Терапия ксеногенным протеомным комплексом из эмбриональных клеток головного мозга тормозит прогрессирование экспериментально вызванной хронической почечной недостаточности
Автор: Кирпатовский В.И., Сивков А.В., Соколов М.А., Голованов С.А., Дрожжева В.В., Синюхин В.Н., Фролова Е.В., Аполихин О.И., Каприн А.Д.
Журнал: Экспериментальная и клиническая урология @ecuro
Рубрика: Экспериментальная урология
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.16, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. В ранее опубликованных экспериментальных исследованиях нами было показано, что у крыс с предварительно смоделированной острой постишемической почечной недостаточностью терапия белково-пептидным комплексом, выделенным из стволовых и прогениторных клеток головного мозга эмбрионов свиней, оказывает значимый терапевтический эффект, уменьшая выраженность функциональных и гистологических нарушений, препятствуя переходу патологического процесса в хроническую болезнь почек. Данное исследование посвящено оценке эффективности влияния этой терапии на течение искусственно вызванной хронической почечной недостаточности (ХПН) у крыс. Материал и методы. Опыты проведены на 45 белых беспородных крысах-самцах массой 200-240 г. ХПН моделировали путем односторонней нефрэктомии и резекции обоих полюсов оставшейся почки, что уменьшало массу функционирующей паренхимы на 80%. В 1-й серии опытов никакой терапии не проводили, во 2-4-й сериях животным внутрибрюшинно вводили фракционированный ксеногенный протеомный комплекс (секретом) стволовых и прогениторных клеток головного мозга эмбрионов свиньи (ССПК) в ежедневной дозе 0,1 мл в разных режимах: два 10-дневных курса с 10-дневным перерывом между ними (2-я серия), увеличение первого курса до 20 дней и повторный 10-дневный курс через 10 дней (3-я серия) и непрерывная терапия в течение 30 дней (4-я серия). 5 серия - интактные животные. Оценку эффективности терапии проводили на основании выраженности развития компенсаторной гипертрофии почки, по динамике биохимических показателей функции почки, активности ферментов (аспартатаминотрансфераза - АСТ, аланинаминотрансфераза - АЛТ, лактатдегидрогеназа - ЛДГ, щелочная фосфатаза - ЩФ) в крови и моче и уровню уремических нейротоксинов 3-индоксил сульфата и р-толил сульфата в крови.
Хроническая болезнь почек, протеомный комплекс, терапия, стволовые клетки, секретом, уремические токсины
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142240016
IDR: 142240016 | DOI: 10.29188/2222-8543-2023-16-3-26-37
Текст научной статьи Терапия ксеногенным протеомным комплексом из эмбриональных клеток головного мозга тормозит прогрессирование экспериментально вызванной хронической почечной недостаточности
Хронические заболевания почек, а также послед ствия тяжелого острого повреждения почек, в конечном итоге могут привести к развитию хронической почечной недостаточности (ХПН) с прогрессированием до терми нальной стадии, требующей органозамещающей терапии (хронический диализ или трансплантация почки). В связи с этим актуальной задачей является изучение воз можности остановки или торможения прогрессивной утраты функции почек. Современные возможности те рапии ХПН весьма ограничены и, хотя несколько и за медляют, но не позволяют остановить прогрессирование заболевания [1, 2]. Регенеративная медицина предлагает несколько подходов к решению данной задачи, включая терапию с использованием стволовых/прогениторных клеток разного происхождения, в том числе индуцированных плюрипотентных клеток, а также продуктов их секреции (секретома), выделенных из самих клеток или из среды их культивирования. Многими экспериментальными исследованиями на животных показана целесообразность использования низкодифференцированных клеток для терапии острого или хронического повреждения почек [3-5]. Тем не менее, ряд вопросов клинической безопасности этого метода остается открытым, в частности, возможность развития иммунной реакции на аллогенные или ксеногенные клетки, опасность тромбоэмболии легочной артерии при внутривенном введении суспензии клеток, нежелательная дифференцировка мезенхимных клеток в костную, хрящевую или жировую ткань, а также риск развития тератом при ис пользовании плюрипотентных клеток [6-8]. В связи с этим более перспективным направлением в настоящее время может считаться использование продуктов секреции эмбриональных стволовых клеток (cell-free cell therapy), как более безопасного варианта терапии, не имеющего юридических и этических ограничений [9-11].
В ранее проведенных исследованиях нами было показано,что терапия ксеногенным протеомным ком плексом (фракционированный секретом ксеногенных эмбриональных стволовых и прогениторных клеток, полученный хроматографическим методом из голов ного мозга свиней) оказывает выраженный нефропро тективный эффект при моделировании острой постишемической почечной недостаточности [12, 13], а также уменьшает риск перехода острого повреждения почек в хроническую болезнь почек [14]. В данном ис следовании мы изучили влияние этого комплекса на течение хронической болезни почек на модели постре зекционной ХПН у крыс.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
Опыты проведены на 45 аутбредных крысах-сам цах массой 200-240 г. Животные содержались в стан дартных условиях вивария с неограниченным доступом к полнорационному брикетированному комби корму для лабораторных грызунов (рецептура ПК-120, ООО «Лабораторкорм», Россия) и питьевой воде. Все манипуляции с животными выполняли в соответствии с Европейской конвенцией о защите животных,ис пользуемых для экспериментов или в иных научных целях (ETS N 123) и Директивой Европейского парла мента и Совета Европейского Союза 2010/63/ЕС о за щите животных, использующихся для научных целей.
У крыс моделировали ХПН путем односторонней нефрэктомии и резекции верхнего и нижнего полюсов оставшейся почки, что приводило к уменьшению массы функционирующей паренхимы почек в среднем на 80%. Анестезию вызывали внутрибрюшинным вве дением смеси Золетила-100 («Valdefarm», Франция) и
Рометара («Биовета», Чешская республика) в соотно шении 1:1 при расчетной дозе Золетила 15 мг/кг.
