Валидация русскоязычной версии опросника P-QOL и его апробация для оценки влияния пролапса тазовых органов на качество жизни женщин и определения эффективности реконструктивных операций
Автор: Шахалиев Р.А., Кубин Н.Д., Никитина Т.П., Ионова Т.И., Метринский Я.Ю., Мкртчян Ж.С., Шкарупа Д.Д.
Журнал: Экспериментальная и клиническая урология @ecuro
Рубрика: Урогинекология
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.17, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. P-QoL (опросник качества жизни при пролапсе) является одним из немногочисленных стандартизированных опросников, разработанных для оценки влияния пролапса тазовым органов (ПТО) на качество жизни (КЖ) пациенток и определения эффективности реконструктивных операций. Отсутствие валидированной русскоязычной версии опросника P-QoL ограничивает в России проведение исследований, направленных на оценку тяжести симптомов и КЖ у женщин с ПТО до лечения, а также после реконструктивной хирургии.
Качество жизни, пролапс тазовых органов, реконструктивная хирургия, опросник, валидность, надежность, чувствительность к изменениям во времени
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142242599
IDR: 142242599 | DOI: 10.29188/2222-8543-2024-17-2-111-121
Текст научной статьи Валидация русскоязычной версии опросника P-QOL и его апробация для оценки влияния пролапса тазовых органов на качество жизни женщин и определения эффективности реконструктивных операций
экспериментальная и клиническая урология № 2 2024
Пролапс тазовых органов (ПТО) – это заболева-ние,которое широко распространено среди рожавших женщин всех возрастных групп. Как известно, ПТО не приводит к сокращению продолжительности жизни пациенток, однако значимо снижает качество их жизни (КЖ) [1-3]. Одной из приоритетных задач лечения ПТО является улучшение КЖ [4, 5]. КЖ является ключевым результатом, на который направлена реконструктивная хирургия ПТО, и оно же может иметь значение для принятия решения о хирургическом лечении [6]. Для оценки состояния и эффективности лечения с точки зрения пациента традиционно используют опросник КЖ, специфичный для конкретного состояния [7]. Опросник КЖ при ПТО (P-QoL) является одним из немногочисленных стандартизированных опросников, разработанных для оценки влияния ПТО на КЖ пациенток [8]. Вопросы опросника охватывают различные аспекты качества жизни при ПТО, которые включают: общее состояние здоровья,влияние ПТО на жизнь,ро-левые ограничения, физические ограничения, социальные ограничения,ограничения личной жизни,эмоции, нарушения сна/энергии и тяжесть симптомов ПТО.
P-QoL был успешно переведен на различные языки и зарекомендовал себя как простой, эффективный и надежный инструмент для определения тяжести симптомов,нарушений качества жизни и оценки результатов лечения у женщин с ПТО [9]. Отсутствие валидированной русскоязычной версии опросника P-QoL ограничивает в России проведение исследований, направленных на оценку тяжести симптомов и нарушения КЖ у женщин с ПТО до лечения, а также после реконструктивной хирургии.
Целью исследования была разработка русскоязычной версии опросника P-QoL и оценка его психометрических свойств,а именно валидности,надежности и чувствительности к изменениям состояния во времени. Также в рамках исследования выполнена апробация применения P-QoL в качестве эталонного инструмента для оценки влияния ПТО на КЖ женщин, перенесших реконструктивную операцию.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
Перевод и культурная адаптация
В соответствии с международными рекомендациями и при согласовании с автором опросника A. Di-gesu (Великобритания) была проведена языковая и культурная адаптация русскоязычной версии опросника P-QoL. На начальном этапе исследования был выполнен прямой и обратный перевод оригинальной версии опросника на русский язык двумя переводчиками, носителями русского языка, имеющими опыт перевода медицинской документации.Переведенный на русский язык опросник был рассмотрен экспертной комиссией и согласован с ней,затем был выполнен обратный перевод на английский язык переводчиком – носителем английского языка.Для проверки сохранности исходного содержания, а также исключения расхождений в понимании текста с оригинальной версией в процессе перевода,была проведена экспертиза прямого и обратного переводов и сравнение их с оригинальной версией. Результатом данного этапа было создание предварительной русскоязычной версии P-QoL. На следующем этапе опросник был протестирован в рамках индивидуального интервьюирования 10 пациенток с ПТО для оценки понятности, удобства заполнения и легкости выбора ответов. После самостоятельного заполнения опросника с пациентками проводили собеседование для выявления и устранения потенциальных трудностей с пониманием вопросов для максимальной адаптации русской версии опросника
В рамках этапа децентеринга были устранены выявленные трудности в понимании, и утверждена русскоязычная версия P-QoL.
Дизайн исследования и участники
Данное наблюдательное исследование было проведено в отделении урологии Клиники высоких медицинских технологий им. Н.И. Пирогова ФГБОУ ВО СПбГУ (Санкт-Петербург) в период с мая по октябрь 2023 года. В исследовании участвовали женщины с различными степенями ПТО. Критерии включения: возраст ≥ 18 лет; подтвержденный диагноз ПТО; показания к реконструктивной хирургии; способность женщины заполнить опросники.Всеми пациентками было подписано добровольное информированное согласие. Были проведены следующие виды реконструктивных операций: реконструкция с использованием сетчатого эндопротеза (гибридная хирургическая реконструкция тазового дна, комбинированная лапароскопическая сакрогистеропек-сия), реконструкция с применением собственных тканей (передняя и/или задняя кольпография, Манчестерская операция). Участницам исследования до операции было предложено заполнить следующие опросники: P-QoL, PFDI-20 (Pelvic Floor Distress Inventory Questionnaire – Анкета по оценке дистресса тазового дна) и SF-36 (Опросник для оценки качества жизни), а также анкету с вопросами медико-социального характера. Затем им был проведен гинекологический осмотр на кресле с использованием системы количественной оценки степени ПТО (POP-Q), одобренной Международным обществом по недержанию мочи (ICS) [11]. Клиническую информацию анализировали на основании данных медицинской карты.
Инструменты
Опросник P-QoL
Опросник P-QoL для оценки тяжести симптомов ПТО и его влияния на качество жизни разработан в 2005 году A. Digesu и соавт [8]. Опросник содержит 20 вопросов, позволяющих оценить восемь наиболее важных аспектов качества жизни при ПТО:
-
• общее восприятие состояния здоровья,влияние ПТО на жизнь,
-
• физические ограничения, социальные ограничения,
-
• ограничения личных взаимоотношений,
-
• эмоции, сон /энергия
-
• тяжесть симптомов (домены опросника).
