Synthesis and structure of iodotris(tryphenylstibine)silver [(Ph 3Sb) 3AgI]
Автор: Sharutin V.V., Sharutina O.K., Senchurin V.S., Neudachina A.N., Andreev P.V.
Журнал: Вестник Южно-Уральского государственного университета. Серия: Химия @vestnik-susu-chemistry
Рубрика: Химия элементоорганических соединений
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.8, 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Interaction of silver iodide with triphenylstibine in dimethyl sulfoxide has led to the neutral complex iodotris(triphenylstibine)silver (1), whose structure has been established by X-ray diffraction analysis. The silver atom has distorted tetrahedral coordination. The angles SbAgSb and SbAgI equal 106.501(13)°, 109.644(13)°, 111.099(13)° и 103.063(13)°, 111.594(14)°, 114.337(14)°, the bond lengths Ag-Sb and Ag-I equal 2.7291(4), 2.7326(4), 2.8087(4) и 2.7600(4) Å.
Iodotris(triphenylstibine)silver, synthesis, structure, x-ray diffraction analysis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147160344
IDR: 147160344 | УДК: 546.865+547.53.024+547.563.4+548.312.5 | DOI: 10.14529/chem160107
Текст научной статьи Synthesis and structure of iodotris(tryphenylstibine)silver [(Ph 3Sb) 3AgI]
Synthesis and structure of molecular complexes of silver that contain the bonds Sb–Ag and Ag–Hal, obtained from silver halide and triphenylstibine in water-alcohol solution, are described in the literature [1–2]. In the present paper the interaction of silver iodide with triphenylstibine in dimethyl sulfoxide has been studied; the characteristic structural features of the obtained Sb-, I-containing silver complex have been investigated.
Experimental
Synthesis of iodotris(triphenylstibine)silver (1). The mixture of 0.529 g (1.50 mmol) triphenylsti-bine, 0.117 g (0.5 mmol) silver iodide and 10 mL dimethyl sulfoxide was stirred for 1 h at room temperature, the volume was reduced to 0.5 mL, then the mixture was cooled. The yield was 0.520 g (80%) of colorless crystals 1 with decomposition temperature 118 ° C. Found, %: С 49.87; Н 3.55. Calculated for C 54 H 45 Sb 3 AgI, %: C 50.08; H 3.48.
X-ray diffraction analysis of the crystal 1 was performed on the Bruker D8 QUEST automatic four-circle diffractometer (Mo K « -emission, X = 0.71073 A, graphite monochromator). The data were collected and analyzed, the unit cell parameters were refined, and the absorption correction was applied using the SMART and SAINT- Plus programs [3]. All calculations for structure determination and refinement were performed using the SHELXL/PC programs [4,5]. The structure 1 was determined by the direct method and refined by the least-squares method in the anisotropic approximation for non-hydrogen atoms. The position of hydrogen atoms was refined according to the riding model ( U iso (H) = 1.2U eq (C)). The main crystallographic data and refinement results for structure 1 are listed in Table 1, the geometric characteristics of the antimony atom coordination tetrahedron are given in Table 2.
