Synthesis and structure of palladium complex [Ph 3PCH=CHPPh 3] 2+[PdBr 3(DMSO)] -2•DMSO
Автор: Sharutin V.V., Sharutina O.K., Senchurin V.S., Ilchenko I.A.
Журнал: Вестник Южно-Уральского государственного университета. Серия: Химия @vestnik-susu-chemistry
Рубрика: Органическая химия
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.7, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The palladium complex [Ph 3PCH=CHPPh 3] 2+[PdBr 3∙DMSO] -2∙DMSO (1) has been synthesized by the reaction of palladium dibromide with 1,2-vinylene-bis-triphenylphosphonium dibromide in the presence of hydrobromic acid in water, followed by recrystallization from dimethylsulfoxide. According to the X-ray diffraction data, the phosphorus atoms in cations have a slightly distorted tetrahedral environment (CPC 107.8(3)°-111.7(3)° Å), the P-С bond lengths are 1.779(6)-1.816(5) Å. In the square planar anions, the SPdBr trans-angles are 176.89(5)° and 178.11(6)° Å, and the BrPdBr trans-angles are 177.59(4)° and 177.82(3)° Å. Dimethylsulfoxide ligands are coordinated to the Pd atoms by the sulfur atoms: the Pd-S bond lengths are 2.2634(17) and 2.2666(18) Å, the Pd-Br bond lengths lie in the range of 2.4200(18)-2.4486(9) Å. Structural organization of the crystal is caused by the interionic H∙∙∙Br (2.90-3.02 Å) and H∙∙∙O (2.30-2.56 Å) hydrogen bonds.
Palladium dibromide, hydrobromic acid, 2-vinylene-bis-triphenylphosphonium dibromide, dimethylsulfoxide, synthesis, 2-vinylene-bis-triphenylphosphonium tribromo(dimethylsulfoxide)palladate, x-ray diffraction analysis, crystal structure
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147160308
IDR: 147160308 | УДК: 547.243;
Текст научной статьи Synthesis and structure of palladium complex [Ph 3PCH=CHPPh 3] 2+[PdBr 3(DMSO)] -2•DMSO
In the chemistry of the platinum-group metals, stable dimethylsulfoxide complexes take important place. Peculiarity of reaction proceeding in dimethylsulfoxide solutions allows to synthesize the compounds, which can not be obtained in aqueous medium. In complexes of the platinum-group metals, the dimethylsulfoxide ligand exhibits the ambidentate coordination mode, being coordinated through oxygen atom and sulfur atom alike, and forms various geometrical and bond isomers [1]. Except theoretical interest, dimethylsulfoxide complexes of the platinum-group metals attract attention of investigators owing to their catalytical and biological activity, in particular, antitumor activity.
Ionic palladium complex compounds with [PdHal 3 (DMSO-S)]–-type anions are represented by a few examples in the literature [2–6]. Phosphororganic cations in the complexes can be mononuclear [6] and binuclear [4]. Structural organization of the crystals strongly depends on the presence of solvent molecules.
In the present paper, the synthesis of 1,2-vinylene- bis -triphenylphosphonium tribro-mo(dimethylsulfoxide)palladate dimethylsulfoxide solvate has been described and the peculiarities of its structure have been considered.
Experimental
Synthesis of [Ph 3 PCH=CHPPh 3 ]2+[PdBr 3 ∙DMSO]– 2 ∙DMSO (1). 0.15 g (0.56 mmol) of palladium dibromide was dissolved in abundance of hydrobromic acid, and added to the solution of 0.41 g (0.56 mmol) of 1,2-vinylene- bis -triphenylphosphonium dibromide monohydrate in 20 mL of hot water with stirring. The obtained red-brown precipitate was filtered off, washed by a 20-mL portion of hot water three times, and dried. The washed precipitate was recrystallized from dimethylsulfoxide to yield the cherry-red crystals of complex 1 , yield 0.331 g (84%), m.p. 150 ° C. Found, %: С 35.66, Н 3.54. Anal. calc. for C 44 H 50 O 3 S 3 P 2 Pd 2 Br 6 (M = 1477.22), %: С 35.75, Н 3.39.
IR (v, cm - 1): 3078, 3055, 3027, 2993, 2911, 1583, 1479, 1436, 1405, 1310, 1288, 1189, 1164, 1111, 1022, 997, 970, 932, 916, 842, 771, 743, 726, 686, 524, 488, 449, 425.
IR spectrum was recorded on the Bruker Tensor 27 IR spectrometer in KBr pellets.
