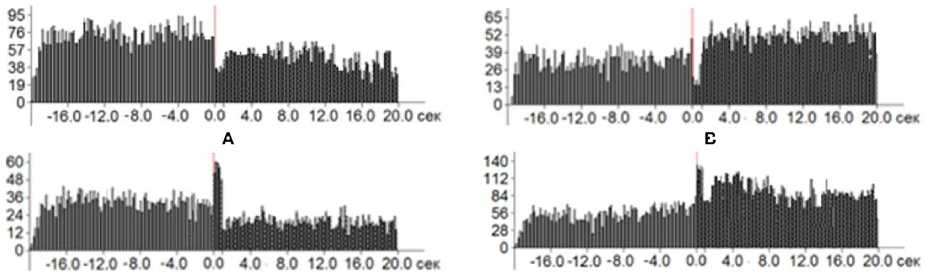
На рис. 1 представлены типичные суммарные гистограммы для четырех выделенных групп нейрональной активности.
В целом была зарегистрирована активность 241 нейрона PAG. Достоверность отличия данных, полученных для различных этапов экспериментов, оценивали с использованием t-критерия Стьюдента при уровне значимости р < 0,05. При оценке эффективности применения гидрокортизона в качестве протектора формирования БП использовали также критерий χ2 [23].
Результаты и обсуждение
В представленных ниже таблице и рис. 2 обобщены результаты анализа реакций нейронов PAG в ответ на ВЧС RMG в различных сериях проведенного исследования.
Проведенный анализ показал, что согласно критерию Стьюдента практически во всех сериях экспериментов частоты нейрональных разрядов у всех типов нейрональных реакций до, во время и после ВЧС RMG достоверно отличаются при уровне значимости p < 0,05. Исключение составляют только данные экспериментов с формированием ротеноновой модели БП. В этом случае отличие в значениях средних частот нейрональных разрядов до и после ВЧС RMG оказывается недостоверным.
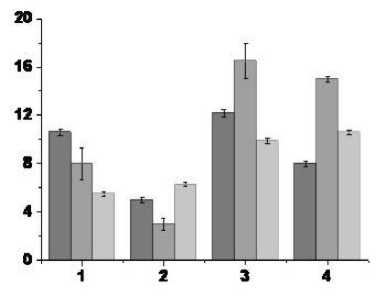
В норме для всех зарегистрированных нейронов RMG до, во время и после ВЧС RMG регистрируется нейрональная активность с частотой от 3 до 17 Гц (см. таблицу, рис. 2А). В целом оценивая отличия в значениях частоты нейронов для различных типов нейрональных реакций при ВЧС RMG в контрольной группе экспериментов можно отметить, что в первой (ТД-ПТД) и третьей (ТП-ПТД) группах нейронов имеет место уменьшение частоты разрядов по сравнению с частотой разрядов до ВЧС в 1,9 и 1,2 раза соответственно. Вместе с тем во второй (ТД-ПТП) и четвертой (ТП-ПТП) группах нейронов имеет место увеличение частоты разрядов по
A
B
C
D
Рис. 1. Суммарные гистограммы нейронов PAG с разным типом реакций в ответ на ВЧС RMG
А – тетаническая депрессия во время и после ВЧС (ТД-ПТД),
B – тетаническая депрессия во время ВЧС и посттетаническая потенциация после ВЧС (ТД-ПТП),
C – тетаническая потенциация во время ВЧС и посттетаническая депрессия после ВЧС (ТП-ПТД), D – тетаническая потенциация во время ВЧС и посттетаническая потенциация после ВЧС (ТП-ПТП). По оси ординат – количество спайков, по оси абсцисс – время. Начало ВЧС – с отметки «0,0» с.
-
Fig. 1. Sum histograms of PAG neuronal responses to HFS of the RMG
A – tetanic depression during and after HFS (TD-PTD),
B – tetanic depression during HFS and post-tetanic potentiation after HFS (TD-PTP),
С – tetanic potentiation during HFS and post-tetanic depression after HFS (TP-PTD),
D – tetanic potentiation during HFS and post-tetanic potentiation after HFS (TP-PTP).
The vertical axis (ordinate) represents the number of spikes, the horizontal axis denotes time. The onset of HFS is marked at “0.0” seconds.
