Talent development strategy during the digital transformation of organizations
Автор: Kharlamova Tatiana Lvovna, Yuxian Yuan, Wenye Zhang
Журнал: Петербургский экономический журнал @gukit-journal
Рубрика: Инновационное развитие экономики и социально-культурной сферы
Статья в выпуске: 4 (42), 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The powerful impact of digital and intelligent technologies is radically changing the appearance of existing industries and sectors of the economy, primarily innovation-oriented ones. As digital transformation expands, the demand for workers supporting it also increases, as well as the requirements for their level of qualifications and the availability of digital skills and competencies. The presence of problems in this area, due to the lack of highly qualified personnel, as well as the high cost of digital talent attracted to organizations, is holding back the growth of the digital economy. Thus, scientific research in the field of developing strategic foundations for talent development in modern organizations is being updated. This study, which is in line with this topic, as well as modern trends in digitalization, is aimed at studying the various approaches of organizations to improving the digital skills of employees and attracting specialists who are most in demand in the context of digital transformation. From these positions, the authors consider the theoretical and practical foundations for the formation of talent development strategies in companies undergoing digital transformation. The article, based on a theoretical analysis of existing talent development models, proposes an integrated model that most fully meets the demands and needs of the modern stage of digitalization.
Organization, digital transformation, talent development, management, strategy, digital literacy
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140303054
IDR: 140303054 | УДК: 65.011.8
Текст научной статьи Talent development strategy during the digital transformation of organizations
Today, we are living in the modern world, where information flows constantly, where data has become a new factor of production [1, p. 169] and where business development increasingly depends on the use of digital technologies [2]. Innovations in the field of digital and intelligent technologies challenge the development of various fields of science, business and management, from different points of view. As powerful as the digital environment is, digital transformation brings increasing uncertainty and complexity to businesses and organizations, making it increasingly difficult to coordinate the interests of individuals and organizations.
In the digital age, many human activities, such as building corporate culture, building employee relationships, training and development, are
important areas that cannot be ignored as the digital environment evolves.
As the digital transformation of various industries moves deeper, a variety of digital and intelligent jobs are emerging. This affects such a promising area of modern management as talent management. The demand for digital talent in information technology-related industries is growing every day, while there is an imbalance between supply and demand in the labor market [3, p. 233; 4, p. 185] becomes an important limiting factor for the development of the digital economy. Organizations often face challenges such as lack of awareness of digital transformation, high cost of digital talent, lack of necessary internal skills and experience to develop their own talent, and problems managing them [5, 6].
What kind of talents does the digital economy really need? The Center for Internet Development and Governance, School of Economics and Management, Tsinghua University, China, classi fi ed six types of talent as digital talent: digital strategy management, deep analytics, product research and development, advanced manufacturing, digital operations, and digital marketing.
This allows us to de fi ne digital talent as a new type of employee who understands their value to the employer, has an entrepreneurial spirit, is focused on decision making through data analysis, is focused on flexible forms of employment, has experience working in multi-disciplinary international teams [7] and exists in many fi elds, for example, in healthcare [8], education [9–11] and automation [12] and others.
In this regard, it is necessary to explore multifaceted approaches that will enable organizations to attract the right talent to manage the digital transformation process. There is also a need to explore how organizations can strategically manage and develop their talent to have the skills, competencies, knowledge and mindset needed to thrive in the digital age. This will enable organizations to effectively respond to the new challenges and opportunities presented by digital transformation. Taking this into account, this study can be considered as closely related and in line with modern digitalization trends.
Based on this, we can determine the purpose of this study as follows: to form a theoretical and practical basis for the formation of talent development strategies in organizations undergoing digital transformation.
Research tasks:
-
1. Analyze the speci fi c skills and competencies required by employees of organizations in the context of digitalization;
-
2. Propose a strategic framework for improving and retraining the skills of the organization’s employees in the context of digital transformation.
-
3. Develop a methodological rationale for the formation of programs for attracting and hiring talent, specially adapted to the digital context of the organization’s development.