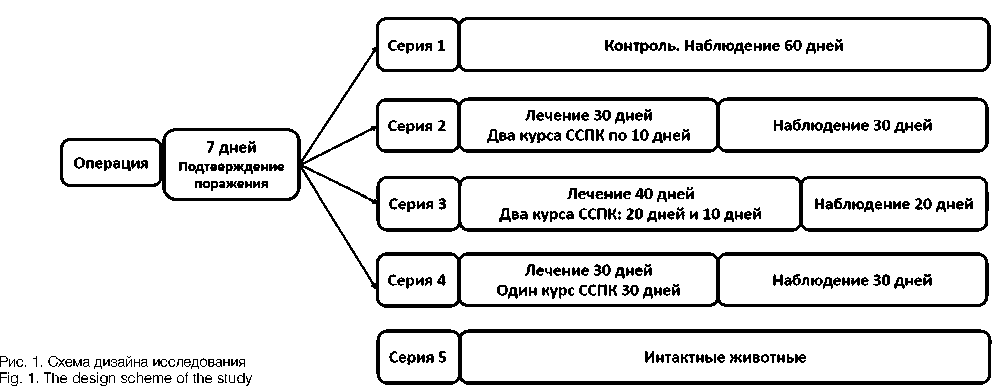
Животных наблюдали в течение 7 дней после опе рации,после чего брали пробы крови из хвостовой вены и суточной мочи для подтверждения формиро вания ХПН, что определяли по повышению концент рации креатинина,мочевины и активности фермен тов в крови и моче. Значения этих показателей слу жили ориентиром для определения динамики разви тия патологического процесса и влияния на него проводимой терапии. После этого животных включали в исследование и начинали отсчет контрольных сроков с 8 дня после моделирования ХПН.
Проведено 5 серий экспериментов. В 1-й серии (контроль, 10 крыс) никакой терапии не проводили. Начиная с 8 дня после моделирования ХПН, во 2-4-й сериях (по 10 крыс в каждой) проводили терапию в различных режимах фракционированным ксеноген ным секретомом эмбриональных стволовых и проге ниторных клеток (ССПК), представляющим собой протеомный комплекс с молекулярной массой компо нентов от 10 до 250 кДа, хроматографически выделен ный из головного мозга эмбрионов свиней и являю щийся активным компонентом фармакопейного пре парата Целлекс (АО «Фарм-Синтез», Россия). Во 2-й серии ССПК вводили внутрибрюшинно курсами (2 курса по 10 дней с 10-дневным перерывом между кур сами) с ежедневными инъекциями в дозе 0,1 мл пре парата на крысу (0,1 мг действующего компонента). В 3-й серии длительность первого курса увеличили до 20 дней, а второй курс проводили, как и во 2-й серии. В 4-й серии осуществляли непрерывную терапию ССПК в течение 30 дней.Пятую серию составили 5 интактных крыс.
Эффективность различных вариантов терапии ССПК оценивали по биохимическим показателям крови и мочи. С этой целью в начале терапии и через 30 и 60 дней крыс высаживали в обменные клетки для сбора суточной мочи с оценкой диуреза и брали пробы крови из хвостовой вены. Схематически дизайн иссле дования представлен на рисунке 1.
В крови и моче на автоматическом биохимиче ском анализаторе ADVIA-2000 (Siemens) с использова нием стандартных наборов реактивов определяли следующие показатели: концентрацию мочевины, креатинина, натрия, калия, кальция, а также актив ность ряда ферментов (aспартатаминотрансфераза – АСТ, aланинаминотрансфераза – АЛТ, лактатдегидро геназа – ЛДГ, щелочная фосфатаза – ЩФ). Из получен ных данных рассчитывали показатели функционального состояния почек: скорость клубочковой фильтра ции, канальцевую реабсорбцию натрия и кальция, су точную экскрецию ферментов с мочой по общепринятым формулам расчета.
В пробах крови, взятых через 2 месяца после на чала эксперимента, методом сверхпроизводительной жидкостной хроматографии (UPLC) с МС/МС детек цией на аппарате ACQUITY UPLC (Waters) определили концентрацию характерных для ХПН нейротоксиче ских метаболитов: 3-индоксил сульфата и р-толил сульфата.
Через 1 и 2 месяца по 5 животных из каждой группы выводили из эксперимента путем передози ровки наркотических веществ. У них удаляли почки и проводили определение их массы взвешиванием на электронных весах Acculab (Sartorius) с целью оценки выраженности компенсаторной гипертрофии органа.
Статистическую обработку цифрового материала провели с помощью программ Excel 2003 и Statistica 10,0 с определением среднегрупповых значений пока зателей и ошибки средней (M±m) и достоверности раз личий между сравниваемыми группами по критерию t Стьюдента. Значимыми различия признавали при значениях р <0,05.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
Для оценки динамики развивающейся компенса торной гипертрофии единственной резецированной почки сравнивали ее массу через 1 и 2 месяца после моделирования ХПН с массой обеих почек интактных животных, а также с массой, резецированной в анало гичных условиях почки. Средние значения массы обеих почек интактных крыс составили 2,75±0,02 г, а масса почки после резекции ее полюсов – 0,54±0,03 г, что соответствовало 19,6% от массы обеих почек в норме. Через месяц у крыс 1-4 серий отмечен рост массы оставшейся почки, причем у получавших терапию ССПК – достоверно больший, чем в контрольной серии. В процентном отношении от исходного показателя масса почек составила: в 1-й (контрольной) серии – 61,4%; во 2-й серии – 68,7%; в 3-й серии – 71,2% и в 4-й серии – 70,2%, а относительно контрольной группы – увеличение составило 11,8% – 16,0% соответственно. Прирост массы органа в течение первого месяца, отражающий интенсивность процесса компенсаторной гипертрофии, оказался достоверно выше (p<0,05) во всех опытных группах, по сравнению с контрольной серией опытов, тогда как между группами с разными вариантами терапии ССПК достоверных различий не выявили. Это свидетельствует, что терапия ССПК стимулирует регенерационные процессы в органе, способствуя более быстрому восстановлению его паренхимы (табл. 1).
Через 2 месяца во всех сериях (кроме интактной) масса оставшейся почки достоверно уменьшалась по сравнению с первым месяцем,достигнув от нормаль ного уровня 49,5%, 58,2%, 62,5% и 60,7% в 1-4 сериях, соответственно.Уменьшение массы почки в течение второго месяца,отмеченное во всех сериях опытов, может быть связано с процессом склерозирования, что характерно для прогрессирования ХПН. Однако, не смотря на это,масса органа во всех опытных сериях, по-прежнему, оставалась статистически достоверно выше ( p <0,05), чем в контроле на 17,6-26,5% (табл. 1).
