The role of interactions between brain neurotransmitters in pathophysiology and treatment of affective disorders
Автор: Dremencov E.
Журнал: Человек. Спорт. Медицина @hsm-susu
Рубрика: Клиническая и экспериментальная медицина
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.16, 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Aim of the review is to summarize the contemporary evidences on interactions between brain neurotransmitters and their role in pathophysiology and treatment of depression. Introduction. Brain neurotransmitters are biological molecules responsible for signal transduction between the neurons. Mammalian brain neurotransmitters belong to the different types of biological molecules, such as amino acids (glutamate and γ-aminobutyric acid, or GABA), monoamines (serotonin (5-HT), norepinephrine (NE), dopamine (DA), and histamine (HA)), neuropeptides (β-endorphin, neurokinin, vasopressin, and oxytocin), or nucleotides (adenosine). Materials and Methods. The author analyzes research papers dedicated to neurotransmitters and their functions in mood regulation and published between 1953 and 2014. The paper focuses on evaluation of data on mechanisms of interactions between different neurotransmitters and their role in development and treatment of certain mental disorders. Results. It has been reported that different neurotransmitters, often belonging to the different types of biological molecules, interact on behavioral, functional, system and molecular levels. These interactions play an important role in pathophysiology of brain diseases, particularly, depression and stress and anxiety-related disorders. Conclusion. Literally all existing antidepressant drugs act on monoamine systems of the brain (5-HT, NE, and DA). Although the last-generation antidepressants and mood stabilizers demonstrated higher safety and efficacy, their therapeutic potential remains limited. The brain adenosine neurotransmission is also a potential target for the future antidepressant, mood stabilizing and antipsychotic drugs. However, these drugs may have severe side effects, for example, on cardiac activity. It is necessary to perform further research and clinical trials to find a solution to the existing difficulties.
Серотонин (5-ht), serotonin (5-ht), norepinephrine, dopamine, glutamate, gaba, neuropeptides, hypothalamus, hippocampus, voltage-dependent calcium channels
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147153469
IDR: 147153469 | УДК: 616.831-001 | DOI: 10.14529/hsm160202
Текст научной статьи The role of interactions between brain neurotransmitters in pathophysiology and treatment of affective disorders
Neural system uses two basic mechanisms of information processing. Within neurons, information is processed via passive (synaptic potential) or active (action potential) flow of the electrical signal. Between the neurons, information is exchanged by chemical mediators, called neurotransmitters. Different type of biological molecules act as neurotransmitters, such as amino acids (glutamate and γ-aminobutyric acid, or GABA), monoamines (serotonin or 5-HT, norepinephrine or NE, dopamine or DA, and histamine or HA) small peptides (so-called neuropeptides, such as encephalin, β-endor-phin), nucleosides (e.g., adenosine), and small organic (such as the ester acetylcholine) and even inorganic molecules (such as nitric oxide or NO) [29].
Some neurotransmitters are specific for central neuronal system (CNS), such as neuropeptides, glutamate and GABA. Others act in both CNS and periphery, such as acetylcholine and monoamines. The majority of neurons projecting from one area of the CNS to another (e.g., between brain hemispheres or between midbrain and cerebral cortex) are secreting glutamate or GABA (Fig. 1). Thus, these two neurotransmitters play a primary role in neuronal functions involving distant exchange of information, such as sensory and motor functions. It is notable that the distantly-projecting cortical usually neurons release glutamate, while midbrain (thalamic and striatal) cells secret GABA. The locally-projecting CNS interneurons express GABA (e.g., cortical interneurons) or acetylcholine (some striatal interneurons).
