The photocatalytic activity of cement-sand plaster under the influence of natural solar radiation
Автор: Dudareva M.O., Kozlova I.V., Zemskova O.V., Borisenkov N.S.
Журнал: Nanotechnologies in Construction: A Scientific Internet-Journal @nanobuild-en
Рубрика: The results of the specialists’ and scientists’ researches
Статья в выпуске: 2 Vol.17, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. Concrete and cement composites can be considered as the most demanded and versatile building materials nowadays. Recently, photocatalytic building materials containing nano- and finely dispersed oxides and salts photocatalyst particles, especially titanium dioxide of anatase modification, are becoming widespread. Under the influence of light, the surface of these materials becomes capable of self-cleaning. The materials photocatalytic activity is usually determined in the laboratory conditions by irradiating samples with an artificial source of light with certain wavelength, which does not fully characterize the behavior of the material in real-life conditions. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to evaluate the photocatalytic activity of cement-sand plaster samples under natural solar radiation. Materials and methods of research. In this study, the properties of cement-sand plaster modified with an additive of industrial TiO2 were studied. The additive was introduced into the plaster compositions in amounts of 0.3; 1.0; 1.7; 3.0; 5.0 and 10.0 wt.% during the dry mixing of the components. At the first stage, the effect of the additive on physical and mechanical properties of the samples was investigated. The second part of the research is devoted to the study of the photocatalytic properties of the material. Mineralization of the model pollutant Methylene blue was carried out in real-life conditions under sunlight irradiation, the photocatalytic activity of the samples was evaluated in accordance with the European standard UNI 11259-2016. Results and discussion. As a result of the study, the authors found that the maximal increase in compressive and flexural strength corresponds to the sample with 5.0 wt.% of TiO2, and the maximum degree of Methylene blue decomposition corresponds to the sample with 10.0 wt.% of TiO2. Thus, compressive strength increases by 69% at 2 days age, by 58% at 7 days age, and by 50% at 28 days age compared to the control sample. Flexural strength increases by 10, 13, and 50% at 2, 7, and 28 days age, respectively. The strength of the samples with 10.0 wt.% of TiO2 remains approximately at the level of the control sample. Compositions with TiO2 starting from 3 wt.% demonstrate photocatalytic activity (R), the highest R corresponds to 10 wt.% sample with R value is 40–78%. It is also noticeable that the maximum Methylene blue mineralization (58–78%) is observed after 2 days of sunlight irradiation, after 7 days there is a significant decrease in the degree of pigment decomposition. Conclusion. As a result of the research, the authors concluded that the optimal amount of TiO2 photocatalyst in the cement-sand plaster is 5.0–10.0 wt.% since these samples exhibit maximum strength characteristics combined with a high ability of model contaminant degradation.
Cement plaster, photocatalytic activity, industrial titanium oxide, anatase, sunlight irradiation, mineralization, Methylene blue
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142243955
IDR: 142243955 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2025-17-2-179-188
Текст научной статьи The photocatalytic activity of cement-sand plaster under the influence of natural solar radiation
Original article
Дударева М.О., Козлова И.В., Земскова О.В., Борисенков Н.С. Фотокаталитическая активность цементно-песчаной штукатурки под воздействием естественного солнечного излучения. Нанотехнологии в строительстве. 2025;17(2):179–188. https://doi. org/10.15828/2075-8545-2025-17-2-179-188. – EDN: XBEDTX.
The increase in the construction industry involves the creation of innovative multifunctional building materials. Research in the field of building materials science include the introduction of nanotechnology, the develop- ment of smart materials and structures with self-cleaning and self-restoring properties. The key role in the modern world is assigned to the problems of ecology and energy saving, occuring during the production and functioning of building materials and constructions. Special attention is paid to environmental aspects that affect the creation of
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS AND SCIENTISTS RESEARCH comfortable conditions in large cities with high pollution level [1–3].
One of the solutions to existing problems is the creation of photocatalytic building materials by adding photocatalysts particles into the composition of traditional building materials. Under the influence of natural solar radiation photocatalytic oxidation of organic and inorganic pollutants adsorbed on the surface occurs, as well as viruses, spores of microscopic fungi, algae and lichens. Photocatalysts can be used to modify building materials of various structure and origin, especially glass and cement compounds. In addition, particles of semiconductor oxide photocatalysts makes the surface of the material hydrophilic. Consequently the surface remains clean longer since pollutant molecules and their oxidation products are easily rinsed by rainwater [4–10].
