Small business development as a factor of increasing financial autonomy of municipal entities
Автор: Uskova Tamara Vitalevna, Gutnikova Elena Aleksandrovna
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Business sectors
Статья в выпуске: 2 (10) т.3, 2010 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article examines the main results of the reform of local government. It shows that along with the positive results achieved during the transformation, a number of problems remain unresolved. The most significant among them is lack of financial autonomy of municipalities. Solutions to this problem are proposed. One of the promising directions of formation and expansion of own economic base of the municipality is the development of small businesses.
Municipalities, local budget, financial independence, development of small and medium business
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223194
IDR: 147223194 | УДК: 332.14(470.12)
Текст научной статьи Small business development as a factor of increasing financial autonomy of municipal entities
Indicators 2005 2008 Thous. rub. % to revenues in all Thous. rub. % to revenues in all Tax on organizations profit 39325.0 8.0 30589.0 3.5 Tax on personal income 142998.0 28.9 110461.0 12.5 Taxes on gross income 5380.0 1.1 21218.0 2.4 Property taxes 20668.0 4.2 24910.0 2.8 Other taxes 4340 0.8 - - Total tax revenues 212711.0 43.0 187178.0 21.1 Revenues from the use of property in the state and municipal ownership 3674.0 0.7 5541.0 0.6 Payments for the use of natural resources 1000.0 0.2 1552.0 0.2 Revenues from the sale of tangible and intangible assets 2550.0 0.5 24926.0 2.8 Fines, penalties, restitution 2531.0 0.5 2000.0 0.2 Other non-tax revenues of municipal budgets 1186.0 0.2 150.0 0.0 Total non-tax revenues 10941.0 2.2 34169.0 3.9 Total budget revenue of the district 223652.0 45.2 221347.0 25.0 Gratuitous revenues 258737.0 52.3 664179.0 75.0 Total revenues 494559.4 100.0 885526.0 100.0 Source: Federal state statistics service [Electronic resourse]. – Access mode:
Source: Federal state statistics service [Electronic resourse]. – Access mode:
Table 5. Structure of revenues of rural settlements budgets of the Vologda oblast in 2008
|
Rural settlements |
Total revenues |
Tax revenues |
Non-tax revenues |
Gratuitous and irreversible revenues |
||||
|
Thous. rub. |
% |
Thous. rub. |
% to revenues in all |
Thous. rub. |
% to revenues in all |
Thous. rub. |
% to revenues in all |
|
|
Votchinskoe |
3316.9 |
100.0 |
168.7 |
5.1 |
7.9 |
0.2 |
3140.3 |
94.7 |
|
Borisovskoye |
3308.2 |
100.0 |
266.6 |
8.1 |
12.6 |
0.4 |
3029.1 |
91.6 |
|
Nefedovskoye |
2884.7 |
100.0 |
236.4 |
8.2 |
24.8 |
0.9 |
2623.5 |
90.9 |
|
Vysokovskoye |
3542.7 |
100.0 |
366.2 |
10.3 |
11.4 |
0.3 |
3165.1 |
89.3 |
|
Nesvoyskoye |
3114.3 |
100.0 |
397.8 |
12.8 |
35.7 |
1.1 |
2680.9 |
86.1 |
|
Bereznikovskoye |
4078.0 |
