The conceptual approaches to definition of internal borders and development of the Russian Arctic in the changing world
Автор: Lukin Y.F.
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Geopolitics
Статья в выпуске: 6, 2012 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The trends of the modern geopolitical situation in the Arctic and the problems of the development of the Russian Arctic zone.
The model “Arctic-ХХI”, the great redistribution, solidarity, the map of the Russia, internal boundaries, proposals of the regions
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148320452
IDR: 148320452 | УДК: 327(985)(045)
Текст научной статьи The conceptual approaches to definition of internal borders and development of the Russian Arctic in the changing world
The relevance of the Arctic research issues objectively substantiated – extracting interest not only to the Arctic (Denmark, Iceland, Canada, Norway, Russia, USA, Finland, Sweden, bur also other countries in the world 9 UK, Germany, China, France, South Corea, Japan, etc) to the end of the Great Atlantic geopolitical redivision of the Arctic in the twenty-first century by peaceful means, including the continental shelf and the circumpolar region, the organization is production of hydrocarbons with a permanent increase in the global economy to the deficit. The Arctic is still inhabited by poor, poorly mastered, easily available and yet become attractive for tourism, oil industry, and transport logistics. Why not? The global North and the Arctic covers less than 10% of the total area of the planet. However, there is concentrated, according to various estimates, between 25 and 30% of the reserves of mineral resources [1, p. 13]. According to the UN, the proven reserves of the Arctic oil account for more than 100 billion tons and recoverable gas reserves estimated at 50 trillion cubic meters. [2]. In addition, the Arctic – is the large reserves of clean air, fresh water, backing the environmental space of the whole world. The shortest sea trade route from the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean due to global warming is quite affordable for shipping both through the Northern Sea Route in Russia, and through the Northwest Passage along the coast and islands of Canada. The shortest cross-polar air routes link regions of the North America and Asia.
The geopolitical importance of the Arctic macro region in the current global society is also not in doubt. Professor J.F/ Kefeli emphasize that once a commonplace phrase, "Who owns Eurasia, owns the world" at the beginning of the twenty-first century takes on a new interpretation: "Who owns the Arctic, owns the world" [3, p. 214]. That is why for Russia, it is actual for adequate responses to the historic challenges of our time in a postmodern world. The undoubted priority for us is the scientific and intellectual support for Russia's national interests, in particular the defini- tion of internal borders, the study of problems of the Arctic Zone of the Russian Federation in close contact with the realities of a changing world.
Methodologically, the key role in the development of the arctic socio-humanitarian paradigm of knowledge is regional studies, objectively investigating a large space in the Arctic and the North of Russia in their unity, the relationship through an interdisciplinary synthesis of all spheres of life - politics, economy, social sphere and culture. Single and together connected an object of the research – is the Arctic as the part of the North and the North of Russia as the part of the Arctic (matryoshka doll in a) reasonably requires the integration of existing sectoral objective scientific knowledge, but in practice – the combining of the existing resources of Russian society, the government and the business of the effective development of the Arctic space. Regiono-logical methodical approach provides a holistic system of knowledge, a complete model for practice, a comprehensive look at the present and the future of any region in the world, including the Russian Arctic. However, this approach requires refinement and serious analysis of used concepts (from Lat. Sonceptus - concept), with their multiplicity, the criteria used - from the standpoint of evaluation, definitions, classifications.
It should be noted that in the scientific community will inevitably arise are many interpretations of the same concepts. Representatives from different disciplines often have difficulty understanding each other, though it often comes to the same object. Were no exception and the Arctic as an object of the research. Depending on your subject of expertise and knowledge provides a variety of its definitions. That is why, it is important to determine the language of scientific knowledge of direct relevance to the Russian Arctic as part of the Russian North. This will enable better focus in the theoretical issues, understand the vocabulary employed the scientific, practical use in strategic planning discussions. In this regard it is expected not only to refine the original concept of Arctic issues, but also to start building at the site of "The Arctic and the North," the relevant information database. The present paper is one of the first steps in that direction. There is no doubt that during the author's further research approaches will be specified and correlated with the light of feedback, suggestions and comments.
The Arctic of the XXI century is defined by me as a multidimensional large space adjacent to the North Pole and includes the suburbs of the continents of Eurasia and the North America, the Arctic Ocean with all its seas and islands, the eight Arctic states, dozens of ethnic groups, a variety of sub-cultures and civilizations. Such an interdisciplinary definition best describes the current multi-space. The Arctic – is a distinct object of the domination "thalassocracy" - the power of water, sea ice and the cold fresh air. Author's model of "Arctic-XXI 'includes conceptually, at least seven layers of spatial subject knowledge1.
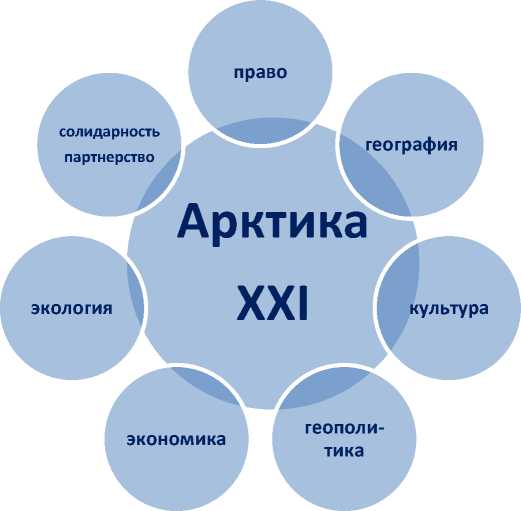
-
1) Administrative and legal space: eight Arctic states, dozens of regional societies, and hundreds of self-governing communities (municipalities) and their relationship over authority and control, life support in the Arctic macro-region, the development of natural resources.
