Use of pulp and paper industry waste in binding and cementitious materials technology
Автор: Sarkisov Yu.S., Gorlenko N.P., Samchenko S.V., Bruyako M.G.
Журнал: Nanotechnologies in Construction: A Scientific Internet-Journal @nanobuild-en
Рубрика: Construction materials science
Статья в выпуске: 4 Vol.16, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. Utilization of chemical cellulose fillers in construction industry is one of the ways of processing unused wastes from pulp and paper industry. Decorative, finishing, and heat insulation materials are widely used as construction materials. This paper proposes various compositions and insulation materials characterized by compressive strength of not less than 10 MPa, water tightness of 0.8, and density of not over 600 kg/m3. The likely curing mechanism is studied for cement systems. The possible mechanism of hardening structures formation in the systems is discussed. Methodology. Corrugated fibreboard МS-5B waste is used as a filler, high-early strength cement М-500 (CEM 47.5) – as inorganic binder, and elemental sulfur, polyethylene terephthalate, cementmodified polyurethane (PU) with the addition of nanosized silicon oxide are used as a polymeric matrix. Infrared spectroscopy, terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS), and scanning electron microscopy are used for investigations. Cement samples undergo compressive strength, water tightness and water absorption testing. Results and discussion. Physical and mechanical properties obtained for composites with the paper filler and polymeric matrix based on cement-modified PU, are described, and testing results are compared with the experimental data obtained for materials based on other binders. It is found that the paper filler–cement-modified PU composition is consistent with the purposes of this research. The understanding is improved for the curing mechanism of the polymeric matrix–paper filler system. The THz-TDS data demonstrate a correlation between the spectral transmission and thermal conductivity and density of synthesized heat insulation materials. Conclusion. Synthesized is the effective heat insulation material with relatively high compressive strength, low density, and high tightness to water. Scientific understanding of the curing mechanism is improved.
Construction materials, paper filler, cementitious materials, polymers, strength, water tightness, water absorption, IR spectroscopy, terahertz time-domain spectroscopy, hydrogen bond
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142242258
IDR: 142242258 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2024-16-4-301-309
Текст научной статьи Use of pulp and paper industry waste in binding and cementitious materials technology
Original article
Sarkisov Yu.S., Gorlenko N.P., Samchenko S.V., Bruyako M.G. Use of pulp and paper industry waste in binding and cementitious materials technology. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2024; 16 (4): 301–309. – EDN: GCICKX.
T he pulp and paper industry in Russia generates about
-
8 million tones of waste, but just 4.1 million tones is recycled [1]. For comparison, the pulp and paper industry in China annually generates about half of world paper waste production for recycling. In China, the pulp and paper industry is profitable and yields high returns. In the European Union, the annual waste generation is 11 mil-
- lion tonnes, 70% of which falls on the paper recycling [2]. At present, our country lacks production facilities for utilization and recycling of already accumulated paper wastes. Most of them decay and contaminate the environment. In this regard, it is relevant to develop compositions and technologies for utilization of wastes from the pulp and paper industry to develop the production of building materials of different engineering purpose. In the first place, it concerns decorative, finishing, and heat insula-
© Sarkisov Yu.S., Gorlenko N.P., Samchenko S.V., Bruyako M.G., 2024
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE tion materials. Cellulose wool is the most known heat insulation material produced from wastes of the pulp and paper industry. It is especially popular in northern countries and humid climate. Cellulose wool contains 81% of recycled cellulose, 7% of sodium tetraborate, and 12% of natural antiseptics [3].
It should be noted that composites obtained from recycled paper are materials usually consisting of more than two components possessing different physical or chemical properties. One of the components is paper, which is the main bulk component. The second is a binder, which provides the final product with strength and stable properties. Modifying additives give functional properties to composites created. Although the binders and paper filler are of different nature, it is possible to achieve high performance characteristics of the created materials due to the introduction of modifying additives.
