The structure of tetraphenylantimony dibenzoylmethanate. The factors affecting the strength of ligand binding in antimony(V) β-diketonate complexes
Автор: Sharutin V.V., Sharutina O.K.
Журнал: Вестник Южно-Уральского государственного университета. Серия: Химия @vestnik-susu-chemistry
Рубрика: Органическая химия
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.7, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Tetraphenylantimony dibenzoylmethanate (1) was obtained by substitution reaction from pentaphenylantimony and dibenzoylmethane (2) in toluene. The ligand is bidentate in molecule 1, antimony atom has octahedral coordination (trans-angles CSbO and CSbC 165.7(1)°, 168.7(1)° and 159.4(2)°, distances Sb-O 2.256(3), 2.235(3) Å, Sb-С 2.157(4)-2.170(4) Å). Compound 2 is in the enol form in the crystal, the length of C=O and O-C bonds are equal to 1.283 (2) and 1.303(2) Å.
Tetraphenylantimony dibenzoylmethanate, dibenzoylmethane, molecularstructures, x-ray analysis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147160306
IDR: 147160306 | УДК: 546.865+547.53.024+547.442.3+548.312.5
Текст научной статьи The structure of tetraphenylantimony dibenzoylmethanate. The factors affecting the strength of ligand binding in antimony(V) β-diketonate complexes
The β-diketones are bidentate chelating ligands, which form many complexes with transition metals. These complexes are well-studied and are of practical use. Chelate complexes with β-diketones are known for some non-transition metals. Thus, the existence of uncompleted d -orbitals with the lowest energy of the antimony atom determines its acceptor properties for electron pairs, provided by various donor molecules or intramolecular donor centers. This type of metal – ligand binding appears in orga-noantimony(V) β-diketonates where antimony atom is hexacoordinated. The synthesis of a sufficiently large number of antimony в—diketonate complexes are described in the literature, for example [1 - 7], but only a few of these complexes with acetylacetonate ligands are characterized structurally: Ph 2 SbCl 2 [OC(Me)CHC(Me)O] [8, 9], MeCl 3 Sb[OC(Me)CHC(Me)O] [8], Me 2 Br 2 Sb[OC(Me)CHC(Me)O] [8], Ph 4 Sb[OC(Me)CXC(Me)O], where Х = H [10], Cl [11], Et, All [12], Ph [13, 14], SBu [14].
Analysis of the geometric characteristics of the established structures has allowed us to identify some dependences of the ligand binding strength, electron density distribution in the chelate cycle and distortion of octahedral polyhedron of the central atom from the nature of the substituents at the antimony atom and γ-substituents of acetylacetone [15].
In continuation of the study of the ligand chemical nature influence on the structure of tetraphenylantimony β-diketonates we have determined the structure of tetraphenylantimony dibenzoylmethanate (1) and the original dibenzoylmethane (2) .
Experimental
Synthesis of tetraphenylantimony dibenzoylmethanate (1) was realized by the method known from [7]. Yield 82 %, mp: 223 - 225°C.
IR spectrum (v, cm - 1): 3067, 3047, 1591, 1518, 1477, 1450, 1429, 1363, 1329, 1303, 1225, 1180 (ср.), 1085, 1021, 998, 935, 842, 771, 730, 718, 694, 656, 619, 520, 458, 450.
IR spectra were recorded on the Bruker Tensor 27 FT-IR spectrometer using KBr pellet, spectra were measured in the range 4000–400 cm–1.
The X-ray diffraction analyses of crystals 1 and 2 were carried out on the D8 Quest Bruker diffractometer (Mo K«-radiation, X = 0.71073 A, graphite monochromator). Data were collected and edited, unit cell parameters were refined, and an absorption correction was applied using the SMART and SAINT-Plus programs [16]. All calculations on structure determination and refinement were performed using the SHELXL/PC programs [17]. The structures 1 and 2 were determined by a direct method and refined by the least-squares method in the anisotropic approximation for non-hydrogen atoms. The main crystallographic data and refinement results for structures 1 and 2 are listed in Table 1. Selected bond lengths and bond angles are given in Table 2.