-
2) The physical and geographical space: 39.6 million square kilometers, or more than 26% of the Earth's land area of 8 Arctic states with geopolitical situation, 12.5 million square kilometers in the circumpolar regional approach. Biological diversity of fauna and flora. The Arctic Ocean area of 14.75 million square meters miles. The Arctic - is pronounced a macro-region "thalas-socracy" - the power of water, sea, ice, ice country with terror.
-
3) The spiritual and the civilizational, geocultural space: 4th of civilization - European, Eurasian (Russian, Russia,), the North American, circumpolar. The ethnic and cultural diversity, tolerance. Widespread and the prevalence of the Christian religion (Catholicism, Orthodoxy, Protestantism) in all the Arctic states.
-
4) Geopolitical Space: Population: 510 million people or 7.5% of the global society (2009) with the geopolitical approach, at least one-tenth of one percent (0.057%) at the regional circumpolar approach (more than 4 million northerners to 7 billion people. in the world). The Arctic strategy, the United States, Russia, Canada, Norway and other circumpolar countries on the basis of their national interests, the real needs of politics and economics, national security, military-strategic presence in the Arctic macro-region.
-
5) The geo-economic space: the total GDP of 8 Arctic countries amounted to 18.1 trillion in 2007 Amer. dollars, or 27.9% of the GDP of the world according to the IMF, 18, 6 trillion American dollars in 2009 on the World Factbook. Large reserves of natural resources, hydrocarbons, mineral raw materials. The Northern Sea Route in Russia and the the Northwest Passage off the coast of Canada. The Arctic logistics and infrastructure.
-
6) The Ecology of the arctic environment of natural and cultural environment, saving people. The Arctic is valued not only for her wealth, but for spiritual purity and freshness of first-salute, the transparency of human relations. The main resource of the Arctic north - they are people, human, creative and intellectual capital.
-
7) The Arctic solidarity and partnership as an imperative of the future - is the general Christian values, cooperation instead of competition, the integration of compliance with the national interests of each of the circumpolar countries, the peaceful development of the Arctic rather than the cold war and military conflicts [4, p. 23, 68-69, 73].
The set of claims on the resources of other states and the space of the Russian Arctic in the twenty-first century under the guise of internationalization, transnationalization of the man- agement should be considered the most important challenge to the globalization of Russia, which is concentrated in about 40% of the world's natural resources and a population of only 2% of the inhabitants of the earth. There is a risk of becoming a global sense of "empty space", whose fate will be decided not by us [5]. This applies not only to the Russian Arctic, and the Russian North, Siberia and the Far East, with reserves of strategic natural resources and vast territory. It would be naive and foolish to assume that other countries would tolerate Russia's national interests without the use of all forms of our own defense, demonstration of these interests, their intellectual and legal support. At the same time will not even take into account the fact that in the Russian Arctic living today as much of the population (more than two million people), but in the Arctic zone of the seven other Arctic countries combined (Alaska, Canada, Greenland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Finland). No country has in the Arctic in the high latitudes of urban settlements and industrial centers, such as Arkhangelsk, Murmansk, Severodvinsk and other Norilsk No country in the world has never invested so much money, resources, lives and destinies in the discovery and development obzhivanie Northern Territories and sea transportation routes in such harsh conditions.
The geopolitical statements, which are used - the Russian Arctic, Arctic Russia, the Russian sector of the Arctic with an apparent at first glance, the identity of yet have a different meaning. The Russian Arctic (abbreviated - RA) – is the most geopolitically neutral concept. We are talking about the part of the area and the Arctic, which in accordance with the international law within the jurisdiction of the Russian state. The concept of the "Arctic Russia" could be perceived in the world public opinion as a claim to the entire Russian Arctic and the North Pole. Russian sector of the Arctic in the twentieth century was defined based on the delineation of the Arctic area in two meridians, from the extreme western and eastern points of land borders Russia to the North Pole. In official documents most frequently used political and legal concept of the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation (hereinafter - AZRF).
Inevitably, there is also the problem of the use of the concepts such as the northern Russia, the Russian North, the northern territories of Russia, the Far North. In contrast to the Russian Arctic, these concepts are related primarily to the land only, including the islands. North of Russia includes three natural zones: 1) absolutely uncomfortable zone for human habitation (Arctic subzone) - 5.4 million square feet. km 2), an extremely uncomfortable - 3.5 million square feet. km, 3) uncomfortable - 2.5 million square feet. miles. The northern regions of Russia held at the beginning of the twenty-first century, three-fourths of the country's total area of 11,400,000 square meters. km [4, p. 175-180]. It is home to eleven million people, including two millionth population tion of the Russian Arctic. It must be clearly understood that AZRF here is just part of the Russian North.