100.0 |
533.8 |
13.1 |
38.1 |
0.9 |
3506.2 |
86.0 |
|
Kipelovskoye |
4818.2 |
100.0 |
846.6 |
17.6 |
47.2 |
1.0 |
3924.4 |
81.5 |
|
Novlenskoye |
5574.8 |
100.0 |
982.2 |
17.6 |
202.6 |
3.6 |
4403.3 |
79.0 |
|
Veprevskoye |
4093.7 |
100.0 |
744.8 |
18.2 |
138.7 |
3.4 |
3210.1 |
78.4 |
|
Goncharovskoye |
4035.3 |
100.0 |
725.6 |
18.0 |
294.1 |
7.3 |
3015.7 |
74.7 |
|
Fedotovskoye |
15071.4 |
100.0 |
3950.1 |
26.2 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
11121.2 |
73.8 |
|
Staroselskoye |
4149.2 |
100.0 |
1104.8 |
26.6 |
132.7 |
3.2 |
2911.7 |
70.2 |
|
Sosnovskoye |
10812.6 |
100.0 |
2816.6 |
26.0 |
577.0 |
5.3 |
7419.0 |
68.6 |
|
Markovskoyе |
5644.3 |
100.0 |
1772.6 |
31.4 |
50.3 |
0.9 |
3821.4 |
67.7 |
|
Pudegskoye |
3976.6 |
100.0 |
473.4 |
11.9 |
817.4 |
20.6 |
2685.8 |
67.5 |
|
Kubenskoye |
7881.6 |
100.0 |
2349.2 |
29.8 |
294.1 |
3.7 |
5238.4 |
66.5 |
|
Oktyabrskoye |
6482.6 |
100.0 |
2023.9 |
31.2 |
174.3 |
2.7 |
4284.3 |
66.1 |
|
Semenkovskoye |
13487.2 |
100.0 |
5017.0 |
37.2 |
903.7 |
6.7 |
7566.5 |
56.1 |
|
Podlesnoye 1 |
16355.2 |
100.0 |
6911.4 |
42.3 |
622.5 |
3.8 |
8849.2 |
54.1 |
|
Raboche-Krestyanskoye |
7229.9 |
100.0 |
3459.3 |
47.8 |
151.0 |
2.1 |
3619.6 |
50.1 |
|
Prylutskoye |
4935.8 |
100.0 |
3257.9 |
66.0 |
222.9 |
4.5 |
1471.1 |
29.8 |
|
Leskovskoye |
17035.3 |
100.0 |
2842.8 |
16.7 |
9139.5 |
53.7 |
5053.0 |
29.7 |
|
Spasskoye |
8960.9 |
100.0 |
5351.6 |
59.7 |
1756.4 |
19.6 |
1870.5 |
20.9 |
Source: Data are provided by the administration of the Vologda oblast.
This is true for other regions: in the majority of rural settlements proportion of own funds in total revenue does not exceed 20% (fig. 2) .
In the structure of budget revenues of urban settlements (compared to rural) proportion of tax and non-tax sources is higher, but here
Figure 2. The distribution of rural settlements of the Vologda oblast depending on the proportion of own funds in total revenues in 2006 – 2008
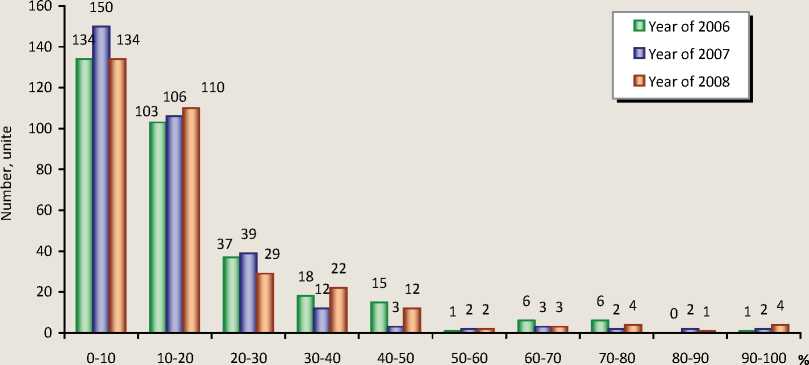
Source: Federal state statistics service [Electronic resourse]. – Access mode:
irreversible revenues are dominated too. In 2008 the number of municipalities (Krasavino, Zhelyabovo, Chebsara and Khokhlovo), they accounted for more than 80%.
Consequently, the functioning of local government at present is largely achieved through financial assistance from higher budgets. For these purposes, the regional budget of the Vologda region formed following regional funds:
-
• financial support to municipal districts (urban districts) and financial support to settlements for levelling local budgets;
-
• for balance of local budgets to provide additional support to local budgets and ensuring their balance;
-
• co-financing of social expenditures for the equity financing of socially significant costs;
-
• compensation for the financial provision of certain state powers allocated to municipalities.
