Study of the stability of zeolite suspensions for cement systems
Автор: Samchenko S.V., Kozlova I.V., Sinotova M.V., Vovchensky D.N., Sirotkina K.A.
Журнал: Nanotechnologies in Construction: A Scientific Internet-Journal @nanobuild-en
Рубрика: Construction materials science
Статья в выпуске: 3 Vol.17, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. In Russia, the focus of scientific research in the construction industry is on the development of new materials with high functionality, durability, and strength. These materials also have various unique properties that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. Fine dispersed additives are used in the binder, for the construction of objects that require increased strength, or for repair work where early strength gain of the repair mixture is important. To improve the physical and mechanical properties of the hardened cement paste, which contains finely dispersed additives, it is necessary to consider the issue of uniform distribution of submicron particles in the volume of the cement composite. The study of this issue is one of the objectives of this study. Materials and methods. Fine dispersed zeolite, which has high ion-exchange, sorption, catalytic properties, was selected as the object of study, and the possibility of its introduction into the cement composition in the form of a stabilized suspension instead of mixing water was assessed/ Zeolite suspension with concentration of 10, 30, 50 g/l was prepared by mechanical stirring with a magnetic stirrer and ultrasonic dispersion under thermostatted conditions. The time of mechanical and ultrasonic treatment of suspensions was 20 min. Suspensions were prepared in two dispersion media – water and water-polymer (water + plasticizer). Physicomechanical tests of samples were carried out in accordance with current national and international standards and methods. Results. Studies of sedimentation stability of suspensions showed that the most stable suspension was stabilized by ultrasonic treatment and plasticizer. The sedimentation velocity of suspension particles in the first period was (3.43÷3.83)•10–6 m/s, in the second period – (0.98÷1.17)•10–6 m/s. The study of zeolite particle dispersion in suspensions showed that ultrasonic dispersion leads to a more significant shift in particle dispersion downwards from 25 μm to 3 μm, both in aqueous and aqueous-polymer suspensions with a concentration of 10–30 g/l. The conducted physical and mechanical tests of the samples showed that the introduction of an ultrasonic-stabilized aqueous-polymer zeolite suspension into the cement composition results in an increase in the initial and grade strength by 3.3 times and 51%, respectively. The analysis of the results for compressive strength showed the greatest efficiency when introducing a zeolite suspension into the cement composition instead of mixing water in an amount of 10–30 g/l. Conclusion. The studies conducted have shown the effectiveness of using ultrasonic treatment in combination with a plasticizer to stabilize the zeolite suspension. Stabilized zeolite particles, uniformly distributed in the volume of the cement matrix, act as a substrate for the nucleation and growth of crystal hydrate phases, thereby intensifying the process of hydration and formation of a crystal hydrate framework with a dense and strong structure of cement stone. Thus, the feasibility of considering zeolites as components of composite materials is a promising direction in solving multifaceted problems in the construction industry.
Zeolite suspension, cement system, dispersion, stability, ultrasonic treatment, mechanical treatment, plasticizer, strength
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142244828
IDR: 142244828 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2025-17-3-224-234
Текст научной статьи Study of the stability of zeolite suspensions for cement systems
Original article
Самченко С.В., Козлова И.В., Синотова М.В., Вовченский Д.Н., Сироткина К.А. Исследование устойчивости цеолитовых суспензий для цементных систем. Нанотехнологии в строительстве. 2025;17(3):224–234. – EDN: ZQIZZV.
In the Russian Federation, much attention is paid to the development of new materials for the development of the construction industry. It is necessary to strive to obtain materials that would have high functionality, durability, strength, and would also have various unique propertires.
Numerous scientific studies are being conducted in this area on the territory of our country, the properties of materials of natural and man-made origin are being studied, including active work related to the disposal of industrial waste [1–4].
For the construction of objects requiring increased strength (foundations, walls, ceilings, columns, beams,
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE etc.), or for carrying out repair work where the early strength gain of the repair mixture is important, various fine dispersed additives are used in the composition of the binder material [5–7].