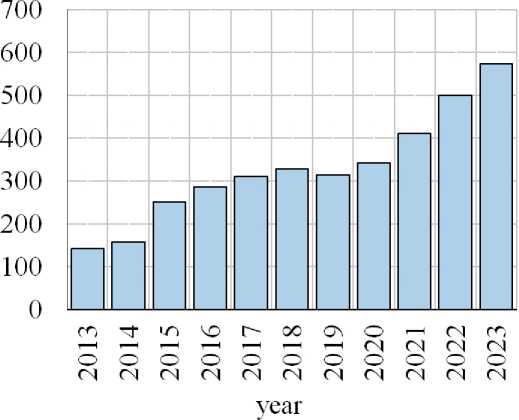
Obviously, the modification of traditional building materials by photocatalysts can be considered as a large field of research in building materials science. This is confirmed by the increasing amount of published scientific articles, conference papers, dissertations and patents on the subject of photocatalysis process research in accordance with Russian Scientific electronic Library «elibrary» database (Figure 1).
The most common photocatalyst is titanium dioxide of anatase modification. Powdered TiO2 has been widely used as a white pigment for centuries because it is cheap, chemically stable and nontoxic. However, scientists and engineers are constantly finding new applications for titanium dioxide: in the 1980s, it was first used for the photocatalytic production of hydrogen. In the late 1990s, photocatalysis was discovered and the ability of polycrystalline TiO2 films to change the contact angle under the ultraviolet irradiation was discovered. Next TiO2 was also used in construction to create materials with a self-cleaning effect due to the photocatalytic oxidation of pollutants adsorbed on the surface (Figure 2) [11–12].
Photocatalysis mechanism for semiconductor photocatalysts, such as titanium dioxide, has been described in details in Russian and foreign literature [13–15]. When a TiO2 particle is irradiated with UV light, electrons in the valence band are activated and transferred to the conduction band to form electron-hole pairs. The electron and the electron vacancy then diffuse to the surface of the TiO2 particle and promote oxidation-reduction reactions with the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can further react with adsorbed pollutants, bacteria and viruses, decomposing them into harmless compounds. TiO2 belongs to wide-bandgap semiconductors with a band gap of 3.2 eV: this means that ROS formation occurs only at radiation wavelength less than 400 nm, that is, in the ultraviolet part of the spectrum.
The self-cleaning ability is especially relevant for finishing materials. The most popular are facade plasters based on white cement, where it is crucial to maintain surface whiteness and to prevent biofouling. In this case, the best solution would be to introduce a photocatalyst additive into plaster composition.
The most well-known photocatalyst nowadays is the nanostructured TiO2 Degussa P25, which is a mixture of anatase and rutile at 20–30% [16, 17]. However, due to its high price and inaccessibility in the Russian Federation, it is necessary to search for alternative additives. In this
-sung〈qsaibboo 一 oqd》 * uo su£w一qnd jo JDqmnu
Fig. 1. Publication activity on the «photocatalyst» request in the Russian Scientific electronic Scientific Library «elibrary» database
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS AND SCIENTISTS RESEARCH

materials production: paints, rubber, paper industry widespread

cheap chemically stable
T1O2
air purification water decomposition designing of sef-cleaning materials (glass, concrete, coatings)
wtocatalyst prevents bio fouling
non toxic

food industry, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics
Fig. 2. TiO2 application work the authors chose industrial titanium oxide TiO2 (anatase) TA-100 manufactured in China.
Industrial photocatalysts are usually highly dispersed powders that are introduced into dry building mixes during the dry mixing of components or as a suspension instead of mixing water. In order to achieve self-cleaning effect, it is necessary to introduce a photocatalyst into the cement composition up to 1–10 wt.%, which affects physical, mechanical and structural properties of modified cement material [18–20]. Thus, one of the objectives of this work was to study the influence of the TiO2 additive on the mobility and strength characteristics of cementsand plaster samples. The photocatalytic activity of the samples was also determined as part of this study. The simplest and most visual methods for assessing R of the modified materials is the European standard UNI 112592016 [21], based on fixing the discoloration process of the organic pigment Rhodamine B applied to the surface of the samples after 4 and 26 hours of irradiation from a light source with a certain wavelength. However, a number of studies indicate the possibility of using other organic dyes, such as, methylene blue, malachite green, methyl orange, etc. [22–24]. Samples can be considered photo-catalytically active if the degree of model contaminant decomposition after 4 and 26 hours of exposure exceeds 20% and 50% respectively.