Russian Arctic zone is positioned as a land (coastal areas, islands), and water - seas of the Arctic Ocean within the Russian Arctic, based on international law and Russian legislation. Concepts AZRF and RA are basically, in my understanding, identical. In Principles of State Policy of the Russian Federation in the Arctic (2008) under AZRF understood the part of the Arctic, which includes all or part of the territory of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), Murmansk and Arkhangelsk regions, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Nenets, Yamalo-Nenets and Chukotka autonomous district, some decision of the State Commission under the USSR Council of Ministers for the Arctic in 1989, as well as land and the islands referred to in the Decree of the Presidium of the Central Executive Committee of the USSR of April 15, 1926 "On Declaring Territories Soviet lands and islands in the Arctic Ocean," and adjacent to the territories, lands and islands of internal waters, territorial sea, exclusive economic zone and continental shelf of the Russian Federation, within which Russia has sovereign rights and jurisdiction in accordance with international law. In the list of 2008 compared to 1989, missing the Taimyr (Dolgan-Nenets) Autonomous District, which as a result of consolidation of the RF subjects to January 1, 2007 was transformed into the Taimyr municipal district of Krasnoyarsk region.
In the discussion of the concept developed GNIU SOPS draft of the new federal law (Federal Law) "On the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation" Russian Arctic includes all or part of the territory of the nine subjects of the federation. Fully incorporated the Murmansk Region, the Nenets, Yamalo-Nenets and Chukotka autonomous district, and in part - the Republic of Karelia in the Louhi, Kem, and the White Sea municipalities, the Komi Republic in the urban district of Vorkuta, Arkhangelsk region in the Onega, Mezen and the Primorsk municipalities, urban districts of Arkhangelsk, Severodvinsk and Novodvinsk and administrative owned the Arctic islands in the Krasnoyarsk region of Taimyr (Dolgan-Nenets), municipal district, urban district Norilsk municipal Igarka Turukhansk City metropolitan region, Sakha Republic (Yakutia) of 11 ulus -Abyyskogo, Allaihovskogo, Anabar, Bulun, Verkhoyansk, Zhigansk, Olenek, Nizhnekolymskiy, Srednekolymsk, Ust-Yana and Eveno-Bytanayskogo.
Compared with the previous lists of 1989, 2008 in AZRF 2012 included additional coastal areas of the White Sea - three municipalities of Karelia and the city of Vorkuta, polar, located at latitude 67 ° 29 '. Thus, the Republic of Karelia and Komi are part of the status of Arctic territories, if adopted this Federal Law.
As one of the criteria for inclusion in AZRF along with other increases the importance of the geopolitical approach, the availability of the subjects of the Russian coastal area with access to the waters of the northern seas of the Arctic Ocean. This approach was explained in my earlier book, published in 2010 [4, p. 163-164]. Only eight subjects of the Russian Federation itself has access to the Arctic Ocean. The White Sea is now in the inland waters of Russia. However, some foreign scholars, so far only in private conversations, is asking questions about the status of the White Sea, the validity of Russia's rights to its use, including a sea-bed for testing submarines, as well as the internationalization features of this part of the Arctic Ocean. It is obvious that Russia's geopolitical interests, to ensure its national security today require adequate justification and legislative consolidation of the status of all coastal areas of the White Sea as an integral part of the Arctic zone of Russia.
The published map below the Arctic zone of Russia, made on the basis of previous conceptual authoring and one of the options for the project of the Federal Law "On the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation" (2011), first introduced in the scientific revolution, reflecting the conceptual approaches, which were discussed above.
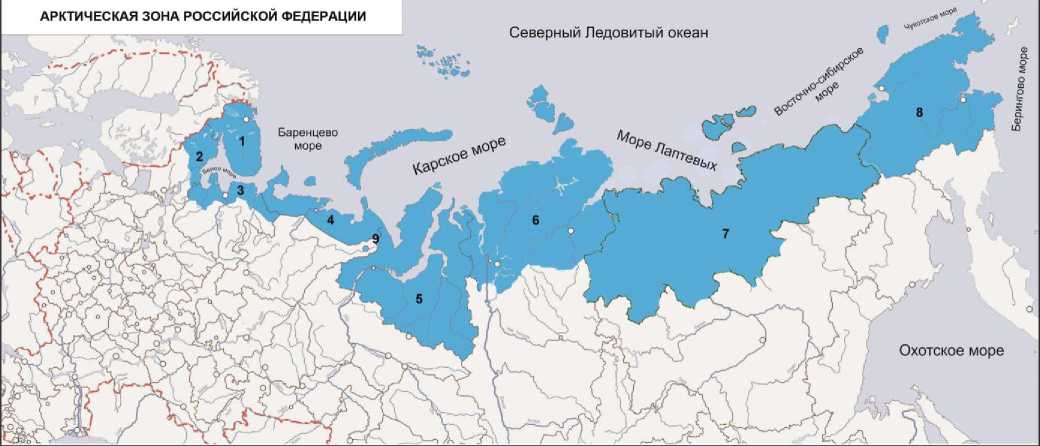
1 - Мурманская область 6 - Красноярский край (в составе Таймырского (Долгано-Ненецкого) муниципального района,
2 - Республика Карелия (в составе Лоухского, Кемского и Беломорского городского округа Норильск, муниципального образования гор. Игарка Туруханского муниципальных районов) муниципального района)
3 - Архангельская область (в составе Онежского, Приморского и Мезенского 7 - Республика Саха (Якутия) (в составе - Абыйского, Аллаиховского, Анабарского, муниципальных районов, городских округов Архангельск, Северодвинск и Новодвинск, Бупунского, Верхоянского, Жиганского, Оленекского, Нижнеколымского, Среднеколымского, а также административно принадлежащих ей арктических островов) Усть-Янского и Эвено-Бытанайского улусов)
4 - Ненецкий автономный округ 8 - Чукотский автономный округ
5 - Ямало-Ненецкий автономный округ 9 - Республика Коми (в составе городского округа Воркута)
In defining the southern boundary of the Arctic are used in modern science interdisciplinary approaches. Without going into details, let me note that the grounds for determining its southern border and the total area ofthe Arctic zone of Russia are the following methods.