Таблица Table
Средние значения частот нейронов PAG до, во время и после ВЧС в различных сериях проведенного исследования
Average frequencies of PAG neuronal responses before, during and after HFS in various series of the study
|
Контрольные эксперименты (n = 46) Control experiments (n = 46) |
|||
|
Характер нейрональных реакций Neuronal response |
До ВЧС Before HFS |
Во время ВЧС During HFS |
После ВЧС After HFS |
|
ТД-ПТД/TD-PTD |
10,6 ± 0,3 |
8,0 ± 1,3 |
5,5 ± 0,2 |
|
ТД-ПТП/TD-PTP |
5,0 ± 0,2 |
3,0 ± 0,5 |
6,3 ± 0,2 |
|
ТП-ПТД/TP-PTD |
12,2 ± 0,3 |
16,5 ± 1,5 |
9,9 ± 0,2 |
|
ТП-ПТП/TP-PTP |
8,0 ± 0,2 |
15,0 ± 0,2 |
10,6 ± 0,2 |
|
Ротеноновая модель БП (n = 80) Rotenone model of PD (n = 80) |
|||
|
Характер нейрональных реакций Neuronal response |
До ВЧС Before HFS |
Во время ВЧС During H FS |
После ВЧС After HFS |
|
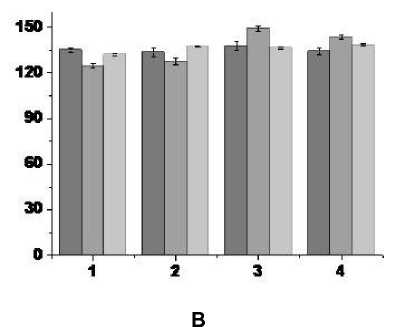
ТД-ПТД/TD-PTD |
135,1 ± 1,4 |
124,7 ± 1,3 |
132,0 ± 0,9 |
|
ТД-ПТП/TD-PTP |
133,5 ± 2,6 |
127,5 ± 2,2 |
137,4 ± 0,6 |
|
ТП-ПТД/TP-PTD |
137,7 ± 2,9 |
149,2 ± 0,2 |
136,6 ± 0,7 |
|
ТП-ПТП/TP-PTP |
134,2 ± 2,0 |
143,5 ± 1,5 |
138,4 ± 0,7 |
|
Ротеноновая модель БП в условиях протекции гидрокортизоном (n = 115) Rotenone model of PD with hydrocortisone (n = 115) |
|||
|
Характер нейрональных реакций Neuronal response |
До ВЧС Before HFS |
Во время ВЧС During H FS |
После ВЧС After HFS |
|
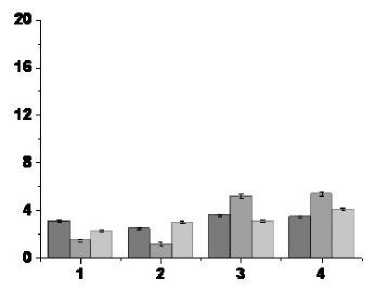
ТД-ПТД /TD-PTD |
3,1 ± 0,1 |
1,5 ± 0,1 |
2,3 ± 0,1 |
|
ТД-ПТП/TD-PTP |
2,5 ± 0,1 |
1,2 ± 0,2 |
3,0 ± 0,1 |
|
ТП-ПТД/TP-PTD |
3,6 ± 0,1 |
5,2 ± 0,2 |
3,1 ± 0,1 |
|
ТП-ПТП/TP-PTP |
3,5 ± 0,1 |
5,4 ± 0,2 |
4,1 ± 0,1 |
Примечание: (ТД-ПТД) – тетаническая депрессия во время и после ВЧС, (ТД-ПТП) – тетаническая депрессия во время ВЧС и посттетаническая потенциация после ВЧС, (ТП-ПТД) – тетаническая потенциация во время ВЧС и посттетаническая депрессия после ВЧС, (ТП-ПТП) – тетаническая потенциация во время ВЧС и посттетаническая потенциация после ВЧС; n – количество отведенных нейронов.
Note: (TD-PTD) – tetanic depression during and after HFS, (TD-PTP) – tetanic depression during HFS and post-tetanic potentiation after HFS, (TP-PTD) – tetanic potentiation during HFS and post-tetanic depression after HFS, (TP-PTP) – tetanic potentiation during HFS and post-tetanic potentiation after HFS; n is the number of recorded neurons.