-
3. Sustainable learning and creative thinking. With the rapid advancement of digital technology, deep collaboration and learning have become essential, requiring employees to continually learn, be creative, remain curious, be willing

Fig. 1. Digital economy innovation talent cultivation model and countermeasures [16, р. 117]
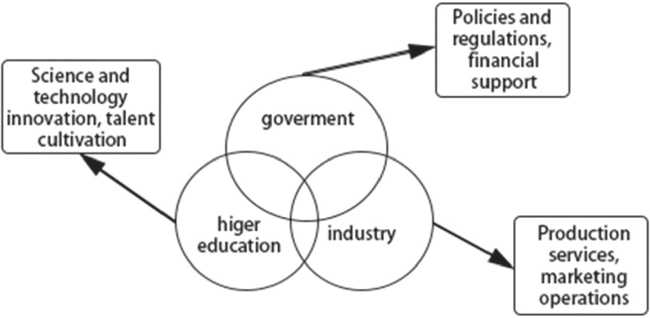
Fig. 2. Overlap model of the Triple helix theory [17, р. 249]
Research methods
The authors used the following research methods: descriptive and comparative analysis (including studying the current situation and characteristics of the internal and external environment of human resources in the enterprise, and identifying the skills and competencies needed by employees in the field of digital transformation); induction and deduction, generalization and comparison (when studying the methods of talent recruitment and training in enterprises engaged in digital transformation).
In today's digital economy development leading industrial change and enterprise transformation [13], the traditional enterprise talent strategy is no longer adapted to the market demand. Traditional enterprise talent strategy no longer adapts to the market demand, enterprises urgently need to adjust the talent development system and make changes in terms of objectives, contents and methods [14, 15]. This can be illustrated by the McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2023 report, which analyzed 3.5 million job postings in the Digital Trends section between 2021 and 2022. It noted that despite a 13 % overall decline in job vacancies worldwide, job postings in areas related to technology trends will continue to grow by 15 % (Source: McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2023. McKinsey Company Research. URL:https://www. accessed: 20.09.2023). Enterprises can build a three-dimensional and multi-dimensional talent strategy from multiple forms and perspectives, such as internal training, external introduction, joint training, employee welfare, value system and fault-tolerance mechanism.
Taking the digital economy innovation talent cultivation model (as show in Fig. 1) constructed by the School of Management of Zhejiang University in China in 2019 as the research basis, we can combined it with the concept of three-helix innovation talent cultivation by the government, enterprises, and colleges and universities proposed by Chunlei Zhang (as show in Fig. 2).
productive work in various situations (work, leisure, study) [19, p. 22; 20, p. 13]. Employees must deeply understand, analyze and interpret data relevant to their responsibilities. This means using digital tools to effectively fi nd, evaluate and use information, as well as the ability to recognize the validity of information and apply it to decision making.
The development of digital technologies and tools has led to the evolution of the description and nature of work, placing new demands on the knowledge, qualities and competencies of human resources [18, p. 148]. Among them the following elements can be distinguished:
-
1. Technical skills. As digital technology evolves, employees must be proficient in a variety of digital tools and platforms that suit the nature of their work. This includes software applications, digital communications tools, data analytics tools, and project management systems.
-
2. Digital literacy: Digital competence is the ability of employees to use ICT for more
-
4. Cybersecurity Awareness: As business changes and organizations rely more and more on digital systems, data, and information, employees must be able to identify cybersecurity risks, protect sensitive information, and strictly adhere to cybersecurity protocols and policies.
to experiment, actively seek opportunities to enhance their skills, research industry trends, and embrace new technologies.
Despite the fact that more and more new entities are being included in the activities of organizations, such as machines and artificial intelligence, people are still the most important core of the production and management process
[21, p.11], since the creativity of people is a source of future income and a guarantee effective innovation and business growth [22, p. 200; 23]. Obviously, over time, it will become increasingly dif fi cult to gain competitive advantages based solely on technological breakthroughs [24]. Because of this, the use of digital management resources provides companies with undoubted competitiveness due to their strengths in divergent thinking and high labor productivity [25, p. 59].