Astronomical approach, geodezia define the boundaries of the Arctic along the North Pole Circle (66 ° 33 'of the north latitude).
Physico-geographical approach is based on the classification of landscapes and geographical territories of differentiation, the delineation of tundra, forest tundra and taiga, differing radiation balance, the duration of the summer, the sum of active temperatures.
Passive approach focuses on the discomfort severe natural conditions of human life (low temperatures, severe wind, humidity, etc.), generates a problem of increased cost of living and associated social and political commitments of the state.
Cultural-ethnic approach actualizes the problem of cultural anthropology, ethnology, resettlement and land and people of ethnic and cultural groups of the Russian Arctic and Subarctic, mostly belonging to the past, the following economic-cultural types: sedentary and half-marine hunters, nomadic herders tundra and forest tundra.
The economic approach examines the nature and the economic potential and its use in the extreme polar conditions, placing major types of mineral deposits, the Arctic logistics, transportation and the economic gravity of territories adjacent to the Northern Sea Route. The politico-legal administrative approach determines the internal boundaries of the Arctic administrative borders of the territories (regions, territories, republics, provinces, provinces, states, municipalities), assigned to the Arctic acts.
The geopolitical approach is one of the main criteria considered in the presence of the five Arctic countries (Canada, Denmark, Norway, Russia, USA), as well as in eight subjects of the RF output to the coast of the Arctic seas of the Arctic Ocean (including the White Sea) some part of its territory [4, p. 8, 169].
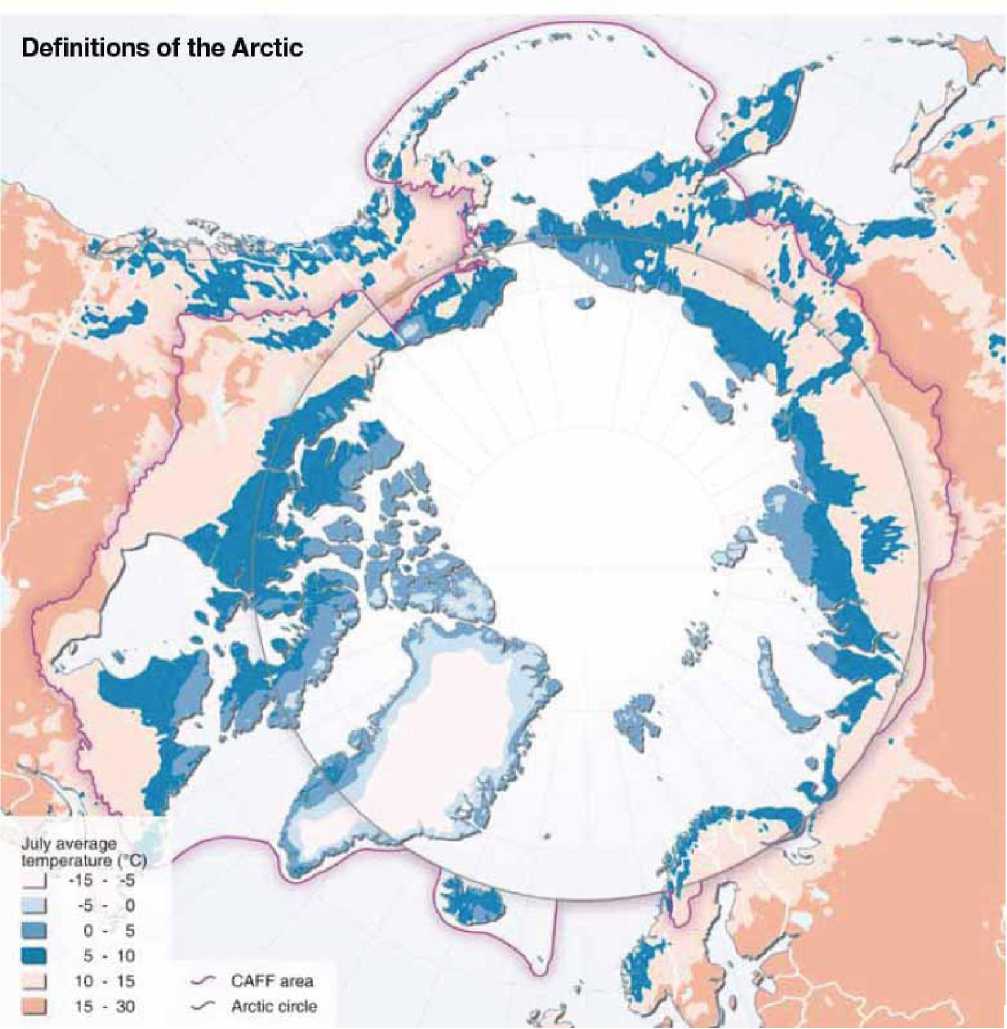
Picture 2. The determine of the Arctic. Johnsen K. I., Alfthan B., Hislop L., Skaalvik J. F. Eds, 2010. Protecting Arctic Biodiversity. United Nations Environment Programme, GRID‐Arendal. URL: , P. By: The concept of the GEF partnership, and the Russian Federation on the sustainable management of the environment in the Arctic in a rapidly changing climatic conditions ("Arctic Agenda 2020") / / Electronic Journal of fund "sustainable development". URL: (date of access:19.02.2012)
In the version of the project of the Federal Law "On the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation" prepared GNIU SOPS (2011), a list of criteria for inclusion in AZRF includes the following:
The boundary between the tundra and forest tundra within the large continental plains, where other natural boundaries are not clearly marked in the terrain and geological structure of the (East European and West Siberian Plain);
Brovku of the coastal lowlands (Eastern Siberia, Yana, Indigirka, Kolyma lowland), adjacent to the surrounding hills and mountains of education;
watershed boundary separating the catchment area of sea and ocean basins (the Cave Hills in the Kola Peninsula, Anadyr Plateau and Chukchi Plateau in the Far East);
the sign referring to the marine water bodies Arctic Basin and the intensity of water exchange between them;
the indivisibility of the territorial-administrative units of the RF subjects, without consideration of which leads to a violation of the integrity of the administrative difficulty of implementation and functions of government;
an access to the Arctic Ocean;
the unity and integrity of the resource and industrial complexes, mainly focused on the transport system of the Northern Sea Route.
