The impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on education – balancing advancements and ethical considerations on human rights
Автор: Lazar Stošić, Aleksandra Janković
Журнал: Pravo - teorija i praksa @pravni-fakultet
Рубрика: Original scientific work
Статья в выпуске: 4 vol.40, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The primacy of artificial intelligence (AI) in education has become increasingly relevant in recent times, aiming to facilitate the easier acquisition of material. There is a growing emphasis on the implementation of AI and the search for ways to incorporate it into everyday work. However, this story brings into play ethical, copyright, and many other rights. The text discusses the growing role of artificial intelligence (AI) in education, emphasizing its potential benefits and ethical challenges. It explores the use of models like Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) to enhance learning processes, yet highlights concerns related to transparency and ethics.
Artificial intelligence, Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), Education, Ethical Considerations, Human right
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170202126
IDR: 170202126 | УДК: 004.8:37 | DOI: 10.5937/ptp2304058S
Текст научной статьи The impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on education – balancing advancements and ethical considerations on human rights
By employing artificial intelligence, students can access solutions or prewritten text more quickly and effortlessly. However, these outcomes might not genuinely reflect their own knowledge, thereby raising concerns about the level of understanding students attain through the utilization of artificial intelligence. Instead of arriving at final solutions through their individual effort and comprehension, students could resort to acquiring ready-made solutions and texts, thereby abbreviating the time they would spend in reading and comprehending the subject matter. This is especially pertinent in the context of initial programming education. The prevalent use of AI, particularly the adoption of ChatGPT, is conspicuous across all spheres of life.
ChatGPT (GPT: Generative Pretrained Transformer, https://chat. , is a natural language processing model developed by OpenAI. OpenAI ChatGPT, which was created especially for conversational and chat-based applications, can understand user requests and produce text that simulates human speech. This makes it practical for systems like conversational AI systems, virtual assistants, and chatbots. Through natural language processing, ChatGPT generates human-like responses based on user input. It is designed to comprehend natural language and produce intelligent and relevant answers to user queries. Within just two months of its launch in November, ChatGPT became the fastest-growing consumer application in history with over 100 million active users. Since its release on November 30, 2022, ChatGPT has accumulated data up until 2021 and does not possess knowledge of events occurring after that date. (Source: ChatGPT Sets Record for Fastest-Growing User Base—Analyst Note).
Graph 1. Display of the ChatGPT Interface
ChatGPT
Examples
"Explain quantum computing in simple terms"-»
Capabilities
Remembers what user said earlier in the conversation
△
Limitations
May occasionally generate incorrect information
"Got any creative ideas for a 10 year old’s birthday?" -»
Allows user to provide follow-up corrections
May occasionally produce harmful instructions or biased content
"How do I make an HTTP request in Javascript?" -»
Trained to decline inappropriate requests
Limited knowledge of world and events after 2021
Send a message.
Free Research Preview. ChatGPT may produce inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. ChatGPT May 3 Version
According to the authors, “an emerging existential threat to the teaching and learning of introductory programming” (Finnie-Ansley et al., 2022). Zhu et al. (2021) describe the application of GPT-3 in various adaptive learning contexts and examine its effectiveness compared to traditional methods. Wu et al. (2021) explore the use of GPT-3 in promoting natural language learning and investigate how GPT-3 can assist students in developing language skills.
According to Lo’s study in 2023, the performance of ChatGPT varied across different subject domains, ranging from exceptional (e.g., economics) and satisfactory (e.g., programming) to unsatisfactory (e.g., mathematics).
2. What are the advantages of using ChatGPT in education?
In order to reduce time and boost writing quality, ChatGPT can be a useful tool in higher education for enhancing writing. It can generate texts, summarize data, and create outlines. Additionally, it can spot grammar and style mistakes, which improves the readability of written content (Atlas, 2023).
When discussing the application of ChatGPT in education, we can enumerate several characteristic advantages:
-
• Providing support to students,
-
• Enhancing the efficiency of the teaching process,
-
• Monitoring student progress,
-
• More efficient communication,
-
• Personalized learning.
