Studying the factor of ice of icing field loss from fresh water in the millimeter range
Автор: Bordonskiy G.S., Gurulev A.A., Orlov A.O., Tsyrenzhapov S.V.
Журнал: Siberian Aerospace Journal @vestnik-sibsau-en
Рубрика: Technological processes and material science
Статья в выпуске: 3 vol.23, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This research aimed at measuring the microwave radiation attenuation in an artificially formed icing field on the ice covering a freshwater lake within the millimeter range. The measurements were made using microwave radiometry at frequencies of 22, 34, 90, and 125 GHz with a cyclic change in the ambient temperature within the range from –19 to –31 C. A special technique is used, which makes it possible to determine the microwave radiation attenuation in it from the increments of radio brightness temperature between ice cover and without icing field. In the proposed method, the loss factor is found under the condition that attenuation in ice is determined by electromagnetic losses in the medium. The measurements were carried out on the ice cover of a fresh lake with a water salinity of about 100 mg/l. As a result of the study, it was found that the formation of radiation by ice is strongly influenced by scattering on the medium inhomogeneities. This conclusion was made based on comparing the calculations of the expected ice loss factor of icing field and the data obtained from measurements by the method used. The greatest difference in the loss factor (several tens of times) was found at frequencies of 90 and 125 GHz. It has been suggested that radiation scattering occurs on crystalline hydrates of salts and can be caused by increased electrical conductivity of thin water films on the crystal surface. This feature can arise, as it has been recently established, during the formation of ice 0 crystals in the medium. This ice is formed from deeply supercooled water at temperatures below –23 C. The observed effect is of interest for developing radar measurements of fresh natural ice at low temperatures and low concentrations in salts (about 100 mg/kg). Such ice can form from slightly salty water with a salt content of up to several grams per liter or when water with a salinity of ~ 100 mg/l freezes in a confined space. The results obtained are of interest for microwave aerospace determination of the ice areas with its structural disturbances, through which the water of the reservoir can penetrate to the ice surface with subsequent freezing. At the same time, radars can be effective at icing field temperatures below –20 °C, when liquid inclusions almost completely freeze out. For the temperature range above the eutectic point, where liquid inclusions appear, passive radiometric measurements can be effective.
Icing field, microwave radiometry, radar measurements, dielectric permeability, ice 0
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148329648
IDR: 148329648 | УДК: 528.88 | DOI: 10.31772/2712-8970-2022-23-3-532-541
Текст научной статьи Studying the factor of ice of icing field loss from fresh water in the millimeter range
Researching the characteristics of the natural environment using aerospace measurement methods in the millimeter range seems promising due to the achievement of a higher spatial resolution compared to the widely used systems of decimeter and centimeter waves [1]. The knowledge of the characteristics of ice and frozen structures presents great interest due to the structures’ rapid variability and the possibility to determine the dynamics of natural structures, including their use as indicators of the state of the natural environment [2]. Simultaneously, a change in the electromagnetic characteristics determined by the values of the dielectric constant of ice makes it possible to determine the influence of the temperature of the medium, the diffusion of contaminants, the characteristics of inclusions and other effects on the object of study and, consequently, its more diverse characteristics (prehistory of growth and degradation of the structure, phase composition, the influence of meteorological parameters and others).
A specific example is the characteristics of frozen layers of ice formations - ice and snow covers, as well as icing on rivers, reservoirs, quarries and other formations where groundwater outlets are observed [3].
Microwave characteristics of ice as a function of frequency and temperature have been fairly well studied [4–6]. The effect of mineralization on the relative permittivity ( ε ) has been studied. At the same time, the study of changes in its imaginary part, the loss factor ( ε '' ) for various objects has not been studied enough. The research [7] outlines that with a cyclic change in fresh ice temperature from –5 to –24 °C over three months of measurements, the value of the fresh ice loss factor at frequencies of 13 and 37 GHz experiences hysteresis. This value could slowly change by 1.5 times, which is associated with the transformation of liquid salt inclusions in the medium. However, this mechanism has not been studied in detail. The issue of the significance of freshly formed ice losses in the microwave range presents a particular interest for the radiometry of ice structures (aucing, ice covers at the initial stage of their formation, during freezing of thawed structures) due to the strong influence of low liquid concentrations on the radio brightness temperature [4; 6; 8]. Particularly strong variations in the loss factor can be expected in the millimeter range due to the increased per unit attenuation of radiation and the influence of the structural transformation of salt inclusions on it.