To ensure an increase in the physical and mechanical properties of the hardened cement paste containing such additives in its composition, it is necessary to consider the issue of uniformity of the distribution of submicron particles in the volume of the cement composite [8–9]. With instability of the distribution of fine dispersed components in the matrix system, a deterioration in the strength of the cement stone is observed [10]. The study of this issue is one of the objectives of this study.
To determine the dosage of fine dispersed materials in the cement system, the water-cement ratio is adjusted. Such manipulations allow for a reduction in cement consumption and an increase in the strength of the final product [11].
The introduction of pozzolanic additives into the composition of cement, which impart specific properties to the material (increased water resistance, resistance to the aggressive effects of mineralized and fresh water, etc.), leads to a decrease in early strength and an increase in late strength when used in optimal proportions [12–14]. A type of pozzolan is zeolite, which is an aluminosilicate with a skeletal structure that has nanoscale cavities filled with alkali and alkaline earth metal cations and water molecules that can be freely removed and absorbed. The processes occurring in the zeolite structure lead to ion exchange and reversible dehydration, while the zeolite structure itself does not change [15, 16].
The physicochemical properties of zeolites depend on the geometry of their porous structure, framework chemistry and the nature of extra-framework structures [17, 18]. Due to this, they have high ion-exchange, sorption, and catalytic properties, which are highly valued in the construction industry. There is a positive trend in obtaining various zeolite-based building materials with unique performance properties [19–22].
An example is the analysis of experimental data presented in [15]. The authors showed that with an increase in the concentration of zeolite to 17%, used as a filler, the strength of concrete at the initial stage increases, since a dense framework of the structure is formed. With a further increase in the concentration of zeolite, there is a decrease in strength, which corresponds to the polystruc-tural theory of composite building materials developed by Academician V.I. Solomatov. The authors [23] argue that with the help of natural zeolites it is possible to produce “green” concrete, significantly reducing the consumption of cement. In [24], the efficiency of using zeolite in multicomponent fine-grained concrete for construction 3D printing was proven. It is proposed to introduce zeolite in an amount of 5–15%, which ensures a reduction in setting time by 1.0–1.20 hours and an increase in the strength of samples. An interesting technological solution for using zeolite was given by Indonesian colleagues in [25]. They proposed to use zeolites for desalination of sea water with subsequent mixing of it into concrete due to the shortage of fresh water. It was found that the increase in the zeolite content for desalination of sea water correlates with the decrease in salinity, thereby increasing the compressive strength of concrete. The work [26] shows the technology of production of heat-insulating material from foam glass ceramics containing zeolite rock by the extrusion method, which is capable of increasing the bulk density of the material to 220 kg/m3 thermal conductivity to 0.078 W/(m °C), which indicates the possibility of its use for road construction in difficult geocryological conditions. The considered examples confirm the expediency of using zeolites in the creation of building materials, which is relevant for solving multifaceted problems of the construction industry.
Thus, we are faced with the task of continuing the study of the properties of zeolites in the composition of cement systems. Fine dispersed zeolites and their possibility of stabilization for introduction into the composition of cement in the form of a stabilized suspension instead of mixing water are proposed for consideration.
MATERIALS AND METHODS OF RESEARCH
During the research, zeolite from the Kholinskoye deposit with a predominant particle size of 25 µm (Fig. 1), Portland cement Eurocement CEM I 42.5N, and plasticizer Sika ViscoCrete-226 P were used as fine dispersed mineral additives. Tables 1 and 2 show the chemical and mineralogical composition of the cement, and Table 3 shows the chemical composition of the Kho-linskoye zeolite.
For the studies, a zeolite suspension with a concentration of 10, 30, 50 g/l was prepared by mixing mechanical with a magnetic stirrer and ultrasonic dispersion (UD) on a UZDN-1 device at a frequency of 44 kHz under thermostatted conditions (t = 25±2 °C) (Fig. 2). The time of mechanical and ultrasonic treatment of the suspensions was 20 min. The suspensions were prepared in two dispersion media – water and water-polymer (water + plasticizer). The dispersion of zeolite particles in suspensions was determined on a Fritsch device. Particle Sizer.