It is remarkable that here as well, along with the physical and geographical criteria, and takes into account such as the way to the coastal water areas of the Arctic Ocean, the indivisibility of the administrative-territorial units of the RF subjects. This approach GNIU SOPS in determining the inner boundary AZRF, although not entirely comprehensive, yet allows for multifactor, multilayer the Arctic space and the inherent geopolitical interests of Russia. Geopolitical approach to the definition of AZRF based on the Metodologii multifactor, thalassocracy seems to me not only fully justified, but also quite relevant in terms of the Great Arctic redistribution, implemented today, mostly peacefully.
Problems of the development of the AZRF, they actively discussed in the Arctic regions, which demonstrated the first held February 29 Day of the Arctic in Russia. Proposals for the development program designed AZRF Arkhangelsk Oblast and Nenets Autonomous District. In the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), January 31, 2012 a meeting of working group on the draft law "On the Arctic zone of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)." It was suggested to use as the southern boundary line of the Arctic Circle with the inclusion of the southern borders of municipalities. Second, create a federal trust fund development in the Arctic (FTSFRA) as sources of which consider the one-time payments from participation in tenders and auctions for subsoil use within the territory of the Arctic zone, the sum of the profits of companies engaged in production activities in the Arctic zone, and other. Third, to introduce a new type of special economic zones such as the example of the Arctic village of Tiksi, setting special conditions for the tax and customs regulation. Fourth, determine the measures to stimulate the development of state of the Arctic transport system based on the revival of the Northern Sea Route, vehicle subsystems, inland waterways, to ensure stable operation of small aircraft. Another proposal concerns the establishment of preferences of Indigenous Peoples of the North in the traditional places of residence [6]. Such proposals are relevant to discuss the draft Federal Law on AZRF allows more time to draw the attention of government and society to the urgent problems of the northern territories, finding financial resources for their development.
However, during discussions on the draft Federal Law on AZRF at the regional level it appears that there are different approaches to the definition of internal borders of the Russian Arctic. President of Yakutia Yegor Borisov, discussing with Russian Security Council Secretary Nikolai Patrushev, the draft Federal Law "On the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation", for example, said: "Yakutia proposes to define as the southern boundary line of the Arctic zone of the Arctic Circle, including the southern border included municipalities". Yegor Borisov believes that this approach would allow to objectively identifying the object of state regulation and the criteria to take into account the populations of discomfort [7]. The proposals of Yakutia is not entirely clear how the mechanical definition of the inner boundary of Geodesy AZRF polar circle combined with a bioclimatic approach, why not take into account the geopolitical and other criteria? With such a narrow approach of the regional AZRF does not include the entire White Sea coast inland as an integral part of the Russian Arctic Ocean? The consequences of underestimating the geopolitical approach undoubtedly affect the security of Russia in the Arctic
At the same time it becomes clear that interdisciplinary synthesis GNIU SOPS, shared, in particular, the Government of the Arkhangelsk region, the Center of the "Arctic Partnership" the Institute of Management and regionologii of NArFU and other stakeholders (interest groups) in the Arctic requires a broader discussion on the regional level and taking into account the views are not only to federal departments and agencies, but also the subjects of the Russian Federation, municipalities, academic community, the population of northern societies.
