The importance of the National CERT institution for the Republic of Serbia
Автор: Milica Lesanovic
Журнал: Pravo - teorija i praksa @pravni-fakultet
Рубрика: Articles
Статья в выпуске: 2 vol.42, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The National CERT is the institution responsible for coordinating, preventing, and protecting against current security risks in the information and communication systems of operators at the national level. This article explores the mechanisms of protection, prevention, and response to security threats, emphasizing the role and importance of the CERT institution for the Republic of Serbia, the application of the Law on Information Security, and the raising of public awareness about information security. Various research methods have been applied, including the method of concretization, the combined method of analysis and synthesis, the inductive-deductive method, the comparative method, and the statistical method. The Law on Information Security regulates protective measures against security risks in information and communication systems, defines the responsibilities of legal entities in managing and using such systems, and determines the competent authorities for implementing those measures. Through supervision, control, and recordkeeping of all security threats in the Republic of Serbia, the National CERT enables proactive engagement by competent institutions, thereby enhancing the level of national security and Serbia’s position on the global stage.
National CERT, information security, Law on information security, cyber threats, Republic of Serbia
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170209495
IDR: 170209495 | УДК: 007:004.056(497.11) | DOI: 10.5937/ptp2502174L
Текст научной статьи The importance of the National CERT institution for the Republic of Serbia
1. Introductory considerations
The National Center for Prevention of Security Risks in ICT Systems of the Republic of Serbia was established within the Regulatory Agency for Electronic Communications and Postal Services, in accordance with the Law on Information Security. The primary responsibilities of the National CERT are coordination, prevention and protection against security risks in information and communication systems (ICT systems), at the national level. National CERT collects and exchanges information, informs, warns and advises persons who manage ICT systems, as well as the public of the Republic of Serbia, about possible risks. The National CERT monitors reported incidents at the national level and, based on the collected data, analyzes risks and incidents with the aim of raising awareness of the importance of information security, both among citizens, as well as among business entities and public authorities. Supervision of the work of the National CERT in the performance of tasks entrusted by this law is carried out by the Competent Authority, i.e. the Ministry of Trade, Tourism and Telecommunications (Computer Emergency Response Team [CERT], 2025).
The establishment of the National CERT represents one of the significant challenges in the modern IT world of every developed country. The establishment of the National CERT institution includes a series of activities that are reflected in the monitoring of certain activities and regulations, as well as in the provision of necessary resources. In order to establish a successful mechanism of the CERT institution at the national level, it is necessary to establish the timely action of experts through clearly defined templates for resolving incidents and dealing with emergency situations.
The importance of this article is reflected in the research of the existing mechanisms of protection, prevention and reaction to security threats, through the prism of the National CERT. Multiple research methods were applied, due to the complexity of the topic of the article, such as the combined method of analysis and synthesis, the inductive-deductive method, the comparative method, and the statistical method, as mentioned earlier. The special contribution of the article is reflected in highlighting the importance of the CERT institution for the Republic of Serbia, the current implementation of the Law on Information Security and raising citizens’ awareness of information security protection.
One of the most important roles of the National CERT is its status as a clearinghouse for information on all incidents, on a statewide level. Also, its significant contribution is reflected in the development and planning of future strategies for combating threats to information systems. What makes the capability of detailed analysis possible is that based on the annual reports of ICT system operators, experts can assess the progress of the society itself in the fight against cyber threats.
2. Challenges in the selection of personnel
3. Public-private partnership and benefits of successful cooperation
The expansion of public-private partnerships in cybersecurity has become a key factor in protecting the nation’s infrastructure from growing cyber threats. About 85% of critical infrastructure is owned and operated by the private sector, making their involvement in information security essential. The private sector has been engaged in the challenges and threats in the digital environment, providing software, hardware and performing functions under applicable government contracts. This way, costs for both sectors are reduced by integrating existing private and public cyber security measures, avoiding redundant and counterproductive activities (Kim, 2024).