The main disadvantage of the cellulose filler is high water absorption and low tightness to water. This problem is solved, first of all, by using traditional hydrophobic compositions. Attempts are being made to extend a range of eco-friendly waterproofing agents. These are, for example, inorganic SiO2 nanoparticle coatings deposited onto cellulose nanofiber [4]. Kunam et al . [5] propose a hydrophobic coating for packaging applications, based on natural rubber latex and butyl stearate. These compositions provide a significant reduction in water absorption from 128 to 0.8 g/m2. At the same time, the surface energy of paper considerably decreases, which is proven by the high value of the contact angle. However, alternative effective hydrophobic compositions, inexpensive and easy to use, are still relevant.
Polymeric matrices are another important component of composites created. Most of them are waterproofing agents. Their main weakness is sensitivity to temperature changes and limited mechanical strength. Polyvinyl alcohol is a highly adhesive substance, followed by carboxymethyl cellulose, soya protein, casein, enzymic and oxidized starches. It is worth noting that inorganic binders, such as gypsum and lime, are inferior to polymeric ones due to the higher density provided by them for materials created. Much research done by Russian and foreign scientists, including preliminary experiments conducted by the authors, show that low density on the one hand and high strength and water tightness on the other, cannot be provided at a time even in porous cement systems. In this regard, glues and adhesives of various organic compositions are widely used as binders, e.g., melamine– urea–formaldehyde resin, vulcanized rubber, casein, urea formaldehyde resin, polyvinyl acetate, polyvinyl alcohol, etc. One of the relevant and complex problems of modern materials science in construction, is a search for and modification of the known compositions providing low values of density and thermal conductivity, high strength and water tightness of construction materials.
The aim of this work is to develop composition and technology of the heat insulation material possessing compressive strength of not less than 10 MPa, water tightness of 0.8, and density of not over 600 kg/m3, and study the probable curing mechanism for the structure formation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Corrugated fibreboard МS-5B waste was used as a paper filler, cement М-500 (CEM 47.5) served as an inorganic binder, and elemental sulfur, polyethylene terephthalate PET [7], cement-modified polyurethane (PU) with the addition of nanosized silicon oxide were used as a polymeric matrix. In accord with the conventional technique, previously sorted waste paper underwent pulping in a paper pulper, in which it was comminuted in water with the formation of cellulose and other elements. Paper swelled, and cellulose laminated to fiber separation. The obtained suspension was then delivered to secondary production. Waste paper pulping in dry and wet states was performed in a rotor mill at a rotation rate of 3000 rpm for 2–4 min.
At the paper dispersion in water, the ratio between corrugated fibreboard and water was 1 to 10, which provided the best conditions for waste paper pulping. The paper filler was further added to the inorganic binder (cement, gypsum) and mixed to obtain a homogeneous mass and form (2×2×2) • 10–3 m samples. After 7-day curing, the samples were subjected to compressive strength, water tightness and absorption testing. The cement paste porosity was obtained after the addition of the aluminum powder. With respect to strength and density of heat insulation materials non meeting the purposes of this work, the main attention was paid to polymeric matrices. Elemental sulfur was used as inorganic polymer, and PET and modified PU were used as an organic polymeric matrix. Reference samples were prepared at the specific molding pressure of 100 kg/cm2. Compressive strength of reference samples was measured on a hydraulic press, water absorption, water tightness, and thermal conductivity were calculated in accordance with GOSTs [6, 8], [9] and [10], respectively. The strength-density ratio indicated the relation between the compressive strength and density of the material.
The investigation of the polymeric matrix/paper filler interaction was based on spectral measurements performed on an Agilent Cary 630 Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometer and a real-time terahertz time-domain spectrometer T-SPEC 1000 equipped with LT-GaAs photoconductive antenna detector. Key specifications for the T-SPEC 1000 included 5 GHz spectral resolution and 90 dB dynamic range at a 400 GHz frequency. These specifications allowed us to obtain temporal waveforms of terahertz pulses passed through the ~ 2 cm thick sample. A scanning electron microscope MIRA 3 LMU (Tescan,
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
Czech Republic) was used to investigate the fine structure of the samples.
