Variations in hematological parameters during the treatment of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity with three different polyherbal formulations
Автор: Sinoriya Sh.K., Singh K.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.20, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Background: Many active chemicals have been identified in therapeutic plants, which are a valuable source of medicine. Many medicinal herbs, including hepatotoxicity, have been utilized to treat a variety of illnesses under the traditional medical system of India. Your liver may be harmed by toxic liver disorders. It's referred to as toxic hepatitis or hepatotoxicity. If you don't get care, it can result in severe symptoms or damage to your liver. Hepatotoxicity may be brought on by drugs, herbal supplements, chemicals, solvents, and alcohol. The goal of the current study was to assess how multiherbal formulations affected hematological markers in albino rats who were experiencing hepatotoxicity caused by carbon tetrachloride. Five plant extracts ( Curcuma longa, Allium sativum, Phyllanthus emblica, Solenum nigrum, and Ocimum tenuiflorum ) were combined to create three distinct formulations. Blood samples were taken from each rat and examined using conventional procedures (parameters) following daily administration of multiherbal formulations at a dose of 200 mg/kg b.wt. and the reference medicine (Silymarin) at a dose of 25 mg/kg b.wt. for 7, 14, and 21 days, respectively. Measurements included hemoglobin, PCV, DLC, TLC, ESR, and PLT count.
Hematological parameters, carbon tetrachloride, hepatotoxicity, toxicity
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143183450
IDR: 143183450
Текст научной статьи Variations in hematological parameters during the treatment of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity with three different polyherbal formulations
There has been extensive discussion on the causes of liver damage as well as their detrimental effects. These include various xenobiotics, such as drugs, alcohol, or toxins, ischemia, autoimmune diseases, and viral infections. Therefore, halogenated alkanes like carbon tetrachloride (CCl 4 ) are frequently utilized as model compounds to produce hepatotoxicity and clarify its methods of action after exposure to these compounds in order to unravel the mechanism of liver injury. CCl 4 toxicity has been linked to effects such as fatty degeneration, fibrosis, hepatocellular apoptosis, and carcinogenicity. After being administered, cytochrome CYP2E1, CYP2B1, CYP2B2, and maybe CYP3A activate CCl 4 to generate the trichloromethyl (CCl 3 *) radical. This radical attaches itself to proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids in cells, hindering vital functions like lipid metabolism and perhaps leading to fatty degeneration. Meanwhile, the interaction of CCl 3 * with DNA is believed to be the trigger for hepatic cancer. Moreover, this radical can combine with oxygen to generate the extremely reactive trichloromethylperoxy (CCl 3 OO*) radical. This substance starts the process of lipid peroxidation, which eventually results in the breakdown of polyunsaturated fatty acids, particularly those linked to phospholipids. The endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrial, and plasma membranes become less permeable as a result, which damages cells by disrupting calcium homeostasis, sequestering intracellular calcium, and causing calcium loss. Furthermore, CCl 4 has been shown to activate the cell's nitric oxide (NO), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)α, and transforming growth factors (TGF)α and -ß. The majority of these actions appear to push the cell in the direction of fibrosis or self-destruction. TGFs appear to encourage fibrosis, yet TNF-α leads a cell toward apoptosis. The hepatotoxic effects of CCl 4 can be reversed by using cytochrome P450 antagonists, antioxidants, and free radical scavengers due to the reducing effect of cytochromes on CCl 4 , the formation of the active trichloromethyl radical, and increased expression of NFкB, TNFα, and TGF-α and -β. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that certain plants, although acting as mitogens, might lessen the hepatotoxic effects of
CCl 4 by acting as antioxidants, inhibiting CYP2E1, activating NFкB, and inhibiting inflammatory cytokines (Saba et al., 2012). When hepatotoxicity is induced by CCl 4 , significant changes are seen in liver enzymes (SGPT, SGOT, and ALP) as well as hematological parameters. The present study reflects the changes in hematological parameters observed during treatment with the three polyherbal formulations (F-I, F-II, and F-III). And in the present study, it was observed that the F-1 formulation was reducing the toxicity caused by the CCl 4 very well compared to the other two formulations (F-II and F-III).
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Clearance of the animal ethical committee
The use of animals for the study was permitted by the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee (CPCSEA) of the Government of India with approval No. BU/Pharm/IAEC/a/17/08, New Delhi. All the experiments and protocols were conducted in strict agreement with the guidelines and ethical principles provided by the Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA).
Purchase of animals
The present study was carried out at the Department of Zoology, Institute of Basic Science, Bundelkhand University Campus, hansi. For experimentation, sexually mature adult female Albino rats of the Wistar strain (200 + 10 gm) for about 3 months were purchased from DRDE (Defence Research and Development Establishment) in Gwalior (M.P.).
Maintenance of animals
Before starting any experiment, it is necessary to maintain the animals properly. After purchasing, the animals were housed in ventilated polypropylene cages in an animal house under controlled hygienic conditions at a temperature of 25–30 °C, relative humidity of 50– 60%, and photoperiod (12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness). It is necessary to keep at least 2 rats in a small cage and a maximum of 4 rats in a large cage. They were fed a rat pellet diet (Amrut Feeds, Pranav Agro Industries Ltd., Sangli) regularly, which is a ready- made diet of rats and water ad libitum. The nozzle of the water bottle is kept in such a way that they are getting a free supply of water, and it should be kept in mind that the water bottle never gets empty and checked regularly. The husk of rice is also put on the bottom surface of cages, and it is changed daily; otherwise, the chances of skin infection increase.
Plants used in study:
-
1 Curcuma longa (Turmeric rhizome)
-
2 Solenum nigrum ( Makoi fruit)
-
3 Allium sativum (Garlic bulb)
-
4 Ocimum tenuiflorum (Tulsi leaf)
-
5 Phyllanthus emblica (Amla fruit)
Collection of the plant material
Garlic’s bulbs, Amla’s fruits, turmeric rhizomes, and Solanum nigrum fruit were purchased from the local market, and Tulsi’s leaves were collected from adjacent areas and air-dried in shade at 25+5 ◦C, which took about 1 week to 1 month to dry till total moisture was removed from the plant. These were subsequently authenticated and identified in the NISCAIR Authentication No.
1 NISCAIR/RHMD/Consult/2019/3450-51-1.
2 NISCAIR/RHMD/Consult/2019/3448-50-1.
3 NISCAIR/RHMD/Consult/2019/3450-51-2.
4 NISCAIR/RHMD/Consult/2019/3448-50-2.
5 NISCAIR/RHMD/Consult/2019/3450-51-3.
These were grind into a fine powder using an electric blender and stored at room temperature.
Preparation of plant extract
The medicinal principle is present in different parts of the plant, like the root, stem, leaf, flower, fruits, or plant exudates. Extraction is the separation of the required constituents from plant materials. These medicinal principles are separated by different processes (the Soxhlet apparatus and the maceration process). Those processes for concentration preparations, which include “triple maceration," Extracts of garlic, tulsi, and turmeric (ethanolic extracts) and Solanum nigrum (hydroalcoholic extract) (60:40 methanol + water) were extracted through the Soxhlet apparatus, and an aqueous extract of amla was extracted through the maceration process.
Ethanolic extract preparation by soxhlet apparatus
The plant materials were separately measured by an electronic balance. The drug to be extracted is packed in a cylinder made from filter paper, and it is placed in the body of the Soxhlet extractor. The solvent, i.e., ethanol, is placed in the flask. When a solvent is boiled on heating, it gets converted into vapors. These vapors move into the condenser through the side tube and get condensed into liquid, which falls on the column of the drug. When the extractor gets filled with the solvent, the level of the siphon tube also rises to its top. The solvent containing active constituents of the drug in the siphon tube runs into the flask, thus emptying the body extractor continuously.
The soluble active components of the drug stay in the flask while the solvent is frequently volatilized. The process of filling and emptying the extractor is repeated until the drug is drained. Usually, the process is repeated about 15 times for complete exhaustion of the drug. Then remove the total solvent from the drug, which is done with the help of a rotavapour evaporator, and then the drug is converted into semisolid form by keeping it on a heating plate. Then put the semi-solid drug inside the desiccators to convert it into solid form. This took about a month to convert into crude form. The crude extract is weighted and used in the preparation of doses.