Defining critical companies for the successful operation of the National CERT also depends on the national context of a particular country, so it is extremely important to include them in all flows and events of public importance for the community. Interested parties or key stakeholders, may include pre-existing CERTs in the country. Some of them can be CERTs established in a certain sector of the company, IT suppliers, Internet providers and large organizations with influence in the private sector. The combined collaboration, connecting with various organizations and individuals in the cyber security community, provides a comprehensive approach to incident response and threat mitigation.
4. International cooperation
The Budapest Convention on Cybercrime remains one of the primary legal frameworks for national and European legislation on cybercrime. The NIS directive also mandates the creation of a Cooperation Group to support strategic cooperation between member states, with a regular update of the work plan every 18 months. In addition, the European Union can enter into international agreements with third parties, in order to expand the scope of cooperation (Rizmal, et al., n.d.). The cooperation of all key factors is needed in order to establish a network of trust between institutions founded for the same reason – information security protection.
Difficulties at the international level that the CERT institution may encounter are problems that may arise at various levels of established international relations. A lot of effort is put into the continuity of international cooperation, and the ways in which this is achieved are being improved from year to year. The lack of effective cooperation between CERTs represents a significant risk, where risks can also be the potential unsystematic use of data and tools, as well as the lack of evaluation of existing resources (Kamara et al., 2022).
5. The most common cyber security threats
One of the biggest threats at the global level is cyber warfare. The seriousness of this threat is so great that even highly developed countries would question whether they have enough resources to respond adequately, if necessary. Cyber attacks, from the most harmless to the most serious, represent a significant threat to the national security of every country. The biggest asset of their attackers is that they target critical infrastructure, financial systems and sensitive data. We are witnessing the accelerated development of digital technologies and software, so it is not surprising that nations and corporations increasingly rely on digital platforms, with a special focus on cyber security. Investments in cyber security are critical to countering the growing sophistication and dynamism of cyber criminals and their innovative methods of attack (Searchinform, 2022).
The most serious attack was recorded in 2024 when the crypto exchange Bybit suffered an attack worth as much as 1.4 billion dollars, making it the largest hacking attack in the history of the industry. A hacker took control of the exchange’s wallet, resulting in the loss of funds and endangering users and company assets (CryptoAdria, 2025). It is interesting to note that the hackers responsible for the biggest cybercrime in modern history have not yet been brought to justice. After this incident, the topics of legal action by competent institutions in cooperation with IT experts and consultants in the field of cyber security were raised. Citizen petitions have been launched, which aim to make the necessary changes to the Law on Information Security, at the level of domestic and international legislation. It is necessary to influence the urgency of adopting regulations that would facilitate international cooperation and bringing to justice of the perpetrators of criminal acts, from whatever continent they operate.
6. The most common cyber security threats in the Republic of Serbia, in the period from 2020 to 2023 6.1. Report for 2020
In the report published on the official website of the National CERT of the Republic of Serbia for the year 2020, information is available on the most common types of cyber attacks in that period. Table 1 shows the five most represented groups of incidents registered in the Republic of Serbia.
Based on the information available, it was observed that the most common attacks relied on weak user passwords rather than specific system vulnerabilities. The group of incidents that is the most dominant is the attempt to break into the ICT system (17,332,830), which includes an attempt to reveal user credentials, as well as an attempt to exploit system vulnerabilities. In second place is the group of incidents of unauthorized data collection (8,470,838), in which port scanning and social engineering are the most represented (CERT, 2020).
An example from March of this year refers to an attack on state structures, when the target of the attack were the servers of the Public Utility Company “Informatika” from Novi Sad. Hackers broke into the information system via a “fake” email, which gave them access to data and gave them the opportunity to block the city administration and prevent it from continuing to work on regular basis (Đurić, 2021).
-
6.2. Report for 2021
-
6.3. Report for 2022
-
6.4. Report for 2023
The report below provides a summary overview of cyber incidents in 2021, with an emphasis on the statistics of attack groups and incidents that occurred in ICT systems of particular importance.