Dry paper pulping resulted in the initial fibrous paper material, whereas its wet pulping provided the formation of aggregates after drying, that required additional paper pulping.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Test results for the samples are presented in Table 1. One can see that the density, strength, and water tightness satisfying the purposes of this study, are achieved only for cement-modified and compressed cement-modified PU.
The strength-density ratio values obtained for organic polymeric matrices exceed that for inorganic binders. Compressed cement-modified PU samples manifest the highest strength-density ratio.
Figure 1 presents different heat insulation materials vs . the proposed composite.
In should be noted that compressed samples of the paper filler–modified PU system, possess the highest strength and water tightness and their density increases also.
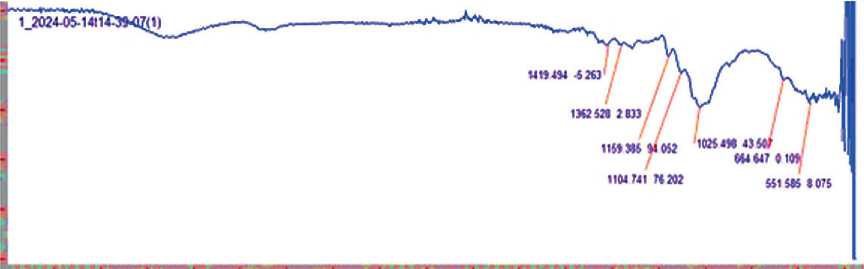
FTIR spectra presented in Fig. 2, are acquired to investigate the polymeric matrix/paper filler interaction and their mixture.
Table 1
Parameters of samples after testing
|
Binders, PF:PM*, wt.% |
Density, g/cm3 |
Compressive strength, MPa |
Water absorption, % |
Water tightness |
Strengthdensity ratio, ·104, cm |
|
Cement (10:90) |
1.31 |
8.1 |
18.0 |
0.62 |
6.2 |
|
Porous cement (10:90) |
0.91 |
6.8 |
38.0 |
0.48 |
7.5 |
|
Elemental sulfur (30:70) |
1.73 |
34.8 |
3.2 |
0.99 |
20.1 |
|
PET (30:70) |
1.32 |
21.4 |
0.5 |
0.98 |
16.2 |
|
Cement-modified PU (30:70) |
0.37 |
11.0 |
0.5 |
0.97 |
29.7 |
|
Compressed cement-modified PU (30:70) |
0.42 |
14.0 |
0.4 |
0.98 |
33.3 |
800 800 1000
0,15 0,18 029
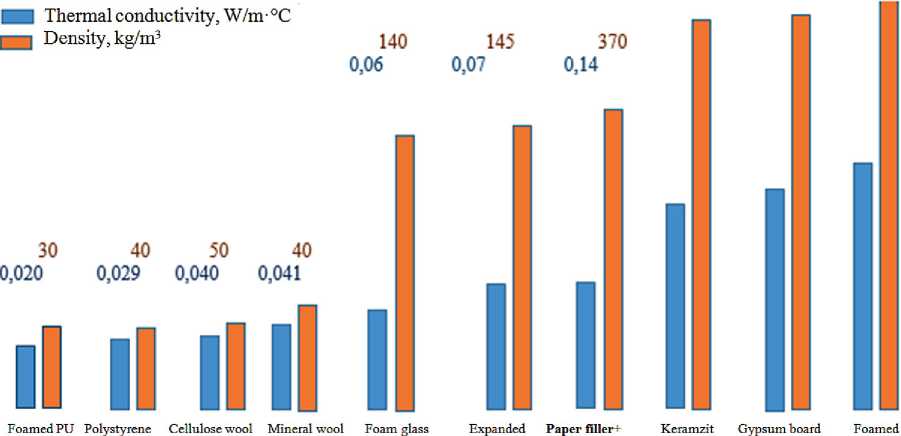
vermiculite modified PU concrete
Fig. 1. Different heat insulation materials vs . the proposed composite consisting of 30 wt.% of paper filler and 70 wt.% of modified PU
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
а
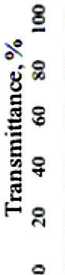

3 及? 44%[4m"^ 01
«I из ow
1MM ОСОІ

Fig. 2. FTIR spectra: a – paper filler, b – modified PU, c – mixture of paper filler and modified PU
The FTIR spectrum of the paper filler (Fig. 2 а ) is mostly determined by the absorption of three hydroxyl groups in each glucopyranose link in cellulose, presented in Fig. 3.