Hydro-alcoholic extract preparation by Soxhlet apparatus
The procedure for the formation of hydro-alcoholic plant extract is the same as that for alcoholic extract preparation; the only difference is that we take the mixture of alcohol and water in the recommended proportion (6:4).
Triple maceration process
In this process, the drug is concentrated three times by using the menstruum, which is divided into three parts in such a manner that the same volume is used for maceration. The whole drug is macerated for one hour, with a portion of the menstruum required for the first maceration and strain. Maceration again for one hour with a part of the menstruum required for the second maceration and strain. Maceration again for one hour with a part of the menstruum required for the third maceration and strain. Press the marc lightly. Then combine the liquids obtained from the 2nd and 3rd macerations and evaporate them to the specified extent. Mix it with the liquid attained from the first maceration. Add absolute alcohol to 1/4th of the volume of the finished product. Adjust the volume with water, allow it to stand for 14 days, filter through silk cloth or Whatman filter paper no. 1, and concentrate the filtrate by using a lyophilizer at -40◦C. The crude extract was stored in the refrigerator until used.
Preparation of the dose
Formulations were prepared in gum acacia and physiological saline (0.9% NaCI) in a ratio of 1:1 of various herbs. Three different herbal formulations (Table 1 ) were used at a dose level of 200 mg/kg b.wt. Then it was given orally (1 ml/day) to rats for different durations, and their effects were studied after 7, 14, and 21 days of treatment.
Preparation of carbon tetrachloride
Hepatotoxicity was induced by a single oral dose of CCl 4 . CCL 4 was dissolved in olive oil in a 1:1 ratio. The CCl 4 solution was made fresh for each experiment at a dose of 1.5 ml/kg.
Standard drug
The standard drug (Sylimarin) was administered to the rats via oral route at 25 mg/kg b.wt. with the help of a gastric feeding needle.
Route of administration
The dosages were administered to the animals via oral route with the help of a gastric feeding needle. The entry was normally obtained without anesthesia. A feeding needle with a ball tip was used to prevent the introduction of the needle into the trachea and prevent trauma to the oral cavity.
Plan of work
For experimentation, selected animals were randomly distributed into two groups.
-
1 Normal control groups (vehicles only)
-
2 Experimental groups (The rats with CCl 4 -induced hepatotoxicity were divided into 5 groups.)
-
(i) Experimental Control
-
(ii) Standard Drug (Sylimarin)
-
(iii) Formulation 1: Curcuma longa, Solanum nigrum, and Allium sativum (in a 1:1:1 ratio).
-
(iv) Formulation 2: Curcuma longa, Occimum tenuiflorum, and Phyllanthus embilica (in a 1:1:1 ratio).
-
(v) Formulation 3: Curcuma longa, Solanum nigrum, Occimum tenuiflorum, Phyllanthus embilica, and Allium sativum (in a 1:1:1:1:1 ratio).
Formulations and standard drugs were given daily for 7, 14, and 21 days, and after 24 hours of last treatment, the autopsy of both groups was done on the same day, and various hematological parameters were performed as mentioned below.
Collection of blood samples
Blood samples were collected from each rat by puncturing the optical vein of the rat eye, i.e., the retroorbital plexus, with the help of capillaries. Blood samples were collected at various durations (7, 14, and 21 days) after the induction of CCL 4 and herbal drug treatment. After daily administration of the dose for the intervals of 7, 14, and 21 days, an autopsy of the animal was also performed. This was done by giving anesthesia with chloroform. The collected blood samples were analyzed according to the standard techniques (parameters) mentioned below.
Hematological parameters and their method: (Table 2)
Hemoglobin (Hb)
Sahli’s method : Sahli’s / acid hematin method
Principle: Blood is mixed with N/10 HCl, resulting in the conversion of Hb to acid hematin, which is brown in color. The solution is diluted until it’s color matches the brown-colored glass of the comparator box. The concentration of Hb is read directly.
Equipment required: a hemocytometer, which consists of:
-
1 Comparator box, which has brown-colored glass on either side
-
2 Hb-pipette, which is marked up to 20 mm (0.02 ml of blood).
-
3 Tube with markings of Hb on one side
-
4 Glass rod
-
5 Dropper
Reagents required: N/10 HCl and distilled water
Sample: Venous blood collected in EDTA as described earlier
Procedure:
-
1 Add N/10 HCl into the tube up to 2 g.
-
2 Mix the EDTA sample by gentle inversion and fill the pipette with 0.02 ml (20 µl) of blood. Wipe the external surface of the pipette to remove any excess blood.
-
3 Add the blood to the tube containing HCl. Wash out the contents of the pipette by drawing in and blowing out the acid two to three times. Mix the blood with the acid thoroughly.
-
4 Allow it to stand undisturbed for 10 minutes.
-
5 Place the hemoglobinometer tube in the comparator and add distilled water to the solution drop by drop, stirring with the glass rod until it’s color matches that of the comparator glass. While matching the color, the glass rod must be removed from the solution and held vertically in the tube.
-
6 Remove the stirrer and take the reading directly by noting the height of the diluted acid hematin and expressing it in g%.
Total Leucocytes Count (TLC)
WBC counts were enumerated using Naubaur’s chamber. The reagents used were:
WBC Fluid or Turk’s Solution
It was prepared by taking 2 ml of oxalic acid and a few drops of an aqueous solution of gentian violet in 100 ml of distilled water.
The following procedure was used:
The blood sucked into WBC pipettes to mark 0.5 was diluted by corresponding WBC fluid up to the mark (1:20). The pipettes were rotated so as to mix the contents, and they were kept for five minutes.
A few drops were discarded, and Naubaur’s chamber was charged with this mixture.
Calculations: The area of each large square is 1 sq mm, the depth of the chamber is 0.1 mm, and the volume of the square is 0.1 cu mm.
Volume of four corner squares = 0.1 × 4 = 0.4 cu mm.
The number of cells in the four-corner square equals N.
0.4 mm3 contains N cells.
. N* 20 ( Diluting factor )
-
1 cu mm contains =
0.4
WBC count = N×50.
Differential leucocyte count (DLC)
By counting from Leishman’s stained slide under an oil immersion lens (100 ×).
Slide preparation:
A small drop of blood was placed in the center line of the slide, about 1-2 cm from one end.
The spreader is placed at an angle of 45° to the slide and then moves back to make contact with the drop.
The drop should spread out quickly along the line of contact of the spreader with the slide.
The moment this occurs, the film should be spread by a rapid, smooth, forward movement of the spreader.
The drop should be of such size that the film is 3–4 cm in length.
Procedure for counting:
The cells should be counted using a high-power or oil immersion lens in a strip running the whole length of the film.
The lateral edges of the film are avoided.
The film should be inspected from the head to the tail.
If less than 100 cells are encountered in a single narrow strip, one or more strips should be examined until at least 100 cells have been counted.
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
If an anticoagulant is added to the blood and the specimen is allowed to stand in a tube, red cells slowly sediment to the bottom of the tube, leaving clear plasma as the supernatant. The rate of sedimentation estimated under standard conditions is known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Sedimentation takes place in three stages:
-
1 Formation of rouleaux.
-
2 Sinking of rouleaux.
-
3 Packing of rouleaux.
Method of estimation: (by the Wintrobe method)
Wintrobe tube: length: 110 mm
Diameter: 3.0 mm
Graduation of the lower 100 mm (0-100)
The tube is filled up to the 100 mm mark, allowed to stand in a vertical position at room temperature, and reads the fall of red cells at the end of one hour.
Pack Cell Volume (PCV) or Hematocrite (HCT)
The wintrobe tube must be clean and dry. Mix the oxalated sample of blood thoroughly by gently shaking for 3 minutes. With the help of the LP niddle, fill the tube up to the 100 mark. There must be no air in the blood column of the tube.
Centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 30 minutes, preferably 60 minutes. Take the reading of the packed cells from the bottom marks (10 marks) to the red cells upper marks. Recentrifuge for 5 minutes more at the same speed and take reading again. There should be no difference between the two readings if the packing has been completed. If there is a difference, further centrifugation is needed until the fixed packing is reached. After fixing the packing, take the final reading.
Platelet Count (PLT Count)
-
1 Draw the blood into a clean, dry RBC pipette up to the mark of 0.5. The accuracy in filling the pipette has to be high.