Providing support to students involves ChatGPT offering pre-formulated solutions or guiding the process of arriving at a solution. In cases where difficulties persist, ChatGPT can, step by step, define and illustrate the approach to solving each task, even the problem itself. Additionally, by furnishing students with access to pertinent information and resources, proposing previously unexplored perspectives, and introducing novel areas of research, ChatGPT can facilitate the cultivation of research skills among students (Kasneci et al., 2023). This equips students with improved abilities to comprehend and evaluate the subject matter at hand.
Enhancing the efficiency of the teaching process is evident in assisting educators in automating various tasks, such as test assessment, test question generation, and assignment grading. For instance, in scenarios involving advanced or struggling students, ChatGPT can subsequently prepare specific tests or provide instructions on how to work with them. This means that the system can be tailored to different categories of students within the same cohort.
Several advantages of ChatGPT were highlighted by Rudolph et al. (2023), encompassing its ability to generate human-like dialogues, its rapidity and efficacy, and its cost-effectiveness due to the elimination of human labor.
When discussing personalized learning, ChatGPT can be adapted to an individualized learning curriculum based on students' interests. Chokshi
Monitoring student progress entails that educators can observe students' advancement through specific tests and, with the assistance of ChatGPT, tailor the curriculum to each age group and cohort, primarily offering individualized support to students.
Enhanced communication is evidenced by students' ability to pose questions at any time and receive answers promptly. However, the validity of the responses is brought into question, especially when questions are not precisely formulated. An illustration of potential responses to the stated question is demonstrated in the practical example below.
Figure 2. ChatGPT output on question: What are the advantages of using ChatGPT in education?
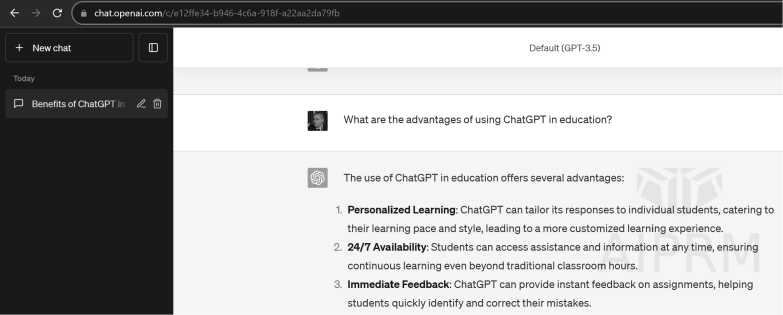
Source: Authors, using ChatGPT 3,5.
3. What are the disadvantages of using ChatGPT in education?
In addition to its positive aspects, ChatGPT also exhibits certain drawbacks. Some of the negative aspects include:
-
• Incomplete accuracy of responses,
-
• Lack of creativity,
-
• Absence of human reaction,
-
• Limited understanding capability,
-
• Potential for misuse,
-
• Dependency on technology,
-
• Inability/weakness in plagiarism detection.
When discussing the lack of human interaction, we primarily refer to the potential for reduced socialization among students and teachers. The teacher undoubtedly serves as a pivotal component in the education process, guiding the student's journey. Interaction with the teacher can make the student feel valued, engaged, and motivated for continued effort and knowledge acquisition.
Without supervision and result validation, not every response is guaranteed to be entirely accurate. Rigorous monitoring of responses can lead to misunderstandings and misconceptions. Therefore, the oversight, validation, and monitoring by teachers during its application are crucial.
Regarding creativity, the provision of ready-made specific solutions can inhibit students' creative thinking. Creativity itself is contingent on cognitive abilities, and the application of ChatGPT without student-teacher interaction might curtail the development of creativity, impeding the fostering of autonomy and critical thinking in students.