Physical and mechanical tests of samples were carried out in accordance with current national and interstate standards and methods.
EXPERIMENTS AND DISCUSSION OF RESULTS
In this work, the dispersion of fine dispersed zeolite particles with a predominant particle size of 25 µm in aqueous and aqueous-polymer suspensions prepared by mechanical mixing and ultrasonic exposure was investi-
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
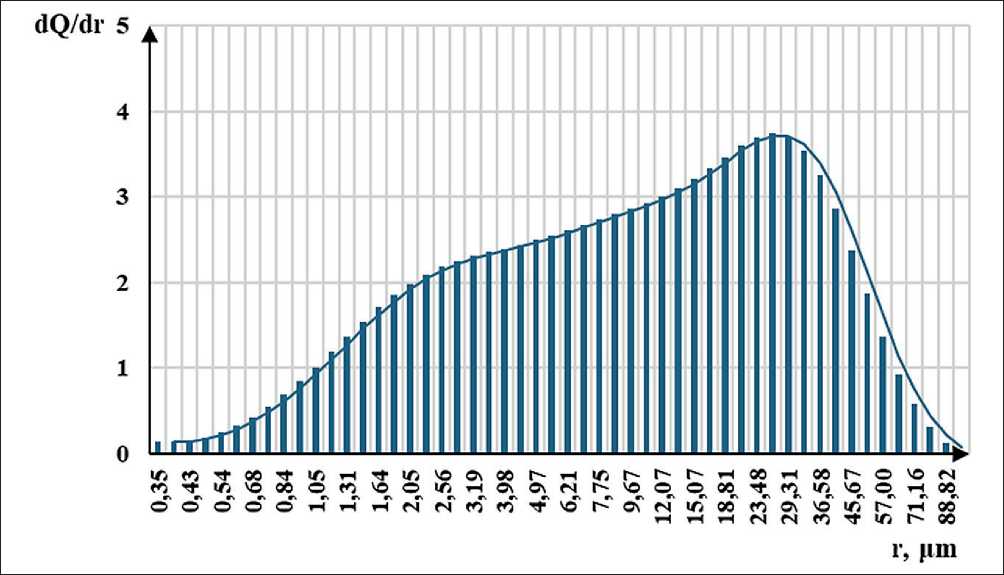
Fig. 1. Distribution curve of zeolite particles in powder
Table 1. Chemical composition of cement clinker
|
Components |
CaО, % |
SiO2, % |
Al2O3, % |
Fe2O3, % |
MgO, % |
SO3, % |
R2O (Na2O), % |
|
Clinker |
66.1 |
21.2 |
5.1 |
4.2 |
0.77 |
0.55 |
0.57 |
Table 2. Mineralogical composition of cement clinker
To establish the sedimentation stability of zeolite particles in suspension, the prepared suspensions were poured into 100 cm3 cylindersand the process of zeolite particle sedimentation was observed. Having measured the height of the column of settling particles and the time of their settlement, the rate of particle settlement in the suspension was calculated.
The settlement of zeolite particles occurred in 3 stages: 1 – the beginning of sedimentation, the largest particles settle; 2 – sedimentation of particles of a finer fraction; 3 – complete sedimentation of particles. Studies have shown that even with mechanical mixing after 7 days, complete sedimentation of zeolite particles in an aqueous dispersion medium was not observed, therefore it was decided to neglect the 3rd period of particle sedimentation, and to limit ourselves to the 2nd period of sedimentation for assessing the sedimentation stability of particles in
Table 3. Chemical compound zeolite
|
Content of components in zeolite, % |
|||||||||||
|
SiО 2 |
TiO 2 |
Al 2 O 3 |
Fe 2 O 3 |
FeO |
CaO |
MgO |
Na2O |
K 2 O |
MnO |
SO 3 |
loss on ignition |
|
67.7 |
0.09 |
11.97 |
0.78 |
0.26 |
1.37 |
0.42 |
2.53 |
3.63 |
0.17 |
0.04 |
11.39 |
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE

Fig. 2. Ultrasonic disperser UZDN-1
a suspension, in which it is assumed that 2/3 of the zeolite particles have undergone sedimentation.