The Russian Arctic is positioned me as well as a large inter-regional space. Author's typology of regions [4, p. 29-30] includes:
microregion (municipalities, local communities);
intermunicipal bushes (clusters, agglomerations, TLC);
mezoregion (subjects of the Russian Federation);
macro-regions (11 economic regions, eight federal districts as a new macro-regions of modern Russia, 8 associations of economic cooperation);
macro-economic zones - Arctic zone of Russia, Western European + Urals, Eastern Asia (Siberia, Far East);
cross-border territory belonging to different states: the Barents Euro-Arctic Region, Asia-Pacific region, and others;
net profit organizations - Arctic regions of Russia Union (ASRR), a virtual Arctic Federal District (Vafo), the Russian Union of International Affairs (INF) and others.
In the Russian Arctic, and includes the microregion and intermunicipal bushes and me-zoregiony. In general, the Russian Arctic – is a macroeconomic area, bringing together as subjects of the Russian Federation and municipal entities, ulus, clusters, metropolitan areas, different infrastructure. At present, Russia has 83 regions, identified with the concept of the "region". Seven of them are wholly or partially included in AZRF, their number may increase to 8-9. Russian Arctic as a union of Arctic regions – are subjects of the federation and municipalities - has the ability to transform in the perspective of a network organization of the Arctic Federal District (abbreviated - AFIs) based on the use of information and communication technologies, people and the dialogue of cultures, horizontal integration and cooperation, implementation of best practices and the creation of public and state institutions of governance, as well as the functioning of the arctic areas of information and intelligence (AIIP)2.
Number of people living in the harsh climate, but rather, in the extreme Arctic conditions, in the general, is low. In determining the population size of the territory of GDP in research on the Arctic, two methods – are the geopolitical and the regional. In the geopolitical approach to the Arctic includes the population-determination, economic potential, the waters and territory of the whole of the eight Arctic states, in contrast to the regional approach, are taken into account when only the southern boundary of the inner zone of the Arctic. We know that space is circumpolar (Arctic Circle, around the pole) in each of the eight states do not fully cover the whole country. Therefore, if we take the purely regional approach, in the circumpolar world just will not subjects of international law – are the sovereign states. There is no country that is absolutely the whole of its territory would be part of the Arctic zone around the North Pole. Calling these eight countries
"priarkticheskimi" rather than "arctic", we thus can also highlight this important feature of the geopolitical status.
In the geopolitical situation in the Arctic, it is home to over 510 million people (2010). In the view of the inner southern boundary of the eight Arctic states using the method of the regional population of the Arctic regions, provinces, municipalities of more than 4 million people, half of whom live in the Arctic zone of Russia. In the Russian Arctic, therefore, reside as many people as in the Arctic zone of the seven other Arctic countries of the world combined. The use of different criteria and uncertainty in the current status of the AZRF, its inner boundary, fixed by law, gives the whole variation in population numbers from 1.9 to 2.6 million people in different sources. In one embodiment, the draft national program of the Russian Federation, "Economic and social development of the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation for 2011-2020" (SE "Arctic"), for example, it was recorded that the population in AZRF on January 1, 2009 exceeded 2 619.3 thousand, or 1.85% of its total population in the country. In the version of the draft "Strategy for development of the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation and national security in 2020" said that there are more than 2.5 million people, representing less than 2% of the population and about 40% of the population across the Arctic. It seems that after the adoption of the Federal Law "On the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation", these discrepancies will be eliminated. However, there is a problem in estimating the population of the Russian Arctic emerges here is quite obvious.
On the solution of practical problems of the development of Russian Arctic considerable influence in the twenty-first century have a number of interrelated processes in a changing world. First, it is climatic changes and its consequences. The actual melting of ice in the Arctic Ocean and other natural transformation has both positive and negative consequences for the socioeconomic and ethno-cultural development priark-cal subjects of Russia. Revived the Northern Sea Route, become more widely available natural raw material resources in the Arctic. However, possible changes in biological diversity, the growth dynamics of animal migration, reduction of land, coastal erosion, the transformation of permafrost, the transition out of it and bogs into the atmosphere large amounts of methane and carbon dioxide. Increase the risks of emergencies in the construction and the infrastructure of the Arctic. Become inevitable changes in the tradinal lifestyle of indigenous people (big and small). In addition, the scientific community, the Internet version of the active discussion of the anomalous cooling of the warm Gulf Stream and the onset of a new ice age. The balance of the consequences if this turns out negative, the risks increase even more3.
Secondly, the activation of all human activities in the Arctic. This process covers almost all spheres of the society, and many kinds of human interests and activities, requiring adequate use of the latest technology, a technological breakthrough. This applies not only to science and technology, geopolitics and economics, and other Arctic states, but also to the spiritual and cultural life, the social sphere of society.