сравнению с частотой разрядов до ВЧС в 1,3 и 1,4 раза, соответственно. Это свидетельствует о наличии определенного баланса депрессорных и возбудительных постстимульных проявлений активности исследуемых нейронов.
В экспериментах с формированием роте-ноновой модели БП до, во время и после ВЧС RMG регистрируется нейрональная активность с частотой от 124 до 150 Гц (см. таблицу, рис. 2B). При оценке характера нейрональных реакций в этой серии экспериментов прежде всего следует отметить многократное (10–40 раз) увеличение (эксайтотоксичность) по сравнению с контролем частоты разрядов нейронов для всех типов их реакций на ВЧС RMG (см. таблицу, рис. 2B). Кроме того, относительные изменения частот нейрональных разрядов во время ВЧС и до нее в различных группах нейронов составляет всего лишь 0,9– 1,06. При этом, как было отмечено выше, согласно результатам статистического анализа средние частоты нейрональных разрядов до и после ВЧС RMG совпадают. Все это свидетельствует об отсутствии превалирования возбудительных или депрессорных постстимульных проявлений активности нейронов PAG при формировании ротеноновой модели БП.
В экспериментах с ротеноновой моделью БП в условиях протекции гидрокортизоном до, во время и после ВЧС RMG формируется нейрональная активность с частотой от 3 до 5 Гц (см. таблицу, рис. 2C).
Оценивая отличия в значениях частоты нейронов для различных типов нейрональных
А
до ВЧС RMG / before HFS RMG
C
Рис. 2. Средние частоты нейронов PAG до, во время и после ВЧС RMG в норме (А), после формирования ротено-новой модели БП (B) и ротеноновой модели формирования БП в условиях протекции гидрокортизоном (С)
По оси ординат – частота спайковой активности в Гц, по оси абсцисс (1–4) – типы нейрональных реакций:
1 – ТД-ПТД, 2 – ТД-ПТП, 3 – ТП-ПТД и 4 – ТП-ПТП (описание типов нейрональных реакций см. рис. 1 или таблицу)

во время ВЧС RMG / during HFS RMG после ВЧС RMG / after HFS RMG
-
Fig. 2. Average frequencies of PAG neuronal responses before, during and after HFS of the RMG: under normal conditions (A), for the rotenone model of PD (B) and for the rotenone model of PD with hydrocortisone protection (С)
The vertical axis: spike activity in Hz, the horizontal axis (1-4): types of neuronal responses:
1 – TD-PTD, 2 – TD-PTP, 3 – TP-PTD and 4 – TP-PTP (see Fig. 1 or table)
реакций при ВЧС RMG этой серии экспериментов, можно отметить, что в первой (ТД-ПТД) и третьей (ТП-ПТД) группах нейронов имеет место уменьшение частоты разрядов по сравнению с частотой разрядов до ВЧС в 1,3 и 1,2 раза соответственно. Вместе с тем во второй (ТД-ПТП) и четвертой (ТП-ПТП) группах нейронов имеет место увеличение частоты разрядов по сравнению с частотой разрядов до ВЧС в 1,2 и 1,2 раза соответственно. Это свидетельствует о восстановлении определенного баланса депрессорных и возбудительных постстимульных проявлений активности исследуемых нейронов. Вместе с тем резкое уменьшение частоты нейрональных разрядов и приближение их значений к показателям контрольных экспериментов может свидетельствовать об успешной протекции гидрокортизоном развития БП.
Для более строгого обоснования сделанного предположения были рассчитаны отношения (F TT / F BE ) и (F PE / F BE ) для всех типов нейрональных реакций в контрольной группе экспериментов и экспериментов с ротеноно-вой моделью БП в условиях протекции гидрокортизоном. Графики для частот F TT и F PE , нормированные на соответствующие значения частоты нейронов до ВЧС – F BE , представлены на рис. 3.
