Use of Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag (BOFS) in geopolymer mortar for modification of concrete in hydraulic structures: stabilization properties and reduction of volume changes
Автор: Imanov A.M., Kareken G.T., Tukhtamisheva A.Z., Ismailova A.B., Moldamuratov Zh.N., Rakhimova G.M.
Журнал: Nanotechnologies in Construction: A Scientific Internet-Journal @nanobuild-en
Рубрика: Manufacturing technology for building materials and products
Статья в выпуске: 3 Vol.17, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. Increasing demands for sustainability and environmental safety in construction materials have encouraged the use of industrial by-products such as Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag (BOFS) and fly ash (FA) as alternative components in geopolymer binders. This study aims to evaluate the physico-mechanical properties, micro- and nanostructure, and resistance to alkali-silica reaction (ASR) of geopolymer mixtures based on BOFS and FA, which are particularly relevant for hydraulic engineering applications. Methods and Materials. BOFS and Class F FA were used as aggregates and pozzolanic components. Compressive strength was measured at 3, 7, 28, and 56 days. Micro- and nanostructural analyses were performed using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS), and X-ray Diffraction (XRD). Expansion tests were conducted according to ASTM C 1260 in both water and 1 M NaOH solution at 80 °C. Results and Discussion. The optimal compressive strength (up to 50 MPa at 28 days) was achieved with 75% replacement of sand by BOFS and an alkali activator ratio of Na2SiO3/NaOH = 1. SEM and EDS analyses revealed the formation of a dense gel-like structure with N-A-S-H and CaCO3 phases. All samples exhibited expansion below 0.1% in water, meeting the criterion for non-reactive aggregates. In alkaline solution, expansion reached 0.25% in some compositions. A correlation was observed between microstructure, the content of reactive phases (Si, Al, Ca), and mechanical performance. Conclusion. The results demonstrate that BOFS and FA can be effectively utilized in geopolymer mixtures, providing adequate strength, dimensional stability, and ASR resistance. Carbonation curing and proper selection of alkali activators enhance BOFS stabilization and reduce its expansive behavior. These findings support the potential use of such mixtures in sustainable and durable construction systems, especially for hydraulic structures.
Micro- and nanostructure, geopolymer binder, basic oxygen furnace slag (BOFS), fly ash (FA), alkali-silica reaction (ASR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142244832
IDR: 142244832 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2025-17-3-273-295
Текст научной статьи Use of Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag (BOFS) in geopolymer mortar for modification of concrete in hydraulic structures: stabilization properties and reduction of volume changes
Original article
Иманов А.М., Карекен Г.Т., Тухтамишева А.З., Исмаилова А.Б., Молдамуратов Ж.Н., Рахимова Г.М. Использование шлаков кислородно-конвертерного процесса (BOFS) в геополимерном растворе для модификации бетона гидротехнических сооружений: стабилизация свойств и снижение объемных изменений. Нанотехнологии в строительстве. 2025;17(3):273–295. – EDN: ARMWJQ.
Current climate change is largely attributed to carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions resulting from the combustion of fossil fuels and industrial activities, including cement production. The cement industry alone accounts for approximately 5 to 8% of global CO₂ emissions. In this regard, the use of alternative binder materials in concrete production is considered a promising approach to significantly reduce the carbon footprint [1–3].
One such alternative material is geopolymer concrete (GPC), also known as alkali-activated concrete, which is regarded as an environmentally sustainable substitute for traditional ordinary Portland cement (OPC) concrete. The primary components of GPC include aluminosilicate materials, alkaline activators (sodium hydroxide NaOH and sodium silicate Na₂SiO₃), as well as mineral and inert aggregates [2, 4–6]. Common sources of aluminosilicates are industrial by-products such as fly ash, ground granulated blast furnace slag, silica fume, and rice husk ash (Figure 1).
Geopolymer concrete exhibits high mechanical performance (compressive and flexural strength), comparable to or exceeding that of OPC-based concrete, and demonstrates excellent durability [3, 6]. Due to its environmental advantages-namely, reduced CO₂ emissions and lower consumption of natural resources-GPC represents a competitive alternative to conventional concrete.
Of particular interest is the use of geopolymer concrete for the modification of concrete in hydraulic structures, where not only strength and deformation properties are critical, but also resistance to moisture, temperature fluctuations, and aggressive environmental conditions [4–6].
Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag (BOFS), a by-product of steelmaking, is a solid waste material generated during the conversion of pig iron in basic oxygen furnaces. This material possesses a range of valuable mechanical and physico-chemical properties, including high compressive strength, hardness, low abrasion rate, and resistance to external loads [5–7]. Due to these characteristics, BOFS is considered a potential substitute for natural aggregates in the production of construction materials, road pavements, and various structural products.
However, the high content of free lime (f-CaO) and free magnesium oxide (f-MgO) in BOFS significantly limits its direct utilization. One of the major challenges is the material’s tendency to expand due to hydrated reactions. When exposed to water, f-CaO and f-MgO transform into calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) and magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂), respectively, leading to volume increase and degradation of the material’s micro- and nanostructure. These reactions are described by equations (1) and (2) and result in a significant reduction in strength [6, 7].
As a result of its susceptibility to volumetric changes and instability in alkaline environments, the application of BOFS as an aggregate is primarily limited to traditional Portland cement (OPC)-based compositions [7, 8]. This limitation is particularly critical in the design and construction of hydraulic structures, where dimensional stability and mechanical performance in moist and aggressive environments are of paramount importance.
Within the framework of research on concrete modification for hydraulic structures, the potential use of BOFS in geopolymer binders is being investigated. Such binders can mitigate the adverse effects of f-CaO and f-MgO through optimized alkali activation and the formation of a more stable matrix resistant to expansion and leaching. Thus, the incorporation of BOFS into geopolymer systems paves the way for the environmentally safe utilization of metallurgical waste and enhances the durability of structures, including under conditions of high humidity and hydrostatic pressure [7–10].
f-CaO+H2O → Ca(OH)2, (1)
f-MgO+H2O → Mg(OH)2. (2)
Geopolymer concrete (GPC) offers new opportunities for the rational and efficient utilization of Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag (BOFS) as an aggregate. During the alkaline activation process, a robust aluminosilicate framework (Si–

Fig. 1. Composition of geopolymer concrete
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
Al) forms on the surface of solid particles within the micro-and nanostructure of GPC. This framework facilitates the development of gel phases-silica gel (Si-gel) and alumina gel (Al-gel)-as shown in Equation (3). These gel phases play a crucial role in establishing a stable three-dimensional network in which SiO₄ and AlO₄ tetrahedra are interconnected via shared oxygen atoms, providing mechanical strength and long-term durability to the material.
Geopolymerization reactions are exothermic, accompanied by heat release, and involve the participation of free silicon (f-Si) present in the system. This f-Si can interact with free lime (f-CaO) and free magnesium oxide (f-MgO) contained in BOFS. As a result, reactions occur that lead to the formation of chemically stable com-pounds-wollastonite (CaSiO₃) and enstatite (MgSiO3)-as illustrated by Equations (4) and (5).
The formation of these stable silicates significantly reduces the expansion potential of BOFS, eliminating one of the main barriers to its use in construction. Thus, the incorporation of BOFS into geopolymer binders enables effective modification of concrete for hydraulic structures, making it more resistant to volumetric deformations, leaching, and other aggressive environmental effects.
The use of BOFS in a geopolymer matrix represents a promising approach for the valorization of industrial waste, while simultaneously enhancing the performance characteristics of concrete used in conditions involving prolonged water exposure, fluctuating moisture levels, and mechanical loads typical of hydraulic infrastructure.
SiO2+Al2O3 → Al2SiO5, (3)
f-CaO+SiO2 → CaSiO3, (4)
f-MgO + SiO2 → MgSiO3. (5)
At present, the Republic of Kazakhstan, like many other countries, is facing serious environmental and technological challenges related to the disposal of industrial waste. Increased CO₂ emissions, the shortage of suitable land for waste storage, and high economic costs associated with waste treatment and landfilling have become issues of growing concern at both national and international levels. In response to these challenges, Kazakhstan is taking steps to develop effective waste management strategies aimed at reuse and integration into sustainable construction cycles [12].
One of the promising directions in this context is the investigation of the potential reuse of autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) products manufactured in Kazakhstan as a component in construction materials. This approach not only helps reduce waste volumes but also increases the resource efficiency of the construction sector, particularly in the context of reducing the carbon footprint and conserving natural resources.
The use of recycled and secondary materials, such as AAC and BOFS slag, is of particular importance in the modification of concrete for hydraulic structures. Given the operational conditions of such structures-exposure to moisture, temperature fluctuations, freeze-thaw cycles, and hydrostatic pressure-it is critical to ensure the dimensional stability and durability of the concrete. The application of geopolymer composites based on industrial waste opens new horizons for the development of environmentally friendly, high-performance, and durable construction materials that meet the demands of modern hydraulic engineering.
