The new economic crisis: a regional projection
Автор: Olga Р. Sushko, Nikolay B. Telegin
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Economics, political science, society and culture
Статья в выпуске: 21, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The economic situation in Russia continues to worsen because of multiple factors. Analysis of the economic situation of the Arkhangelsk region 1999—2015 reveals an earlier manifestation of the negative effects of economic recession. Currently, the crisis is manifesting itself in the reduction of investment, increase in unemployment rates, fluctuations of prices for some industrial products. The forecast for the end of the year 2015 and for 2016 is not encouraging also.
Еconomy, crisis, Arkhangelsk region, the processing industry, the prices, the dynamics of trade, investments
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148318690
IDR: 148318690 | УДК: 338.12.017 | DOI: 10.17238/issn2221-2698.2015.21.70
Текст научной статьи The new economic crisis: a regional projection
The economic situation in Russia remains tense. Several reasons cause the economic crisis and lead to its consequences. Low oil prices in the world market, the declining exchange rate of the ruble against the major currencies, the economic sanctions of the West and the response of the Russian food embargo, falling stocks of leading Russian companies on the stock exchange, the credit policy of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, the political conflict between Russia and Ukraine and other determinants exacerbate ongoing recession. But is the economic situation in the country and in its regions so heavy and what might be called a crisis situation?
The relevance of this topic has been identified an objective of the study, which is the analysis of the current state of the economy of the Arkhangelsk region. In this article we will look at the economic situation in the Arkhangelsk region, operating the actual data over a long period, since 1999. Also we intend to present a more detailed analysis of statistical indicators of recent years (2009-2015), because it is the time of an economic recovery between the last crisis periods.
The object of study is the economy of the Arkhangelsk region, which is a key area for mathematical methods of analysis, based on accurate baseline data, measurement and evaluation.
Results of the study
Let's start with the fact that the economic situation does not develop according to the rules, which were common for the past crises of 1998 and 2008—2009, when the impact on the economy was strong, but relatively short. First of all, the crisis has a negative impact on the development of the industry, and the volume of production in key sectors. The opposite effect was observed during the crisis in 2014, when industrial production in Russia grew by 1.7%. This growth was ensured by the release of manufacturing industries, which helped the devaluation and the empowerment of import substitution. But if Russia’s industrial production has a positive dynamics, the Arkhangelsk region and its manufacturing sector has opposite dynamics (Pictures 1 and 2). Thus, the production of building materials and products for machine-building industry has a positive trend dynamics of production from 2009 to the first quarter of 2015. The situation is different in the wood industry where the output began to slow even before the last crisis. In 2012 the output fell by 7% compared to 2011. On the contrary, in 2014 the volume of manufacture of timber was growing in comparison to 2013.
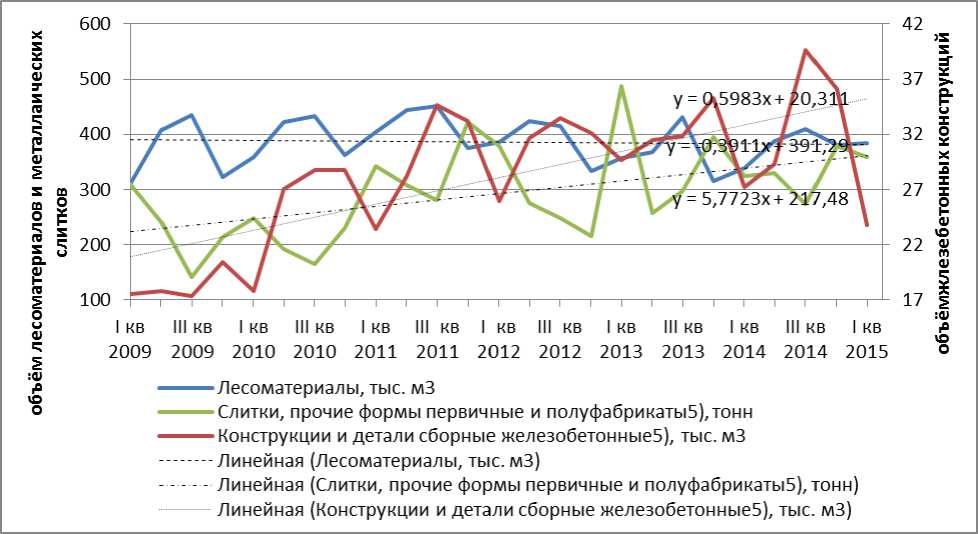
Picture1. Quarterly dynamics of industrial production combined with a projection for 4 quarters in Arkhangelsk region URL: (Accessed: 02 June 2015).