Table 1
Crystallographic data and the experimental and structure refinement parameters for compounds 1–2
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
Empirical formula |
C 39 H 31 O 2 Sb |
C 15 O 2 H 12 |
|
Formula weight |
653,40 |
224,25 |
|
Т , К |
296(2) |
296(2) |
|
Crystal system |
Мonoclinic |
Orthorhombic |
|
Space group |
P2 1 /n |
Pbca |
|
a , Å |
11.3741(3) |
8.7609(3) |
|
b , Å |
14.9349(4) |
10.8556(3) |
|
c, Å |
18.9137(6) |
24.4698(8) |
|
α , deg |
90.00 |
90.00 |
|
β, deg |
101.7630(10) |
90.00 |
|
γ , deg |
90.00 |
90.00 |
|
V , Å3 |
3145.42(15) |
2327.20(13) |
|
Z |
4 |
8 |
|
ρ (calcd.), g/сm3 |
1.380 |
1.280 |
|
µ , mm–1 |
0.910 |
0.084 |
|
F (000) |
1328.0 |
944.0 |
|
Crystal size, mm) |
0.33 × 0.14 × 0.11 |
1.37 × 0.6 × 0.39 |
|
θ Range of data collection, deg |
2.9 - 26.41° |
3.1 - 26.41° |
|
Range of refraction indices |
–14 ≤ h ≤ 14, –18 ≤ k ≤ 18, –23 ≤ l ≤ 23 |
–10 ≤ h ≤ 10, –13 ≤ k ≤ 13, –30 ≤ l ≤ 30 |
|
Measured reflections |
42462 |
55097 |
|
Independent reflections |
6450 |
2387 |
|
R int |
R int = 0.0677 |
R int = 0.0393 |
|
Refinement variables |
379 |
155 |
|
GOOF |
1.042 |
1.468 |
|
R factors for F2 > 2 σ (F2) |
R 1 = 0.0438, wR 2 = 0.0995 |
R 1 = 0.0553, wR 2 = 0.1672 |
|
R factors for all reflections |
R 1 = 0.0834, wR 2 = 0.1190 |
R 1 = 0.0663, wR 2 = 0.1825 |
|
Residual electron density (min/max), e /Å3 |
2.17/Å–0.58 |
0.26/–0.32 |
Table 2
Selected bond lengthes and bond angles in the structures of compounds 1 - 2
|
Bond |
d , Å |
Angle |
ω , deg |
Bond |
d , Å |
Angle |
ω , deg |
|
1 |
2 |
||||||
|
Sb(1)–С(1) |
2.157(4) |
C(1)Sb(1)C(21) |
159.37(17) |
С(1)–C(7) |
1.481(2) |
С(1)С(7)С(8) |
122.57(13) |
|
Sb(1)–С(11) |
2.157(5) |
C(11)Sb(1)О(1) |
165.68(14) |
С(7)–C(8) |
1.409(2) |
С(7)С(8)C(9) |
120.93(13) |
|
Sb(1)–С(21) |
2.160(4) |
C(31)Sb(1)О(2) |
168.70(15) |
С(8)–С(9) |
1.389(2) |
C(8)С(9)С(10) |
124.07 (13) |
|
Sb(1)–С(31) |
2.170(4) |
O(1)Sb(1)O(2) |
79.10(11) |
С(9)–С(10) |
1.480(2) |
С(1)С(7)О(1) |
117.53(12) |
|
Sb(1)–О(1) |
2.256(3) |
C(1)Sb(1)C(31) |
96.00(16) |
О(1)–С(7) |
1.283(2) |
С(8)С(7)О(1) |
119.89(13) |
|
Sb(1)–O(2) |
2.235(3) |
C(1)Sb(1)C(11) |
97.14(17) |