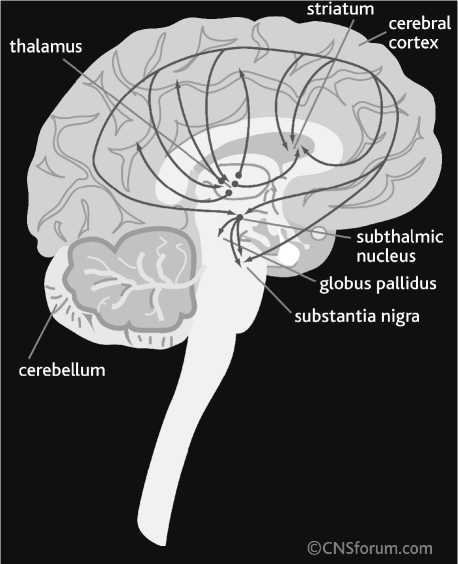
A
Fig. 1. Glutamate and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) pathways of human brain:
Glutamate pathways (A); GABA pathways (B). From CNS Forum (; published with the permission of Lundbeck Institute, Valby, Denmark
B
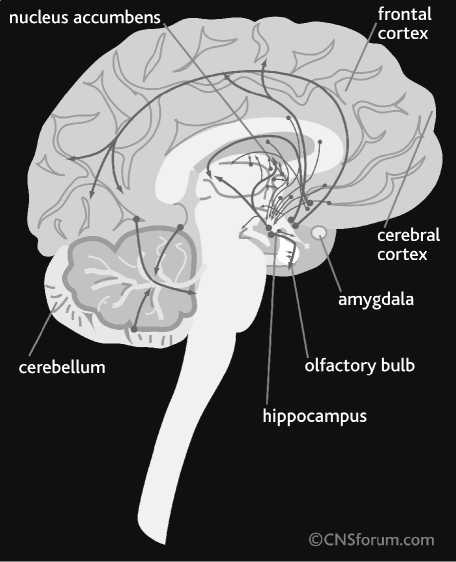
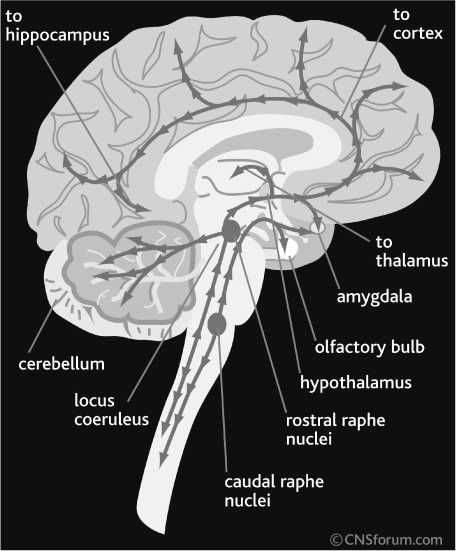
Neuronal systems expressing monoamines and neuropeptides have different functional anatomy (Fig. 2), suggesting a unique biological function. For several reasons will be explained below, these neurotransmitters are considered as a primary target for the treatment of mood disorders.
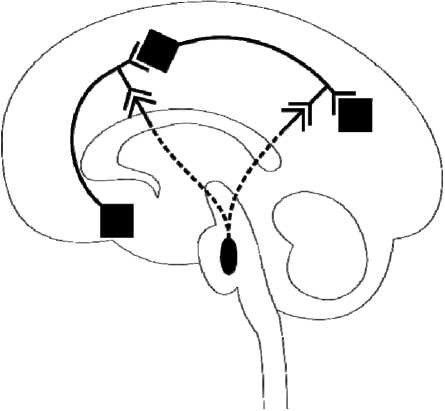
Fig. 2. Serotonin (5-HT), norepinephrine (NE), and dopamine (SA) pathways of human brain. From CNS Forum (; published with the permission of Lundbeck Institute, Valby, Denmark
-
2. Role of monoamines in the regulation of the mood
The catecholamines d o pamine and norepinephrine and indolamine serotonin (or 5 -HT) are traditionally referred to as monoamines. Monoamines share several features, such as chemical stru c ture, metabolism, and functional o rganization of monoamine-secreting neurons.
