Time-to-reperfusion in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing interhospital transfer using WhatsApp smartphone application
Автор: Bendary Ahmed, Mansour Ahmed, Mostafa Shaymaa, Kabeel Hamza
Журнал: Cardiometry @cardiometry
Рубрика: Original research
Статья в выпуске: 15, 2019 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Current guidelines recommend that patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) receive primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with a door-to-balloon (D2B) time of 90 minutes. This time frame has been difficult to achieve in developing countries. We aimed to test the hypothesis that using WhatsApp for inter-hospital transfer in STEMI primary PCI would result in shorter D2B time through avoiding emergency department (ED) waiting.
Reperfusion time, stemi, primary pci, whatsapp
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148311455
IDR: 148311455 | DOI: 10.12710/cardiometry.2019.15.5662
Текст научной статьи Time-to-reperfusion in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing interhospital transfer using WhatsApp smartphone application
Ahmed Bendary, Ahmed Mansour, Shaymaa Mostafa, Hamza Kabeel. Time-to-reperfusion in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing interhospital transfer using WhatsApp smartphone application. Cardiometry; Issue 15; November 2019; p.56-62; DOI: 10.12710/cardiometry.2019.15.5662; Available from:
Primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is the preferred reperfusion strategy in patients with St-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Current guidelines for the treatment of STEMI recommend a door-to-balloon (D2B) time of 90 minutes or less for patients undergoing primary PCI, with the D2B time has become a performance measure and is the focus of regional and national quality improvement initiatives [1]. This strict time limits for reperfusion is stemming from data showing that patients with longer D2B times will experience longer periods of vessel occlusion, resulting in more ischemia and greater necrosis than patients with shorter times to treatment [2], and that early reperfusion results in superior clinical outcomes, enhanced microvascular reperfusion, and better recovery of left ventricular function [3]. However, with a closer look, D2B time is one component of total ischemic time; so that as D2B time is reduced, it becomes a smaller fraction of total ischemic time, making the time before arrival at a hospital a more important factor to focus on. Hence, it has been stated that efforts with potential to improve outcomes should include increasing patients' awareness of symptoms, reducing the interval from the time of symptom onset to treatment, and shortening the transfer time between medical facilities [4].
Accordingly, pre-activation of cardiac catheterization laboratory (CCL) when STEMI is diagnosed in the pre-hospital setting has become an increasingly adopted strategy to reduce reperfusion times and improve outcomes [5]. This strategy could allow for by-passing any emergency department (ED) delays, with some evidence now linking this to shorter treatment times without adverse impact on mortality [6].
Unfortunately, many developing countries (including Egypt) are lagging behind achieving these strict time goals in reperfusion of STEMI. This is due to factors related to burdened economies which hinders the widespread availability of 24-hour ready primary PCI-capable centers, making inter-hospital transfer for primary PCI or pahr-maco-invasvie strategies more viable options for many patients [7, 8]. Therefore, any strategy that could allow for reduction of STEMI reperfusion in developing countries will be a step-forward, and here comes the importance of new smartphone technology.
WhatsApp (WhatsApp Inc., Mountain View, CA) is a mobile-based software messaging application that is used by millions all over the world and allows free sharing of text messages, unlimited number of images, voice notes and videos. It has been basically used for social communication, so it requires very little, if any, training. We thought that it may be of considerable interest to test the hypothesis if using this application for pre-activation of CCL and for inter-hospital transfer for primary PCI between non-PCI capable and PCI-capable centers would translate into meaningful reduction of reperfusion times of STEMI and potentially in-hospital outcomes.
Patients and methods
Study design
In the period from May 2018 to April 2019, 300 patients with STEMI treated with primary PCI were prospectively enrolled in this multi-center observational study in 3 PCI-capable centers in Cairo city, Egypt. STEMI was defined as follows: ongoing ischemic symptoms (within 12 h) together with ST-seg-ment elevation (measured at the J-point) in at least two contiguous leads of 2.5 mm in men < 40 years, 2 mm in men > 40 years, or 1.5 mm in women in leads V2–V3 and/or 1 mm in the other leads [in the absence of left ventricular(LV) hypertrophy or left bundle branch block (LBBB)] [1]. We excluded patients with previous history of documented myocardial infarction, patients presenting in cardiogenic shock, those with other concomitant valvular or structural heart diseases and those patients with advanced illnesses that limit life expectancy such as terminal cancer and advanced chronic kidney or liver diseases.
