The role of patiral hormones in metabolism
Автор: Seyidova L.
Журнал: Бюллетень науки и практики @bulletennauki
Рубрика: Медицинские науки
Статья в выпуске: 7 т.10, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
After the removal of the pancreas and during its hypofunction, a severe and difficult-to-treat disease called diabetes and sugary urine is observed in humans and animals. Under the influence of glucagon, the process of converting glycogen into glucose begins to take an active form in the liver and some other organs. Glucagon helps to increase the amount of glucose in the blood due to the activation of phosphorylase, which is involved in the breakdown of glycogen in the presence of glucose. Different animals have different sensitivity to glucagon. Glucagon affects fat metabolism and stimulates the breakdown of fat in adipose tissue.
Pancreas, insulin, endocrine, hormone, metabolism
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14130522
IDR: 14130522 | УДК: 612.018+612.34 | DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/104/34
Текст научной статьи The role of patiral hormones in metabolism
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice
The pancreas is made up of two types of tissue. The acini secrete digestive juices, which flow into the duodenum. The hormones produced by the islets of Langerhans (insulin and glucagon) enter the blood directly. In the human pancreas, there are up to 2 million islets of Langerhans, each of which is about 0.3 mm in diameter. These cells, concentrated along small capillaries, secrete their hormones into those capillaries [1, 2].
The cells of the islet apparatus are composed of 3 main cells - α, β, δ. These cells differ both in their morphological characteristics and in their attitude to dyes. β cells make up almost 60% of the cells of the islets of Langerhans and produce the hormones insulin and aminin. Amilin hormone is mainly secreted in parallel with insulin, but its function is still not fully understood. Glucagon is the hormone synthesized by α cells, which make up 25% of the total number of islet cells. δ cells make up 10% of the total number of islet cells and produce somatostatin [3]. A small number of P-P cells synthesize a hormone called pancreatic-polypeptide, which has various functions. All types of cells of the islets of Langerhans form tight, interacting cell-to-cell connections that control the secretion of any hormone by other hormones. For example, insulin inhibits glucagon synthesis, amin slows insulin secretion, and somatostatin weakens both insulin and glucagon secretion Müasir dövrdə daxili sekresiya vəzilərinin funksiyasını öyrənmək üçün aşağıdakı metodlardan istifadə edilir [4].
Material and methodology of the research
-
1. Extrinsic or surgical removal of the gland from the body. The method is widely used in veterinary medicine. At this time, information about the function of the gland is obtained based on the changes that occur in the body after the removal of the gland.
-
2. Transplantation - transfer of an organ or its tissue to a living organism. The transplanted organ is called a transplant. a) Autotransplantation - the transfer of an organ belonging to the body from one place to another; b) Homotransplantation - the transfer of a gland or its tissue from one animal of the same species to another; c) Heterotransplantation - the transfer of an animal's gland to a creature belonging to another species [5-8].
-
3. The introduction of the extract of the internal secretion gland or its raw tissue into the body, or feeding with the raw tissue or dried powder of the gland. These methods have a similar effect to transplantation, as in this case the function of the removed gland is replaced for a short time [9].
-
4. Parabiosis method. Cross joining of two living organisms or their vessels to the surgical path. This method works well in experimental rats. No changes were observed in the other animal, whose gland was removed due to the introduction of hormones from another animal.
-
5. Observation of patients with endocrine gland hyperfunction or hypofunction. Removing part of a hyperfunctioning gland, transplanting a suitable gland from an animal to increase the function of a hypofunction gland creates new clinical scenarios. Such a study of diseases of internal secretion glands is of great importance.
-
6. Injection of radioactive isotopes into the body and their detection in the glands. The fact that the hormone is synthesized in the examined gland can also be revealed as a result of the comparative analysis of the chemical composition of the blood flowing into and leaving the gland. Chemical and biological reactions can also be used to detect the hormone in the blood.
Transplantation completes extirpation. The function of the gland removed as a result of extubation is restored as a result of the activity of the newly transplanted gland. Due to the gradual recovery of the lost functions, it is believed that the newly transplanted gland has internal secretion activity. In other words, the studied gland affects the body through blood. The transplanted transplant becomes numb to the body and releases hormones into the blood for a while, then it is absorbed and lost. Autotransplants adapt successfully to their host. As a result of heterotransplantation, only a short-term effect is obtained.