Monoamine systems share similar neuroanatomy. The cell bodies of monoamine - secreting neurons are located in one or several closely located brain midbrain areas and their ax o ns innervate distant areas of the C N S, such as cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, cereb e llum, brain stem and spinal cord (Figs. 2 and 3). The majority of project i ons of monoamine-secreting neurons innervate limbic areas of the brain, such as hippocampus, amygdala, nucleus accu m bens, and p refrontal cortex [17, 20, 22]. These special neuroanatomi-cal features of monoami n e-secreting neurons sug g est that they play a unique role in t he CNS. While amino acid (glutamate and GABA) secreti n g neurons are respons i ble for the flow of information from one brain area to another, monoamine neurons modulate information flow and processing across the CNS. This feature, together with the fact that the higher density of axons of
Receptors to monoamines
Table 1
|
Serotonin (5-HT) Receptors |
Norepinephrine (NE) Receptors |
Dopamine (DA) Receptors |
|
|
GI/O-Coupled |
5-HT 1A , 5-HT 1B , 5-HT 5 |
α1-adrenergic |
D2-like receptors (D 1 , D 4 ) |
|
GS-Coupled |
5-HT 2A , 5-HT 2B , 5-HT 2C |
β-adrenergic |
D2-like receptors (D2, D3, D5) |
|
G Q/Z -Coupled |
5-HT 4 , 5-HT 6 , 5-HT 7 |
α 2 -adrenergic |
|
|
Other |
5-HT 3 (super-family-coupled to K+ channels) |
monoamine-secreting neurons arrive to the limbic system, suggest that brain monoamines play a primary role in memory, learning, cognition, and emotional processing.
Almost all receptors to monoamines are G-protein coupled (Table 1), with the only known exception is “superfamily” ion-channel coupled 5-HT 3 serotonin receptors. There are one or two receptor in each monoamine system which are acting as autoreceptor. All known autoreceptors are coupled to G I proteins. Activation of these receptors usually leads to the opening of second-messenger-mediated ion channels (such as G Iβγ -dependent K+channels) and to the hyperpolarization of cell membrane.
There are four sources of evidence on the role of monoamines in mood regulation. The first is depletion studies in humans, meaning artificial reduction of biosynthesis of specific monoamine, e.g., by specific diet lacking precursor for this transmitter. For instance, reserpine, a blocker of vesicular monoamine transporter, can induce depressive symptoms. Down-regulation of 5-HT system by the dietary depletion of its precursor tryptophan results in rapid relapse of depression in successfully treated patients. Partial relapse on depressive symptoms was also observed after catecholamine depletion [14]. Second source of evidences is clinical observations of the effects of antidepressant drugs. This topic will be elaborated in depth in the next paragraph.
Third source of evidences is neuroimaging studies in animals or human subjects. The advanced imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET), allow quantitative detection of levels of specific neurotransmitters, using radioactive-labeled ligands to the receptors (usually autoreceptors) of this transmitter.
The forth source of evidence are behavior and in vivo studies in laboratory animals, and especially combination of these methods. Behavior neuroscience techniques are used to investigate the effects of psychoactive compounds on certain behavior characteristics of laboratory animals, such as motivation, reward, cognition, anxiety, and exploratory behavior. In vivo microdialysis and electrophysiology are used to study the effects of CNS drugs on the release of neurotransmitters and electrical activity of neurons (synaptic and action potentials, respectively).
-
3. Development of the antidepressant drugs: from multiple-target medicines to highly-selective medicines and back to multiple-target drugs
The first antidepressant drug, isoniasid, was coincidentally discovered in 1953, when the aim was to develop new anti-tuberculosis medication [4]. It was suggested that the antidepressant effect of isoniaside could be explained by its ability to inhibit monoamine oxidase (MAO), an enzyme metabolizing serotonin (5-HT), norepinephrine (NE) and dopamine (DA). It was therefore hypothesized that depression and affective disorders result from reduced transmission within 5-HT, NE and/or DA systems [13, 39].
-
4. Histamine, a forgotten monoamine
Based on this hypothesis, two first families of antidepressant drugs were developed. They are MAO inhibitors (like the above-mentioned iso-niasid) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs). MAO inhibitors increase 5-HT, NE and DA availability by suppressing their metabolism [6, 7]. TCAs stimulate monoamine tone by inhibiting the reuptake of 5-HT, NE and/or DA [10, 35].
Further research and development of antidepressant medications have been motivated by two main goals: reducing toxicity and side effects of the drugs and improving their clinical efficacy. The first attempt to increase clinical efficacy of antidepressant drugs was to increase their selectivity to the NE system. NE transmission is causally related to fear, stress and anxiety. The NE system was therefore suggested to play a central role in mood and affective disorders. Indeed, the selective NE reuptake inhibitors that were developed demonstrated effectiveness in the treatment of depression. However, it was sug- gested that the antidepressant effect of NE reuptake inhibitors is mediated by their indirect stimulatory effect on the 5-HT system rather than by their direct effect on the NE system. Thus, depressive symptoms return when 5-HT, but not NE depletion is following the treatment with NE reuptake inhibitors [14]. Moreover, all antidepressants, including selective NE reuptake inhibitors, stimulate 5-HT transmission, whereas some antidepressants suppress NE transmission [19, 20, 30].