Enrolled patients were categorized into 3 groups based on the mode of presentation to the centers participating in the study:
-
• Group 1: Self-presenting to the ED.
-
• Group 2: Transferred by ambulance to the ED.
-
• Group 3: Patients who were transferred directly to CCL (bypassing the ED as possible) after the team has been alerted and pre-activated through an ECG image sent (using WhatsApp) on their route from non-PCI-capa-ble to the participating PCI-capable centers.
Endpoints
The primary endpoints were between-group differences in total ischemic time (defined as time from symptom onset to balloon inflation) and D2B time (defined as time from arrival to PCI-capable center to balloon inflation).
Primary PCI
According to the American Heart Association (AHA) 2016 criteria for STEMI systems of care [9], for the operator to participate in the study by performing pPCI, he/she should have done at least 11 cases of pPCI and a total of 75 PCI procedures per year. All centers providing cases for the study are experienced pPCI centers with a minimum of 36 cases of pPCI and a total of 200 cases of PCI done per year. All patients received, on a routine basis, 300 mg acetylsalicylic acid and a 600 mg loading dose of clopidogrel (per local protocol) before the intervention. Unfractionated hepa-rin (UFH) of 10000 units bolus dose was given after sheath insertion. The procedure was done according to the standard technique for coronary angiography and PCI. Trans femoral approach was done in all patients using 6 Fr sheaths. Diagnostic coro-nary angiography was done to explore non-infarct related artery. XB or Judkin left guide catheters were used for lesions in the left system, while Judkin right catheters for lesions in right coronary artery (RCA). Thrombus aspiration and glycoproteins inhibitors (Eptifibatide or Tirofiban intracoronary bolus followed by intravenous infusion for 12 hours) were left at the operators’ discretion. The operator determined the length and diameter of implanted stents. Sheaths were removed 4 hours post procedure. Coronary angiograms were recorded in digital media for quantitative analysis (Dicom-viewer; Germany). Digital angiograms were analyzed by two independent and experienced cardiologists, who were blinded to all data. In case of variabilities, the final decision was made by a consensus. Coronary blood flow patterns before and after pPCI were evaluated based on thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) flow grade using grades 0, 1, 2, and 3 [10].
Statistical analysis
Results
Three hundred patients with STEMI treated with primary PCI were included (100 patients in each group). There were no statistically significant differences between study groups regarding all baseline criteria (Tab 1).
Peri-procedural characteristics of STEMI
We showed no significant difference between study groups regarding location of STEMI, use of P2Y12 inhibitors, glycoprotein 2b/3a antagonists and thrombectomy devices. All groups were also similar in terms of stents’ use including types, average lengths and di- 58 | Cardiometry | Issue 15. November 2019
ameters of used stents (Tab 2). Importantly, there was a trend towards lesser incidence of any intra-procedural complication (total of thrombosis, no-reflow, dissections and perforations) in group 3 compared to the other 2 groups (20 vs 18 vs 8% in groups 1, 2 and 3 respectively, P= 0.041). There was also a significantly higher rate of obtaining TIMI-3 flow after primary PCI in group 3 compared to the other 2 groups (Tab 2).
Key time intervals
All key time intervals were significantly shorter in group 3 compared to the other 2 groups. For the ED time (30.9±4.6 vs 26.9±5.2 vs 6.5±1.5 minutes in groups 1, 2 and 3 respectively, P < 0.001). For the D2B time (166.5±33.8 vs 157.8±29.6 vs 120.8±35.2 minutes in groups 1, 2 and 3 respectively, P < 0.001). For the total ischemic time (258.9±33.9 vs 249.6±29.4 vs 212.7±35.4 minutes in groups 1, 2 and 3 respectively, P < 0.001). (Fig 1). Linear regression analysis considering transfer by ambulance (group 2) as a reference condition with a mean ED time of 26.9 minutes, self-presentation to emergency room (group 1) significantly increase the time by about 4.0 minutes (95% CI 2.8–5.1 minutes, P < 0.001), while WhatsApp referral (group 3) significantly reduces it by about 20.4 minutes 95% CI -21.6 – -19.3 minutes, P < 0.001). This model explains 87.1% of the variability of ED time in our study. No other fac-tors/covariates were significant.