Three types of hydrogen bonds may be present in the cellulose structure, namely two intramolecular and one intermolecular band with respective absorption bands at 3200 to 3400 cm–1 [11]. Infrared spectra for the paper filler show stretches of CH– groups (2923 cm–1), carbonyl region (1378 cm–1), and asymmetric vibrations of the pyran ring (near 1113 cm–1). It is interesting that the displacement of peaks relative to each other can be observed on IR spectra for the paper filler and modified PU.
The most pronounced peaks for modified PU (Fig. 2 b ) are observed at 1400–1500, 1700 and 2800–2900 сm–1 relating to stretching of C–N, N–H, C=O and CH2–CH3
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
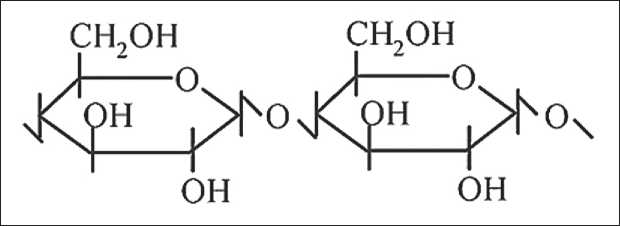
Fig. 3. Glucopyranose link in cellulose
groups presenting in the urethane bond [12]. The absorption band at 1113 сm–1 relates to asymmetric vibrations of the pyran ring. FTIR spectra consist of many narrow bands, that is associated with the presence of large regions with high molecular ordering. According to Varepo [13], the structure of paper with the polymeric matrix consisting of natural and chemical fiber, strongly depends on the polymer microstructure. Organic polymeric matrices usually provide the formation of the aggregated structure of cellulose fiber, as presented in Fig. 4.
Comparing the FTIR spectra of the initial components and their mixture in the spectral range from 400 to 1800 сm–1, one can see that in the mixture intensive interaction of the components with each other takes place, which is evidenced by a dramatic change in the transmission band intensity. Peaks at 1728 and 1228 сm–1 are quite representative. They are induced by vibrations of the carbonyl part of the mixture. Peaks at 400 to 1000 сm–1com-pletely disappear. These results indicate to the intensive interaction between the components, crystallinity level, and adhesion between the components. The crystallinity
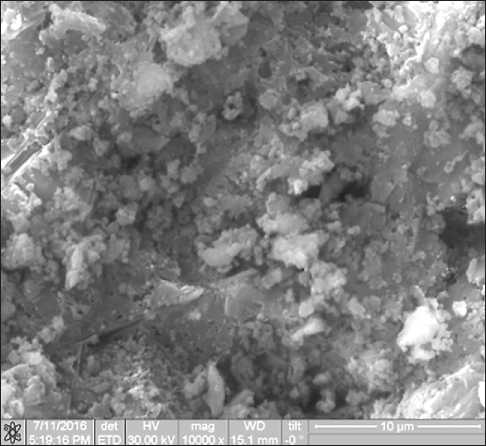

Fig. 4. SEM image of aggregated structure of paper filler–modified PU composite level is determined by the ratio between absorption band intensities at 1372 and 2900 сm–1 [14]. The absorption bands at 1372 and 2900 сm–1 determine crystalline and amorphous regions, respectively. As shown in Fig. 2b, this ratio in the composite significantly reduces, indicating to the prevalence of amorphous components. The 1431–1434 сm–1 absorption band relates to deformation vibrations of СН2– and СН– groups, while 1372 сm–1 band belongs to those of ОН– groups.
According to the experimental data, the composite structure formation is based on the interaction between the paper filler and modified PU with the involvement of hydrogen bonds along with covalent and intermolecu-lar/van der Waals forces. The presence of the hydrogen bond is proven by the wide transmission spectra in the range of 3200 to 3600 сm–1. The structure of the main cellulose link (Fig. 3) suggests the formation of hydrogen bonds between macromolecules of cellulose, that leads to manifestation of the mechanical rigidity. On average, two inter-chain and up to three intra-chain hydrogen bonds fall on one glucopyranose link in natural cellulose [15].