-
2 Wipe off the outside of the pipette.
-
3 Draw the diluting fluid (Rees-Ecker) up to mark 101.
-
4 Shake the pipette for 5 minutes.
-
5 Discard the first four drops. Load the chamber; both the hemocytometer and the cover slip must be clean.
-
6 Allow the preparation to stand for 15 minutes in a moist chamber. An inverted petri dish with a piece of wet filter paper on top makes a good moist chamber.
-
7 Count under the high power with the light partially cut off. Platelets are lilac-colored. And calculated by the following formula:
PLT / cumm =
RESULTS
Hemoglobin:
In the present study, the Hb level was reduced after hepatotoxicity induction. And after treatment with different formulations and standard drugs, the Hb level increased, as mentioned in. The Hb level increased significantly (P<0.01). The final results suggested that Formulation-I is better than others (Table 3 and Figure 1).
Total Leucocyte Count (TLC)
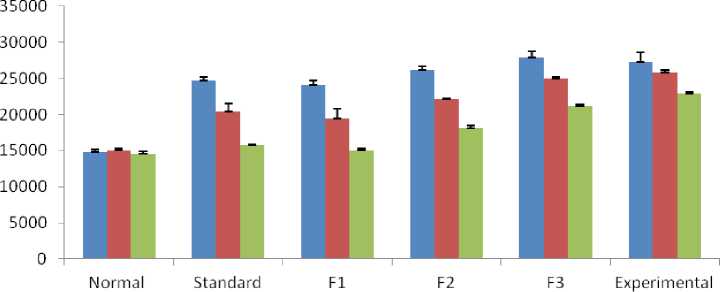
In the present study, when we induced hepatotoxicity in rats, it was observed that the TCL level raised and when we treated the rats with different formulations, the TLC level significantly reduced, mostly with F1 and the standard drug, compared to other formulations. All the formulations were able to reduce the raised TLC level in rats, but the F1 formulation shows a greater effect on TLC level than the others (Table 4 and Figure 2) . TLC level reduced significantly (P < 0.01) at all the durations of 7, 14, and 21 days.
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR):
After 24 hours of the last administration of the drug, the level of ESR decreased simultaneously. It was observed that significant recoupment was seen at 21 days of duration (P < 0.01). Though gradual recoupment was also seen at earlier durations of 7 and 14 days, maximum recovery was seen at later durations. And maximum recovery was also seen in the case of F1 and the standard drug as compared to F-II and F-III (Table 5 and Figure 3) .
Platelet Count (PLT):
In the present study, we observed that the hepatotoxicity induced by carbon tetrachloride causes a loss of platelet count. Rats have more platelets in their blood than humans. But due to hepatotoxicity, they reduced, and when these rats were treated with different formulations (I, II, and III) as well as a standard drug, the platelet count increased day by day, as mentioned in statistical ( T ables 6 and Figure 4) . They increase at a significant rate (P <0.01) from the 7th day to the 21st day. According to the statistical analysis, it seems that formulation I is a better healer than others in the case of platelet recovery from hepatotoxicity induced by carbon tetrachloride.
Pack Cell Volume (PCV):
On the basis of the present study, we found that hepatotoxicity induced by carbon tetrachloride creates a huge reduction in PCV levels. It was observed that when the hepatotoxicity-induced rats were treated with different formulations, the PCV level increased gradually with all the formulations (Table 7 and Figure 5). it was noticed that Formulation-I seemed to be a better healer than the other. The values seem to be significant throughout the study with respect to control (P < 0.01).
Differential Leucocyte cout (DLC):
In the present study, differential leucocyte count (DLC) seems to be changed during the induction of hepatotoxicity due to CCL 4. As a result of acute toxicity, neutrophil% increased and leucocyte% decreased. The changes were significant and tend to become normal due to the administration of various herbal formulations and standard drug (Table 8, 9 and Figure 6, 7) . The most significant values were observed for Formulation-(P < 0.01).
Table 1. Preparation of 3 multi herbal formulations
|
S.No. |
Multiherbal Formulation |
Plant Extract |
Ratio |
|
1. |
Formulation 1 (F1) |
Curcuma longa (Turmeric rhizome), Solenam nigrum (Makoi fruit), and Allium sativum (Garlic’s Bulb) |
1:1:1 |
|
2. |
Formulation 2 (F2) |
Curcuma longa (Turmeric rhizome), Ocimum tenuiflorum (Tulsi’s Leafs), and Phyllanthus emblica (Amla’s Fruit) |
1:1:1 |
|
3. |
Formulation 3 (F3) |
Curcuma longa (Turmeric rhizome), Solenam nigrum (Makoi fruit), Allium sativum (Garlic’s Bulb), Ocimum tenuiflorum (Tulsi’s Leafs), and Phyllanthus emblica (Amla’s Fruit) |
1:1:1:1:1 |
Table 2: Following hematological parameters were performed:
|
S.No. |
Parameters |
Methods to be followed |
|
1 |
Haemoglobin (Hb) |
Sahli’s Method |
|
2 |
TLC |
Naubaur’s Chamber |
|
3 |
DLC |
By leisman’s stained blood slides |
|
4 |
ESR |
Wintrobe & Landsberg (1935) |
|
5 |
PCV (HCT) |
Wintrobe & Landsberg (1935) |
|
6 |
Platelet’s count |
Naubaur’s Chamber |
Table 3. Table shows the variation in Hb% due to the administration of various formulations at different durations in experimental rats.
|
Parameter (Unit) Groups |
7 Days 14 Days 21 Days |
|
Normal |
14.21 + 0.45 14.19 + 0.18 14.5 + 0.46 |
|
Standard |
11.65 + 0.42 12.2 + 0.34 13.22 + 0.39* |
|
F1 Haemoglobin (gm/dl) F2 |
11.73 + 0.42 13.11 + 0.17 14.2 + 0.19* 10.06 + 0.30 11.54 + 0.39 13.15 + 0.22* |
|
F3 |
10.47 + 0.30 11.17 + 0.34 11.91 + 0.17* |
|
Experimental |
9.53 + 0.39 10.70 + 0.38 11.44 + 0.48 |
Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6. (*P<0.01)
|
Table 4. Table shows the variation in TLC due to the administration of various formulations at different durations in experimental rats. |
|||
|
Parameter Groups (Unit) |
7 Days |
14 Days |
21 Days |
|
Normal |
14783.3 + 348.8 |
14983.3 + 279.3 |
14583.3 + 371.0 |
|
Standard |
24683.3 + 511.5 |
20383.3 + 1192.2 |
15733.3 + 216.0* |
|
F1 |
24066.6 + 588.7 |
19500.0 + 254.3 |
15050.0+ 87.0* |
|
TLC (/cmm) |
|||
|
F2 |
26133.3 + 531.6 |
22083.3 + 211.4 |
18150.0 + 273.8* |
|
F3 |
27883.3 + 808.5 |
24950.0 + 221.7 |
21150.0 + 273.8* |
|
Experimental |
27266.6 + 1412.3 |
25800.0 + 326.6 |
22850.0 + 288.0 |
|
Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6. (*P<0.01) |
|||
|
Table 5. Table shows the variation in |
ESR due to the administration of various formulations at different durations in |
||
|
experimental rats. |
|||
|
Parameter (Unit) Groups |
7 Days |
14 Days |
21 Days |
|
Normal |
1.16 + 0.40 |
1.33 + 0.51 |
1.16 + 0.40 |
|
Standard |
19.5 + 1.04 |
11.6 + 1.03 |
7.33 + 0.81* |
|
F1 |
17.5 + 1.04 |
10.3 + 0.75 |
4.16 + 0.75* |
|
ESR (mm after 01 hour) |
|||
|
F2 |
19.5 + 1.04 |
15.0 + 0.89 |
9.83 + 0.75* |
|
F3 |
21.0 + 0.89 |
17.0 + 0.89 |
11.8 + 0.75* |
|
Experimental 27.8 + 1.47 |
22.3 + 1.21 |
14.5 + 1.04 |
|
|
Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6. (*P<0.01) |
|||
|
Table 6. Table shows the variation in |
PLT due to the administration of various formulations at different durations in |
||
|
experimental rats. |
|||
|
Parameter (Unit) Groups |
7 Days |
14 Days |
21 Days |
|
Normal |
8.45 + 0.23 |
8.41 + 0.13 |
8.55 + 0.24 |
|
Standard |
5.8 + 0.14 |
6.36 + 0.20 |
7.66 + 0.21* |
|
F1 |
6.48 + 0.23 |
6.98 + 0.14 |
8.08 + 0.24* |
|
PLT (Lakhs/cmm) |
|||
|
F2 |
5.56 + 0.17 |
6.05 + 0.10 |
7.07 + 0.19* |
|
F3 |
5.15 + 0.10 |
5.66 + 0.12 |
6.70 + 0.14* |
|
Experimental 4.75 + 0.24 |
5.05 + 0.18 |
6.33 + 0.13 |
|
|
Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6. (*P<0.01) |
|||
|
Table 7. Table shows the variation in |
PCV due to the administration of various formulations at different durations in |
||
|
experimental rats. |
|||
|
Parameter (Unit) Groups |
7 Days |
14 Days |
21 Days |
|
Normal |
43.33 + 1.21 |
43.33 + 1.63 |
43.50 + 1.04 |
|
Standard |
28.16 + 1.17 |
33.16 + 0.75 |
38.16 + 0.75* |
|
F1 |
32.16 + 0.75 |
35.8 + 1.16 |
42.5 + 1.04* |
|
PCV (%) |
|||
|
F2 |
27.83 + 1.83 |
31.0 + 0.89 |
37.0 + 0.89* |
|
F3 |
25.66 + 1.5 |
27.83 + 0.75 |
34.83 + 0.75* |
|
Experimental |
20.5 + 1.04 |
23.0 + 0.89 |
30.33 + 0.81 |
|
Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6. (*P<0.01) |
|||
Table 8. Table shows the variation in neutrophil% due to the administration of various formulations at different durations in experimental rats.