Table 6. Distribution of answers of Heads of municipal districts given to the question: “Please, assess the provision of your municipal entity with own and total revenues” (in % of respondents)
|
Municipal entities |
Total revenue proision |
Own revenue provision |
||||||
|
extremely low (0-30%) |
low (40-60%) |
middle (70-90%) |
high (more than 90%) |
extremely low (0-30%) |
low (40-60%) |
middle (70-90%) |
high (more than 90%) |
|
|
Year of 2006 |
||||||||
|
Urban settlements |
40 |
40 |
- |
20 |
63.7 |
27.3 |
9 |
- |
|
Rural settlements |
40.1 |
23.4 |
31.7 |
4.8 |
87.2 |
7.8 |
4 |
1 |
|
Municipal districts |
40 |
40 |
- |
20 |
85.8 |
14.2 |
- |
- |
|
Year of 2007 |
||||||||
|
Urban settlements |
- |
33.4 |
66.6 |
0 |
40 |
20 |
40 |
- |
|
Rural settlements |
25.4 |
22.5 |
38.1 |
14.2 |
87.3 |
6.3 |
3.8 |
2.6 |
|
Municipal districts |
7.7 |
38.5 |
38.5 |
15.4 |
50 |
42.8 |
- |
7.1 |
|
Year of 2008 |
||||||||
|
Urban settlements |
23.1 |
46.2 |
30.7 |
- |
43.7 |
25 |
25 |
6.3 |
|
Rural settlements |
50 |
28.7 |
18.3 |
3 |
77.9 |
14.6 |
7.5 |
- |
|
Municipal districts |
23.5 |
47.1 |
29.4 |
- |
52.9 |
41.2 |
5.9 |
- |
The total amount of transfers from the regional budget to district and settlement budgets has increased from 9878.23 million rubles. (41.5% of total expenditures) in 2006 to 17223.16 million rubles (43.6%) in 2008. However, despite this positive development, the problem of local government finances remains unsolved.
According to the survey, 80% of Heads of rural settlements consider provision of municipal entities as low and extremely low. About 70% of Heads of urban settlements take the same view (tab. 6) .
In addition, significant funds of interbudget transfers are allocated for target use. Lack of “free funds” is resulting in limited capacity of local governments in addressing the challenges of socio-economic development of the municipality. In accordance with Federal law № 131 in 2008 the transition period of the reform of local government ended, and its full implementation began. It was expected that by 2009 the municipalities will have formed its own economic base, which will ensure financial independence of local budgets. But, as it is shown in the analysis, the situation of municipalities with its own revenues is rather difficult. And in connection with the crisis in the economy, the expenditures of higher-level budgets have reduced (in 2009 the budget of the Vologda region was “cut” by 9.1 billion rubles), including the support of municipalities. The issue of the possibility of performing functions carried on local government is remained open. In this respect, it is actual to find and develop measures which will form and expand the economic base of municipalities, “the transfer of the center of gravity to domestic sources calling for funds in” [7].
The Heads of local administrations believe that the most promising measures that contrib-
Table 7. The distribution of respondents' answers to the question: “In your opinion, what measures should the local authorities of the municipal entity take to expand its economic base?” (in % of respondents)
I t is evident that high expectations in the municipalities are connected with the development of private business. The most promising according to the administrative Heads are: economically active population, primarily based on the labor of family members (this is indicated by 43% of Heads of rural settlements and municipal districts) and the development of small and medium-sized enterprises, which main activity is the forest industry, tourism, building, etc. (48% of Heads of administration of rural settlements, 72% – urban and 95% – areas).
The forms of self-employment include work in individual farmsteads (especially in rural areas), farming, home-based work, small retail trade, services for processing gardens, harvesting. “All these forms “are useful because they can serve as a “primitive accumulation of capital” and create the material basis transition for theirs owners to the productive activities” [8]. As for the development of small business, according to the Chief of the Department of Economics, L.G. Iogman, in some districts it brings a quarter of all tax revenues [9].
However, many unsolved problems inhibit the development of small enterprises and individual entrepreneurs. The existing problems are: excessive administrative pressure of monitoring bodies, the high tax burden and rents, poor access to government contracts, the difficulty to connect small businesses to power transmission lines and other infrastructure, difficulties in obtaining bank loans and the need to purchase the leased premises on a shortage of funds.
The main condition for overcoming the difficulties, as emphasized in [10], is a joint coordinated action between the authorities of Russia, the subjects of the federation, as well as local authorities.