The same dynamics is in food industry.
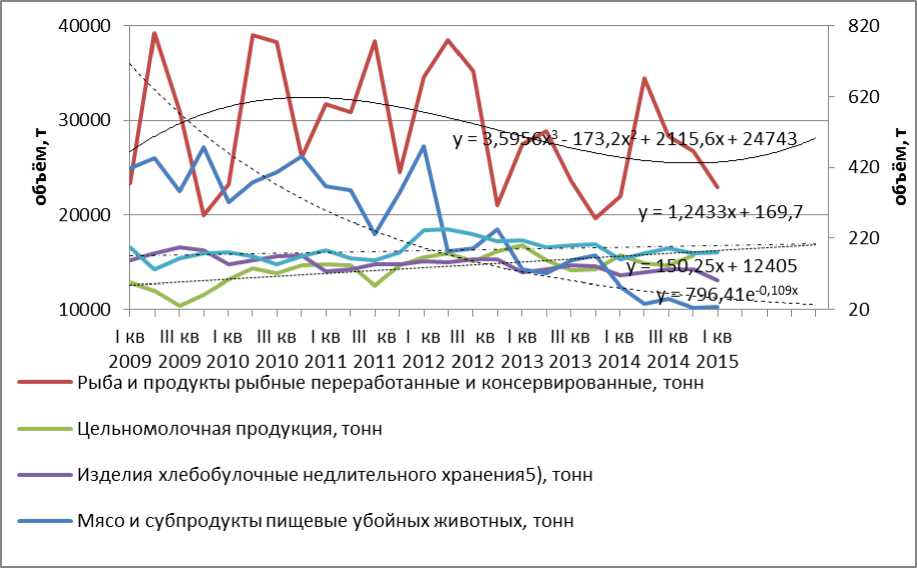
Picture 2. Quarterly dynamics of food production combined with a projection for 4 quarters in Arkhangelsk region URL: (Accessed: 02 June 2015).
The increase in output in 2014 is observed in the milk production (+ 1.2% compared to 2013) and fishing (+ 12.1%). Release of bread and bakery production in 2014 was by 4%, but this decrease was observed in 2013 (5%) as well and it cannot be linked to the causes of the crisis 2014—2015. Sad is the situation with the production of meat (Table 1), where the decline in output is taking place during the last six years. In 2013, the output of meat processing industry fell by almost 2 times in comparison with 2012, and in 2014 — by 3 times to the level of 2013.
-
Table 1
Food production in Arkhangelsk region
|
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
|
|
Meat and sub-products, tons |
1 695 |
1 557 |
1 302 |
1 100 |
580 |
195 |
|
Fish and fish products, tons |
113 551 |
126 663 |
125 486 |
129 281 |
99 542 |
111 614 |
|
Milk products, tons |
46 867 |
55 811 |
56 439 |
62 650 |
60 149 |
60 878 |
|
Bread and bakery products of a long |
63 822 |
61 208 |
57 609 |
60 470 |
571 334 |
55 951 |
|
term storage, tons Bread and bakery products of a short term storage, tons |
665 |
665 |
688 |
929 |
813 |
707 |
Source: Arkhangelsk Regional Statistic Service.
The trend dynamics of prices for industrial products and food industries, observed since 1999, shows periodic fluctuations, but the overall trend component is negative and shows a significant increase in producer prices in 2014 — 20151 (Pic. 3).