It is well established today that the main therapeutic effects of antidepressants is explained by their ability to stimulate 5-HT transmission, either directly or non-directly. As a result, SSRIs are used as a first-line treatment in depression. However, the clinical efficacy of SSRIs is still limited. The major limitations are the lack of adequate response to the treatment (estimated to be at approximately 30%), risk of post-treatment relapse of the disease (~ 30%) and delay between beginning of the treatment and the onset of the first clinical effect (2-3 weeks) [31, 38].
Depression is characterized by multiple cognitive, emotional and physical symptoms. It is therefore likely that several different neuronal systems and transmitters are involved in the pathophysiology of the disease. For example, an abnormality in DA and endorphin transmission might be relevant to anhedonia, NE to fatigue and anxiety, histamine and acetylcholine to cognitive disturbances. Most neurotransmitter systems in the brain are auto-regulated and crossregulated by other systems. Antidepressant medications that directly modulate one system will indirectly affect others as well. For example, since 5-HT inhibits NE and DA neuronal firing activity, SSRIs stimulate 5-HT transmission directly and might suppress NE and DA tone indirectly. The lack of adequate treatment response observed in some patients might actually be explained by this inhibition of catecholamine neurotransmission [15, 16].
Histamine (HA) is a monoamine synthesized from the amino acid histidine. Histamine is primary known as an important mediator of the immune system. However, it is also acting as a CNS neurotransmitter.
It was discussed in the previous paragraphs that the functional interactions between 5-HT, norepinephrine NE and dopamine DA systems play an important role in the response to antidepressant and antipsychotic treatments [18, 22, 23,
24, 25]. The interaction HA and other monoamines (5-HT, NE, and DA) received, however, lesser attention.
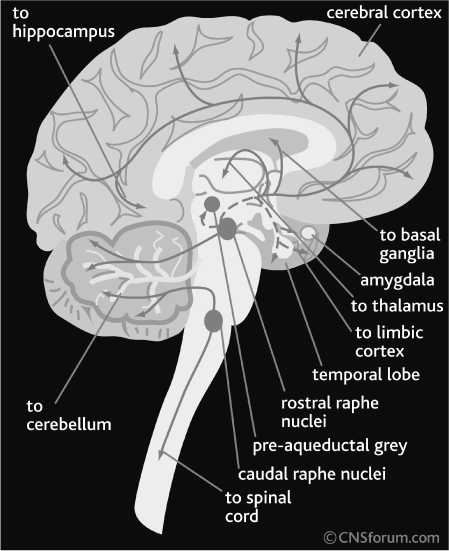
The neuroanatomy of brain HA system is similar to other monoamine systems. The cell bodies of HA neurons are located in the tubero-mammillary nucleus (TMN) of the hypothalamus. Their projections innervate different areas of midbrain and telencephalon, including the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN), locus coeruleus (LC) and ventral regimental area (VTA), the brain areas consist of cell bodies of 5-HT, NE and DA neurons, respectively [1, 2, 3, 28, 33, 36, 43]. This suggests that HA functionally interacts with 5-HT, NE, and DA systems.
There are four HA receptors: H 1 -H 4 [5, 8, 26, 32]. Histamine-1, H 2 , and H 2 receptors are expressed both in the immune system and in the brain [9]. The H 3 receptors are expressed nearly exclusive in the CNS. They are widely distributed across the brain; the highest density of H 3 receptors has been observed in the striatum, hippocampus and cerebral cortex [1, 34, 37]. Hista-mine-1 receptors are G Q , H 2 - G S and H 3 and H 4 -G I/O protein-coupled. The activation of H 1 and H 2 receptors leads to neuronal excitation and H 3 to inhibition [41, 42]. Histamine-3 receptors are only inhibitory histamine receptors widely and densely expressed in the brain, on both nerve terminals of histamine neurons and on post-synaptic cells [26].