О(2)–С(9) |
1.303(2) |
С(8)С(9)О(2) |
120.52(13) |
|
О(1)–С(49) |
1.277(5) |
C(11)Sb(1)C(31) |
104.49(18) |
С(1)–C(2) |
1.384(2) |
С(10)С(9)О(2) |
115.41(13) |
|
O(2)–С(47) |
1.287(5) |
C(11)Sb(1)C(21) |
95.46(19) |
С(1)–C(6) |
1.396(2) |
||
|
С(48)–C(49) |
1.392(6) |
C(21)Sb(1)C(31) |
96.57(17) |
С(2)–C(3) |
1.380(2) |
||
|
С(48)–C(47) |
1.395(6) |
C(1)Sb(1)О(1) |
82.28(14) |
С(10)–C(11) |
1.397(2) |
||
|
С(49)–С(51) |
1.491(6) |
C(1)Sb(1)О(2) |
80.58(14) |
С(10)–C(15) |
1.383(2) |
||
|
С(47)–С(41) |
2.490(6) |
С(47)С(48)С(49) |
126.9(4) |
С(12)– C(13) |
1.372(3) |
||
The full tables of atomic coordinates, bond lengths, and bond angles were deposited with the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC 998579, and 998580 for compounds 1 and 2, respectively; ; .
Results and Discussion
According to the X-ray diffraction data, in the complex 1 the antimony atom has a distorted octahedral coordination with the chelate ring in the equatorial position (Fig. 1). The axial angle C(1)SbC(21) is equal to 159.37(17) ° , the diagonal angles at the equatorial plane C(11)SbO(1) and C(31)SbO(2) are equal to 165.68(14) ° and 168.70(15) ° , respectively. Deviations of the atoms O(1), O(2), C(11), C(31) and Sb from the equatorial plane are +0,036, –0,035, +0,030, –0,029 and +0,005 Å, respectively. The sum of angles in the equatorial plane is equal to 360°. Six-membered metallocycle [SbO 2 C 3 ] is distorted so that the planes of the two half-cycles [O 2 Sb] and [O 2 C 3 ] form an angle of 156.4°, i.e. there is an inflection on the O - O diagonal. The planes of the phenyl rings C(41) - C(46) and C(51) - C(56) form angles of 27.8° and 7.8° with the plane [O 2 C 3 ], respectively.
The Sb - C bond lengths in the equatorial (2.157(4), 2.170(4) A) and axial (2.157(4), 2.160(4) A) positions are not very different from each other. The ligand demonstrates anizobidentate character of coordination: the Sb - O(1) and Sb - O(2) distances are 2.256(3) and 2.235(3) A. The O(1) - C(49) and O(2) - C(47) bonds in the cycle do not differ much (1.277 (5) and 1.287 (5) A), the same is true about the C(48) - C(49) and C(48) - C(47) (1.392(6) and 1.395(6) A).