Government of the Vologda region has developed and adopted a series of laws aimed at the organizational and economic support to this sector of the economy [11 – 13]. Most significant among them are the following.
-
• Law “On the development of small and medium enterprises in the Vologda oblast” (from 05.12.2008). In order to stimulate development of small and medium enterprises law defined such forms of state support as financial, property, information, consulting, support in training, retraining and upgrading skills of workers. The measures to promote innovation and production activities of small businesses are included.
-
• Target Program “Development of small and medium enterprises in the Vologda oblast in 2009 – 2012” (from 27.01.2009). For its implementation more than 65 million rubles were allocated from the budget in 2009. In addition to the regional funding, were received federal appropriations of $74.9 million.
-
• The Law of the oblast “On the application by individual entrepreneurs of simplified system of taxation based on the patent within the territory of the Vologda oblast” (adopted 27.11.2009, entered into force 01.01.2010). With the adoption of the law, individual entrepreneurs – small businesses have the right to work on the simplified tax system – based on the patent. The purpose of the law is to simplify the procedure for record-keeping by individual entrepreneurs, to create favorable conditions for their work. Now the entrepreneur can make a choice between a patent, a single tax on imputed income and a simplified tax system and apply the most favorable tax treatment.
In the crisis, the patent system will stimulate the legalization of proceeds from activities traditionally located in the “shadow”, such as the transport of passengers, renting, housing, household services, carried out at home.
However, some problems still remain unsolved. To eliminate them, we should develop mechanisms for increasing the interest of regional administrations in the development of small businesses.
First, it is necessary to improve the existing budgeting and tax legislation. One of their main shortcomings is the lack of direct interest of local authorities in the development of small business in its municipal entity. The first step in this direction is the adoption of the law “On the application by individual entrepreneurs of simplified system of taxation on the basis of a patent on the territory of the Vologda oblast”. It is assumed that this law will force municipal governments to work with areas of active individual entrepreneurs, as well as 90% of the collected taxes will remain in the local budgets (this practice should be extended to the settlements). Secondly, we should develop and implement a methodology to assess the work of the municipal administrations to develop small businesses, aimed at monitoring the effectiveness of ongoing activities of regional and municipal development programs to small businesses.
An equally important task of the local administrations in the lack of its own economic base is to increase the efficiency of cooperation with the government, primarily with the departments and local authorities to create conditions for the development of small businesses. While such interaction, in the opinion of the Heads, can hardly be called effective (tab. 8) .
The problem of the formation of municipal property requires a fast solution. During the reform of local self-government the government of the Vologda oblast has already taken 38 laws on the division of property of 24 districts. In particular, in 2008 the settlements have been given equipment to perform powers on culture and sport, in 2009 work was conducted on the delimitation of the municipal housing stock, housing and communal services facilities [14].
Table 8. The effectiveness of the interaction of local government and executive authorities in the oblast (estimated by the Heads of municipalities, in % of respondents)
|
Bodies of executive power |
Efficiency of interaction |
|||
|
adequate |
acceptable |
inadequate |
extremely low |
|
|
Department of Finance |
18.8 |
50.6 |
26.1 |
4.5 |
|
Department of municipal development |
16.9 |
47.9 |
28.9 |
6.2 |
|
Department of land relations |
9.4 |
44.3 |
36.2 |
10.2 |
|
Department of Property Relations |
9.7 |
44.3 |
35.4 |
10.5 |
|
Department of Agriculture |
7.7 |
39.2 |
36.5 |
16.7 |
|
Department of Forestry |
7 |
35.7 |
37 |
20.4 |
Table 9. Distribution of the Heads’ answers on the question: “Please, assess your municipal property provision” (in% of respondents)
|
Municipalities |
Property provision |
|||
|
extremely low (0-30%) |
low (40-60%) |
middle (70-90%) |
high (более 90%) |
|
|
Year of 2006 |
||||
|
Urban settlements |
100 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Rural settlements |
56.6 |
15 |
25 |
3.4 |
|
Municipal districts |
40 |
- |
60 |
- |
|
Year of 2007 |
||||
|
Urban settlements |
70 |
20 |
10 |
0 |
|
Rural settlements |
40.1 |
23.2 |
32.6 |
4.1 |
|
Municipal districts |
14.2 |
42.8 |
35.7 |
7.1 |
|
Year of 2008 |
||||
|
Urban settlements |
68.8 |
25 |
6.2 |
- |
|
Rural settlements |
38.9 |
31.5 |
29.1 |
0.5 |
|
Municipal districts |
11.8 |
23.5 |
64.7 |
- |
However, the Heads of local administrations in the settlements, especially rural, are dissatisfied with facilities with a high moral and physical wear. Currently, most Heads (almost 70% of Heads of rural settlements, 94% – urban and 35% – municipal) evaluate the provision of their municipal property as very low and low (tab. 9) .