Ответы в опроснике P-QoL представлены в виде 4 вариантов: «нет/совсем нет», «незначительно/немного», «умеренно» и «значительно». На основании четырехбальной системы, оценки по каждому вопросу шкалируют и получают балл по каждому домену в диапазоне от 0 до 100. Чем выше балл, тем хуже качество жизни. Кроме того, опросник включает 18 дополнительных вопросов, касающихся симптомов нарушения мочеиспускания, дефекации и опущения тазовых органов, которым не присваиваются баллы в процессе шкалирования. В настоящее время имеется перевод опросника P-QoL на различные языки [9].
Опросник PFDI-20
Опросник состояния тазового дна PFDI-20 содержит 20 вопросов, разделенных на три субшкалы: симптомы пролапса тазовых органов, симптомы нарушения дефекации и симптомы нарушения мочеиспускания. Чем выше балл для каждой субшкалы и чем выше общий балл PFDI-20, тем сильнее выражены проблемы из-за ПТО [12].
Опросник RAND SF-36
RAND SF-36 – широко известный общий опросник качества жизни, используемый как у условно-здоровых респондентов, так и у пациентов с хроническими заболеваниями [13]. Опросник предназначен для респондентов в возрасте от 14 лет и состоит из 36 вопросов, которые формируют восемь шкал:
-
• физическое функционирование (PF),
-
• ролевое функционирование, обусловленное физическим состоянием (RPF),
-
• боль (BP),
-
• общее здоровье (GH),
-
• жизнеспособность (V),
-
• социальное функционирование (SF),
-
• ролевое функционирование, обусловленное эмоциональным состоянием (RPF)
-
• психическое здоровье (MH).
После процедуры шкалирования результаты варьируют от 0 до 100 баллов по каждой из восьми шкал. Чем выше балл, тем лучше качество жизни.
Проверка психометрических свойств и статистический анализ
В рамках валидации была выполнена оценка психометрических свойств русскоязычной версии P-QoL – валидности, надежности, чувствительности к изменениям, а также изучена его практическая применимость. Процедура валидации выполнена в соответствии с международными рекомендациями COSMIN (COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement Instruments – Стандарты выбора медицинских инструментов) [14]. Надежность оценивали с помощью определения внутреннего постоянства и воспроизводимости опросника. Внутреннее постоянство определяли на основании расчета коэффициента α Кронбаха. Для оценки воспроизводимости рассчитывали коэффициенты внутриклассовой корреляции (ICC) методом тест-ретест. Для этого 30 женщинам до операции было предложено заполнить опросник при их первичном посещении врача и две недели спустя.
В рамках оценки валидности изучали содержательную и конструктную валидность (конвергентную и дискриминантную) русской версии P-QoL Для оценки содержательной валидности русскоязычной версии P-QoL 7 врачей-урологов приняли участие в анкетировании для оценки понятности, удобства, информативности и полезности опросника при оценке симптомов и качества жизни при ПТО. Для проверки конвергентной валидности были оценены корреляции между показателями доменов P-QoL, субшкал PFDI-20 и SF-36 с использованием корреляции Спирмена (r). Для проверки дискриминантной валидности сравнивали показатели P-QоL у женщин с различными стадиями POP-Q с помощью дисперсионного анализа.
Чувствительность опросника к изменениям оценивали в группе, состоящей из 57 женщин, которые дважды заполнили P-QoL: до и через 8 недель после операции. Для оценки чувствительности были использованы величина эффекта (Effect size, ES) и стандартизированное значение изменения (Standardized response mean, SRM) для изменения показателей между до- и послеоперационным периодом. ES – это соотношение разницы среднего значения показателя на двух точках измерения и SD показателя на исходной точке. SRM – это соотношение разницы среднего значения показателя на двух точках измерения и SD разницы показателя на двух точках измерения. Для SRM и ES значение 0,2–0,5 считалось малым, 0,5–0,8 – умеренным, > 0,81,0 – достаточным и > 1,0 – отличным [15, 16]. Значения ES и SRM, превышающие 0,80, соответствуют оптимальной чувствительности инструмента. Для сравнения показателей до и после операции был использован ранговый критерий Уилкоксона.
Для оценки пригодности русскоязычной версии опросника мы проанализировали процент пропущенных ответов в 20 вопросах доменов P-QoL и в 18 дополнительных вопросах о симптомах ПТО.Приемлемым считался процент пропущенных ответов ≤5. Кроме того,оценивали среднее время заполнения опросника.
Все статистические тесты были двусторонними,и значение p менее 0,05 принималось в качестве уровня статистической значимости. Статистический анализ выполнен с использованием SPSS 23.0.
Исследование было одобрено локальным комитетом по Биомедицинской этике Клиники высоких медицинских технологий им. Н.И. Пирогова ФГБОУ ВО СПбГУ, все пациентки подписали добровольное информированное согласие (EC № 05/23 от 18.05.2023).