Thus, integrating approaches to industrial waste recycling and its rational application as components in geopolymer systems contributes to environmental sustainability and expands the potential of modified concrete mixtures for next-generation hydraulic structures.
Cement, widely used in the construction industry, does not fully meet current requirements for environmentally safe and sustainable infrastructure. Cement production is accompanied by significant carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions, resulting from the combustion of coal and other fossil fuels. This contributes to air pollution, soil and water acidification, and eutrophication [8–12].
To mitigate the negative environmental impacts of cement production, several solutions have been proposed:
-
1. Use of alternative binder materials.
-
2. Replacement of conventional fossil fuels with cleaner energy sources during clinker calcination.
-
3. Optimization of technological processes and reduction of energy consumption in production.
One of the most promising directions is the use of geopolymer concrete (GPC), which represents an efficient and environmentally sustainable alternative to ordinary Portland cement (OPC). The adoption of GPC in the construction industry can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and lower energy consumption across all stages of the material’s life cycle [9–11].
According to several researchers [10–14], geopolymer binders are a safe and eco-friendly substitute for OPC. The primary components of GPC include aluminosilicate materials such as fly ash, ground granulated blast furnace slag, and rice husk ash (a source of amorphous silica), as well as natural minerals like kaolin and bentonite [11, 15]. These materials are activated using alkaline solutions (e.g., sodium or potassium hydroxide) and silicates (e.g., sodium silicate or water glass). Figure 2 presents the main components used to produce geopolymer concrete.
The use of geopolymer binders is especially relevant for the modification of concrete in hydraulic structures, where, in addition to strength, enhanced resistance to moisture, chemical aggression, and freeze-thaw cycles are required. Utilizing industrial waste as feedstock for GPC not only facilitates the effective recycling of significant
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS

Fig. 2. Main components for the production of geopolymer concrete/mortar
volumes of secondary materials but also helps reduce the overall environmental impact.
In conclusion, the recycling of industrial waste, including BOFS slag and fly ash, for subsequent use in geopolymer composites represents an efficient pathway toward the creation of next-generation high-performance construction materials suitable for critical infrastructure applications, including hydraulic structures.
METHODS AND MATERIALS
Characteristics of Binder Materials
The primary components used in the production of geopolymer material (GPM) for the modification of concrete in hydraulic structures were Class F fly ash (FFA), classified according to ASTM standards, and ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS), as shown in Figure 3.
The selection of these components is based on their high reactivity and beneficial impact on the physical and mechanical properties of the geopolymer matrix. According to previous studies [13–17], the optimal mass ratio of
FFA to GGBFS that ensures enhanced adhesive strength and good workability is 60% FFA to 40% GGBFS. This combination provides a balance between the reactivity of aluminosilicate phases and the chemical stability of the binder system under aggressive environmental conditions typical for hydraulic structures.
The specific gravity (SG) of both components was determined according to ASTM C 188-17 (Standard Test Method for Density of Hydraulic Cement Using a Pycnometer). The measured values were: 1.91 for fly ash (FFA) and 2.92 for slag (GGBFS).
This difference in density was considered in mixed design calculations and plays an important role in forming a dense, homogeneous, and stable micro- and nanostructure of the geopolymer mortar. Such characteristics are critical for concrete systems operating under conditions of variable water saturation and mechanical loading.
Characteristics of Aggregates
To evaluate the physical, mechanical, and chemical properties of mineral aggregates used in modified concretes for hydraulic structures, tests were conducted in

Fig. 3. Class F fly ash (a) and ground granulated blast furnace slag, GGBFS (b)

MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS accordance with ASTM C1260 – Standard Test Method for Potential Alkali Reactivity of Aggregates (Mortar-Bar Method).
The relative specific gravity (RS) and particle size distribution of the aggregates were determined as part of this method. These parameters play a critical role in ensuring the density, strength, and durability of geopolymer concrete, especially under conditions of cyclic water saturation typical for hydraulic structures.
The chemical composition and particle size distribution of the aggregates are presented in Table 1. Particular attention was paid to selecting fractions with low alkali reactivity, which is especially important when incorporating BOFS and other potentially reactive components into the geopolymer mixture.
To investigate the influence of BOFS aggregate content on the properties of geopolymer mixtures (GPM) intended for the modification of concrete in hydraulic structures, a series of mix designs were developed with varying ratios of traditional aggregate (RS) and basic oxygen furnace slag (BOFS):
– 100% RS;
– 75% RS + 25% BOFS;
– 50% RS + 50% BOFS;
– 25% RS + 75% BOFS;
– 100% BOFS.
The physical and mechanical properties of the aggregates are presented in Table 1. All tests were conducted in accordance with ASTM C1260, which regulates the assessment of the potential alkali reactivity of aggregates. A particle size distribution analysis was performed, classifying the aggregates into five gradation groups, the characteristics of which are shown in Table 2.
To determine the physical characteristics of the aggregates, testing methods consistent with ASTM C128 were employed. Gravimetric techniques-particularly the pycnometer method-were used to ensure high measurement accuracy. The key measured parameters include:
Table 1. Classification of fine aggregate according to ASTM C 1260
|
Aggregate Gradation |
||||||||||
|
Passing |
Retained |
Passing |
Retained |
Passing |
Retained |
Passing |
Retained |
Passing |
Retained |
|
|
Sieve size |
4.75 mm |
2.36 mm |
2.36 mm |
1.18 mm |
1.18 mm |
600 μm |
600 μm |
300 μm |
300 μm |
150 μm |
|
Mass (%) |
10 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
15 |
|||||
Table 2. Classification of fine aggregate according to ASTM C 1260
Aggregate Gradation
Passing
Retained
Passing
Retained
Passing
Retained
Passing
Retained
Passing
Retained
Sieve size
4.75 mm
2.36 mm
2.36 mm
1.18 mm
1.18 mm
600 μm
600 μm
300 μm
300 μm
150 μm




Fresh BOFS




River sand
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
-
– WSSD – weight of the sample in the saturated surfacedry condition, g;
-
– WOD – weight of the oven-dried sample, g;
– Wpyc+water– weight of the pycnometer filled with water only, g;
– Wpyc+water+SSD – weight of the pycnometer filled with water and the SSD sample, g.
Based on these values, aggregate properties were calculated using standard equations (6) and (7). The analysis of the results made it possible to determine how the variation in BOFS content affects water absorption, density, volumetric stability, and potential chemical compatibility with the geopolymer alkaline matrix.
The obtained data form is the basis for selecting the optimal geopolymer mix design for the modification of concrete used in hydraulic structures, considering the requirements for durability, strength, and resistance to aggressive environmental conditions.
AC (%) = 100*WssD W°D,
,
Gssd —
WSSD
. (7)
Wpyc+ water +Wssd ^pyc+water+SSD
Considering that the specific gravity (SG) of the RS and BOFS aggregates is 2.77 and 3.16, respectively (Fig. 4), their absorption capacity (AC) was calculated based on experimental data. The results showed that the water absorption for RS was 2.67%, while for BOFS it was 5.12% (Table 3).
The higher absorption capacity of BOFS is attributed to its porous microstructure and the presence of microcracks formed during the cooling and grinding processes of the slag. This parameter is critical in designing
Table 3. Specific gravity and absorption capacity of fine aggregate
Accounting for these characteristics is essential for enhancing the stability and durability of the final product, particularly under conditions of constant water exposure typical of hydraulic facilities. The inclusion of BOFS as an active aggregate requires precise adjustment of the geopolymer mix design to mitigate potential moisture redistribution and prevent premature deformations associated with volumetric changes.
Chemical Composition of the Binder
To determine the chemical composition of the geopolymer binder intended for the modification of concrete in hydraulic structures, tests were conducted using an AxiosmAX X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometer (manufactured by PANalytical).
Sample preparation for analysis involved the production of pressed pellets. In accordance with the methodology, the tablets were fabricated using a mixture contain-
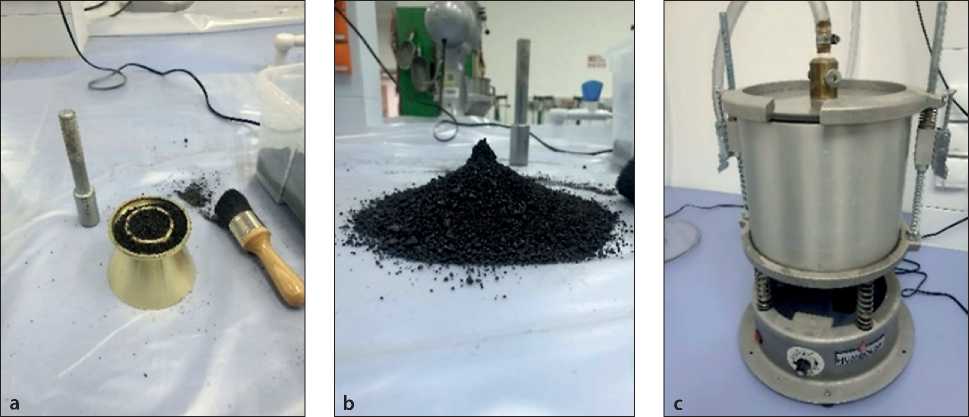

Fig. 4. Inspection of solid-state sample: (a) and (b) – visual examination of aggregates; (c) – pycnometer used for determining specific gravity
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS ing 20% binder by total sample mass, including additives such as fly ash (FA) or ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS). The mixture was thoroughly homogenized and then compacted in a pellet press under controlled pressure to ensure tablet strength and stability.