Table 1
Crystallographic data and the experimental and structure refinement parameters for compound 1
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
Empirical formula |
C 54 H 45 Sb 3 AgI |
|
Formula weight |
1293.92 |
|
Т , К |
296(2) |
|
Crystal system |
Monoclinic |
|
Space group |
P2Jn |
|
a , Å |
17.7497(6) |
Шарутин В.В., Шарутинa O.K., Синтез и строение
Сенчурин В.С. и др. иодотрис(трифенилстибин)серебра [(Ph 3 Sb) 3 AgI]
Table 1 (end)
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
b , Å |
14.4787(4) |
|
c, Å |
19.6167(7) |
|
α , deg |
90.00 |
|
β, deg |
98.2820(10) |
|
γ , deg |
90.00 |
|
V , Å3 |
4988.8(3) |
|
Z |
4 |
|
ρ (calcd.), g/сm3 |
1.723 |
|
- 1 µ , mm |
2.646 |
|
F (000) |
2488 |
|
Crystal size, mm |
0.52 × 0.28 × 0.19 |
|
2 θ Range of data collection, deg |
3.449 - 27.189 |
|
Range of refraction indices |
- 22 ≤ h ≤ 22, - 18 ≤ k ≤ 18, - 25 ≤ l ≤ 25 |
|
Measured reflections |
82314 |
|
Independent reflections |
11060 ( R int = 0.0294) |
|
Refinement variables |
533 |
|
GOOF |
1.100 |
|
R factors for F2 > 2 σ (F2) |
R 1 =0.0321, wR 1 =0.0648 |
|
R factors for all reflections |
R 1 =0.0436, wR 1 =0.0725 |
|
Residual electron density (min/max), e /Å3 |
0.824/ - 0.673 |
Table 2
Selected bond lengths and bond angles in the structure of compound 1
|
Bond |
d , Å |
Angle |
ω , deg. |
|
Sb(1)–С(1) |
2.132(4) |
C(1)Sb(1)C(11) |
101.16(15) |
|
Sb(1) - C(11) |
2.131(4) |
C(1)Sb(1)C(21) |
97.96(16) |
|
Sb(1) - C(21) |
2.126(4) |
C(11)Sb(1)C(21) |
101.78(17) |
|
Sb(2) - C(31) |
2.128(4) |
C(1)Sb(1)Ag(1) |
122.48(10) |
|
Sb(2) - С(41) |
2.129(4) |
C(11)Sb(1)Ag(1) |
117.10(11) |
|
Sb(2) - C(51) |
1.140(4) |
C(21)Sb(1)Ag(1) |
112.92(12) |
|
Sb(3) - C(61) |
2.137(4) |
Sb(1)Ag(1)I(1) |
111.594(14) |
|
Sb(3) - С(71) |
2.143(4) |
Sb(2)Ag(1)I(1) |
114.337(14) |
|
Sb(3) - C(81) |
1.125(4) |
Sb(3)Ag(1)I(1) |
103.063(13) |
|
Ag(1) - Sb(1) |
2.7291(4) |
Sb(1)Ag(1)Sb(2) |
111.099(13) |
|
Ag(1) - Sb(2) |
2.7326(4) |
Sb(1)Ag(1)Sb(3) |
106.501(13) |
|
Ag(1) - Sb(3) |
2.8087(4) |
Sb(2)Ag(1)Sb(3) |
109.644(13) |
|
Ag(1) - I(1) |
2.7600(4) |
C(31)Sb(2)Ag(1) |
114.86(11) |
The full tables of atomic coordinates, bond lengths, and bond angles were deposited with the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC 1440827; ; .
Results and Discussion
It is known that mixing aqueous solutions of silver halides with the methanol solution of triphenyls-tibine (1:3 mol) leads to formation of colorless crystals of addition complexes with the general formula [(Ph 3 Sb) 3 AgHal] (Hal = Cl, Br, I) [1]. The interaction of silver iodide with triphenylstibine in dimethyl sulfoxide, a strong n-donor solvent, has not been studied previously. The choice of the solvent is due to the fact that in the presence of two n-donor ligands in the reaction mixture, containing silver iodide, competition between them arises together with the possibility of complex formation, in which the coordination sphere of the metal atom would include one of them or both at once.
Химия элементоорганических соединений
We have established that at mixing silver iodide with triphenylstibine in dimethyl sulfoxide the solven molecules are not coordinated with the metal atom, so the sole product of the reaction is the molecular complex 1 :
Agl + 3 Ph 3 Sb ^ [(РЬ з 8Ь) з Ад1].
The structure 1 is proven by the X-ray diffraction method. The silver atom in 1 has distorted tetrahedral coordination (Fig. 1).
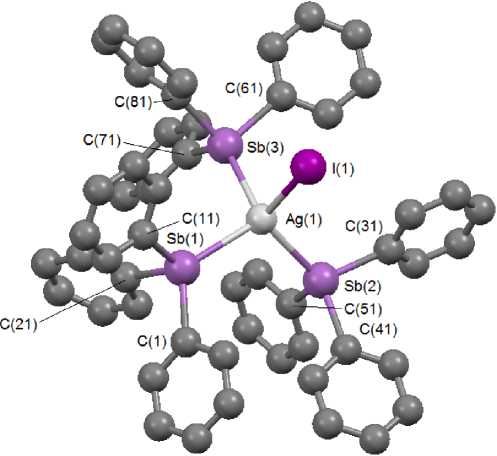
Fig. 1. The structure of compound 1
The angles SbAgSb and SbAgI equal 106.501(13) ° , 109.644(13) ° , 111.099(13) ° and 103.063(13) ° , 111.594(14) ° , 114.337(14) ° . The bond lengths Ag-Sb and Ag-I equal 2.7291(4), 2.7326(4), 2.8087(4) and 2.7600(4) Å, which exceed the sums of the covalent radii of atoms Ag, Sb (2.67 Å [6]) and Ag, I (2.58 Å [6]). Note that in a similar chlorine-containing complex (Ph 3 Sb) 3 AgCl the bond lengths Ag–Sb are smaller (2.720, 2.722, 2.764(4) Å) [1]. In the complex of silver iodide with morpholine [AgI·C 4 H 9 NO], in which the coordination sphere is formed by nitrogen and three iodine atoms, the lengths Ag-I equal 2.824(6), 2.845(6) and 2.908(6) A [7].