Расчеты с использованием критерия χ2 показали, что при уровне значимости p < 0,05 распределения частот в контрольной группе экспериментов совпадают с распределением частот нейронов в экспериментах с ротеноновой моделью БП в условиях протекции гидрокортизоном (χ2 = 0,14, C = 7). Полученные результаты приводят к однозначному заключению об эффективности ис-
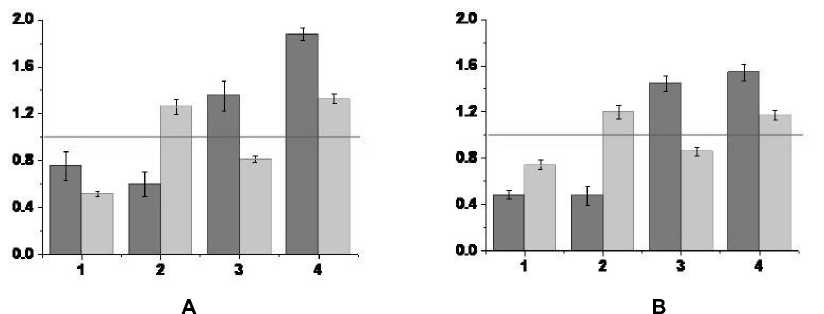
Отношение средних частот нейрональных разрядов во время ВЧС RMG к значениям средних частот разрядов до ВЧС
Ratio of average frequencies of neuronal discharges during and after HFS of the RMG

Отношение средних частот нейрональных разрядов после ВЧС RMG к значениям средних частот разрядов до ВЧС
Ratio of average frequencies of neuronal discharges after and before HFS of the RMG
Рис. 3. Относительные к значениям средних частот престимульных гистограмм частоты нейронов PAG во время и после ВЧС RMG для различных серий проведенных экспериментов
А – в норме, B – в условиях протекции гидрокортизоном формирования ротеноновой модели БП.
По оси ординат – значения относительных частот, по оси абсцисс (1–4) – типы нейрональных реакций:
1 – ТД-ПТД, 2 – ТД-ПТП, 3 – ТП-ПТД и 4 – ТП-ПТП (описание типов нейрональных реакций см. рис. 1 или таблицу).
-
Fig. 3. Frequencies of PAG neuronal responses during and after HFS of the RMG relative to the values of the average frequencies of prestimulus histograms for various series of experiments: under normal conditions (A), for the rotenone model of PD with hydrocortisone protection (B)
On the vertical axis: relative frequencies, the horizontal axis: (1–4) types of neuronal responses:
-
1 – TD-PTD, 2 – TD-PTP, 3 – TP-PTD and 4 – TP-PTP (see Fig. 1 or Table)
пользования гидрокортизона для протекции формирования БП.
Заключение
В настоящем исследовании на ротеноновой модели БП в нейронах PAG, активированных ВЧС RMG, выявлено мощное превышение возбудительных синаптических эффектов, представленных в виде чрезмерно высокой частоты импульсной активности до, во время и после ВЧС RMG. Принято считать ее проявлением эксайтотокcичности, возникающей в результате снижения возбуждения глутаматных рецепторов [24] и приводящей к апоптозу с последующей гибелью нейронов [25, 26].
Вместе с тем в рамках ротеноновой модели БП показана выраженная протекторная роль гидрокортизона. Предположительно это может стать основанием для использования гидрокортизона в качестве первого фармакологического шага в купировании боли, связанной с БП.
Список литературы Синаптические процессы в околоводопроводном сером веществе мозга на модели болезни Паркинсона с протекцией гидрокортизоном
- Yi G., Wang Y., Wang L. et al. Capturing the Abnormal Brain Network Activity in Early Parkinsons Disease with Mild Cognitive Impairment based on Dynamic Functional Connectivity. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering. 2023;31;1238–1247. DOI: 10.1109/TNSRE.2023.3243035
- Broom D.M. Evolution of pain. In Pain: its nature and management in man and animals. Ed. Soulsby, Lord and Morton, D. Royal Society of Medicine International Congress Symposium Series. 2001;246:17–25.
- Walters E.T., de C Williams A.C. Evolution of mechanisms and behaviour important for pain. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 2019;374(1785):20190275. DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0275
- Nesse R.M., Schulkin J. An evolutionary medicine perspective on pain and its disorders. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 2019;374(1785):20190288. DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0288
- Strausfeld N.J., Hirth F. Introduction to Origin and evolution of the nervous system. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 2015;370(1684):20150033. DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0033
- Wenzel J.M., Oleson E.B., Gove W.N. et al. Phasic Dopamine Signals in the Nucleus Accumbens that Cause Active Avoidance Require Endocannabinoid Mobilization in the Midbrain. Current Biology. 2018;28(9):1392–1404.e5. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.03.037.