|
Parameter (Unit) |
Groups 7 Days 14 Days 21 Days |
|
Neutrophil (%) |
Normal 33.66 + 1.12 34.16 + 0.75 35.5 + 1.04 Standard 55.50 + 1.04 45.83 + 1.16 41.0 + 0.89* F1 50.83 + 0.75 42.00 + 0.89 35.5 + 1.04* F2 60.83 + 0.75 53.0 + 0.89 44.5 + 1.04* F3 64.0 + 1.50 57.5 + 1.87 48.33 + 0.89* Experimental 71.33 + 1.21 64.83 + 1.16 53.0 + 0.89 |
Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6. (*P<0.01)
Table 9. Table shows the variation in lymphocyte percentage due to the administration of various formulations at different durations in experimental rats.
|
Parameter (Unit) |
Groups 7 Days 14 Days 21 Days |
|
Lymphocyte (%) |
Normal 61.33 + 1.12 60.53 + 0.75 59.5 + 1.04 Standard 39.5 + 1.04 49.16 + 1.16 54.0 + 0.89* F1 44.16 + 0.75 53.0 + 0.89 59.5 + 1.04* F2 34.16 + 0.75 42.0 + 0.89 45.5 + 1.04* F3 31.0 + 1.15 37.5 + 1.87 46.66 + 0.89* Experimental 23.66 + 1.21 30.16 + 1.16 42.0 + 0.89 |
Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6. (*P<0.01)
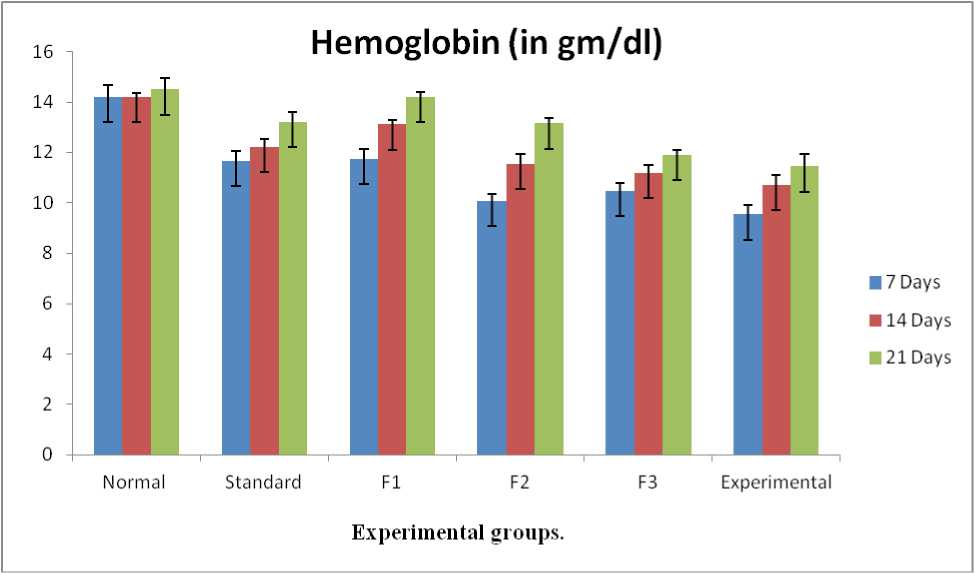
Figure 1: Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6
TLC{in /Cubic mm)
■ 7 Days
■ 14 Days
21 Days
Figure 2: Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6
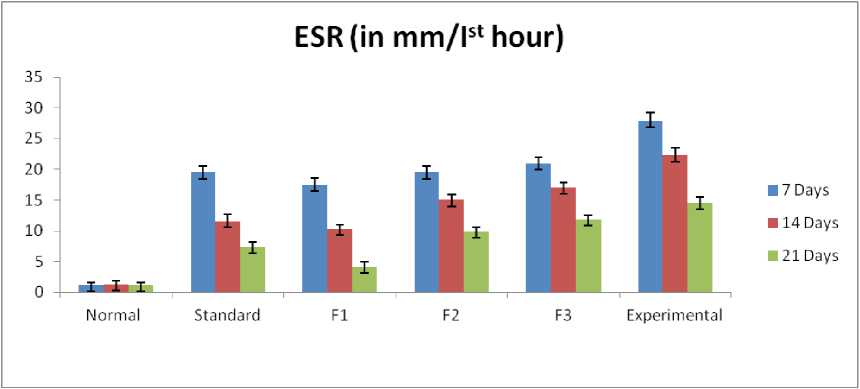
Figure 3: Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6
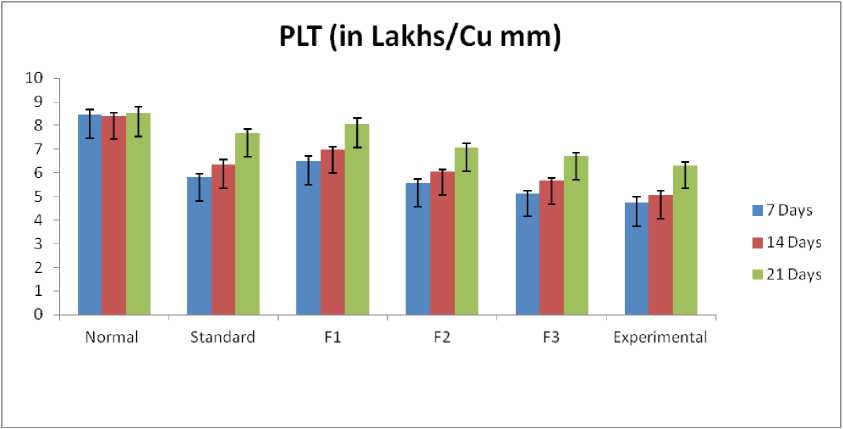
Figure 4: Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6
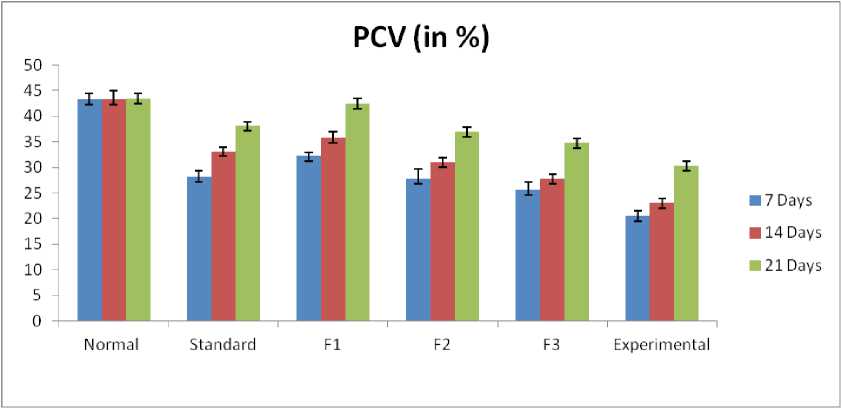
Figure 5: Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6
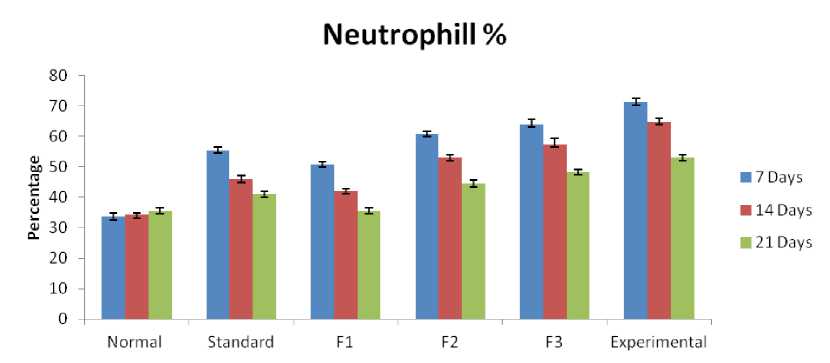
Figure 6: Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6
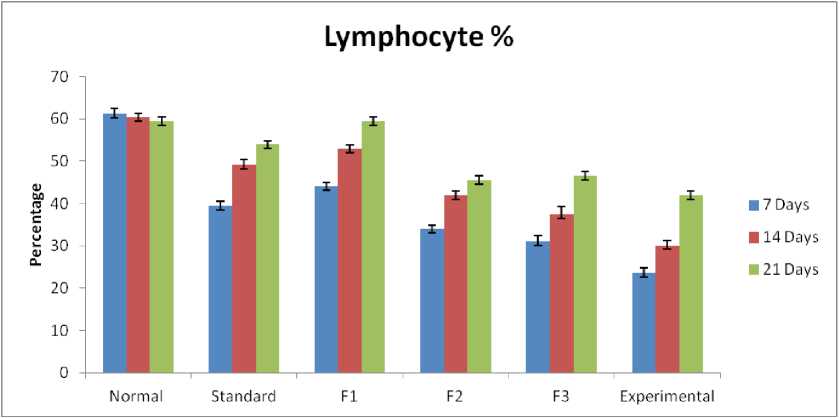
Figure 7: Values are expressed as Mean + SD, where N=6
DISCUSSION
In the present study, we are working on the effect of three different multiherbal formulations (F-I, F-II, and F-III) on the hepatotoxicity induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl 4 ). To evaluate the effect of these formulations, we were using some hematological parameters, as mentioned in previous chapters. We also used a standard drug (Sylimarin) along with these formulations, which are used worldwide for the treatment of liver damage, compression, or CCl 4 toxicity.
Hemoglobin (Hb):
Hemoglobin is a protein found in the blood. It carries oxygen to the different organs of the body. It contains iron (Fe) at the center of its structure and globin protein. Due to its presence, the color of blood is red. At the beginning, when hepatotoxicity was induced, we examined the hemoglobin levels of the rats in different groups, as mentioned in the plan of work. We found that, due to CCl4 toxicity, the Hb level decreased gradually, and after treatment, it seemed to be normal for F-I and the standard drug. It was also found that the Hb level is also increased by F-II and F-III, but formulation-I showed a greater effect on the reduced Hb level than the other two formulations due to the presence of various chemical constituents found in plants like Viz: antioxiants, alkaloids, etc. Various previous workers have reported medicinal plants in this formulation possessing properties to overcome hepatotoxicity. Chattopadhyay et al. suggested that Curcuma longa has properties to help with the recovery from anemia. It may be due to the antioxidant properties of its chemical constituents, like curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin (Chattopadhyay et al., 2004). However, Samson et al. reported that Allium sativum can be used in the treatment of hematological defects like anemia (Samson et al., 2012). It may be due to the presence of its active constituents like alicin, alliin, ajoene, etc. Moreover, Das et al. reported that the tulsi can be useful as an immunobooster, and it can also increase the RBC count as well as hemoglobin (Das et al., 2015). It may be due to the presence of its active chemical constituents like oleanolic acid, ursolic acid, rosmarinic acid, eugenol, carvacrol, linalool, and β-caryophyllene. aiswal et al. reported that the rats were treated with Phyllanthus emblica for sixty consecutive days. There was an alteration in various hematological parameters, viz. hemoglobin concentration and total erythrocyte count, and biochemical parameters like blood urea nitrogen, serum aspartate transaminase, and serum alanine transaminase, reflecting that Phyllanthus emblica L. protected the hematological, renal, and hepatic systems of Wistar rats from lead toxicity (Jaiswal and Qureshi, 2010). It may be due to the presence of the active constituents present in Phyllanthus emblica, like punicafolin and phyllanemblin A, as well as other polyphenols such as flavonoids, kaempferol, ellagic acid, and gallic acid. Uduwamai et al. also reported that the methanol leaf extract of S. nigrum possesses anti-anemic potential, and this may be attributed to the phytochemicals, antioxidant vitamins such as folic acid and vitamin C, and minerals such as iron, zinc, and calcium (Uduwamai et al., 2017). In the present study, all of the above-mentioned herbs were used to overcome hepatotoxicity.