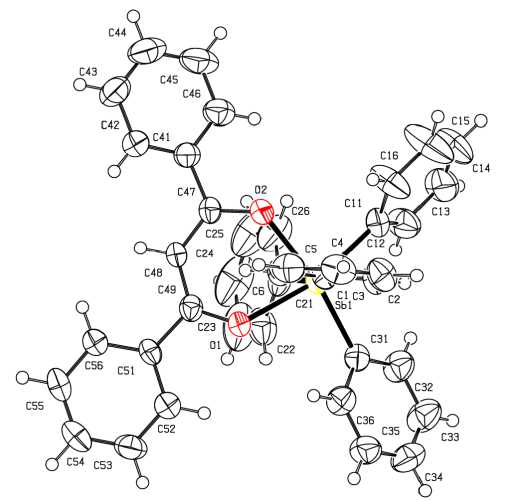
Fig. 1. The structure of the compound 1
The valence angles at the antimony atom in the molecule of tetraphenylantimony y-phenylacetylacetonate are close to those observed in the compound 1, however, the binding of ligand to the central atom (the Sb-O distances are 2.215(1) and 2.228(1) A [14]) is stronger. Since the strength of the donor-acceptor interaction is due to both the acceptor ability of the metal and donor properties of the ligand, it can be assumed that the methyl groups with the positive inductive effect play the decisive role in strengthening these properties of γ-penylacetylacetonate ligand. The effect of the group nature at the antimony atom and the chelate cycle on the ligand binding strength to the central atom can be seen in the inorganic complexes Cl4Sb[OC(Ph)CHC(Ph)O] [18] and Cl4Sb[OC(Me)CHC(Me)O] [18, 19]. In tetrahloroantimony dibenzoylmethanate with symmetrical ligand coordination the Sb-O bond length (2.011(4) Å) is close to the sum of the covalent radii of antimony and oxygen atoms (2.07 Å [20]) that can be explained by an increase in acceptor properties of the antimony atom having four electronwithdrawing substituents (Cl atoms). Replacement of the phenyl groups, showing a weak negative inductive effect, by methyl groups in the chelate cycle of tetrachloroantimony acetylacetonate leads to greater consolidation of ligand binding (the Sb-O bonds are 1.928(11) and 1.991(14) A). Strengthening of the Sb-O bonds in inorganic complexes is accompanied by some lengthening of the C-O bonds in the chelate cycle (1.298(5) and 1.318(19), 1.320(19) Å, respectively).
The above analysis of the structural data demonstrates that the strength of the chelate cycle in tetraphenylantimony β -diketonate is significantly affected by the nature of the substituent not only in the γ -position, as stated previously [15].
β-Diketone 2 is in the enol form in the crystal (Fig. 2). The planes of the phenyl ring C(1) - C(6) and fragment O(1)C(7)C(8)C(9)O(2) are coplanar, the C(10) - C(15) plane amounts to angle 14.4° with this plane. The C(7) - O(1) bond length (1.283(2) Å) is shorter than the C(9) - O(2) bond (1.303(2) Å), while the C(7) - C(8) bond length (1.409(2) Å) is greater than the C(9) - C(8) bond (1.389(2) Å). The distances C(1) - C(7) and C(9) - C(10) (1.481(2), 1.480(2) Å) are less than the corresponding distances of 1 (1.490(6), 1.491(6) Å).The angle C(7)C(8)C(9) is equal to 120.93(13)º and corresponds to the valence angle at the carbon atom in the sp 2-state. In compound 1 the angle at the atom C(48) in the chelate ring is 126.9(4)º.
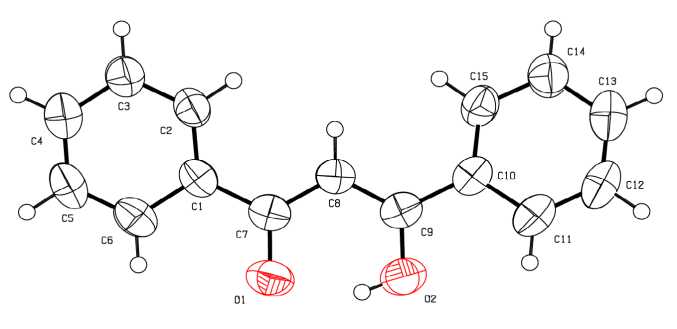
Fig. 2. The structure of the compound 2
Intramolecular hydrogen bond has parameters: O (2) - H 0.82 Å, O(1) ⋅⋅⋅ H 1.72 Å, angle O(2)HO(1) 149°.
Conclusions
Thus, the nature of the substituent groups in the cycle determines the chelate ligand binding strength in the antimony(V) β-diketonate, but has virtually no effect on both the distortion of the coordination polyhedron antimony atom and the complex structure as a whole.