To counteract the talent shortage, it is not enough to rely solely on universities to nurture young digital talent while the real economy harvests large numbers of traditional talent with deep industry experience. Therefore, it is advisable to activate this part of the population by allowing them to develop a digital mindset [26, 27] and improving incentive policies to promote the development of cross-cultural talents. This involves creating platforms for studying digital thinking and technologies, as well as creating an ecosystem that brings together industry enterprises and research organizations in the process of training. This will ensure the integration of the digital economy and the real economy to support innovative development.
Organizations can develop the digital literacy and skills of their employees through the following methods:
-
1. Determine the key digital skills needed by employees and departments, as well as training plans, learning metrics, etc., in accordance with corporate transformation goals and future strategic development objectives.
-
2. Improving digital literacy and technical skills of employees through the organization of seminars, online and offline courses and continuous monitoring of skills.
-
3. Development of projects of digital leadership of managers and digital literacy of employees.
-
4. Development of a culture of continuous learning and adaptation in the organization.
-
5. Strengthening the positive attitude of employees towards change and reducing their resistance, for which it is necessary to constantly inform them and convey to them the importance of digital transformation.
In the digital era, human resource management faces challenges such as the difficulty of introducing new technologies and organizing interaction across the boundaries of an individual workplace and the organization as a whole [28]. Given the existing gap between the developed skills of employees and the demands of digital transformation, it is necessary not only to improve the skills of existing employees, but also to attract new talents that can stimulate the processes of innovative and digital development.
Organizations can attract new digital talent in several ways:
-
a) explore opportunities for cooperation with educational institutions and business structures to organize interaction with professionals in the fi eld of digitalization;
-
b) regularly hold online marathons, open days, events and competitions for working with digital products;
-
c) develop corporate training programs [29]. These efforts can disseminate cutting-edge industry ideas and initially address the discrepancy between college graduates' theoretical knowledge and actual work content in enterprises;
-
d) implement proprietary training courses on digitalization issues, such as cloud computing and big data, to develop adaptable talent beyond the enterprise;
-
e) incorporate online candidate testing into recruitment standards to expand the range of talent selection and promote sustainable growth of enterprise human resources.
-
f) use digital platforms to hire temporary employees to perform simple and non-core duties, thereby saving personnel costs.
The importance of corporate culture, employee engagement and loyalty is increasing every day [30]. High-tech, intelligent management systems in organizations should provide people with more choice, prospects, freedom and control over their lives [31, p. 78]. Reducing brain drain to maintain good organizational structure and company sustainability is also an important area of human resource management and talent development strategy. This implies:
-
1. Creating value for employees. An incentive mechanism is needed that is focused on achieving measurable results. To do this, it is necessary to determine the core value of each position/ employee and follow the principle of recognizing the contribution to value.
-
2. Strengthening interaction between departments and employees. To this end, it is necessary to enrich the thinking of employees, deeply study the potential and interests of each person, and help them fi nd the direction of future development and advancement.
-
3. Ensuring employee well-being. In addition to developing technological digital capabilities, companies must prioritize employee well-being to ensure continued growth in productivity and engagement.
-
4. Implementing policies that promote work-life balance by setting clear boundaries on technology use and creating a supportive, inclusive company culture (for example, offering employees fl exible work hours and the ability to work remotely). Companies should also promote a healthy lifestyle and work, encourage rest and physical activity among staff, reduce perfectionism, reduce the level of organizational stress and maintain the mental health of employees [32, р . 226].
-
5. Empowering employees. The goal of an organization's digital transformation should be to shift decision-making power to frontline staff, empowering employees to make decisions and giving them ownership of their work.
Decentralization of management decisions contributes to the accumulation of human capital, the development of internal entrepreneurship and an increase in the speed of diffusion of innovations [33, р . 438].
According to the above strategic directions, an enterprise talent development strategy model can be formed, which includes internal talent development, talent deployment, and ensuring employee loyalty (as shown in Fig. 3).
The presented development reflects the fact that in the evolving digital environment, traditional methods of recruiting and training talent are no longer sustainable. Based on this, the authors made an attempt to integrate the basic provisions of the talent development models proposed by Tsinghua University and Zhejiang University. It combines theory and practice by creating a three-dimensional, diversi fi ed model of talent development strategy. It provides the most important areas in terms of developing, attracting and maintaining digital talent, which does not contradict the main points of existing research in the fi eld of digital talent development.
