Торкрет-бетон с добавками для облицовки оросительных каналов
Автор: Молдамуратов Жангазы Нуржанович, Игликов Алтайы Аманкулович, Сенников Михаил Николаевич, Мадалиева Эльмира Бегалиевна, Туралина Майра Туралиевна
Журнал: Нанотехнологии в строительстве: научный интернет-журнал @nanobuild
Рубрика: Технологии производства строительных материалов и изделий
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.14, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Из всех известных разновидностей бетонных облицовок наиболее экономичной и достаточно полно механизированной в изготовлении является торкретная облицовка. Строительная практика гидротехнических сооружений накопила многочисленные примеры использования в облицовках самые различные строительные материалы - от камня до современных пленок из синтетических смол. Несмотря на очень активные поиски более подходящих материалов, бетонные облицовки еще надолго останутся основными. Это требует дальнейших усовершенствований их, повышения долговечности и снижения стоимости. Методы и материалы. Исследовования проводились методом сравнения лабораторных испытаний торкрет-бетона с наноструктурированными добавками поверхностно-активных веществ. В виде наноструктурированных добавок использовались ССБ (сульфитно-спиртовая барда), СНВ (смола нейтрализованная воздухововлекающая), хлопковое мыло и битум в различных консистенциях. Испытания проводились на прочностные свойства, усадку, деформируемость при растяжении, силу сцепления с арматурой и водонепроницаемость. Структурные изменения свойств изучались методом электронно-микроскопического анализа. Результаты и обсуждение. Установлено, что оптимальной добавкой ССБ в торкрет с водой затворения при условии набрызгивания является 0,5% от веса цемента. Оптимума добавки СНВ не наблюдается. При введении в торкрет хлопкового мыла с водой затворения содержание воды в уложенном торкрете по мере увеличения количества вводимой добавки увеличивается, оптимальное содержание цемента в торкрете наблюдается при введении 0,3% хлопкового мыла от веса цемента, «отскок» уменьшается при увеличении количества вводимой добавки. При введении 0,3% ССБ от веса цемента в торкрет-состав сухой смеси 1:4 повышается прочность его при сжатии на 16%, при изгибе на 1% и при разрыве на 20%. Заключение и выводы. Все наноструктурированные добавки поверхностно-активных веществ повышают усадку торкрета. Наименьшее повышение ее дает торкрет с ССБ, а наибольшее - с битумной эмульсией. Добавки в торкрет значительно повышают его деформируемость при растяжении, а также в широких пределах понижают значения модулей мгновенной упругости торкрета, т.е. повышают его пластические свойства. Поверхностно-активные вещества и битумные эмульсии понижают силу сцепления арматуры с торкретом, однако она остается на более высоком уровне, чем у обычных бетонов.
Наноструктурированные добавки, торкрет-бетон, поверхностно-активные вещества, битум, смола нейтрализованная воздухововлекающая, сульфитно-спиртовая барда
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142234154
IDR: 142234154 | УДК: 691.58.691.587
Текст научной статьи Торкрет-бетон с добавками для облицовки оросительных каналов
Б ольшинство оросительных систем Казахстана не имеет антифильтрационных одежд на каналах. Это одна из основных причин очень низких КПД систем, а также вторичного засоления и заболачивания подвешенных к ним земель [1].
Задачи дальнейшего подъема сельского хозяйства в Казахстане обуславливают коренное изменение сложившихся взглядов на облицовку оросительных каналов. Сокращающиеся резервы земель для нового орошения и все возрастающие нужды в капитальных затратах на мелиорацию земель старого орошения рано или поздно потребуют перехода к полностью
ТЕХНОЛОГИИ ПРОИЗВОДСТВА СТРОИТЕЛЬНЫХ МАТЕРИАЛОВ И ИЗДЕЛИЙ облицованным системам. Поэтому уже сейчас назрела самая серьезная необходимость в широкой постановке научных и производственных исследований всевозможных материалов и конструкций, методов производства работ и проектирования машин для создания облицовок [2].
Строительная практика гидротехнических сооружений различных стран уже накопила многочисленные примеры использования в облицовках самых различных строительных материалов - от камня до современных пленок из синтетических смол. Однако, несмотря на очень активные поиски более подходящих материалов, бетонные облицовки еще надолго останутся основными. Это требует дальнейших усовершенствований их, повышения долговечности и снижения стоимости [1–5].
Из всех известных разновидностей бетонных облицовок наиболее экономичной и достаточно полно механизированной в изготовлении является торкретная облицовка [6].
В Казахстане и Центральной Азии облицовок из торкрета практически нет, есть только небольшие участки, хотя в некоторых зарубежных странах, например, в США и Китае, они уже давно эксплуатируются и вновь возводятся [7, 8].
В связи с простотой, механизированностью возведения и большей экономичностью по сравнению с монолитными и сборными облицовками из обычного бетона торкретные облицовки найдут законное место в ирригационном строительстве.
МЕТОДЫ И МАТЕРИАЛЫ
Исследованиями [9–12] определены оптимальные параметры производства торкретных работ. В опытах угол между направлением материального потока и обрабатываемой поверхностью равнялся 90 градусам с расстоянием от сопла до щита 90–110 см. В опытах использовали песок, взятый на реке Сырдарья, объемным весом 1,44 кг/л, удельным весом 2,7 кг/л и пу-стотностью 46,5%, портландцемент марки 400 Жам-былского цементного завода и воду из «Тараз-Су».
Нанесением торкрета на специальные щиты под углом 90 градусов к их поверхности изготавливали торкретные плиты, которые разрезали при горизонтальном положении щита на фигуры определенных размеров. Этим облегчалось изготовление образцов и повышалось их качество.
Для прочностных испытаний торкрета на сжатие брали кубики с гранями 3×3×3 см, на изгиб – ба-лочки размером 3×3×24 см. Готовили балочки размерами 3×3×8 см, которые укладывали в формы для восьмерок нормального типа и «заплечики» заливали цементным тестом на тонкопомольном цементе. При испытании на разрыв бывали случаи среза «заплечиков», поэтому мы запроектировали, а мастерские изготовили специальные штампы из кровельного железа с деревянными плунжерами.
Дозировку песка и цемента для приготовления сухой смеси брали по весу. Состав торкрета определяли по методике [10, 11]. Испытания опытных образцов производили после хранения их во влажном песке на протяжении 7, 28, 60, 90, 180, 360, 720 дней. В каждом возрасте испытывали не менее трех образцов-близнецов. Прочностные свойства торкрета (кг/см2) без добавок в возрасте 28 дней приводятся в табл. 1.
