The Strategic Performance Measurements in Educational Organizations by Using Balance Scorecard
Автор: Thitirath Cheowsuwan
Журнал: International Journal of Modern Education and Computer Science (IJMECS) @ijmecs
Статья в выпуске: 12 vol.8, 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The Balanced Scorecard has been adopted as a management and measurement system around the world. It is adopted as a measure to assess the efficiency of an organization's activities. The Balanced Scorecard measures four dimensions of organizational activities – internal processes, financial, external customers and learning and growth perspective. These focus on critical issues impacting modern business organizations that are the effective measurement of corporate performance and evaluation of the success of implementation of corporate strategy. This study explores the Balanced Scorecard as applied in higher education through a case study of the, School of Information and Communication Technology, Phayao University. This study seeks to explore the application of the Balanced Scorecard as a measurement system and its effectiveness in organizational evaluation within the School. In identifying a strategy to implement the Balanced Scorecard within the School each dimension is considered such as internal processes, financial, internal customer and learning and growth. This research began by examining practices in place and linking them to a Balanced Scorecard approach. The intention is being to identify administrative and tracking systems for performance measurement within the School. A model is then identified to collect data across the dimensions of the balanced scorecard, and performance criteria identified. In implementing this phase scores will be associated with performance within the four dimensions. This will enable an evaluation of the model, contribute to software improvement and assist users in conducting accurate and effective strategic planning. It is then hoped to implement the model within the School in strategy plans and operation of the School to improve the assessment of the performance, and identify areas of improvement and change that is desirable.
Balance Scorecard, Decision Support System, Strategic Measurements
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15014926
IDR: 15014926
Текст научной статьи The Strategic Performance Measurements in Educational Organizations by Using Balance Scorecard
Published Online December 2016 in MECS DOI: 10.5815/ijmecs.2016.12.03
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) has been designed by R. S. Kaplan and D. P. Norton [1], [2]. In order to improve and develop strategic measurements in educational organizations, BSC is a tool designed to support the administration and to measure organizational performances. BSC is the organization assessment and tool for management to communicate with employees and external stakeholders [3]. It elevates the administrative standards to meet the highest customers’ satisfactions. Management control scholars who apply stakeholder theory to performance measurement, believe “performance measurement design starts with stakeholders” [4]. Moreover, it is a tool designed to put strategic organizations into actual practices as to enhance organization to become successful, alignment and focus to success of the organization [5]. The successes of the organization are the series of missions, visions, strategies, aims, related rules, and regulations. They would support the organization to reach its goals. The use of BSC in organizational administration requires accurate and practical performance indicators as to reflect four major aspects. Firstly, the internal process perspective, it emphasizes on administration within the organization such as the procedure of annual project, the concept of identifying key factors responsible for performance was well received by all concerned, the concept permits stakeholders to Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA), which follows a continuous improvement cycle [6]. Secondly, the financial perspective, it accentuates on effectiveness and capabilities of both monetary matters and budgeting. Thirdly, the external customer perspective, it focuses on customers’ satisfactions. Finally, the learning and growth perspective, it concentrates on initiating both new innovations and encouraging employees.
The employees dominantly perform the performances of the organization within the arrays of BSC. For customers, the demands of the customers need to be response accurately and effectively in both strategic and practical levels. For leaders, they educate employees to Become effective and qualified leaders of the organization.
For information and technologies leaders, they elevate organizational standards by using both information and technologies as the tools. The provided tools would allow all employees to be able to make effective, accurate and prompt judgments for reaching major goals of the organization. Finally, for initiation leaders, they continuously develop the best and appropriate innovation for the organization. By covering all four strategic administration aspects, BSC was accepted and widely used worldwide by both profit and non-profit organizations as well as the leading educational organizations such as Glasgow Caledonian University, Napier University, University of California and Ohio State University [7]. There is challenge for Thai education system to utilize BSC. For university’s administrators, BSC is considered as a mechanism that encourages all administrative levels to be able to control and follow up the four dimensions of the organizational goals. The goals are combined with missions, visions, strategies, and aims. In addition, the BSC becomes a tool to measure the management abilities of the administrators whether their capabilities and effectiveness. Administrators need to be aware of the relationship between the BSC with strategy maps as well as management tools [8]. It levels of social expectation and evaluates an internal development process of the organization in accordance with the standard of high educational committee. For the use of the BSC in administration processes, it enables effective and punctual communications and administrations. The strategy is to develop a plan to achieve long-term objectives of the organization [9] to achieve the objectives and mission of the organization and its operations to ensure it is able to achieve the strategic objectives set [10].