The current research measures the attenuation of microwave radiation in the millimeter range of artificial ice formed in winter on the fresh ices surface covering a lake (with a water salinity of about 100 mg/l) at an extremely low temperature. As far as we are aware, such research has not been performed before. Observations were carried out within two days from the moment of ice formation at an air temperature below –19 °C and with a cyclic daily change in ice temperature with a minimum value of –31 °C.
Measurement methodology
Fig. 1 shows a scheme to measure the loss factor of artificial ice (1) on the surface of the ice cover (2) using measurements of radio brightness temperature with a microwave radiometer (3). The technique feature is that due to the equality of the real part of the dielectric permeability of the ice of the ice cover and ice crust, the reflection coefficient of the radiation power (R) is the same from the surface surfaces (4) and (5). As a result, it is possible to accurately determine the electromagnetic losses and their change with temperature and time of ice crust by measuring increments of radio brightness temperature.
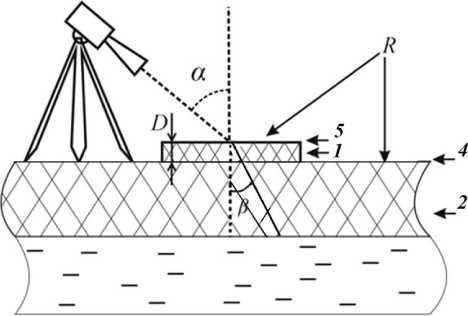
Рис. 1. Схема измерений фактора потерь искусственной наледи на поверхности ледяного покрова: D – толщина наледи; α – угол наблюдения, равный углу преломления;
β – угол падения теплового излучения из льда на границу наледь – воздух
Fig. 1. Scheme for measuring the loss factor of artificial icing field on the surface of the ice cover:
D is the icing crust thickness; α is the observation angle equal to the angle of refraction;
β is the angle of thermal radiation incidence from ice onto the ice crust
The ice crust was formed from the water of the lake by filling the corresponding understructure with water. For this occasion, limiters were installed along the perimeter of the square, on the bottom of which a polyethylene film was placed to prevent the migration of salt inclusions from the ice water in case of their possible migration into the underlying layer. Instrument signals and ice temperature ( Т ) were recorded using an Agilent data acquisition system. The temperature measurement accuracy was 1°C.
Measurements were made at frequencies of 22, 34, 94, 125 GHz on ice crust with flat boundaries and a surface area of 1 m2. At the same time, the mineralization of the upper layer of the lake ice cover was about 10 mg/kg. Four radiometers with a fluctuation sensitivity of 0.05 K at a time constant of 4 s were placed on a mobile platform, which was sequentially moved between areas with ice crust, ice cover without snow, and a metal sheet. To calibrate the radiometers, we used the open water surface of the ice hole and the reflected sky radiation from the metal sheet, the areas and dimensions of which corresponded to ice crust. The measurements were carried out during cloudless atmosphere. In this scheme, a comparison was made of the radio brightness temperature of ice crust (T ) formed on the surface of the ice cover (i.e., the total radiation of the layer of ice crust and ice cover on the water) and the ice cover (T ) cleared of snow. We would like to note that the snow cover was carefully removed before the formation of ice, and the ice surface was leveled from roughness. Fig. 2 demonstrates a photograph of the installation.