It has been previously reported that H 3 receptors play an important role in the regulation of brain HA system. Thioperamide, an inverse agonist of H 3 /H 4 receptors [27], increased extracellular HA levels in the TMN and prefrontal cortex (PFC). Systemic administration (1 mg/kg, s.c.) of the selective agonist of H 3 receptors, im-mepip dihydrochloride [44], decreased HA concentrations in the TMN and PFC. Local intra-PFC perfusion of thioperamide increased, and of immepip decreased extracellular HA in both TMN and PFC. Local intra-TMN perfusion of thioperamide or immepip decreased HA levels in the TMN, but in the PFC. It was therefore concluded that cortical H 3 receptors negatively regulate HA neurotransmission, possibly through the inhibition of excitatory cortical neurons projecting into the TMN.
It was recently observed that the systemic administration of the inverse agonist of H 3 /H 4 receptors, thioperamide, stimulate 5-HT, NE, and DA release in the prefrontal cortex (PFC). Thioperamide stimulate the firing activity of DA
A
B
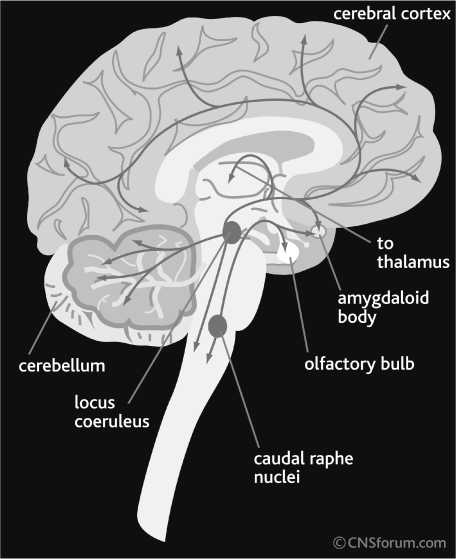
C
Fig. 3. The difference between neuromodulators and other brain neurotransmitters: Serotonin pathways ( A ); Norepinephrine pathways ( B ); Dopamine pathways ( C ). “Regular” neurotransmitters, such as glutamate and GABA, perform the flow of neural information from one brain area to another. The cell bodies of glutamate and GABA-secreting neurons (shown with black rhombs) are distributed across the whole brain. Neuromodulators, however, modulate the flow of neural information across of the brain. The cell bodies of neuromodulatory neurons (shown with black oval) are concentrated in one brain area (raphe nuclei for serotonin, locus coeruleus for norepinephrine, ventral tegmental area and substantia nigra for dopamine, and tuberomammillary nucleus for histamine), and their axons innervate distant areas of the brain
neurons in the VTA, and immepip reversed the stimulatory effect of thioepramide on DA neuronal activity. Direct local iotophoretic application of HA into the VTA mimicked the effect of systemic administration of thioperamide, suggesting that the effect of thioperamide is mediated via the activation of brain HA release (and subsequent activation of H 1 receptors in the VTA) rather than via direct effect of thioperamide on VTA H 3 receptors (Fig. 3).
-
5. Role of brain amino acids (glutamate and GABA) and autoregulation of monoaminergic systems
-
6. Nucleotide adenosine, the most prevalent and the less studied neurotransmitter
-
7. Interaction between different neurotransmitters, acting via different G-protein coupled receptors,
and interactions between them
Brain monoamine systems are auto-regulated and interact each another either directly (mono-synaptically) or via polysynaptic loops, involving glutamate and GABA neurons. Thus, an increase in 5-HT or HA levels in the PFC leads to the activation of inhibitory 5-HT 1A or H 3 receptors on cortical neurons projecting to the DRN and TMN, respectively. Serotonin-2A receptors activate GABA neurons projecting into the LC. This pathway plays a central role in 5-HT-NE interactions [15, 19]. Finally, the activation of 5-HT 2C receptors, expressed on the GABA neurons projecting into the DRN and VTA, play an important role in autoregulation of 5-HT system and in 5-HT-DA interactions, respectively [11, 12, 18].
The DRN-projecting GABA neurons, activated by 5-HT 2C receptors, on their torn, inhibit 5-HT neurons via GABAB receptors. It is suggesting that some antagonists of GABAB receptors might be used in the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders [11, 12].
Adenosine is a purine nucleoside playing an important role in numerous biological functions, such as storage and translation of genetic information (as a part of DNA and RNA), metabolism and energy accumulation (within ATP and NADH), and signal transduction (within the second messenger molecules such as cAMP.
