The inflammatory status and lymph node metastases in non-small cell lung cancer
Автор: Pismenny Dmitry S., Savelieva Olga E., Zavyalova Marina V., Rodionov Evgeny O., Tashireva Liubov A., Tuzikov Sergey A., Pankova Olga V., Perelmuter Vladimir M.
Журнал: Сибирский онкологический журнал @siboncoj
Рубрика: Клинические исследования
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.19, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. The development of inflammation is characterized by changes in blood hematology parameters and indices. Various inflammatory parameters are used to assess the inflammatory status (iS) during cancer treatment. Recent studies have revealed a relationship between tumor progression and the presence of chronic inflammation. Consequently, there have been many attempts to predict the risk of tumor recurrence and distant metastases, as well as patient's survival assessing the various inflammatory markers. The relationship between iS parameters and lymph node metastasis remains poorly understood in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Material and Methods. The prospective study included 35 patients with NSCLC (T1-4N0-2M0). Seventeen patients received 2-3 cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC). A leukocyte formula was determined in the peripheral blood and inflammatory indices, such as neutrophils to lymphocytes ratio (NLR), platelets to lymphocytes ratio (PLR), lymphocytes to monocytes ratio (LMR) and systemic immuno-inflammatory index (Sii) were calculated. in addition, the concentrations of fibrinogen, C-reactive protein (CRP) and cortisol were evaluated. Results. NAC alone did not significantly change the parameters of patients' iS. Lymph node metastases were associated with changes in parameters indicating the enhanced iS. in the group of patients who did not receive NAC, lymph node metastasis was associated with fibrinogen blood levels (cut-off value 5.35 g/L), PLR index value (cut-off value 7.18) and cortisol blood concentration (cut-off value 414 nmol/mL). The confidence level was x2=10.118; р=0.018. in the group of patients who received NAC, lymph node metastasis was associated with the leukocyte count (cut-off value 7.1*109/L), PLR index value (cut-off value is 7.18) and CRP blood concentration (cut-off value is 8.5 mg/L). The confidence level was x2=8.193; р=0.042. Conclusion. Risk of lymph node metastasis in NSCLC is associated with iS. Parameters of iS can be used to predict the risk of lymph node metastases.
Non-small cell lung cancer, inflammatory status, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, lymph node metastasis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140254353
IDR: 140254353 | УДК: 616.24-006.6-002-033.2 | DOI: 10.21294/1814-4861-2020-19-3-54-63
Текст научной статьи The inflammatory status and lymph node metastases in non-small cell lung cancer
Chronic inflammation contributes to the onset and progression of the tumor (recurrence, metastasis). It has been shown that the chronic inflammation often precedes the development of some malignant tumors [1]. The focus of chronic persistent inflammation may be the site of the pre-niche formation [2], then the pre-metastatic niche [3] and, subsequently, metastasis. Additionally, it is known that surgical removal of a primary tumor is a stressor, on the one hand, and the cause of local inflammation and a source of pro-inflammatory factors on the other hand. Thereby, the risk of metastases and relapses in the early postoperative period is increased. The use of anti-inflammatory drugs during this period prevents their occurrence [4].
The term «inflammatory status» (IS) is rarely used. Inflammatory status is the state of the macroorganism characterized by elevated biochemical, cytokine, and cellular parameters traditionally associated with the development of inflammation and determined in peripheral blood. The counts of neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes and platelets, as well as their ratios – inflammatory indices (NLR [5, 6], PLR [7, 8], SII [9–11], LMR [12, 13] and others) are used as the parameters of IS.
It has been shown that the values of these inflammatory indices are associated with the patient’s survival in various types of cancer. Recently, there have been many attempts to predict the risk of recurrence and distant metastases, as well as patient’s survival after assessing the various inflammatory indices. The systemic immuno-inflammatory index (SII) is the most informative among these indices [10, 11]. However, it should be noted that the relationship between IS parameters and lymph node metastasis remains poorly understood.
Although inflammatory indices as well as the count of different forms of blood leukocytes characterize systemic IS, it is well known that all these parameters are sensitive to changes in the concentration of glucocorticoids and other hormones that reflect the general adaptation syndrome. In this regard, the level of IS indices simultaneously reflects the activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis [14, 15]. The patient’s IS parameters are influenced by the primary tumor, neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC), as well as the development of recurrence and metastases, which are inducers of the pro-inflammatory cytokine synthesis and other pro-inflammatory factors, on the one hand, and stressors, on the other hand.