All other things being equal, the formation of intermo-lecular hydrogen bonds occurs between the strongest proton donors and acceptors. In cellulose, the electron pair donors are oxygen atoms of the pyranose cycle, whereas in modified PU, this is the N–H protodonor group in the urethane cycle and proton-acceptor hydrogen atoms in the carboxyl group. Synthetic polymers, including modified PU, provide hydrogen bond linkage, resulting in aggregation of components and relatively high mechanical strength of the samples. This is consistent with the data obtained by Grunin et al . [16].
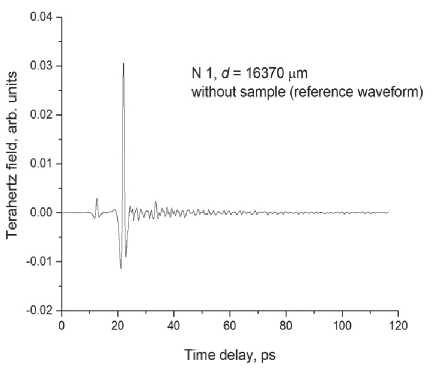
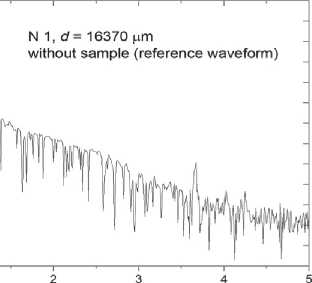
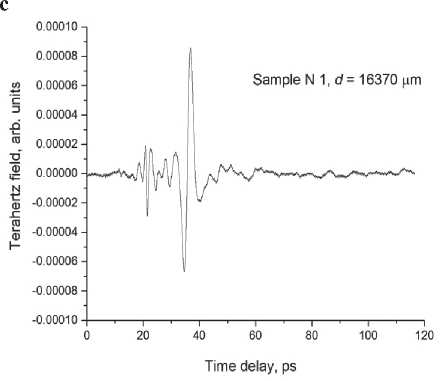
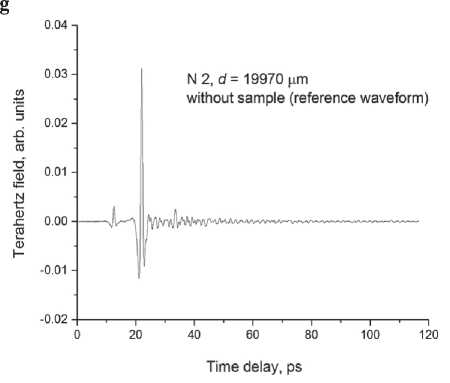
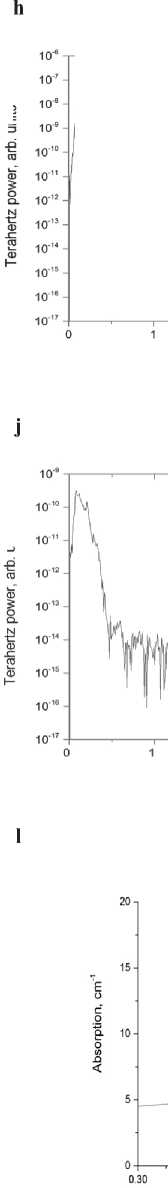
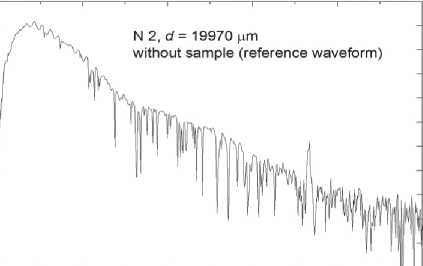
In materials science in construction, terahertz spectroscopy gives useful information about the density of materials, the presence of voids, water, etc. [17, 18]. Let us study compressed modified PU samples (Sample N 1 ) and those obtained by the conventional technique (Sample N 2 ). Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) results are presented in Fig. 5. One can see that in case with Sample N 1 (Fig. 5 c ), a part of the terahertz pulse passes through it without any delay. The temporal waveforms of the reference and pulse passed through the sample demonstrate peaks at delay times t = 22 ps
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
а
Frequency, THz
e
Frequency, THz
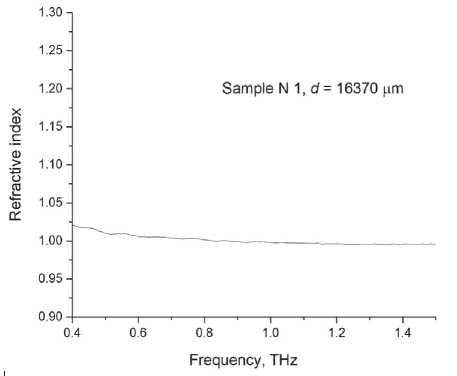
Fig. 5. Temporal (а) and spectral (b) waveforms of reference signal, signal passed through Samples N 1 and N 2 (c and d), calculated spectra of the effective index of refraction (e) and absorption coefficient (f). Sample thicknesses are shown in the figures
Sample N 1, d= 16370 卩 m
0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6