Данная статья является переводом ранее опубликованной статьи в International Urogynecology Journal 13.03.24. Авторский коллектив считает, что данная статья должна быть опубликована на русском языке ввиду необходимости всеобщего применения P-QоL как эффективного и чувствительного инструмента для опроса пациенток с ПТО.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
Характеристика пациенток
В общей сложности в исследовании приняли участие 303 женщины с симптомами ПТО. Основные демографические и клинические характеристики выборки представлены в таблице 1. Пациенткам были проведены следующие виды реконструктивных операций:
Таблица 1. Социально-демографические и клинические характеристики выборки
Table 1. Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics
|
Характеристики Characteristics |
Значения Value |
|
Возраст, лет / Age, years среднее значение ± SD / Mean±SD медиана (Q1; Q3) / Median (Q1; Q3) размах / Range |
58,6±11,7 62 (50; 67) 33–87 |
|
Место проживания / Living, Place n (%) город / Urban село/ Rural нет данных/ ND |
254 (83,8) 48 (15,9) 1 (0,3) |
|
Образование / Education, n (%) среднее/ Primary среднее специальное или высшее неоконченное/ College or University высшее / High нет данных / ND |
3 (1,0) 127 (41,9) 151 (49,8) 22 (7,3) |
|
Семейное положение / Family status, n (%) замужем / Married не замужем / Single в разводе / Divorced вдовы / Widow нет данных / ND |
187 (61,7) 11 (3,6) 46 (15,3) 41 (13,5) 18 (5,9) |
|
Занятость / Employment, n (%) работают / Employed не работают / Housewife на пенсии / Retired нет данных / ND |
126 (41,6) 47 (15,5) 119 (39,3) 11 (3,6) |
|
Характер работы (для занятых), n (%) Nature of work (for those employed), n (%) физический / Physical умственный / Mental смешанный / Combined нет данных / ND |
20 (15,8) 68 (54,0) 35 (27,8) 3 (2,4) |
|
Индекс коморбидности / Comorbidity Index среднее значение ± SD / Mean±SD медиана (Q1; Q3) / Median (Q1; Q3) размах / Range |
2,6±1,9 3 (1; 4) 0-9 |
|
Индекс массы тела, кг/м2 / Body mass index среднее значение ± SD / Mean±SD медиана (Q1; Q3) / Median (Q1; Q3) размах / Range |
28±5,3 27,6 (24,8; 30,4) 16,1-59,5 |
|
Стадия POP-Q / POP-Q stage, n (%) 2 3 4 |
84 (27,7) 204 (67,3) 15 (5,0) |
|
Распределение по количеству родов, n (%): Parity, n (%), out of them: 1 2 3 4 |
295 (97,4) 77 (26,1) 175 (59,3) 33 (11,2) 10 (3,4) |
|
Продолжительность жалоб, связанных с ПТО, годы Duration of complaints related to POP, years среднее значение ± SD / Mean±SD медиана (Q1; Q3) / Median (Q1; Q3) размах / Range |
6,6±6,6 5 (3; 10) 0–43 |
POP – pelvic organ prolapse (пролапс тазовых органов); (Q1; Q3) – межквартильный размах реконструкция с использованием сетчатого эндопротеза – n=211 (69,6%) (гибридная хирургическая реконструкция тазового дна, n=198; комбинированная лапароскопическая сакрогистеропексия, n =13), реконструкция с применением собственных тканей – n=92 (30,4%) (передняя и/или задняя кольпоррафия, n=82; Манчестерская операция, n=10).
Языковая и культурная адаптация опросника P-QoL
Окончательная русскоязычная версия P-QoL имела структуру,эквивалентную оригинальной версии. В рамках интервьюирования было установлено, что большинство вопросов понятны женщинам и не вызывают трудностей. Дословный перевод одного вопроса и двух вариантов ответа вызвали сложности Использование дословного перевода мы посчитали нерациональным,так как он не передавал необходимое значение текста и трудно интерпретировался рус-скоговорящими пациентками. В этой связи было принято решение откорректировать данные формулировки, предварительно согласовав их с автором P-QoL и экспертной комиссией. Пункт «Пожалуйста, заполните опросник,даже если Вы чувствуете,что у Вас нет пролапса» был изменен на «Пожалуйста, заполните опросник,даже если Вы не ощущаете опущения тазовых органов».Вариант ответа «Неприменимо» для всех пунктов, касающихся симптомов пролапса, был изменен на «Нет симптомов/проблемы». В варианте ответа «Раз в неделю или чаще» на вопрос «Как часто Вы опорожняете кишечник?» мы изменили формулировку на «Раз в неделю или реже». Кроме того, позиция варианта ответа «Неприменимо» для элементов домена «Личные отношения» была размещена после других вариантов ответа, поскольку на русском языке это звучало более естественно.В ходе дополнительного интервьюирования 3пациенток была одобрена и утверждена окончательная русская версия P-QoL, состоящая из 3 страниц.
Надежность опросника P-QoL
Опросник P-QoL имеет высокое внутреннее постоянство – значение α Кронбаха составило 0,92. Высокое внутреннее постоянство было продемонстрировано для всех доменов опросника (значение α Крон-баха в диапазоне от 0,80 до 0,92), за исключением доменов «сон/энергия» (0,68) и «тяжесть симптомов» (0,65), которые, тем не менее, являются приемлемыми Оценку внутреннего постоянства в доменах «общее восприятие состояния здоровья» и «влияние ПТО на жизнь» не проводили, поскольку в обоих доменах есть только по одному пункту. Что касается воспроизводимости, коэффициенты внутриклассовой корреляции ICC варьировали от 0,7 до 0,96 для всех доменов, за исключением «социальных ограничений» (ICC=0,62) (табл. 2). Все внутриклассовые корреляции были статистически значимыми ( р <0,001).
Валидность опросника P-QoL
Для проверки содержательной валидности русскоязычной версии P-QoL провели анкетирование 7 урологов (средний возраст 34,6±5,9 лет; мужчины/ женщины – 6/1), которые согласились с тем, что опросник удобен и полезен для оценки влияния ПТО
Таблица 2. Результаты анализа надежности опросника P-QoL методом тест-ретест Table 2. Test–retest reliability scores for the P-QoL
|
Домены P-QoL P-QoL domain scores |
ICC |
95% CI Нижняя / Lower Верхняя / Upper |
|
|
Общее восприятие состояния здоровья General health perceptions |
0,67 |
0,44 |
0,82 |
|
Влияние ПТО на жизнь Prolapse impact |
0,66 |
0,41 |
0,81 |
|
Ролевые ограничения Role limitations |
0,73 |
0,52 |
0,86 |
|
Физические ограничения Physical limitations |
0,76 |
0,56 |
0,87 |
|
Социальные ограничения Social limitations |
0,62 |
0,31 |
0,80 |
|
Ограничения личных взаимоотношений Personal relationships |
0,96 |
0,91 |
0,98 |
|
Эмоции Emotions |
0,79 |
0,60 |
0,89 |
|
Сон / Энергия Sleep / Energy |
0,77 |
0,58 |
0,88 |
|
Тяжесть симптомов Severity measures |
0,85 |
0,72 |
0,92 |
ICC – Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (коэффициент внутриклассовой корреляции) 95% CI – 95% Confidence Interval (доверительный интервал)
на качество жизни женщин и отражает все важные аспекты влияния пролапса.Коэффициент содержательной валидности был максимально высоким,и его среднее значение было равно 1,0. Также специалисты подтвердили ясность и понятность опросника.