Methods of determining blood sugar. Currently, blood sugar is determined by the two most common methods:
-
1) Haghedorn-Jensen method. This is an ancient method, and since other reducing substances are determined in the blood besides sugar, the amount of sugar determined by this method is slightly higher than the actual level of glucose in the blood. That is, with this method, the level of sugar in the blood is within the range of 4.44-6.66 mmol∕l, (80-120 mg%).
-
2) Somoci-Nelson method (glucooxidase method). The normal level of sugar (glucose) determined by this method is within the range of 3.33-5.55 mmol∕l (60-100 mg%). Sugar in urine is determined with a sugar polarimeter, or by using ready-made reagents soaked miliamil papers (testpapers).
Discussion and conclusions of the study
In addition to the exocrine gland epithelium, the pancreas contains tissue with endocrine function located in the form of small granules-islets (Figure 1). Hormones secreted from islets - insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, VIP, PP, etc. they play an important role in regulating the gastrointestinal system, the body's general activity and metabolism. The main function of the hormones secreted by the islets is the regulation of the energy balance in the body, which is mainly carried out by controlling carbohydrate and fat metabolism. Insulin and glucagon play a key role in this regulation. The total weight of this endocrine tissue, called islets of Langerhans, is 1 gram. Islets consist of 5 types of basic (α, β, δ, PP, EC) and several additional (G, D2) cells [10].
Neonatal islets also contain gastrin-secreting G cells that are not normally seen in the elderly. It should be noted that islet cells are developed from ectoderm and belong to neuroendocrine cells. These cells have neuronal endolases and, like APUD cells, have properties to capture and decarboxylate amine precursors. Therefore, tumors that develop from islet cells can secrete several hormones, even hormones that are not normally secreted [11].
Islets are normally diffusely located in the pancreatic tissue. The most common cells in islets are β-65%, α-15% and PP-15% cells. Despite the predominance of β cells in the majority of islets, there are also differences depending on their location. There are more PP cells in the islets located in the head, and more δ cells in the body and tail. This feature is an important diagnostic sign in locating islet tumors [12].
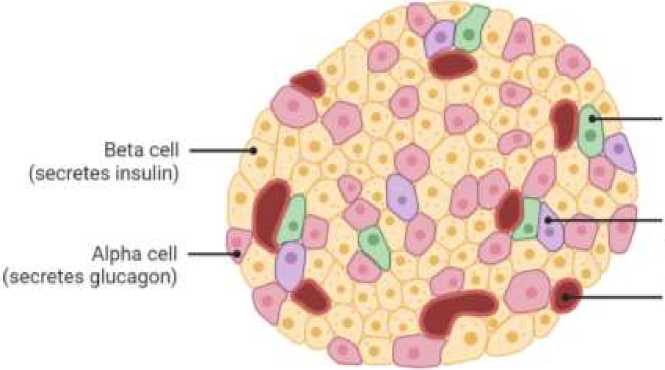
F cell (secretes pancreatic polypeptide)
Delta cell
(secretes somatostatin)
Capillary
Figure 1. Functional anatomy of the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas. α cell - cells that synthesize glucagon; β cell - a cell that synthesizes insulin; δ cell - somatostatin-secreting cell; F cell - pancreatic polypeptide (P - P) secreting cell; D2 cell - vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) secreting cell; EC cells -enterochromaffin cells that secrete serotonin
The main function of the islets of the pancreas is to perform the function of energy regulator in the body. Hormones synthesized from islets play an important role in the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats, which are the main energy substances of the body. Insulin and glucagon, which are antagonists of each other, play a key role in these processes, while somatostatin and PP participate in the regulation of the secretion and effect of these two hormones. Insulin ensures the transfer of glucose to cells (except for hepatocytes, brain cells and erythrocytes), increases glycogenesis, reduces lipolysis, increases and protects the body's energy reserves. Glucagon increases glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, lipolysis and accelerates the consumption of energy sources. Somatostatin reduces the synthesis of both hormones [13-17]. And PP causes an increase in insulin sensitivity. Another function of islets is their role in regulating MAV exocrine activity. Antagonistic hormones — insulin and glucagon play a key role in this process (Table).