The purpose of our study was to examine the relationship between the IS parameters and lymph node metastasis in NSCLC before and after NAC.
Material and Methods
The prospective study included 35 patients, male – 27 (77 %), female – 8 (23 %) with T1–4N0–2M0 NSCLC treated at Cancer Research Institute, Tomsk National Research Medical Center (tabl. 1). The study was approved by the Local Committee for Medical Eth- ics of our Institute, and informed consent was obtained from all patients prior to analysis. Seventeen (49 %) of the 35 patients received 2–3 courses of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (paclitaxel 175 mg/m2, IV day 1 + carboplatin AUC 6, IV day 1 with a 3-week interval). Dexamethasone was given to patients to reduce adverse reactions to paclitaxel + carboplatin. Patients were followed up for 5 years after treatment initiation.
The histological diagnosis of lung cancer was made according to «Histological classification of lung tumors» (WHO, Geneva, 2003). Squamous cell carcinoma was diagnosed in 20 (57 %) cases and lung adenocarcinoma was diagnosed in 14 (40 %) cases. Squamous cell carcinoma was more frequently observed in men (20 cases, 74 %). Adenocarcinoma was revealed in 7 women and mucoepidermoid carcinoma in 1 woman. Synchronous lymph node metastases were detected in 13 patients (37 %).
Venous ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) blood samples were taken 12 days before surgery, but not earlier than 23 weeks after the last course of NAC and glucocorticoids in the scheme «paclitaxel + car-boplatin». Indicators of the general blood test and the leukocyte formula, as well as the concentration of the
Таблица 1/Table 1
Клинико-патологические показатели пациентов с немелкоклеточным раком легкого
The clinicopathological parameters of the patients with the non-small cell lung cancer
|
Число больных |
|
|
Клинико-патологические показатели/ |
(n=35)/ |
|
Clinicopathological parameters |
Number of patients |
|
(n=35) |
All statistical analyses were performed in the GraphPad Prism version 8.3.0 (GraphPad Software, USA). The assessment of the normal distribution of the results was performed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. The significance was assessed using the nonparametric Mann–Whitney test (for independent samples). The data were presented as the median (Me) and the upper and lower quartiles (Q1–Q3). The logistic regression models were developed for predicting lymph node metastases. The threshold level of indicators was determined using ROC analysis for development of the logistic regression models. Two-sided p-values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant, p-values of ≤0.1 were considered as trends.
Results
The IS parameters were analyzed in patients with NSCLC before surgical treatment. The clinicopatho-logical parameters of the patients with NSCLC are presented in Tabl. 1. A tentative comparison of patients’ parameters with regard to the age, gender, and NSCLC type showed no statistical differences. This made it possible to exclude the influence of these parameters on the study results.
Effects of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on the IS parameters
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy did not cause significant changes in the IS parameters in patients with NSCLC regardless of the presence or absence of lymph node metastases (fig. 1).