In neurons, adenosine aggregated within the synaptic vesicles as a product of metabolism of ATP, which is required for the active transport of the molecules of neurotransmitters into the vesicles. Adenosine aggregated within the synaptic vesicles is co-released together with the primary neurotransmitter into the synaptic shelf and activate specific receptors on the post-synaptic neurons. Thus, adenosine can be considered as one of the most universal and prevalent brain transmitter. However, the neuronal adenosine and its interactions with other neurotransmitters are poorly understood. It is possible that CNS adenosine interact with monoamine systems, suggesting that this transmitter can be involved in pathophysiology and treatment of mood disorders, as will be described in the next paragraph.
on intracellular signal transduction level
It has been observed that some G S -coupled receptors, such as D 1 and A 2A , interact with G I -coupled receptors, such as D 2 and A 1 , by forming a G Q -protein coupled dimmer (Fig. 4). Thus, dimmerization of these receptors, which occurs in the CNS under certain condition, leads to the activation of different pathways of intracellular signal transduction: activation of phosholypase C (PLC) instead of activation or inhibition of adenylate cyclase (AC).
The recent studies suggest that this molecular interaction has an clinically-important functional output. Thus, an antagonist of adenosine A 2A receptors, ZM 241385, potentiates the D 2 antagonist haloperidol-induced increase in DA and NE levels in the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) and PFC, respectively. This may explain the beneficial role of some A 2A antagonists in reduction of the side effect of classical antipsychotic drugs (such as catalepsy) and enhancing of their clinical effect on negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia [1]. It is also possible that the G S -coupled A 2A receptors also interact with other than D 2 G I /G O -coupled monoamine receptors, such as α 2 -adrenergic and 5-HT 1A/1B serotonin receptors. It is making A 2A receptor-making agents potential adjuncts to antidepressant and anxiolytic drugs.
Furthermore, NE plays an important role in the feeling of energy and modulation of feeding behavior. On the other side, adenosine levels correspond to the actual energetic level of the organism. In high energy levels, ATP metabolism is usually stops at ADP level, when in the low-energy situations ADP can further metabolite into the AMP and/or adenosine (Berg et al., 2002). Adenosine-norepinephrine interactions may, therefore, mediate the cross-talk between the energetic level and feeling of energy and to adapt the feeding behavior to the real energetic needs.
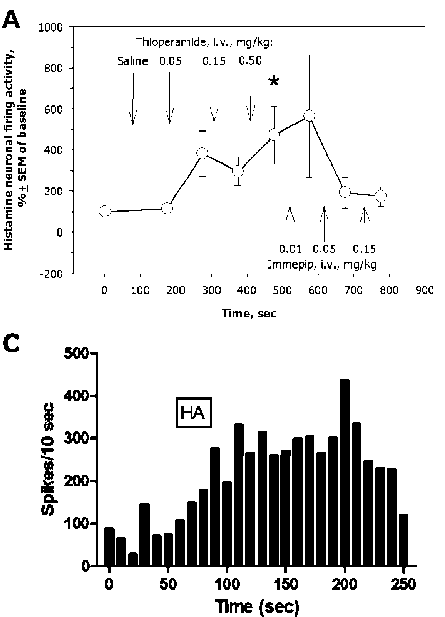
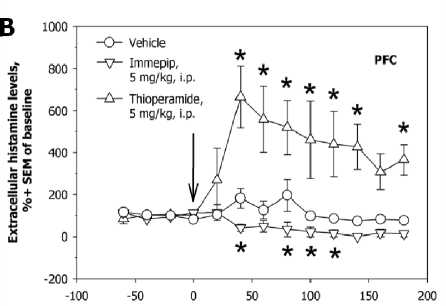
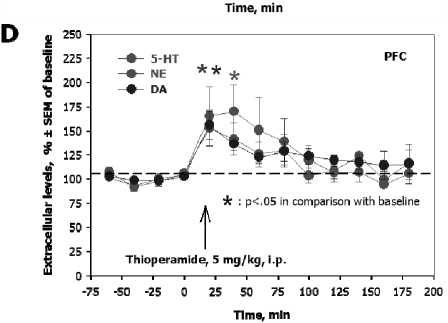
Fig. 4. Autoregulation of brain histamine system and interactions between histamine and other monoamines of the brain. The reverse agonist of histamine-3 and histamine-4 receptors, thioperamide, and the selectiv agonist of histamine-3 receptors, immepip, oppositely regulate the firing activity of histamine-secreting neurons of the rat tubero-mammillary nucleus in a dose-dependent mater ( A ); immepip increases, and thioperamide decreases, extracellular levels of histamine in the rat prefrontal cortex (PFC, B ); local iont o phoretic administration of hi s tamine into the rat ventral tegmental area activates the firing activity of dopamine-secreting neurons ( C ); systemic administration of thioperamide increases serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine evels in the rat prefrontal cortex (PFC, D )