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2, the methods of the proposed project is introduced. In section 3, all the results are presented. Finally, the conclusion is described in section 4.
-
II. Methods
-
2. Model synthesis
1.Prerequisites
• SWOT Analysis
-
• Setting Vision • Strategy Map
-
• Strategy • KPIs
-
3. Technical implementation
-
• Basic training for the persons building scorecards, Building of the scorecards (KPI’s)
-
• Setting target and alarm levels, Setting calculation formulas to consolidate the data
-
• Installation of the software
-
• Defining graphical properties for graphs possible customized reports
-
4. Organizational integration
-
• Definition of persons who are responsible for measure data and their empowerment
-
• Explanation of objectives of BSC implementation to employees
-
• Re-engineering the management and strategy process, Re-engineering the report process
-
5. Technical integration
-
• Identification of imported measures and source systems
-
• Analysis of database structure and exporting capabilities of operative systems
-
• Defining procedure to get measure data from data sources including data identification, modification, scheduling
-
• Implementation of link between scorecards and operative systems
-
6. Operation
-
• Day-to-day operations • Report BSC results
-
• Update measure values • Refine BSC model
-
• Analyze BSC results
Fig.1. The BSC Implementation Steps.
The purpose of this research is focused on School of Information and Communication Technology (SICT), University of Phayao. By using BSC in the processes, it develops the administration and tracking systems of the SICT Performance. The processes are Prerequisites,
Model synthesis, Technical implementation,
Organizational integration, Technical integration, and
Operation [11]. They are able demonstrated in figure 1.
-
III. RESULTS
From the study, the SICT has been set both mission and vision. The mission of the SICT is “Wisdom for Community Empowerment” and the vision of the SICT is “Information and Communication Technology empower knowledge and open up international opportunities for a better life”. Both mission and vision take along with five major strategies. First, an effective and efficient management, it is committed to good governance. Second, a teaching and learning management (or live and learn), it is focused on students happiness so that they would become moral and qualified graduates. Third, an initiated research, it is focused on the creation of intellectual property rights (The Collective Intelligence supports the idea of One University One Province) along with the community. Fourth, the provided academic services, they are focused on the use of intellectual property rights as well as the development of strong community. Finally, minister wisdom arts, culture, and the environment of the local wisdom are provided to students [12]. By using all gathered data to develop strategic plans for the organization, there are four results. First, an internal process perspective, it emphasizes on developing the management plan in accordance with several parts such as the policies, the good governance principles in personnel development, the quality assurance system, and the graduate development. The goal is to meet the needs of the customers in accordance with core mission and two strategies, which are teaching and managing of eleven projects per activities with five strategies. Second, a learning and growth perspective described the goals for employees, information systems, and organizational alignment [13], it is concentrated on researching and initiating knowledge to improve organization growth under missions and strategies of two issues. The issues are researching and administrating in three projects per activities under strategy 1. Third, a financial perspective, it is focused on the sources of capital budget management in accordance with its value for money under mission and strategic issues with two projects per activities under two strategies because business needs information about activities, not accounting costs, to manage competitive operations and to identify profitable products and services [14]. Finally, an external customer perspective, it is concentrated upon the building customers’ satisfaction under fourteen projects per activities under strategy 2. However, if the organization has been accomplished the above processes, it was believed by organizational members. Moreover, it would enable the organization to reach its mission and vision. The processes are able to describe as the figure 2.
Wisdom for Community Empowerment
Converting Strategy into Action
Information and Communication Technology empower knowledge and open up international opportunities for a better life
Management

Financial perspective which emphasize on effectiveness and capabilities of monetary matters and budgeting

Academic Service
External Customer perspective emphasizes on customers’ satisfactions
• Provide the student
Strategy
• professional development
• Funding sources
reporting.
Financial strategies.