At the same time, today there is no standard answer to the question of a strategy for further
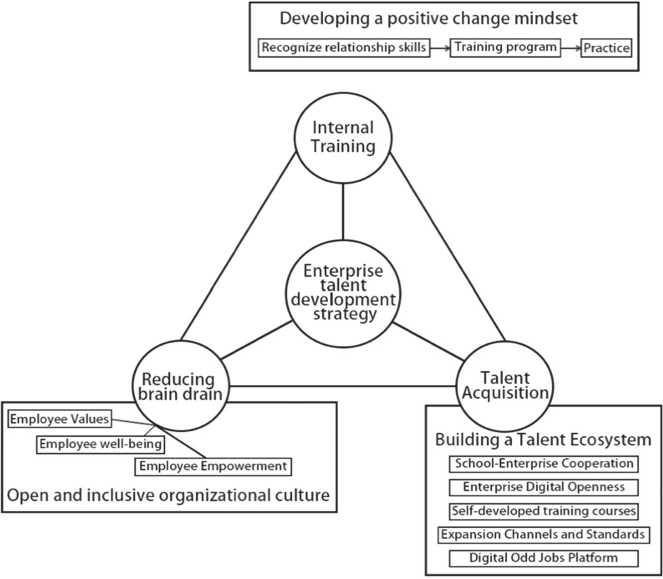
Fig. 3. Modeling talent development strategies in the context of digitization (developed by the authors)
talent development. Different industries and areas of business must prioritize different key skills and the unique challenges they face. For example, Internet technology should emphasize programming skills, while industries such as healthcare place more emphasis on sensitive data and data analysis skills. This means that organizational management needs to expand the horizons of thinking, and the results of this study can help with this, systematizing new approaches to identifying key digital skills and increasing the level of digital literacy and digital maturity, which is necessary for modern organizations developing and adapting corporate search and retention strategies digital talents.
Conclusion
The article examines the rapid development of the digital sphere and the associated changes in talent development strategies. The authors note that in the digital era, we need not only trained, adaptable personnel, but also promising human resources that can provide strategic competitive advantages to the organization, primarily in the market of innovative, high-tech products. At the same time, digital talents are the key to successful transformation and sustainable innovative development of an organization.
This study emphasizes that modern organizations and their management need to act in line with digital transformation trends and effectively solve the problems arising from this. This is due to areas such as developing HR strategies aligned with digital goals, integrating digital skills, creating employee training programs, expanding talent acquisition channels, sharing information with the external environment of the enterprise, creating an ecosystem for the development of digital talent and creating a favourable organizational environment and organizational culture .An equally promising direction is also the study of the interaction and integration of new technologies into the talent management system, primarily such as arti fi cial intelligence.
At the same time, due to the speci fi c nature of the digital environment and constant updates of digital technologies, digital talent strategies also need to be adjusted and developed. Based on this, future research will focus on assessing the effectiveness of strategies already implemented and developing more personalized industry strategies.
Список литературы Talent development strategy during the digital transformation of organizations
- Li Ning, Wang Yujing, Wang Xin. Research on training strategies for new business talents in the digital economy era. Science and Technology Entrepreneurship Monthly. 2023, no. 36(08), рр. 169–171. DOI: CNKI:SUN:KJCK.0.2023-08-031 (accessed: 19.09.2023).
- Zakharov V. Ya., Ludushkina E. N., Kornilova E. V., Kislinskaya M. V. Security of complex economic systems: managing the risks of their digital transformation. Economic analysis: theory and practice. 2021, vol. 20, no. 4(511), pp. 592–623. DOI: 10.24891/ea.20.4.592 (accessed: 19.09.2023).
- Akulova P. E. Analysis of the external market of digital talents and improvement of the IT recruitment system. Russia and the world in new realities: changing world economic relations: materials of the XII Eurasian Economic Youth Forum, Yekaterinburg, April 26–29, 2022. Ural State Economic university. Ekaterinburg, Ural State Economic University, 2022, vol. 1, pp. 233–235.