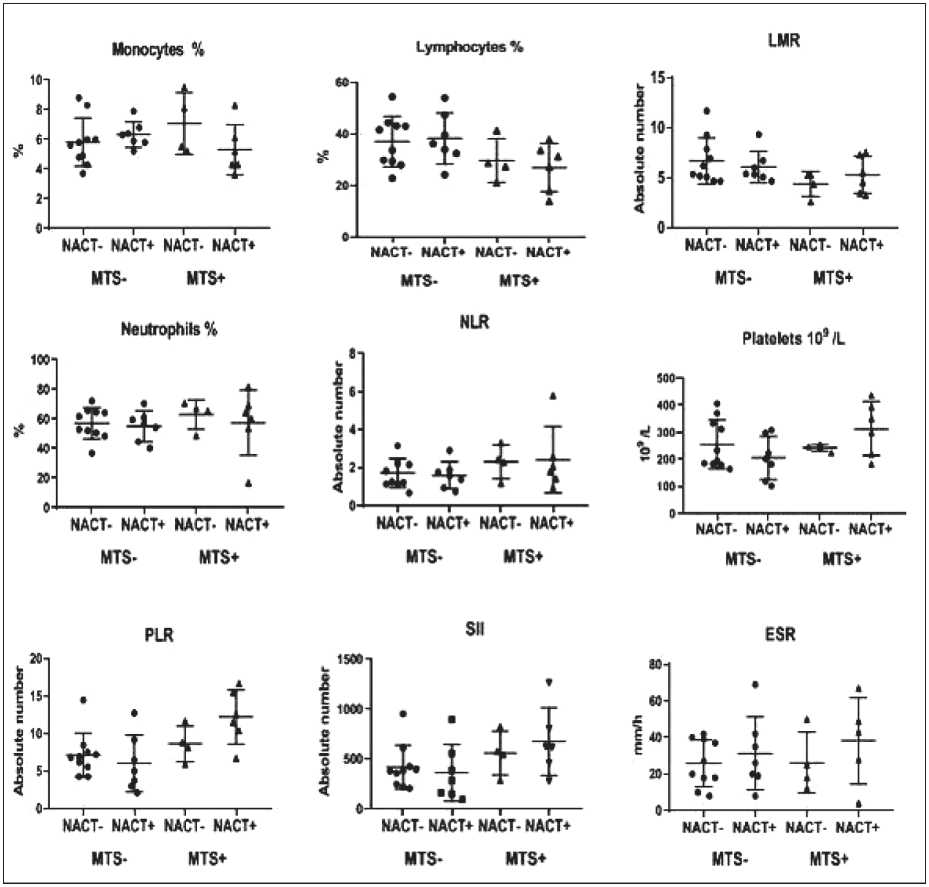
Рис. 1. Параметры воспалительного статуса у пациентов с НМРЛ с наличием или отсутствием метастазов в лимфатических узлах в зависимости от НАХТ
Fig. 1. IS parameters in NSCLC patients with presence or absence of lymph node metastases depending on NAC administration
Association of IS parameters with lymph node metastasis in patients without NAC
The relationship between the IS parameters and lymph node metastasis was analyzed in patients, who did not receive NAC before surgical treatment. Lymph node metastases in NSCLC patients were shown to be associated with decreased lymphocyte count (p=0.09) and LMR index (p=0.09) compared to patients without lymph node metastases (fig. 2). Besides, the neutrophil (p=0.1) and monocyte (p=0.1) counts and the NLR index (p=0.1) were tended to increase (fig. 2). The platelet count and PLR index, as well as the SII index and ESR (fig. 2) were not associated with the presence of lymph node metastases.
Thus, lymph node metastasis was associated with a strong trend towards enhanced IS, in which the lymphocyte count and the LMR index were decreased and the neutrophil count and the NLR index were increased. However, similar changes (drift in the lymphocyte and neutrophil ratio in favor of neutrophils) were also typical for the glucocorticoid effects.
Association of the IS parameters with lymph node metastasis in patients with NAC
After NAC, a strong trend towards decrease in the lymphocyte count (p=0.06) and increase in the platelet count (p=0.07) and SII index (p=0.08) was observed. The PLR index was significantly higher (p=0.02) in NSCLC patients with lymph node metastases compared to patients without lymph node metastases (fig. 3). Thus, IS parameters were higher in patients with lymph node metastases compared to patients without metastases regardless of NAC administration.