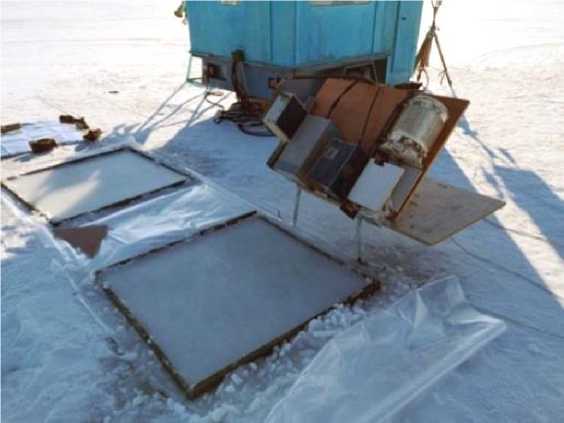

Рис. 2. Фотография установки для измерения фактора потерь искусственной наледи
Fig. 2. Photo of the installation to measure the loss factor of artificial icing field
As it has been mentioned above, the idea of the experiment was to determine the value of the increment of radio brightness temperatures (TН- TЛ), which was used to determine the power transmission coefficient of radiothermal radiation ( G ) through ice crust. Losses (L) were found from the values of G : L = in the layer , which is determined by the Snell refraction law: D′ = . In G cosα this research, we compared ε'' for D' ; therefore, we used the data for L, referred to to this length. The observation angle α and the polarization of the received radiation were set based on the purpose of the measurements.
The ɛʹʹ value for fresh ice was determined by a similar method, using the increment of radio brightness temperature, for example, in [4; 2].
TЛ is related to the power of radiation propagating through the boundary (4), and below this T boundary (in the medium) Тл = ——, where R is the power reflection coefficient from the ice-air 1 - R boundary.
For extremely small values s'' of fresh ice and equality a' for ice crust and ice cover, there is no reflection at the boundary between ice crust and ice cover (that is it is the same for the ice crust–air and ice cover–air boundaries), and for the ice cover–ice crust boundary, it is equal to zero. Since there are no interference phenomena in ice crust, the radiation emerging at an angle α can be represented by the formula
Th =
, G + To (1 - G) (1 - R ) .
Here, the first term in square brackets corresponds to the temperature of the radiation arriving at the ice-air boundary in the ice crust. The second term characterizes the own radio-thermal radiation of the ice crust coming to the same boundary (attenuator radiation [9]). The factor ( 1 - R ) determines the power of radiothermal radiation that has passed through the interface into the upper half-space.
After transformations, we find the power transfer coefficient through ice crust at an angle в :
G = 1 - тм ля г , where A T = T H - т л . (2)
T o t 1 R ) Т Л
From this formula demonstrates that there is no need to consider the reflected sky radiation, since it is automatically set to zero (when equal R for ice cover and ice crust). The loss factor is determined from (2) for the case s'' □ s' from the formula [10] for absorption:
N ( дБ ) = 10 lgL = 8,68 — 1%0.
After transformations
s'' , . , . . . n s —D , where X 0 - wavelength in free space. s'
„ = X 0 JsigL
£ 0,868n D'
The loss factor is determined by the ice crust thickness and the losses in the layer in which the radiation propagates at an angle в . For the occasion D = 0,04 м and a = 45 ° , used in the experiment s"« 14,3 % 0 IgL .
In the proposed methodology, when determining the increment A Т я , it is possible to increase the accuracy of measurements s'' , since the influence of the drift of the parameters of radiometers, as well as changes in the temperature of the sky radiation, is largely eliminated. The denominator of the second term of equation (2) has a value of several tens of degrees. An error in determining T Л of a few degrees gives an error G of no more than 10%. T 0 is determined using a temperature sensor placed in ice crust with an accuracy of ~0.1 °C.
Measurement results
The studies were carried out from February 1 to 3, 2019 on the fresh lake Arakhley (Trans-Baikal Territory) in a region with a sharply continental climate. Ice thickness measured was 117 cm. Ice thickness was 4 cm. The measurements were performed on horizontal polarization at an observation angle of 45°. For this case, R = 0,14 with s' ice was 3.15. Distance from ice crust radiometer antennas is ~ 0.5 m. The ice crust temperature on the days of measurements varied from -19 up to -31 ºC, wind speed was 3...5 m/s.