В возрасте 18 месяцев торкрет имел следующую прочность (% от 28-дневной): состав сухой смеси 1:2 – 116, 1:3 и 1:4 – примерно 100, 1:5 – 106 (при сжатии), 1:4 – 184 и 1:5 – 164 (при изгибе). С возрастом прочность значительно увеличивается при изгибе и незначительно – при сжатии. В возрасте 24 месяца при сжатии у торкрета отмечена такая прочность (% от 28-дневной): для состава сухой смеси 1:3 – примерно 100 и 1:5 – 174.
Средние для различных сроков хранения отношения прочностей при изгибе к прочностям при сжатии возрастают при снижении жирности сухой смеси от 0,32 (для состава 1:2) до 0,42 (для состава 1:6). Средние отношения прочностей при разрыве к прочностям при сжатии возрастают от 0,13 (для состава сухой смеси 1:2) до 0,29 (для состава 1:6).
Для облицовочного материала, кроме достаточной прочности при сжатии, изгибе и разрыве, большое значение имеет водонепроницаемость. Торкрет с ненарушенной структурой обладает высокой водонепроницаемостью [15]. При облицовке каналов
Таблица 1
Прочностные свойства торкрета (кг/см2)
|
Вид испытания |
Состав сухой смеси |
||||
|
1:2 |
1:3 |
1:4 |
1:5 |
1:6 |
|
|
Сжатие |
281 |
230 |
179 |
150 |
100 |
|
Изгиб |
105 |
73 |
72 |
62 |
40 |
|
Разрыв |
38 |
32 |
27 |
32 |
19 |
ТЕХНОЛОГИИ ПРОИЗВОДСТВА СТРОИТЕЛЬНЫХ МАТЕРИАЛОВ И ИЗДЕЛИЙ

Рис. 1. Опытные участки торкретной облицовки оросительных каналов на юге Казахстана
К-18, К-20 в Мактаральском районе Туркестанской области торкрет-состава сухой смеси 1:5 на цементе марки 400 и жетысайском песке (толщина облицовки 5–7 см) в 28-суточном возрасте выдержал давление 6–8 атм. (рис. 1).
Усадку определяли на образцах в виде призм размерами 5×5×50 см с помощью спроектированного и изготовленного индикаторного тензометра седельного типа. Относительные показатели усадки (ε×10–5) для торкрета в возрасте 14 и 28 дней следующие (табл. 2).
Таблица 2
Относительные показатели усадки торкрета
|
Состав торкрета |
14 суток |
28 суток |
|
1:3 |
36,0 |
57,0 |
|
1:4 |
35,0 |
53,5 |
Для выяснения влияния испарения воды из образца на его усадку часть образцов покрывали парафином. Состав сухой смеси 1:4. Усадку замеряли на образце размерами 5×5×50 см. Парафинированный образец усаживался в течение 2 суток, очевидно, вследствие контракции, затем усадка прекратилась, составив 9,4 µ. Непарафинированный образец дал за это время усадку 49,6 µ, т.е. в 5,3 раза больше, и она продолжалась, достигнув к 90-дневному возрасту 467,2 µ, причем 383,2 из них или 82% приходились на первые 30 дней. Из опытов ясно, как важно для уменьшения усадки исключить испарение воды из торкрета в процессе твердения. Для создания пароводонепроницаемой пленки на торкретной облицовке можно использовать тяжелые высокополиме-ризующиеся кызылординские и актюбинские нефти.
К недостаткам цементных материалов с точки зрения применения их для облицовок каналов относятся их чрезмерная жесткость и хрупкость, растущие со временем, и достаточно большие температурноусадочные деформации. Первый из этих недостатков не допускает возведения тонких (5–7 см) облицовок из бетона, так как они даже при незначительных де- формациях оснований (просадок и суффозионных процессов) оказались бы в сильной степени подверженными разрушению. Поэтому облицовки из монолитного бетона имеют обычно толщину 10–15 см и часто армируются железом. Второй недостаток приводит к необходимости нарушать сплошность покрытий разрезом температурно-усадочными швами, а это ухудшает их эксплуатационные показатели и усложняет строительные работы. В связи с этим желательно было бы увеличить деформативные свойства и ползучесть цементных материалов, в частности, торкрета [11–14].
Влияние наноструктурированных поверхностноактивных добавок на ползучесть торкрета выяснялось введением в воду затворения ССБ (сульфитноспиртовой барды), СНВ (смолы нейтрализованной воздухововлекающей) и хлопкового мыла. Высокими пластическими свойствами в определенных условиях обладают битумные вещества. Они могут передавать эти свойства материалам, получаемым при их введении. В торкрет битумные вещества вводились в виде раствора битума в керосине и битумной эмульсии.
Введение органических поверхностно-активных веществ должно как-то отражаться на смачивающей способности воды затворения и влиять на механические свойства торкрета [16]. Влияние органических поверхностно-активных веществ на смачивающую способность воды с добавкой определялось измерением капиллярного подсоса растворов. Для определения капиллярного подсоса дистиллированной воды без добавок и с разным количеством добавок изготовлен простой прибор, состоящий из четырех трубочек диаметром 3,2; 1,2; 0,5 и 0,3 мм, закрепленных на мерной шкале с выходом концов трубочек за шкалу на 20 мм. Трубочки погружались в жидкость. При определении капиллярного подсоса брали среднее трех опытов.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
ССБ вводили в количестве 0,5, 1 и 1,5%, СНВ – 0,05, 0,1 и 0,15, хлопковое мыло – 0,1, 0,3 и 0,5%. В результате выявлено, что ССБ увеличивает смачивающую способность воды, и тем больше, чем боль-
ТЕХНОЛОГИИ ПРОИЗВОДСТВА СТРОИТЕЛЬНЫХ МАТЕРИАЛОВ И ИЗДЕЛИЙ ше добавка, СНВ вызывает небольшое увеличение, а хлопковое мыло значительно снижает ее.
Для выяснения влияния добавок на процесс набрызгивания торкрета осуществлена серия опытов, результаты которых приведены ниже. В опытах использовали торкрет-состав сухой смеси 1:4 с различной дозировкой добавок ССБ, СНВ и хлопкового мыла. Для исследований брали по 10 кг сухой смеси и определяли состав нанесенного на щит торкрета и его вес. Из условий набрызгивания оптимальная добавка ССБ – 0,5% от веса цемента. При такой добавке торкрет содержит минимальное количество воды, максимальное – цемента и имеет наименьший «отскок».
Оптимума добавки СНВ не наблюдается. По мере увеличения ее от 0,05 до 0,1% от веса цемента содержание воды в уложенном торкрете повышается от 12,4 до 13,1%, цемента – от 29,5 до 30,9 и вес торкрета – с 4,3 до 5,3 кг, т.е. «отскок» уменьшается.