However, increased availability of municipal property will create an attractive environment for small business development, for example, local governments will be able to rent space on favorable terms, to provide land for agriculture or construction, etc.
Also, regional authorities, according to the Heads of local governments, should adopt more effective measures to promote agriculture, forestry, tourism industry, to develop clear rules of volumes, timing and frequency of checks by supervising bodies of small businesses, provide more significant tax benefits, deferral of lease payments.
Municipal authorities have a special role in the development of small businesses. Their activity depends directly on the ground implementation of decisions taken by higher regional authorities. Available resources in the municipality are needed in order to identify areas and mechanisms for their best use for the development of small forms of economic activity and on the basis of information received to develop a comprehensive program for the development of small businesses.
Among its main objectives can be identified (tab. 10) .
First, the removal of bureaucratic obstacles and barriers from the part of municipal employees (this is indicated 50% by Heads of urban settlements, 28% – rural and 52% – municipal areas). Currently, according to managers of small firms, the most pressing issues are: delays in the timing of consideration of applications from business representatives (on participation in tenders, municipal orders, lease or sale of municipal property, etc.) and transfer of municipal property to inefficient users. Therefore it is necessary to strengthen the responsibility of officials for violation of their duties.
Secondly, the organization of dialogue and interaction with business representatives, during which will be revealed factors that had a negative impact on their activities, and developed recommendations to remedy the situation [15]. At present, the effectiveness of the interaction of governments with local entrepreneurs is very low (fig. 3) . Particularly difficult situation is in rural areas.
Thirdly, the improvement of information and advisory services for small business, that is the creation on the municipal level of information management system for small and medium businesses, containing information about:
-
- regulatory framework of small forms of management;
Table 10. Distribution of answers of the heads of municipalities to the question: “What should the local authorities do for the development of interaction between local authorities of your municipal entity and private business?” (in % of Heads who answered)
|
Optional responses |
Municipal entities |
||
|
urban settlements |
rural settlements |
municipal regions |
|
|
Create conditions for the legalization of private business |
22.2 |
27.4 |
52.4 |
|
Eliminate bureaucratic obstacles on the part of municipal servants |
50 |
28.3 |
52.4 |
|
Organize dialogue and interaction with representatives of business |
50 |
21 |
47.6 |
|
Improve municipal infrastructure |
33.3 |
26.5 |
47.6 |
|
Provide advice help in establishing inter-farm relations (e.g., the formation of the resource-production chains, cooperatives, etc.) |
16.7 |
11.4 |
38.1 |
|
Coordinate the interests of subsoil, forest, water and land use |
27.8 |
27.4 |
38.1 |
|
Involve workforce in business, to carry out their training |
27.8 |
22.8 |
33.3 |
|
Provide legal support (acquaintance with the normative base, etc.) |
5.6 |
19.6 |
28.6 |
|
Create a database of reliable information about the municipality |
22.2 |
3.7 |
14.3 |
|
Assist in the technological upgrading of enterprises, creating new products |
5.6 |
11 |
9.5 |
Figure 3. Distribution of answers of the Heads of municipalities to the question: “Assess the effective interaction of bodies of local self-government of your municipal entity with local businesses in 2008” (in% of respondents)
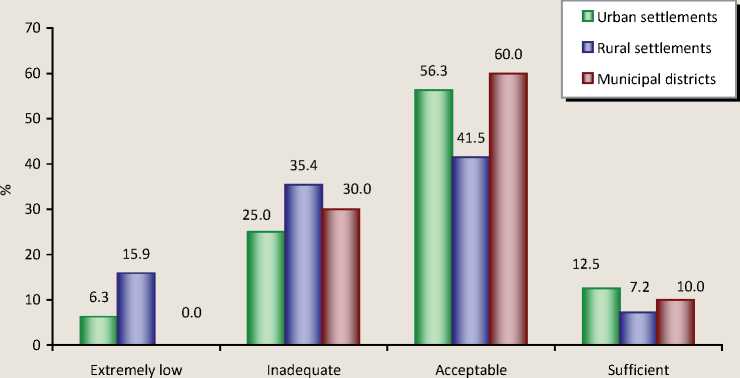
Interection effectiveness
-
- associations of small forms of management;
-
- existing infrastructure support for small businesses;
-
- bodies of exercising control and supervisory functions;
-
- existing organizations for training, marketing and other types of services for small forms of management;
-
- programs and projects of sector development of the economy of the region and municipal entity;
-
- contests and the conditions of competition;
-
- organizing and conducting business, for example, choice of tax regimes, sale channels.