Prediction of lymph node metastasis in patients with NSCLC depending on the NAC administration
Differences in the IS parameters associated with lymph node metastases allowed us to use a multifactor analysis to predict NSCLC progression. The method of logistic regression revealed a complex of relationships between the studied parameters, which was associated with a high risk of lymph node metastases in patients with NSCLC. The logistic regression model also included parameters which did not differ in groups with the presence and absence of lymph node metastases after the Mann-Whitney test (tabl. 2). The cut-off value of indicators was determined using ROC analysis for development of the logistic regression
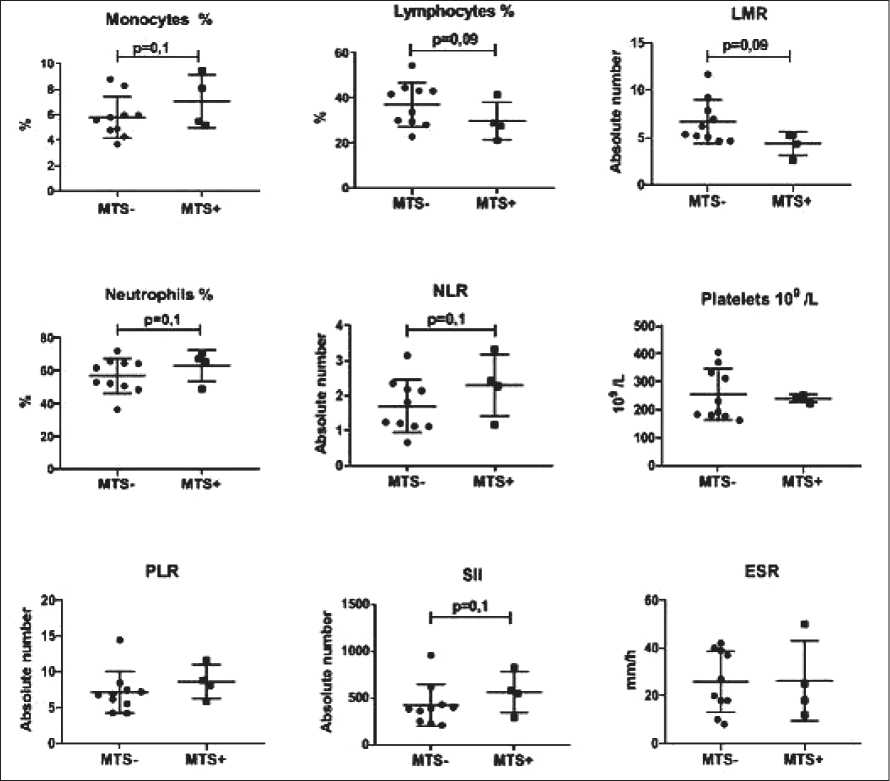
Рис. 2. Параметры ВС в зависимости от наличия метастазов в лимфатических узлах у пациентов с НМРЛ, которые не получали НАХТ Fig. 2. The IS parameters depending on the presence of lymph node metastases in NSCLC patients, who did not receive NAC
Таблица 2/Table 2
Концентрации СРБ, кортизола и фибриногена у больных НМРЛ в зависимости от метастазов в лимфатических узлах и НАХТ
The CRP, cortisol and fibrinogen concentrations in NSCLC patients depending on the lymph node metastases and NAC administration
|
Параметры/ Parameters |
НАХТ-/NAC- |
НАХТ+/NAC+ |
||
|
N- |
N+ |
N- |
N+ |
|
|
СРБ, мг/л/ CRP, mg/L |
5.6 (2.8–7.8) |
8.8 (4.5–9.1) р=0.8 |
6.3 (4.2–8.3) |
11.4 (4.7–18.0) р=0.7 |
|
Кортизол, nmol/L/ Cortisol, nmol/L |
403 (312–488) |
350 (307–364) р=0.3 |
387 (321–454) |
377 (231–524) р=0.4 |
|
Фибриноген, g/L Fibrinogen, g/L/ |
5.4 (4.7–6.8) |
5.4 (4.7–6.6) р=0.6 |
6.9 (5.7–7.0) |
6.5 (5.6–7.6) р=0.8 |
Таблица 3/Table 3
Площадь под кривой (AUC), пороговые значения, чувствительность и специфичность для параметров ВС у пациентов с НМРЛ
Area under curve (AUC), cut-off values, sensitivity and specificity for IS parameters in NSCLC patients
The leukocyte blood count (cut-off value: 7.1×109/L), PLR index value (cut-off value: 7.18) and CRP blood concentration (cut-off value: 8.5 mg/L) before surgical treatment were included in the logistic regression model for patients with NAC administration. Regression model confidence level was χ2=8.193; р=0.042. The sensitivity of this model was 100 %, the specificity was 100 %.
Discussion
The levels of different leukocyte forms and inflammatory indices, such as CRP, fibrinogen and ESR are a combination of parameters characterizing the IS. In recent years, an increasing number of studies have shown a relationship between inflammatory indices and cancer progression [5, 6, 9–13]. Based on these data, some inflammatory indices are recommended as the prognostic factors of carcinoma progression [16, 17].