The limited understanding capability implies that without a properly and clearly defined prompt, ChatGPT will not provide a clear answer, thus questioning only the understanding of the issue. ChatGPT provides answers based on a clearly defined question, and logical reasoning alone does not lead to obtaining logical solutions. This change, these logical solutions, can be identified and addressed only by the teacher. Concerns have been raised about students using ChatGPT to copy and paste texts without critically evaluating what has been highlighted or selected from a source, without attributing the original sources, and without being aware of the possibility of plagiarism (García-Peñalvo, 2023).
When considering the potential for misuse, it primarily pertains to the utilization of pre-existing materials, texts, or the paraphrasing of published content. Detecting generated text is notably challenging, especially using anti-plagiarism software. However, versions have emerged in the market that recognize writing styles produced by artificial intelligence, thereby alerting us or categorizing the text as AI-generated. Illustrative cases include instances where certain authors have begun publishing works with ChatGPT listed as the primary author or cite text provided by ChatGPT. Any form of employing ChatGPT devoid of logical reasoning and independent conclusion-drawing jeopardizes the integrity of the educational process.
In his research, Mhlanga discovered that educators are concerned about the use of ChatGPT in education. In conducted studies, teachers expressed apprehension that students might submit work generated by ChatGPT due to its rapid ability to produce acceptable texts (Mhlanga, 2023). Another study revealed that the usage of ChatGPT in education presented various issues in studies, ranging from plagiarism to inaccurate answers and citations (Sallam, 2023).
Inadequate or weak plagiarism detection is a prominent concern when utilizing AI, particularly ChatGPT. In an experiment examining essays generated with ChatGPT, Khalil and Er (2023) discovered that 40 out of the 50 essays examined had a similarity score of 20% or less, indicating a high level of originality. ChatGPT produces high-quality outputs that are likely to evade plagiarism detection software. One potential solution for working with students has been the restriction of ChatGPT during instructional sessions.
While ChatGPT can assist in generating ideas for a specific subject, familiarizing oneself with its concepts and issues, or even generating potential application program code, the produced texts should not be regarded as final products (Halaweh, 2023).
An example of obtaining potential responses to the stated question is demonstrated in the practical example below.
Figure 3. ChatGPT output on question: What are the disadvantages of using ChatGPT in education?
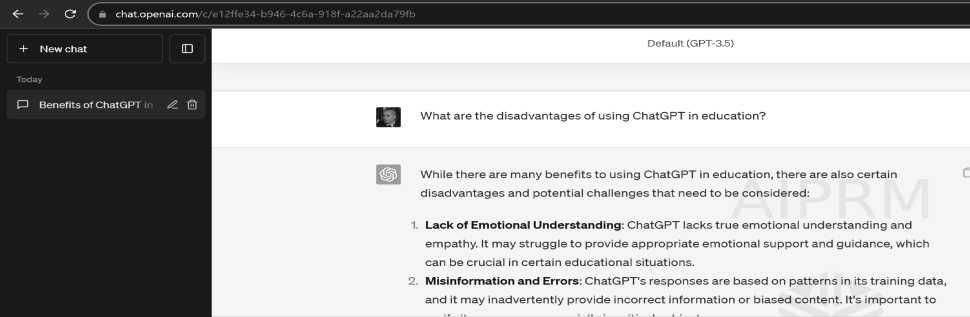
Source: Authors, using ChatGPT 3,5.
4. The impact of artificial intelligence on human rights
It can be said that among other events, the year 2023 was marked by debates on the topic of artificial intelligence (AI), its use for societal advancement, and the risks it brings. For this reason, Colinson's Dictionary declared artificial intelligence (AI) as the word of the year in 2023. (Collins Dictionaries, 2023). What can be observed as a common result of all debates on the use of artificial intelligence is the consensus that, on the one hand, it can be a driver of societal development, but on the other hand, it can pose a risk to the security of citizens and be an instrument for violating basic human rights. Concerns about potential misuse of artificial intelligence are also expressed through increasingly frequent international congresses on the topic of AI and the risks it brings. One such conference was held on November 1st and 2nd, 2023, by the United Kingdom government under the theme "AI Safety Summit." (Government of the United Kingdom, 2023). The goal of international conferences is to achieve consensus on a global level regarding the measures that need to be taken to ensure global security in light of the increasing use of artificial intelligence.