Figure 5 illustrates the step-by-step sample preparation procedure-from mixing the components to producing the final tablets suitable for X-ray phase analysis.
Accurate determination of the binder’s chemical composition enables the identification of key elements (Si, Al, Ca, Fe, Mg, and others) that influence the kinetics of geopolymerization, the formation of gel phases, and the long-term stability of the concrete’s micro- and nanostructure, particularly under aggressive environmental conditions typical of hydraulic infrastructure.
Mineralogical Analysis of the Binder
To perform a mineralogical analysis of the binder components used in the geopolymer mortar for the modification of concrete in hydraulic structures, X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques were applied.
Class F fly ash (FFA) and ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS) were analyzed using a Rigaku Smart Lab X-ray diffractometer, as shown in Figure 6. As a prerequisite for the test, fine powder samples passing through a No. 325 sieve (mesh size 45 µm) were used to ensure sufficient homogeneity and accuracy of the diffraction analysis.
The experiment was carried out with variable scan durations ranging from 5 to 70 minutes, recording X-ray intensity at a rate of 3 counts per second. This scanning mode provides high sensitivity to both amorphous and crystalline phases present in the nanostructure of the raw materials.
The mineralogical composition of the resulting binder plays a critical role in the formation of the geopolymer matrix. The presence of reactive phases, such as amorphous aluminosilicates, significantly affects the activity of the polycondensation process, as well as the strength and deformation characteristics of the modified concrete used in hydraulic structures, particularly under prolonged exposure to moisture, temperature fluctuations, and alkaline environments.
Mineralogical Analysis of the Adhesive
The morphology and mineralogical composition of fly ash (FA), used as part of the geopolymer binder for the modification of concrete in hydraulic structures, were studied using a JEOL JSM-IT 200 (LA) scanning electron microscope (SEM).

Fig. 5. Procedure for preparing a pelletized sample for X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis

Fig. 6. Procedure for conducting X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of the binder material
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS

Fig. 7. Sample preparation for scanning electron microscopy (SEM)

For the analysis, FA samples were pre-sieved through a No. 325 mesh (with 45 µm openings) to obtain a homogeneous fine fraction. The prepared particles were then evenly distributed on the surface of a conductive sample holder and placed into the microscope chamber for visualization and detailed analysis (Fig. 7).
Scanning electron microscopy enabled high-resolution imaging of the particle surfaces, revealing the spherical morphology of the FA and the presence of a glassy amorphous phase, which plays a crucial role in the geopolymerization process. In addition, spot energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analysis was performed, confirming the presence of key chemical elements such as silicon, aluminum, calcium, and iron.
The study of FA morphology is essential for assessing its reactivity and its ability to form a strong aluminosilicate matrix. This is particularly important in the development of modified geopolymer mixtures for hydraulic structure applications, where resistance to leaching, microcracking, and volumetric deformation is of critical importance.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Chemical Composition of the Binders
According to ASTM classification, Class F fly ash (FA) is characterized by a low calcium (Ca) content and a high concentration of silicon- and aluminum-bearing compounds. As shown in Table 4, the chemical composition of FA indicates the predominance of aluminosilicate phases: the content of silicon dioxide (SiO2) is 65.34%, and aluminum oxide (Al2O3) is 24.85%, which confirms the high reactivity of FA in alkaline environments.
In the context of modifying concrete for hydraulic structures, an important parameter is the sulfur content in the form of sulfur trioxide (SO3), since excessive SO₃ may negatively impact concrete durability in aqueous environments. According to the literature [12, 18–21], the permissible SO₃ content should not exceed 1%. X-ray fluorescence analysis showed that the SO3 content in the tested FA sample was 0.31%, indicating high suitability of FA as a component in geopolymer mixtures, ensuring both material strength and long-term stability.
The calcium oxide (CaO) content in Class F FA, as reported in the literature, should be below 10%. In this study, FA was found to contain only 1.86% CaO, which also contributes positively to the stability of the geopolymer matrix, particularly under constant moisture exposure typical of hydraulic structures.
The chemical composition of ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS) depends on the raw materials and the specific metallurgical processing conditions. As a byproduct of steelmaking, the composition of GGBFS varies depending on the charge materials used and the cooling rate of the molten slag. Table 4 shows that GGBFS exhibits hydraulic properties, and its micro- and nanostructure consists of a combination of amorphous and crystalline phases.
The combined content of silicon dioxide (SiO2) and aluminum oxide (Al2O3) in GGBFS amounts to 48.27%, confirming its high reactivity in an alkaline environment. At the same time, the CaO content reaches 33.06%, which is associated with the use of limestone in slag production to remove impurities during the reduction of iron ore.
The formation of hydration phases such as calcium silicate hydrate (C–S–H) and calcium aluminum silicate hydrate (C–A–S–H) occurs because of the reaction of Ca(OH)2 with SiO2 and Al2O3 found in both BOFS and GGBFS [13–16, 22–25]. These hydration products play a key role in forming a strong and dense structure in geopolymer concrete modified for hydraulic applications, ensuring resistance to aggressive environments, cracking, and long-term operational cycles.
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
Table 4. Chemical composition of binders (F-FA and GGBFS)
|
Chemical Composition (Wt, %) |
|||||||||||
|
Na2O |
MgO |
Al 2 O 3 |
SiO 2 |
SO 3 |
K 2 O |
CaO |
TiO 2 |
MnO |
Fe 2 O 3 |
ZnO |
|
|
FA |
1.03 |
0.53 |
24.85 |
65.34 |
0.31 |
0.68 |
1.86 |
1.10 |
0.07 |
4.01 |
0.04 |
|
GGBFS |
1.08 |
12.07 |
12.43 |
35.84 |
2.67 |
0.69 |
33.06 |
1.34 |
0.37 |
0.34 |
– |
Particle Size Distribution (PSD)
The particle size distribution (PSD) analysis for the materials used in this study is presented in Figure 8. One of the key factors influencing the effectiveness of concrete modification in hydraulic structures is the fineness of grinding and the uniformity of the particle size distribution of the geopolymer binder components.
The results show that the average particle size of ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS) allows for 100% passing through a No. 325 sieve, corresponding to a mesh size of 45 µm. Such fineness ensures high reactivity of the GGBFS and facilitates more complete activation in an alkaline environment.
In contrast, the fly ash (F-FA) used in this study demonstrated only 47% passing through the same sieve. This is attributed to the classification of the material as a low-grade Class F fly ash in accordance with ASTM C618. Nevertheless, the total percentage passing across other size fractions meets the ASTM C618 requirements for pozzolanic materials, making it suitable for use in geopolymer systems.
The median particle size values (D50), which indicate the central point of the distribution, were as follows: 55.73 µm for Class F fly ash (F-FA); 2.60 µm for GGBFS.
The finer particle size of GGBFS promotes an accelerated geopolymerization process and contributes to the formation of a dense gel-like structure, enhancing resistance to water absorption and leaching. The inclusion of such components in geopolymer concrete for hydraulic structures improves the material’s physicochemical properties, including strength, resistance to aggressive environments, and durability under variable climatic conditions.
Mineralogical Analysis of Binders
Figure 9 presents the interpretation of the X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern, highlighting the crystalline phases identified in the studied binder materials, along with the symbols and chemical formulas of the corresponding minerals.