• Monitoring/tracking/
• Implementation of

Management
Research
Learning and Growth perspective emphasizes on initiating new innovations and encouraging employees

• Community development
• Cultural Arts Publishing
• aesthetic development
• 1 school 1 model
Strategy
Strategy
1. Knowledge Management 3. Research and publication promotions
2. Network Development 4. QA research and benchmarking
anagement

Teaching I
Strategy
Internal process perspective which emphasizes on administration within the organization, HRD, Quality Assurance, Student Quality Development, Ethics, of good governance., University policy support, etc.
A Motivated and Prepared Workforce
• Manage the principles of good governance.
• HR Development, Produce quality graduates
• Development Graduate identities
• Integrated teaching with other ministries
• Student Development, moral, evaluation, etc.
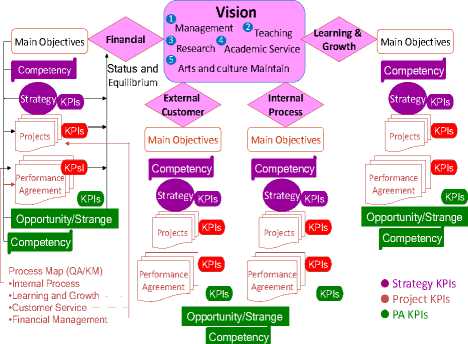
Fig.4. The Converting Strategy into Action.
Fig.2. The Strategic Map .
For the use of the strategic map to analyses and design as the main operation, it is able to reach organization stone miles towards its mission and vision. The organization needs to improve internal processes, which are included with a personnel development, an administrative process development, and a graduate development. The personnel development is included with both teachers and teaching assistants’ development. They have to elevate both the qualification and standards to support and stimulate working atmosphere to become familiar with the use of BSC. For an administration development process, it starts with conducting the order of operations including developing information systems. These systems create consumers reliability, seeking funds, developing academic services, building strong cooperation, stimulating continuous knowledge management for continuous growth, elevating qualification of the graduates by developing graduates within the frame of “TQF”, and developing graduates identities in accordance with the terms of the university. The processes have been conducted to reach the milestone “Knowledge Building for strong Communities” as shown in figure 3 and 4 respectively.
It is start with to put strategic map and stone miles into practices in the organization. We determine both the strategies and the indexes that are complied with the view of BSC in the levels of several KPI classes such as strategy KPIs, project KPIs, and performance agreement KPIs. The above methods are also taken along with performance agreement of the SICT in the fiscal years of 2014-2016. Hence, the followings illustrate the percentile of using BSC at the levels of Strategy KPIs and performance agreement (PA) KPIs which can be categorized as the internal process (40%), the learning and growth (20%), the financial performance (20%), and the external customer (20%). The Table 1 illustrates the breakouts of previously mentioned figures.
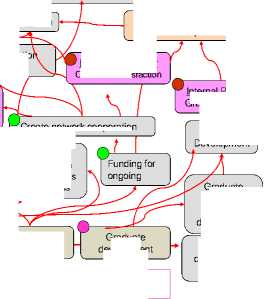
BSC Milestones
Create new knowledge
Create Learning Social
Achieve the vision
Wisdom for Community Empowerment

KM System
Motivation/understanding the process of BSC.
Human resources development
Internal Process Streamlines workflow/rules/quality.
procedures development
enerate more revenue
Vbreakeven
Graduate qualified identity
Financial Perspective
Budget plan and cost-effectively achieve the vision.
Creating PR system, Activities build confidence among clients, Partnerships with community activities
Quality of educatio service
Graduate development
A Motivated and Prepared Workforce
Work System Development
Student development within TQF
Graduate unwanted о identity development
Fig.3. The BSC Milestones.