As a rule, study of photocatalytic activity are laboratory tests with an artificial source of light of certain wavelength not considering real-life conditions such as climate zone, temperature and illumination daily changes, clouds, precipitation, and the geographical location of the samples. In addition, the intensity of ultraviolet radiation depends on the local climate, but usually accounts for about 5.5% of global solar radiation. Thus, the behavior of self-cleaning plaster compositions modified by the photocatalyst at real-life conditions may differ significantly from the results obtained during the laboratory tests. Thus, another step in this study was to conduct real-life tests of cement-sand plaster modified with anatase TiO2 to assess its photocatalytic activity. The main task of the article was to determine the optimal TiO2 concentration capable of providing the highest strength and photocatalytic characteristics.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this work, to obtain samples modified with industrial titanium oxide, we used Cemix PRO WHITE cement PCB 1-500-D0 from Cemix LLC, its chemical and mineralogical composition is shown in Tables 1 and 2, white quartz sand of 0.1-0.4 mm fractions (Table 3). As a photocatalytic additive industrial anatase titanium oxide TiO2 TA-100 (China) was selected with characteristics presented in Table 4.
At first, it was necessary to determine W/C to prepare samples for the study of strength and photocata-lytic characteristics. For this purpose, the mobility of cement-sand mortar with TiO2 additive was determined according to GOST 310.4. Sand : cement ratio was 3:1 (mass), fine photocatalyst powder was added in amounts of 0.3; 1.0; 1.7; 3.0; 5.0 and 10.0 wt.%, the amount of mixing water corresponded to a consistency characterized by a cone spreading of 106-115 mm. Next, samples of a 40×40×160 mm were prepared from a cement-sand
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS AND SCIENTISTS RESEARCH
Table 1. Chemical composition of clinker
|
Component |
Oxide content, % |
|||||||
|
Calcination loss |
SiO 2 |
Al 2 O 3 |
Fe 2 O 3 |
CaO |
MgO |
SO 3 |
R 2 O |
|
|
Clinker |
1.0 |
21.0 |
5.5 |
0.5 |
65.0 |
1.0 |
3.3 |
0.1 |
Table 2. Mineralogical composition of clinker
|
Clinker |
Mineral content, % |
|||
|
C 3 S |
C 2 S |
C 3 A |
C4AF |
|
|
Content |
66.0 |
8.5 |
13.5 |
1.5 |
Table 3. Characteristics of sand
|
Bulk density, g/cm3 |
Specific density, g/cm3 |
Average grain size, μm |
Oxide content, % |
|||||||
|
1.403 |
2.637 |
235.23 |
Clay |
SiO 2 |
Al 2 O 3 |
Fe2O3 |
CaO |
MgO |
K 2 O |
TiO 2 |
|
0.10 |
99.857 |
0.130 |
0.026 |
– |
0.003 |
0.021 |
0.018 |
|||
Table 4. Characteristics of TiO 2
The ultraviolet index is an indicator adopted by the World Health Organization that characterizes the level of ultraviolet radiation in the spectrum of sunlight on the
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS AND SCIENTISTS RESEARCH
Table 5. Weather conditions during the photocatalytic activity test period: July 2024 according to World Weather /)
|
Parameter |
24.07 |
25.07 |
26.07 |
27.07 |
28.07 |
29.07 |
30.07 |
31.07 |
|
T, oC (day/night) |
+25/+12 |
+22/+14 |
+24/+14 |
+26/+12 |
+24/+15 |
+19/+16 |
+19/+13 |
+18/+13 |
|
Clouds |
0 |
… |
… |
”。:。 *u*® Л |
»%送 |
|||
|
UV-index |
6 |
4 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
3 |
Earth’s surface, takes values from 0 to 11 and shows the degree of danger to humans. The value of the UV index in this study is important, since the processes of photo-catalytic oxidation on the surface of TiO2 particles are promoted by UV irradiation. In our study, the values of UV index vary from medium to high with average value of 4.5, which corresponds to the average ultraviolet activity.