Total leucocytes count (TLC):
Leukocytes, or white blood cells (WBCs), are part of the immune system of our body. There are five types of WBCs (neutrophil, lymphocyte, eosinophil, monocyte, and basophil) in blood. The total leukocyte count test measures the total amount of all the eukocytes in the blood. Blood is made up of different types of cells suspended in a fluid called plasma. These include erythrocytes, or red blood cells; leukocytes, or white blood cells; and platelets. Blood cells are produced by the hematopoietic cells in bone marrow and are then released into circulation. RBCs carry oxygen to the tissues, platelets help in blood clotting at a site of injury, and leukocytes form a part of the immune system of the body. WBCs are of five primary types: neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are further divided into three types: B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, and natural killer (NK) cells. Neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils are collectively called granulocytes since they contain granules in the cytoplasm. Depending on various factors like age, gender, health condition, environmental factors, etc., varying amounts of different types of WBCs circulate in the blood. The bone marrow increases the production of WBCs in response to an infection or inflammation anywhere in the body. These WBCs are called to the site by a series of chemical signals, where they work to treat the condition. During this time, the total leukocyte count remains high in the blood. Once the infection or inflammation subsides, WBC production by the bone marrow decreases, and the WBC count in circulation falls back to normal levels. A continuously elevated WBC count may thus be an indication of a chronic condition that is not resolving naturally and might need urgent attention. Apart from an infection or inflammation, the WBC count in the blood can also be affected by other conditions like disorders of the immune system, autoimmune conditions, cancer, etc. The WBC count may be higher or lower than normal in these cases. A WBC count test serves as an indication of a condition affecting the body. Further tests are performed to confirm a particular condition and direct treatment. TLC was elevated at the initial stage of the experiment in all groups, but after treatment with the herbal formulations, the TLC was reduced by all the formulations and standard Formulation- I look better than others according to the final results; this may be due to the combination of various medicinal herbs in this formulation, as they possess various medicinal properties like antioxidant, antimicrobial, immunobooster, etc., as reported by various previous workers. According to Khakpour et al., their experimental results suggested that the extract of turmeric rhizome normalized the red blood cell counts, white blood cell count, hematocrit, and percentage of neutrophils and monocytes. It may be due to the antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of the chemical constituents present in it (Khakpour et al., 2017). Whereas Mirabeau and Samson reported that Allium sativum and Allium cepa have immune-boosting properties, they can significantly normalize the WBC count and their percentage (Mirabeau and Samson, 2012). Das R. et al. reported that the tulsi can be useful as an immunobooster and can also improve WBC count as well as their percentage (Das et al., 2015). It may be due to the presence of its active chemical constituents like oleanolic acid, ursolic acid, rosmarinic acid, eugenol, carvacrol, linalool, and β-caryophyllene. However, according to Kapoor et al., amla showed a significant improvement in endothelial function as well as a reduction in biomarkers of oxidative stress. Also, the results suggest that amla intake may increase plasma antioxidant potential and decrease oxidative stress, which can help promote oxidative homeostasis. All of these benefits are possible without influencing hepatic or renal function or diabetic indices in healthy humans. Lastly, the results from this human clinical study conclusively established that amla has an acceptable sensory and safety profile while providing enormous potential for the management of a healthy lifestyle. Due to its powerful antioxidant properties, amla has the ability to decrease the elevated WBC count (Kapoor et al., 2020). Rahim et al. reported that the rats exposed to CdCl2 induced remarkable changes in body weight gain, feed efficiency, Hb, Hct, RBC, and WBC counts, and MCHC. After treatment with Solanum nigrum extract, these hematological parameters tend to be normal (Rahim et al., 2014).