При оценке динамики показателей, характеризующих выделительную функцию почек, выявили, что через 7 дней после моделирования ХПН у животных наступали характерные для этого состояния изменения в виде полиурии и повышения концентрации мочевины и креатинина в крови. К 30-м суткам наблюдения полиурия и концентрация мочевины продолжали возрастать, а уровень креатинина крови снижался ( p <0,05), но оставался достоверно выше нормальных значений, что свидетельствовало об определенной тенденции к компенсации развившихся функциональных нарушений. К 60-м суткам
Таблица 1. Влияние разных режимов терапии ССПК на увеличение массы единственной почки (в граммах) через 1 и 2 месяца после ее резекции
Table 1. The effect of SSPC therapy in different modes on the increase in the mass of a single kidney (in grams)
1 and 2 months after its resection
|
Серия / Срок Series / Term |
1 месяц 1 month |
2 месяца 2 months |
|
Серия 1 (контроль) Series 1 (control) |
1,69±0,03 |
1,36±0,09 |
|
Серия 2 Series 2 |
1,89±0,06* (+11,8%) |
1,60±0,06* (+17,6%) |
|
Серия 3 Series 3 |
1,96±0,04* (+16,0%) |
1,72±0,04* (+26,5%) |
|
Серия 4 Series 4 |
1,93±0,03* (+14,2%) |
1,67±0,03* (+22,8%) |
наблюдения все показатели оставались стойко повы шенными (табл. 2).
Терапия ССПК в различных вариантах при сроке 30 суток после начала терапии не привела к достовер ным изменениям диуреза и уровня креатинина крови, хотя выявлялась тенденция к уменьшению степени по лиурии и гиперкреатининемии в сериях с более дли тельной терапией ССПК (20-дневный первый курс и непрерывная 30-дневная терапия в 3-й и 4-й сериях). В отношении уровня мочевины крови во 2-й серии из менений не выявили, в 3-й серии обнаружили тенден цию к снижению этого показателя, а у крыс 4-й серии концентрация мочевины достоверно снизилась.
Через 60 дней наблюдения в опытах с терапией ССПК во всех сериях наблюдали достоверное уменьше ние выраженности полиурии и достоверное уменьше ние уровня мочевины крови в 3-й и 4-й сериях, тогда как средние значения концентрации креатинина в крови во всех опытных группах достоверно не отлича лись от значений в контрольной серии, хотя тенденция к более низким значениям сохранялась (табл. 2).
Определение расчетных показателей функцио нального состояния почек показало, что скорость клу бочковой фильтрации (СКФ), характеризующая состояние фильтрационной функции,в контрольной серии опытов через 7 дней после резекции единственной почки уменьшалась до 45% от нормальных значений
(табл. 2). Через 30 суток отмечено некоторое возраста ние СКФ до 67% от нормы, но через 60 дней СКФ вновь снизилась до 47% от нормы. В сериях с терапией ССПК через 30 суток после моделирования ХПН во 2-й серии значения СКФ не отличались от показателей в конт рольной серии, тогда как в 3-й и 4-й сериях отмечены достоверно более высокие значения. Через 60 суток во всех опытных сериях значения СКФ были достоверно выше, чем в контроле, оставаясь примерно на том же уровне, что и через 30 суток (рис. 2).
Таблица 2. Показатели функционального состояния почек интактной и опытных серий крыс
Table 2. The effect of SSPC therapy on the indicators of the functional state of the kidneys of rats with CRF
|
Показатели Parameters |
Норма Normal |
7 дней ХПН (1-4 серии) 7 days CRF1-4 Series |
Серии опытов Series |
Терапия ССПК / SCS therapy |
|
|
30 дней 30 days |
60 дней 60 days |
||||
|
1-я |
27,5±0,7 |
28,5±0,6 |
|||
|
Диурез, мл/сут |
11,3±0,2 |
14,3±0,3 |
2-я |
29,5±0,7 |
24,7±0,5* |
|
Diuresis, ml/day |
3-я |
25,6±0,5 |
21,4±0,4* |
||
|
4-я |
23,6±0,5 |
22.9±0,5* |
|||
|
1-я |
13,6±0,7 |
11,5±0,4 |
|||
|
Мочевина крови, ммоль/л |
6,8±0,2 |
8,9±0,3 |
2-я |
13,3±0,4 |
10,5±0,3 |
|
Urea, mmol/l |
3-я |
11.4±0,6 |
9,7±0,3* |
||
|
4-я |
9,8±0,6* |
10.0±0,3* |
|||
|
1-я |
80±3 |
82±4 |
|||
|
Креатинин крови, ммоль/л |
60±2 |
112±7 |
2-я |
81±2 |
73±3 |
|
Creatinine, mmol/l |
3-я |
76±2 |
71±3 |
||
|
4-я |
71±2 |
74±3 |
|||
|
1-я |
1,11±0,02 |
0,77±0,02 |
|||
|
СКФ, мл/мин |
1,64±0,07 |
0,73±0,03 |
2-я |
1,12±0,03 |
1,14±0,03*** |
|
Glomerular filtration rate, ml/min |
3-я |
1,36±0,03* |
1,22±0,03*** |
||
|
4-я |
1,48±0,04** |
1,45±0,03*** |
|||
|
1-я |
98,75±0,14 |
98,82±0,13 |
|||
|
Канальцевая реабсорбция Na+, % |
99,32±0,04 |
98,64±0,21 |
2-я |
99,03±0,05 |
98,89±0,15 |
|
Tubular reabsorption of Na+, % |
3-я |
98,92±0,11 |
99,01±0,11 |
||
|
4-я |
99,14±0,11 |
99,06±0,14 |
|||
|
1-я |
96,19±0,09 |
98,28±0,04 |
|||
|
Канальцевая реабсорбция Ca++, % |
99,68±0,04 |
97,19±0,36 |
2-я |
98,51±0,11*** |
98,60±0,05 |
|
Tubular reabsorption of Ca++, % |
3-я |
98,35±0,13*** |
98,78±0,09* |
||
|
4-я |
98,67±0,13*** |
98,95±0,11* |
|||
Примечание: достоверность различий по сравнению с 1-й серией: * p <0,05, ** p <0,01, *** p <0,001
Note: the reliability of the differences compared to the 1-st series: * p <0.05, ** p <0.01, *** p <0.001
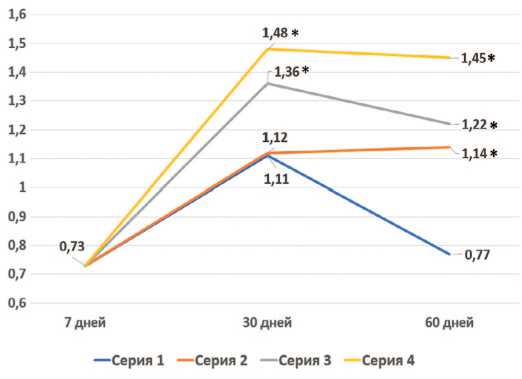
Рис. 2. Динамика СКФ в опытных группах
Fig. 2. Dynamics of glomerular filtration rate in the studied series
Оценка влияния ССПК на состояние канальцевого аппарата почек показала, что все варианты терапии достоверно не изменяли показатели канальцевой реабсорбции натрия. Как в контрольной, так и во всех опытных сериях этот показатель сохранялся на стабильно сниженных значениях, как через 30, так и через 60 суток. В то же время в отношении реабсорбции кальция в почечных канальцах выявили статистически значимое положительное влияние всех вариантов терапии ССПК. Если в контроле отмечали снижение этого показателя через 30 суток после моделирования ХПН с его возрастанием к 60 суткам (но оставаясь ниже нормальных значений), то при терапии ССПК во всех сериях опытов через 30 суток реабсорбция кальция оказалась достоверно выше, чем в контроле, а через 60 суток достоверные различия сохранялись в 3-й и 4-й сериях.