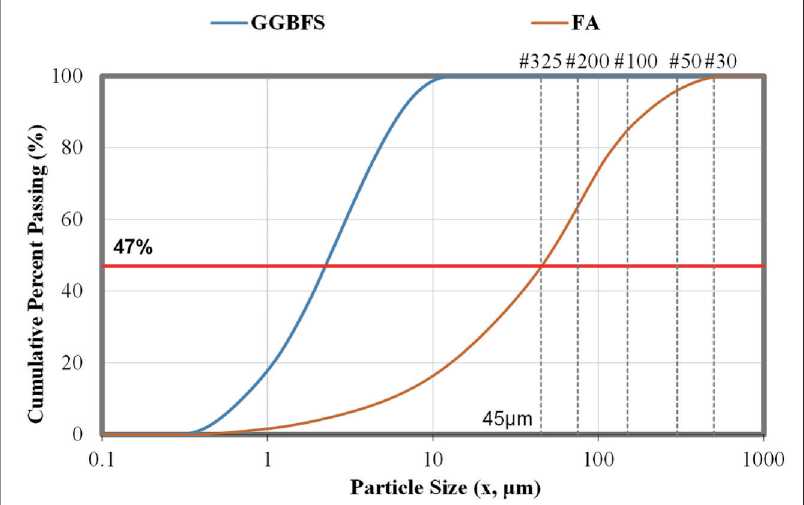
Fig. 8. Results of particle size distribution (PSD) analysis
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
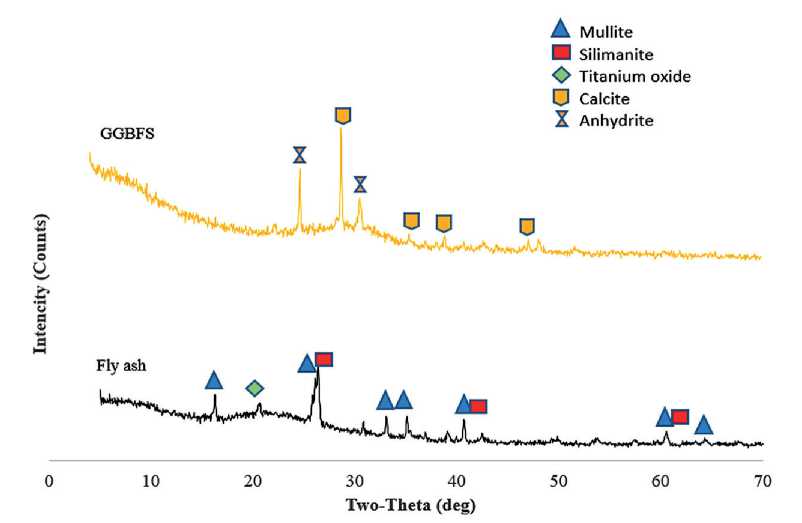
Fig. 9. Morphological structure of binder materials
According to the literature [14–19, 21–25], Class F fly ash (F-FA) primarily consists of crystalline phases, unburned lignite particles, and amorphous aluminosilicates. Similar findings have been reported in other studies [6–8, 11–13, 16–22], where the XRD patterns of fly ash show the presence of mullite (3Al2O3·2SiO2) and sillimanite (Al2SiO5), with prominent diffraction peaks at 2θ angles of approximately 28°, 42°, and 60°. Peaks corresponding to metal oxides, including titanium dioxide (TiO2), are also observed, with the highest TiO₂ intensity recorded at 20°.
The X-ray phase analysis of GGBFS, regardless of the proportion of FA present, reveals distinct peaks indicating a high content of calcite (CaCO3) and nickel carbide (Ni3C), typically found at 30° and 50°, respectively. These compounds play a key role in enhancing the strength characteristics of the material by participating in hydration and geopolymerization reactions.
Additionally, crystalline phases of mineral gypsum were identified, along with trace amounts of titanium hydride (TiH2) and stibnite (Sb2S3)-a sulfide mineral-whose characteristic peaks were detected at 25°, 35°, and 42° in GGBFS samples.
The identified mineral phases significantly influence the formation of the geopolymer matrix’s nanostructure and the mechanical performance of the final composite. In particular, the presence of aluminosilicate phases in FA promotes active polycondensation in alkaline media, while the content of calcite and nickel carbide in GGBFS enhances early-age strength and thermal stability.
Mineralogical Analysis of Adhesive Materials
The Class F fly ash used in this study is a valuable poz-zolanic material obtained as a by-product of coal combustion. Due to its high content of reactive aluminosilicate components and amorphous structure, this material is widely used in alkali-activated systems for modifying concrete in hydraulic structures where enhanced resistance to moisture, temperature fluctuations, and aggressive environments is required.
Figure 10 presents the results of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), demonstrating the spherical morphology of fly ash particles and the presence of characteristic cenospheres-hollow microspheres with thin shells. These structures help reduce the material’s density and improve its thermal insulation properties. The cracks observed on the surface of the particles are likely related to loss of elasticity of the shell during thermal processing, which may affect the dynamic behavior of the composite [15–23].
According to literature data [16, 26–28], the spherical FA particles contain both calcium compounds and aluminosilicate minerals, including sillimanite (Al2SiO5). The SEM analysis confirmed the presence of the following major chemical elements in the ash (by mass fraction): silicon (Si) – 24.67%, aluminum (Al) – 9.52%, and carbon (C) – 7.08%.
In addition, a gold (Au) content of 10.71% was recorded; however, this element is not part of the fly ash composition and is attributed to the use of a gold-coated substrate as a conductive base for SEM analysis (Fig. 11).
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
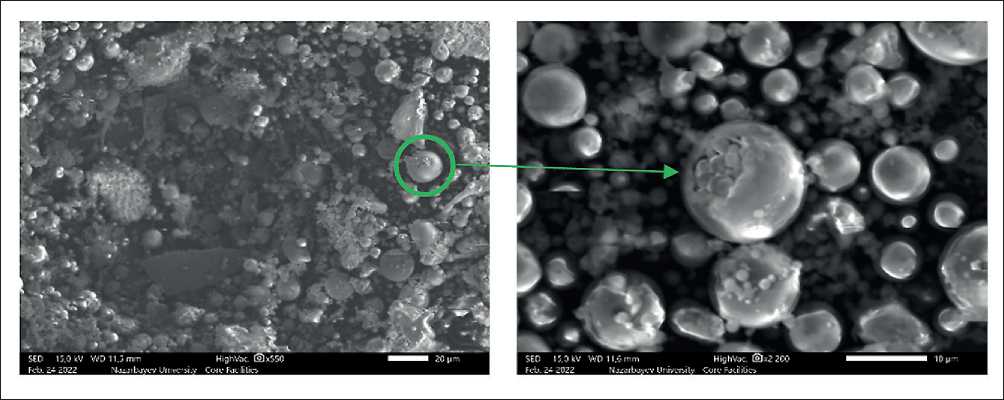

Fig. 10. Morphology of Class F fly ash based on scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis
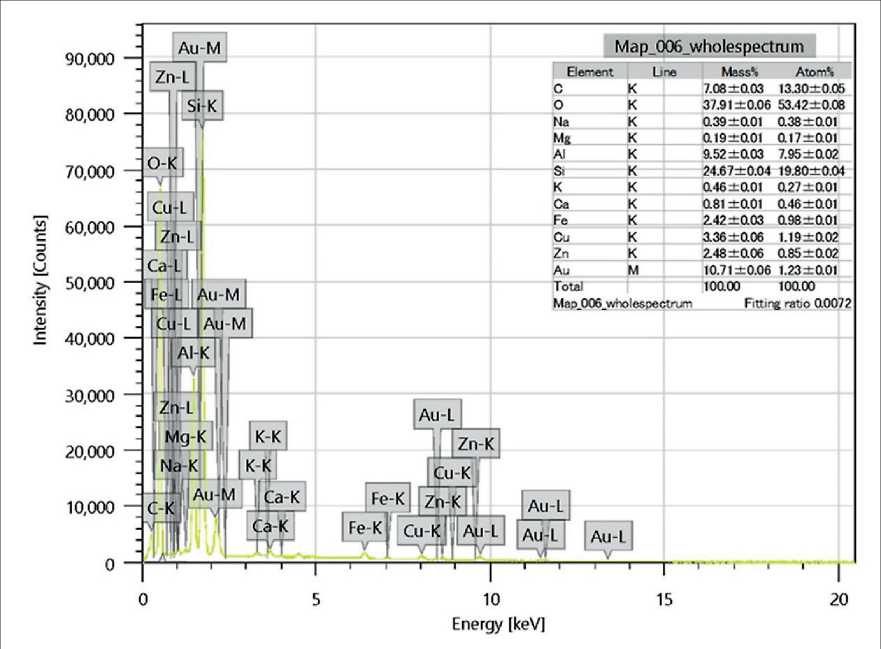
Fig. 11. Results of energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis of Class F fly ash
The morphological and chemical characteristics of FA confirm its suitability for inclusion in geopolymer binder systems. The presence of amorphous aluminosilicate phases facilitates active interaction with alkaline activators, the formation of gel phases, and, consequently, the production of high-strength and durable concrete modified for use in hydraulic infrastructure.
Chemical Compositionof Aggregates
The particle size of the aggregates used in this study is less than 45 µm, allowing for accurate chemical analysis with a high degree of precision. The main characteristics are presented in Table 5.
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
Table 5. Chemical composition of fine aggregates
|
Chemical Composition (Wt, %) |
|||||||||||
|
Na2O |
MgO |
Al 2 O 3 |
SiO 2 |
SO 3 |
K 2 O |
CaO |
TiO 2 |
MnO |
Fe2O3 |
ZnO |
|
|
BOFS* |
0.00 |
11.26 |
1.66 |
8.73 |
1.65 |
0.11 |
47.95 |
0.38 |
1.88 |
24.82 |
0.82 |
|
RS |
2.97 |
2.29 |
11.83 |
55.85 |
0.67 |
1.88 |
16.13 |
0.77 |
0.85 |
6.53 |
– |
* Note: free CaO content: 4.47%
Particular attention was given to analyzing the chemical composition of Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag (BOFS), which is considered a potential reactive aggregate in geopolymer concrete systems modified for application in hydraulic structures. One of the limiting factors is the presence of free lime (f-CaO), the concentration of which has a significant impact on the behavior of the binder mixture.