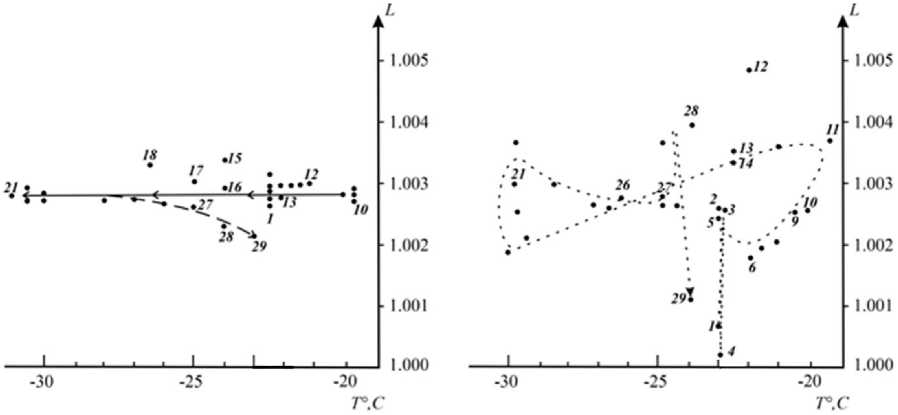
The experiments began after nine hours of exposure to water in the matrix to form ice crust. The measurements were performed with a 1 hour interval, and the radio brightness increments were recorded as a function of temperature and time. The change in temperature was determined by its diurnal variation. Fig. 3 shows the results of measurements in the form of dependences of transmission losses in ice crust for frequencies 34 and 125 GHz.
б
а
Рис. 3. Зависимости потерь пропускания от времени (последовательность отмечена цифрами:
1 – начало измерений; 29 – завершение измерений) на частотах: а – 34 ГГц; б – 125 ГГц
Fig. 3. Dependences of transmission losses on time (the sequence is marked with numbers:
1 – beginning of measurements; 29 – completion of measurements) at frequencies: a – 34 GHz; b – 125 GHz
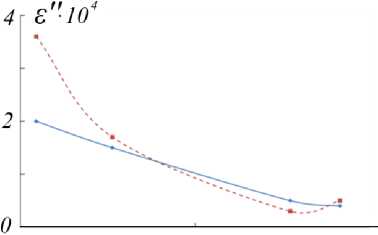
Comparing the fresh ice data available in the literature [11] with the results presents interest. Fig. 4 shows the average values in the icing crust ice layer, found using formula (3) from the values L depending on the frequency logarithm.
The results of measurements of the loss factor on the third day of observations were also obtained, when stabilization L occurred. Its values were presented for ice temperature –25 °С.
ln[f(GHz)]
Рис. 4. Средние значения ε′′ льда наледи за время наблюдения в зависимости от натурального логарифма частоты (сплошная линия); значения фактора потерь при температуре –25 °С через 2,5 суток после образования наледи (штриховая линия)
Fig. 4. Mean values of ε′′ of ice crust during the observation time depending on the natural of the frequency logarithm(solid line); values of the loss factor at a temperature of –25 °C 2.5 days after ice crust (dashed line) is formed
Discussing results
When setting up the experiments, we used the idea that the radiothermal radiation attenuation was determined by losses in the medium. However, in many cases it is required to consider the scattering of radiation by internal inhomogeneities of the object [2]. The frequency dependence ε′′ (Fig. 4) shows a decrease in this value as the frequency increases. Calculations according to the formulae from research [6; 12] gave the value of the loss factor for pure ice approximately 3 times higher at a frequency of 22 GHz, 10 times higher for 34 GHz, and 20...100 times higher at frequencies of 90–125 GHz, that is ε′′ of homogeneous ice increases with frequency. In addition, it should be taken into account that the ice of the studied lake contains approximately an order of magnitude of more salt inclusions; therefore, an even higher value ε′′ is expected in the natural environment. However, it manifests itself at temperatures above –21.4 °C (eutectic temperature of sodium chloride) – the main salt component of lake water, when salt inclusions present in the form of liquid capsules and films between crystallites. In the case of the formation of crystalline hydrates, it is considered that the loss of the medium is close to the case of pure ice.
The obvious reason for the detected feature is associated with a significant scattering of radiation. During the measurements, a positive increment ( T - T ) is observed in most cases, which indicates the predominance of the contribution from electromagnetic losses in the formation of the radiothermal radiation flux. Scattering effects, obviously, weaken with decreasing frequency, and the ice crust will be most contrasting with this mechanism of radiation formation at frequencies below 22 GHz. This was observed at a frequency of 13.5 GHz in [3], where the increments of radio brightness temperature on ice (with ice crust) of a quarry in the coastal zone in winter at temperatures above –20 °C reached tens of degrees Kelvin.