In-hospital echocardiographic parameters and clinical outcome
Patients in group 3 showed a significantly lesser propensity to develop mitral regurgitation (MR), with non-significant difference between groups regarding MR severity. End-systolic volume (ESV) and end-diastolic volume (EDV) were significantly lesser in group 3 compared to the other 2 groups. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) [as assessed by Simpson’s method] was significantly higher in group 3 compared to the other 2 groups. Wall motion score index (WMSI) was significantly lesser in group 3 compared to the other 2 groups (Tab 3).
In-hospital stay was significantly shorter in group 3 compared to the other 2 groups (4.2±0.8 vs 4.2±0.8 vs 3.8±0.6 days for groups 1, 2 and 3 respectively, P < 0.001 for group 1 vs others). There was a trend towards reduced all-cause mortality in group 3 compared to the other 2 groups (12 vs 11 vs 3% in groups 1, 2 and 3 respectively, P = 0.046 for group 1 vs others).
Table 1. Baseline criteria of study population
|
Variables |
Group-1 (N=100) |
Group-2 (N=100) |
Group-3 (N=100) |
p |
|
|
Age (years) |
Mean ±SD |
57.0±5.3 |
56.6±6.3 |
57.2±6.4 |
^0.791 |
|
Range |
45.0–70.0 |
39.0–69.0 |
40.0–71.0 |
||
|
Sex (n, %) |
Male |
76 (76.0%) |
77 (77.0%) |
74 (74.0%) |
#0.881 |
|
Female |
24 (24.0%) |
23 (23.0%) |
26 (26.0%) |
||
|
Obesity (n, %) |
25 (25.0%) |
24 (24.0%) |
26 (26.0%) |
#0.948 |
|
|
Smoking (n, %) |
69 (69.0%) |
65 (65.0%) |
70 (70.0%) |
#0.725 |
|
|
DM (n, %) |
56 (56.0%) |
54 (54.0%) |
52 (52.0%) |
#0.851 |
|
|
HTN (n, %) |
73 (73.0%) |
76 (76.0%) |
74 (74.0%) |
#0.885 |
|
|
Dyslipidemia |
35 (35.0%) |
34 (34.0%) |
38 (38.0%) |
#0.828 |
|
|
FH of CAD (n, %) |
21 (21.0%) |
22 (22.0%) |
20 (20.0%) |
#0.942 |
|
|
PH of CAD (n, %) |
31 (31.0%) |
32 (32.0%) |
29 (29.0%) |
#0.896 |
|
|
PH of coronary interventions (n, %) |
8 (8.0%) |
9 (9.0%) |
9 (9.0%) |
#0.959 |
|
^ANOVA test, #Chi square test
CAD= Coronary artery disease, DM= Diabetes mellitus, FH= Family history, HTN= Hy-pertension, PH= Past history
Table 2. Peri-procedural characteristics of STEMI
|
Variables |
Group-1 (N=100) |
Group-2 (N=100) |
Group-3 (N=100) |
p |
|
|
Location (n, %) |
Inferior |
55 (55.0%) |
59 (59.0%) |
56 (56.0%) |
#0.840 |
|
Anterior |
38 (38.0%) |
36 (36.0%) |
35 (35.0%) |
||
|
Lateral |
7 (7.0%) |
5 (5.0%) |
9 (9.0%) |
||
|
P2Y12 (n, %) |
Clopidogrel |
