The taxonomic spectrum and bioecological characteristics of species of the genus Alchemilla L. from the family Rosaceae Juss. in the flora of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic
Автор: Babayeva S., Memmedova L.
Журнал: Бюллетень науки и практики @bulletennauki
Рубрика: Естественные науки
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.11, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article provides information about the taxonomic spectrum and bioecological characteristics of the species belonging to the genus Alchemilla L. of the Rosaceae Juss. family, which are spread across the flora of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. Through a comparative analysis of collected herbarium materials and literature sources, it has been revealed that the genus Alchemilla is represented by 13 species in the Nakhchivan AR, and information about the current state of these species is also reflected in the article. Based on our research, the ecological groups and geographical elements of the species belonging to the Alchemilla L. genus of the Rosaceae family have also been studied.
Alchemilla l, taxonomic composition, genus, family, species
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14132537
IDR: 14132537 | УДК: 582.71 | DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/112/06
Текст научной статьи The taxonomic spectrum and bioecological characteristics of species of the genus Alchemilla L. from the family Rosaceae Juss. in the flora of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice
UDC582.71
The Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic is distinguished by its unique nature, diverse biogeographical characteristics, rich xerophytic-type flora, and ecosystems. The region is formed by a combination of mountainous, steppe, and semi-desert landscapes. The flora of the area has deep historical roots, undergoing a complex natural and historical development process, and over time, has been subjected to various physical and anthropogenic influences, leading to the changes that have resulted in its current state.
In the flora of the Autonomous Republic, the basis of dicot plants begins with the relatively polymorphic family Rosaceae, and species from this family play a special role. Plants from the Rosaceae family are widespread in nature, encompassing more than 3,000 species. The species in this family are mainly perennial herbs, shrubs, and tree plants. In Azerbaijan, 195 wild species belonging to 29 genera of the Rosaceae family have been recorded. In the territory of Nakhchivan AR, it is characterized by 153 species belonging to 30 genera. Due to its wide range of uses and species diversity, the genus Alchemilla L. holds a unique place.
The study of species belonging to the genus Alchemilla L. is of scientific and practical importance for identifying the species spread across the flora of the Autonomous Republic and understanding their bioecological characteristics. Therefore, it is advisable to conduct research in this area.
Material and research methods
The research utilized widely accepted floristic, geobotanical, bioecological methods, and phenological observations. The main research materials were based on literature sources and actual data obtained during field studies, with the research object being various areas of the region and the research material consisting of species belonging to the genus Alchemilla L. In the study area, material related to species of the Rosaceae family is mentioned in several publications [2-6, 16, 17, 20, 23, 26-31]. The identification and clarification of the names of species belonging to the Alchemilla L. genus were based on works such as Flora of Azerbaijan [13], Flora of the Caucasus [14], A.M. Asgarov's Flora of Azerbaijan [1], and others. Recent taxonomic changes were carried out based on the World Flora Online .
Discussion and conclusions of the study
In the flora of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, species belonging to the genus Alchemilla L. hold a significant role among economically important plants. Based on literature data and personal field research material, it has been found that there are 22 species of the Alchemilla L. genus in Azerbaijan, with 13 species occurring in the Nakhchivan AR. The taxonomic spectrum and bioecological characteristics of these species are presented in the following table (Table ).
Table
TAXONOMIC SPECTRUM AND BIOECOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SPECIES BELONGING TO THE GENUS Alchemilla L.
|
Species |
Ecological groups |
Area class |
Flowering and fruiting stages |
|
Alchemilla amicta |
Mesophytes |
Asia Minor |
VI-VIII |
|
A. epipsila |
Mesophytes |
Northern Atropatan |
VII-VIII |
|
A. erythropoda |
Mesophytes |
Asia Minor |
VI-VIII |
|
A. grossheimii |
Mesophytes |
Asia Minor |
VI-VIII |
|
A. orthotricha |
Mesophytes |
Asia Minor |
VI-VIII |
|
A. persica |
Mesophytes |
Northern Iran |
VII-IX |
|
A. raddeana |
Mesoxerophytes |
Northern Atropatan |
VI-VIII |
|
A. retinervis |
Mesoxerophytes |
Asia Minor |
VII-VIII |
|
A. sedelmeyeriana |
Mesoxerophytes |
Asia Minor |
VI-VIII |
|
A. sericata |
Mesoxerophytes |
Caucasus |
VI-VIII |
|
A. sericea |
Mesoxerophytes |
Asia Minor |
VI-VIII |
|
A. smirnovii |
Mesophytes |
Northern Atropatan |
VI-VIII |
|
A. venosa |
Mesoxerophytes |
Northern Iran |
VII |
When examining the morphological structure, species of the Alchemilla genus are creeping, rhizomatous, perennial herbaceous plants. The basal leaves form a rosette, with long petioles, while the stem leaves are smaller than the basal ones and are palmately lobed. The flowers are small, bisexual, and are grouped in clustered inflorescences resembling a panicle. The calyx consists of 4 lobes, there are no petals, the stamens are poorly developed, and the pistil is solitary. The fruit resembles a nutlet. In the identification of species within the genus, the characteristics of the leaves and the degree of pubescence of the plant are considered the main features. There are 22 species of the genus in Azerbaijan, 13 species in the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, and 12 species in the protected area [7-12, 15].
Since the external environment is constantly changing, water plays a significant role as an ecological factor in the widespread distribution of plants across various climatic conditions and the formation of different plant communities. Depending on their water requirements, plants are divided into several ecological groups. The distribution of species belonging to the genus Alchemilla L. from the Rosaceae family in the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic according to ecological groups has been carried out based on Shennikov’s classification system [18, 19, 21, 22, 33].