To explain the strong scattering at frequencies of 90–125 GHz, it is suggested that scattering occurs on small crystals of crystalline hydrates from salts available in the source water [13] ice crust. Fig. 3 demonstrates the fact that the formation of crystalline hydrates leads to scattering, where near the eutectic temperature of sodium chloride (–21…–22 °C) a decrease L was observed. The proposed specific mechanism for this effect is as follows: when the temperature drops below the eutectic point, a transitional phase from supercooled water to ice Ih appears in the medium of liquid water, which is called ice 0 [14]. For nanosized ice crystals 0, the temperatures of its formation are below –23 °С. This value may vary within certain limits depending on the volume and geometry of the frozen formation. The same is true for the process of heating such ice, when, above the phase transition point, it turns into ice Ih.
This modification of ice was experimentally discovered in [15]. Ice 0 is a ferroelectric, and a layer with high electrical conductivity appears at the interface of this ice with dielectrics, as it is established in [16]. Small particles coated with a conductive layer are strong scatterers due to plasmon resonance in conductor layers of nanoscale thickness [17]. Moreover, scattering occurs at frequencies below the plasma frequency and extends to zero frequencies. In this regard, for example, a hypothesis has been put forward that the glow of “silvery” clouds formed in the atmosphere at altitudes of 80–90 km is associated with condensation on dust particles covered with ice 0 [18]. They scatter solar radiation. If, after the formation of ice 0 in the ice structure, the temperature rises from the point of its formation, then the transformation of crystalline hydrates will appear in the medium and liquid inclusions (weakly conductive) will appear. In this case, the scattering will also weaken, and the losses will increase [19]. Therefore, for warm ice (with temperatures above –20…–18 °C), even with a low salt concentration, the ice will have an increased value L determined by absorption. Accordingly, an increased value of the radio brightness temperature will also be observed.
The presence of snow cover complicates the analysis and requires a special study.
Conclusion
-
1. A study of the microwave characteristics of centimeter-thick freshwater ice crust at its existence temperatures of –19…–31 °С in the millimeter range at frequencies of 22–125 GHz revealed strong radiation scattering, especially in the high-frequency part of this area.
-
2. The effect is associated with the formation of crystalline hydrates of sodium chloride, the main component of the water of the studied reservoir, at a temperature of –21.4 °C and the appearance of thin layers of water on the surface of crystalline hydrates with their subsequent freezing with the formation of small ice crystals 0. Also, crystals (even nanometer sizes) in contact with a dielectric medium (water or ice crystals Ih and crystalline hydrates) form nanometer layers with a very high electrical conductivity, which leads to strong scattering of radiation in the millimeter range.
-
3. At frequencies below 20 GHz, the effect of scattering on inclusions of small sizes (micro and nano) in fresh ice should be significantly reduced, so the “cold” ice will hardly stand out against the background of the ice cover. However, at temperatures above the eutectic point of salts, the radio brightness temperature of ice will increase in all ranges due to the existence of inclusions in the liquid state. The temperature boundary between the two regions is determined by the chemical composition of the water, i.e., by the eutectic points of the salts. For sodium chloride, this value is close to -21 ... -22 ° С (depending on the influence of other salts).
-
4. Scattering of radiation for "cold" ice at ice formation temperatures of 0 (that is below -23 °C) makes it possible to use millimeter-wave radars (at frequencies of 90–125 GHz) to detect ice crust from fresh water.
Список литературы Studying the factor of ice of icing field loss from fresh water in the millimeter range
- Sharkov E. A. Radioteplovoye distantsionnoye zondirovaniye Zemli: fizicheskiye osnovy [Radiothermal remote sensing of the Earth: physical foundations]. Moscow, IKI RAN Publ., 2014, 544 p. (In Russ.).
- Bordonskiy G. S. Elektromagnitnoye izlucheniye kriogennykh prirodnykh sred [Electromagnetic radiation of cryogenic natural environments. Dr. diss.]. Chita, 1994, 321 p. (In Russ.).