Frequency, THz
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
k
1.2-1
Sample N 2, d = 19970 цт

о.з
0.4
Frequency, THz
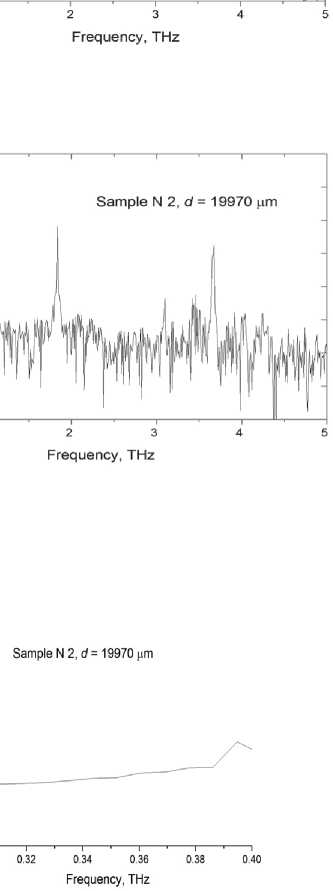
Fig. 5. The end
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
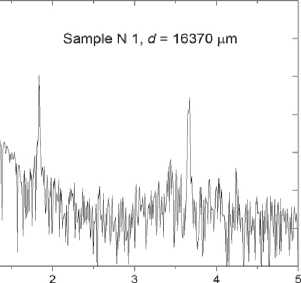
(Fig. 5 а , c ), that indicates to voids in the sample. The density of Sample N 1 is lower than that of Sample N 2 . The signal passed through Sample N 1 , consists of spectral components with amplitudes exceeding the noise level up to frequency ~2 ТHz (Fig. 5 d ). The maximum transmittance is observed near 170 GHz, while the maximum intensity of the reference signal occurs at 420 GHz (Fig. 5 b ).
The index of refraction n for Sample N 1 is 1.28, and it reduces for the sample obtained by the conventional technique. Figure 5 e presents the spectrum for the index of refraction obtained from the conventional THz-TDS analysis, using the Blackman window [19] with no account for the sample inhomogeneity. Our calculations are performed using the TeraLyzer software (LyTera, Germany) [20]. The value α = 21 сm–1can be obtained using the simplified formula of the frequency-averaged absorption
coefficient, viz . α = –ln( E / E 0)2/ d , where E and E 0 are maximum absolute field intensities of the terahertz signal for the reference pulse and the pulse passed through the sample, respectively (Fig. 5 а , c ).
Our experiments show that the lowest thermal conductivity belongs to the material obtained by the conventional molding technique, that is in agreement with the experimental data from [20].
CONCLUSION
Based on the results, it can be concluded that the material with the efficient heat insulation and relatively high compressive strength, low density, and high water tightness was possible to synthesize and thus satisfy the purposes of our research and improve scientific understanding of the material curing mechanism.