External Customer Customer Satisfaction
Internal Process
Graduate Quality
Create network cooperation
QA Development
Table 1. The Example Of Criteria And Indication For Measuring Level Of Success In Strategic Mission Plan Of The Fiscal Year 2015
|
Internal process (40%) |
Target value |
% |
|
1. Management: The evaluation results of academic quality assurance in accordance with the measurement of the Office of the Higher Education Commission (Average 4.51 Points) |
5 |
10 |
|
2. Management: The evaluation results of academic quality assurance in accordance with the measurement of the Office of the Higher Education Commission (Average Score 4.00) |
5 |
10 |
|
3. Teaching: The success in supporting Cooperative Education (With numbers of student participants not less than 50 people) |
5 |
10 |
|
4. Teaching: The success in establishing conventional academic project (1 assembly). |
5 |
5 |
|
5. Teaching: The success in reducing the number of students who are not able to complete the study. (Reduced to not less than 5 percent). |
5 |
5 |
|
Learning and growth (20%) |
Target value |
% |
|
1. Management and Research: Successful development of young researchers (not less than 10 contracts). |
5 |
10 |
|
2. Management and Research: The success in bringing research and creative work of teachers and students to use (at least 10) |
5 |
10 |
|
Financial (20%) |
Target value |
% |
|
1. Management: The success in obtaining research funding, both within and outside the university (not less than 10 million Baht). |
5 |
20 |
|
External Customer (20%) |
Target value |
% |
|
1. Arts & culture maintain : The Level of achievement identity development plan of the UP |
5 |
10 |
|
2. Academic service: The success in integration of academic services with teaching and researching |
5 |
10 |
It is assigned a score based on the perspective of the balanced scorecard. In order to present the results of progress in the implementation of the BSC perspectives and views on the strategic plan with easy clarification and understandings, the following charts define a score scale and a color indicator (or scorecard presentation) into five levels. The design of the strategic performance measurements in educational organizations by using balance scorecard affect decision support system shown as the Use Case Diagram in figure 5.
Associate Dea Assistant Dean Program Header
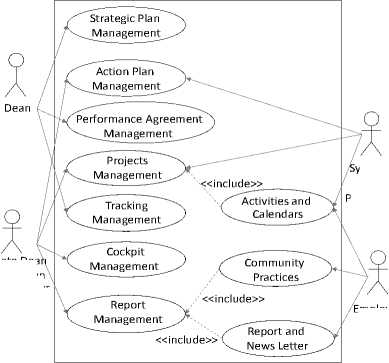
ystem Admin and
Planning Officer
Employees
Fig.5. The Use-case Diagram.
The executive decision support is designed by the technology that is connected with organization’s missions, visions, core strategies, operations, and performance agreements. The goals of the designed technology are several aspects. First, the tracking progressive performances in term of both the BSC and strategic planning are provided. Second, the progression of the achievement for the vision, mission, and main objectives of the strategic plans is given. Finally, the performance agreement evaluation is able to demonstrate.
As the results, the goals are provided to executives and employees in term of the management cockpit as the individually. The system will automatically display in strategy data management, graphs and cockpits management as Figure 6 and 7 respectively.
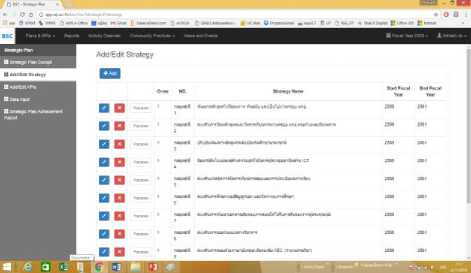
Fig.6. The Captured Screen of Strategies Data Management.
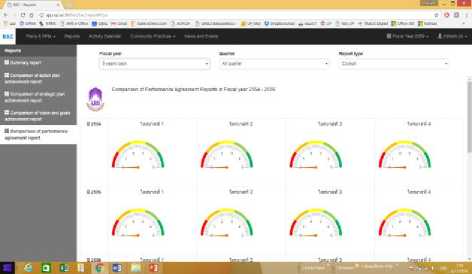
Fig.7. The Captured Screen of Graphs and Cockpits Management
In Figure 8, the system evaluation, executives and employees of the SICT are the highest rate of satisfaction with the system design. In addition, both usability performance and system performance are still the same performance as the system evaluation, executives and employees of the SICT.
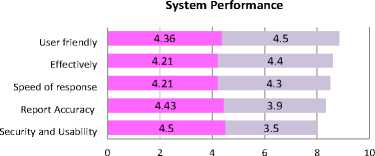
Fig.8. (a) System Performance.
Usability Performance
Follow-up and Tracking
Documentation and reports
Decision support
Paperless
Support work faster
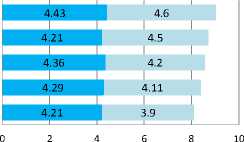
Executives
Employees
Fig.8. (b) Usability Performance .
System Design
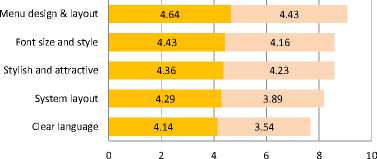
Executives
Employees
Fig.8. (c) System Design.