Differential leucocytes count (DLC):
In differential leucocyte count, we measure the percentage of five different types of WBC (neutrophils, lymphocytes, eosinophils, monocytes, and basophils). They play different roles in immune reactions. For example, in acute infection or toxicity, the percentage of neutrophils is increased, while lymphocyte counts also increase in chronic infection. The eosinophil count normally increases in allergic reactions, parasitic infections, etc. The percentage of every type of WBC varies from species to species. In humans, normally neutrophils are found more than other kinds of WBC, but we observed during experimental work that the rats have a higher lymphocyte percentage than neutrophils. In the present study, when toxicity was induced, the neutrophil count and percentage were raised in every group. All the formulations show the ability to reduce the increase in neutrophil count, but the final result suggests that formulation I has a greater effect on reducing the increase in neurophil count than other formulations (II and III). The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of C. longa extract and its constituent curcumin in an animal model promote a decrease in the elevated neutrophil count (Shakeri et al., 2014). Shrivastava and Pathak. reported that the prophylactic efficacy of garlic (Allium sativum Linn) (Alliaceae) extract was studied on changes in the WBC differential count pattern in female albino rats. The rats were divided into four groups: A, B, C, and D, keeping group A as a healthy control. The garlic extract was tried in three different doses (1 ml, 2 ml, and 4 ml/kg body weight) as low, medium, and high doses, respectively, and given orally for the period of 7, 14, 21, or 28 days daily to the rats of groups B, C, and D, as stated above. The results clearly indicate a significant increase (P<0.01) in lymphocyte and eosinophil percent and a significant decrease (P<0.01) in neutrophil and monocyte percent at low and medium doses, but at higher doses their percentage increases within the normal values. This investigation indicates not only the benefits and drawbacks of raw garlic but also its uses in the regulation of certain parameters for the wellbeing of individuals (Shrivastava and Pathak, 2012). Ocimum sanctum, tulsi have the immune booster property, due to which they have the ability to decrease the elevated neutrophil count (Mukharjee and Ram, 2005). According to antan et al., Phyllanthus species have immunomodulatory activity due to the presence of their bioactive constituents like phyllanthin, hypophyllanthin, gallic acid, niranthin, ellagic acid, geraniin, corilagin, etc. (Jantan et al., 2019). The presence of vitamin C also boosts the immune power of animals. Aduwamia et al. suggested Solanum nigrum has the ability to decrease elevated neutrophils, and this may be attributed to phytochemicals, antioxidant vitamins such as folic acid and vitamin C, and minerals such as iron, zinc, and calcium present in it (Uduwamai et al., 2017).
Platelets count (PLT):
Platelets are the tiny, particle-like structures present in the blood. They play an important role in the bloodclotting mechanism. PLT counts are decreasing in some infections, like dengue, and also in patients with liver disease. In the present study, the PLT count was reduced in all the groups after CCL4-induced hepatotoxicity, and after treatment with various herbal formulations and standard drugs, the PLT count seemed to increase. But final results suggested that Formulation-I provides better support to increase the reduced PLT count than the other two formulations (F-II and F-III) due to their phytochemical contents. Manasha et al. suggested that many plants have been recognized to have medicinal properties and beneficial impacts on health; for example, turmeric has antioxidant activity, digestive stimulation action, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, hypolipidemic, and anticarcinogenic potential. It also affects thrombocytopenia, a common and complex bleeding disorder. When the platelet count decreases below 150,000/µl, it causes thrombocytopenia. This bleeding disorder is observed in 2.5% of the normal population. The risk of spontaneous mucocutaneous bleeding and life-threatening intracranial hemorrhage or gastrointestinal bleeding increases rapidly when the platelet count decreases below 10,000/µl. Due to the active chemical constituents like curcumin in Curcuma longa, it is able to cure the liver and improve platelet count (Manasha et al., 2016). Shrivastava et al. suggested that garlic has been used for more than 4000 years in traditional medicine against a variety of conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and infections. Claims of its healing properties are being confirmed by various scientific studies. Garlic's value in preventing cardiovascular disease has been acclaimed by several researchers. It also provides protection against cancer, as reported by experimental data on animals and some epidemiological studies. As a natural antibiotic, it has been found effective against several microorganisms, and due to these properties, it also seems to be useful in thrombocytopenia due to the presence of its active chemical constituent, ajoene (Shrivastava et al., 1995). Sundaramurthi et al. suggested that tulsi is an erect, sweet, scented pubescent herb, 30–100 cm tall. Tulsi is often enjoyed as a simple herbal tea and is frequently blended with other herbs and spices for various medicinal and culinary purposes. A variety of biologically active compounds, such as ursolic acid, apigenin, and luteolin, have been isolated from the leaves. Phytochemical compounds in leaves include eugenol (volatile oil), ursolic acid (triterpenoid), and rosmarinic acid
(phenylpropanoid). Other active compounds include caryphyllene and oleanolic acid. Seeds contain linoleic acid and linolenic acid. Nutritional components include vitamins A and C, the minerals calcium, iron, and zinc, as well as chlorophyll. Tannins, alkaloids, glycosides, and saponins are abundant in Tulsi. The main properties of Ocimum sanctum are that it lowers blood sugar levels, is antispasmodic and analgesic, and lowers blood pressure. Tulsi leaves have antiinflammatory, anabolic hypoglycemic, cardiac depressant, antifertility, antiulcer, antidiabetic, anticancer, antioxidant, antistress, immunostimulant, smooth muscle relaxant, adaptogenic, and immune modulator properties. Due to the presence of ursolic acid-like constituents, it is very useful in hepatic diseases. And due to their hepatoprotective nature, they seem to be useful in thrombocytopenia due to liver damage (Sundaramurthi et al., 2012). The fruits of amla are a rich source of vitamin C and are of dietary and culinary use in India. In the traditional system of medicine, amla is used to treat a variety of ailments such as anemia, hyperacidity, diarrhea, eye inflammation, leucorrhea, jaundice, nervine debility, liver complaints, cough, and anomalies of urine. Scientific studies have shown that amla possesses antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antidiabetic, hypolipidemic, antiulcerogenic, free radical scavenging, antioxidant, antimutagenic, antiinflammatory, immunomodulatory, antipyretic, analgesic, antitussive, antiatherogenic, adaptogenic, snake venom neutralizing, gastroprotective, antianemia, antihypercholesterolemia, wound healing, antidiarrheal, antiatherosclerotic, nephroprotective, neuroprotective, and hepatoprotective properties. Due to various properties, the fruit of amla is able to recover from platelet deficiency due to liver damage (Balinga et al., 2019). Oxidative stress due to the formation of free radicals was identified as one of the mechanisms underlying ethanol-induced toxicity. Chronic alcohol intake generates excess production of free radicals where the antioxidant defenses are impaired, which results in the sequential degradation of cell membranes by a process known as lipid peroxidation. In line with our findings, this process may destroy the integrity of the membranes both within and surrounding the cells, seriously compromising cell function. Researchers have demonstrated that chronic alcohol consumption induces lipid peroxidation in rats and that the degree of lipid peroxidation is related to the extent of liver injury. An increased level of lipid peroxidative markers, such as TBARS, in the circulation and tissues of alcoholic rats when compared to controls has been observed. On the other hand, treatment with SNFEt and silymarin causes a significant decline in the levels of lipid peroxidation products to near normal. This protective effect is probably based on the antioxidant activity of the extract, which reduces oxidative damage by blocking the production of free radicals and inhibiting lipid peroxidation. It has also been reported that the Solanum nigrum extract inhibits the progress of lipid peroxidation in CCl4-administered rats (Arumozhi et al., 2010). Due to the antioxidant properties of S. nigrum, it has the ability to reduce oxidative stress and promote the health of the liver, thereby normalizing the reduced platelet count.