The IS parameters reflect not only the influence of various factors that can cause inflammation, but also a variety of stressful effects. Our data indicate that changes in the studied IS parameters in NSCLC are associated with lymph node metastases and NAC. Moreover, each of these factors simultaneously has a potential pro-inflammatory and a stressor effect that changes the concentration of adaptive hormones, including cortisol.
The results of our study suggest that lymph node metastasis is associated with a more pronounced level of IS. This is confirmed by changes in the studied parameters, indicating the enhanced IS in patients who did not receive NAC. Apparently, the stress plays a significant role in the mechanism of changes in pro-inflammatory markers. This may explain why the cortisol concentration, along with other parameters, was included in the regression model for predicting lymph node metastases in NSCLC patients who did not receive NAC; and the total leukocyte count was included in the prediction model in patients who received NAC. Changes in the leukocyte count, if they are not associated with a clinically inflammatory process, may be explained by glucocorticoid effects. An increase in the leukocyte count in this case is due to an increase in the neutrophil count [16, 18].
The influence of NAC on the IS parameters is ambivalent. On the one hand, preoperative chemotherapy
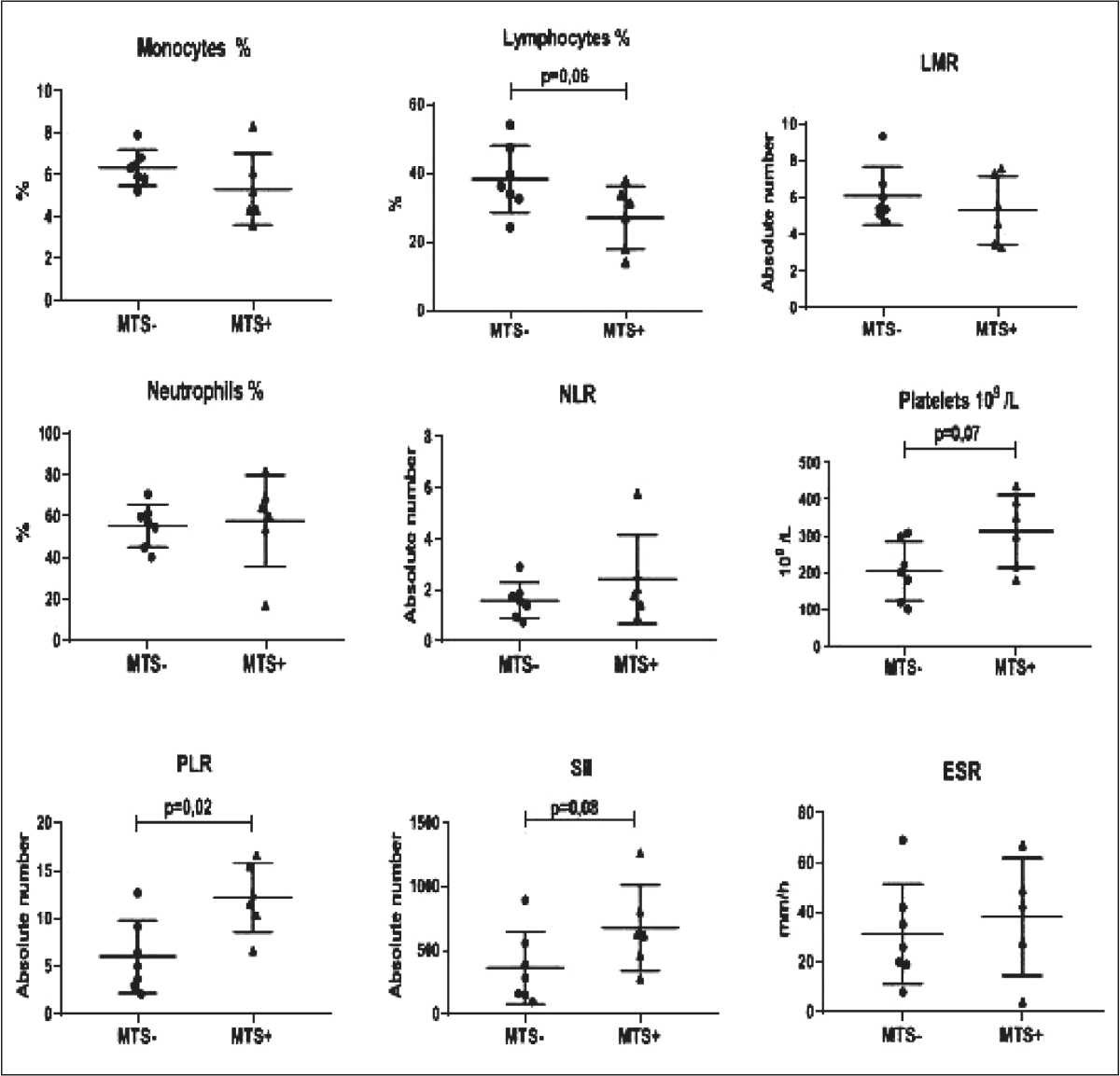
Рис. 3. Параметры ВС у пациентов с НМРЛ в зависимости от наличия метастазов в лимфатических узлах после НАХТ Fig. 3. The IS parameters in NSCLC patients depending on presence of the lymph node metastases after NAC
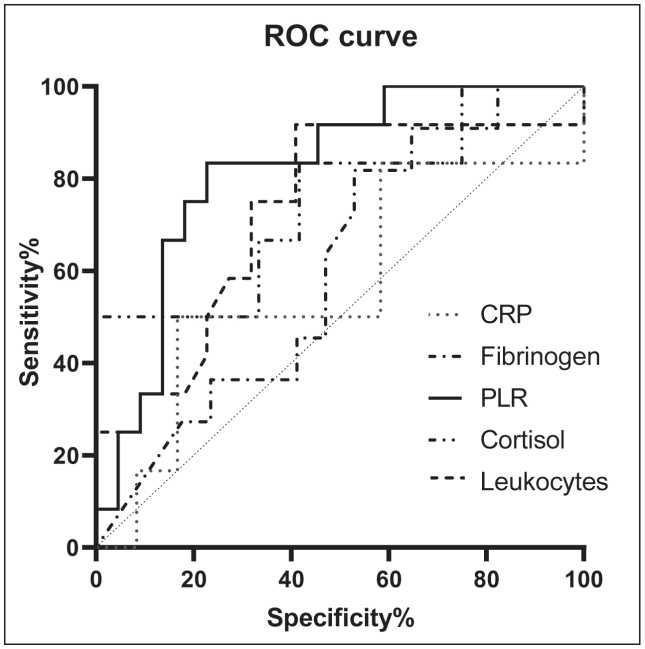
Рис. 4. Кривая ROC демонстрирует AUC параметров ВС у пациентов с НМРЛ
Fig. 4. ROC curve demonstrates AUC of parameters of IS in NSCLC patients