В рамках оценки конвергентной валидности были продемонстрировали статистически значимые положительные слабые/умеренные корреляции всех доменов P-QoL с общим баллом PFDI-20 (табл. 3). Что касается корреляций с субшкалами PFDI-20, то, как и ожидалось, для домена ПТО, а именно POPDI, они были самыми высокими, а для домена дисфункции кишечника, а именно CRADI, самыми низкими. Кроме того, все домены P-QoL, за исключением «сон/энергия», имели значимые отрицательные слабые/умеренные корреляции с большинством шкал SF-36, а именно такие показатели, как общее восприятие состояния здоровья, влияние пролапса на жизнь,ролевые ограничения,фи-зические и социальные ограничения, а также тяжесть симптомов, сильнее коррелировали со шкалами SF-36, связанными с физическим функционированием ,тогда как ограничения личных взаимоотношений и эмоции имели более высокую корреляцию со шкалами SF-36, связанными с психологическим благополучием (табл. 3).
В ходе оценки дискриминантной валидности было показано, что показатели по доменам P-QoL различались у пациенток с разными стадиями ПТО (рис. 1).
Показатели общего восприятия состояния здоровья ( p <0,001), ролевых ограничений ( p =0,001), физических ограничений ( p =0,004), социальных ограничений ( p <0,001) и тяжесть симптомов ( p <0,001) у женщин с POP-Q 3-й стадии и POP-Q 4-й стадии были значительно выше (хуже) по сравнению с женщинами при 2-й стадии POP-Q (ANOVA Крускала-Уоллиса). Кроме того, показатели общего восприятия состояния здоровья выше (хуже) у женщин с 4-й стадией ПТО, по сравнению с женщинами с 3-й стадией ( р =0,002). Что
Таблица 3. Результаты анализа конвергентной конструктной валидности опросника P-QoL с помощью оценки корреляций с опросниками PFDI-20 и SF-36 (коэффициент Спирмена r)
Table 3. Results from the analysis of convergent construct validity for P-QoL with PFDI-20 and SF-36 (Spearman´s coefficient r)
|
Домены P-QoL P-QoL domain scores |
POP DI-6 |
CRA DI-8 |
UDI-6 |
Общий балл PFDI-20 |
ФФ |
РФФ |
Б |
ОЗ |
Ж |
СФ |
РЭФ |
ПЗ |
|
Общее восприятие состояния здоровья |
0,361 |
0,149 |
0,192 |
0,288 |
-0,368 |
-0,268 |
-0,290 |
-0,340 |
-0,247 |
-0,224 |
-0,192 |
- 0,220 |
|
General health perceptions |
<0,001 |
0,014 |
0,002 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
0,002 |
<0,001 |
|
Влияние ПТО на жизнь |
0,289 |
0,243 |
0,231 |
0,305 |
-0,219 |
-0,158 |
-0,271 |
-0,138 |
-0,175 |
-0,212 |
-0,166 |
-0,148 |
|
Prolapse impact |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
0,012 |
<0,001 |
0,031 |
0,005 |
<0,001 |
0,01 |
0,018 |
|
Ролевые ограничения |
0,511 |
0,227 |
0,314 |
0,450 |
-0,481 |
-0,507 |
-0,412 |
-0,273 |
-0,294 |
-0,391 |
-0,417 |
-0,303 |
|
Role limitations |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
|
Физические ограничения |
0,523 |
0,359 |
0,461 |
0,570 |
-0,463 |
-0,387 |
-0,340 |
-0,240 |
-0,271 |
-0,368 |
-0,329 |
-0,297 |
|
Physical limitations |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
|
Социальные ограничения |
0,492 |
0,393 |
0,452 |
0,553 |
-0,367 |
-0,372 |
-0,358 |
-0,219 |
-0,294 |
-0,423 |
-0,333 |
-0,349 |
|
Social limitations |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
|
Ограничения личных взаимоотношений |
0,270 |
0,135 |
0,146 |
0,226 |
-0,070 |
-0,168 |
-0,190 |
-0,052 |
-0,197 |
-0,274 |
-0,107 |
-0,222 |
|
Personal relationships |
<0,001 |
0,053 |
0,036 |
0,001 |
0,324 |
0,017 |
0,005 |
0,467 |
0,004 |
<0,001 |
0,137 |
0,001 |
|
Эмоции |
0,357 |
0,329 |
0,324 |
0,403 |
-0,202 |
-0,246 |
-0,304 |
-0,221 |
-0,447 |
-0,394 |
-0,296 |
-0,504 |
|
Emotions |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
|
Сон / Энергия |
0,546 |
0,368 |
0,483 |
0,577 |
-0,364 |
-0,408 |
-0,386 |
-0,231 |
-0,380 |
-0,394 |
-0,272 |
-0,340 |
|
Sleep / Energy |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
|
Тяжесть симптомов |
0,703 |
0,314 |
0,463 |
0,624 |
-0,400 |
-0,323 |
-0,339 |
-0,209 |
-0,225 |
-0,253 |
-0,266 |
-0,165 |
|
Severity measures |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
0,002 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
<0,001 |
0,01 |
Примечание: Коэффициент Спирмена r выделен жирным шрифтом, уровень p – обычным шрифтом; POPDI-6 – Pelvic Organs Prolapse Distress Inventory (шкала оценки симптомов пролапса тазовых органов); CRADI-8 – Colorectal-Anal Distress Inventory (шкала оценки расстройств со стороны кишечника); UDI-6 – Urinary Distress Inventory (шкала оценки расстройств мочеиспускания); Total PFDI-20 – Pelvic Floor Distress Inventory (шкала оценки нарушения функции тазового дна); ФФ – физическое функционирование; РФФ – ролевое функционирование, обусловленное физическим состоянием; Б – боль; ОЗ – общее здоровье; Ж – жизнеспособность; СФ – социальное функционирование; РФ – ролевое функционирование, обусловленное эмоциональным состоянием; ПЗ – психическое здоровье
Note: Spearman's r coefficient is in bold, p level is in regular font. POPDI-6 - Pelvic Organs Prolapse Distress Inventory (pelvic organ prolapse symptom rating scale); CRADI-8 - Colorectal-Anal Distress Inventory (scale for assessing bowel disorders); UDI-6 - Urinary Distress Inventory (scale for assessing urinary disorders); Total PFDI-20 - Pelvic Floor Distress Inventory (pelvic floor dysfunction scale); FF – physical functioning; RFP – role functioning due to physical condition; B – pain; OZ – general health; F – viability; SF – social functioning; RF – role functioning determined by emotional state; MH – mental health
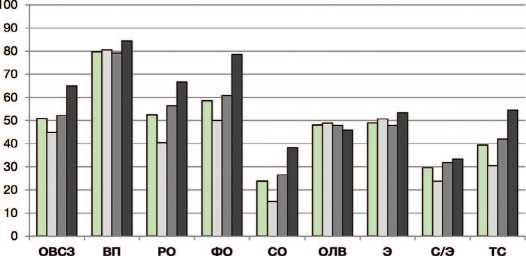
□ Вся выборка П2 стадия ПТО 03 стадия ПТО 04 стадия ПТО
Рис. 1. Показатели по доменам P-QOL при разных стадиях POP-Q
Примечание: ОВСЗ – общее восприятие состояния здоровья, ВП – влияние пролапса на жизнь, РО – ролевые ограничения, ФО – физические ограничения, СО – социальные ограничения, ОЛВ – ограничения личных взаимоотношений, Э – эмоции, С/Э – сон/энергия, ТС – тяжесть симптомов
Fig. 1. Distribution of P-QOL score according to the POP-Q stage
Note: OВСЗ – general perception of health, ВП – impact of prolapse on life, РО – role limitations, ФO – physical limitations, СO – social limitations, ОЛВ – limitations in personal relationships, Э – emotions, S/Э – sleep/energy, TС – severity of symptoms касается показателей сна/энергии, то статистически значимые различия были выявлены только между женщинами со 2-й стадией и 3-й стадией ПТО (р=0,033).