Показателем выраженности повреждения клеток почки может служить активность ферментов в крови и моче.Определение уровня ферментемии показало, что через 7 суток после моделирования ХПН активность всех ферментов, за исключением АЛТ, в среднем по опытным сериям, достоверно возрастала (р<0,05-p< 0,01) (табл. 3). В определенной степени это могло быть связано с последствиями операционной травмы (резекция почки), но свой вклад могут также вносить влияния остро возникшей гиперфункции единственной резецированной почки, о чем свидетельствуют данные, полученные в более позднем периоде. В контрольной серии опытов через 30 суток наблюдения ранее повышенная активность ЛДГ и ЩФ снижалась до практически нормальных значений (различия с нормальными показателями статистически недостоверны). При этом активность АСТ сохранялась на повышенных значениях, а ранее нормальная активность АЛТ достоверно возрастала. Через 60 суток наблюдения отмечали возрастание активности в крови ЛДГ и АСТ, тогда как активность АЛТ и ЩФ оставалась на значениях, близких к норме.
В опытах с разными вариантами терапии ССПК через 30 суток активность АСТ и ЛДГ существенно снижалась, как и в контрольной серии, но в отношении ЛДГ в 3-й и 4-й сериях снижение было более выражено, чем в контроле, достигая нормальных значений, а в отношении АСТ различий между контрольной и всеми опытными сериями не получено (табл. 3). Активность АЛТ в крови у крыс всех опытных серий нормализовалась, в отличие от контроля, а активность ЩФ во всех опытах оказалась близкой к норме или нормальной.
Через 60 суток терапия ССПК оказала положительное влияние на активность АСТ, которая оказалась достоверно ниже в 4-й серии опытов, не отличаясь от нормальных значений, а также в отношении активности ЛДГ, которая, в отличие от контрольной серии, нормализовалась во всех опытных группах.
В отличие от уровня ферментемии,повышенного в ранние сроки формирования ХПН, активность всех изучаемых ферментов в моче снижалась в большей или меньшей степени, что, видимо, было связано с уменьшением клеточной массы органа при развитии полиурии. Для объективизации степени повреждения
Таблица 3. Влияние терапии ССПК на уровень ферментемии у крыс с моделированной ХПН
Table 3. Effect of SSPC therapy on the level of enzymemia in rats with CRF
|
Показатели Parameters |
Норма Normal |
7 дней ХПН (1-4 серии) 7 days CRF (1-4 Series) |
Серии опытов Series |
Терапия ССПК / SCS therapy |
|
|
30 дней 30 days |
60 дней 60 days |
||||
|
1-я |
85±5 |
90±3 |
|||
|
АСТ, МЕ/л |
68±2 |
140±28 |
2-я |
87±8 |
78±5 |
|
AST, ME/l |
3-я |
75±7 |
77±6 |
||
|
4-я |
79±8 |
74±5* |
|||
|
1-я |
58±4 |
42±3 |
|||
|
АЛТ, МЕ/л |
36±3 |
34±3 |
2-я |
37±3* |
38±3 |
|
ALT, ME/l |
3-я |
34±3* |
33±2 |
||
|
4-я |
42±3* |
39±3 |
|||
|
1-я |
378±26 |
928±57 |
|||
|
ЛДГ, МЕ/л |
320±22 |
569±35 |
2-я |
313±18 |
339±29** |
|
LDH, ME/l |
3-я |
239±17* |
276±23*** |
||
|
4-я |
261±15* |
293±19*** |
|||
|
1-я |
172±15 |
190±13 |
|||
|
ЩФ, МЕ/л |
169±8 |
256±17 |
2-я |
253±24 |
180±11 |
|
Alkaline phosphatase (AF), ME/l |
3-я |
207±14 |
173±15 |
||
|
4-я |
239±18 |
151±13 |
|||
Примечание: достоверность различий по сравнению с 1-й серией: * p <0,05, ** p <0,01, *** p <0,001
Note: the reliability of the differences compared to the 1-st series: * p <0.05, ** p <0.01, *** p <0.001
клеток почки мы рассчитывали суточную экскрецию ферментов с мочой, считая этот показатель не связан ным с величиной диуреза, а, следовательно, более объ ективно отражающим выраженность цитолиза.
Полученные данные показали, что суточная экс креция с мочой всех ферментов также снижалась ( p <0,05) (табл. 4), что свидетельствовало о преимуще ственной роли в уменьшении ферментурии снижения клеточной массы.
В более отдаленные сроки в контрольной серии опытов отметили достоверное возрастание экскреции ферментов с мочой как через 30, так и через 60 дней наблюдения. Развитие компенсаторной гипертрофии и увеличение массы органа могут вносить в увеличе ние ферментурии лишь незначительный вклад,по скольку масса гипертрофированной почки оставалась примерно в 2 раза меньше, чем масса обеих почек тогда как экскреция ферментов возрастала практиче ски в 2 раза по сравнению с нормой и в 2-5 раз по сравнению со значениями через 7 дней после модели рования ХПН. То есть основной вклад в увеличение ферментурии вносят деструктивные изменения в структурах почки, вызванные стойкой гиперфунк цией почечных структур.
Подтверждением этому служат прогрессирующее увеличение экскреции АЛТ и ЩФ с увеличением срока, прошедшего после формирования ХПН при со храняющейся гиперэкскреции АСТ и ЛДГ, а также данные опытов с терапией ССПК. Через 30 суток те рапии достоверное уменьшение степени ферментурии выявлено в отношении АСТ и АЛТ, причем экскреция этих ферментов осталась сниженной и через 60 суток. Экскреция ЩФ через 30 суток достоверно не меня лась, но через 60 суток выявлено достоверное умень шение экскреции этого фермента с мочой.Экскреция ЛДГ с мочой на фоне терапии ССПК не менялась ни через 30, ни через 60 суток.