does not cause significant quantitative changes in the studied IS factors. On the other hand, there are no significant differences in the values of the IS indices associated with the lymph node metastases in patients treated with NAC. These results indicate that NAC has a significant impact on the processes underlying the regulation of the studied IS parameters.
Conclusion
The IS parameters are integral values associated with lymph node metastasis and NAC in patients with NSCLC. The presence of synchronous lymph node metastases in NSCLC can be predicted using mathematical models based on the appropriate IS parameters before surgical treatment. To predict the presence of lymph node metastases in patients treated and not treated with NAC, different prognostic models have been developed. Further studies are needed to clarify the contribution of inflammation itself and stress changes into the IS parameters.
Список литературы The inflammatory status and lymph node metastases in non-small cell lung cancer
- Candido J., Hagemann T. Cancer-related inflammation. J Clin Immunol. 2013 Jan; 33 Suppl 1: S79-84. doi: 10.1007/s10875-012-9847-0.
- ПерельмутерВ.М., МанскихВ.Н. Прениша как отсутствующее звено концепции метастатических ниш, объясняющее избирательное метастазирование злокачественных опухолей и форму метастатической болезни. Биохимия. 2012; 77(1): 130-139. [Perelmuter V.M., Manskih V.N. Preniche as missing link of the metastatic niche concept explaining organ-preferential metastasis of malignant tumors and the type of metastatic disease. Biochemistry. 2012; 77(1): 130-139. (in Russian)]. doi: 10.1134/ S0006297912010142.
- Barcellos-Hoff M.H., Lyden D., Wang T.C. The evolution of the cancer niche during multistage carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Jul; 13(7): 511-8. doi: 10.1038/nrc3536.