83 (83.0%) |
80 (80.0%) |
79 (79.0%) |
#0.757 |
|
Ticagrelor |
17 (17.0%) |
20 (20.0%) |
21 (21.0%) |
||
|
GP2b/3a (n, %) |
22 (22.0%) |
21 (21.0%) |
21 (21.0%) |
#0.980 |
|
|
Thrombectomy (n, %) |
19 (19.0%) |
23 (23.0%) |
20 (20.0%) |
#0.768 |
|
|
Stent (n, %) |
100 (100%) |
100 (100%) |
100 (100%) |
-- |
|
|
Stent type (n, %) |
BMS |
28 (28.0%) |
26 (26.0%) |
28 (28.0%) |
#0.935 |
|
DES |
72 (72.0%) |
74 (74.0%) |
72 (72.0%) |
||
|
Length (mm) |
Mean ±SD |
22.8±6.4 |
21.6±4.7 |
21.6±5.3 |
^0.227 |
|
Range |
12.0–38.0 |
9.0–33.0 |
10.0–33.0 |
||
|
Diameter (mm) |
Mean ±SD |
2.9±0.3 |
2.9±0.2 |
2.9±0.2 |
^0.108 |
|
Range |
2.3–3.5 |
2.5–3.8 |
2.5–3.5 |
||
|
Complications TIMI flow Before (n, %) After (n, %) |
Thrombosis |
8 (8.0%) |
8 (8.0%) |
3 (3.0%) |
#0.245 |
|
No reflow |
5 (5.0%) |
4 (4.0%) |
3 (3.0%) |
&0.932 |
|
|
Dissection |
4 (4.0%) |
4 (4.0%) |
1 (1.0%) |
&0.405 |
|
|
Perforation |
3 (3.0%) |
2 (2.0%) |
1 (1.0%) |
&0.874 |
|
|
Any |
20 (20.0%) a |
18 (18.0%) a |
8 (8.0%) b |
#0.041* |
|
|
Grade-0 |
100 (100.0%) |
100 (100.0%) |
100 (100.0%) |
-- |
|
|
Grade-II |
21 (21.0%) a |
14 (14.0%) a |
2 (2.0%) b |
<0.001* |
|
|
Grade-III |
79 (79.0%) |
86 (86.0%) |
98 (98.0%) |
||
BMS= Bare metal stents, DES= Drug eluting stents, GP 2b/3a= Glycoprotein 2b/3a inhib-itors, TIMI= Thrombolysis in myocardial infarction
Table 3. In-hospital echocardiographic parameters
|
Variables |
Group-1 (N=100) |
Group-2 (N=100) |
Group-3 (N=100) |
p |
|
|
MR (n, %) |
14 (14.0%) a |
12 (12.0%) a |
3 (3.0%) b |
#0.020* |
|
|
MR grade (n, %) |
Mild |
11 (78.6%) |
10 (83.3%) |
3 (100.0%) |
&1.000 |
|
Moderate |
3 (21.4%) |
2 (16.7%) |
0 (0.0%) |
||
|
ESV (ml) |
Mean ±SD |
85.2±4.1 a |
84.3±3.8 a |
74.8±4.1b |
^ <0.001 |
|
Range |
77.9–93.0 |
78.1–92.8 |
60.6–81.7 |
||
|
EDV (ml) |
Mean ±SD |
163.2±3.3 a |
163.4±3.3 a |
159.8±3.9b |
^ <0.001 |
|
Range |
154.7–171.2 |
154.5–170.0 |
148.4–169.6 |
||
|
EF (%) |
Mean ±SD |
47.8±2.4a |
48.4±1.9a |
53.2±1.8b |
^ <0.001 |
|
Range |
40.0–51.0 |
41.0–51.0 |
51.0–60.0 |
||
|
WMSI |
Mean ±SD |
1.8±0.08a |
1.8±0.06a |
1.6±0.07b |
^ <0.001 |
|
Range |
1.70–2.00 |
1.70–2.00 |
1.40–1.70 |
||
EDV= End-diastolic volume, EF= Ejection fraction, ESV= End-systolic volume, , MR= Mitral regurgitation, WMSI= Wall motion score index
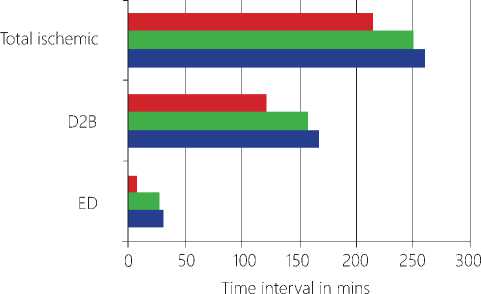
■ Group - 3 ■ Group-2 ■ Group-1
Figure 1. Key time intervals among study groups.