Fourth, the organization of clear control over the use of subsoil resources in the field, forest, water and land use to prevent abuse. Particular attention should be paid to land traffic, as well as the participation of the unauthorized transfer of agricultural land in the land of other categories. This prevents the development of personal subsidiary plots and farms.
Fifth, the provision of certain services produced by public institutions, such as the strengthening and development of training system for small forms of management.
Sixth, the financial support of small forms of farming, granting, tax credits, project financing, assistance in obtaining resources (e.g., mortgages, loans, etc.), assistance in obtaining provincial, federal and other investments.
Seventh, assistance in finding markets and establishing production and technological linkages, cooperation and integration of small farms, which will improve efficiency, promote cooperation between large and small businesses.
Small business development is possible only through joint and concerted action by regional and municipal authorities, in which businessmen should be able to deal with the material, credit and financial, staffing and other issues in his district. This will facilitate the development of small businesses in the municipalities, on the stability of which depends increased the local budget, expanding of the economic base of the municipality – that is of all that will allow local authorities to achieve the strategic goal of the municipality – to maximize the welfare of their citizens.
Список литературы Small business development as a factor of increasing financial autonomy of municipal entities
- Tatarkin, A.I. Theoretical, organizational and economic approaches to improve local governance/A.I. Tatarkin, V.S. Bochko//Economic science of modern Russia. -2008. -№ 2. -P. 7.
- Batov, G. Problems of organization of local government/G. Batov//The Economist. -2008. -№ 3. -P. 81.
- Local government in the Vologda oblast: inf. newsletter/The government of the Vologda oblast. -Vologda, 2007. -№ 1. -59 p.
- Local government in the Vologda oblast: inf. newsletter/The government of the Vologda oblast. -Vologda, 2007. -№ 2. -127 p.
- Problems of reforming of local self-government and their solutions: a report on R&D/E.A. Gutnikova, T.V. Uskova. -Vologda, 2009. -73 p.
- Spatial aspects of the region development/V.A. Ilyin, M.F. Sychev, K.A. Gulin; ed. by V.A. Ilyin. -Vologda: VSCC CEMI RAS, 2008. -298 p.
- The development potential of municipal entities: the content, assessment, management (on materials of the Komi Republic); ed. by V.N. Lazhentsev. -Syktyvkar: KSC UD RAS, 2008. -344 p.
- Assessment and capacity building of the municipal district/S. Yahnyuk//Agricultural sector: economics, management. -2007. -№ 11. -P. 21.
- Support in many ways//Red North. -2009. -Dec. 22.
- Minakir, P.A. Economy and space/P.A. Minakir/Spatial economy. -2005. -№ 1. -P. 4.
- Anti-crisis “recipes”//Red North. -2009. -Jan. 27.
- Address from the Governor of the Vologda oblast Vyacheslav Pozgalev to legislative Assembly of the Vologda oblast//Red North. -2009. -Dec. 3.
- Save jobs, support business//Red North. -2009. -May 16.
- Anticrisis: what has been done?//Red North. -2009. -Feb. 19.
- Osipova, A.A. Promotion of small business development in the region/A.A. Osipova, O.V. Sidorenko//Spatial economics. -2007. -№ 2. -P. 61.