- Retsky M., Demicheli R., Hrushesky W.J., Forget P., De Kock M., Gukas I., Rogers R.A., Baum M., Pachmann K., Vaidya J.S. Promising development from translational or perhaps anti-translational research in breast cancer. Clin Transl Med. 2012 Aug 28; 1(1): 17. doi: 10.1186/20011326-1-17.
- Zhao Z., ZhaoX., Lu J., Xue J., Liu P., MaoH. Prognostic roles of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio in ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis of retrospective studies. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2018 Apr; 297(4): 849-857. doi: 10.1007/s00404-018-4678-8.
- YuX., Wen Y., Lin Y., ZhangX., Chen Y., Wang W., Wang G., ZhangL. The value of preoperative Glasgow Prognostic Score and the C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio as prognostic factors for long-term survival in pathological T1N0 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer. 2018 Feb 12; 9(5): 807-815. doi: 10.7150/jca.22755.
- Chen S., Guo J., Feng C., Ke Z., Chen L., Pan Y. The preoperative platelet-lymphocyte ratio versus neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: which is better as a prognostic factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma? Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2016 May; 8(3): 160-7. doi: 10.1177/1758834016638019.
- SunH., Yin C.Q., Liu Q., WangF., Yuan C.H. Clinical Significance of Routine Blood Test-Associated Inflammatory Index in Breast Cancer Patients. Med Sci Monit. 2017 Oct 25; 23: 5090-5095. doi: 10.12659/ msm.906709.
- Feng J.F., Chen S., YangX. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) is a useful prognostic indicator for patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96(4): e5886. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005886.
- Geng Y., Shao Y., Zhu D., Zheng X., Zhou Q, Zhou W, Ni X., Wu C., Jiang J. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Predicts Prognosis of Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Propensity Score-matched Analysis. Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 21; 6: 39482. doi: 10.1038/ srep39482.
- Ma M., Yu N., Wu B. High systemic immune-inflammation index represents an unfavorable prognosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Manag Res. 2019 May 2; 11: 3973-3979. doi: 10.2147/CMAR. S201269.
- Stotz M., Pichler M., Absenger G., Szkandera J., Arminger F., Schaberl-MoserR., SamoniggH., Stojakovic T., GergerA. The preopera-tive lymphocyte to monocyte ratio predicts clinical outcome in patients with stage III colon cancer. Br J Cancer. 2014 Jan 21; 110(2): 435-40. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.785.
- Chan J.C., Chan D.L., Diakos C.I., Engel A., Pavlakis N., Gill A., Clarke S.J. The Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio is a Superior Predictor of Overall Survival in Comparison to Established Biomarkers of Resectable Colorectal Cancer. Ann Surg. 2017 Mar; 265(3): 539-546. doi: 10.1097/ SLA.0000000000001743.
- СельеГ., СаармаЮ.М., ЛукаА.Н., ХоролИ.С. Стресс без дистресса. М., 1979. 126 с. [Selye H., Saarma Ju.M., Luka A.N., Horol I.S. Stress without Distress. Moscow, 1979. 126 p. (in Russian)].
- Гаркави Л.Х., Квакша Е.Б., Уколова М.А. Адаптационные реакции и резистентность организма. Ростов-на-Дону, 1990. 256 с. [Garkavi L.H., Kvakina E.B., UkolovaM.A. Adaptation reactions and body resistance. Rostov-on-Don, 1990. 256 p. (in Russian)].
- Karagiannis G.S., Pastoriza J.M., Wang Y., Harney A.S., Entenberg D., Pignatelli J., Sharma V.P., Xue E.A., Cheng E., D'Alfonso T.M., Jones J.G., Anampa J., RohanT.E., Sparano JA., Condeelis J.S., OktayM.H. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy induces breast cancer metastasis through a TMEM-mediated mechanism. Sci Transl Med. 2017 Jul 5; 9(397): eaan0026. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aan0026.
- Zhang Y., Xiao G., Wang R. Clinical significance of systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) and C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio (CAR) in patients with esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer Manag Res. 2019 May 7; 11: 4185-200. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S190006.
- Shoenfeld Y., Gurewich Y., Gallant L.A., Pinkhas J. Prednisone-induced leukocytosis. Influence of dosage, method and duration of administration on the degree of leukocytosis. Am J Med. 1981 Nov; 71(5): 773-8. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90363-6.