The X-ray diffraction experiment for complex 1 crystal was carried out on the automatic four-circle Bruker D8 QUEST diffractometer (Mo K α radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å, graphite monochromator). Data collection, their editing, and refinement of the unit cell parameters, as well as the accounting for absorption, were conducted with the use of programs SMART and SAINT-Plus [7]. All calculations for structure determination and refinement were carried out by the program SHELXL/PC [8]. The structure was determined by the direct method and refined by the least-squares method in the anisotropic approximation for non-hydrogen atoms.
The main crystallographic data and structure refinement details are given in Table 1. Atomic coordinates and isotropic equivalent thermal factors are given in Table 2. The main bond lengths and bond angles are listed in Table 3.
Table 1
Crystallographic data and the experimental and structure refinement parameters for compound 1
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
Formula weight |
1477.22 |
|
Т , К |
296(2) |
|
Crystal system |
Monoclinic |
|
Space group |
P2 1 /c |
|
a , Å |
22.4176(7) |
|
b , Å |
9.5016(2) |
|
c, Å |
26.2637(8) |
|
α , deg |
90.00 |
|
β, deg |
109.5400(10) |
|
γ , deg |
90.00 |
|
V , Å3 |
5272.1(3) |
|
Z |
4 |
|
ρ (calcd.) , g/сm3 |
1.861 |
|
µ , mm–1 |
5.445 |
|
F (000) |
2872.0 |
|
Crystal size, mm |
0.33×0.14×0.12 |
|
θ Range of data collection, deg |
5.96–52.84 |
|
Range of refraction indices |
–28 ≤ h ≤ 27, –11 ≤ k ≤ 11, –32 ≤ l ≤ 32 |
|
Measured reflections |
93694 |
|
Independent reflections |
10790 |
|
Refinement variables |
547 |
|
GOOF |
1.026 |
|
R factors for F2 > 2 σ (F2) |
R 1 = 0.0481, wR 2 = 0.1333 |
|
R factors for all reflections |
R 1 = 0.0872, wR 2 = 0.1571 |
|
Residual electron density (min/max), e /Å3 |
2.53/–1.66 |
Таble 2
Atomic Coordinates (×104) and isotropic equivalent thermal factors (Å2×103) in the structure of substance 1
|
Атом |
x |
y |
z |
* U экв / U изо |
Атом |
x |
y |
z |
* U экв / U изо |
|
Pd(1) |
4811.7(2) |
4159.1(5) |
799.37(19) |
44.88(15) |
C(5) |
2370(5) |
–5926(8) |
–4007(3) |
72(2) |
|
Pd(2) |
–52.9(2) |
–4435.9(5) |
–5974.0(2) |
40.28(14) |
C(46) |
2272(3) |
–475(8) |
–947(3) |
55.2(17) |
|
Br(4) |
–1077.4(3) |
–3708.6(8) |
–6583.8(3) |
55.0(2) |
C(32) |
2412(3) |
–4305(7) |
–1190(3) |
57.1(18) |
|
Br(2) |
4887.7(4) |
1589.9(8) |
782.7(3) |
61.0(2) |
C(2) |
3443(3) |
–4270(8) |
–3577(3) |
56.3(18) |
|
Br(6) |
284.2(4) |
–1976.0(8) |
–5878.6(3) |
65.2(2) |
C(52) |
1300(3) |
–92(6) |
–2507(2) |
42.1(14) |
|
Br(1) |
3689.0(4) |
4032.1(9) |
295.7(3) |
70.0(2) |
C(12) |
3954(3) |
–1826(7) |
–2558(3) |
53.6(16) |
|
Br(3) |
5928.7(4) |
4257.0(8) |
1338.7(4) |
76.8(3) |
C(33) |
2329(4) |
–5679(9) |
–1065(3) |
88(3) |
|
Br(5) |
964.2(4) |
–5144.8(10) |
–5331.8(3) |
75.4(3) |
C(34) |
1892(4) |
–6510(8) |
–1423(3) |
73(2) |
|
P(1) |
2762.3(7) |
–2122.3(15) |
–3315.2(6) |
34.2(3) |
C(35) |
1536(3) |
–5990(7) |
–1923(3) |
58.2(18) |
|
P(2) |
2149.8(6) |
–1981.7(15) |
–1860.2(6) |
31.8(3) |
C(16) |
3677(3) |
–171(7) |
–3286(3) |
49.7(16) |
|
S(2) |
–356.2(8) |
–6717.0(17) |
–6106.0(7) |
48.9(4) |
C(3) |
3479(4) |
–5594(9) |
–3802(3) |
74(2) |
|
S(1) |
4767.4(9) |