The photos of the samples were taken at initial time, after 4 and 26 hours, then once a day. The photos were processed using ImageJ software, which was used to convert the RGB color parameters into the LAB color model, where L is the brightness of the object; a is the axis with hues from red to green; b is the axis with hues from yellow to blue. The photocatalytic activity of the samples was evaluated by changing parameter b and calculated using formulas (1)–(3):
R4 =^^x 100%,(1)
R26 = "^х 100%,(2)
R2day = %产.X 100%,(3)
where: b0 is the value of the color coordinate at initial time; b4 is the value after 4 hours of UV radiation; b26 is the value after 26 hours of UV radiation; b2day is the value after 2 days of UV radiation. The R values should be more than 20% after 4 hours and more than 50% after 26 hours of UV exposure, according to the UNI 11259 standard, which determines whether a sample exhibits photocatalytic activity.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
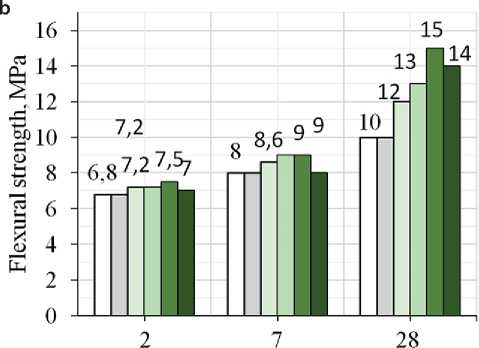
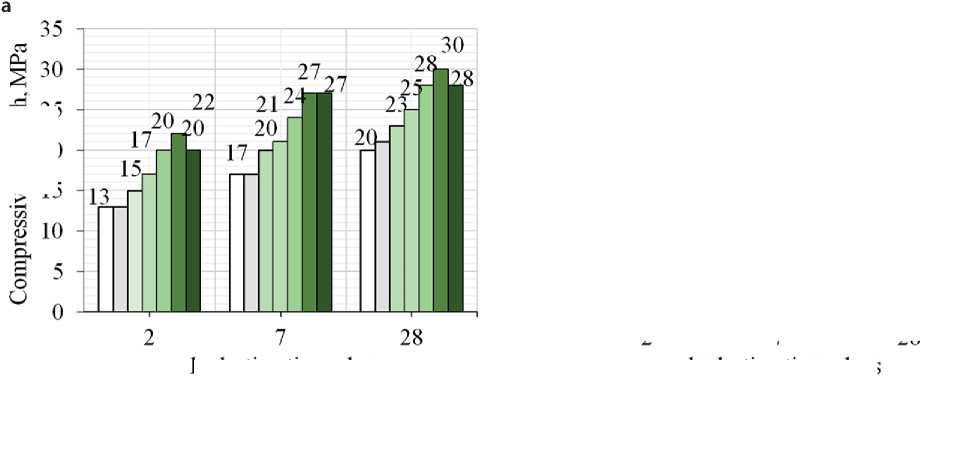
In this work the authors studied the influence of industrial TiO2 on the properties of cement-sand mortar and mechanical characteristics (compressive and flexural strength) of 40×40×160 mm prism samples made from a mixture of the required mobility at 2, 7 and 28 days age. The average W/C ratio was 0.70 which was used to prepare control and modified samples for further testing. Such a high value of W/C is due to the high dispersion of the dry building mix components. An increase in water consumption was observed with the introduction of TiO2 additive in the amount of 1.7, 3.0, 5.0 and 10.0 wt.%. The volume of mixing water increased from 90.0 to 105.0 ml (by 6-24%), respectively: the sample with 10% TiO2 additive showed the highest water consumption. For the control and 0.3 and 1.0% samples, the volume of water needed to achieve the required cone spreading was 85 ml. The strength parameters were evaluated on 40×40×160 mm prism samples. It follows from Fig. 2 that the maximum increase in compressive and flexural strength is observed for samples containing 5.0 wt.% of the additive: thus, compressive strength increased by 69% on the second day age, by 58% and 50% at 7 and 28 days age compared with the control sample. Flexural strength increased by 10, 13, and 50% at 2, 7, and 28 days age respectively. Introduction of 10.0 wt.% of the additive leads to a slight decrease in the strength of the modified samples at all periods of hardening. It is known that titanium oxide is a chemically resistant inert compound that has no hydraulic activity and does not interact with water. Thus, the presence of inert finely dispersed TiO2 in such a high amount probably serves as an obstacle to the interaction of cement clinker minerals with water and the formation of hydration products.