Таким образом, по данным динамики уровня ферментемии и ферментурии, терапия ССПК оказы вает существенный цитопротективный эффект, что может служить основой для сохранения функцио нального состояния почки и предупреждения про грессирования ХПН.При этом позитивный эффект оказывали все варианты терапии,но при использова нии более длительных курсов (20-дневный первый курс или непрерывный 30-дневный курс) выявлена тенденция к более выраженному эффекту.
Одним из признаков тяжести ХПН является сте пень накопления в крови уремических токсинов, об разование которых в организме превышает их выведение из-за сниженной экскреторной функции почек. К таким токсинам относят мочевую кислоту, 3-индоксил сульфат, р-толил сульфат (паракрезолсуль фат), а также ряд цитокинов. Чрезмерное накопление этих соединений оказывает токсический эффект на почки, способствуя дальнейшему прогрессированию ХПН, а также на центральную нервную систему, лег кие и сердечно-сосудистую систему [15-18].
Таблица 4. Влияние терапии ССПК на суточную экскрецию ферментов у крыс с ХПН
Table 4. The effect of different variants of SSPC therapy on the daily excretion of enzymes in rats with CRF
|
Показатели Parameters |
Норма Normal |
7 дней ХПН (1-4 серии) 7 days CRF1-4 Series |
Серии опытов Series |
Терапия ССПК / SCS therapy |
|
|
30 дней 30 days |
60 дней 60 days |
||||
|
1-я |
153±26 |
103±20 |
|||
|
Экскреция АСТ, МЕ/сут |
74±9 |
34±11 |
2-я |
53±11* |
15±3** |
|
AST excretion, ME/day |
3-я |
42±9** |
27±5** |
||
|
4-я |
48±8** |
33±3** |
|||
|
1-я |
120±6 |
172±21 |
|||
|
Экскреция АЛТ, МЕ/сут |
45±8 |
25±3 |
2-я |
66±4** |
67±11** |
|
ALT excretion, ME/day |
3-я |
62±5** |
53±8** |
||
|
4-я |
58±4** |
56±7** |
|||
|
1-я |
210±23 |
142 ±16 |
|||
|
Экскреция ЛДГ, МЕ/сут |
116±8 |
90±4 |
2-я |
244±34 |
104±11 |
|
LDH excretion, ME/lday |
3-я |
196±19 |
143±14 |
||
|
4-я |
177±14 |
129±12 |
|||
|
1-я |
178±13 |
265±18 |
|||
|
Экскреция ЩФ, МЕ/сут |
120±10 |
86±6 |
2-я |
147±11 |
136±27* |
|
AF excretion, ME/day |
3-я |
152±13 |
145±21** |
||
|
4-я |
142±9 |
131±19** |
|||
Примечание: достоверность различий по сравнению с 1-й серией: * p <0,05, ** p <0,01 Note: the reliability of the differences compared to the 1-st series: * p <0.05, ** p <0.01
В связи с этим, мы провели определение концент рацию 3-индоксил сульфата и р-толил сульфата в крови крыс с ХПН и влияние на их уровень терапии ССПК. При этом, учитывая вышеприведенные данные о большей эффективности длительной терапии ССПК определение токсинов провели в серии с непрерывной 30-дневной терапией (4-я серия).
Результаты показали, что через 2 месяца после моделирования ХПН в контрольной серии опытов кон центрация уремических токсинов достоверно возрас тала: для 3-индоксил сульфата в 2,5 раза – с 935±123 нг/мл до 2504±141 нг/мл, а для р-толил сульфата в 10 раз – с 42±4 нг/мл до 426±38 нг/мл ( p <0,05 и p <0,001 соответственно). В серии опытов с терапией ССПК по вышение уровня токсинов было достоверно меньше: концентрация 3-индоксил сульфата возрастала до 1790±132 нг/мл, а уровень р-толил сульфата – до 173±24 нг/мл (достоверность различий по сравнению с контролем, p <0,01) (рис. 3).
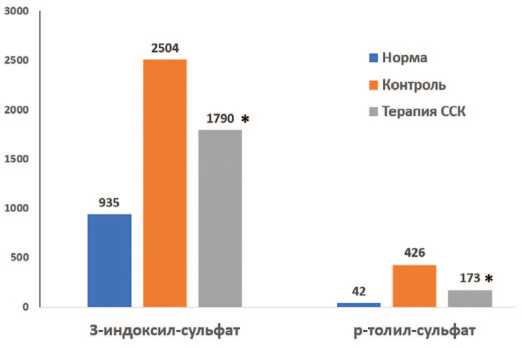
Рис. 3. Влияние терапии ССПК на накопление нейротоксинов в крови крыс с ХПН Fig. 3. The effect of SSPC therapy on the accumulation of neurotoxins in the blood of rats with CRF
Менее выраженное накопление уремических ней ротоксинов при моделировании ХПН в опытах с тера пией ССПК свидетельствует о торможении прогрес сирования ХПН под действием препарата и об умень шении потенциальных осложнений ХПН со стороны центральной нервной системы.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Современной тенденцией в разработке методов лечения хронических заболеваний жизненно важных органов является изучение эффективности разных ва риантов «бесклеточной» регенерационной терапии, учитывая сохраняющиеся в настоящее время юриди ческие и этические ограничения использования ство ловых/прогениторных клеток различного происхождения. Законодательные акты по биомедицинским клеточным продуктам [19, 20], предписывающие куль тивирование стволовых клеток на терапевтических клеточных средах, с одной стороны, привели в поря док многочисленные терапевтические эксперименты в этой области,а с другой – существенно осложнили технологию исследований и производства, что повы сило себестоимость работ и курса клеточной терапии. В то же время имеются многочисленные данные о том, что продукты секреции стволовых клеток (секретом) обладают не меньшей эффективностью,чем исполь зование самих клеток [21, 22]. Изучают возможность применения с этой целью кондиционированной среды культивирования стволовых/прогениторных клеток [23-2 5], внеклеточных везикул, микросом, экзосом, секретируемых этими клетками [26-28], а также ком плексов биоактивных молекул, выделенных непосред ственно из стволовых клеток [29-32].