-
8. Neuropeptides of the hypothalamus and their role in pathophysiology and treatment of mood disorders
Oxytocin (OXT) and arginine (AVP) vasopressin are two related neuropeptides, acting as peripheral hormones and CNS neurotransmitters. The majority of OXT and AVP secreting neurons are located in the paraventricular (PVN) and supraoptic (SON) nuclei of the hypothalamus. The axons of the OXT and AVP-secreting neurons located in the SON projecting into the pituitary. OXT and AVP secreted in the SON are released into the blood circulation and act as peripheral hormones. OXT stimulate the uterus contractions during the labor and subsequent milk secretion. AVP is responsible for the water and electrolyte balance.
The axons of OXT and AVP-secreting neurons located in the PVN project into the pituitary, as well as into other brain areas, such as hippocampus, medial amygdala, VTA, substantia nigra, olfactory bulbs and medial preoptic and medial basal areas of the hypothalamus, bed nucleus of stria terminalis, and septum.So far, one type of OXT (OXTR) and two subtypes of AVP (V1A and V1B) have been identified in the CNS. The OXTR and V1A and V1B are GαQ-protein coupled. Their activation leads to the activation of phospholipase C (PLC), protein kinase C (PKC) and Ca2+ influx into the cells. The OXY and AVP projections are, therefore, “classical” neuromodu-latory pathways and play an important role in memory, cognition, and emotional processing.
OXT and AVP may play an important role in stress response, anxiety, and depression. One study reported that OXT-knockout male and O X T-deficient female mi c e show increased anxiety. The anxiety level in OXT-defic i ent female mice was reserved by OXT treatme n t and enhanced by OXTR antagonist. Acute and chronic O X T had also an antidepressant-lik e effect in normal rats, as was measured using the forced swim test. Another study, however, reported that O X T knockout mice show similar anxiety level,
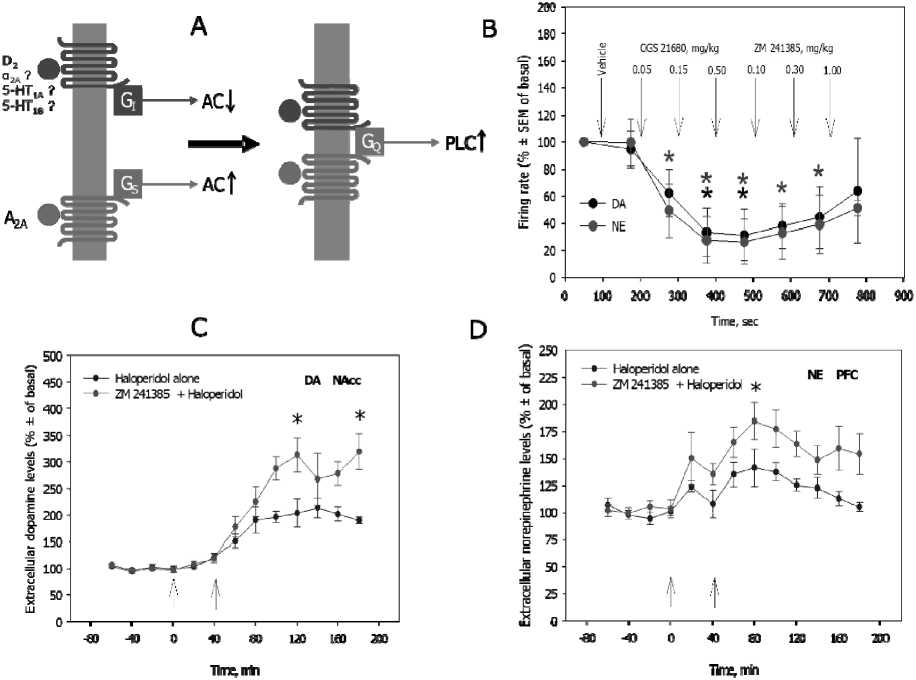
Fig. 5. Interactions between brain adenosine and monoamines. Adenosine-2A (A 2A ) is a Gα S -coupled receptor. Its activation stimulates the adenylyl cyclase (AC)-mediated cyclic adenosine monophosp h ate (cAMP)formation. Dopamine-2 (D 2 ), α 2 -adrenergic, and serotonin-1A/1B receptors (5-HT 1A/1B ) are Gα I -coupled. Its activatio inhibits the adenylyl cyclase (AC)-mediated cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)formation.Adenosine-2A and dopamine-2 (and perhaps also α 2 -adrenergic and serotonin-1A/1B receptors) form a dimmer which is Gα Q -coupled and stimulates phospholipase-C (PLC, A ); CGS 21680, a selective adenosine-2A adenosine receptor agonist, and ZM 241385, a selective adenosine-2A adenosine receptor antagonist, oppo s itely regulate the firing activity of norepinephrine neurons of the locus coeruleus and dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area ( B ); ZM 241385 potentiates the haloperidol-induced increase in dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens (NAcc, C ) and norepinephri n e levels in the prefrontal cortex (PFC, D )