D2B= Door-to-balloon , ED= Emergency department
Discussion
“Time is muscle” when it comes to emergent reperfusion of patients presenting with STEMI. Therefore, recent guidelines still recommend strict time frames for primary PCI in the setting of STEMI (with a D2B time of < 90 minutes) [1]. In recent years, the focus has shifted towards reduction of out-of-hospital component of the total ischemic time, but these efforts are faced with some difficulties related to public awareness, traffic infrastructure, etc. [11]. One of the components of the D2B time is the ED waiting time, which can be reduced by a strategy of pre-activation of the CCL team before patient arrival [5]. This requires a communication between non-PCI capable and PCI capable centers through an established system. Construction of such a system in many developing countries with burdened economies (including Egypt)
may not be ready for the prime time. Accordingly, we set out to test the hypothesis that utilizing free smartphone messaging applications that are used by millions all over the world such as WhatsApp for inter-hospital transfer for primary PCI in STEMI could translate into reduction of D2B times through avoiding ED waiting.
Our main finding is that using WhatsApp for pre-activation of CCL teams during inter-hospital transfer for primary PCI in STEMI was associated with a significant reduction in ED waiting times and hence D2B times and total ischemic time as well. To the best of our knowledge, data on using smartphone messaging applications for facilitating inter-hospital transfer for primary PCI in STEMI are scarce and this is the 1st study on a national base and may be in the Arab world evaluating this issue.
Astarcioglu et al [12] evaluated 108 patients with STEMI in a rural hospital with emergency department but without PCI capability to determine the impact of WhatsApp triage and activation of the CCL team on D2B time. They found that this strategy was associated with shorter D2B time (109±31 minutes in the intervention group vs. 130±46 minutes in the control group, p<0.001) and results in a greater proportion of patients achieving guideline recommendations. Another study [13] showed that smartphone-based TeleECG support for primary care physicians reduced the hospital-to-Aspirin time in acute coronary syndrome significantly (p<0.0001). Another unpublished work presented at the Argentine Congress of Cardiology (SAC 2017) [14] concluded that among 900 STEMI patients, symptom-onset-to-treatment time was significantly lower for those in the WhatsApp group compared with the other patients 150 vs 200 minutes (P < 0.001).
The novelty of the current study (apart from being the 1st on a national base and may be in the Arab world) emerges from the fact that we not only evaluated the impact of WhatsApp transfer on key time intervals, but also we discussed in details its impact on various important echocardiographic parameters and selected in-hospital outcomes (namely, hospital stay and all-cause in-hospital mortality). Notably, the D2B times in the current study were exceedingly higher than what’s recommended in the guidelines (this was true even among the group with the best-case-scenario ‘group 3’). Taking the observational nature of the current study into consideration, this might represent a call for action, that much effort is still needed to the close the gap between the real situation in a developing country like Egypt and the guideline-recommended time frames.
Two main limitations deserve mention, first, the relatively small sample size did not allow the power for calculation of the full spectrum of in-hospital clinical outcomes. Second, no formal calculation of the doorin-door-out (DIDO) time was done. This is because patients in groups 1 and 2 were mixed population (including those who were transferred from a non-PCI capable centers and those who presented directly to the PCI centers included in the study).
Conclusions
Using smartphone messaging applications such as WhatsApp for pre-activation of CCL teams during inter-hospital transfer for STEMI primary PCI is associated with scientifically shorter ED waiting and D2B times. This might be relevant for develop-ing countries lacking inter-hospital robust communication systems. Adequately powered randomized trial is needed to evaluate the impact of such a strategy on clinical outcomes.