In this research, attention was paid not only to threats at the given moment, but also to the importance of a strategic approach to protecting the system from such attacks in the future. In 2021, the trend of increasing malicious campaigns through fake electronic messages and links (phishing) and misuse of the circumstances of the pandemic and the impact of remote work continued. Compared to the previous year, the introduction of automation in information security is becoming more pronounced in the defense of system security and information security (CERT, 2021).
The importance of continuous monitoring and updating of necessary IT system upgrades, as well as the importance of continuous education of experts in this field, clearly indicate that a comprehensive approach of the National CERT is necessary for a successful response to modern security threats. This type of annual report and display of registered threats can be very helpful in making decisions to strengthen defense mechanisms against future attacks. In 2020, the total number of the most represented groups of incidents (25,954,294) is significantly higher than the total number of incidents in 2021 (13,261,258), which indicates that the establishment of the National CERT significantly contributed to the reduction and better response to existing incidents. From the comparative view, we conclude that in 2021, serious progress was made in modernizing access and solving security incidents, which makes the fight against security risks and threats in information technologies more advanced.
From the annual report on statistical data on all incidents in the field of cyber security, it is noted that attacks on ICT systems of particular importance in 2022 were more diverse than in previous years, but certain trends were still widely represented.
The biggest number of incidents recorded in 2022 refers to a group of incidents of unauthorized data collection, among which the type of attack called port scanning is the most common (CERT, 2022). This attack aims to gather information about systems without immediate and direct damage and most often serves as preparation for further research and planning of future attacks. Another common attack in this group of incidents, is an attempt to discover user credentials, that is, attacks that rely on trying out different combinations of usernames and passwords, until a credential takeover and data misuse is established.
The example from June 2022 indicated the increased danger of the most notorious hacker attacks, such as those in developed and modern countries of the world. On this occasion, hackers successfully took over the cadastre database, causing serious difficulties in the work and preserving the credibility of data on property records in the Republic of Serbia. The consequences of this attack were reflected in difficulties in property transactions and legal affairs of citizens (Aničić, 2024). This attack triggered many events in all aspects at the state level, such as the consideration of the amendment of the Law on Information Security, with the aim of timely response to security incidents and prescribing adequate punishments for the perpetrators.
The 2023 Incident Report provides a concise overview of the types of attacks that were most prevalent in ICT systems of particular importance. As the most common attack this year, the type of attack that deals with port scanning stands out. These attacks are represented on an increased scale due to the automation of processes and include ICT systems that are represented in the digital infrastructure and electronic communications (CERT, 2023).
The example of the hacker attack on the Electric Power Company of Serbia, which surprised state authorities and citizens at the end of December, represented a serious security problem and an appeal to institutions to more actively deal with these security segments. Namely, the hacker group “Qilin” took responsibility for this attack, which was carried out with the aim of extorting money by “taking over” the company’s server (Vlaović, 2024). It is interesting to note that the authorities from the National CERT were not open to cooperation in informing the public about the incident at the given moment, which is not in accordance with their postulates. Transparency and work with citizens and competent institutions would increase the level of trust in the institution of the National CERT, while also facilitating the acceptance of new regulations in the planned amendments to the Law on Information Security.
It is important to note that the human factor remains the main source of risk in the information security of the Republic of Serbia. The number of security incidents at all levels is constantly increasing, the variety of groups of incidents is not negligible and requires special attention when creating strategies and defense mechanisms against future cyber threats.
6.5. Analysis
Chart 1. Presentation of the most represented groups of incidents, in the period from year 2020-2023.