The atoms Sb(1,2,3) are tetracoordinated, at that the angles CSb(1)C (97.96(16) °- 101.78(17) ° ), CSb(2)C (98.20(16) °- 102.28(16) ° ), CSb(3)C (97.22(16) °- 99.70(15) ° ) are less than the ideal values, while CSb(1)Ag (112.92(12)°-122.48(10)°), CSb(2)Ag (114.18(11)°-124.41(12)°), CSb(3)Ag (111.91(11)°-128.03(11)°) are greater than them. The lengths Sb-C (2.125(4) - 2.143(4) A) are smaller than in the molecule of free triphenylstibine (2.140(4) - 2.168(4) A) [8]).
It is notable that the molecular and crystal structure of complex 1 was discussed previously in [1], but the experiment was carried out imperfectly.
Conclusions
Hence, the interaction of silver iodide with triphenylstibine in dimethyl sulfoxide solution leads to formation of iodotris(triphenylstibine)silver; dimethyl sulfoxide does not exhibit the properties of a ligand capable of coordination with the silver cation.
Синтез и строение иодотрис(трифенилстибин)серебра [(Ph 3 Sb) 3 AgI]
Список литературы Synthesis and structure of iodotris(tryphenylstibine)silver [(Ph 3Sb) 3AgI]
- Effendy. Lewis-Base Adducts of Group 11 Metal(I) Compounds. LXVIII. Synthesis and Structural Systematics of Some 1: 3 Adducts of Silver(I) Compounds with Triphenylstibine, , X = Cl, I, SCN, NCS, CN, ONO2/Effendy, J.D. Kildea, A.H. White//Aust. J. Chem. -1997. -V. 50, № 6. -P. 587-604.
- Lewis-Base Adducts of Group 11 Metal(I) Compounds. LXXII† Synthesis, Spectroscopy and Structural Systematics of Some 1: 2 Binuclear Complexes of Silver(I) Halides with Triphenylstibine, , X = Cl, Br, I/G.A. Bowmaker, Effendy, E.N. Silva et al.//Aust. J. Chem. -1997. -V. 50, № 6. -P. 641-651.
- Bruker (2000) SMART. Bruker Molecular Analysis Research Tool, Versions 5.625 Bruker AXS, Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2000) SAINTPlus Data Reduction and Correction Program Versions 6.02a, Bruker AXS, Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Sheldrick, G.M. A Short History of Shelx/G.M. Sheldrick//Acta Cryst. -2008. -V. A64, № 1. -P. 112-122.
- Бацанов, С.С. Атомные радиусы элементов/С.С. Бацанов//Журн. неорган. химии. -1991. -Т. 36, вып. 12. -С. 3015-3037.
- Ansell, G.B. Crystal Structure of 1:1 Complex between Silver Iodide and Morpholine/G.B. Ansell//J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans., II. -1976. -№ 1. -P. 104-106.
- Structure Analysis of Triaryl Derivatives of the Group V Elements. Crystal and Molecular Strycture of Tri-p-tolylantimony, C21H21Sb/A.N. Sobolev, I.P. Romm, V.K. Belskii et al.//J. Organomet. Chem. -1979. -V. 179, № 2. -P. 153-157.

![Synthesis and structure of iodotris(tryphenylstibine)silver [(Ph 3Sb) 3AgI] Synthesis and structure of iodotris(tryphenylstibine)silver [(Ph 3Sb) 3AgI]](/file/cover/147160344/synthesis-and-structure-of-iodotris-tryphenylstibine-silver-ph-3sb-3agi.png)