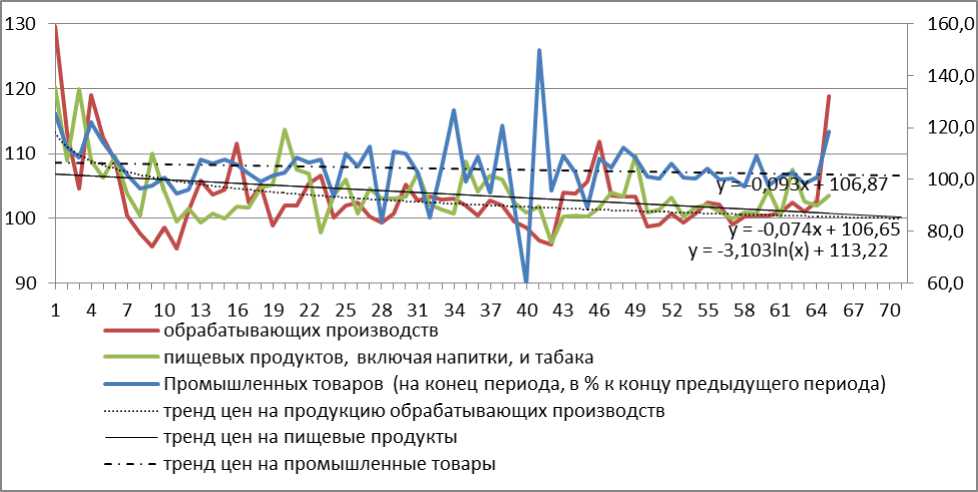
Picture 3. Dynamics of prices for processing industry and food industry products in Arkhangelsk Region 1999—2015 URL: (Accessed: 02 June 2015).
Most likely, a significant increase in prices in 2015 will be fixed in the final product in the trading industry and products in a subsequent period if the economy continues to stagnate. But the outlook for inflation done by the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Economic Development is very positive and diverge slightly (10—11.5% and 11.9%, respectively). In contrast, producer prices and consumer prices increased significantly in 2014. Thus, in December 2014 the index of food prices was 119.9%, non-food products — 108.7%, services — 110.8%2.
During the 2013—2015 business of the Arkhangelsk region had a positive dynamics of development in spite of the crisis and strengthening stagnation of the Russian economy. In 2014 retail trade turnover increased by 3.2% compared to 2013 and was 200,5 billion rub. The favorable situation is important for the regional economy, as the share of the trade in the structure of the gross regional product of the region and it is 11.7%3. At the same time the financial position of the majority of enterprises remains stable. Approximation of data on the volume of trade in the Arkhangelsk region shows a positive trend for the next year.
Thus, in general we can speak about the absence of the catastrophic situation in the industry of the Arkhangelsk region in 2014-2015 and an earlier manifestation of the negative effects of the recession. One could enjoy the results established in the industrial production output, growth of trade turnover, small fluctuations in prices for products of various industries, but all are interested in what should be expected in the short term. The food industry and export of raw materials will benefit from the devaluation, the fall may occur, but it will be more moderate. It is much harder to have less competitive sectors, particularly engineering, agriculture and innovative industry that will suffer more as it had happened in 2008 [1]. As for keeping the positive results or the negative correction position, investments and technologies continue to decline or remain inaccessible, and the demand for the products is compressed due to falling incomes, which will inevitably lead to a decrease in consumption.
We summarize that “proper crisis” is characterized by reduced capital investment, budget and incomes. Statistics also show that a new crisis 2014 did not cause a global impact on the money of the region: the budget, investments and income. It is typical for the Arkhangelsk region, but for the other regions of Russia the situation is different. Economic situation in areas of Russia is different due to a number of objective reasons [2, p. 221]. In those regions a destabilization of the budget, and it should be noted, began not in the past crisis year, but in 2012—2013, when profits of tax revenues and federal transfers had reduced. Therefore, in 2013 the deficit of regional budgets came up to 642 billion rub or almost three times, and “by the end of December 2014 the total regional debt was 2.1 trillion rubles4 and reached 1/3 of profits of the regions (without transfers). A half of the regions has more debts — 50—130% of their profits. Only the richest regions (Moscow, Tumen and Sakhalin regions, oil extraction autonomous districts) are able to provide a balanced budget policy” [3]
Analyzing the economic results of the Arkhangelsk region in 2014, we see a different situation: the increase in tax revenues from the organizations by 9% compared with 2013, and from individuals by 6% (Pic. 4). But if the dynamics of income from taxes of individuals in 1999 is positive, the companies paid taxes evenly. The strong decline occurred there in 2013 (11% compared with 2012).