- Fahmy S., Deraman A., Puteh M., Nasir A., Roslina W. and Haslinda N. An Analysis of Digital Talent in Academic Publications: Refl ection on Malaysia’s Digital Transformation Strategies // International Journal of Integrated Engineering. 2022, no. 14. pp. 184–192.
- Cardenas-Navia I., Fitzgerald B. K. The digital dilemma: Winning and losing strategies in the digital talentrace. Ind. High. Educ. 2019, vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 214–217. DOI: 10.1177/0950422219836669 (accessed: 19.09.2023).
- Kane G. The Technology Fallacy: People Are the Real Key to Digital Transformation. Res. Technol. Manag. 2019, vol. 62, no. 6, pp. 44–49. DOI: 10.1080/08956308.2019.1661079 (accessed: 19.09.2023).
- Barinova E. P., Sheremetyeva E. N., Zotova A. S. Digital Talents: Realities and Prospects. Lect. Notes Networks Syst. 2020, vol. 84, pp. 327–334. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-27015-5_39 (accessed: 20.09.2023).
- Huang Y. H., Wu H. J., Yeh C. H., Wang C. P., Lu L. H., Tsai I. C. Innovative training model of crossdomain digital ICT talent development for training application of data analysis in medical fi eld. Proc. 2020 IEEE Int. Conf. Teaching, Assessment, Learn. Eng. TALE. 2020, pp. 601–605. DOI: 10.1109/TALE48869.2020.9368422 (accessed: 20.09.2023).
- Bernsteiner R., Ploder C., Dilger T., Probst A. Motivating Students to Acquire Digital Skills. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2021, vol. 1329, pp. 853–862. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-68201-9_84 (accessed: 20.09.2023).
- Gama J. A. P. Intelligent educational dual architecture for university digital transformation. Proc. Front. Educ. Conf. FIE. 2019, vol. 2018-Octob. DOI: 10.1109/FIE.2018.8658844 (accessed: 20.09.2023).
- Kharlamova T. L. Innovative education system and development of human capital. Russian economic online journal. 2019, no. 1, p. 74.
- Weng T. S. Using the 3D digital orchid design program to cultivate digital talents. Comput. Aided. Des. Appl. 2017, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 180–192. DOI: 10.1080/16864360.2016.1223430 (accessed: 19.09.2023).
- Yuan Yu., Kharlamova T. L. Using the capabilities of digital platforms for the strategic development of an enterprise. Fundamental and applied research in the fi eld of management, economics and trade: Collection of proceedings of the All-Russian scientifi c, practical and educational conference, St Petersburg, May 15–19, 2023, p. 2. St Petersburg, Polytech-Press, 2023, pp. 361–370.
- Jin Chunhua, Zhang Man. Exploration and practice of information technology ability training model for new business majors. Exploration in higher education. 2023, no. 3, pp. 51–56. DOI: CNKI:SUN:GJTA.0.2023-01-008 (accessed: 20.09.2023).
- Yao Kai, Gui Hongyi. Big data human resources management: changes and challenges. Journal of Fudan University (Social Science Edition). 2018, vol. 60(03), pp. 146–155. DOI: CNKI:SUN:FDDX.0.2018-03-025 (accessed: 20.09.2023).
- Wu Huabin, Xu Qingrui, Chen Zhengrong. Research on innovative talent cultivation mode and countermeasures under the background of digital economy. Research on Science and Technology Management. 2019, no. 39(08), pp. 116–121. DOI: CNKI:SUN:KJGL.0.2019-08-018 (accessed: 21.09.2023).
- Zhang Ch. Triple helix theory as the conceptual platform for innovative talent cultivation in digital economy. State and Municipal Management. Scholar Notes. 2021, no. 4, pp. 246–252. DOI: 10.22394/2079-1690-2021-1-4-246-252 (accessed: 21.09.2023).
- Wu Yue'e, Lin Bingkun. Research on the cultivation of business big data talents in digital economy. Journal of Hubei Open Vocational College. 2021, no. 36(16), pp. 148–150. DOI: CNKI:SUN:HBHS.0.2023-16-054 (accessed: 21.09.2023).