7. Criminal acts against the security of computer data – the most common criminal acts in the Republic of Serbia
7.1. Unauthorized access to a protected computer, computer network and electronic data processing7.2. Computer fraud
When it comes to the criminal offense of computer fraud (Criminal Code, 2005, Art. 301), it is necessary to point out the financial aspect in punishing the perpetrators, where the perpetrator in this case is punished more severely, because the goal is to acquire (most often significant) illegal property benefits. The range from four hundred and fifty thousand dinars to over one million and five hundred thousand dinars indicates the seriousness of these crimes and the prison sentence of up to 10 years.
7.3. Computer sabotage
When we talk about computer sabotage, the Law prescribes that any person who enters, destroys, deletes, changes, damages, conceals or otherwise renders computer data or programs unusable or destroys or damages a computer or other device for electronic processing and data transmission (Criminal Code, 2005, Art. 299), it is necessary to analyze the motive for such illegal action in depth. Perpetrators can be employed in a certain company, which is of national importance, in the event that they misuse and manipulate data of state importance, they can be punished with imprisonment from six months to five years. The perpetrators of this criminal act may have different intentions, from obtaining illegal benefits (as in the cases we dealt with in the analysis), or even problematic behavior of employees within the company (risk of inadequate personnel). On the example of the National CERT, a risk of incredible proportions would follow in the event that an employee of this institution commits a criminal act, similar to this one, considering that the data that the authorities in the CERT have are usually (strictly) confidential.
7.4. Creating and introducing computer viruses
An unavoidable topic in the cyber world and the cyber space of the Republic of Serbia are various computer viruses and fake emails that contain links to such programs. The reason for the creation of computer viruses and their distribution is widespread among world hackers, because it represents a way to manipulate data and files on the “infected computer”. In the Republic of Serbia, a fine or a prison sentence of 6 months to two years, depending on the seriousness of the crime (Criminal Code, 2005, Art. 300), is prescribed for the execution of this criminal offense. We have witnessed that in the modern world of digital technologies and the constant improvement of the hacking abilities of the perpetrators, the questioning of the adequacy of the punishment for this crime will be a potential item in the coming period. Amendments to the Law envisage the improvement of measures and sanctions for perpetrators in accordance with current statistical data on crimes committed in the Republic of Serbia.
8. Positive and negative aspects of the implementation of the Law on Information Security in the Republic of Serbia
THE MOST COMMON GROUP OF INCIDENTS
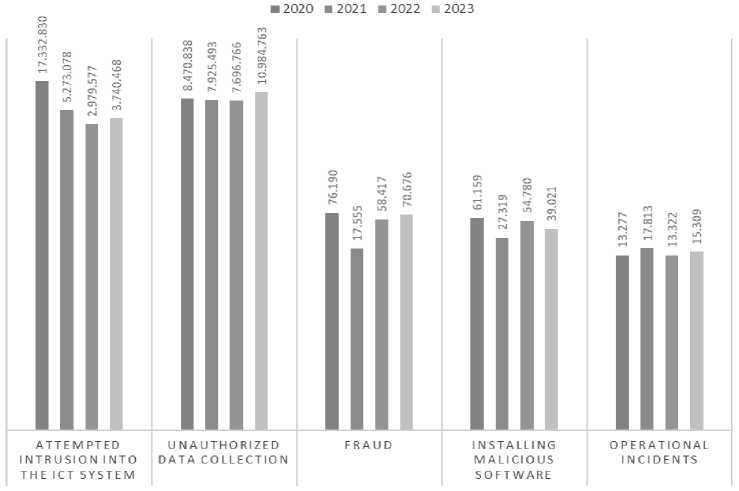
Source: Author’s research
By comparing data from available annual reports and monitoring trends in the total number of recorded security incidents, we can proactively respond to future threats and incidents. Using the graph shown above, we can see the trend of growth and decline in the number of registered incidents and compare it with available data for the period from 2020 to 2023. The group of attacks of attempts to break into the ICT system dominates in 2020 (13,592,362 fewer registered cases were recorded in 2023), while the group of incidents of unauthorized data collection reaches its growth peak in 2023 (2,513,925 more registered cases compared to 2020). During the entire research period, cases of malicious software installation, fraud and operational incidents were recorded, which indicates the need to plan protection mechanisms against these groups of incidents. After the publication of the annual report for 2025, we will be able to create a broader picture of the activities undertaken and analyze the level of improvement of defense mechanisms against cyber attacks.