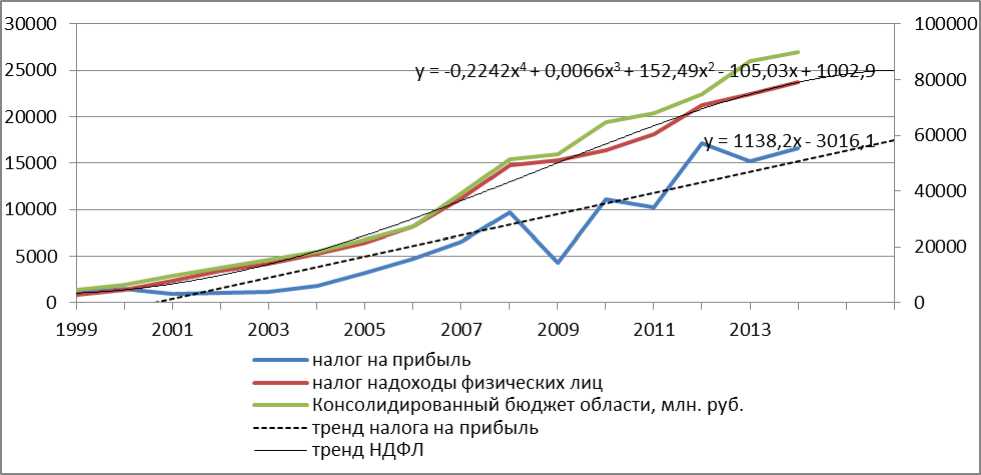
Picture 4. Arkhangelsk Regional budget 1999—2015.
URL: (Accessed: 02 June 2015).
The investments in fixed capital, which is essential for intensive and extensive economic growth, got a decline since 2013 manifested in stagnation before the impact of the latest crisis factors. So, in 2013, the decline in investment was 3% compared with the previous period, and in 2014 — 6% (Table 2). According to macroeconomic analysts, the decline in investment in the Russian economy will grow 5, and, therefore, the national industry will continue to go on reduction of output and productivity.
-
Table 2
Investments in fixed capital of the Arkhangelsk Region6
|
Year |
Investments in fixed capital, mln. rub. |
Changes to the previous period, % |
Year |
Investments in fixed capital, mln. rub. |
Changes to the previous period, % |
|
1999 |
4 018 |
2007 |
130 642 |
147,8 |
|
|
2000 |
10 471 |
260,6 |
2008 |
145 622 |
111,5 |
|
2001 |
15 114 |
144,3 |
2009 |
74 284 |
51,0 |
|
2002 |
23 809 |
157,5 |
2010 |
99 686 |
134,2 |
|
2003 |
28 629 |
120,2 |
2011 |
134 722 |
135,1 |
|
2004 |
32657 |
114,1 |
2012 |
162 514 |
120,6 |
|
2005 |
47 710 |
146,1 |
2013 |
157 276 |
96,8 |
|
2006 |
88 413 |
185,3 |
2014 |
148 129 |
94,2 |
Source: Arkhangelsk Regional Statistic Service.
And first of all it will affect regions with low investment attractiveness. Arkhangelsk region has a low investment grade rating, which means that we should expect an even greater decline in investment, followed by the decline in industrial production.