Contemporary processes of the globalization and regionalization of the world-changing identified two diametrically opposite trends of public and human competition in the Arctic. On the one hand, it is an objective trend towards the development of international cooperation in developing Arctic cooperation and logistics of production of hydrocarbons, the internationalization of the Arctic transportation routes, the formation of transnational management model, resuscitation undeveloped the northern circumpolar civilization of the ethnic groups. The main socio-economic problem in the Arctic, the twenty-first is that the available resources and projected Arctic Russia, and any other Arctic countries, today it is difficult to learn alone. This will require trillions of dollars, the latest technology and modern equipment, joint consortia, the arctic partnership. In addition to the new industrial and postindustrial development of existing and future, not yet proven reserves of the Arctic hydrocarbon resources, cost-effective operation of transcontinental transport corridors there is a need in the accumulation and use of creative and intellectual potential of the northern territories, human capital, the development of social, cultural and other infrastructure.
On the other hand, the existing national interests of sovereign states, including Russia, Canada, Iceland, Denmark, Norway, Finland, Sweden, and the United States often come into conflict with the first conflicting trend. According to the principle of self-reliance, when "every man for himself ',' self comes to the body." Each country, solving their problems in the Arctic, using the national capabilities and resources, not very trusting their neighbors.
Manifestation of the contradiction between the two trends is an acute struggle for the Arctic area in a variety of forms: diplomatic, political, economic, scientific, educational, conceptual, legal, informational, spiritual, intellectual, cultural, ethnic, and psychological. The purpose of this multi-faceted struggle can be formulated as a "war for the Arctic resources and communications," and the dynamics of the process – is as a "great redistribution of the Arctic." An alternative to this may be a gradual and very slow formation of the Arctic solidarity and partnership as the main imperative of this century in the Arctic. This, in my opinion, one of the major, but long-term, solutions to problems in a changing Arctic, bustling world.
The war for Arctic resources and communication is not a traditional "hot war" with different types of weapons and the death of people who are not armed conflicts. This is a peaceful competition of the U.S. economy, Norway, EU, Russia, China and other countries, their modernization, technological and financial capabilities that allow the most efficient, with a reasonable cost acceptable to the development of natural resources and to monitor communications and space in the harsh Arctic conditions. This is a real information-psychological warfare with the use of modern ICT, which is manifested, inter alia, in the distribution of the Arctic phobias, injection Russophobia, a big lie and manipulate of people's minds, especially young people. This ethnic and cultural expansion in all conceivable azimuths of the indigenous peoples of the North (large and small), their identification (Pomors, the Russian coast-dwellers, the Siberians). Finally, it is a creative struggle of intellects, the scan results of research activities for the meager grants and foreign training, spiritless internationalization of education. In public opinion, mass media while slowly going on the understanding that "a new race in the Arctic" does not imply new topic areas, and focused on the most effective learning environment hostile to the man on the planet, the problems return on investment in the extraction of hydrocarbons is by radiation profits, to ensure environmental safety fragile and very vulnerable of the arctic environment, the internationalization of the management.
The relevance of the problem of the redistribution of the Great Arctic shows a great interest in this subject, which is manifested not only by politicians, military men, diplomats, but also the general public of the global society. Federal Information Agency REGNUM in the plot of "The Struggle for the Arctic," published in February 2002 to February 2012 news 840. The struggle for the Arctic resources in recent years not only did not disappear from the news feeds of news agencies, but also the permanent discussion forums on various scales and levels. As recently as January 29, 2012, the Italian newspaper «Il Sole 24 Ore» Lara Ricci published an article under the heading of knowledge in Small «La nuova corsa all'Artico». This paper mainly presents interest, it is not the thesis that "the beginning of a new race in the Arctic" and a statement of the fact that in the struggle for the redivision of the Arctic has begun a new era of the operation, aimed at making a profit, "One hundred years after the conquest of the North Pole explorers in the Arctic rather than compete with oil and shipping companies. The aim – is not to achieve the coveted the first North Pole, and reap the benefits ... Without any ads in the most remote oceans on the earth began a new era of exploitation "[8, 2012]. Renowned journalist Roger Howard just noticed that two themes - natural resources and strategy - will inevitably add fuel to the fire of the growing world of political confrontation and to determine "who is boss" [9, 2009]. "Arctic Five" - the U.S., Russia, Norway, Canada and Denmark (Greenland) - are trying to race to consolidate the right to dispute and therefore no man's land until the last unspoiled parts of the globe. The actual practice of the international relations and the analysis of the situation in the Arctic indicate that the redistribution of the Great Arctic is far from complete. Today he just transformed into other forms of modern and context.
Analyzing the situation in the Arctic and the North of Russia, have also regret a clear underestimation of the human factor, the problems of inter-ethnic relations and multiculturalism. The main resource of the Arctic Severs up today do not even oil and gas, and the people, human, creative and intellectual capital. Objectively, therefore, requires transparent (transparent, honest and without the crooks), Arctic tolerant sociocultural environment.
The priorities of the national strategy of the Arctic and of the real policy of Russia, the practice AZRF regions in the foreseeable future are:
Firstly, people, human capital, creative class, saving AZRF population, the growth of wealth, the level and the quality of the life for the northerners as a result of the government policy and the economic development services in all areas;
Secondly, the creation of the modern Arctic infrastructure, including financial, economic, transportation and logistics, cultural, social and domestic (housing, utilities, education, science, health, polar medicine, services), information and communication, management); Thirdly, the Arctic economy, natural resources, the development in the interests of Russia and all over the world, safe transportation of oil and gas, the development of the Arctic tourism, fisheries, etc.;
Fourth, the environment, preservation of the natural and cultural environment, saving people, the indigenous languages (both large and small), socio-cultural diversity, multiculturalism and tolerance;
Fifth, security and the protection of the Arctic borders of Russia, the development of military-industrial complex, anticipatory modernization of armaments, the Northern Navy, Border Troops, the creation of the Arctic crews, a clever defense against new threats in the Arctic and the North of Russia;
Sixth, the operation of the Northern Sea Route railway in Europe and Asia, modernization of communications, transport, port infrastructure and all forms of management and service (customs, border guards, bunkering, breaking, tariffs, taxes, insurance, crew and others .)