При введении в торкрет добавки хлопкового мыла с водой затворения по мере увеличения ее количества содержание воды в торкрете увеличивается. Оптимальное количество цемента в нем отмечается при добавке 0,3% хлопкового мыла от веса цемента, или 0,57% от веса воды. Содержание уложенного торкре- та возрастает с 4,38 кг при добавке 0,1% хлопкового мыла от веса цемента до 5,88 кг при добавке 0,5%, т.е. «отскок» уменьшается.
С целью определения влияния добавок поверхностно-активных веществ на прочностные свойства изготавливали кубики 5×5×5 см, балочки 5×5×31 см, восьмерки нормального типа. Балочки 5×5×50 см испытывали на усадку, балочки таких же размеров с выпущенными концами арматуры d = 10 мм – на деформируемость под действием медленно возрастающей статической растягивающей нагрузки и ползучесть торкрета при растяжении под постоянной статической нагрузкой, кольца диаметром 20 см, толщиной 5 см – на водопроницаемость (рис. 2).
Оптимальные дозировки добавок в бетоны и обычные растворы установлены в лабораторных и производственных опытах: для ССБ — примерно 0,25, СНВ — 0,03 и для мыла – 0,1% от веса цемента.
При испытаний торкрета на прочность использовали по три образца-близнеца. Испытания проводили в 28, 90, 180 и 270-суточном возрасте хранения образцов во влажном песке. Состав сухой смеси 1:4. Результаты приведены в табл. 3.
Добавка ССБ в количестве 0,3% от веса цемента повышает прочность при сжатии в среднем на 16,

Рис. 2. Образцы торкрет-бетона
Таблица 3
Результаты испытания торкрета на прочность
|
Вид торкрета |
Кол-во добавки, % от веса цемента |
В/Ц в торкрете |
Пределы прочности образцов в кг/см2 в возрасте суток |
|||||||||||
|
сжатие |
изгиб |
разрыв |
||||||||||||
|
28 |
90 |
180 |
270 |
28 |
90 |
180 |
270 |
28 |
90 |
180 |
270 |
|||
|
Без добавки |
– |
0,52 |
259 |
218 |
259 |
– |
94 |
85 |
142 |
– |
34 |
33 |
37,9 |
– |
|
С добавками |
0,3 |
0,43 |
317 |
270 |
301 |
– |
108 |
– |
125 |
– |
38 |
38 |
50,8 |
– |
|
ССБ |
0,5 |
0,28 |
293 |
328 |
247 |
377 |
83 |
83 |
132,5 |
136 |
23 |
31 |
35,6 |
47,9 |
|
1,0 |
0,47 |
255 |
190 |
301 |
471 |
103 |
128 |
139 |
128 |
31 |
32 |
41,3 |
– |
|
|
СНВ |
0,03 |
0,37 |
183 |
260 |
165 |
293 |
74 |
83 |
78 |
131 |
26 |
24 |
36,8 |
38,5 |
|
0,06 |
0,58 |
147 |
265 |
273 |
– |
65 |
85 |
69 |
– |
22 |
25 |
32,4 |
– |
|
|
0,12 |
0,74 |
131 |
142 |
195 |
– |
55 |
62 |
– |
– |
12 |
27 |
25,2 |
– |
|
|
Хлопкового мыла |
0,1 |
0,71 |
166 |
156 |
138 |
182 |
65 |
76 |
97 |
55 |
20 |
19 |
31,8 |
– |
|
0,2 |
0,93 |
176 |
243 |
181.5 |
192,5 |
92 |
65 |
125 |
45 |
12 |
14,7 |
16,8 |
18,1 |
|
|
0,6 |
0,61 |
134 |
163 |
231 |
278 |
75 |
60 |
88,5 |
65 |
18 |
14 |
27,0 |
– |
|
|
Битумной |
0,25 |
0,6 |
137 |
174 |
180 |
263 |
77 |
60 |
87 |
96 |
20 |
– |
27,6 |
– |
|
эмульсии* |
0,5 |
– |
91 |
– |
154 |
– |
27 |
– |
57 |
– |
10 |
– |
14,2 |
– |
* Содержание битума дано в процентах от веса торкрета
ТЕХНОЛОГИИ ПРОИЗВОДСТВА СТРОИТЕЛЬНЫХ МАТЕРИАЛОВ И ИЗДЕЛИЙ при изгибе – на 1 и при разрыве – на 20%. При введении в торкрет 0,5% ССБ от веса цемента прочность при сжатии увеличилась в среднем на 16%, при изгибе и разрыве снизилась по сравнению с соответствующими прочностями торкрета без добавки. При введении 1% ССБ от веса цемента средние показатели прочности при сжатии и разрыве остались примерно на уровне соответствующих прочностей торкрета без добавки, а при изгибе прочность повысилась на 20%.
По результатам опытов можно сделать вывод, что ССБ повышает прочностные свойства торкрета примерно в тех же пределах, что и в обычных цементных растворах и бетонах, поэтому добавки его в количестве 0,3% от веса цемента могут быть рекомендованы к применению с целью повышения прочности торкрета в конструкциях.
Добавки СНВ и хлопкового мыла снижали прочностные свойства торкрета, причем с увеличением процента добавки закономерно снижалась прочность. Принятые в опытах дозировки добавок показали, что мыло понижает прочность при сжатии и растяжении в большей степени, чем СНВ, и только при испытании на изгиб у торкрета с добавкой мыла прочность была выше, чем у торкрета с СНВ. Это объясняется тем, что поверхностно-активные добавки гидрофобизующего типа, адсорбируясь на поверхностях составляющих бетона, образуют пленки водонерастворимых кальциевых мыл и потому понижают скорость гидратации и гидролиза клинкерных минералов и, следовательно, приращение прочности во времени. Основа их пластифицирующего действия состоит в воздухововлекании, появляющемся при перемешивании бетонных смесей, но при пневматическом набрызгивании этот процесс не происходит, поэтому нет и пластифицирующего эффекта [17].
Деформируемость торкрета с различными добавками при разных их дозировках определялась под действием непрерывной и ступенчатой статической нагрузок.
В проведенных опытах скорость приложения нагрузки примерно постоянна, поэтому задача определения сравнительных показателей деформируемости торкрета с добавками может считаться полностью выполненной.
Испытания проводились на призмах 5×5×50 см в возрасте 28 суток. Деформацию замеряли индикаторными тензометрами. Отчеты деформаций брали через интервалы напряжений в 2 кг/см2. Испытывали по три образца-близнеца, причем количество циклов загрузки и разгрузки колебалось от 4 до 15. Два образца доводили до разрушения, а один оставляли для повторных испытаний в трехмесячном возрасте. Кроме зависимости деформаций от напряжений определяли и накопление пластических деформаций при определенных уровнях напряжений (иногда близких к Rp), предельную растяжимость и пределы прочности при растяжении.