The establishment of the optimal dosage of plasticizer for the preparation of water-polymer suspensions was carried out by determining the sedimentation stability of suspensions in cylinders with a volume of 100 cm3. In the experiment, suspensions with the maximum zeolite content, ie 50 g/l, were considered, which contained a plasticizer with a concentration of 1.0 to 5.0 g/l (Table 4).
During the studies it was established that the plasticizer concentration from 3.0 g/l and higher ensures sedimentation stability of suspensions with a zeolite content of 50 g/l in the first period of sedimentation up to 2.5 hours with mechanical mixing and 12.5 hours after ultrasonic treatment. In this regard, in further studies it was decided to use a plasticizer concentration of 3.0 g/l.
The sedimentation rate of zeolite particles in a suspension prepared by mechanical and ultrasonic treatment in the presence of a plasticizer and without it in the 1st and 2nd periods of particle sedimentation is shown in
Fig. 3. It is evident from the graphs that the particle settling velocity is the highest during mechanical treatment, especially where there are 50 g of zeolite particles per 1 l of suspension (Fig. 3a). The particle settling velocity in the first period of settling is (283÷455)·10–6 m/s; in the second period – (21.1÷26.1)·10–6 m/s. The most stable suspension is that stabilized by ultrasonic treatment and a plasticizer (Fig. 3d). The particle settlement velocity of the suspension in the first period is (3.43÷3.83)·10–6m/s, in the second period – (0.98÷1.17)·10–6m/s.
In parallel with the establishment of the sedimentation stability of the suspensions, the size of the zeolite particles in the suspension was determined. The results of the determinations are presented in Fig. 4.
Differential particle distribution curves showed that in aqueous and aqueous-polymer suspensions with a zeolite concentration of 10 g/l, prepared by mechanical mixing, the predominant particle size is 10-12 µm with d Q / dr = 4.1–4.2 (blue and orange curves in Fig. 4a).
With a concentration of 30–50 g/l in the same suspensions, it is quite difficult to establish the predominant size; a polyfractional distribution of particles is observed within 3–25 µm at dQ / dr = 3.0–3.5 (blue and orange curves in Fig. 4 b, c).
Under the influence of ultrasound in aqueous and aqueous-polymer zeolite suspensions with a concentration of 10–30 g/l, the predominant particle size is 3 µm with dq / dr = 4.6–5.2 (gray and yellow curves in Fig. 4 a, b). With an increase in the zeolite concentration in the aqueous suspension to 50 g/l, a polyfractional composition is observed with predominant particle sizes of 1, 5, 32 µm with dQ / dr = 2.2; 6.7; 3.1, respectively (gray curve in Fig. 4c). When studying the yellow curve in Fig. 4c, which is responsible for the distribution of the zeolite particle size in the aqueous-polymer suspension subject to ultrasonication, a predominant particle size of 3 µm with dQ / dr = 5.2 was revealed.