С появлением новой парадигмы «стволовых ниш» взрослого организма, т.н. тканевых «депо» ство ловых и прогениторных клеток, регулирующих по пуляцию транзиторного клеточного пула каждого органа, стала понятна важная роль внеклеточного матрикса в регуляции процессов дедифференци ровки/дифференцировки, как одной из основных со ставляющих репаративного процесса. Успехи протеомики, липидомики и метаболомики обратили взгляды ученых многих лабораторий мира, занимаю щихся репаративной клеточной терапией,к новому виду – «клеточной терапии без клеток» (cell-free cel therapy), используя в качестве биологически активных субстанций сигнальные белки внеклеточного мат рикса и/или клеточные среды после культивирования стволовых клеток. Наиболее перспективным и эконо мически выгодным направлением оказалось исполь зование эмбриональных тканей сельскохозяйственных животных, т.к. именно в эмбриогенезе на опреде ленных сроках гестации при мощной стимуляции роста происходит четкая регуляция процессов диффе ренцировки за счет митогенов и транскипционных белков путей биологии развития, управляющих про цессами апоптоза/аутофагии, чего трудно добиться при использовании культивированных пулов стволо вых клеток.Именно эмбриональные факторы роста и дифференцировки позволяют управлять репаратив ными процессами (протекции и репарации) без риска возникновения неопластических процессов. Совре менные методы фракционирования и очистки биоло гически активных молекул позволяют решать вопросы вирусной и прионовой безопасности, а также изучать основные фармакокинетические параметры этих сложнокомпонентных препаратов.
К этой категории относится отечественный пре парат «Целлекс», представляющий собой фракциони рованный протеомный секретом стволовых и про-гениторных клеток – белково-полипептидный ком плекс биологически активных молекул,хроматогра фически выделенный из мозга эмбрионов свиньи,на сегодня первый представитель новой группы препаратов репаративной медицины – клеточной те рапии без клеток (cell-free cell therapy). В ранее про веденных исследованиях нами была доказана его эффективность при терапии крыс с острой постише мической почечной недостаточностью и профилак тике перехода острого повреждения почки в хроническую болезнь почек [12-14]. Полученные данные послужили основой для данного исследования с оценкой возможного применения нового репаранта – ксеногенного секретома стволовых и прогениторных клеток при ХПН.
Результаты проведенного исследования пока зали, что терапия ССПК оказывает достоверный неф ропротективный эффект на модели ХПН, полученной путем субтотальной резекции единственной почки. Учитывая хронический характер индуцированной патологии и тенденцию к прогрессированию при уве личении длительности ХПН, мы использовали более длительные протоколы терапии,чем в ранее прове денных опытах с моделированием острой почечной недостаточности (ОПН) [12, 13]. Если в опытах с ОПН проводили 10-дневный курс терапии ССК, то в данном исследовании – в виде 2-х курсов по 10 дней с 10-дневным интервалом или 2-х курсов с первым курсом в 20 дней и вторым – в 10 дней, а также в виде непрерывной терапии в течение 30 дней. При этом во всех 3-х опытных сериях проявилось выраженное нефропротективное действие ССПК с тенденцией к увеличению терапевтического эффекта при более длительной терапии. На фоне лечения улучшались ос новные показатели функциональных возможностей оставшейся ткани почки, и снижалась активность ряда ферментов в крови и моче, что является отраже нием менее выраженного повреждения клеток почки. Важно отметить, что в контрольной серии с увеличе нием длительности наблюдения (с 1 до 2 месяцев) мы отметили усугубление ХПН, что проявилось сниже нием СКФ и ростом активности ряда ферментов в крови и моче. В то же время, во всех опытных сериях мы не наблюдали прогрессирования ХПН при ста бильном уровне всех изучаемых показателей даже в 4-й серии, где после 30 дней терапии ССПК в течение следующего месяца терапии не проводили. То есть была достигнута стабилизация процесса. Улучшение всех показателей на фоне терапии ССПК коррелиро вало с более выраженной компенсаторной гипертро фией оставшейся почечной ткани: масса органа возрастала достоверно в большей степени во всех опытных сериях по сравнению с контрольными опы тами, где терапию не проводили. Некоторое уменьше ние массы почки, произошедшее во всех сериях опытов с 30-го по 60-й дни, видимо, обусловлено не избежно развивающимся склерозом почечной ткани, связанным со стойкой гиперфильтрацией в почечных клубочках, негативное влияние которой на состояние клубочкового аппарата хорошо известно [33, 34]. Но, тем не менее,масса почки во всех опытных сериях оставалась достоверно больше, чем в контроле. Именно с повреждением клубочков связано прогрес сивное снижение СКФ, выявленное нами в контроль ной серии опытов. Терапия ССПК в разных вариантах способствовала сохранению фильтрационной функ ции почки, что, видимо, связано со стимуляцией ги пертрофии клубочков и уменьшением процесса гломерулосклероза, что мы выявляли в опытах при терапии ССПК крыс с ОПН [12]. Пролифератив ный и антисклеротический эффекты секретома ство ловых клеток подтверждены в ряде исследований [35-37].
Ухудшение экскреторной функции почек приво дит к накоплению ряда токсических метаболитов, на зываемых «уремическими токсинами», которые негативно влияют как на саму почку, так и на функции других органов.К таким токсическим метаболитам относят сульфатные производные ароматических аминокислот – 3-индоксил сульфат и р-толил суль фат, которые образуются в кишечнике под действием микрофлоры толстой кишки. При этом из-за снижен ной экскреторной функции почек они прогрессивно накапливаются в организме,оказывая токсический эффект за счет усиленной продукции активных форм кислорода и оксидантного повреждения клеточных структур, что ведет к развитию асептического воспа ления с фиброзированием тканей [17, 38]. Эти токси ческие метаболиты, попадая в кровь, связываются с альбумином плазмы,что затрудняет их выведение при гемодиализе (удается вывести лишь 29-32% образующихся метаболитов) [39], в результате чего их концентрация у уремических больных возрастает в 11-43 раза [38, 40]. Чрезмерное накопление 3-индоксил сульфата и других сульфатных производ ных ароматических аминокислот приводит к про грессированию ХПН за счет токсического поражения почечных канальцев, к выраженным неврологическим и когнитивным расстройствам, прогрессированию кардиомиопатии и атеросклероза [15, 17, 41].