In the process of aligning legal regulations with the expansion of the use of artificial intelligence, the Republic of Serbia has adopted a series of documents to regulate its use and align with international documents that govern the application of artificial intelligence. One of the more important documents in this field is the Strategy for the Development of Artificial Intelligence in the Republic of Serbia for the period 2020-2025. (2019). In addition to measures aimed at promoting the development and application of artificial intelligence in various areas of society to enhance economic development and improve services, the strategy also includes measures necessary to ensure its safe use. This involves preventing its misuse and protecting citizens. Based on the analysis of documents that regulate the application of artificial intelligence, both at the international and national levels, we can conclude that the common characteristic of all these documents is the emphasis on the need to strike a balance between the development of artificial intelligence and its safe use. "While there are potential benefits in terms of economic development and improved efficiency, the development of artificial intelligence also brings certain challenges. These include data protection, the risk of inheriting biases and discriminatory factors from data, and other ethical concerns”( The Strategy for the Development of Artificial Intelligence in the Republic of Serbia for the period 2020-2025, 2019, 1.2, paragraf 6).
The Republic of Serbia adopted the Law on Personal Data Protection in 2018 (National Assembly of the Republic of Serbia, 2018), which guarantees the protection of personal data during collection and processing. In the previous period, competent authorities observed different interpretations of the Data Protection Law (The Strategy for the Development of Artificial Intelligence in the Republic of Serbia for the period 2020-2025, 2019), leading to legal uncertainty.
5. Conclusion
Despite the existence of negative aspects, the advantages of utilization far outweigh the drawbacks when it comes to the application of GPT in education. The use of GPT in education undeniably yields positive effects, albeit contingent upon proper implementation. Foundational training and knowledge about its usage are imperative. The negative impacts themselves can be mitigated through thoughtful question design, training educators and students for effective technology use, and the seamless integration of ChatGPT into the educational curriculum. Educating students about the rules of ChatGPT use and monitoring its application are pivotal factors in safeguarding the integrity of the educational process.
The implementation of GPT in education holds the potential for significantly enhancing efficiency and personalization in education. However, concurrently, we must remain cognizant of the potential negative consequences. Therefore, further research and the development of appropriate regulations can aid in ensuring responsible adoption of this technology within an educational context. While the application of ChatGPT demonstrates positive outcomes, a more comprehensive assessment is required to gain a deeper understanding of its potential benefits and threats to education.
At the end, the incorporation of artificial intelligence in education holds immense potential to transform the educational process, providing advantages like enhanced productivity and tailored instruction. But one must carefully weigh potential downsides, transparency challenges, and ethical considerations. The more general conversations about the dangers and effects of AI on society highlight the necessity of international cooperation as well as laws to guarantee the responsible application of AI. Finding a balance between advancement and protecting human rights is still a critical concern as the AI landscape changes.
Stošić Lazar
Fakultet za menadžment, Sremski Karlovci, Univerzitet UNION Nikola Tesla, Beograd, Srbija; Don State Technical University, Rostov-on-Don, Ruska Federacija
Janković Aleksandra
Akademija strukovnih studija Južna Srbija – Leskovac, Odsek Visoka škola za vaspitače Bujanovac, Srbija
UTICAJ VEŠTAČKE INTELIGENCIJE
-
(VI) NA OBRAZOVANJE – BALANSIRANJE NAPRETKA I ETIČKIH
RAZMATRANJA LJUDSKIH PRAVA
REZIME: Primat veštačke inteligencije (VI) u obrazovanju postao je sve relevantniji u poslednje vreme, sa ciljem olakšavanja lakšeg usvajanja materijala. Postoji sve veći naglasak na implementaciji VI i potraga za načinima kako je uključiti u svakodnevni rad. Međutim, ova priča uvodi etička, autorska i mnoga druga prava. Tekst razmatra rastuću ulogu veštačke inteligencije (VI) u obrazovanju, ističući njene potencijalne prednosti i etičke izazove. Istražuje korišćenje modela kao što je Generativno Predtrenirani Transformator (GPT) u svrhu unapređenja procesa učenja, ali istovremeno ističe zabrinutosti u vezi sa transparentnošću i etikom.