Crisis in the economy is always accompanied by rising unemployment and poverty. So in crisis years 1998 and 2008 the unemployment rates grew up by 2 times7. Contemporary crisis employment and unemployment may not be clearly revealed in statistics due to demographic sitation. Reduction of the workforce in Russia could be invisible for a long time due to declining birth rates and a growing population of retirement age, leveled migratory influx and cheap labor from the CIS countries. The labor market of the Arkhangelsk region is characterized by long-term negative trends, increase in the unemployment rate, which emerged much earlier than the effects of the crisis. Reducing the number of employed people in our area has been observed since 2006. The unemployment rate, after its minimum in 2012, is constantly increasing, and in 2014 it had reached 44.3 thousand people (Pic. 5). Thus, the unemployment rate in the Arkhangelsk region in 2014 exceeded the value of 7%, which is significantly higher than the average unemployment rate in Russia (4.8%)8.
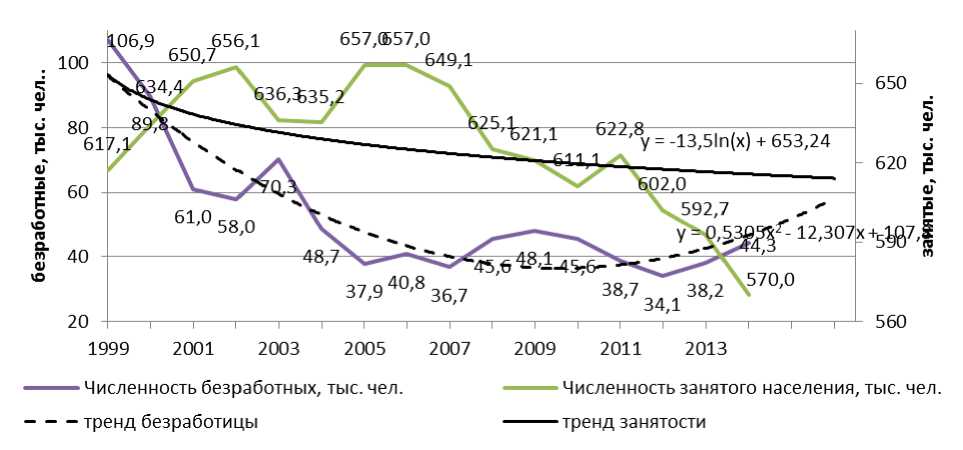
Picture.5. Employed and unemployed people in the Arkhangelsk Region 1999 - 2015 URL: (Accessed: 02 June 2015).
Conclusion
The statistical analysis showed the expectation of a strong downturn in the economy of the Arkhangelsk region in 2014-2015 years had failed to materialize, although there had been tension in the investment development of the region.
Reduction of the number of employed population in the region continues over the past fifteen years and it is not associated with a new economic crisis. The present economic crisis is of a different character, it is going to be slow and long.
Studying the economic dynamics of the region 1999—2015, we see that the causes of economic stagnation are much deeper. Overlay of numerous factors and their impact on institutional changes in the economy may lead to more negative effects of the crisis with a deferred time lag.
Therefore, an innovative program of economic transformation aimed at the development of modern infrastructure (technology parks, industrial platforms, and clusters), the introduction of tax holidays for less competitive and protected from imports industries and special conditions for the regions are in demand.
However, the positive changes in the dynamics of the main determinants of the crisis have not yet been seen. Consequently, economic growth and the positive economic and social development in the 2015-2016 should not be expected. Some weakening in the development of the crisis is possible by the end of 2015 and it is well seen in slowing rates of inflation and reduced consumption.
Список литературы The new economic crisis: a regional projection
- Krizisnaya ekonomika sovremennoj Rossii: tendencii i perspektivy / E.T. Gajdar. M.: Prospekt, 2010. 656 p.
- Korchagin Yu. A. Sovremennaya ekonomika Rossii / Yu.A. Korchagin.2e izd., dop.i pererab. Rostov n/D.: Feniks, 2008. 670 p.
- Zubarevich N. Krizis v regionakh: nastalo vremya platit za «Krymnash». URL: https://slon.ru/insights/1218531/ (Аccessed: 14.09.2015).
- Aganbegyan A. Krizis. Beda i shans dlya Rossii. M.: AST, 2009.