The analysis results revealed that the f-CaO content in fresh BOFS reaches 47.95%, which is relatively high. Such concentration may lead to undesirable volumetric changes, accelerated setting, and, consequently, a reduction in early-age strength. This factor is especially critical when designing mixes for hydraulic infrastructure, where high stability of both geometric and mechanical properties is required.
In addition to free lime, BOFS is rich in iron oxide (Fe2O3) at 24.82% and magnesium oxide (MgO) at 11.26%. These components also influence the material’s structure and strength by participating in reactions with the aluminosilicate matrix and promoting the formation of secondary phases such as ferrites and magnesian compounds.
Standard quartz sand was used as a control material in the study. Its chemical composition shows a high content of silicon dioxide (SiO2) at 55.85%, along with calcium oxide (CaO) at 16.13%, which is typical for natural quartz-calcium sands commonly used in construction.
Therefore, the high chemical activity of BOFS requires a tailored approach to the formulation of geopolymer mixtures. With appropriate alkaline activation and stabilization, BOFS can be effectively used for concrete modification in hydraulic structures, contributing to the sustainable utilization of metallurgical waste and the improvement of the environmental performance of construction materials.
Mineralogical Analysis of Aggregates
Similar to the binder materials, the mineral aggregates used in this study were analyzed using a Rigaku Smart Lab X-ray diffractometer (Fig. 12). The analysis was conducted under comparable conditions, allowing for an objective comparison of the phase composition of various components in the geopolymer mixture.
The investigated aggregates were exposed to air and underwent natural weathering during storage, which may influence their surface structure and reactivity in an alkaline environment. According to the X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, the main crystalline phase in BOFS is calcite (CaCO3), with a characteristic peak observed at 30° 2θ. Additionally, peaks corresponding to iron oxide (FeO) were recorded at 43° and 63° 2θ, consistent with the previously established high iron content in the chemical composition of BOFS.
A comparative analysis with natural river sand revealed significant differences in mineralogical composition. The sand spectrum showed high-intensity peaks corresponding to quartz (SiO2) and its polymorphs, confirming a high silicon content-up to 280 relative intensity units. This is particularly important in the context of geopolymerization, as silicon plays a key role in forming the durable aluminosilicate framework in geopolymer concrete designed for hydraulic structures.
In contrast to sand, the XRD spectrum of BOFS does not fully reflect the typical mineralogy of conventional aggregates, indicating the need for preliminary stabilization and consideration of potential reactivity during geopolymer mix design. Nevertheless, with proper processing, the incorporation of BOFS can contribute to increased density, strength, and long-term resistance of the material under continuous moisture and thermal loading conditions.
Mineralogical Analysis of Aggregates
Figures 13 and 14 present the results of morphological studies of basic oxygen furnace slag (BOFS), performed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). For analysis, fine BOFS particles were selected and pre-sieved through a No. 325 mesh (45 µm), in accordance with the procedures used in other laboratory tests.
The SEM analysis revealed that BOFS particles exhibit pronounced surface porosity, which may contribute to increased water absorption and, consequently, prolonged leaching of mineral components when exposed to moisture. These properties are critical in assessing the suitability of BOFS as an aggregate in geopolymer systems intended for modifying concrete in hydraulic structures,
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
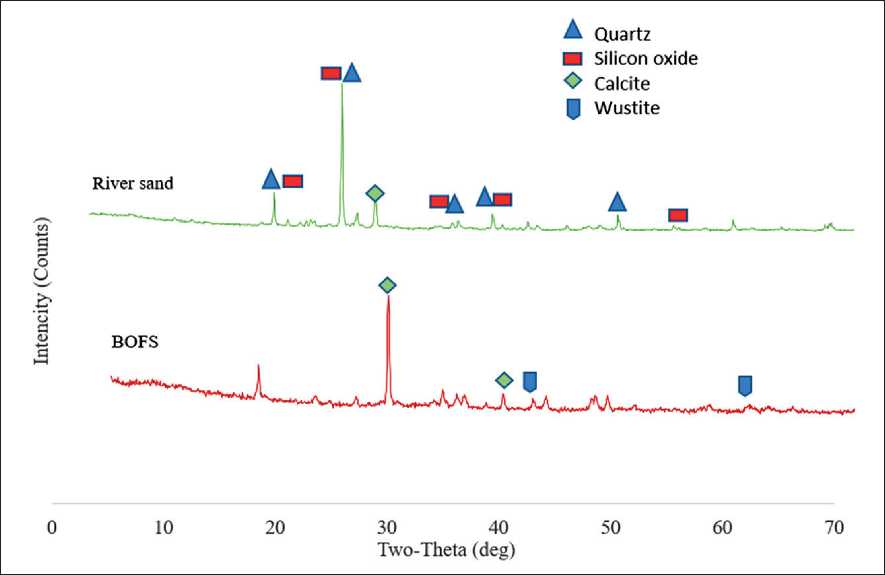
Fig. 12. Results of X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of mineral aggregates (BOFS and river sand)
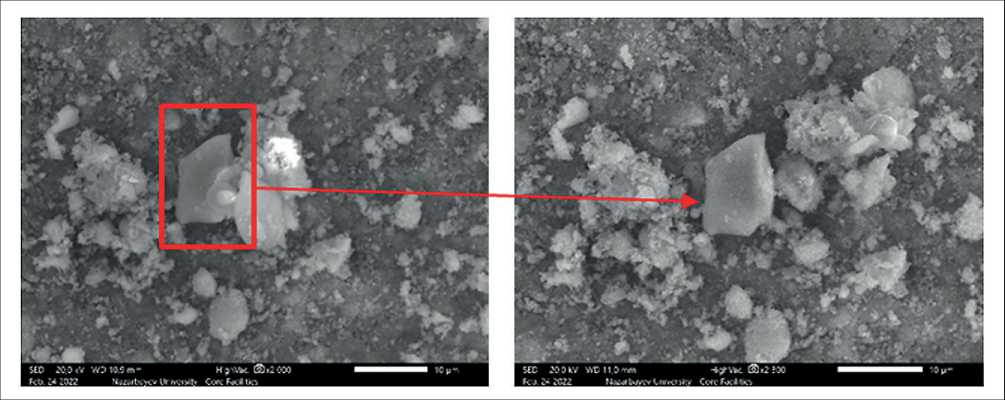

Fig. 13. Morphology of BOFS particles based on scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis
where long-term stability under saturation conditions is essential.
In addition, the surface of the particles showed fine dust-like formations, likely resulting from partial hydration. Their presence indicates active interaction of the material with the surrounding alkaline environment, which may lead to alkali activation and undesirable expansion if the slag is not properly stabilized.
Larger, rectangular-shaped particles were also observed, indicating the presence of heterogeneous fractions within the material mass. These fractions may differ in chemical composition, density, and strength, necessitating separate evaluation during the formulation of geopolymer mixes.
Thus, SEM analysis confirms the need for a comprehensive approach to the pre-treatment and stabilization of BOFS prior to its use in geopolymer systems. Only with proper preparation can this material be effectively employed in modifying concrete for hydraulic structures, ensuring the durability and resilience of constructions under challenging service conditions.
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
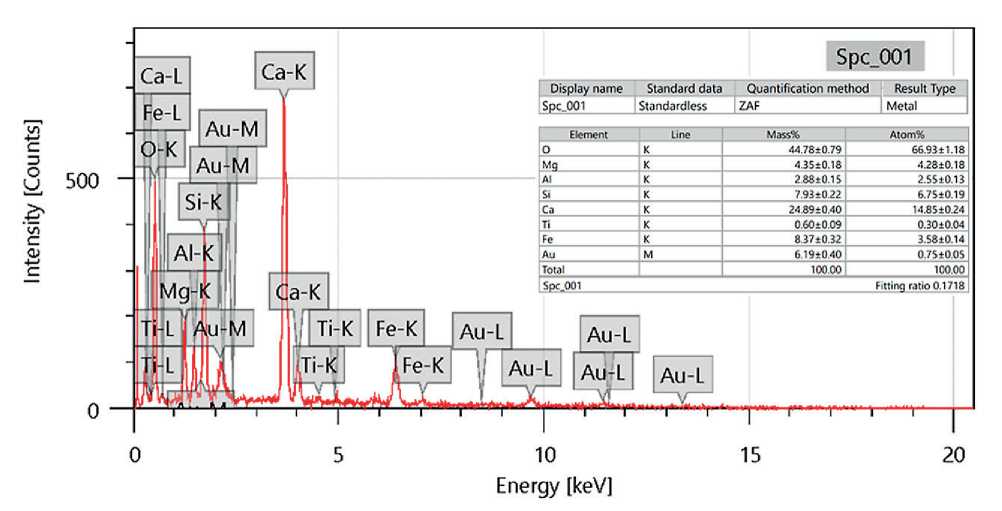
Fig. 14. Results of energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis of BOFS particles based on SEM data
Compressive Strength
The results of compressive strength tests conducted at 3, 7, 28, and 56 days are presented in Figures 15(a), (b), (c), (d), and (e). These data illustrate the effect of varying replacement ratios of conventional aggregate with BOFS on the curing of geopolymer material (GPM) under ambient conditions (room temperature of 23 °C).