Photocatalytic activity of the samples in relation to organic dye Methylene blue decomposition was studied at real-life conditions under natural solar radiation. The conventional determination of material’s photooxidation ability is based on fluorescent xanthene red dye Rhodamine B discoloration. In this work, an organic derivative of thiazine Methylene blue was selected with a structure different from Rhodamine B and absorption in another part of the spectrum. which will expand the understanding of photooxidation of pigments of different structure and color when applied to the surface of a photocatalytic cement material.
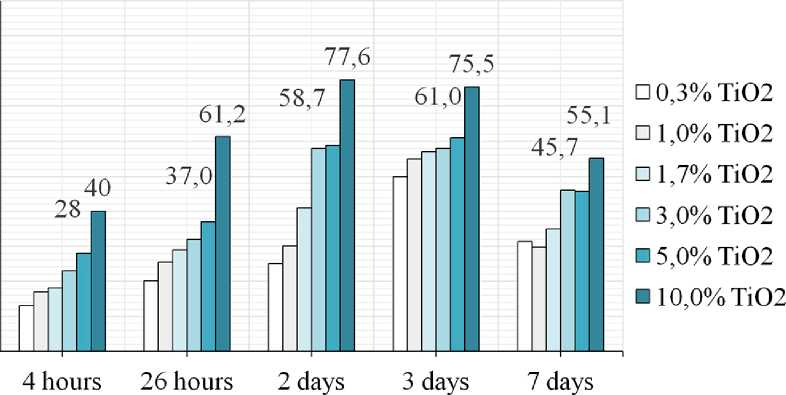
As can be seen from Figures 5 and 6, compositions with a TiO2 content starting from 3 wt.% are photocata-lytically active with 10 wt.% sample having the highest
hydration time, days
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS AND SCIENTISTS RESEARCH
hydration time, days
□ control П0,3%ТіО2
□ 3,0%TiO2 □ 5,0% ТІО2
□ 1,0%ТІ02 П 1,7% ТІО2
□ 10,0% ТІО2
5 о 5
2 2 1
I 区 upns•.
Fig. 3. Compressive (a) and flexural (b) strength of the samples
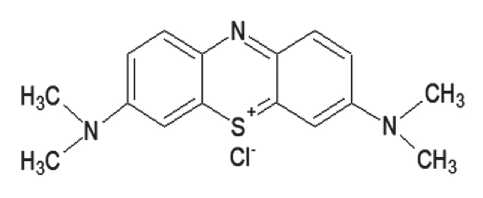
Fig. 4. The structural formula of Methylene blue
* ГМ XJI>OE о^ззо^о^л
exposure time
Fig. 5. Photocatalytic activity of cement-sand plaster samples with TiO 2 additive
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS AND SCIENTISTS RESEARCH
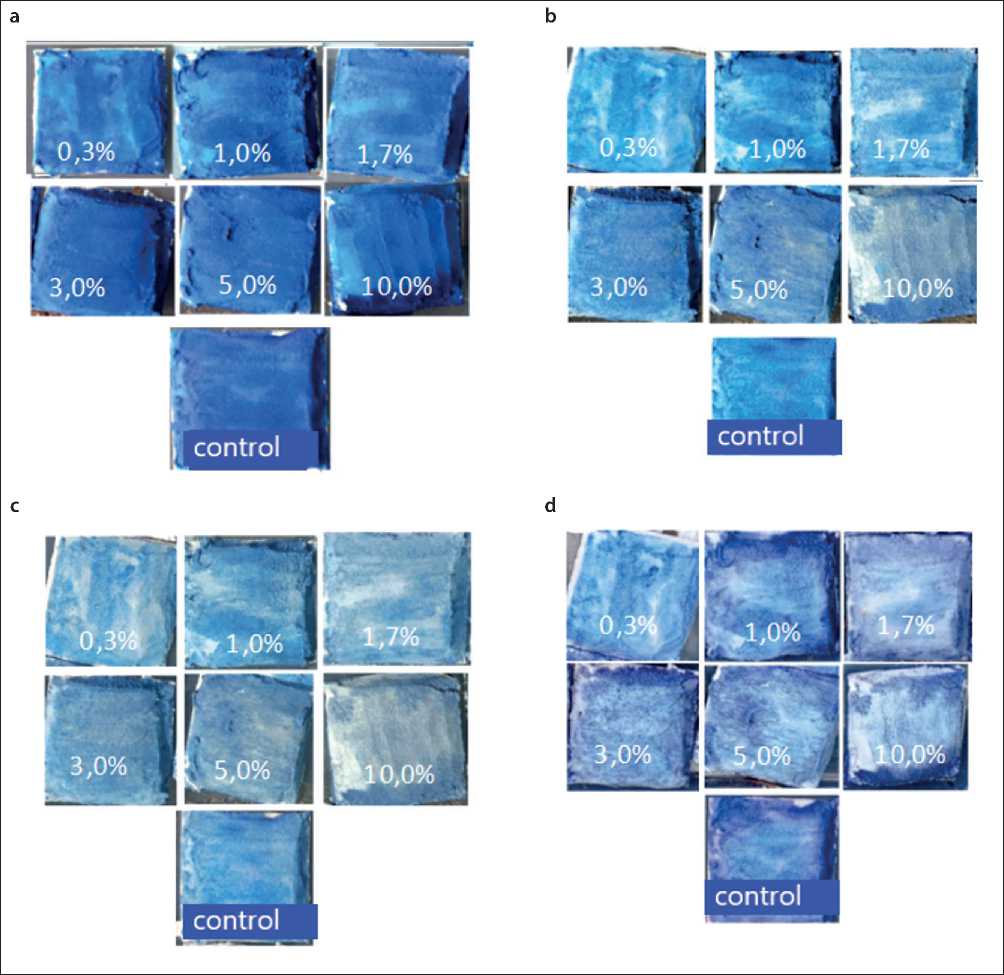
Fig. 6. Methylene blue discoloration after irradiation of the samples with natural sunlight: (a) at the initial moment; (b) after 26 hours; (c) after 3 days; (d) after 7 days
activity where R value is 40–78%. It is also noticeable that the maximum activity in relation to the dye mineralization is observed after 2 days of exposure of the samples to natural sunlight. At 7 days there is a significant decrease in the degree of pigment decomposition, which could serve several reasons: the first is the lighting mode. According to Table 2, it was on the 6th–7th day of the study that the weather conditions worsened – cloudy weather with rain, the UV-index values vary in the range of 3–4 points, which corresponds to a moderate level of UV activity compared to 5–6 points in the initial period of the study.