6537.7(19) |
841.6(7) |
56.9(4) |
O(2) |
–972(2) |
–7063(5) |
–6501(2) |
81.8(17) |
Таble 2 (end)
|
Атом |
x |
y |
z |
* U экв / U изо |
Атом |
x |
y |
z |
* U экв / U изо |
|
C(54) |
217(3) |
73(7) |
–2561(3) |
50.8(16) |
O(1) |
4773(3) |
7108(5) |
1351(2) |
82.9(17) |
|
C(27) |
2372(3) |
–2356(6) |
–2823(2) |
38.7(13) |
C(21) |
2255(3) |
–1126(6) |
–3864(2) |
40.4(13) |
|
C(56) |
886(3) |
–1659(6) |
–1988(2) |
38.2(13) |
C(26) |
1894(3) |
–17(7) |
–3779(3) |
55.2(17) |
|
C(31) |
2055(3) |
–3776(6) |
–1693(2) |
34.9(12) |
C(22) |
2204(3) |
–1489(8) |
–4392(3) |
61.8(19) |
|
C(41) |
2594(3) |
–1048(6) |
–1263(2) |
34.5(12) |
C(15) |
4277(4) |
421(9) |
–3071(3) |
69(2) |
|
C(55) |
307(3) |
–1001(7) |
–2197(3) |
49.6(16) |
C(13) |
4550(3) |
–1220(9) |
–2353(3) |
69(2) |
|
C(42) |
3234(3) |
–911(6) |
–1106(3) |
45.8(15) |
C(25) |
1505(4) |
706(8) |
–4212(3) |
69(2) |
|
C(1) |
2862(3) |
–3813(6) |
–3566(2) |
39.8(13) |
C(24) |
1462(4) |
351(9) |
–4735(3) |
75(2) |
|
C(45) |
2604(4) |
241(9) |
–482(3) |
69(2) |
C(14) |
4703(4) |
–93(10) |
–2612(4) |
78(2) |
|
C(4) |
2953(5) |
–6395(8) |
–4010(3) |
75(2) |
C(23) |
1799(4) |
–711(9) |
–4821(3) |
80(3) |
|
C(11) |
3518(3) |
–1287(6) |
–3024(2) |
38.5(13) |
C(61) |
5368(5) |
7319(9) |
651(4) |
91(3) |
|
C(51) |
1383(2) |
–1210(6) |
–2154(2) |
32.9(12) |
C(62) |
4126(5) |
7313(11) |
317(5) |
130(5) |
|
C(28) |
2571(3) |
–1849(6) |
–2340(2) |
38.1(13) |
C(64) |
–314(4) |
–7517(9) |
–5494(3) |
79(2) |
|
C(53) |
711(3) |
532(7) |
–2712(3) |
52.8(17) |
C(63) |
218(4) |
–7708(9) |
–6287(3) |
79(2) |
|
C(43) |
3570(3) |
–190(7) |
–633(3) |
56.8(18) |
S(3) |
3083.5(18) |
2337(3) |
–2080,1(2) |
128.8(11) |
|
C(44) |
3247(4) |
377(7) |
–330(3) |
62(2) |
O(3) |
2679(4) |
1117(7) |
–2444(4) |
156(4) |
|
C(36) |
1624(3) |
–4627(6) |
–2061(3) |
46.7(15) |
C(66) |
2930(6) |
3110(30) |
–2553(4) |
319(18) |
|
C(6) |
2328(3) |
–4635(7) |
–3783(3) |
55.3(17) |
C(65) |
3819(6) |
2158(18) |
–2123(7) |
225(11) |
Table 3
Selected bond lengths and bond angles in the structure of compound 1
|
Bond |
d , Å |
Angle |
ω , deg |
|
P(1)–С(1) |
1.779(6) |
C(1)P(1)C(21) |
107.8(3) |
|
P(1)–С(11) |
1.794(6) |
C(11)P(1)C(21) |
111.5(3) |
|
P(1)–С(21) |
1.780(6) |
C(21)P(1)C(27) |
108.4(3) |
|
P(1)–С(27) |
1.801(5) |
C(31)P(2)C(28) |
111.7(3) |
|
P(2)–С(31) |
1.791(6) |
C(41)P(2)C(28) |
108.0(3) |
|
P(2)–С(41) |
1.787(5) |
Br(1)Pd(1)Br(2) |
90.36(3) |
|
P(2)–С(51) |
1.788(5) |
Br(2)Pd(1)Br(3) |
89.10(3) |
|
P(2)–С(28) |
1.816(5) |
Br(1)Pd(1)Br(3) |
177.59(4) |
|
C(27)–С(28) |
1.288(8) |
S(1)Pd(1)Br(1) |
91.26(5) |
|
Pd(1)–Br(1) |
2.4231(9) |
S(1)Pd(1)Br(3) |
89.24(5) |
|
Pd(1)–Br(2) |
2.4486(9) |
S(1)Pd(1)Br(2) |
178.11(6) |
|
Pd(1)–Br(3) |
2.4317(9) |
Br(4)Pd(2)Br(6) |
89.27(3) |
|
Pd(1)–S(1) |
2.2666(18) |
Br(5)Pd(2)Br(6) |
90.45(3) |
|
Pd(2)–Br(4) |
2.4200(8) |
Br(4)Pd(2)Br(5) |
177.82(3) |
|
Pd(2)–Br(5) |
2.4341(8) |
S(2)Pd(2)Br(4) |
90.12(5) |
|
Pd(2)–Br(6) |
2.4433(8) |
S(2)Pd(2)Br(5) |
90.28(5) |
|
Pd(2)–S(2) |
2.2634(17) |
S(2)Pd(2)Br(2) |
176.89(5) |
Results and Discussion
To synthesize new palladium complexes, we have investigated the reaction of 1,2-vinylene- bis -triphenylphosphonium dibromide with palladium dibromide in the presence of hydrobromic acid.