but decreased aggression in comparison to wild type controls.
It was reported that Brattleboro AVP knockout rat demonstrate decreased anxiety and depressive-like behaviour following stress). Similarly, decreased anxiety was observed in V 1A knockout mice, when the overexpression of this receptors leaded to increased anxiety. The V 1B knockout mice did not demonstrate, however, any behavior changes related to the anxiety.
The neuropeptide β-endorphin are belongs to the family of endogenous opiates, or opioids. Similarly to monamines, OXT, and AVP, brain β-endorphin pathways demonstrate “classical” features of neuromodulatory system. The cell bodies of β-endorphin-secreting neurons are concentrated in the arcuate nucleus (ARN) of the hypothalamus and their axons innervate distant areas of the brain, such as periaqueductal area of the brain stem (where they activate other opioidsecreting neurons projecting into the spinal cord), hypothalamus, thalamus, prefrontal and cingulate cortex, and hippocampus. Similarly to other opoids, β-endorphin plays a central role in pain modulation. However, β-endorphin system is also fundamental in the mediation of motivation, reward, memory, and emotional processing [21, 40].
The CNS receptors to β-endorphin are divided into three subtypes: μ, κ, and δ. All these receptors are GαI/O-protein coupled. The μ-opioid receptors play a central role in pain modulation and euphoria; these receptors are also primarily responsible for the addictive properties of opiates. The κ-receptors have an analgesic effect similar to μ-opioid receptors; however, their effect on reward feeling is opposite. The δ-opioid receptors are out of special interest, since they play an important role in stress response, anxiety, and depression. Some agonists of these receptors are under preclinical and early clinical investigations as potential antidepressant and antiolytic drugs.
-
9. Conclusion
-
10. Acknowledgements
This author of this work was supported via the Slovak Academy of Sciences Scholarship Program and Vega Grant 2/0024/15.
Interactions between different neurotransmitter systems, rather than an individual neurotransmitter, play a key role in pathophysiology and treatment of depression and related mood and anxiety disorder. Literally all existing antidepressant drugs act on monoamine systems of the brain (5-HT, NE, and DA). Although the lastgeneration antidepressants and mood stabilizers demonstrated higher safety and efficacy, their therapeutic potential remains limited. To achieve the better outcome in the treatment of depression, new medications and/or adjuncts to the existing ones should be developed. These new medications may target brain histamine and neuropeptide (β-endorphin, oxytocin, and vasopressin) systems. The brain adenosine neurotransmission is also a potential target for the future antidepressant, mood stabilizing, and antipsychotic drugs. Since adenosine receptors are widely expressed over the body and mediate numerous crucial physiological functions, such as regulation of cardiac activity, these drugs may have severe side effects. The direct targeting of these drugs into the site of their action (e.g., PFC), using advanced neurosurgical and/or pharmaceutical means, can provide a solution to this difficulty.