Fig.8. The Effectiveness of The Proposed System by Managers and Employees.
-
IV. Conclusion
The application of the balanced scorecard strategic management system to decision support of SICT has analyzed, designed and developed in accordance with the requirements of the executives and staffs. It is served as a tool to transform strategy into practice. The results of the comprehensive decision support system for strategic management of the organization enable organizations to track performance, processing, and display operations in four BSC dimensions. The process by which administrators assure that resources are obtained and used effectively and efficiently in the accomplishment of the organization’s objectives [15]. This system can be used to work in the organization. It is developed under the concept of flexibility in applications, enabling organizations to change strategies plan and easily measurable indicators in the organization. The system presents quantitative indicators on all dimensions. Moreover, it can be applied to organizations in both the business and education. However, the system is designed for the operation in the organization. It also requires planning, corporate strategy, consistent with the dimensions of the BSC can be applied effectively. And to measure the balance is to convert the vision, mission and strategy of the organization to a series of key performance measure that defines the strategy and management. The level of achievement of the organization including finance and non-financial [16]. This research is application of the BSC with educational institute compliance with Hanne’s research to study and focus on strategy and measurement of financial and NonFinancial. Results from the BSC application can be achieved to organizational goals [17]. It is evident, that the Balanced Scorecard method could help to our businesses not only to measure the performance but also to manage the strategies which are needed to be adopted so that the long-term goals are achieved. Thus, in other words, the application of this tool could help to ensure the consistency of vision and action which is the first step towards the development of successful businesses [18]
Список литературы The Strategic Performance Measurements in Educational Organizations by Using Balance Scorecard
- R.S. Kaplan and D.P. Norton, "Using the Balanced Scorecard as a Strategy Management System," Harvard Business Review, pp. 75-85, 1996.
- R.S. Kaplan and D.P. Norton, "Strategy-Focused Organization," Harvard Business Press, 2000.
- P.R. Niven, Balanced Scorecard step by step: Maximizing performance and maintaining result. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2002.
- A. Neely and C. Adams, Performance Prism: The Scorecard for Measuring and Managing Stakeholder Relationships. Financial Times: Prentice Hall, 2002.
- C. S. Moser, "Designing, Creating and implementing balanced scorecard guidelines for the architectural firm," Ph.D. dissertation, California State University, 2004.
- G. Propa, D.K. Banwet, and K.K. Goswami, "Sustainable Operation Management Using the Balanced Score Card as a Strategic Tool - A Research Summary," Social and Behavioral Sciences, vol. 189, pp. 133-143, May 2015.
- P. Coronel and A. Evans, The balanced scorecard in facilities management, March 2016. [Online]. Available: http://www.tefma.com.
- K. Phusawat and P. Jaiwong, "Formulating the strategy map: Case studies on SMEs in Thailand," International Journal of Management and Enterprise Development, vol. 5, pp. 1-17, 2008.
- S. C. Certo and S. T. Certo, Modern management concept and skills, New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 2009.
- W. Wattananimitkul, An Application of Balanced Scorecard as A Technique for University Improvement, May 2016. [Online]. Available: http://www.kmutt.ac.th.
- QPR Software Plc. Guidelines for Implementing Balanced Scorecard. October 2016. [Online]. Available: http://www.qpr.com.
- University of Phayao, University of Phayao Development Plan, October 2016. [Online]. Available: http://www.up.ac.th.
- R. S. Kaplan, Conceptual Foundations of the Balanced Scorecard, May 2016. [Online]. Available: http://www.hbs.edu.
- H. T. Johnson, "Managing Costs: An Outmoded Philosophy," Manufacturing Engineering, pp. 44-45, May 1980.
- R. N. Anthony, Planning and Control Systems: A Framework for Analysis. Boston: Harvard Business School, 1965.
- P. Decharin, Balance Scorecard and Key Performance Indicators. Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University, 2004.
- H. Norreklit, "The Balanced on the Balanced Scorecard-A Critical Analysis of Some of Its Assumptions," Management Accounting Research, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 65-88, March 2000.
- D. Lesáková and K. Dubcová, "Knowledge and Use of the Balanced Scorecard Method in the Businesses in the Slovak Republic," Social and Behavioral Sciences, vol. 230, pp. 39-48, February 2016.