На рисунках приводятся графические зависимости ∆ l = f (σ p ), построенные по результатам опытов, причем почти во всех трафиках взяты кривые второго цикла загружения, для образцов, показавших наиболее закономерное (из трех образцов-близнецов) изменение этой зависимости. Определение ползучести производили на базе замеров 28,5 см.
На рис. 3 приводятся зависимости деформируемости от напряжений для торкрета с различным содержанием добавки ССБ и СНВ, а также помещены контрольные кривые для торкрета без добавок. Все серии образцов приготовлены из сухих смесей цемента и песка в соотношении 1:4. Графики показывают, что добавки ССБ в большой степени повышают деформируемость торкрета под нагрузкой; чем больше добавки, тем резче повышается деформируемость, и этот факт наблюдается при общем повышении прочностных свойств торкрета с добавками ССБ. ССБ повысила удельную деформируемость и, следовательно, снизила значение модулей мгновенной и длительной деформаций, т.е. повысила и пластические деформации. Об этом свидетельствует также значительное уменьшение длины начальных прямолинейных участков на графиках.
Влияние добавок на значение предельной растяжимости 28,5 см участка призмы характеризует следующие данные (состав сухой смеси 1:4, табл. 4).
Графики деформируемости торкрета с добавками СНВ показывают, что СНВ еще резче, чем ССБ повысило деформативные способности торкрета, однако это наблюдается уже на фоне довольно заметного понижения прочностных свойств. СНВ несколько меняет характер кривых деформаций: они приближаются к прямым, и кривая 8 меняет знак кривизны.
Мыло более значительно, чем ССБ и СНВ, повышает деформируемость торкрета, но это проявляется при более высоком снижении прочности и предельной растяжимости по сравнению с торкретом при добавке СНВ (рис. 4а).
Битум вводился в торкрет с водой затворения в виде эмульсии в количестве 0,25 и 0,5 % (рис. 4б). Кривая 2 соответствует деформации образцов с 0,25% добавкой; при малой добавке разница в показателях удлинения по сравнению с торкретом без добавок мало существенна. Добавка 0,5% значительно повысила деформируемость торкрета (как и в случае добавки СНВ), кривая 3 имеет уже более четкую обратную кривизну, что логически должно свидетельствовать о снижении пластической составляющей деформации по мере повышения напряжений. Добавки битума резко снизили прочность при
Таблица 4
Влияние добавок на значение предельной растяжимости
|
Количество добавки, % |
Предел прочности, кг/см2 |
Предельное удлинение, µ |
|
Без добавки |
28 |
22 |
|
ССБ |
||
|
0,3 |
34,6 |
21 |
|
0,5 |
27,9 |
26–27 |
|
1,0 |
20 |
33 |
|
СНВ |
||
|
0,03 |
20 |
42 |
|
0,06 |
19 |
46–47 |
|
0,12 |
14 |
20 |
|
Мыло |
||
|
0,1 |
20,4 |
35 |
|
0,2 |
16,1 |
32 |
|
0,6 |
11 |
22 |
|
Битум |
||
|
0,25 |
16 |
8 |
|
0,5 |
11 |
18 |
ТЕХНОЛОГИИ ПРОИЗВОДСТВА СТРОИТЕЛЬНЫХ МАТЕРИАЛОВ И ИЗДЕЛИЙ
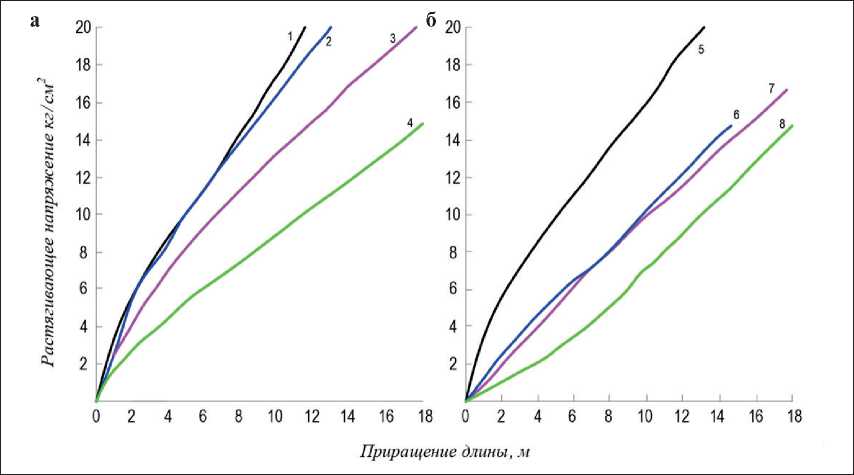
Рис. 3. График зависимости деформаций торкрета от нагрузки и добавки ∆ l = f (σ pД ): 1 и 5 без добавки, ∆ l = 0,3–0,86; 2 – 0, % ССБ, ∆ l = 0,4–0,62; 3 – 0,5% ССБ, ∆ l = 0,5–1,2; 4 – 1,0% СС p Б, ∆ l = 0,6–1,5; 6 – 0,03%
СНВ; 7 – 0,06% СНВ; 8 – 0,12% СНВ (для СНВ ∆ l = 1,0)
растяжении и даже предельную растяжимость, хотя удельная растяжимость осталась примерно на том же уровне.
Для более рельефного сравнения растяжимости торкрета (в 28-суточном возрасте) в зависимости от его состава и добавок ниже приводятся значения суммарных приращений длины образцов µ на при- нятой базе замеров при достижении образцами напряжений в 5 и 10 кг/см2 (при добавках состав сухой смеси 1:4, табл. 5).
ССБ увеличивает деформируемость при статическом приложении нагрузки в 2–2,5 раза, СНВ – в 2,5–4, хлопковое мыло – в 3–5, битум – примерно в 2 раза.
Определение деформируемости торкрета осуществлялось от 4 до 15 циклов попеременного за-гружения и снятия нагрузки.
На рис. 5 даются графические зависимости испытания торкрета из сухой смеси состава 1:4 без добавок при 5 циклах загружения. Кривые разных циклов почти параллельны (параллельность касательных в точках равных нагружений), хотя принципиально с увеличением числа циклов они должны были бы выпрямляться вследствие протекания процесса, аналогичного «наклепу». При сбросе нагрузки очередного цикла загружения стрелка индикатора не возвращается в начальную позицию, а показывает всегда большую длину образца на величину a' , a'ʹ и т.д. По мере увеличения количества циклов за-гружения значения а , являющегося остаточной деформацией, уменьшаются и практически сводятся к нулю. Абсолютные значения а зависят, видимо, от материалов образцов, возраста и действующих напряжений.