Терапевтические возможности влияния на на копление уремических токсинов в крови больных ХПН крайне ограничены и связаны с использованием энтеросорбентов,назначением пробиотиков и кор рекцией диеты [38, 42]. Полученные нами результаты показали, что примененная терапия ССПК, наряду с поддержанием функции почек,существенно тормо зит накопление таких уремических токсинов,как 3-индоксил сульфат и р-толил сульфат, что может оказывать значительный эффект в профилактике нев рологических и сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, вызванных уремией.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Разработка новых подходов к терапии острых и хронических заболеваний центральной и перифери ческой нервной системы, поджелудочной железы, па ренхиматозных органов – почек, печени, легких позволяет надеяться на значительные успехи приме нения терапии с использованием стволовых/прогени торных клеток или продуктов их секреции. Отечественный препарат «Целлекс» – белково-поли пептидный комплекс, хроматографически выделен ный, фракционированный протеомный ксеногенный секретом – первый представитель новой группы пре паратов репаративной медицины – «клеточной тера пии без клеток»,в состав которого входят белки и полипептиды внеклеточного матрикса,цитозоля и ор ганелл стволовых и прогениторных клеток головного мозга эмбрионов поросят. Результаты настоящего ис следования подтвердили, что терапия ССПК не только оказывает достоверный нефропротективный эффект на модели экспериментально вызванной острой по стишемической почечной недостаточности,что было показано в ранее проведенных исследованиях,но и позволяет стабилизировать течение ХПН в экспери ментальной модели с резекцией 80% ткани почек за счет стимуляции компенсаторной гипертрофии ор гана и цитопротективного эффекта, а также снизить риск развития осложнений,связанных с накоплением уремических токсинов.
Список литературы Терапия ксеногенным протеомным комплексом из эмбриональных клеток головного мозга тормозит прогрессирование экспериментально вызванной хронической почечной недостаточности
- Perico N, Remuzzi G. Chronic kidney disease: a research and public health priority. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012;27(Suppl 3):iii19–26. https://doi.org/10.1093/ ndt/gfs284.
- Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, Li Z, Naicker S, Plattner B, et al. Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 2013;382(9888):260–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60687-X.
- Tögel FE, Westenfelder C. Kidney protection and regeneration following acute injury: progress through stem cell therapy. Am J Kidney Dis 2012;60(6):1012–22. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.08.034.
- Pan B. Fan G. Stem cell-based treatment of kidney diseases. Exp Biol Med 2020;245(10):902–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370220915901.
- Torrico S, Hotter G, Játiva S. Development of cell therapies for renal disease and regenerative medicine. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23(24):15943. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415943.
- Jeong JO, Han JW, Kim JM, Cho HJ, Park C, et al. Malignant tumor formation after transplantation of short-term cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in experimental myocardial infarction and diabetic neuropathy. Circ Res 2011;108(11):1340–7. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.239848.
- Herberts CA, Kwa MS, Hermsen HP. Risk factors in the development of stem cell therapy. J Transl Med 2011;9:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-9-29.
- Hickson LJ, Eirin A, Lerman LO. Challenges and opportunities for stem cell therapy in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2016;89(4):767-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2015.11.023.
- Tran C, Damaser MS. Stem cells as drug delivery methods: application of stem cell secretome for regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2015;82-83:1-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2014.10.007.
- van Koppen A, Joles JA, van Balkom BWM, Lim SK, de Kleijn D, Giles RH, et al. Human embryonic mesenchymal stem cell-derived conditioned medium rescues kidney function in rats with established chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2012;7(6):e38746. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038746.
- Maeshima A, Nakasatomi M, Nojima Y. Regenerative medicine for the kidney: renotropic factors, renal stem/progenitor cells, and stem cell therapy. Biomed Res Int 2014;2014:595493. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/595493.
- Кирпатовский В.И., Сивков А.В., Голованов С.А., Дрожжева В.В., Самойлова С.И., Рабинович Э.З., и др. Профилактика развития острой постишемической почечной недостаточности с использованием белково-пептидного комплекса эмбриональной ткани. Экспериментальная и клиническая урология 2019;(3):32-9. [Kirpatovskiy V.I., Sivkov A.V., Golovanov S.A., Drozhzheva V.V., Samoylova S.I., Rabinovich E.Z., et al. Prevention of the development of acute post-ishemic renal insufficiency using a protein-peptide complex of embryonal tissue. Eksperimentalnaya i Klinicheskaya urologiya = Experimental and Clinical Urology 2019;(3):32-9. (In Russian)]. https://doi.org/10.29188/2222-8543-2019-11-3-26-31.
- Кирпатовский В.И., Сивков А.В., Ефремов Г.Д., Самойлова С.И., Фролова Е.В., Аполихин О.И. Применение ксеногенного фракционированного протеомного секретома стволовых и прогениторных клеток при остром ишемическом повреждении почек в эксперименте. Экспериментальная и клиническая урология 2022;15(1):10-9. [Kirpatovskiy V.I., Sivkov A.V., Efremov G.D, Samojlova S.I., Frolova E.V., Apolikhin O.I. Experimental application of xenogenic fractionated proteomic secretome of stem and progenitor cells in acute ischemic kidney injury. Eksperimentalnaya i Klinicheskaya urologiya = Experimental and Clinical Urology 2022;15(1):10-9. (In Russian)]. https://doi.org/10.29188/2222-8543-2022-15-1-10-19.
- Кирпатовский В.И, Орлова Е.В., Харламова Л.А., Голованов С.А., Дрожжева В.В., Фролова Е.В. Значимость динамического определения концентрации Цистатина С в крови как маркера риска перехода острого повреждения почек в хроническую почечную недостаточность и эффективности нефропротективной терапии. Экспериментальная и клиническая урология 2021;14(4):20-9. [Kirpatovskiy V.I., Orlova E.V., Kharlamova L.A., Golovanov S.A., Drozhzheva V.V., Frolova E.V. The significance of dynamic detection of cystatin c concentration in the blood as a marker of the risk of transition of acute kidney injury to chronic renal failure and the effectiveness of nephroprotective therapy. Eksperimentalnaya i Klinicheskaya urologiya = Experimental and Clinical Urology 2021;14(4):20-9. (In Russian)]. https://doi.org/10.29188/2222-8543-2021-14-4-20-29.
- Синюхин В.Н., Рабинович Э.З., Соколов М.А., Сивков А.В. Неврологические расстройства при хронической болезни почек. Экспериментальная и клиническая урология 2017;(2):92-101. [Sinjuhin V.N., Rabinovich E.Z., Sokolov M.A., Sivkov A.V. Neurological disorders in patients with chronic kidney disease. Eksperimentalnaya i Klinicheskaya urologiya = Experimental and Clinical Urology 2017;(2):92-101. (In Russian)].
- Watanabe K, Watanabe T, Nakayama M. Cerebrorenal interactions: impact of uremic toxins on cognitive function. Neurotoxicology 2014;44:184–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2014.06.014.
- Yabuuchi N, Sagata M, Saigo C, Yoneda G, Yamamoto Y, Nomura Y, et al. Indoxyl sulfate as a mediator involved in dysregulation of pulmonary aquaporin-5 in acute lung injury caused by acute kidney injury. Int J Mol Sci 2017;18(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010011.