Regarding their relationship and water demands, mesophytes occupy an intermediate position between hydrophytes and xerophytes. Mesophyte plants are mainly found in forests, shrublands, subalpine, and alpine regions, and they are more widely distributed. These plants, influenced by their natural feeding environment, not only differ in terms of species composition but also in various ecological characteristics. Examples of mesophyte species include Alchemilla amicta, A. epipsila, A. Orthotricha, A. persica , etc. (Figure 2).
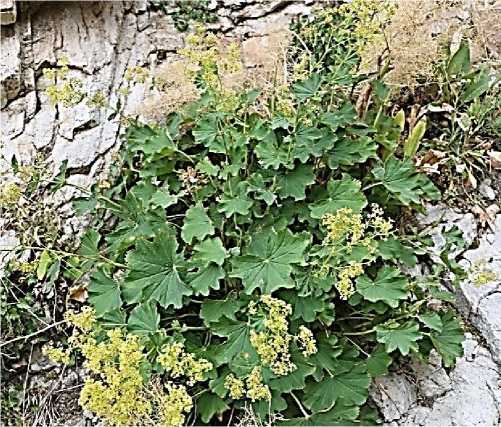

Figure 1. Alchemilla persica
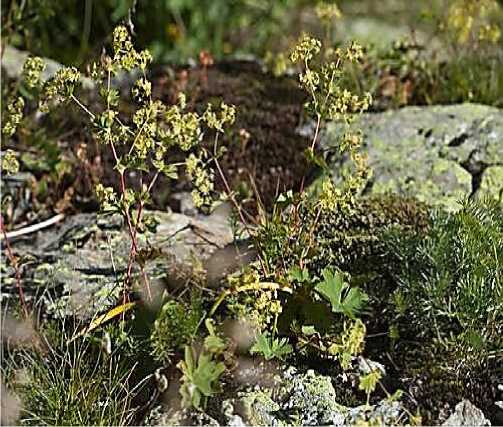

Fiqure 2. Alchemilla venosa
Mesoxerophytes are found in drier areas compared to mesophytes, but they are more humid than xerophyte plants. These species are primarily found in forest clearings, forest-edge shrubs, and on the northern-western and northern-southern slopes of mountains. Mesoxerophytes, with 6 species, account for 46% of the total species. These plants include species such as A. retinervis, A. sedelmeyeriana, A. sericea, A. venosa, and others.
As shown in the image, mesophytes dominate the species of the Alchemilla L. genus of the Rosaceae family, representing 54% (with 7 species), while mesoxerophytes are represented by 6 species, making up 46%. Among the species in the genus, xerophyte and xeromesophyte plants have not been encountered.
Recently, the N. N. Portenier system is used for geographic analysis in the Caucasus region. The areal types of species reflect the relationship between the flora of the studied area and the flora of the larger surrounding regions, leading to the study of migration paths of species from a historical perspective [23-25, 32].
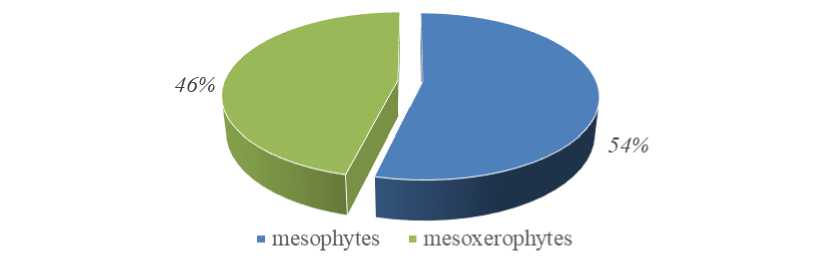
Figure 3. Distribution of species belonging to the genus Alchemilla L. according to ecological groups
Based on herbarium material collected from the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, the investigation of the herbarium collections of the Botanical and Nakhchivan Branch of the Institute of Bioresources, and literature sources, it has been determined that species of the Alchemilla L. genus belong to different areal types, which allows for the identification of migration routes of the species. Considering the above, the species of the genus have been grouped into 4 areal classes based on zonal and regional principles. As shown in the image, 7 species (53.8%) are found in the Asia Minor areal class, 3 species (23%) in Northern Atropatan, 2 species (11.7%) in Northern Iran, and 1 species (%) in the Caucasus areal class (Figure 4).
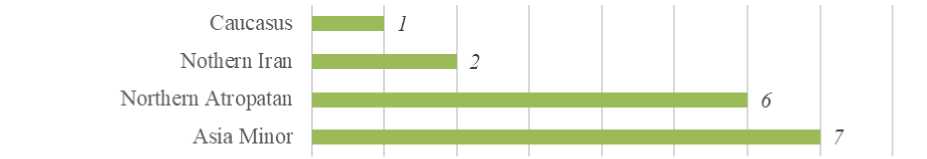
Figure 4. Geographical area classes of species belonging to the genus Alchemilla L.
Conclusions
As a result of conducted research, the systematic composition of the Alchemilla L. genus from the Rosaceae family in the flora of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic has been studied, and it has been found that 13 species of this genus are encountered in the research area. Based on zonal and regional principles, the species of the Alchemilla genus have been grouped into 4 area classes, and it has been found that 7 species (53.8%) are distributed in Asia Minor, 3 species (23%) in Northern Atropatan, 2 species (11.7%) in Northern Iran, and 1 species (9%) in the Caucasus area class. According to ecological groups, mesophytes are represented by 7 species (54%), and mesoxerophytes by 6 species (46%).
Acknowledgments: I would like to express my gratitude to Professor Dashgin Ganbarov for identifying the species studied.
Financing: The research it is financed and supported on the basis of the "Herbari Fund of Biology Department of Nakhchivan State University" project.