In summary, it can be concluded that ultrasonic dispersion leads to a shift in particle dispersion downwards from
Table 4. Sedimentation stability of zeolite suspension with different plasticizer content
|
Name indicator |
Cylinder No. |
||||||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
|
Concentration plasticizer, g/l |
1.0 |
1.5 |
2.0 |
2.5 |
3.0 |
4.0 |
5.0 |
|
Protective number of suspension S, *10–3 g/l |
1.00 |
2.25 |
4.00 |
6.25 |
9.00 |
16.00 |
25.00 |
|
Sedimentation stability of zeolite suspension in the first period of particle sedimentation without ultrasonic treatment, h-min |
1–00 |
1–20 |
1–50 |
2–10 |
2–30 |
2–30 |
2–40 |
|
Sedimentation stability of zeolite suspension in the first period of particle sedimentation after ultrasonic treatment, h-min |
6–00 |
8–00 |
10–00 |
11–30 |
12–30 |
12–30 |
12–30 |
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
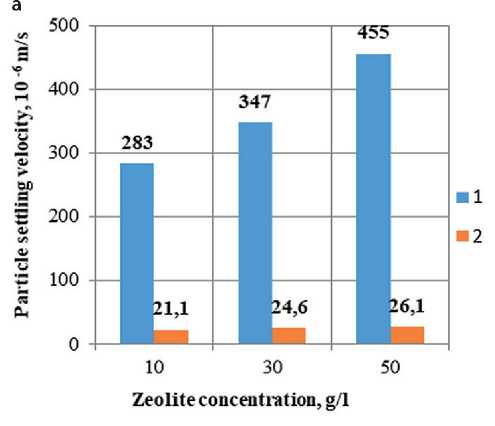
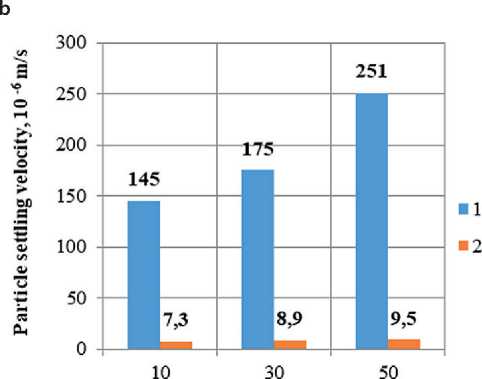
Zeolite concentration, g/1
d
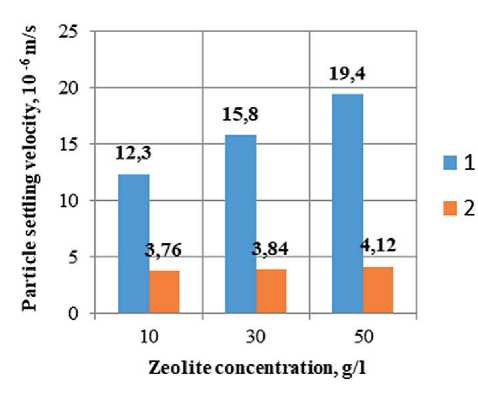
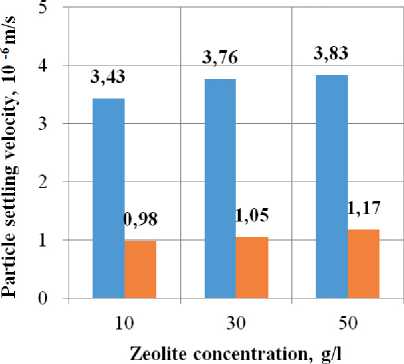
Fig. 3. Sedimentation stability of zeolite suspension: a) mechanical processing; b) ultrasonic processing; c) mechanical processing + plasticizer; d) ultrasonic processing + plasticizer
25 µm to 3 µm, both in aqueous and aqueous-polymer suspensions with a concentration of 10–30 g/l. An aqueous suspension containing 50 g/l of fine dispersed zeolite particles is more difficult to ultrasonicate, due to the fact that in a more concentrated suspension the number of collisions between particles is higher than in a diluted one. This leads to coagulation processes. When a plasticizer is introduced, zeolite particles are stabilized, which allows minimizing the coagulation processes in the suspension.
During mechanical processing, a slight shift in particle dispersion towards a decrease is also observed (from 25 to 10–15 µm), but it is insignificantly expressed; to a greater extent, such particle distribution is of a polyfractional nature.