- Langston J.W. The Parkinsons complex: Parkinsonism is just the tip of the iceberg. Annals of Neurology. 2006;59:591–596. DOI: 10.1002/ana.20834
- Blanchet P.J., Brefel-Courbon C. Chronic pain and pain processing in Parkinsons disease. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry. 2018;87(Pt.B):200–206. DOI: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.10.010
- Antonini A., Tinazzi M., Abbruzzese G. et al. Pain in Parkinsons disease: facts and uncertainties. European Journal of Neurology. 2018;25(7):917–e969. DOI: 10.1111/ene.13624
- Nguy V., Barry B.K., Moloney N. et al. The associations between physical activity, sleep, and mood with pain in people with Parkinsons disease: an observational cross-sectional study. Journal of Parkinsons Disease. 2020;10:1161–1170. DOI: 10.3233/JPD-201938
- Brunner R., Gerberich A. Managing Pain in Parkinsons Disease. Practical Pain Manage-ment. 2021;21(1). URL: https://www.medcentral.com/neurology/parkinsons/managing-pain-parkinson-disease (accessed 24.11.2023)
- Gandolfi M., Geroin C., Antonini A. et al. Understanding and treating pain syndromes in Parkinsons disease. International Review of Neurobiology. 2017;134:827–858. DOI: 10.1016/bs.irn.2017.05.013
- Rukavina K., Leta V., Sportelli C. et al. Pain in Parkinsons disease: new concepts in path-ogenesis and treatment. Current Opinion in Neurology. 2019;32:579–588. DOI: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000711
- Suppa A., Leone C., Di Stasio F. et al. Pain-motor integration in the primary motor cortex in Parkinsons disease. Brain Stimulation. 2017;10(4):806–816. DOI: 10.1016/j.brs.2017.04.130
- Sung S., Vijiaratnam N., Chan D.W.C. et al. Parkinson disease: A systemic review of pain sensitivities and its association with clinical pain and response to dopaminergic stimulation. Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 2018;395:172–206. DOI: 10.1016/j.jns.2018.10.013
- Joseph C., Jonsson-Lecapre J., Wicksell R. et al. Pain in persons with mild-moderate Parkinsons disease: a cross-sectional study of pain severity and associated factors. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research. 2019;42(4):371–376. DOI: 10.1097/MRR.0000000000000373
- Back F.P., Carobrez A.P. Periaqueductal gray glutamatergic, cannabinoid and vanilloid receptor interplay in defensive behavior and aversive memory formation. Neuropharmacology. 2018;135:399–411. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.03.032
- Bourbia N., Pertovaara A. Involvement of the periaqueductal gray in the descending antinociceptive effect induced by the central nucleus of amygdala. Physiological Research. 2018;67(4):647–655. DOI: 10.33549/physiolres.933699
- Wang Q.P., Nakai Y. The dorsal raphe: an important nucleus in pain modulation. Brain Research Bulletin. 1994;34(6):575–585. DOI: 10.1016/0361-9230(94)90143-0
- Ham S., Lee Y.I., Jo M. et al. Hydrocortisone-induced parkin prevents dopaminergic cell death via CREB pathway in Parkinsons disease model. Scientific Reports. 2017;7(1):525. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-00614-w
- Paxinos G., Watson C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Elsevier. Academic Press. 2005:367.
- Kilkenny C., Browne W., Cuthill I.C. et al. Animal research: Reporting in vivo experiments: The ARRIVE guidelines. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2010;160(7):1577–1579. DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00872.x
- Орлов А.И. Прикладная статистика. М.: Изд-во «Экзамен». 2004. 656 c.
- Hynd M.R., Scott H.L., Dodd P.R. Glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity and neurodegeneration in Alzheimers disease. Neurochemistry International. 2004;45(5):583–595. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2004.03.007.
- Lucas D.R., Newhouse J.P. The toxic effect of sodium L-glutamate on the inner layers of the retina. AMA Archives of ophthalmology. 1957;58(2):193–201. DOI: 10.1001/archopht.1957.00940010205006.
- Olney J.W. Brain lesions, obesity, and other disturbances in mice treated with monosodium glutamate. Science. 1969;164(3880):719–721. DOI: 10.1126/science.164.3880.719.