Statement on ethical issues
Research involving people and/or animals is in full compliance with current na-tional and international ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author contributions
The authors read the ICMJE criteria for authorship and approved the final manuscript.
Список литературы Time-to-reperfusion in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing interhospital transfer using WhatsApp smartphone application
- Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, et al. 2017 ESC Guide¬lines for the management of acute myocardial infarc¬tion in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute myo¬cardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-seg¬ment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European heart journal. 2017; 39: 119-77. Doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx393
- Stone GW, Dixon SR, Grines CL, et al. Predictors of infarct size after primary coronary angioplasty in acute myocardial infarction from pooled analysis from four contemporary trials. The American journal of cardiology. 2007; 100: 1370-5. Doi: 10.1016/j.amj¬card.2007.06.027
- Brodie BR, Stone GW, Cox DA,et al. Impact of treatment delays on outcomes of primary percuta¬neous coronary intervention for acute myocardial infarction: analysis from the CADILLAC trial. Amer¬ican heart journal. 2006; 15: 1231-8. Doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2005.07.016
- Menees DS, Peterson ED, Wang Y, et al. Door-to-balloon time and mortality among patients undergo-ing primary PCI. New England Journal of Medicine. 2013; 369: 901-9. Doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1208200
- Fordyce CB, Al-Khalidi HR, Jollis JG, et al. Associ¬ation of rapid care process implementation on reper-fusion times across multiple ST-segment–elevation myocardial infarction networks. Circulation: Cardio-vascular Interventions. 2017; 10: e004061. Doi: 10.1161/ CIRCINTERVENTIONS.116.004061
- Bagai A, Jollis JG, Dauerman HL, et al. Emergency department bypass for ST-segment–elevation myo-cardial infarction patients identified with a prehos¬pital electrocardiogram: a report from the American Heart Association Mission: Lifeline Program. Circu¬lation. 2013; 128: 352-9. Doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIO-NAHA.113.002339
- Helal AM, Shaheen SM, Elhammady WA, et al. Pri¬mary PCI versus pharma-coinvasive strategy for ST elevation myocardial infarction. IJC heart & vascu-la¬ture. 2018; 21: 87-93. Doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2018.10.006
- Bendary A, Tawfek W, Mahros M, et al. Primary PCI versus Pharmaco-Invasive Strategy in Patients with ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction; a Random ized Clinical Study. Journal of Cardiovascular Disease Research. 2018; 9. Doi: 10.5530/jcdr.2018.1.7
- Recommendations for criteria for STEMI sys¬tems of care [internet]. American Heart Association. 2016. Accessed June 2018. Available at: http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/Professional/MissionLife-lineHomePage/EMS/Recommendations-for-Crite¬ria-for-STEMI-Systems-of-Care_UCM_312070_Arti-cle.jsp#. Wziut9Iza00
- Gibson C, Cannon C, Murphy S, et al. Relationship of the TIMI myocardial perfusion grades, flow grades, frame count, and percutaneous coronary intervention to long-term outcomes after thrombolytic adminis¬tration in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2002; 105: 1909-13. Doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000014683. 52177.B5
- Denktas AE, Anderson HV, McCarthy J, et al. To¬tal ischemic time: the correct focus of attention for optimal ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction care. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions. 2011; 4: 599-604. Doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2011.02.012
- Astarcioglu, M.A., Sen, T., Kilit, C., et al. Time-to- reperfusion in STEMI undergoing interhospital trans-fer using smartphone and WhatsApp messenger. The American journal of emergency medicine. 33:1382-4. Doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2015.07.029
- Chauhan V, Negi PC, Raina S, et al. Smartphone-based tele-electrocardiography support for primary care phy¬sicians reduces the pain-to-treatment time in acute cor¬onary syndrome. Journal of telemedicine and tel-ecare. 2018; 24: 540-6. Doi: 10.1177/1357633X17719395
- Maxwell Y. WhatsApp Enables Swift Diagnosis of STEMI and Cath Lab Ac-tivation 2017. Accessed May 2018. Available from: https://www.tctmd.com/news/whatsapp-enables-swift-diagnosis-stemi-and-cath-lab-activation