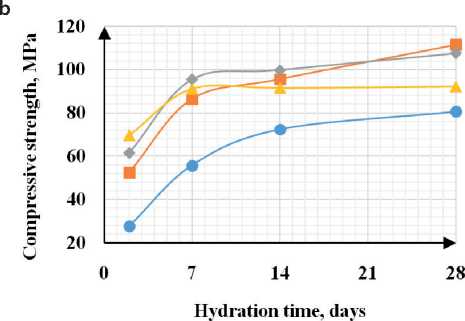
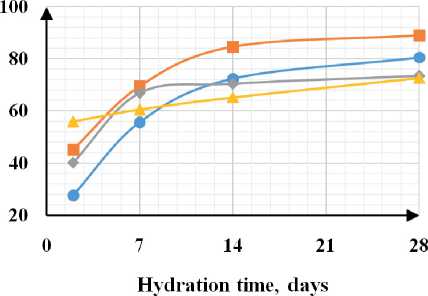
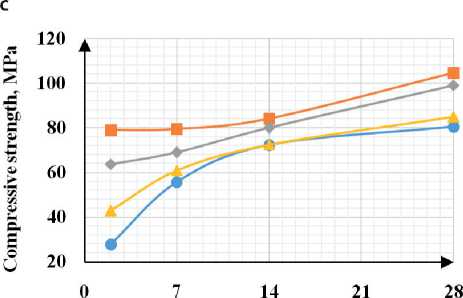
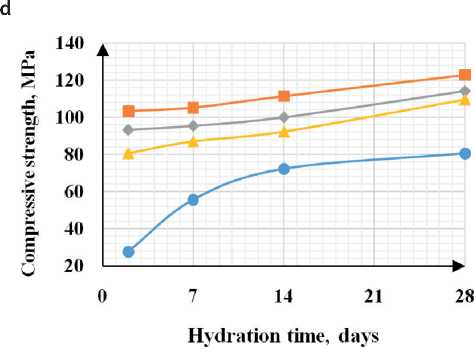
Based on the data obtained in the study of sedimentation of fine dispersed zeolite particles, it can be con- cluded that the use of ultrasonic treatment for aqueous and aqueous-polymer zeolite suspensions allows obtaining sedimentation-resistant suspensions that can be uniformly distributed in the volume of the cement matrix and contribute to an increase in the physical and mechanical properties of the hardened cement paste. In this regard, 20×20×20 mm cubes were molded and maintained in air-humidity conditions. In modified samples, the zeolite suspension was introduced into the cement composition instead of mixing water. Results The results of the tests are shown in Fig. 5.
The analysis of the obtained results showed that with the introduction of the zeolite suspension, a significant increase in the initial stages of hardening is observed (by 70%), and at the grade age, the strength increases with an additive containing zeolite in the amount of 10 g/l
b
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
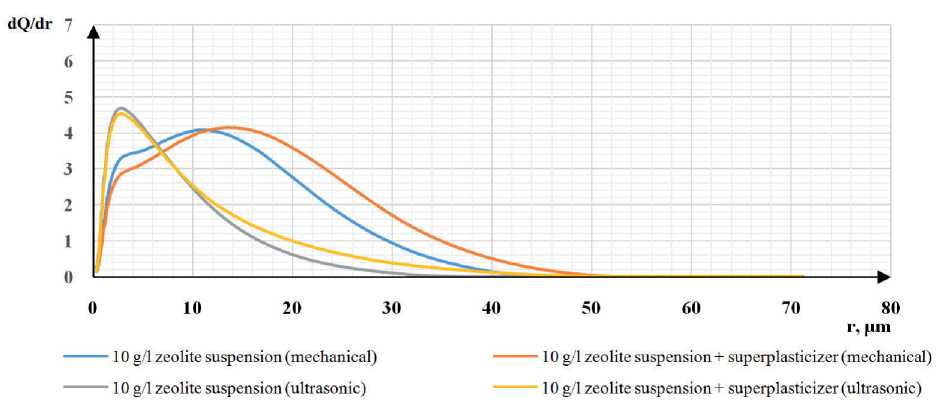
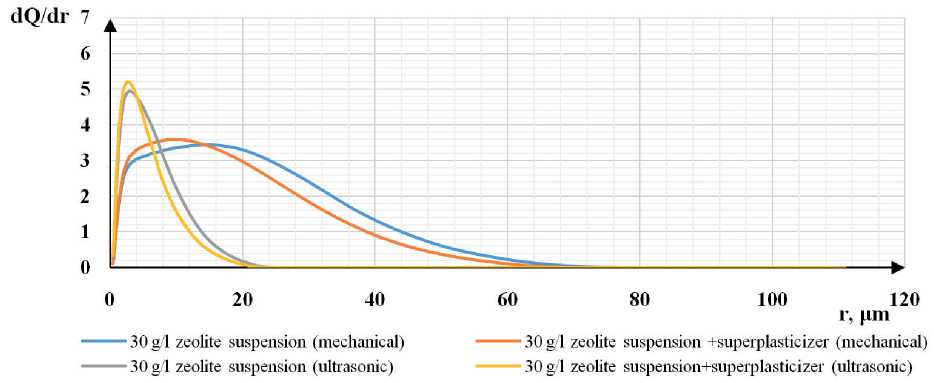
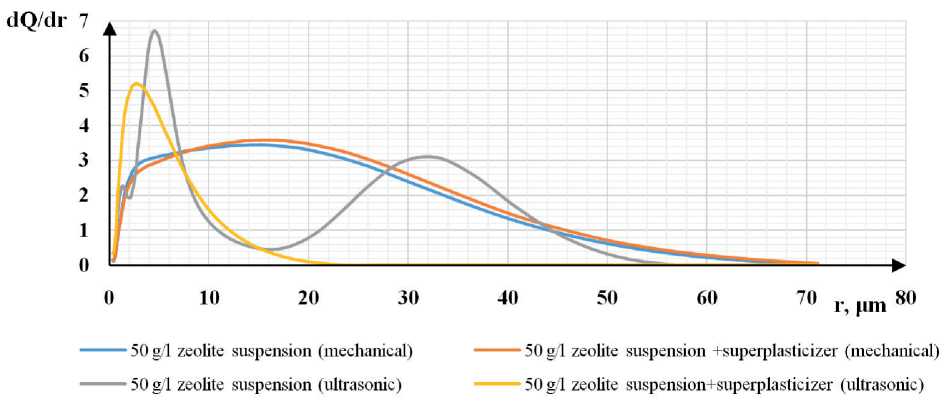
Fig. 4. Differential distribution curves of zeolite suspension particles: a) with a concentration of 10 g/l; b) with a concentration of 30 g/l; c) with a concentration of 50 g/l
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE was 10.6%. With the introduction of a plasticizer into the zeolite suspension, an increase in strength is observed at all stages of hardening: on the 2nd day, the strength increased by 2.2 times, at the grade age – by 29%. With ultrasonic