Table
PANCREATIC HORMONES AND THEIR EFFECT ON METABOLIC PROCESSES
|
Islets of Langerhans |
Place of impact |
Physiological effect |
|
|
Cells |
Hormones |
||
|
β-beta |
Insulin |
The whole organism |
It regulates the absorption of glucose in all cells of the body, with the exception of nerve cells |
|
α-alpha |
Glucagon |
Liver |
It ensures the conversion of glycogen into glucose |
|
δ-delta |
Somatostatin |
Pituitary gland and other tissues |
Growth hormone, insulin, glucagon weakens peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract. It weakens the activity of the digestive system |
|
From the |
Lipocaine |
Liver |
It ensures the oxidation and assimilation of fatty acids |
|
epithelium of the |
Vagotonin |
CNS, skeletal system |
The parasympathetic nervous system provides active erythropoiesis |
|
gland ducts |
Centropenin |
It awakens the respiratory center and widens the bronchi |
It widens the bronchi and increases the transport of oxygen |
|
Kallikerin |
muscle, skin, liver |
It generalizes arterial and capillary drainage |
|
|
Retardin |
It slows down its activity in hyperfunction |
||
Although hormones differ in their place of origin, distribution method, chemical composition and nature of action, they are united under a very important common biological law: they participate in metabolism, morphological differentiation of the organism, growth and development, reproduction and regulation and coordination of its main functions. The nervous system communicates and influences different parts of the body directly through hormones. Hormones are proteinaceous or steroid substances that act in very small amounts. Their effect is carried out in 2 ways: through the nervous system and directly through the blood to the organs [18].
Physiological importance of hormones becomes more obvious during various diseases caused by dysfunction of endocrine glands. Such disorders consist of increased function of glands -hyperfunction and its weakened function - hypofunction. Hypofunction of the gland disappears in most cases after introducing a certain amount of the missing hormone into the body. In some cases, good results are obtained by taking the appropriate endocrine gland itself or its dried powder with food. Such treatment is called organotherapy.
The molecular formula of human insulin is as follows (Figure 2):
It should be noted that the breaking of disulfide bridges, oxidation or removal of sulfur and esterification of carboxyl groups lead to the loss of biological activity of insulin. The biosynthesis of the hormone takes place in the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans. Experimental diabetes can be created by damaging those cells. It has now been established that insulin is initially synthesized in the form of a single polypeptide chain called "proinsulin" consisting of 84 amino acid residues. As a result of breaking the proinsulin chain at 2 points, it becomes insulin with 2 disulfide bridges. Proinsulin itself is not biologically active. Most likely, some forms of diabetes are related to defects in the conversion of proinsulin to insulin. Insulin increases enzyme synthesis in exocrine glands, while glucagon decreases it. Somatostatin is thought to affect exocrine function by reducing insulin. Other hormones are also secreted from the islet cells. The physiological significance of some of them has not been clarified (YY), while others are important mainly in pathological cases (VIPoma). There are 2 nervous and neuro-humoral mechanisms of insulin secretion regulation. Islets of Langerhans are innervated by efferent and sympathetic nerves. Irritation of the afferent nerve causes a flow of efferent impulses to the gland. This causes the secretion of insulin and the reduction of glucose in the blood [19].