The second reason is the blocking of active photooxidation centers by decomposition products of pollutants and the adsorbtion of dust particles from the environment. The third is the carbonization process of the surface as a result of the reaction of carbon dioxide from the air with calcium hydroxide formed as a result of the hydrolysis and hydration reactions of cement clinker minerals, which also isolates the catalytic centers from sunlight. On the seventh day, the samples appear brighter, probably due to the moistening of the sample surface with rainwater. However, it is obvious that the degree of Methylene Blue discoloration is slowing down.
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS AND SCIENTISTS RESEARCH
CONCLUSION
In this work, the authors investigated the physical, mechanical and photocatalytic characteristics of cement-sand plaster samples modified with industrial titanium dioxide of anatase modification. As a result of the study, the authors found that the greatest increase in compressive (by 69%, 58% and 50% on the 2nd, 7th and 28th days age) and flexural strength (by 10, 13 and 50% at the same age) corresponds to a sample with 5.0 wt.% of TiO2 additives. Compositions with a TiO2 content starting from 3 wt.% are photocatalytically active where maximum degree of Methylene blue decomposition corresponds to the samples
with 5.0–10.0 wt.% of TiO2 (58–78% at the 2nd and 3rd days of exposure). It was also revealed that by day 7, there is a significant decrease in the degree of pigment decomposition, which is probably due to the processes of blocking the active photooxidation centers by oxidation products, pollutants adsorbed from the environment, insufficient sunlight intensity caused by weather conditions, as well as carbonation processes. Thus, as a result of the conducted research, the authors concluded that the optimal amount of TiO2 photocatalyst for introducing into the cement-sand composition is 5.0–10.0 wt.%, since these samples exhibit maximum strength characteristics combined with a high mineralization ability of the model contaminant.