treatment of the zeolite suspension, an increase in strength is observed at the initial stages for all modified samples by an average of 2.2 times, at the grade age with the addition of zeolite 10–30 g/l – by 23–29%, with the addition of zeolite 50 g/l the strength is comparable to the sample without additives. With the introduction of a complex additive, a maximum increase in the initial and grade strength is noted by 3.3 times and 51%, respectively. Analysis of the results on compressive strength showed the greatest efficiency when introducing a zeolite suspension into the cement composition instead of mixing water in an amount of 10-30 g/l.
Based on the above, it follows that the use of ultrasonic treatment to stabilize the zeolite suspension allows increas-
ing the strength both at the initial stages of hardening and at the brand age. This indicates that the fine dispersed zeolite is uniformly distributed in the matrix of the cement stone, concentrates hydrate new formations around itself, thereby intensifying the nucleation and growth of crystal hydrate phases that compact and strengthen the hardening conglomerate, which is confirmed by the microphotographs of the samples presented in Fig. 6.
They show a pore in the structure of the cement stone at the age of 2 days without additives and a sample sealed with ultrasonic treatment-stabilized zeolite suspension. When examining the pores in the structure of cement stone, it is noted that with the same increase in the sample with the addition of zeolite, it is more intensively overgrown with hexagonal hydrosilicates and calcium hydroaluminates, which have good reinforcing capacity, which confirms the compaction and strengthening of the structure of cement stone in the early stages of hardening.