- Gileva T. A. Competences and skills of digital economy: development of personnel development programme. Vestnik UGNTU. Science, Education, Economics. Series: Economics. 2019, no. 2(28), pp. 22–35. DOI: 10.17122/2541-8904-2019-2-28-22-35 (accessed: 21.09.2023).
- Gu Tianlong. Construction of new engineering disciplines from the perspective of digital economy. Chinese University Teaching. 2019, no. 06, pp. 12–15. DOI: CNKI:SUN:JXCY.0.2019-06-004 (accessed: 21.09.2023).
- Yang Sizhuo. Six Dimensions of Leadership. Beijing, Peking University Press, 2008, 226 p.
- Kharlamov A., Kharlamova T. Human capital development in the digitalization risk management process. Atlantis Highlights in Computer Sciences: Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Technologies in Logistics and Infrastructure (ICDTLI 2019), Saint Petersburg, 2019, April, 04–05. Atlantis Press, 2019, vol. 1, pp. 199–203.
- Baykova E. R. Digital competency model as a talent management tool. Economics and management: scientifi c and practical journal. 2020, no. 1(151), pp. 58–61. DOI: 10.34773/EU.2020.1.14 (accessed: 21.09.2023).
- Yakovleva A. V. Strategy for managing human capital of enterprises in the context of the development of the digital economy. Results of modern scientifi c research and development: collection of articles of the XVII All-Russian Scientifi c and Practical Conference, Penza, June 17, 2022. Penza, Science and Enlightenment (IP Gulyaev G.Yu.), 2022, pp. 135–138.
- Larionov V. G. Digital management: education and talents. Innovations in management. 2019, no. 2(20), pp. 56–63.
- Zagrebelnaya N. S., Bostoganashvili E. R. Human resource management in the digital economy. Economics: yesterday, today, tomorrow. 2019, vol. 9, no. 1-1, pp. 374–384. DOI: 10.25799/AR.2019.80.1.038 (accessed: 21.09.2023).
- Barykin S. Y., Kapustina I. V., Kalinina O. V. [et al.] The career choice motivation in view of Maslow's hierarchy in innovative economy: The case of Russia. Academy of Strategic Management Journal. 2021, vol. 20, no. Special Iss. 2, pp. 1–17.
- Okorokov R., Timofeeva A., Kharlamova T. Building intellectual capital of specialists in the context of digital transformation of the Russian economy. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Saint-Petersburg, 21–22.11.2018, Saint Petersburg, Institute of Physics Publishing, 2019, vol. 497, p. 012015. DOI: 10.1088/1757-899X/497/1/012015 (accessed: 22.09.2023).
- Kosterova O. A., Kalinina O. V. Features of managing the experience of personnel in Russia and abroad. Fundamental and applied research in the fi eld of management, economics and trade: Collection of proceedings of the All-Russian scientifi c-practical and educational-methodological conference, at 4 hours. St Petersburg, June 01-04, 2021. Part 3. St Petersburg, POLYTECH-PRESS, 2021, pp. 50–54.
- Wu Xunya. Exploration of talent training model that empowers the digital economy. Science and Technology Vision. 2020, no. 12, pp. 98–100. DOI: 10.19694/j.cnki.issn2095-2457.2020.12.037 (accessed: 22.09.2023).
- Sobolevskaya A. A. Organizational fl exibility in the context of digital transformation. Digital and industry economics. 2023, no. 1(29), pp. 76–81.
- Antonova N. V. Digital transformation of the organization and psychological wellbeing of employees. Institute of Psychology of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Social and economic psychology. 2022, vol. 7, no. 3(27), pp. 201–233. DOI: 10.38098/ipran.sep_2022_27_3_07 (accessed: 22.09.2023).
- Ivinskaya E. Yu., Abdrakhmanova D. R. Interrelation of technological and organizational innovations in the conditions of digital transformation of the economy. Issues of innovative economics. 2021, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 431–442. DOI: 10.18334/vinec.11.2.112040 (accessed: 22.09.2023).