Ključne reči: veštačka inteligencija, Generativno predtrenirani tdransformator (GPT), obrazovanje, etička razmatranja, ljudska prava.
Список литературы The impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on education – balancing advancements and ethical considerations on human rights
- Arora, S., Yadav, D., & Goyal, P. (2021). Assessing English Writing Skills with Generative Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.03636
- Atlas, S. (2023). ChatGPT for higher education and professional development: A guide to conversational AI. Downloaded 2023, October 28 from Downloaded 2023, October 28 from https://digitalcommons.uri. edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article= 1547&context=cba_facpubs
- Avramović, D. S., & Jovanov, I. D. (2023). Sudijska (ne)pristrasnost i veštačka inteligencija. [(Im)partiality of a judge and artificial intelligence] Strani pravni život, 67(2), pp. 161-177. https://doi.org/10.56461/SPZ_23201KJ
- Bjelajac, Ž., Filipović, A. M., & Stošić, L. V. (2022). Internet Addiction Disorder (IAD) as a Consequence of the Expansion of Information Technologies. International Journal of Cognitive Research in Science, Engineering and Education (IJCRSEE), 10(3), pp. 155–165. https://doi.org/10.23947/2334-8496-2022-10-3-155-165
- ChatGPT Sets Record for Fastest-Growing User Base—Analyst Note. Downloaded 2023, October 28 from https://www.reuters.com/technology/chatgpt-sets-record-fastest-growing-user-base-analyst-note-2023-02-01
- Chokshi, A., & Thakkar, P. (2021). Personalized Learning with GPT-3: The Future of Educational Chatbots. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.15538
- Connolly, V., & Watson, S. (2023). Chat GPT (We need to talk). Faculty of Education, University of Cambridge. Downloaded 2023, October 22 from https://news.educ.cam.ac.uk/230403-chat-gpt-education
- García-Peñalvo, F. J. (2023). The perception of artificial intelligence in educational contexts after the launch of ChatGPT: Disruption or panic? Education in the Knowledge Society, 24, e31279. https://doi.org/10.14201/eks.31279
- Gasmi, G., & Prlja, D. (2021). Ugrožavanje ljudskih prava i veštačka inteligencija [Violation of Human Rights and Artificial Intelligence], Zbornik radova 34. Susreta Kopaoničke škole prirodnog prava – Slobodan Perović, Tom III [Proceedings of the 34th Meeting of the Kopaonička School of Natural Law – Slobodan Perović, Volume III], (pp. 323-335). Beograd: Kopaonička škola prirodnog prava – Slobodan Perović. Downloaded 2023, September 25 from https://kopaonikschool. org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/KOP_PZivot_2021_WEB_TOM_III. pdf.