One of the key findings was the implementation of carbonation treatment applied to the mix containing 75% BOFS as a replacement for river sand. This mixture was selected as the base for carbonation because it demonstrated the best overall suitability for producing a workable geopolymer mortar applicable for modifying concrete in hydraulic structures.
As expected, the compressive strength of all GPM mixes increased progressively up to 28 days, with a tendency to decline by day 56. Despite this, most mixes reached strengths of around 30 MPa by day 7, and exceeded 30 MPa by day 28, meeting the strength requirements for concrete used in hydraulic engineering applications.
An exception was observed in the mixes with low BOFS content (25% BOFS + 75% RS) at two different sodium silicate to sodium hydroxide ratios. These mixes exhibited relatively low strength-19 MPa and 23 MPa, respectively. The strength decline observed at 56 days may be attributed to the lower density of the GPM, as confirmed by X-ray imaging (Fig. 12), as well as to the limited dissolution of aluminosilicates under normal temperature curing conditions.
According to research [17, 23, 27], effective dissolution of silica and aluminosilicates occurs at approximately 80 °C, whereas at 20 °C, micro- and nanostructural cracks are often observed in the geopolymer matrix. This impairs the formation of N-A-S-H gel (sodium-aluminosilicate-hydrate), which plays a crucial role in the strength development of geopolymer concrete.
In the present study, strength gain continued up to 28 days due to the sufficient availability of active aluminosilicates in the system. However, beyond that period, as the available silica and alumina phases become depleted, strength either stabilizes or begins to decrease.
It is important to note that all tested specimens shown in Figures 15(a–e) were cured in air at room temperature, which approximates real-world service conditions for modified hydraulic concrete that does not require special thermal treatment.
As shown in Figure 15, the effect of replacing conventional aggregate with BOFS on the compressive strength of the geopolymer material (GPM) at various curing ages is additionally illustrated.
At the early stage (up to 7 days), all mixtures containing BOFS exhibited lower compressive strength than the control mix with 100% river sand (RS GPM), regardless of the replacement level. This can be attributed to the slower activation kinetics of BOFS in the alkaline environment and the potential influence of increased poverty during the initial curing phase.
However, on 28 and 56 days, the mixes containing 25% RS + 75% BOFS, 75% RS + 25% BOFS, and 100% BOFS surpassed the strength of the mix with a 50%
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
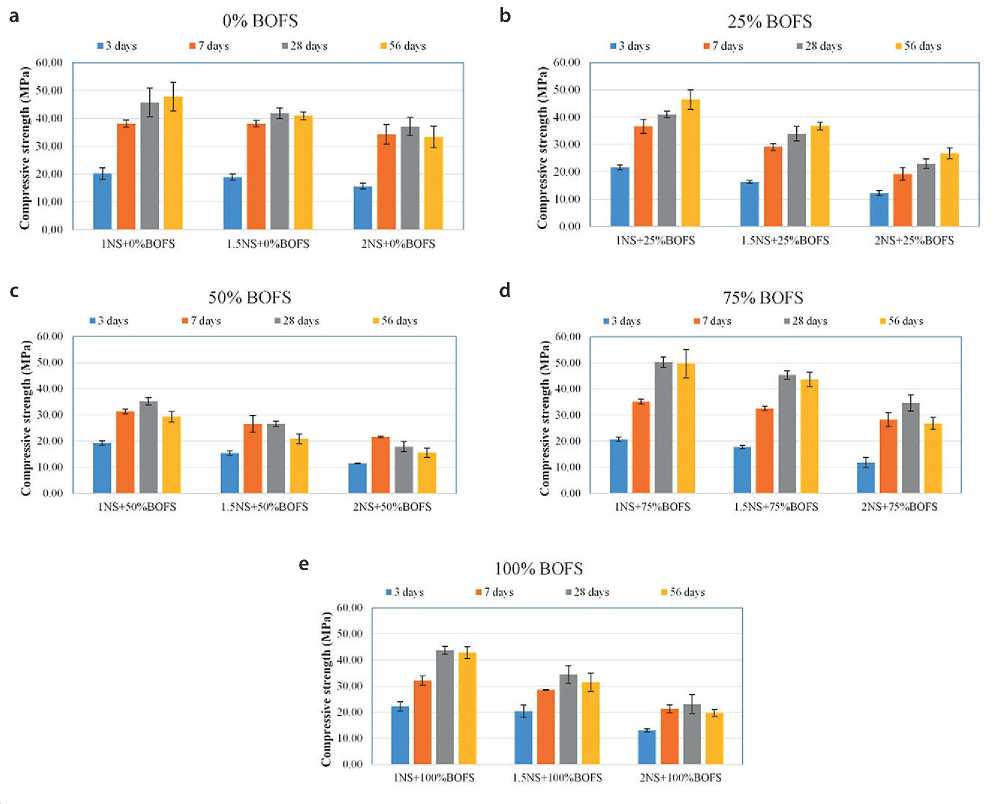
Fig. 15. Compressive strength of GPM mixes with varying BOFS content: (a), (b), (c), (d), and (e) – samples cured under ambient conditions
BOFS replacement. This indicates a nonlinear relationship between BOFS content and the compressive strength characteristics of GPM.
The strength gain observed in these mixtures may be explained by the combined effect of the formation of N-A-S-H gel (sodium-aluminosilicate-hydrate) and the presence of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). The free lime (f-CaO) present in BOFS reacts with atmospheric CO2 to form CaCO3, which acts as a micro-filler, reducing porosity and enhancing strength via a pore-filling mechanism [18, 22, 28].
At the same time, an excessive amount of BOFS (100%) can lead to the formation of excess CaCO3. Upon its subsequent dissolution, this may promote calcium leaching from the GPM structure, adversely affecting the long-term stability of the material, reducing strength, and increasing susceptibility to degradation under moisture and CO2 exposure.
The analysis of the results presented in Figure 15 also shows that the 50:50 mix of RS and BOFS is the least effective in terms of compressive strength. This mix is characterized by increased porosity and reduced nano-structural integrity of the geopolymer matrix, making it less suitable for use in critical structural applications, including hydraulic concrete, where high density and impermeability are required.
Within the scope of this study, an alternative curing method-carbonation-was also tested on the mix with 75% BOFS and 25% RS, at all alkaline activator ratios (Na2SiO2 to NaOH = 1, 1.5, and 2, respectively, referred to as AAS). The goal of this method was to improve the stability and strength of geopolymer concrete by inducing targeted carbonation-based densification of the matrix.
Expansion
The volumetric expansion characteristics of various geopolymer mix designs (GPM) are presented in Figures 16 and 17. To evaluate the expansion potential of
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
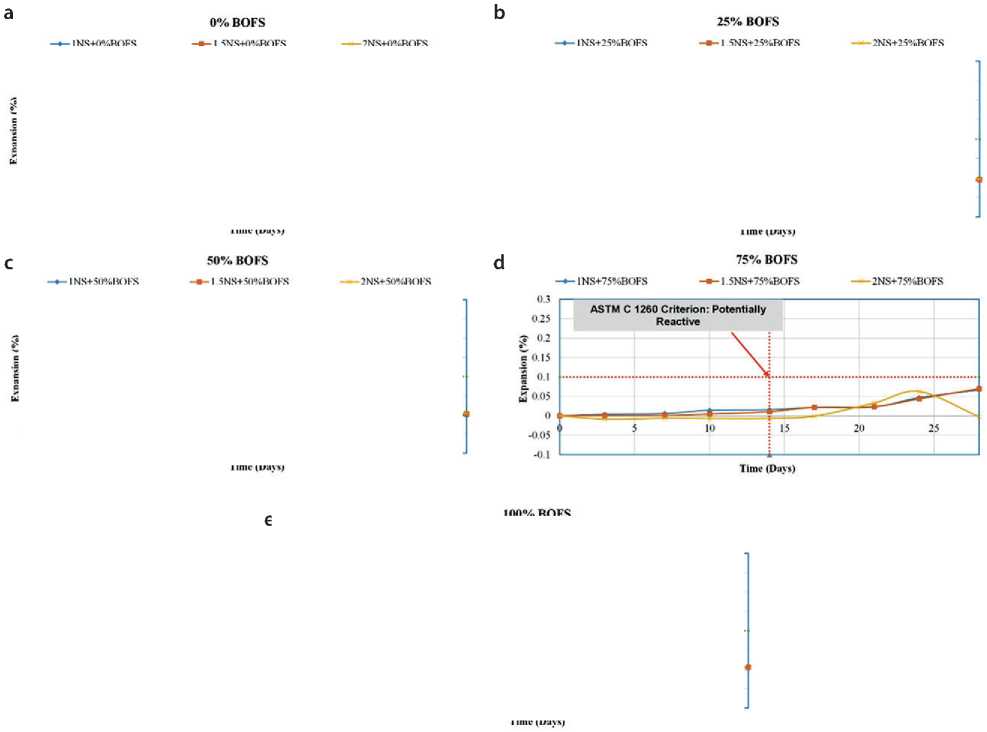
Fig. 16. Expansion coefficient of GPM samples in water under ambient curing conditions
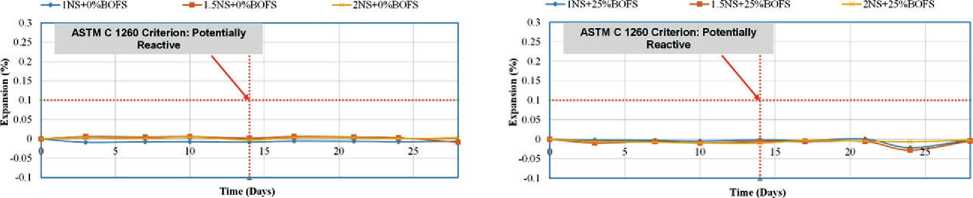
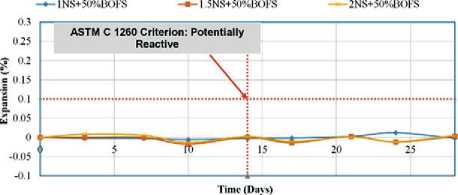
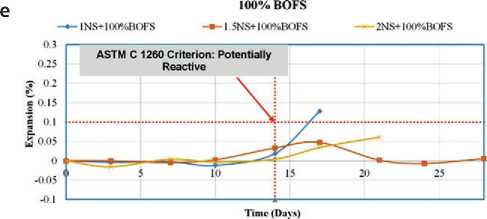
BOFS aggregate used in modified concrete for hydraulic structures, two testing environments were employed: – Immersion in water (Fig. 16);
– Immersion in a 1M NaOH solution (Fig. 17);
– Both test conditions were maintained at 80 °C.