Pack cell volume (PCV):
Packed cell volume is also known as hematocrite (HCT). The PCV usually decreases in the deficiency of hemoglobin and in infections, which may cause a reduction in the size of RBCs (microcytic RBCs). In the present study, PCV levels were also decreased after hepatotoxicity induction. And results suggested that the F-I formulation is a much better healer than the other two herbal formulations (F-II and F-III). Sharma et al. reported that the effect of AFB1 (Aflatoxin B1) on Hb content was similar to its action on TEC (total erythrocyte count) and TLC. After administration of AFB1, Hb content was lowered (p<0.001), as compared to the control group. Oral administration of low and high doses of Curcuma longa and Curcumin to mice raised Hb content as compared to the control group. Mice, when administered with low and high doses of Curcuma longa and Curcumin, along with AFB1, showed protective effects in comparison to the AFB1-treated group. In the case of PCV, AFB1 exposure produced an insignificant decline in the PCV of mice as compared to the control group. Administration of low and high doses of Curcuma longa and Curcumin showed a significant increase in PCV content (p<0.001) as compared to the control group. Treatment of mice with low and high doses of Curcuma longa and Curcumin, along with
AFB1, also showed a significant (p<0.001) increase in PCV% as compared to the AFB1-treated group. In mice treated with AFB1, the average PLTC count was lower after 45 days when compared to the control group. Administration of low dose and high dose of Curcuma longa and Curcumin to animals showed improved PLTC count as compared to the control group, and when mice were treated with low dose and high dose of Curcuma longa and Curcumin, along with AFB1, they showed increased values of PLTC (p > 0.05), (p<0.001), (p<0.02), and (p<0.001) in groups VII and X, respectively, when compared to the AFB1-treated group (Sharma et al,. 2011). Similarly, garlic aiso plays a significant role in the recoupment of hepatic damage. Ajayi et al. reported that results confirm that administration of lead in rats caused some level of liver or hepatic damage in the animals, and post-lead treatment with A. sativum (garlic) and vitamin C also had some hepatoprotective and hematological effects on these rats. Moreover, efforts are currently underway to look at the effect of increasing the post-treatment period in rats. Administration of lead significantly increased (p < 0.05) the percentage (%) PCV by 21.1% and non-significantly decreased (p < 0.05) the percentage (%) Hb by 10.4% compared to the control. However, treatment with A. sativum produced a significant decrease (p <0.05) in PCV by 30.0% and a non-significant increase (p <0.05) in Hb by 16.3% in the post-lead-treated rats compared to the lead-treated rats. The treatment with vitamin C produced a significant decrease (p < 0.05) in PCV and Hb by 41.4 and 30.0%, respectively, compared to the lead-treated rats. It was found that the values of PCV and Hb were further significantly lowered (p < 0.05) by 29.2 and 37.3%, respectively, in vitamin C-treated rats, and the PCV value was non-significantly lowered (p < 0.05) by 15.2% in A. sativum-treated rats compared to the control (Ajayi et al., 2009). Certain natural antioxidants like turmeric and tulsi are also affected, as Swathi et al. reported that heat stress reduced the performance as well as had an adverse effect on hematological constituents in broilers. The herbals, turmeric followed by tulsi at either dose as sole supplements, improved the body weights, feed efficiency, and Hb, RBC, and PCV values and lowered the WBC count in heat-stressed birds. They were comparable to the results obtained with the supplementation of vitamin E and its combination with Se. However, no synergistic effect of the combination of herbals was observed on broiler performance or hematological attributes. Hence, it could be concluded that dietary natural antioxidants Turmeric and Tulsi supplemented at 0.2 and 0.25% were effective in improving broiler performance and hematological parameters during heat stress (Swathi et al., 2012). Sarvaiya et al. reported that 28 days of repeated oral administration of aqueous and alcoholic extracts of P. emblica fruits at 200 and 400 mg/kg body weight produced an anti-gout effect in rats in a dose-dependent manner. Finally, they suggested that P. emblica has the potential to improve the PCV and have newer therapeutic applications in the future (Sarvaiya et al., 2015). Whereas Uduwamai et al. suggested that the results obtained from their study indicate that the methanol leaf extract of S. nigrum possesses anti-anemic potential, and this may be attributed to the phytochemicals, antioxidant vitamins such as folic acid and vitamin C, and minerals such as iron, zinc, and calcium content of S. nigrum leaf. It, therefore, supports the therapeutic use of the plant in traditional medicine for the treatment of anemia. It is further reported that Solanum nigrum has the ability to recoup the PCV after anemia induced by phenylhydrazine (Uduwamai et al., 2017). Similar results were observed in the present study, in which all the above-mentioned herbs were used in the same ratio to overcome hepatic toxicity.
Erythrocytes sedimentation rate (ESR):
ESR is the test that is used to detect mainly inflammation in the inner organs of the body. It is also increased by different kinds of infections. In the present study, the ESR level increased after hepatotoxicity was induced in each group. After the treatment of each group, the ESR level returns to normal in the F-I and standard drug groups. It is also reported that F-II and F-III also have the ability to reduce the elevated ESR level but F-I has a greater ability to reduce the elevated ESR level than F-II and F-III due to its herbal combination. Lal et al. describe the clinical efficacy of curcumin, the active constituent of the rhizomes of Curcuma longa, in the treatment of patients suffering from idiopathic inflammatory orbital pseudotumors. Curcumin was administered orally at a dose of 375 mg three times per day for a period of 6–22 months in eight patients. They were followed up for a period of 2 years at 3 monthly intervals. Five patients completed the study, of whom four recovered completely. In one patient, the swelling regressed completely, but some limitations of movement persisted. No side effect was noted in any patient, and there was no recurrence. It is suggested that curcumin could be used as a safe and effective drug in the treatment of idiopathic inflammatory orbital pseudotumors (Lal et al., 2000). As it possesses antioxidant properties, Singh et al. reported that, in this meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (RCTs), they found that garlic supplementation reduced serum concentrations of CRP, TNF, and IL-6 but did not affect serum adiponectin and leptin in adults. More RCTs are needed to test the effects of garlic supplementation on inflammation (Mofrad et al., 2019). Allium sativum has anti-inflammatory properties; therefore, it has the ability to decrease ESR. Similarly, Singh and Majumdar reported that Ocimum sanctum fixed oil and linolenic acid were found to possess significant antiinflammatory activity against PGE2, leukotriene, and arachidonic acid-induced paw edema. Plant lipids like linseed oil and soyabean oil containing linolenic acid, when tested along with O. sanctum fixed oil, also showed significant inhibition of carrageenan-induced paw edema. The results suggest that linolenic acid present in O. sanctum fixed oil has the capacity to block both the cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase pathways of arachidonate metabolism and could be responsible for the antiinflammatory activity of the oil (Singh and Majumdar, 1997). Dang et al. studied various plants, viz., Phyllanthus emblica (Pe), Plumbago zeylanica (Pz), and Cyperus rotundus (Cr), plants from the medohara group of Ayurveda that possess antiatherosclerotic activity. As inflammation is also one of the pathophysiological factors, it was of interest to evaluate whether these drugs exhibit any antiinflammatory activity. Two models of acute inflammation, namely carrageenan-induced rat paw edema and acetic acid-induced peritonitis in mice, were used. In the model of carrageenan-induced paw edema, Pe, Pz, and Cr showed a trend to reduce the edema, while the combination of Pe and Pz (PI: 20.64%) showed results comparable to aspirin (23.74%). Whereas in a model of acetic acid-induced peritonitis, all the plant drugs, i.e., Pe, Pz, Cr, and a combination of Pe and Pz, showed a significant decrease in the protein content of the peritoneal exudates compared with the disease control group (p < 0.05); however, only Pe and Pz exhibited activity comparable to aspirin (Dang et al., 2011). Even Solanum nigrum possesses anti-inflammatory action, as Ravi et al. reported in the anti-inflammatory activity of the methanolic extract of the berries of Solanum nigrum Linn. in rats. The medicinal values of the berries of Solanum nigrum (black night shades) have been mentioned in ancient literature as useful in disorders of inflammation. The effect of methanolic extracts of the berries of Solanum nigrum was studied on carrageenan-induced paw edema. The methanolic extract of Solanum nigrum (375 mg/kg b.w.) has shown significant antiinflammatory effects (Ravi et al., 2009). All the abovementioned herbs were used in herbal formulations in the present study. On the basis of various medicinal properties and phytochemical constituents, it has been established that the herbal formulation (F-I) is a good hepatoprotective drug.