- Gordon, C. (30. April 2023). How Are Educators Reacting To Chat GPT? Forbes Media LLC. Downloaded 2023, October 23 from https://www.forbes.com/sites/cindygordon/2023/04/30/how-are-educatorsreacting-to-chat-gpt/?sh=7c6ca7cf2f1c
- Halaweh, M. (2023). ChatGPT in education: Strategies for responsible implementation. Downloaded 2023, October 28 from https://digitallibrary.aau.ac.ae/handle/123456789/980
- Kasneci, E., Seßler, K., Küchemann, S., Bannert, M., Dementieva, D., Fischer, F., Gasser, U., Groh, G., Günnemann, S., Hüllermeier, E., Krusche, S., Kutyniok, G., Michaeli, T., Nerdel, C., Pfeffer, J., Poquet, O., Sailer, M., Schmidt, A., Seidel, T., …, & Kasneci, G. (2023). ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learning and Individual Differences,Volume 103, https://doi. org/10.35542/osf.io/5er8f
- Khalil, M., & Er, E. (2023). Will ChatGPT get you caught? Rethinking of plagiarism detection. arXiv. In: Learning and Collaboration Technologies, (pp. 475-487). https://doi.org/10.35542/osf.io/fnh48
- Konstantinos, K., & Lambrou, E. (2023). ChatGpt – another step towards the digital era or a threat to fundamental rights and freedoms? Pravo –teorija i praksa, 40(3), pp. 1-18. https://doi.org/10.5937/ptp2303001K
- Liu, X., Li, B., Li, C., Li, T., & Li, X. (2021). GPT-3 for Language Learning: A Pilot Study of the Usability and Perceived Usefulness of a Conversational Agent in Learning English. IEEE Access, 9, 106532-106544
- Lo, C. K. (2023). What is the impact of ChatGPT on education? A rapid review of the literature. Education Sciences, 13(4), pp. 410-424. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13040410
- Mhlanga, D. (2023 Open AI in education, the responsible and ethical use of ChatGPT towards lifelong learning. Education, the Responsible and Ethical Use of ChatGPT Towards Lifelong Learning (February 11, 2023). http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4354422
- Milošević Grbić, T. (2023). CHAT GPT ima dva velika problema: delom će ih rešavati nauka, ali i zakoni moraju da se menjaju [CHAT GPT has two major issues: some of them will be addressed by science, but laws also need to change.]. EURACTIV Srbija, 18. February. Downloaded
- , October 20 from https://euractiv.mondo.rs/tehnologija/a412/ChatGPT-izazovi-i-prednosti.html
- Zakon o zaštiti podataka o ličnosti [The Law on Personal Data Protection]. Službeni glasnik RS, br. 87/18
- Ustav Republike Srbije [The Constitution of the Republic of Serbia]. Službeni glasnik RS, br. 98/06 i 115/21
- Prlja, D., Gasmi, G., & Korać, V. (2021). Veštačka inteligencija u pravnom sistemu EU [Artificial Intelligence in the EU Legal System].
- Beograd: Institut za uporedno pravo. Downloaded 2023, October 20 from https://iup.rs/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/2021-Veštačka-inteligencijau-pravnom-sistemu.pdf
- Rudolph, J., Tan, S., & Tan, S. (2023). ChatGPT: Bullshit spewer or the end of traditional assessments in higher education? Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching, 6(1), pp. 1-22, https://doi.org/10.37074/ jalt.2023.6.1.9
- Sallam, M. (2023). The utility of ChatGPT as an example of large language models in healthcare education, research and practice: Systematic review on the future perspectives and potential limitations. medRxiv 2023.02.19.23286155, https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.19.23286155
- Strategija razvoja veštačke inteligencije u Republici Srbiji za period 2020- 2025. godina [The Strategy for the Development of Artificial Intelligence in the Republic of Serbia for the period 2020-2025.]. Službeni glasnik RS, br. 96/19
- Zaključak o usvajanju etičkih smernica za razvoj, primenu i upotrebu pouzdane i odgovorne veštačke inteligencije [Conclusion on the Adoption of Ethical Guidelines for the Development, Implementation, and Use of Reliable and Responsible Artificial Intelligence], Službeni glasnik RS, br. 23/23
- Xiang, J., Zhang, X., & Yang, B. (2021). GPT-3 for Education: A Systematic Literature Review. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 16(23), pp. 224-238
- Government of the United Kingdom (2023). AI Safety Summit. Conference was held on November 1st and 2nd, 2023. Downloaded, November 5 from https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/ai-safety-summitprogramme/ai-safety-summit-day-1-and-2-programme
- Collins Dictionaries (2023). The Collins Word of the year 2023 is.... Downloaded, October 28 from https://www.collinsdictionary.com/woty