Апостериорные сравнения: для ОВСЗ – р <0,001 между стадией POP-Q 2 и стадией POP-Q 3, р <0,001 между стадией POP-Q 2 и стадией POP-Q 4, р =0,002 между стадией POP-Q 3 и стадией POP-Q 4; для РО – р =0,001 между стадией POP-Q 2 и стадией POP-Q 3, р =0,009 между стадией POP-Q 2 и стадией POP-Q 4; для ФО – р =0,017 между стадией POP-Q 2 и стадией POP-Q 3, р =0,003 между стадией POP-Q 2 и стадией POP-Q 4. Стадия 4 POP-Q; для СО – р =0,003 между стадией 2 POP-Q и стадией 3 POP-Q, р =0,004 между стадией 2 POP-Q и стадией 4 POP-Q; для С/Э – p =0,033 между стадией 2 POP-Q и стадией 3 POP-Q; для ТС р =0,001 между стадией POP-Q 2 и стадией POP-Q 3, р =0,001 между стадией POP-Q 2 и стадией POP-Q 4.
Пригодность опросника P-QoL
Количество пропущенных ответов по 20 вопросам доменов P-QoL составило 3,7%, что указывает на приемлемость использования P-QoL. Количество пропущенных ответов по всем дополнительным вопросам о симптомах составило 5%, что считается допустимым. Среднее время заполнения русскоязычной версии P-QoL составило 7 (5-10) минут.
Чувствительность опросника P-QoL к изменениям
Для оценки результатов лечения 57 пациенткам было предложено заполнить P-QoL до и через 2 месяца после операции.
Значения размера эффекта (ES) и стандартизированное значение изменения (SRM) представлены в таблице 4. Значения ES были отличными (ES >1,0) для большинства доменов,за исключением «социальных ограничений» и «сна/энергии», которые были удовле-творительными,и «ограничения личных взаимоотношений», которые были малыми. Значения SRM были отличными (SRM >1,0) для пяти доменов, хорошими или удовлетворительными для трех доменов («сон/ энергия» и «тяжесть симптомов», а также «ограничения личных взаимоотношений»)и малыми для «социальных ограничений».
Апробация русской версии P-QoL для оценки влияния ПТО на качество жизни и эффекта лечения у женщин после реконструктивных операций
Использование русскоязычной версии P-QoL в выборке из 303 госпитализированных пациенток с ПТО позволило описать данную группу женщин с точки зрения нарушения качества жизни и выраженности симптомов пролапса.Средний балл по опроснику (стандартное отклонение) выше 50 был получен по следующим доменам – «влияние ПТО на жизнь» – 79,8 (25,2), «физические ограничения» – 58,6 (33,4), «ролевые ограничения» – 52,5 (34,1) и «общее восприятие состояния здоровья» – 50,8 (15,8) (рис. 1). Примечательно, что наихудшим оказался показатель «влияние ПТО на жизнь»,который был высоким независимо от стадии. Кроме того, ПТО негативно влиял на «ограничения личных взаимоотношений» и «эмоции» также независимо от стадии ( р >0,05). Средние баллы по этим доменам были близки к 50-48,
Таблица 4. Результаты анализа чувствительности опросника P-QoL
Table 4. Results from the analysis of responsiveness for P-QoL
|
Домены P-QoL P-QoL domain scores |
Размер эффекта ES |
Стандартизированное значение изменения SRM |
|
Общее восприятие состояния здоровья General health perceptions |
2,147 |
1,432 |
|
Влияние ПТО на жизнь Prolapse impact |
1,821 |
1,158 |
|
Ролевые ограничения Role limitations |
1,214 |
1,314 |
|
Физические ограничения Physical limitations |
1,189 |
1,212 |
|
Социальные ограничения Social limitations |
0,533 |
0,461 |
|
Ограничения личных взаимоотношений Personal relationships |
0,384 |
0,531 |
|
Эмоции Emotions |
1,091 |
1,163 |
|
Сон / Энергия Sleep / Energy |
0,761 |
0,876 |
|
Тяжесть симптомов Severity measures |
1,008 |
0,935 |
1 (40,0) и 49,0 (31,4) соответственно. Что касается показателей «тяжести симптомов ПТО»,то средний балл составил 39,4 (25,6) и, что вполне ожидаемо, был выше у женщин с 4-й стадией и ниже при 2-й стадии ПТО ( р =0,001).