We have ascertained that the addition of the equmolar amount of palladium dibromide, which is dissolved in hydrobromic acid, to the hot aqueous solution of 1,2-vinylene- bis -triphenylphosphonium dibromide leads to the red-brown precipitate formation. After its recrystallization from dimethylsulfoxide, it represents the cherry-red needle crystals of 1,2-vinylene- bis -triphenylphosphonium tribro-mo(dimethylsulfoxide)palladate dimethylsulfoxide solvate [Ph 3 PCH=CHPPh 3 ]2+[PdBr 3 DMSO]– 2 ∙ ∙DMSO ( 1 ):
-
1. PdBr 2 + HBr [Ph 3 PCH=CHPPh 3 ]Br2 ---------* [Ph 3 PCH=CHPPh 3 ]2+[PdBr 3 ∙DMSO]– 2 ∙DMSO
-
2. DMSO 1
According to the X-ray diffraction data, the phosphorus atoms in [Ph 3 PCH=CHPPh 3 ]2+ cations have a slightly distorted tetrahedral coordination geometry (Fig. 1).
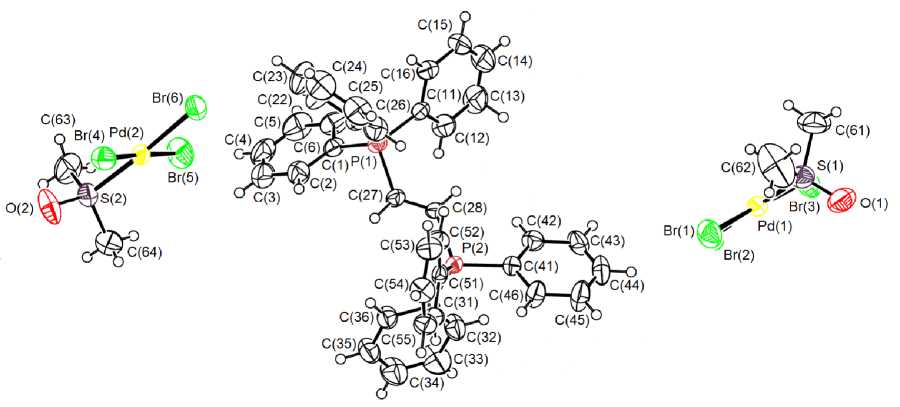
Fig. 1. The structure of the compound 1 (solvating toluene molecule doesn’t show)
The valence angles CPC (107.8(3)-111.7(3) ° ) differ but little from the theoretical value. The P-C lengths (1.779(6)–1.816(5) Å) are close to the sum of covalent radii of the phosphorus and carbon atoms 1.88 Å [9]. The Ph 3 P groups are in trans -positions relative to the vinyl fragment. The bond length С(27) - С(28) equals 1.288(8) A, which is less than the reference value for the C( sp 2) - C( sp 2) bond (1.34 Å [10]).