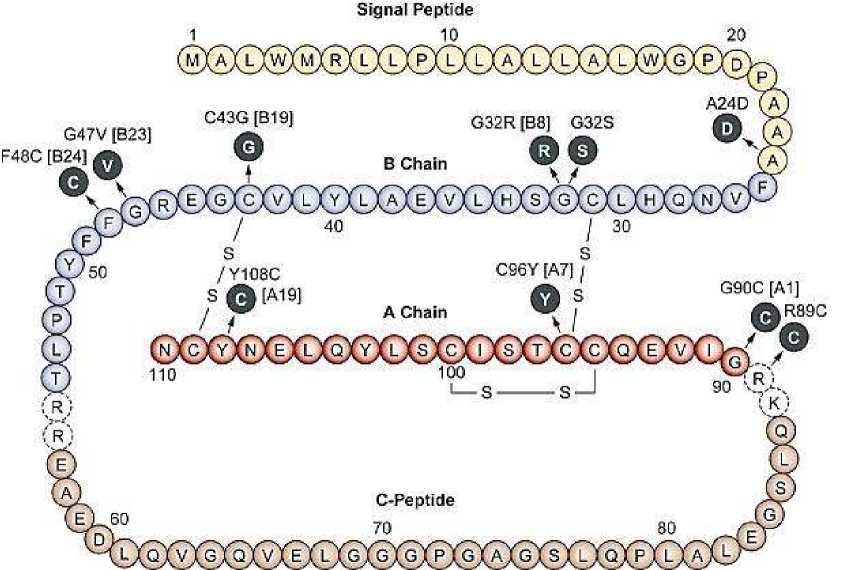
Figure 2. The molecular formula of human insulin
Sympathetic nerves slow insulin secretion. The transplanted, in other words, denervated gland retains the ability to produce insulin. Elevation of blood sugar increases the secretion of insulin and decreases the secretion of glucagon. A decrease in glucagon secretion causes a decrease in blood sugar. Both hormones affect carbohydrate metabolism by activating appropriate enzymes. It turns out that the internal secretion of the gland is regulated by the amount of sugar in the blood and at the same time insulin in the blood.
Under the influence of insulin, the absorption of glucose by almost all cells of the body increases and its concentration in the blood decreases again. At a normal concentration of glucose (about 100 mg/100 ml), insulin is practically not found in the plasma, but with an increase in the amount of sugar in the blood, the concentration of insulin rises suddenly under physiological conditions [20].
The introduction of insulin into the blood causes conditioned reflexes. The changed composition of the blood regulates the secretion of insulin through the nervous system. Insulin secretion increases during hyperglycemia and decreases during hypoglycemia.
Insulin secretion increases when carbohydrates are absorbed from the digestive system into the blood, and decreases when the body is starving. In addition, the hormone of the anterior lobe of the adenohypophysis also affects the secretion of insulin. Recently, a substance with similar effects to insulin is believed to be produced in the salivary glands [21].
Insulin-like substances involved in carbohydrate metabolism are widely distributed in nature. Plant-derived substances are available in nature as a source of insulin. Diabetes is a calm landscape when you prefer a plant-based diet. The reason is the presence of substances in plant-based foods that can act like insulin. According to the amount of insulin-like substances, plant-based foods can be arranged as follows: millet-legumes-lentils-peas-rice-wheat-potatoes.
During diabetes, lipocaine prevents fatty liver because it accelerates the breakdown of fatty acids. The hormone was obtained from the pancreas of cattle after insulin. Kallikrein or padutin has also been obtained from pancreatic extract. This hormone is not a stable substance, it quickly decomposes when heated to 60oC, as well as under the influence of acids, alkalis and alcohol. The hormone lowers blood pressure, expands arteries and capillaries. The pancreas also produces the vagotonin hormone, which increases the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system, and the centroptein hormone, which stimulates the awakening of the respiratory system and the transport of oxygen with hemoglobin. The main physiological effect of insulin consists of accelerating the use of glucose by tissues, its transport from the blood to the intracellular content, and the completion of the assimilation and breakdown of glucose as a result of the activation of the glucokinase enzyme [22].
Insulin increases the penetration of glucose into cells, the assimilation of sugar by muscle tissues, maintains the stability of water in tissues, activates the synthesis of proteins from amino acids, and weakens the synthesis of fats from proteins and carbohydrates. As a result of the effect of insulin, the amount of sugar in the blood decreases due to the opening of holes in the membranes of muscle cells and neurons for sugar to enter. Since small doses of insulin accelerate the conversion of carbohydrates into fat and its accumulation in adipose tissue, they are prescribed to thin people for the purpose of increasing body mass [23].