On the basis of Article 302 of the Criminal Code, measures of protection and responsibility of perpetrators of criminal acts, due to violations of the regulations provided for in the document, are prescribed. The law stipulates that any person who has unauthorized access to a computer or computer network will be punished with a fine or imprisonment for up to 6 months (Criminal Code, 2005, Art. 302). In the previous analysis of the most common crimes against the security of computer networks in the Republic of Serbia, based on publicly available reports of the National CERT, we concluded that this is one of the most common crimes. It should be pointed out that it is often difficult to detect the perpetrator and hold him accountable for the crime, while the prescribed “mild” punishment leaves room for the perpetrator’s recovery. Perpetrators can be punished with a prison sentence of up to 3 years, in the event that more serious consequences have occurred (disruption of the network’s functioning or serious system downtime, for example). We should remember examples from the world where the material benefit is so great that it motivates the perpetrator to engage in illegal activities, and in case he is caught, the benefit is much greater than the defined sanctions.
In the examples discussed in the previous part, the process was mostly conducted against an unknown perpetrator, in cases where there was significant material damage. Namely, mostly the perpetrators who are charged with the most serious crimes against the security of computer data, are members of organized criminal groups, “operate” from various locations in the world and are practically uncatchable. One of CERT’s tasks is to collect relevant information on computer fraud crimes, among others, as well as planning future protection mechanisms and legal regulation.
The Law on Information Security in the Republic of Serbia represents a significant step in the direction of harmonization with European standards. This Law more closely regulates the necessary protection measures against security risks in ICT systems, considers and prescribes the responsibilities of legal entities in the management and use of information and communication systems, and determines the competent authorities for the implementation of prescribed protection measures.
The negative aspect of the adopted Law on Information Security is reflected in the fact that it does not provide enough transparency regarding key data on ICT systems of particular importance. The idea that the entire records of ICT operators of special importance should be secret may seem like an excessive measure, however, it is necessary to make specific technical information publicly unavailable, in order to prevent misuse.
The establishment of the Information Security Office (ISO), which would include the National CERT, raises a number of questions related to political influence, transparency and available professional capacities. It is recommended that ISO must publish annual reports containing analyzes of the most significant incidents (like the National CERT), which would help monitor security trends over a longer period of time (Ministry of Innovation and Technological Development [MIT], 2023).
In the long term, the Law on Information Security should provide more effective supervision over the implementation of security regulations, over the work of the National CERT, special CERTs and private companies, because the current supervision system did not show the necessary level to achieve the desired results. Cooperation with key institutions, clearly defined consequences of unwanted criminal acts, the expertise of personnel and the developed awareness of citizens about potential security threats can also contribute to the effective implementation of the Law on Information Security.
We pay special attention to certain articles of the Law on Information Security, because they concern the National CERT and the powers that are defined and stipulated. The Law on Information Security envisages an important role for this institution in the coordination and protection of ICT systems in Serbia, as well as in the exchange of information on security risks and security incidents. National CERT is authorized to perform defined activities, including monitoring security incidents, providing early warnings, advising ICT system operators, as well as working to raise awareness among citizens and private organizations about the importance of information security (Information Security Law, 2016, Art. 15).
The National CERT is also responsible for establishing coordination with other CERTs in Serbia, as well as with similar organizations abroad, in order to ensure an effective response to incidents and exchange of information. Nowadays, it is necessary, through cooperation with domestic and foreign institutions (state and private), to establish the possibility of anticipating future incidents, using pre-tested response patterns and predictions based on past events. Also, the Law on Information Security stipulates the obligation to hold regular meetings between different CERTs in Serbia, in order to exchange information and coordinate activities related to the security of ICT systems (Information Security Law, 2016, Art. 15a).