The change in the length of reference specimens was monitored over a 28-day period. The test procedure was based on ASTM C1260, which classifies aggregates according to their susceptibility to alkali-aggregate reaction: – <0.10% at 14 days – non-reactive aggregate;
– 0.10–0.20% – potentially reactive;
– 0.20% – reactive aggregate, likely to cause matrix deterioration due to the formation of Ca(OH)2 and associated expansion.
The results of the immersion-in-water tests indicated that all GPM mixtures-regardless of composition-showed expansion of less than 0.10% on both day 14 and day 28. For example, the mixture with 25% RS and 75% BOFS exhibited only 0.011% expansion after 14 days and 0.070% after 28 days. These low values confirm the hypothesis that free lime (f-CaO) and free magnesium oxide (f-MgO) in BOFS react with available free silica (f-Si) in the al- kaline matrix, forming stable, insoluble silicates-CaSiO3 and MgSiO3. These phases suppress swelling and expansion, thereby stabilizing the structure of the modified geopolymer concrete.
It is important to note that, according to [19, 22], a standard specimen containing 100% BOFS exhibited structural failure as early as day 8, with expansion reaching 0.882%. This emphasizes the need for chemical stabilization of BOFS prior to use.
The 1M NaOH immersion tests showed that most mixtures met ASTM C1260 criteria for 14-day expansion. The only exception was the mixture with 25% RS and 75% BOFS, which showed 0.034% expansion in 14 days, but exceeded the 0.10% threshold by day 28.
This anomalous behavior is likely due to the excess f-CaO in BOFS reacting with highly concentrated dissolved silica from the matrix, resulting in the formation of alkali-silica reaction (ASR) gel. This gel has the capacity to swell, generating internal stresses and expansion, which is typical of alkali-aggregate reactivity [20–26]. Nevertheless, further research is required to verify this hypothesis.
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
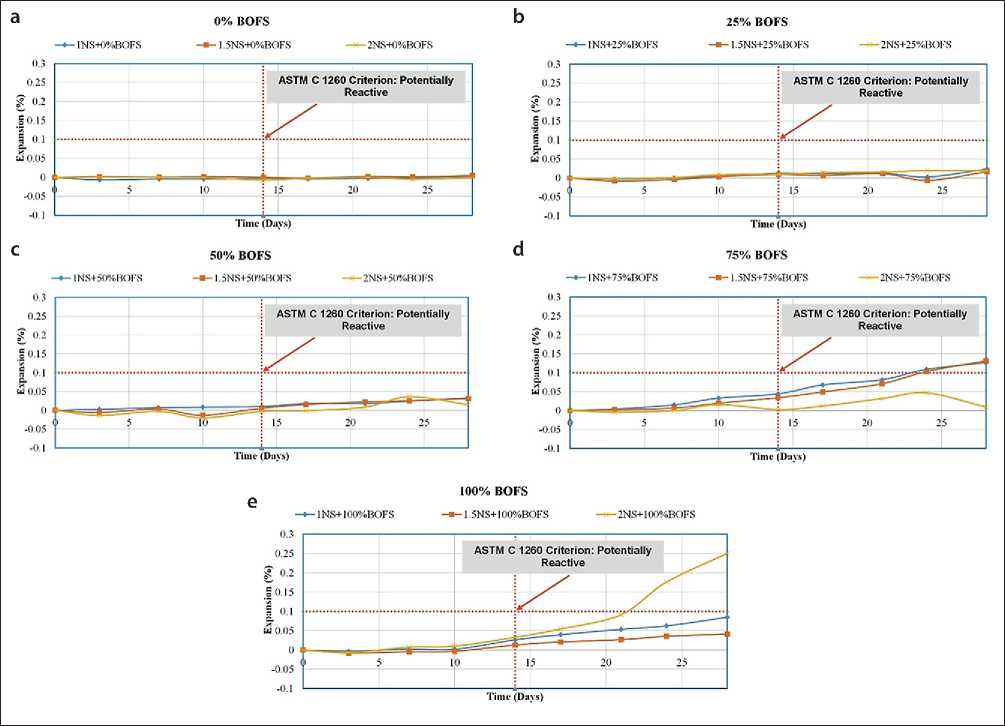
Fig. 17. Increase in expansion (ASR) of GPM geopolymer mixes for hydraulic concrete modification, cured under ambient conditions
Overall, the test results demonstrated that most GPM compositions developed with BOFS remain within acceptable expansion limits, thus qualifying BOFS as a stabilized aggregate suitable for use in geopolymer mixtures for hydraulic concrete modification. The only exception was the 1NS + 100% BOFS sample, where one of the three control specimens failed by day 14, thereby affecting the average expansion value due to reduced sampling.
According to the ASTM C 1260 criterion, the specimens exposed to water and subjected to expansion testing showed satisfactory results. Compared to previous studies in which BOFS was used as an aggregate in ordinary Portland cement (OPC)-based concrete, the behavior of BOFS in the present study was stabilized through geopolymerization using an alkaline activator (AAS). The GPM samples did not exhibit expansion, even under water bath testing conditions. As shown in Equations (1) and (2), the interaction of BOFS with water leads to the formation of free calcium hydroxide, which can result in dimensional increase and even cracking. However, the presence of silicates can mitigate this effect.
Samples with identical mix compositions but cured under different conditions showed varying results. The GPM mix containing 75% BOFS as aggregate, when subjected to carbonation treatment, demonstrated less expansion than the same mix cured under ambient conditions.
Figures 16 and 17 present the trend of increasing BOFS content from the control value (0%) to 100%. GPM samples with BOFS contents of 0%, 25%, and 50% exhibited minimal expansion-less than 0.1%. In contrast, GPM mixes labeled 1NS, 1.5NS+75%, and 2NS+100% showed expansion levels of up to 0.12% and 0.25%, respectively.
X-ray Analysis (Samples Tested for Compressive Strength)
Figure 18 presents the results of X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of geopolymer samples modified with BOFS after compressive strength testing. Scanning was performed in the range of 0° to 75° 2θ with a step size of 0.01°, and data integration was carried out with a step of 3 seconds. Three types of geopolymer mixes with
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
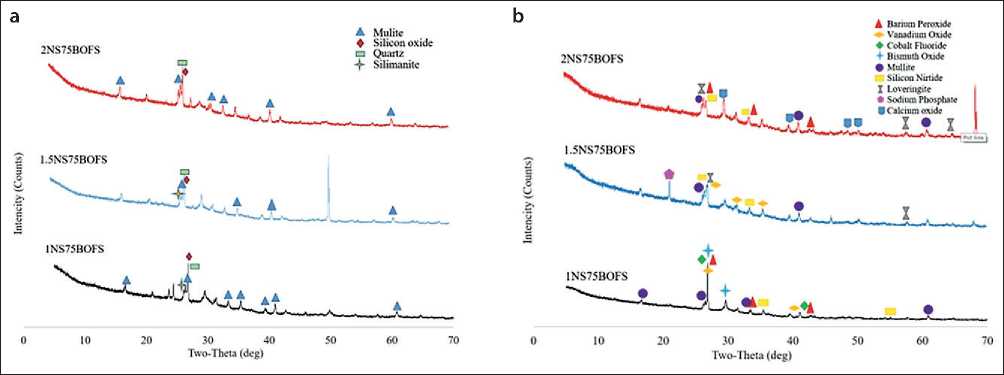
Fig. 18. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of samples after compressive strength testing: (a) – samples after 3 days of curing under ambient conditions; (b) – samples after 28 days of curing under ambient conditions
75% BOFS content and different alkaline activator ratios (Na2SiO3/NaOH)-designated as 1NS, 1.5NS, and 2NS-were selected for analysis. The samples were cured both under ambient conditions and using carbonation treatment.