Insulin exists in the body mainly in two forms - monomeric and hexameric. As we mentioned above, the effect of insulin on the body is multifaceted. However, historically, the problem of the occurrence of diabetes due to insulin's effect on carbohydrate metabolism has always been the center of attention of doctors, biologists, and chemists, and has always attracted their interest. It is known that when there is a lack of insulin, the amount of glucose in the blood increases rapidly. If insulin is introduced into the body, the amount of glucose in the blood decreases. Currently, there is little information about its mechanism. It is believed that insulin binds to the protein receptor on the surface of the target cell and facilitates 2 independent processes. First, glucose enters the cells easily and quickly from the blood. This is explained by the fact that the permeability of the cell membrane for glucose increases under the influence of insulin. Secondly, the use of glucose in cells, especially its conversion into glycogen, improves. Because, in this case, the activity of the hexakinase enzyme increases and has a catalytic effect on the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, which will be included in the metabolism [24-26].
Insulin affects almost all types of metabolism in the body. It easily passes through the cell membrane and enters the cell. It is believed that the S-S bond (bridge) in the A chain of insulin combines with the SH (sulfhydryl) group of the specific insulin receptors of the cell membrane, as a result of which the permeability of the cell membrane increases and the entry of glucose into the cell becomes easier. Adenyl cyclase is the primary cell membrane receptor that insulin binds to. Due to the influence of insulin, the process of pinocytosis in adipose tissue is strengthened, as a result, the fluid surrounding the fat cells is completely transferred inside the cell. Insulin increases the permeability of the cell membrane to glucose, amino acids, fats, ketone bodies and P, K, Na ions: it accelerates the process of glucose phosphorylation in the cytoplasm of the cell in the presence of hexokinase, ATF and oxygen. This process eliminates the inhibitory effect of glucocorticoids and somatotropic hormone. As a result of the phosphorylation process, depending on the conditions, glucose is used either for the oxidation process until the end or for glycogen synthesis [25].
Insulin inhibits the process of lipolysis, accelerates lipogenesis and inhibits glycogenesis. The liver is one of the organs of the body that store glucose in the form of glycogen. Glucose can freely diffuse into the liver cells, and when its level in the blood decreases, it can freely leave it and enter the blood. Under the influence of insulin in the liver cells, glucose is converted into glycogen and its amount in the blood decreases. One of the main biochemical effects of insulin is the activation of glucokinase, which catalyzes the phosphorylation of glucose entering liver cells. In normal nutrition, 60% of the glucose taken with food is temporarily stored in the liver, then the amount of sugar in the blood is quickly released by the breakdown of glycogen and enters the blood.
Results
-
1. After the removal of the pancreas and during its hypofunction, a severe and difficult-to-treat disease called diabetes and sugary urine is observed in humans and animals. Sugary urine starts within the next few hours after the gland is removed. Animals with a high appetite and tendency to drink a lot of water take on a thin, bloated appearance. Pathological changes are always detected in the tissues of the islets of Langerhans during dissection after the death of patients.
-
2. Under the influence of glucagon, the process of converting glycogen into glucose begins to take an active form in the liver and some other organs. Glucagon helps to increase the amount of glucose in the blood due to the activation of phosphorylase, which is involved in the breakdown of glycogen in the presence of glucose. In addition, glucagon stimulates the acidification of glucose in tissues. Different animals have different sensitivity to glucagon. Glucagon affects fat metabolism and stimulates the breakdown of fat in adipose tissue.
Список литературы The role of patiral hormones in metabolism
- Yakovlev, V. N. (2005). Normal'naya fiziologiya. Voronezh. (in Russian).
- Poltyr'ev, S. S. (1980). Fiziologiya pishchevareniya. Moscow. (in Russian).
- Ammann, D., & Warshaw, A. L. (1985). Acute pancreatitis: Clinical aspects and medical and surgical management.‘Bockus Gastroenterolojy.