The law provides for the supervision of the work of the National CERT, which is carried out by the competent authority, in order to ensure compliance with the predefined activities. Oversight is necessary to verify that CERT has adequate resources and responds in a timely manner, in the event of a security incident. The supervision of the work of this institution is of great importance, it enables transparency over the work of CERT and the use of resources, it allows citizens to have an insight into the results achieved by the National CERT and, perhaps most importantly, whether it fulfilled what was expected of it.
Independent operators of ICT systems are obliged to form their own CERTs, which perform tasks prescribed by internal acts, from the development of Procedures, Regulations, Plans, to mandatory employee training (Information Security Law, 2016, Art. 19).
The Law on Information Security was adopted in order to improve the ICT system protection system in Serbia. National CERT was created for the same reason. It is inevitable that the existing Law on Information Security needs to be amended (the amendment is planned), but considering that CERT was only recently established in the Republic of Serbia, many activities are largely covered by the Law on Information Security.
9. Concluding considerations
The National CERT (Computer Emergency Response Team) institution for responding to computer incidents in the Republic of Serbia plays a key role in protecting information systems and preventing cyber threats at the national level. National CERT’s mission is accomplished by coordinating cyber attack response activities, gathering and sharing information about security incidents, and providing timely guidance and notifications. Providing support to both state and private organizations is one of the basic tasks of the National CERT.
The aim and importance of this article is reflected in the research of the mechanisms of protection, prevention and reaction to security threats, with an emphasis on the importance of the CERT institution for the Republic of Serbia, the application of the Law on Information Security and raising the awareness of citizens on the protection of information security. The importance of this article is also reflected in the research of the existing mechanisms of protection, prevention and reaction to security threats, through the prism of the National CERT.
The organizational structure of the National CERT includes cooperation with similar security centers in the country and abroad, which enables efficient and timely exchange of critical information at all levels. It is important to note that the effectiveness of the National CERT may depend on several factors, including employee education, standardization of security incident management mechanisms, and cooperation with private and international partners and organizations. It is necessary to provide a sufficient number of experts, with the active participation of all employees in the company, in order to respond to potential threats and establish complete protection of information and information systems. The Law on Information Security of the Republic of Serbia lays the foundation for the efficient work of the National CERT institution, and its implementation enables activities to be harmonized with European and international standards.
The reports of the National CERT of the Republic of Serbia in the period from 2020 to 2023 provide a concise overview of the evolution of registered cyber threats, with an emphasis on different types of attacks and trends that developed during those years. In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic led to a significant increase in the number of attacks, especially on weak user passwords and access via VPN, which has become common due to the conduct of business activities from home. Phishing attacks, as well as attacks on user credentials, were among the most prevalent in 2021, while in 2022, the attacks became more diverse, but the key trends remained unchanged. In 2023, attacks via fake e-mails and links, especially in healthcare, banking and online commerce, were also in focus.
Although the Law on Information Security has given the necessary attention to the CERT institution, it is important to emphasize that the legislative framework should enable not only technical security, but through transparency, also influence the raising of citizens’ awareness of security incidents. Preservation of data confidentiality is an indispensable item in the Law on Information Security, while open communication and incident reporting would be essential to create long-term trust in the institution of the National CERT, as well as to improve the reaction and preparedness of all actors to future threats.
Effective oversight of the work of the National CERT and the private sector can help in preventive actions and responses to cyber attacks, as well as in the formation and implementation of harmonized legal frameworks to ensure accountability of all actors. Cooperation with relevant competent institutions and clear definition of legal consequences are key factors in maintaining security in information systems. Personnel training within the institution of the National CERT, political independence of the institution from possible external influences, are key to creating an effective system of protection against security threats in the Republic of Serbia.
Lešanović Milica
Univerzitet Privredna akademija u Novom Sadu, Pravni fakultet za privredu i pravosuđe u Novom Sadu, Novi Sad, Srbija