CONCLUSION
The objective of this study was to find out which of the three polyherbal formulations might most effectively reverse the hematological alterations caused by carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity, and we found that Formulation-I has the ability to reverse the hematological changes much better than the other two formulations. Hematological parameters like TLC, ESR, and neutrophil% were elevated due to CCl 4 -induced heptotoxicity, and after treatment, they were recouped to normal by the treatment of formulation-I. On the other hand, the decreased Hb, PCV, PLT count, and lymphocyte% were increased to be normal. It was thus concluded in the present study that formulation-provides better protection against CCl 4 toxicity than formulation-II and formulation-III.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We would like to thank the HOD, Department of Zoology, Bundelkhand University Campus, for providing experimental facilities to my guide, Dr. Kusum Singh, for guiding me. This research received no particular grant from any financial body.
AUTHOR’S CONTRIBUTIONS
The present research work was designed by Dr. Shekhar Kumar Sinoriya. The experiment was performed by Dr. Shekhar Kumar Sinoriya under the supervision of Dr. Kusum Singh.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Variations in hematological parameters during the treatment of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity with three different polyherbal formulations
- Ajayi G.O., Adeniyl T.T. and Babayemi D.O., (2009). Hepatoprotective and some haematological effects of Allium sativum and vitamin C in lead-exposed Wistar rats, International Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, 1(3), 064-067.
- Arumozhi V., Krishnaveni M. and Kathishwaran K., Dhamodharan G. and Mirunalini S. (2010). Antioxidant and antihyperlipidemic effect of Solanum nigrum fruit extract on the experimental model against chronic ethanol toxicity, Parmacogn Mag. 6(21), 42-50.
- Baliga M.S., Shivashankara R.A., Thilakchand K.R., Baliga-Rao M.P., Palatty P.L., George T. and Rao S. (2019). Hepatoprotective Effects of the Indian Gooseberry (Emblica officinalis Gaertn): a revisit, Ronald Ross Watson, Victor R. Preedy, Dietary Interventions in Liver Disease. Academic Press. 193-201.
- Chattopadhyay, I., Biswas, K., Bandyopadhyay, U., & Banerjee, R. K. (2004). Turmeric and curcumin: Biological actions and medicinal applications. Current science, 44-53.
- Dang G.K., Parekar R.R., Kamat S.K., Scindia A.M. and Rege N.N. (2011). Antiinflammatory activity of Phyllanthus emblica, Plumbago zeylanica and Cyperus rotundus in acute models of inflammation, Phytotherapy research. 25(6), 904-8.
- Das R., Reman R.P., Saha, H. and Singh R. (2015). Effect of Ocimum sanctum Linn. (Tulsi) extract on the immunity and survival of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila, Wiley online library, Aquaculture research. 46(5), 1111-1121.
- Jaiswal S.A. and Qureshi M.I. (2010). Effect of Phyllanthus emblica L. (Amla) on haematological and biochemical parameters in lead acetate induced toxicity in Wistar rats, Animal science reporter. 4(1), 22-26.
- Jantan, I., Haque, M. A., Ilangkovan, M., & Arshad, L. (2019). An insight into the modulatory effects and mechanisms of action of Phyllanthus species and their bioactive metabolites on the immune system. Frontiers in pharmacology, 10, 878.
- Kapoor, M. P., Suzuki, K., Derek, T., Ozeki, M., & Okubo, T. (2020). Clinical evaluation of Emblica officinalis Gatertn (Amla) in healthy human subjects: Health benefits and safety results from a randomized, double-blind, crossover placebo-controlled study. Contemporary clinical trials communications, 17, 100499.
- Khakpour S., Mirlohi S.M.J., Akhlaghdoust M., Koochak E., Aref N.M. and Masoodi H. (2017). The effect of Curcuma longa rhizome extract on blood cells of mice: an animal trial, Pharmacophore. 8(3), 19-23.
- Lal B., Kapoor A.K., Agarwal P.K., Asthana O.P. and Shrimal R.C. (2000). Role of curcumin in idiopathic inflammatory orbital pseudotumours, Phytotherapy research. 14(6), 443-7.
- Manasha K. Soumya R. and Vani, R. (2016). Phytochemicals as potential therapeutics for thrombocytopenia, Journal of thrombosis and thrombolysis. 41(3), 436-440.
- Mirabeau, T. Y., & Samson, E. S. (2012). Effect of Allium cepa and Allium sativum on some immunological cells in rats. African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines, 9(3), 374-379.
- Mofrad M.D., Milajerdi A., Koohdani F., Surkan P.J. and Azadbhakt L. (2019). Garlic Supplementation Reduces Circulating C-reactive protein, Tumor Necrosis Factor, and Interleukin-6 in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, The journal of nutrition. 149(4), 605-618.
- Mukharjee R. and Ram G.C. (2005) Immunotheraptic potential of Ocimum sanctum in bovine subclinical mastitis, Research in veterinary science. 79 (1), 3743.
- Rahim E.A.A., Mobdy Y.E.A., Ali R.F. and Mahmoud, H.A. (2014). Hepatoprotective effects of Solanum nigrum Linn fruits against cadmium chloride toxicity in albino rats, Biol Trace Elem res. 160(3), 400-408.
- Ravi V., Saleem T.S.M., Patel S.S., Raamamurthy J. and Gauthaman K. (2009). Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Methanolic Extract of Solanum nigrum Linn Berries, International Journal of Applied Research in Natural Products. 2(2), 33-36.
- Saba A.B., Oyagbemi A.A., and Azeez O.I. (2010). Amelioration of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity and haemotoxicity by aqueous leaf extract of Cnidoscolus aconitifolius in rats. Nig. J. Physiol. Sci. 25, 139 - 147.
- Samson E.S., Olasunkanmi A.K., Joel J.S. and Alfred E.F.(2012) Haematological and Hepatotoxic Potential of Onion (Allium cepa) and Garlic (Allium sativum) Extracts in Rats, Europian journal of medicinal plant, Vol.2(4).
- Sarvaiya, V. N., Sadariya, K. A., Pancha, P. G., Thaker, A. M., Patel, A. C., & Prajapati, A. S. (2015). Evaluation of antigout activity of Phyllanthus emblica fruit extracts on potassium oxonate-induced gout rat model. Veterinary world, 8(10), 1230.
- Shakeri F., Saukhtanloon M. and Boskabady M.H. (2017). The effect of hydro-ethanolic extract of Curcuma longa rhizome and curcumin on total and differential WBC and serum oxidant, antioxidant biomarkers in rat model of asthma, Iran J Basic Med Sci. 20 (2), 155-165.
- Sharma V., Sharma C. and Sharma S. (2011). Influence of Curcuma longa and curcumin on blood profile in mice subjected to Aflatoxin B1, International journal of pharmaceutical science and research. 2(7), 17401745.
- Srivastava, S., & Pathak, P. H. (2012). Effect of Garlic (Allium sativum) Extract in Pattern Of Differential Count Of WBC In Female Albino Rats. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research, 13(2), 83-86.
- Shrivastava S.K., Bordia K.C. and Verma A. (1995). Garlic (Allium sativum) for disease prevention, South African Journal of Science. 91 (2), 68-77.
- Singh S. and Majumdar D.K. (1997). Evaluation of antiinflammatory activity of fatty acids of Ocimum sanctum fixed oil, Indian Journal of Experimental Biology. 35(4), 380-383.
- Sundaramurthi, P., Dhandapani, S., Ponnusamy, S., & Subbaiyan, M. (2012). Effect of Tulsi (Ocimum sanctum) as a disinfectant for water treatment. Hitek Journal of Bio Sciences and Bioengineering, 1(1), 17.
- Swathi B., Gupta P.S.P. and Nagalakshmi D. (2012). Effect of tulsi (Occimum sanctum) and Turmeric (Curcuma longa) on broiler performance and blood constituents during heat stress in broilers, International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences. 3(3), 446-453.
- Uduwamai U.H., Abimbola, M.M. and Ahmed Z.H. (2017). Effect of Solanum nigrum Methanol Leaf Extract on Phenylhydrazine Induced Anemia in Rats, Jordan Journal of Biological Sciences. 11, 65-71.