- Gurulev A. A., Orlov A. O., Tsyrenzhapov S. V. [Influence of icing on the radiothermal radiation of fresh ice covers]. Yestestvennyye i tekhnicheskiye nauki. 2018, No. 8(122), P. 109–111 (In Russ.).
- Matzler C., Wegmuller U. Dielectric properties of freshwater ice at microwave frequencies. J. Phys. D.: Appl. Phis. (UK). 1987, P. 1623–1630.
- Fujita S., Matsuoka T., Ishida T., Matsuoka K., Mae S. A summary of the complex dielectric permittivity of ice in the megahertz range and its applications for radar sounding of polar ice sheets. In Physics of Ice Core Records. Edited by Takeo Hondoh, 2000, Hokkaido University Press, P. 185–212.
- Bordonskiy G. S. [Dielectric losses of fresh ice on microwave]. Radiotekhnika i elektronika. 1995, Vol. 40, No. 11, P. 1620–1622 (In Russ.).
- Bordonski G. S., Krylov S. D. Loss factor behavior of freshwater ice at 13.5 and 37.5 GHz. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing. 1998, Vol. 36, No 2, P. 678680.
- Tikhonov V. V., Khvostov I. V., Romanov A. N. et al. [Features of the natural radiation of the Ob Bay in the L-band during the freezing period]. Issledovaniye Zemli iz kosmosa. 2020, Vol. 3, P. 59–76 (In Russ.). DOI: 10.31857/S0205961420030070.
- Kraus D. Radioastronomiya [Radio astronomy]. Ed. prof. V. V. Zheleznyakova, Moscow, Sov. Radio Publ., 1973, 456 p.
- Bogorodsky V. V., Gavrilo V. P. Led: Fizicheskiye svoystva. Sovrememennyye. metody glyatsiologii. [Ice: Physical properties. Modern. methods of glaciology]. Leningrad, Gidrometeoizdat Publ., 1980, 384 p.
- Bordonskiy G. S., Gurulev A. A., Orlov A. O., Tsyrenzhapov S. V. [Difference between radar and radiometric measurements (on the example of the ice cover of a eutrophic lake)]. Sovremennyye problemy distantsionnogo zondirovaniya Zemli iz kosmosa. 2014, Vol. 11, No. 2, P. 228–240 (In Russ.).
- Warren S. G. Optical constants of ice from ultraviolet to the microwave. Applied Optics. 1984, Vol. 23, P. 1206–1225.
- Borzenko S. V., Zamana L. V. [Hydrogeochemistry of the ivano-arakhleisky lakes]. Geospheric Research. 2020, Vol. 3, P. 69–79 (In Russ.). DOI: 10.17223/25421379/16/6.
- Russo J., Romano F., Tanaka Y. New metastable form of ice and its role in the homogeneous crystallization of water. Nature Materials. 2014, Vol. 13, No 7, P. 733–739. DOI:10.1038/nmat3977.
- Bordonskiy G. S., Krylov S. D., Gurulev A. A. [Ice 0 in the natural environment. experimental data and supposed areas of its existence]. Led i sneg. 2020, Vol. 60, No. 2, P. 263–273 (In Russ.). DOI: 10.31857/S2076673420020039.
- Korobeynikov S. M., Melekhov A. V., Soloveitchik Yu. G. et al. Surface conductivity at the interface between ceramics and transformer oil. Journ. of Physics. D: Applied Physics. 2005, Vol. 38, No 6, P. 915–921.
- Boren K., Huffman D. Pogloshcheniye i rasseyaniye sveta malymi chastitsami [Absorption and scattering of light by small particles]. M0scow, Mir Publ., 1986, 664 p. (In Russ.).
- Bordonskiy G. S., Gurulev A. A., Orlov A. O. The possibility of observing noctilucent clouds in microwave radiometric measurements. Proc. SPIE 11208. 25th International symposium on atmospheric and ocean optics: Atmospheric Physics, p. 1120818 (18 December 2019). DOI: 10.1117/12.2539769.
- Meissner T. Wentz F. J. The complex dielectric constant of pure and sea water from microwave satellite observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Rem. Sens. 2004, Vol. 42, No 9, P. 1836–1849. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.831888.