Для того,чтобы проанализировать изменения качества жизни пациенток после реконструктивной операции, сравнивали показатели по доменам P-QoL до и через 2 месяца после лечения (рис. 2). Было отмечено, что,по сравнению с показателями до лечения,средние баллы P-QoL после операции значительно снизились Это было особенно заметно в отношении доменов «влияние ПТО на жизнь»,«физические ограничения», «ролевые ограничения» и «эмоции»,где баллы стали ниже (лучше) в несколько раз. На основании полученных результатов, демонстрирующих статистически значимые изменения, можно сделать вывод о существенном улучшении качества жизни после операции. Также мы проанализировали изменения качества жизни у женщин в зависимости от типа операции.В результате проведения реконструкции с использованием сетчатого имплантата (n=46) и реконструкции нативными тканями (n=11) у пациенток значительно улучшилось качество жизни. Изменения были статистически значимыми для всех доменов в группе, подвергшейся дополнительному восстановлению с использованием сетчатого импланта ( р =0,001 для «социальных ограничений», р =0,035 для «ограничений личных взаимоотношений», р <0,001 для всех остальных доменов). В группе, которой была проведена реконструкция нативными тканями, было показано статистически значимое улучшение по всем доменам, за исключением «социальных ограничений» и «ограничений личных взаимоотношений» ( р =0,010 для «общего восприятия состояния здоровья», р =0,016 для
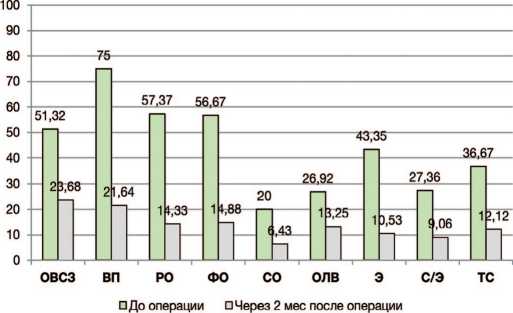
Рис. 2. Средние показатели по доменам P-QoL до и через 2 месяца после реконструктивной операции
Примечание: ОВСЗ – общее восприятие состояния здоровья, ВП – влияние пролапса на жизнь, РО – ролевые ограничения, ФО – физические ограничения, СО – социальные ограничения, ОЛВ – ограничения личных взаимоотношений, Э – эмоции, С/Э – сон/энергия, ТС – тяжесть симптомов
Fig. 2. P-QoL mean scores before and 2 months after reconstructive surgery Note: ОВСЗ – general perception of health, ВП – impact of prolapse on life, РО – role limitations, ФО – physical limitations, СO – social limitations, ОЛВ– limitations in personal relationships, Э – emotions, С/Э – sleep/energy, TС – severity of symptoms
«влияния пролапса», р =0,017 для «ролевых ограничений», р =0,03 для «физические ограничения», р =0,008 для «эмоций», р =0,025 для «сна/энергии» и р =0,014 для «тяжести симптомов»).
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Очевидно,что для оценки результата лечения недостаточно только определения степени ПТО до и после реконструктивной операции.Исходя из этого, решение о ведении женщины с ПТО также должно приниматься на основе информации об уровне ее КЖ Клиническая тактика при выборе оптимального лечения и оценка его эффективности должны учитывать тяжесть симптомов и влияние ПТО на КЖ женщины [17, 18]. Другими словами, улучшение КЖ должно быть основной целью лечения пролапса любой степени тяжести. Поскольку ПТО может влиять на различные аспекты жизни женщины,ограничивая эмоциональную, физическую, социальную и сексуальную сферы ее жизни,серьезность этих ограничений и их влияние на качество жизни пациентки становятся важным источником информации для хирурга при принятии решения. Таким образом, опросник P-QoL является полезным инструментом для оценки КЖ у женщин с ПТО в рутинной клинической практике и последующем наблюдении за результатами лечения [8]. Как и другие диагностические процедуры,инструменты для оценки КЖ должны быть валидными, надежными и чувствительными к изменениям во времени [19]. Ранее показано, что P-QoL является валидным и надежным инструментом для оценки качества жизни женщин с симптомами ПТО в клинической и исследовательской практике [20-26]. До сих пор русскоязычная версия P-QoL ранее никогда не разрабатывалась и не тестировалась в популяции российских пациенток с данной проблемой. В настоящем исследовании рассматриваются результаты разработки и валидации русскоязычной версии P-QoL. Языковая и культурная адаптация P-QoL была проведена в соответствии с международными рекомендациями [10], а содержательная валидность была определена,как описано в других вали-дационных исследованиях различных языковых версий P-QoL [20-28]. Акцент был сделан на сохранении концептуальной и структурной эквивалентности,а не на прямом дословном переводе. В окончательную версию было внесено несколько поправок путем перефор-мулировки,чтобы фразы звучали более естественно Кроме того, русскоязычная версия P-QoL выполнена в 3-страничном формате (по сравнению с 5-страничным форматом оригинала), для удобства пациенток. Русскоязычная версия опросника P-QoL имеет приемлемые показатели содержательной валидности (индекс содержательной валидности равен 1,0) и внешней ва-лидности,что продемонстрировано в ходе интервьюи- рования фокусной группы женщин,имеющих ПТО. Опросник понятен пациенткам и не представляет дополнительной нагрузки для специалистов.Наряду с другими исследователями мы считаем, что P-QoL прост в использовании в условиях большой клинической нагрузки [29].
Для обеспечения качества всех этапов разработки русскоязычной версии необходимо провести тестирование ее психометрических свойств.Валида-ция необходима для подтверждения того,что русскоязычная версия P-QoL соответствует оригиналу и обладает аналогичной валидностью и надежностью. Результаты нашего исследования показали высокую степень надежности и валидности опросника.Внут-реннее постоянство было очень высоким по всем доменам, за исключением доменов «сон/энергия» и «тяжесть симптомов»,которые были приемлемыми. Эти данные аналогичны тем,что были представлены в других валидационных исследованиях [20-23]. Нами наблюдалось высокая воспроизводимость результатов при повторном заполнении опросника пациентками через короткий интервал времени – коэффициенты ICC варьировали от 0,7 до 0,96 для всех доменов, за исключением «социальных ограничений» (ICC=0,62). Двухнедельный период между заполнениями опросника был выбран из соображений,что этого времени достаточно, чтобы избежать систематической ошибки при заполнении,и при этом состояние оставалось неизменным. Полученные нами данные сопоставимы с результатами для оригинальной версии и других языковых версий P-QoL [8, 24, 25].
В нашем исследовании мы подтвердили конвергентную и дискриминантную валидность русскоязычной версии P-QoL. Чтобы измерить конвергентную валидность, мы проанализировали корреляции между показателями доменов P-QoL с доменами PFDI-20 и шкалами SF-36. PFDI-20 является опросником который часто используется в клинической практике и клинических исследованиях для оценки состояния, вызванного наличием дисфункции органов тазового дна [12]. Данный опросник получил рекомендацию класса А Международной ассоциации по недержанию для клинической практики [30] и был переведен на несколько языков, включая русский. Поскольку у женщин, страдающих ПТО, качество жизни ухудшается до операции и может значительно улучшиться после лечения,в этой популяции пациенток часто используются общие опросники, такие как SF-36. Согласно полученным результатам, показатели P-QoL имели статистически значимые корреляции с субшкалами PFDI-20 и шкалами SF-36. Что касается дискриминантной валидности, мы наблюдали значительные различия в показателях P-QoL у женщин в зависимости от стадии POP-Q (p<0,001) – более высокая стадия связана с худшими показателями P-QoL. Связь пока- зателей P-QoL со степенью ПТО наблюдали и в других исследованиях [20, 21, 29]. Следует отметить, что наличие корреляции со стадией не означает,что оценка P-QoL заменяет физикальное обследование.