Таким образом, кривая зависимости ∆ l = f (σ p ) при прямом ходе (возрастании напряжений) суммирует упругую и пластическую составляющие деформации, а вторая ветвь кривой, соответствующая сбросу на-
Таблица 5
Сравнение растяжимости торкрета
|
Состав сухой смеси и процент добавки |
5 кг/см2 |
10 кг/см2 |
|
Без добавки 1:2 |
0,2 |
0,4 |
|
1:3 |
0,7 |
2,0 |
|
1:4 |
1,8 |
5,0 |
|
ССБ 0,3 |
2,1 |
5,0 |
|
0,5 |
2,7 |
6,7 |
|
1,0 |
5,0 |
11,5 |
|
СНВ 0,03 |
5,0 |
10,0 |
|
0,06 |
5,2 |
10,2 |
|
0,12 |
8,0 |
13,4 |
|
Мыло 0,1 |
8,8 |
16,2 |
|
0,2 |
10,0 |
18,6 |
|
0,6 |
10,6 |
21,0 |
|
Битум 0,25 |
2,0 |
5,3 |
|
0,5 |
5,6 |
9,5 |
ТЕХНОЛОГИИ ПРОИЗВОДСТВА СТРОИТЕЛЬНЫХ МАТЕРИАЛОВ И ИЗДЕЛИЙ
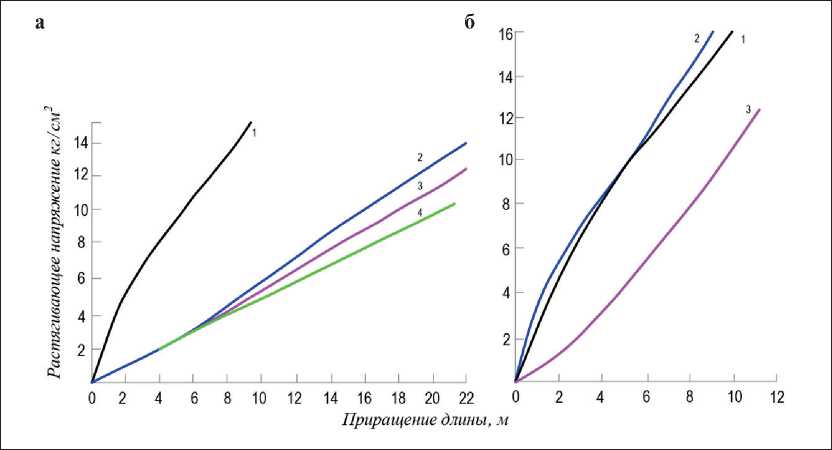
Рис. 4. График зависимости деформаций торкрета от нагрузки и добавки ∆ l = f (σ pД ): а – добавка мыло, %;
1 – без добавки, ∆ l = 0,3–0,86; 2 – 0,1, ∆ l = 1,5; 3 – 0,2, ∆ l = 1,7; 4 – 0,6, ∆ l = 2,15; б – добавка битума, %;
1 – без добавки, ∆ l = 0,3–0,85; 2 – 0,25, ∆ l = 0,3–0,86; 3 – 0,5, ∆ l = 0,74
пряжений, наоборот, дифференцирует их. В опытах скорости возрастания и сброса нагрузки достаточно велики, можно считать, что пластическая составляющая деформации восстанавливается. По мере увеличения количества циклов загрузки и разгрузки угол наклона графика (линии 1, 2 и 3) к оси абcциcc уменьшается, а значение модуля упругости падает вместе с нарушением целостности структурных построений торкрета.
Это явление наблюдается при всех испытаниях, проделанных нами при большом количестве циклов загрузки и разгрузки. Испытание образца из сухой смеси 1:4 при добавке 0,06% СНВ модуль мгновенной упругости, найденный по графику второго цикла, равнялся 285 000 кг/см2, а по графику 15-го – 259 000.
При постановке опытов по выявлению усадки торкрета нас интересовали, во-первых, его усадочные деформации, так как торкрет сильно отличается от обычных бетонов и растворов по методу укладки и расходам воды, и, во-вторых, влияние на усадку торкрета добавок поверхностно-активных веществ и битума.
Усадку определяли на образцах в виде призм размерами 5×5×31 см и 5×5×50 см с помощью специальных приспособлений. Серия контрольных замеров показала, что относительные усадки, получаемые на образцах разной длины, практически мало различаются. За усадкой образцов наблюдали в течение 2–3 месяцев. По графикам усадки образцов из торкрета без добавок при составе исходных сухих смесей 1:3 и 1:4, а также с добавками ССБ в количестве 0,3 и 0,5% (от веса цемента) можно судить, что первые три состава обладают примерно одинаковой, а четвертый – несколько более высокой интенсивностью усадки (рис. 6а). Это объясняется большим содержанием цемента в четвертом составе, а также ускорением гидратации цемента в результате пепти-
ТЕХНОЛОГИИ ПРОИЗВОДСТВА СТРОИТЕЛЬНЫХ МАТЕРИАЛОВ И ИЗДЕЛИЙ
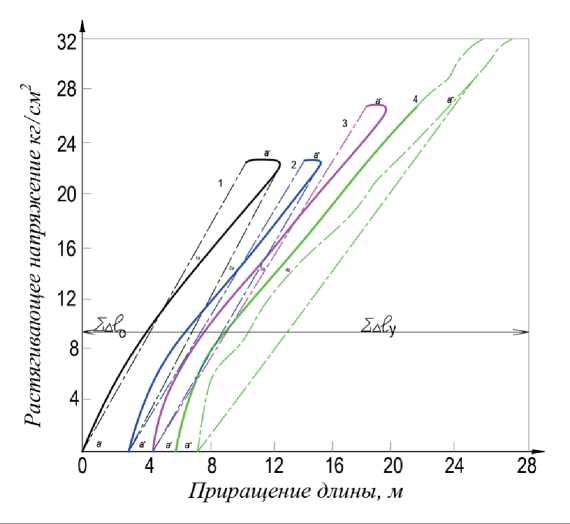
Рис. 5. Кривые зависимости деформации торкрета от нагрузки ∆ l = f (σ p ) при 5 циклах нагрузки
зирующего действия ССБ и ускоряющихся процессов диффузного поглощения воды цементом.
Торкрет с добавками СНВ (состав сухой смеси 1:4) обладает большей усадкой, чем торкрет без добавки. По расположению кривых (рис. 6б) можно судить о том, что на интенсивность усадки количество цемента оказывает большее влияние, чем вода, поэтому составам с большими содержаниями цемента соответствуют кривые большей интенсивности усадки.
Торкрет с добавками соапсточного мыла и битума в первые 15 суток испытаний обладает несколько меньшей интенсивностью усадки, а в последующие – большей (рис. 6в). К концу месяца торкрет с битумом имеет наибольшую усадку. Для сравнения ниже приводятся относительные показатели усадки для всех составов торкрета (для торкрета с добавками 1:4) в возрасте 14 и 28 дней. Все примененные добавки в первый месяц увеличивают усадку торкрета, наибольшие показатели выявились у торкрета с битумом (табл. 6).