а
Fig. 5. Dependence of strength on hydration time: a) mechanical processing; b) mechanical processing + plasticizer; c) ultrasonic processing; d) ultrasonic processing + plasticizer
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
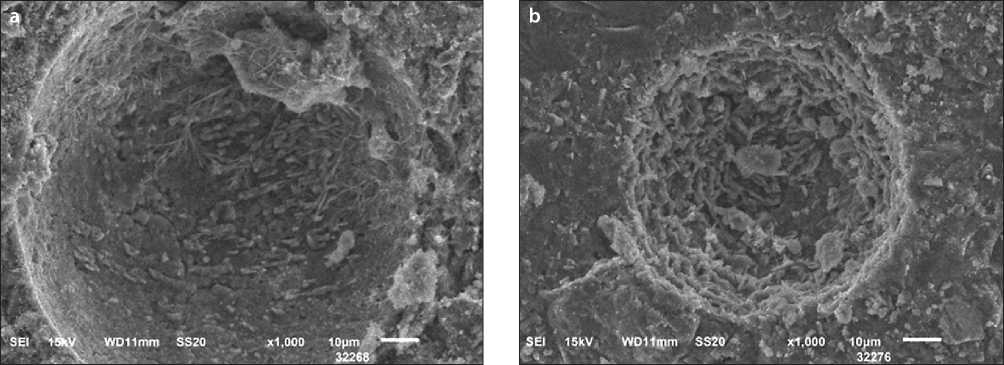
Fig. 6. Electron microscopic images of samples after 2 days of hardening: a) control sample; b) zeolite suspension with a concentration of 10 g/l, stabilized by ultrasonic treatment
CONCLUSION
To establish the uniformity of distribution of fine dispersed zeolite particles in the composition of the cement matrix, studies were conducted to determine the sedimentation stability of suspensions, and the dispersion of zeolite particles was determined after mechanical and ultrasonic treatment in aqueous and aqueous-polymer dispersion media.
During the research, the optimal dosage of anionic plasticizer for the preparation of water-polymer suspensions of zeolite was established. It was 3.0 g/l.
Studies of sedimentation stability of suspensions have shown that the most stable suspension is the one stabilized by ultrasonic treatment and plasticizer. The sedimentation rate of suspension particles in the first period is (3.43÷3.83)·10–6 m/s, in the second period – (0.98÷1.17)·10–6m/s.
The study of the dispersion of zeolite particles in suspensions showed that ultrasonic dispersion leads to a more significant shift in the dispersion of particles towards a decrease from 25 µm to 3 µm, both in aqueous and aqueous-polymer suspensions with a concentration of 10–30 g/l. An aqueous suspension containing 50 g/l of fine dispersed zeolite particles is more difficult to ultrasonic treatment, due to the fact that in a more concentrated suspension the number of collisions between
particles is higher than in a diluted one. This leads to the occurrence of coagulation processes. When a plasticizer is introduced, the zeolite particles are stabilized, which allows minimizing the occurrence of coagulation processes in the suspension.
The physical and mechanical tests of the samples showed that the introduction of a water-polymer zeolite suspension stabilized by ultrasonic treatment into the cement composition resulted in an increase in the initial and grade strength by 3.3 times and 51%, respectively. Analysis of the results for compressive strength showed the greatest efficiency when introducing a zeolite suspension into the cement composition instead of mixing water in an amount of 10–30 g/l.
Based on the obtained data, it is possible to note the efficiency of using ultrasonic treatment in combination with a plasticizer to stabilize the zeolite suspension, which indicates the uniformity of the distribution of zeolite particles in the matrix of cement stone. Stabilized zeolite particles, acting as a substrate for the nucleation and growth of crystal hydrate phases, intensify the process of hydration and formation of a crystal hydrate framework with a dense and strong structure of cement stone. The studies conducted confirm the feasibility of considering zeolites as components of composite materials, which is relevant for solving multifaceted problems of the construction industry.