Palladium atoms in the two kinds of crystallographically independent square mononuclear anions are tetracoordinated. Level difference of atoms Pd(1) and Pd(2) compared to the average plane [Br 3 S] is 0.035 and 0.008 Å. The valence trans -angles BrPd(1,2)Br and BrPd(1,2)S equal 177.59(4), 177.82(3)° and 178.11(6), 176.89(5)°. The bond lengths Pd(1)–Br and Pd(2)–Br equal 2.4231(9), 2.4317(9), 2.4486(9) Å и 2.4200(8), 2.4341(8), 2.4433(8) Å; at this the longest bonds Pb-Br are in trans -positions relative to the dimethylsulphoxide ligand. Dimethylsulphoxide ligands are coordinated by the palladium atom through sulfur atoms, the lengths Pd(1)–S(1) and Pd(2)–S(2) equal 2.263(2) и 2.267(2. The bond lengths S(1) - O(1) and S(2) - O(2) are 1.440(6) and 1.460(4) A, respectively; they are smaller than the similar length in the molecule of uncoordinated dimethylsulfoxide (1.581 Å). This is compatible with the literature data, which indicate that the bond order S=O increases at dimethylsulfoxide coordination with the metal atom through sulfur.
In the complex crystal numerous hydrogen bonds exist between cations, anions and the solvate molecules of the solvent, such as H --- Br (2.90-3.02 A) and H --- O (2.30-2.56 A)
Conclusion
Thus, for the first time the palladium complex [Ph 3 PCH=CHPPh 3 ][PdBr 3 ∙DMSO] 2 ∙DMSO has been synthesized and characterized as to its structure. The peculiarities of the complex structure are the existence of two types of dimethylsulfoxide molecules (coordinated by palladium and free), as well as the observed redistribution of the electron density in anions, which appears as the trans -bond Pd–Br lengthening and the bond order S=O increasing.
Список литературы Synthesis and structure of palladium complex [Ph 3PCH=CHPPh 3] 2+[PdBr 3(DMSO)] -2•DMSO
- Кукушкин, Ю.Н. Вклад исследований диметилсульфоксидных комплексов в теории координационной химии/Ю.Н. Кукушкин//Коорд. химия. -1997. -Т. 23, № 3. -С. 163-174.
- Mono-, Di-and Poly-nuclear Transition-metal Complexes of a Bis(tridentate) Ligand: Towards p Phenylenediamine-bridged Co-ordination Polymers/A. Hazell, C.J. McKenzie, L.P. Nielsen//J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. -1998. -P. 1751-1756.
- Palladium Complexes with Pyrimidine-Functionalized N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands: Synthesis, Structure and Catalytic Activity/D. Meyer, M.A. Taige, A. Zeller et al.//Organometallics. -2009. -Vol. 28, Iss. 7. -P. 2142-2149.
- Bis Di-µ-bromo-bis/S.H. Dale, M.R.J. Elsegood et al.//Acta Cryst. -2005. -Vol. C61. -P. m40-m42.
- Синтез и строение комплекса палладия /В.В. Шарутин, В.С. Сенчурин, О.К. Шарутина и др.//Бутлеровские сообщения. -2012. -Т. 29, № 2. -С. 2630.
- Особенности взаимодействия тетрабромопалладийводородной кислоты с бромидами тетраорганилфосфония в различных растворителях. Синтез и строение комплексов палладия: +2-, +2-, +2-, + -, +-и +-/В.В. Шарутин, В.С. Сенчурин, О.К. Шарутина и др.//Бутлеровские сообщения. -2012. -Т. 30, № 6. -С. 4149.
- SMART and SAINT-Plus. Versions 5.0. Data Collection and Processing Software for the SMART System. -Madison (Wisconsin, USA): Bruker AXS Inc., 1998.
- SHELXTL/PC. Versions 5.10. An Integrated System for Solving, Refining and Displaying Crystal Structures From Diffraction Data. -Madison (Wisconsin, USA): Bruker AXS Inc., 1998.
- Бацанов, С.С. Атомные радиусы элементов/С.С. Бацанов//Журн. неорган. химии. -1991. -Т. 36. -Вып. 12. -С. 3015-3037.
- Гордон, А. Спутник химика/А. Гордон, Р. Форд. -М.: Мир, 1976. -437 с.
- Calligaris, M. Structure and bonding in metal sulfoxide complexes/M. Calligaris, О. Carugo//Coord. Chem. Rev. 1996. V. 153. P. 83154.

![Synthesis and structure of palladium complex [Ph 3PCH=CHPPh 3] 2+[PdBr 3(DMSO)] -2•DMSO Synthesis and structure of palladium complex [Ph 3PCH=CHPPh 3] 2+[PdBr 3(DMSO)] -2•DMSO](/file/cover/147160308/synthesis-and-structure-of-palladium-complex-ph-3pchchpph-3-2-pdbr-3-dmso.png)