These compositions were chosen to identify the optimal curing regime and mix design that ensures the best early-age (3-day) and standard (28-day) strength characteristics. This is critical for geopolymer materials intended for the repair and modification of concrete in hydraulic structures, where both early strength and long-term durability are essential.
The compressive strength results (in MPa) were as follows:
– 3 days (ambient curing): 1NS + 75% BOFS – 20.71;
-
1. 5NS + 75% BOFS – 17.77; 2NS + 75% BOFS – 11.85;
– 28 days (ambient curing): 1NS + 75% BOFS – 50.29;
-
1. 5NS + 75% BOFS – 45.37; 2NS + 75% BOFS – 34.59;
– 3 days (carbonation curing): 1NS + 75% BOFS – 21.66; 1.5NS + 75% BOFS – 18.92; 2NS + 75% BOFS – 13.42;
– 28 days (carbonation curing): 1NS + 75% BOFS – 27.88; 1.5NS + 75% BOFS – 24.72; 2NS + 75% BOFS – 17.85.
As evident from the results, the maximum compressive strength was achieved with the 1NS ratio. Increasing the sodium silicate content to 2NS led to a decrease in strength. This finding is consistent with previous studies, which reported that an excess of undissolved sodium silicate hinders effective geopolymerization of aluminosilicate components, reducing the formation of the N-A-S-H gel and, consequently, the overall strength.
The mineralogical phases identified through XRD analysis (Fig. 18) confirm the presence of calcite, quartz, hydroxides, and aluminosilicate compounds. These phases play a key role in forming a structurally sound and chemically stable geopolymer concrete matrix, which is particularly relevant for improving the operational reliability of hydraulic infrastructure.
SEM Analysis (Damaged Samples for ASR Testing)
Samples subjected to alkali–silica reaction (ASR) testing after 28 days of curing were analyzed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Particular attention was given to samples exhibiting the highest expansion values. The greatest expansion under ambient curing conditions was recorded in GPM specimens with 75% BOFS content. Figure 19 shows the micro- and nanostructure of one such sample, revealing crystallization and the formation of numerous pores, which may indicate the material’s tendency to develop internal stresses.
Energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) results revealed the presence of the following elements: carbon (C), sodium (Na), magnesium (Mg), aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), sulfur (S), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), titanium (Ti), and iron (Fe). Notably, a high concentration of crystalline silicon dioxide (SiO₂) was identified in the 1NS + 75% BOFS sample cured under ambient conditions, as confirmed by both SEM imagery and EDS data.
Under high silicon concentrations in an alkaline environment, the formation of oligomeric silicates occurs, which subsequently evolve into three-dimensional polymeric structures. Since poly(sialate) (N-A-S-H) gels are typically formed at relatively low silicon content, the elevated Si level in mature specimens suggests active polymerization rather than residual crystalline silica. Moreover, the Si/Al ratio can serve as an indicator of the material’s susceptibility to expansion-more balanced ratios tend to reduce ASR vulnerability.
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
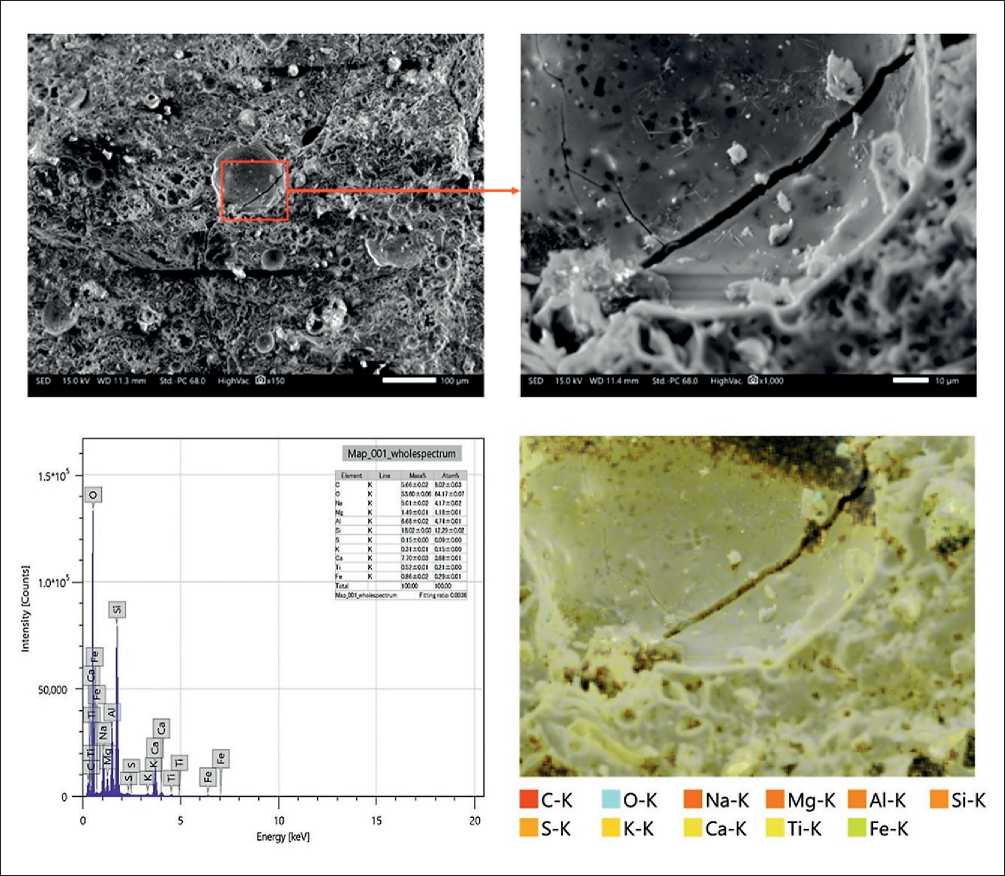
Fig. 19. Micro- and nanostructure of the 1NS + 75% BOFS sample after ambient curing (SEM analysis)
The presence of fly ash particles within the matrix contributes to the development of a denser gel structure, enhancing the mechanical performance of the geopolymer concrete. Due to their small particle size, GGBFS grains effectively fill pores and participate in reactions with fly ash, reinforcing the material. SEM images show both partially and fully reacted fly ash particles in a random distribution. Signs of particle debonding from the polymer matrix and distinct structural porosity are also observed, in agreement with findings from previous sections of this study.
Thus, the results of micro- and nanostructural analysis support the article’s central hypothesis: the use of BOFS in geopolymer mixes can be effective, provided that appropriate component ratios and curing conditions are applied to stabilize material properties and minimize volumetric changes. SEM and EDS techniques enable identification of the underlying mechanisms responsible for improved strength and ASR resistance, particularly relevant for hydraulic infrastructure applications.
CONCLUSION
The experimental results obtained in this study lead to the following key conclusions:
-
1. Micro- and nanostructural as well as mineralogical analyses confirmed the presence of active phases (CaCO3, SiO2, Al2SiO5, etc.) that contribute to the formation of a geopolymer matrix. SEM and EDS analyses revealed a high degree of interaction between fly ash and GGBFS, resulting in a strong structure with a dense gel-like phase.
-
2. The compressive strength of the geopolymer mortars (GPM) increased up to 28 days of curing, after which a decline was observed. The optimal mix was achieved by
-
3. The expansion tests (ASR) indicated that the f-CaO content in BOFS can be effectively stabilized through carbonation and geopolymerization. In water immersion tests, all mixtures met ASTM C1260 requirements. However, under alkaline conditions, some combinations exhibited a tendency for expansion, highlighting the need for further investigation.
-
4. X-ray diffraction analysis before and after mechanical testing confirmed that an increase in BOFS content and AAS concentration leads to a higher proportion of
-
5. The inclusion of fly ash improved structural compactness and reduced porosity, enhancing mechanical performance. Partially reacted FA particles contributed to the formation of secondary gel phases, increasing longterm durability.
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS replacing 75% of sand with BOFS at an alkali activator ratio of Na2SiO3/NaOH = 1. Mixes subjected to carbonation treatment demonstrated stable strength and reduced shrinkage.
unreacted components, negatively affecting the strength and durability of the material.
In conclusion, the use of BOFS and fly ash in geopolymer mortars presents a promising approach for the sustainable and environmentally responsible production of construction materials. However, further research is necessary to fully implement these technologies in practice, particularly regarding long-term strength, resistance to aggressive environments, and process scalability.