Seventh, the Arctic solidarity, an appropriate response to the changing challenges of the environment, arctic partnership, the activities of the Russian Council on Foreign Affairs on the implementation of the roadmap for international cooperation in the Arctic;
Eighth, the creation of network-profit organizations, a single Arctic information and communication space (Union Arctic regions of Russia, Arctic information and intelligence platforms).
The search for effective responses to global challenges of rapidly changing world
The great interest is the project "road map for the international cooperation in the Arctic", launched in 2012 by the Russian Council on Foreign Affairs (INF)4. The project aims to create a concrete action plan to promote the international cooperation in the Arctic States 2012-2018 years. Road Map - is a document that defines the interaction between the successive steps of the Russian Federation with foreign states and international organizations on important policy issues in the Arctic. The project involves consideration of various aspects: legal, institutional, natural resource, transportation, environmental, military, scientific research.
Conclusions. In conclusion, I want to notice, that the depth of the ongoing Russian Arctic research complex, no doubt, it’s the most important competitive advantage in a changing world. Russia not only has virtually proven by centuries of civilization priority in the development of the Arctic, but also multiplies it. XXI century is called the century of the Arctic Russia. However, many important issues of the Arctic issues had not been sufficiently in-depth analysis in the literature require a clearer conceptual studies, definition of costs and benefits of the new industrial and postindustrial, creative exploration in the Arctic in the XXI century.
In the sphere of geopolitics is no more important task of minimizing the risks of a new military-political confrontation in the Arctic. Even a limited, local war in the Arctic is very fragile natural environment will inevitably lead to unpredictable consequences, and perhaps to a global catastrophe that would have an impact on the subsequent evolution of human society. Occurring in the Arctic and around the long process of slow maturation of the Arctic elements of solidarity is basically like a mirror reflects the processes that are taking place in the world global society by the name of the Earth. There is a very real struggle for the redivision of the world from the standpoint not of goodness and humanity, and from a position of strength, military and financial power.
Alternative appearnce of power in geopolitics, in practice, the Arctic may be a road map for humanitarian cooperation and integration of financial, technological, intellectual, information, human resources for the future peace of the Arctic projects on the basis of consensus. Some people initially call a utopian solidarity of the Arctic and will be wrong. To the Arctic is necessary to apply the same approaches that are now really being put into practice in the study of outer space.
The Arctic, Space, World Ocean – is the implementation of these and other planetary projects today is unthinkable without a global human solidarity, without the use of the intellect of mankind, without the cooperation of all kinds of resources available, including the creation of the modern Arctic infrastructure. Therefore, perhaps the most important conclusion is that, without dialogue, people and cultures of the Arctic will be difficult to master. Development of a real trust in each other is possible only in the organization of a joint process of positive change. Are today, Russia, China, USA, Canada, Norway and the EU to start such a dialogue in the Arctic?
Список литературы The conceptual approaches to definition of internal borders and development of the Russian Arctic in the changing world
- Celine V. S., Vasiliev V. V. Interaction of global, national and regional economic interests in the development of the North and the Arctic. Apatity, 2010. P. 13.
- Zonn I. S., Jilzov S. S. The Arctic oil and gas front. Data on stocks of resources in the Far North needs to be clarified. 13/12/2011. URL: http://www.ng. ru/energy/2011-12- 13/15_arctic.html (date of access: 27/02/2012).
- Kefeli J. F. Geopolitics of Eurasia. St. Petersburg, 2010. P. 214.
- Lukin Y. F. The great redistribution of the Arctic: a monograph. Arkhangelsk: Northern (Arctic) Federal University named after M. V. Lomonosov, 2010. 400 p.
- Putin V. V. Construction of justice. Social policy for Russia. URL: http://www.putin2012.ru/# article-5 (date of access: 02/13/2012).
- Dmitry Gorokhov chaired a meeting of working group on the bill to the Arctic zone of Yakutia. URL: http://www.iltumen.ru/node/1522 (date of access: 03/03/2012).
- President of Yakutia announced proposals for the development of the Arctic zone. December 22, 2011. URL: http://www.arctic-info.ru/News/Page/prezident-akytii-ozvycilpredlojenia- po-razvitiu-arkticeskoi-zoni (date of access: 03/03/2012).
- Ricci L. La nuova corsa all'Artico. URL: http://www.ilsole24ore.com/art/cultura/ 2012-01- 29/nuova-corsa-artico-081316.shtml? Uuid = AaJT9pjE (date of access: 01/31/2012).
- Howard R. The Arctic Gold Rush: The New Race for Tomorrow's Natural Resources. London: First published in 2009. 259 p. (date of access: 03.03.2012).