Чувствительность к изменениям оценивали в подгруппе женщин, которые заполняли P-QoL до и через 2 месяца после операции. Мы использовали расчет величин ESES и SRM, которые часто применяют для изучения чувствительности опросника. Значения ES и SRM были высокими для большинства доменов, что указывает на чувствительность к изменениям после лечения. Отметим, что наши данные даже превосходят результаты, полученные в предыдущих исследованиях [22, 24, 29].
Кроме того, мы изучили пригодность русскоязычной версии опросника P-QoL. Наши результаты аналогичны результатам для других языковых версий [20-25]. Это свидетельствует о простоте заполнения, хорошей приемлемости опросника и указывает на то, что его русская версия применима в отечественной клинической практике.
Наконец, мы продемонстрировали применимость русскоязычной версии P-QoL в качестве эффективного инструмента для оценки влияния ПТО на качество жизни и эффекта лечения у женщин после реконструктивных операций. Значительное улучшение качества жизни после операции было продемонстрировано по всем доменам P-QoL, что указывает на то, что этот инструмент способен обнаруживать изменения в самочувствии у женщин с данной патологией. Таким образом, P-QoL – это информативный инстру-мент,который может использоваться в клинической практике и научных исследованиях с целью выявления и оценки влияния ПТО на качество жизни женщин и определения эффективности реконструктивных операций.
Наше исследование обладает рядом преимуществ. Во-первых, мы использовали рекомендации COSMIN при оценке психометрических свойств опросника [14]. Во-вторых, мы проанализировали чувствительность опросника P-QoL к изменениям у женщин с ПТО,перенесших реконструктивную опе-рацию.Чувствительность имеет особое значение в урогинекологии,где основной целью вмешательства является, главным образом, улучшение качества жизни пациентки [16]. Поэтому мы считаем чувствительность фундаментальной психометрической характеристикой, которую следует оценивать в ходе валидации опросника. Чувствительность русскоязычной версии P-QoL удалось подтвердить на основании значительных положительных изменений качества жизни после операции.Примечательно,что через 2 месяца после реконструктивной операции показатели по таким доменам,как «влияние ПТО на жизнь»,«фи-зические ограничения», «ролевые ограничения»
и «эмоции» улучшились в несколько раз по сравнению с исходными показателями до операции. Кроме того, все изменения после операции были статистически значимыми.
Вместе с тем имеются некоторые ограничения исследования, требующие обсуждения. Во-первых, у всех женщин в нашей выборке присутствовали симптомы ПТО, что отличается от других выборок [20-29], которые включали в качестве контрольной группы женщин без симптомов ПТО.У нас отсутствовала бессимптомная группа,так как все пациентки,которые обращались за хирургическим лечением, имели симптомы ПТО. Во-вторых, все они проходили лечение в отделении урологии Клиники высоких медицинских технологий им. Н.И. Пирогова ФГБОУ ВО СПбГУ в Санкт-Петербурге,что могло оказать влияние на репрезентативность выборки. В-третьих, как и в любом опросе, женщины могли иметь собственные мотивы для участия (или неучастия) в исследовании, что потенциально может оказывать влияние на их ответы и вносить определенную предвзятость в наши результаты. Это ограничение присуще любому исследованию в данной области и неизбежно. Кроме того, группа женщин,прошедших обследование до и после опера-ции,была небольшой,поскольку большинство из них не являлись местными жительницами,а прибыли на лечение из различных регионов России,что ограничивало их последующие визиты.Оптимальным решением в этом случае является внедрение онлайн версии P-QoL. Однако перед ее использованием необходимо протестировать психометрические свойства данного формата опросника.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Русскоязычная версия опросника P-QoL является валидным, надежным, чувствительным к изменениям и практичным инструментом для оценки качества жизни у пациенток с ПТО.Продемонстрирована применимость P-QoL в качестве информативного инструмента для оценки влияния ПТО на качество жизни и определения эффекта лечения у женщин после реконструктивных операций. Дальнейшее внедрение P-QoL в повседневную практику несомненно окажет значительное влияние на оценку результатов реконструктивной хирургии. Включение P-QoL наряду с другими опросниками в исследования,оценивающие эффект реконструктивной хирургии у женщин с ПТО,позво-лит получить более полное представление о послеоперационных изменениях состояния пациенток.
ИШАТУРАШЕЕЕЕШЕ
Список литературы Валидация русскоязычной версии опросника P-QOL и его апробация для оценки влияния пролапса тазовых органов на качество жизни женщин и определения эффективности реконструктивных операций
- Cronje HS. Pelvic organ prolapse. In: Kruger TF, Botha MH, eds. Clinical Gynaecology, 4th ed. Cape Town: Juta & Co 2011:487-515.
- Lagana AS, La Rosa VL, Rapisarda AMC, Vitale SG. Pelvic organ prolapse: the impact on quality of life and psychological well-being. J Psychosom Obstet Gynecol 2018;39(2):164-6. https://doi.org/10.1080/0167482X.2017.1294155
- Digesu GA, Chaliha C, Salvatore S, Hutchings A, Khullar V. The relationship of vaginal prolapse severity to symptoms and quality of life. BJOG 2005;112(7):971-6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-004-1225-x.
- Ghanbari Z, Ghaemi M, Shafiee A, Jelodarian P, Hosseini RS, Pouyamoghaddam S, Montazeri A. Quality of life following pelvic organ prolapse treatments in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med 2022;11(23):7166. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237166.
- Barber MD, Maher CF. Epidemiology and outcome assessment of pelvic organ prolapse. Int Urogyn J 2013;24:1783-90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-013-2169-9.
- Cichowski S, Grzybowska ME, Halder GE, Jansen S, Gold D, Espuna M, et al. International urogynecology consultation: patient reported outcome measures (PROs) use in the evaluation of patients with pelvic organ prolapse. Int Urogynecol J2022;33(10):2603-31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-022-05315-1.