- Yaffe K, Kurella-Tamura M, Ackerson L, Hoang TD, Anderson AH, Duckworth M, et al. Higher levels of cystatin C are associated with worse cognitive function in older adults with chronic kidney disease: the chronic renal insufficiency cohort cognitive study. J Am Geriatr Soc 2014;62(9):1623-9. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.12986.
- Федеральный закон от 23 июня 2016 г. N 180-ФЗ «О биомедицинских клеточных продуктах» Вступил в силу в РФ c 1 января 2017 года; часть 2 и пункт 2 части 5 статьи 35 вступили в силу с 1 января 2018 года, как «Закон о БМКП». [Federal'nyy zakon ot 23 iyunya 2016 g. N 180-FZ «O biomeditsinskikh kletoch-nykh produktakh» Vstupil v silu v RF c 1 yanvarya 2017 goda; chast' 2 i punkt 2 chasti 5 stat'i 35 vstupili v silu s 1 yanvarya 2018 goda, kak «Zakon o BMKP». = Federal Law No. 180-FZ of June 23, 2016 «On Biomedical Cellular Products» Entered into force in the Russian Federation on January 1, 2017; part 2 and paragraph 2 of part 5 of Article 35 entered into force on January 1, 2018, as the «Law on the BMCP». (In Russian)].
- Федеральный закон от 03.08.2018 N 323-ФЗ «О внесении изменений в отдельные законодательные акты РФ по вопросу обращения биомедицинских клеточных продуктов». [Federal'nyy zakon ot 03.08.2018 N 323-FZ «O vnesenii izmeneniy v otdel'nyye zakonodatel'nyye akty RF po voprosu obrashcheniya biomeditsinskikh kletochnykh produktov» = Federal Law No. 323-FZ of August 3, 2018 «On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation on the Issue of Circulation of Biomedical Cellular Products». (In Russian)].
- Hu C, Zhao L, Zhang L, Bao Q, Li L. Mesenchymal stem cell-based cell-free strategies: safe and effective treatments for liver injury. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020;11(1):377. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01895-1.
- Rota C, Morigi M, Cerullo D, Introna M, Colpani O, Corna D, et al. Therapeutic potential of stromal cells of non-renal or renal origin in experimental chronic kidney disease. Stem Cell Res Ther 2018;9(1):220. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-0960-8.
- Hu J, Zhu Q, Li PL, Wang W, Yi F, Li N. Stem cell conditioned culture media attenuated albumin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 2015;35(5):1719-28. https://doi.org/10.1159/000373984.
- Kepecs DM, Yuen DA, Zhang Y, Thai K, Connelly KA, Gilbert RE. Progenitor cell secretory products exert additive renoprotective effects when combined with ace inhibitors in experimental CKD. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 2016;17(3). https://doi.org/10.1177/1470320316668434.
- Timmers L, Lim SK, Hoefer IE, Arslan F, Lai RC, van Oorschot AA, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium improves cardiac function following myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Res 2011;6(3):206–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scr.2011.01.001.
- Birtwistle L, Chen XM, Pollock C. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles to the rescue of renal injury. Int J Mol Sci 2021;22(12):6596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126596.
- Cao Q, Huang C, Chen XM, Pollock CA. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in chronic kidney disease. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022;9:816656. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.816656.
- Lu Y, Wang L, Zhang M, Chen Z. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles: a novel approach for kidney disease treatment. Int J Nanomedicine 2022;17:3603-18. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S372254.
- Gao L, Zhong X, Jin J, Li J, Meng XM. Potential targeted therapy and diagnosis based on novel insight into growth factors, receptors, and downstream effectors in acute kidney injury and acute kidney injury-chronic kidney disease progression. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2020;5(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1038/ s41392-020-0106-1.
- Togel F, Weiss K, Yang Y, Hu Z, Zhang P, Westenfelder C. Vasculotropic, paracrine actions of infused mesenchymal stem cells are important to the recovery from acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2007;292(5):F1626–35. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00339.2006.
- Zarjou A, Kim J, Traylor AM, Sanders PW, Balla J, Agarwal A, et al. Paracrine effects of mesenchymal stem cells in cisplatin-induced renal injury require heme oxygenase-1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2011;300(1):F254–62. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00594.2010
- Cho KS, Ko IK, Yoo JJ. Bioactive compounds for the treatment of renal disease. Yonsei Med J 2018;59(9):1015-25. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.9.1015.
- Brenner BM, Lawler EV, Mackenzie HS. The hyperfiltration theory: a paradigm shift in nephrology. Kidney Int 1996;49(6):1774-7. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1996.265.
- Hostetter TH, Olson JL, Rennke HG, Venkatachalam MA, Brenner BM. Hyperfiltration in remnant nephrons: a potentially adverse response to renal ablation. Am J Physiol 1981;241(1):F85-93. https://doi.org/10.1152/ ajprenal.1981.241.1.F85.
- Eirin A, Lerman LO. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles for chronic kidney disease: Are we there yet? Hypertension 2021;78(2):261-9. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.14596.
- Gao Z, Zhang C, Peng F, Chen Q, Zhao Y, Chen L, et al. Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate renal fibrosis after ischemia-reperfusion injure by restoring CPT1A mediated fatty acid oxidation. Stem Cell Res Ther 2022;13(1):191. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-022-02861-9.
- Yuen DA, Connelly KA, Zhang Y, Advani SL, Thai K, Kabir G, et al. Early outgrowth cells release soluble endocrine antifibrotic factors that reduce progressive organ fibrosis. Stem Cells 2013;31(11):2408-19. https://doi.org/10.1002/ stem.1502.
- Lim, Y.J. Sidor, N.A.Tonial, N.C. Che, A. Urquhart, B.L. Uremic toxins in the progression of chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease: mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Toxins 2021;13(2):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ toxins13020142.
- Madero M, Cano KB, Campos I, Tao X, Maheshwari V, Brown J, et al. Removal of protein-bound uremic toxins during hemodialysis using a binding competitor. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2019;14(3):394–402. https://doi.org/10.2215/ CJN.05240418.
- Duranton F, Cohen G, De Smet R, Rodriguez M, Jankowski J, Vanholder R, et al. A. Normal and pathologic concentrations of uremic toxins. J Am Soc Nephrol 2012;23(7):1258–70. https://doi.org/ 10.1681/ASN.2011121175.
- Iwata K, Watanabe H, Morisaki T, Matsuzaki T, Ohmura T, Hamada A. et al. Involvement of indoxyl sulfate in renal and central nervous system toxicities during cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. Pharm Res 2007;24(4):662-71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9183-2.
- Leong SC, Sirich TL. Indoxyl sulfate-review of toxicity and therapeutic strategies. Toxins 2016;8(12):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8120358.