At binding of dibenzoylmethane in the complex there is redistribution of the electron density, which causes the alignment of C - O and C - C bonds in the cycle. In addition, the formation of the chelate ring is accompanied by distortion of the CCC bond angle compared with the theoretical value.
Список литературы The structure of tetraphenylantimony dibenzoylmethanate. The factors affecting the strength of ligand binding in antimony(V) β-diketonate complexes
- Meinema, H.A. Preparation and Properties of Ogano(acetylacetonato)antimony (V) Compounds/H.A. Meinema, I.G. Noltes//J. Organomet. Chem. -1969. -V. 16. -N. 2. -P. 257-263.
- Matsumura, Y. Hexacoordinated Tetraphenylantimony complexes/Y. Matsumura, R. Okawara//Inorg. Nucl. Chem. Lett. -1968. -V. 4. -N. 9. -P. 521-524.
- Singhal, K. Studieson β-Diketonate and β-Diketones ter Derivatives of Tri-and Tetraorganoantimony(V)/K. Singhal, A.K. Aggarwal, P. Ray//Indian J. Chem. -1992. -V. 31A. -N.10. -P. 797-799.
- Jain, V.K. Synthesis and Spectral Studies of (1,3-Diketonato)triphenylantimony (V) Complexes/V.K. Jain, B. Bohra, R.C. Mehrotra//J. Organomet. Chem. -1980. -V. 184. -N. 1. -P. 57-62.
- Otero, A. Pentafluorophenylantimony Compounds/A. Otero, P. Royo//J. Organomet. Chem. -1978. -V. 154. -N. 1. -P. 13-19.
- Pentahalophenyl Derivatives of Antimony (V) with Bidentate Ligands/A. Espinosa, A.J. Barbero, J.M.G. Sanchez et al.//An. Quim. -1983. -V. 79B. -N. 2. -P. 217-220.
- Cинтез β-дикетонатов тетраарилсурьмы из пентаарилсурьмы и β-дикетонов/В.В. Шарутин, О.К. Шарутина, О.П. Задачина и др.//Журн. общ. химии. -2000. -Т. 70. -Вып. 5. -С. 746-747.
- The Crystal and Molecular Structures of three Acetylacetonato-Organoantimony (V) Compounds /N. Kanehisa, K. Onuma, S. Uda et al.//Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan. -1978. -V. 51. -N. 8. -P. 2222-2233.
- Kroon, J. The Molecular Structure of (Acetylacetnato)dichlorodiphenylantimony in the Crystalline State/J. Kroon, J.B. Hulscher, A.F. Peerdeman//J. Organomet. Chem. -1972. -V. 37. -N. 2. -P. 297-301.
- Шарутин, В.В. Кристаллическая и молекулярная структура ацетилацетоната тетрафенилсурьмы/В.В. Шарутин, О.К. Шарутина//Бутлеровские сообщения. -2014. -Т. 38. -№ 5. -С. 118-121.
- Синтез и строение хлорацетилацетоната тетрафенилсурьмы/В.В. Шарутин, О.К. Шарутина, О.П. Задачина и др.//Журн. общ. химии. -2000. -Т. 70. -№ 10. -С. 1672-1674.
- Синтез и строение γ-алкилацетилацетонатов тетрафенилсурьмы/В.В. Шарутин, О.К. Шарутина, О.П. Задачина и др.//Коорд. химия. -2003. -Т. 29. -№ 1. -С. 8-12.
- Синтез и строение γ-фенилацетилацетоната тетрафенилсурьмы/В.В. Шарутин, А.П. Пакусина, О.К. Шарутина и др.//Химия и компьютерное моделирование. Бутлеровские сообщения. -2003. -Т. 4. -№ 1. -С. 34-35.
- Синтез и строение γ-фенил-и γ-тиобутилацетилацетонатов тетрафенилсурьмы/В.В. Шарутин, А.П. Пакусина, И.В. Егорова и др.//Коорд. химия. -2008. -Т. 34. -№ 4. -С. 267-271.