Сила сцепления арматуры с бетоном - важнейший фактор, обеспечивающий их совместную и надежную работу в конструкциях. Она обусловливается тремя основными причинами: трением, сопротивлением срезу и скалыванием. Численная величина ее определяется опытным путем, а сопротивление сдвигу ( R сц и τ сц) выражается через силу сцепления (кг/см2), отнесенную к суммарной наружной поверхности арматуры. Опытами установлено, что τ сц для обыкновенных бетонов колеблется от 25 до 40 кг/см2, а для торкрета она несколько выше – 38–62 кг/см2 [18].
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
В опытах мы преследовали цель проследить влияние добавок, вводимых в торкрет, на его сцепление с арматурой. Сцепление определяли выдергиванием 10–12 миллиметровых арматурных стержней из призм сечением 50×50 мм и длиной 15–17 см. Длина защемления арматурного конца составляла 10–12 см. Сцепление торкрета с арматурой находится в той же связи, что и прочностные свойства. ССБ сильно повысила сцепление (почти в два раза), а все остальные добавки понизили его (табл. 7).
Однако к 3-месячному сроку ССБ не дала приращения силы сцепления, в то время как у торкрета без добавок и с добавками гидрофобных веществ наблюдается приращение ее. В отдельных случаях сила сцепления торкрета с арматурой достигает 200% силы сцепления в возрасте 28 суток. К 3-месячному возрасту все составы торкрета получили τ сц, близкое к τ сц для обычных бетонов, или более высокое. Таким образом, можно отметить, что τ сц арматуры с торкретом с добавками (ССБ, СНВ, мыла, битума в пропорциях, близких к нашим) находится на вполне удовлетворительном уровне, а поэтому минимальная длина заделки арматурных концов может приниматься согласно принципам, действующим в обычном бетоне, т.е.
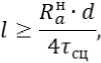
где l – наименьшая необходимая длина заделки; Ra H – нормативное сопротивление арматуры.
a
ТЕХНОЛОГИИ ПРОИЗВОДСТВА СТРОИТЕЛЬНЫХ МАТЕРИАЛОВ И ИЗДЕЛИЙ
б
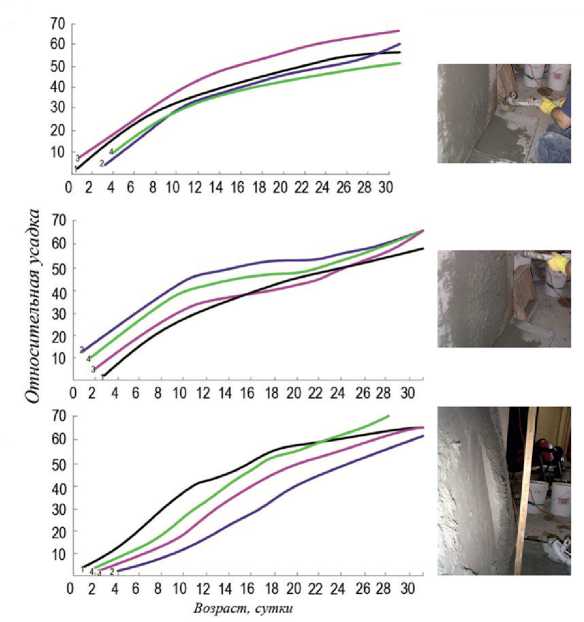
Рис. 6. Графики зависимости усадочных деформаций торкрета от времени εy = f (t): а – добавка ССБ, %; 1 и 2 – без добавки (смеси 1:4); 3 – 0,3, смесь 1:4; 4 – 0,5, смесь 1:4; б – добавка СНВ (смесь 1:4), %; 1 – без добавки; 2 – 0,03; 3 – 0,06; 4 – 0,12; в – добавка мыла (1 – 0,1%, 2 – 0,2, 3 – 0,6) и битума (4 – 0,25%, 5 – 0,5); смесь 1:4.
Таблица 6
Относительные показатели усадки
|
Состав сухой смеси и процент добавки |
Относительная усадка 14 суток |
t y × 10–5 в возрасте 28 суток |
|
Без добавки |
||
|
1:4 |
35,0 |
53,5 |
|
1:3 |
36,0 |
57,0 |
|
ССБ |
||
|
0,3 |
39,0 |
55,0 |
|
0,5 |
48,0 |
63,7 |
|
СНВ |
||
|
0,03 |
49,0 |
59,5 |
|
0,06 |
44,0 |
58,5 |
|
0,12 |
36,0 |
55,0 |
|
Мыло |
||
|
0,1 |
44,0 |
62,5 |
|
0,2 |
23,4 |
55,0 |
|
0,6 |
35,0 |
60,3 |
|
Битум |
||
|
0,25 |
40,0 |
68,0 |
|
0,5 |
37,0 |
66,0 |
Для компенсации усадочных деформаций большое значение имеет ползучесть торкрета под действием статической нагрузки [19–27]. Усадочные деформации образцов в месячном возрасте, взятых для испытаний из влажного песка, за определенный промежуток времени оказались большими, чем ползучесть: это стало ясным после испытания 9 серий образцов (торкрет без добавок, а также с ССБ и СНВ).
Начиная с 10-й серии, т.е. с образцов, изготовленных из сухой смеси цемента с песком 1:4 при добавке 0,6% хлопкового мыла (от веса цемента), деформации, показываемые образцом под действием растягивающей нагрузки, разделялись на усадочные и ползучесть вычитанием из них показаний усадки, получаемых на ненарушенном образце-близнеце. Установлено, что интенсивность и мера ползучести торкрета зависят от уровня напряженного состояния образца: чем ближе действующая нагрузка к пределу прочности, тем интенсивнее ползучесть.
При невысоких нагрузках – 0,2÷0,3 Rp –вслед-ствие проявления усадки ползучесть торкрета непосредственными замерами не отмечается. С увели-
ТЕХНОЛОГИИ ПРОИЗВОДСТВА СТРОИТЕЛЬНЫХ МАТЕРИАЛОВ И ИЗДЕЛИЙ
Таблица 7
Показатели сцепления торкрета с арматурой
Образец, приготовленный из сухой смеси состава 1:4 с 0,5% добавкой ССБ, испытан на ползучесть. Независимо от напряжений, действующих в нем, суммарные деформации (ползучесть, усадка) были постоянно отрицательными, т.е. образец укорачивался, причем укорочение на базе 11 см колебалось в следующих пределах (табл. 8).
Повышение растягивающей нагрузки на торкрет снижает его усадочные деформации: это происходит вследствие повышения интенсивности ползучести и в результате возрастания усилий, сопротивляющихся деформациям усадки. В табл. 9 показан характер приращения упругих деформаций торкрета при ступенчатом сильно рассредоточенном во времени приращении нагрузок.