Список литературы Use of pulp and paper industry waste in binding and cementitious materials technology
- Available: www.gazeta.ru/social/news/2023/10/26/21582229.shtml.
- Monte M. C., Fuente Е., Blanco А., Negro С. Waste management from pulp and paper production in the European Union. Review Waste Manag. 2009; 293–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2008.02.002
- Properties of cellulose wool as paper heat insulation. Available: https://ekovata-msk.ru/stati/ekovata-utepliteliz-bumagi/ (accessed 17. 06. 2024).
- Bang J., H. Choi Y., Ahn K.-S., Yeo H., Oh. J.-K., Kwak H. W. Sustainable cellulose nanofiber/hydrophobic silica nanoparticle coatings with robust hydrophobic and water-resistant properties for wood substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024; 654: 159419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.159419
- Kunam P. K., Anushikha, Gaikwad K. K. Water resistant paper based on natural rubber latex from Hevea brasiliensis and butyl stearate hydrophobic coating for packaging applications. Industrial Crops and Products. 2023; 205: 117480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.117480
- GOST 125-2018. Gypsum binders. specifications. Moscow: Standard inform. 2018; 12.
- GOST Р 51695-2000. Polyethylene terephthalate. General specifications. Moscow: Gosstandart Rossii. 2000; 12.
- GOST 12730.3-2020. Concrete. Determination method for water absorption. Moscow: Standard inform. 2020; 12.
- GOST 32496-2013. Porous aggregates for lightweight concrete. Moscow: Standard inform. 2013; 12.
- GOST 7076-99. Group Zh19. Interstate standard. Materials and building products. Determination method for thermal conductivity and thermal resistance under stationary thermal conditions. 1999; 14.
- Ivanova N. V. Mathematical processing of IR spectrum. Zhurnal prikladnoi spektroskopii. 1989; 51(2): 301–306.
- Moghadam S. G., Momen G., Bakhshandeh E., Jafari R. To be or not to be a hydrophobic matrix? The role of coating hydrophobicity on anti-icing behavior and ions mobility of ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. J., 2024; 485: 149696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.149696
- Varepo L. G. Infrared spectroscopy of paper properties. Fundamental’nye issledovaniya. 2007; 12: 463–464. Available: https://fundamental-research.ru/ru/article/view?id=4369 (accessed 29. 04. 2024).
- Eshbaeva U. Zh., Dzhalilov A. A. Infrared spectroscopy of polymer-bonded paper properties. Universum: tekhnicheskie nauki. 2022; 1(94). Available: https://7universum.com/ru/tech/archive/item/12936 (accessed 08. 06. 2024). https://doi.org/10.32743/UniTech.2022.94.1.12936
- Mikhaleva M. G. Supercoiled anisometric phases in biomimetic and cellulose systems [in Russian], PhD thesis. Moscow, 2017; 135.
- Grunin Y. B., Grunin L. Yu., Schiraya V. Yu., Ivanova M. S., Masas D. S. Cellulose–water system’s state analysis by proton nuclear magnetic resonance and sorption measurements. Bioresources and Bioprocessing. 2020; 7(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-020-00332-8
- Abina A., Puc U., Jeglič A., Zidanšek A. Applications of terahertz spectroscopy in the field of construction and building materials. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev., 2014; 50(4): 279–303.
- Abina A., Puc U., Jeglič A., Zidanšek A. Structural characterization of thermal building insulation materials using terahertz spectroscopy and terahertz pulsed imaging. NDT & E Int., 2016; 77: 11–18.
- Jepsen P.U., Cooke D.G., Koch M. Terahertz spectroscopy and imaging–Modern techniques and applications. Las. Phot. Rev. 2011; 5(1): 124–166. https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.201200505
- Yang Y., Wu T.V., Sempey A., Pradere C., Sommier A., Batsale J.-C. Combination of terahertz radiation method and thermal probe method for non-destructive thermal diagnosis of thick building walls. Energy Build., 2018; 158: 1328–1336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.11.029