- Barrett, E. J. (2003). Insulin’s effect on glucose production: direct or indirect?. The Journal of clinical investigation, 111(4), 434-435. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI17881
- Barthel, A., & Schmoll, D. (2003). Novel concepts in insulin regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 285(4), E685-E692. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00253.2003
- Caumo, A., & Luzi, L. (2004). First-phase insulin secretion: does it exist in real life? Considerations on shape and function. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 287(3), E371-E385. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00139.2003
- DeWitt, D. E., & Hirsch, I. B. (2003). Outpatient insulin therapy in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: scientific review. Jama, 289(17), 2254-2264. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.17.2254
- Gunn, I. R., Faye, S., & Clayton, M. G. G. (1986). Prospective evaluation of urinary amylase test strip. The Lancet, 327(8490), 1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(86)91878-7
- Hall, J. E., Summers, R. L., Brands, M. W., Keen, H., & Alonso-Galicia, M. (1994). Resistance to metabolic actions of insulin and its role in hypertension. American journal of hypertension, 7(8), 772-778. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/7.8.772
- Hattersley, A. T. (2004). Unlocking the secrets of the pancreatic β cell: man and mouse provide the key. The Journal of clinical investigation, 114(3), 314-316. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI22506
- Corfield, A. P., Cooper, M. J., & Williamson, R. C. (1985). Acute pancreatitis: a lethal disease of increasing incidence. Gut, 26(7), 724-729.
- Korsten, M. A., Dlugozs, J. W., Saeli, J., & Lieber, C. S. (1990). İnhibition of Cathepsin B reduces the severity of experimental pancreatitis in the rat. Gastroenterol, 98, 223-226.
- Kowluru, A. (2003). Regulatory roles for small G proteins in the pancreatic β-cell: lessons from models of impaired insulin secretion. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 285(4), E669-E684. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00196.2003
- List, J. F., & Habener, J. F. (2004). Glucagon-like peptide 1 agonists and the development and growth of pancreatic β-cells. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 286(6), E875-E881. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00007.2004
- Mann, G. E., Yudilevich, D. L., & Sobrevia, L. (2003). Regulation of amino acid and glucose transporters in endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Physiological reviews, 83(1), 183-252. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00022.2002
- Pessin, J. E., & Saltiel, A. R. (2000). Signaling pathways in insulin action: molecular targets of insulin resistance. The Journal of clinical investigation, 106(2), 165-169. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI10582
- Rinderknecht, H., & Geokas, M. C. (1972). Anionic and cationic trypsinogens (trypsins) in mammalian pancreas. Enzyme, 14(2), 116-130. https://doi.org/10.1159/000459469
- Russell, D. W. (2003). The enzymes, regulation, and genetics of bile acid synthesis. Annual review of biochemistry, 72(1), 137-174. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161712
- Schmid, S. W., Uhl, W., Friess, H., Malfertheiner, P., & Büchler, M. W. (1999). The role of infection in acute pancreatitis. Gut, 45(2), 311-311.
- Schoenberg, M. H., Büchler, M., Gaspar, M., Stinner, A., Younes, M., Melzner, I., ... & Beger, H. G. (1990). Oxygen free radicals in acute pancreatitis of the rat. Gut, 31(10), 1138. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.31.10.1138
- Shi, Y., Taylor, S. I., Tan, S. L., & Sonenberg, N. (2003). When translation meets metabolism: multiple links to diabetes. Endocrine reviews, 24(1), 91-101. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2002-0018
- Tenner, S. M., & Steinberg, W. (1992). The admission serum lipase: amylase ratio differentiates alcoholic from nonalcoholic acute pancreatitis. American Journal of Gastroenterology (Springer Nature), 87(12).
- Chen, H. M., Sunamura, M., Shibuya, K., Yamauchi, J. I., Sakai, Y., Fukuyama, S., ... & Matsuno, S. (2001). Early microcirculatory derangement in mild and severe pancreatitis models in mice. Surgery Today, 31, 634-642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005950170098
- Thomson, S. C. & Townsend, C. M. Endocrine Pancreas. Sabiston. 2001. P. 646-661.
- Williams, J. A. (2001). Intracellular signaling mechanisms activated by cholecystokininregulating synthesis and secretion of digestive enzymes in pancreatic acinar cells. Annual review of physiology, 63(1), 77-97. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.63.1.77
- Yeo, C. J., & Cameron, J. L. (2001). The pancreas. İn: Sabiston DC, editor. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery.