Опыт, результаты которого сведены в табл. 9, проводился следующим образом. Образец получал нервную ступень нагрузки, до 6,4 кг/см2, при этом брали отсчет по тензометрам, затем через 21 час нагрузка снималась полностью, стрелку тензометра переводили на нулевое деление, и после этого образец получал новую ступень загрузки, до 9 кг/см2.
Удлинение образца равнялось соответственно 15,2 и 14,5 µ. Через 48 часов все повторялось.
Данные таблиц и графиков (приведены только для одной серии торкрета) показали, что в общем случае зависимость ∆ l = f (σ p ) криволинейна, причем кривизна графиков того же направления (знака), что и в испытаниях торкрета при непрерывном статическом загружении.
Испытания водопроницаемости проводили на образцах-дисках диаметром 200 мм, высотой 50 мм (по три образца на точку в возрасте 28 дней). Давление повышалось на 1 атм. через 4 часа. Образцы нареза-
Таблица 8
Показатели ползучести торкрета
|
σ p , кг/см2 |
Укорочение, µ |
|
16 |
12–9,5 |
|
23 |
7,8–7,3 |
|
25 |
3,3–3,0 |
|
28 |
2,0–1,4 |
|
32 |
1,9–1,2 |
|
33 |
1,8–0,8 |
|
37 |
1,7–0,6 |
|
40 |
0–0 |
ТЕХНОЛОГИИ ПРОИЗВОДСТВА СТРОИТЕЛЬНЫХ МАТЕРИАЛОВ И ИЗДЕЛИЙ
Таблица 9
Характер приращения упругих деформаций торкрета
Введение наноструктурированных поверхностноактивных добавок не снижает водонепроницаемости торкрета, даже образцы с добавкой 1% ССБ от веса цемента выдерживают давление 6 атм. Если добавки ССБ повышают прочность торкрета на сжатие или сохраняют ее на уровне прочности на сжатие его без добавок, снизить водонепроницаемость они также не могут.
Электронно-микроскопический анализ торкрет-бетона с наноструктурированными добавками поверхностно-активных веществ показал, что прочностные свойства, усадка, деформируемость при растяжении и водонепроницаемость имеют значительно улучшенные показатели по сравнению с обычным бетоном и подтверждают результаты экспериментальных работ. Исследования микроструктуры образцов были проведены на сканирующем электронном микроскопе JЕОL JSM7500 с приставкой рентгеноспектрального анализа (рис. 7).
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
По результатам выполненного исследования можно сделать следующие выводы:
-
1. Наноструктурированные добавки поверхностно-активных веществ по-разному влияют на смачивающую способность воды и прочность торкрета: ССБ и СНВ увеличивают их, причем СНВ – незначительно, хлопковое мыло значительно уменьшает смачивающую способность воды и, вероятно, поэтому снижает прочность торкрета при введении в него с водой затворения.
-
2. Оптимальной добавкой ССБ в торкрет с водой затворения при условии набрызгивания является 0,5% от веса цемента. Оптимума добавки СНВ не на-
- Таблица 10
-
3. При введении 0,3% ССБ от веса цемента в торкрет-состав сухой смеси 1:4 повышается прочность его при сжатии на 16%, при изгибе на 1% и при разрыве на 20% (по сравнению с соответствующими прочностями торкрета без добавки).
-
4. Добавки ССБ в количестве 0,5 и 1%, СНВ 0,06 и 0,12%, хлопкового мыла 0,1, 0,2 и 0,6% от веса це-
ТЕХНОЛОГИИ ПРОИЗВОДСТВА СТРОИТЕЛЬНЫХ МАТЕРИАЛОВ И ИЗДЕЛИЙ
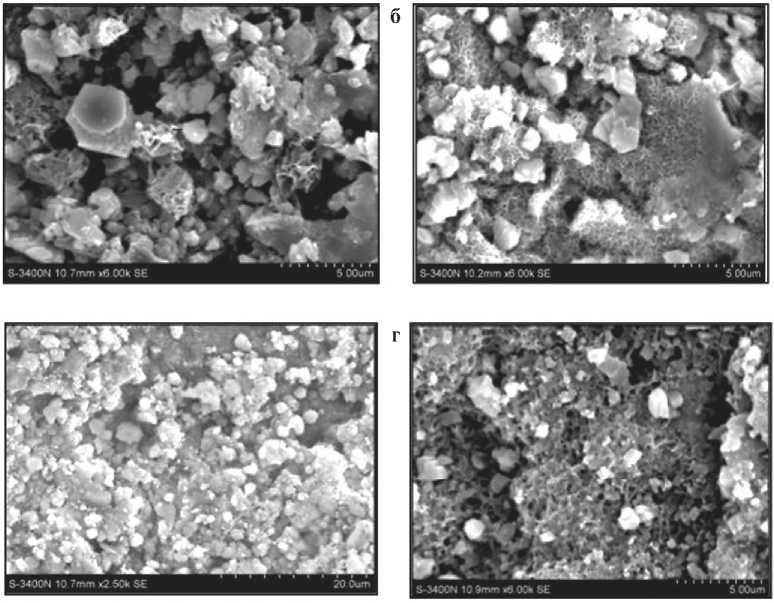
Рис. 7. Микроструктура образцов торкрет-бетона: а – с добавкой ССБ; б – с добавкой СНВ; в – с добавкой хлопкого мыла; г – с добавкой битума
-
5. Все наноструктурированные добавки поверхностно-активных веществ повышают усадку торкрета. Наименьшее повышение ее дает торкрет с ССБ, а наибольшее – с битумной эмульсией.
-
6. Наноструктурированные поверхностно-активные добавки в торкрет (к 28-дневному возрасту)
-
7. Наноструктурированные добавки поверхностно-активных веществ в широких пределах понижают значения модулей мгновенной упругости торкрета, т.е. повышают его пластические свойства.
-
8. Поверхностно-активные вещества и битумные эмульсии понижают силу сцепления арматуры с торкретом (за исключением ССБ)‚ однако она остается на более высоком уровне, чем у обычных бетонов.
Результаты испытания торкрета на водопроницаемость
|
Количество добавки, % |
Состав сухой смеси |
Давление, выдержанное образцами, атм |
|
Без добавки |
1:4 1:2 |
6 6 |
|
ССБ 0,3 0,3 1,0 |
1:3 1:4 |
6 6 6 |
|
СНВ 0,03 0,06 |
* * |
6 6 |
|
Мыло 0,1 0,2 |
* * |
1* 6 |
* При повышении давления лопнули образцы блюдается. При введении в торкрет хлопкового мыла с водой затворения содержание воды в уложенном торкрете по мере увеличения количества вводимой добавки увеличивается, оптимальное содержание цемента в торкрете наблюдается при введении 0,3% хлопкового мыла от веса цемента, «отскок» уменьшается при увеличении количества вводимой добавки.