- 0vretveit J, Zubkoff L, Nelson EC, Frampton S, Lehmann Knudsen J, Zimlichman E. Using patient-reported outcome measurement to improve patient care. Int J Qual Health Care 2017;29(Issue 6):874-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzx108.
- Digesu GA, Khullar V, Cardozo L, Robinson D, Salvatore S (2005) P-QOL: a validated questionnaire to assess the symptoms and quality of life of women with urogenital prolapse. Int Urogynecol J 2005;16:176-81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-004-1225-x.
- Belayneh T, Gebeyehu A, Adefris M, Rortveit G. A systematic review of the psychometric properties of the cross-cultural adaptations and translations of the Prolapse Quality of Life (P-QoL) questionnaire. Int Urogynecol J 2019;30:1-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-019-03920-1.
- Rothman M, Burke L, Erickson P, Leidy NK, Patrick DL, Petrie CD. Use of existing patient-reported outcome (PRO) instruments and their modification: The ISPOR good research practices for evaluating and documenting content validity for the use of existing instruments and their modification PRO task force report. Value Health 2009;12(8):1075-83. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4733.2009.00603.x.
- Bump RC, Mattiasson A, Bo K, Brubaker LP, DeLancey JOL, Klarskov P, et al. The standardization of terminology of female pelvic organ prolapse and pelvic floor dysfunction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996l;175(1):10-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/ s0002-9378(96)70243-0.
- Barber MD, Walters MD, Bump RC. Short forms of two condition-specific quality-of-life questionnaires for women with pelvic floor disorders (PFDI-20 adn PFIQ-7). Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;193(1):103-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2004.12.025
- Hays RD, Sherbourne CD, Mazel RM. User's Manual for Medical Outcomes Study (MOS) Core measures of health-related quality of life. 1995. RAND Corporation; MR-162-RC. [Electronic resource]. URL: www.rand.org.
- Mokkink LB, Terwee CB, Patrick DL, Alonso J, Stratford PW, Knol DL, et al. The COSMIN study reached international consensus on taxonomy, terminology, and definitions of measurement properties for health-related patient-reported outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol 2010;63(7):737-45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.02.006.
- Crosby RD, Kolotkin RL, Williams GR. Defining clinically meaningful change in health-related quality of life. J Clin Epidemiol 2003;56(5):395-407. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0895-4356(03)00044-1.
- Terwee CB, Dekker FW, Wiersinga WM, Prummel MF, Bossuyt P. On assessing responsiveness of health-related quality of life instruments: Guidelines for instrument evaluation. Qual Life Res 2003;12(4):349-62. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1023499322593.
- Chan SSC, Cheung RYK, Yiu KW, Lee LL, Pang AWL, Chung TKH.Symptoms, quality of life, and factors affecting women's treatment decisions regarding pelvic organ prolapse. Int Urogynecol J 2012;23(8):1027-33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-012-1698-y.
- Aponte MM, Rosenblum N. Repair of pelvic organ prolapse: What is the goal? Curr Urol Rep 2014;15(2):385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-013-0385-y.
- Mokkink L, Terwee C, Patrick D, Alonson J, Stratford P, Knol D, et al. The COSMIN checklist for assessing the methodological quality of studies on measurement properties of health status measurement instruments: an international Delphi study. Quality of Life Research 2010;19(4):539-49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-010-9606-8.
- Digesu GA, Santamato S, Khullar V, Santillo V, Digesu A, Cormio G, et al.Validation of an Italian version of the prolapse quality of life questionnaire. Eur J Obstet Gynecol ReprodBiol 2003;106(2):184-92. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-2115(02)00229-4.
- Lenz F, Stammer H, Brocker K, , Rak M, Scherg H, Sohn C. Validation of a German version of the P-QoL Questionnaire. Int Urogynecol J 2009;20(6):641-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-009-0809-x.
- Claerhout F, Moons P, Ghesquiere S, Verguts J, De Ridder D, Deprest J. Validity, reliability and responsiveness of a Dutch version of the prolapse quality-of-life (P-QoL) questionnaire. Int Urogynecol J 2010;21(5):569-78. https://doi.org/10.1007/ s00192-009-1081-9.
- De Oliveira MS, Tamanini JTN, de Aguiar Cavalcanti G. Validation of the Prolapse Quality-of-Life Questionnaire (P-QoL) in Portuguese version in Brazilian women. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 2009;20(10):1191-202. https://doi.org/10.1007/ s00192-009-0934-6.
- Sánchez-Sánchez B, Yuste-Sánchez MJ, Arranz-Martín B, Navarro-Brazález B, Romay-Barrero H, Torres-Lacomba M. Quality of life in POP: validity, reliability and responsiveness of the Prolapse Quality of Life Questionnaire (P-QoL) in Spanish Women. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020;17(5):1690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051690.
- Rzepka J, Zalewski K, Stefanowicz A, Khullar V, Swift S, Digesu GA. Validation of the Polish version of P-QoL questionnaire. Ginekol Pol 2016;87(7):477-83. https://doi.org/10.5603/GP.2016.0029.
- Belayneh T, Gebeyehu A, Adefris M, Rortveit G, Genet T. Translation, transcultural adaptation, reliability and validation of the pelvic organ prolapse quality of life (P-QoL) in Amharic. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2019;17( 1): 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/ s12955-019-1079-z.
- Fukumoto Y, Uesaka Y, Yamamoto K, Ito S, Yamanaka M, Takeyama M, et al. Assessment of quality of life in women with pelvic organ prolapse: conditional translation and trial of P-QOL for use in Japan. Nippon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi 2008;99(3):531-42. https://doi.org/10.5980/jpnjurol1989.99.531.
- Nojomi M, Digesu GA, Khullar V, Morovatdar N, Haghighi L, Alirezaei M, Swift S. Validation of Persian version of the Prolapse Quality-of-Life questionnaire (P-QOL). Int Urogynecol J 2012;23(2):229-33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-011-1529-6.
- Scarlato A, Souza CCC, Fonseca ESM, Sartori MGF, de Castello Giräo Manoel Joao Batista Castro RA. Validation, reliability, and responsiveness of Prolapse Quality of Life Questionnaire (P-QOL) in a Brazilian population. Int Urogynecol J 2011;22(6):751-5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-010-1354-3.
- de Arruda GT, de Andrade DF, Virtuoso JF. Internal structure and classification of pelvic floor dysfunction distress by PFDI-20 total score. J Patient Rep Outcomes 2022;6(1):51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41687-022-00459-6.