мента, битума в виде эмульсии 0,25 и 0,5% от веса торкрета (из сухой смеси 1:4) снижают прочность при сжатии, изгибе и разрыве по сравнению с соответствующими прочностями его без добавок.
значительно повышают его деформируемость при растяжении.
Список литературы Торкрет-бетон с добавками для облицовки оросительных каналов
- Jakiyayev B.D., Moldamuratov Z.N., Bayaliyeva G.M., Ussenbayev B.U., Yeskermessov Z.E. Study of local erosion and development of effective structures of transverse bank protection structures. Periodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences (PEN). 2021. 9(3): 457. Available from: https://doi.org/10.21533/pen.v9i3.2191
- Sennikov M.N., Omarova G.E., Moldamuratov Z.N. Study of the development of soil in the formation of channels hydraulic and static stability of cross-sectional shapes. World Applied Sciences Journal. 2014. 30(1): 99–104. Available from: https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wasj.2014.30.01.14008
- Hammer A.L., Thewes M., Galler R. Empirical forecasting model to determine the strength development of shotcrete. Geomechanik Und Tunnelbau. 2019. 12(6): 730–738. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/geot.201900054
- Çakıroğlu M.A., Kaplan A.N., Süzen A.A. Experimental and DBN-Based neural network extraction of radiation attenuation coefficient of dry mixture shotcrete produced using different additives. Radiation Physics and Chemistry. 2021. 188. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2021.109636
- Kloft H., Krauss H.W., Hack N., Herrmann E., Neudecker S., Varady P.A., Lowke D. Influence of process parameters on the interlayer bond strength of concrete elements additive manufactured by Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP). Cement and Concrete Research. 2020. 134. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2020.106078
- Armengaud J., Casaux-Ginestet G., Cyr., Husson B., Jolin M. Characterization of fresh dry-mix shotcrete and correlation to rebound. Construction and Building Materials. 2017. 135: 225–232. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.220
- Bekbasarov I., Nikitenko M., Shanshabayev N., Atenov Y., Moldamuratov Z. Tapered-prismatic pile: driving energy consumption and bearing capacity. News of the National Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Series of Geology and Technical Sciences. 2021. 6(450): 53–63. Available from: https://doi.org/10.32014/2021.2518-170X.119
- Wang J., Niu D., Wang Y., Wang B. Durability performance of brine-exposed shotcrete in salt lake environment. Construction and Building Materials. 2018. 188: 520–536. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.08.139
- Shen Y., Wang Y., Yang Y., Sun Q., Luo T., Zhang H. Influence of surface roughness and hydrophilicity on bonding strength of concrete-rock interface. Construction and Building Materials. 2019. 213: 156–166. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.04.078
- Watanabe T., Hosomi M., Yuno K. Hashimoto C. Quality evaluation of shotcrete by acoustic emission. Construction and Building Materials. 2010. 24(12): 2358–2362. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.05.007
- Wang J., Niu D., He H. Frost durability and stress–strain relationship of lining shotcrete in cold environment. Construction and Building Materials. 2019. 198: 58–69. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.11.264
- Chen L., Ma G. Liu G., Liu Z. Effect of pumping and spraying processes on the rheological properties and air content of wet-mix shotcrete with various admixtures. Construction and Building Materials. 2019. 225: 311–323. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.104
- Armengaud J., Cyr M., Casaux-Ginestet G. Husson B. Durability of dry-mix shotcrete using supplementary cementitious materials. Construction and Building Materials. 2018. 190: 1–12. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.09.107
- Cui S., Liu P., Cui E., Su J., Huang B. Experimental study on mechanical property and pore structure of concrete for shotcrete use in a hot-dry environment of high geothermal tunnels. Construction and Building Materials. 2018. 173: 124–135. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.191
- Khooshechin M., Tanzadeh J. Experimental and mechanical performance of shotcrete made with nanomaterials and fiber reinforcement. Construction and Building Materials. 2018. 165: 199–205. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.199
- Trujillo P.B., Jolin M., Massicotte B., Bissonnette B. Bond strength of reinforcing bars encased with shotcrete. Construction and Building Materials. 2018. 169: 678–688. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.02.218
- Liu P., Cui S., Li Z., Xu X., Guo C. Influence of surrounding rock temperature on mechanical property and pore structure of concrete for shotcrete use in a hot-dry environment of high-temperature geothermal tunnel. Construction and Building Materials. 2019. 207: 329–337. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.02.125
- Kaufmann J., Loser R., Winnefeld F., Leemann A. Sulfate resistance testing of shotcrete – Sample preparation in the field and under laboratory conditions. Construction and Building Materials. 2021. 276. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.122233
- Pan G., Li P., Chen L., Liu G. A study of the effect of rheological properties of fresh concrete on shotcreterebound based on different additive components. Construction and Building Materials. 2019. 224: 1069–1080. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.060
- Duarte G., Bravo M., de Brito J., Nobre J. Mechanical performance of shotcrete produced with recycled coarse aggregates from concrete. Construction and Building Materials. 2019. 210: 696–708. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.03.156
- Liu G., Zhao J., Zhang Z., Wang C., & Xu Q. Mechanical properties and microstructure of shotcrete under high temperature. Applied Sciences (Switzerland). MDPI. 2021. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199043
- Zhu C., Zhou N., Guo Y., Li M., & Cheng Q. Effect of doped glass fibers on tensile and shear strengths and microstructure of the modified shotcrete material: An experimental study and a simplified 2D model. Minerals. 2021. 11(10). Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/min11101053
- Liu M., Liu D., Qiao P., & Sun L. Characterization of microstructural damage evolution of freeze-thawed shotcrete by an integrative micro-CT and nanoindentation statistical approach. Cement and Concrete Composites. 2021. 117. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2020.103909
- Wang Y., Shi C., Ma Y., Xiao Y., & Liu Y. Accelerators for shotcrete – Chemical composition and their effects on hydration, microstructure and properties of cement-based materials. Construction and Building Materials. Elsevier Ltd. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122557
- Xu Y., He T., Ma X., & Yang R. The research on mechanism of C–S–H nanocrystal improving early properties of shotcrete at low temperature by thermodynamic modeling. Construction and Building Materials. 2022. 325. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126738
- Shang Y., Guo Y., Zhang W., Zhao W., & Tan Y. Influence of new compound admixture on shotcrete performance. Journal Wuhan University of Technology, Materials Science Edition. 2017. 32(6): 1392–1396. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-017-1758-8
- Zaki Saaid I. Application of ultra cellulose fiber for the enhancement of the durability and shrinkage of cement pastes exposed to normal and aggressive curing conditions. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2015. (7)4: 121–142. Available from: https://doi.org/10.15828/2075-8545-2015-7-4-121-142


