Взаимодействие кислородчувствительных механизмов в клетке
Автор: Ветош Александр Николаевич
Журнал: Ульяновский медико-биологический журнал @medbio-ulsu
Рубрика: Физиология
Статья в выпуске: 3, 2019 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Реакции организма человека на хроническую, острую или интервальную гипоксическую гипоксию различны и, возможно, запускаются отдельными внутриклеточными молекулярными механизмами. Для проверки этого предположения был проведен анализ литературных данных базы PubMed по ключевым словам «intracellular oxygen sensing». За период 1977-2019 гг. по данному вопросу было опубликовано почти 1000 работ, среди которых более 50 обзоров. Для анализа выбирались публикации, касающиеся молекулярной чувствительности к кислороду клеток тахитрофных тканей Metazoa, по преимуществу животных. Реакции клеток на хроническую гипоксию определяются HIF-пулом, локализованным в их цитоплазме. Кислородная чувствительность клеток к острой гипоксии обусловлена молекулярными механизмами при участии калиевых каналов плазматических клеточных мембран и ассоциированных с ними околомембранных комплексов. Молекулярные внутриклеточные реакции на интервальную гипоксию запускаются путем активизации прооксидантных процессов в митохондриях клеток. В данном обзоре обсуждаются особенности взаимодействия этих трех механизмов кислородной чувствительности клеток.
Кислород, калиевые каналы плазматических мембран, митохондрии, афк
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14116387
IDR: 14116387 | УДК: 612.26; | DOI: 10.34014/2227-1848-2019-3-52-62
Текст научной статьи Взаимодействие кислородчувствительных механизмов в клетке
Варьирование*временными параметрами предъявления человеку обедненных кислородом дыхательных газовых смесей ведет к тому, что в практике клинической и экспериментальной физиологии дыхания складываются представления о трех формах гипоксического воздействия. Это хроническая гипоксия, острая гипоксия и промежуточная, включающая черты обеих крайних форм, – интервальная гипоксия [1–3]. Длительное время применение этих трех подходов осуществлялось изолированно. Успехи молекулярной биологии и цитологии позволяют сегодня поставить вопрос о степени общности механизмов реагирования клеток на предъявление гипоксического стимула с разным временным масштабом и периодичностью. Молекулярную базу для анализа динамики внутриклеточных процессов в условиях гипоксии обеспечили работы Грега Семензы [4].
Хроническая гипоксия. Четверть века назад в терминологический обиход специалистов вошло понятие о внутриклеточном факторе, индуцированном гипоксией, – HIF. Было показано, что он имеется в цитоплазме всех клеток Metazoa [4]. Открытию HIF предшествовало многолетнее изучение роли эритропоэтина (Еро) в регуляции процессов кроветворения, завершившееся открытием Еро-гена, а затем и фактора цитоплазматической локализации, участвующего в процессах транскрипции этого гена [5, 6]. Более поздние исследования показали, что HIF инициирует запуск не одного, а множества генов в клетках млекопитающих на фоне снижения поступления кислорода в цитоплазму [7]. В условиях нормоксии, когда напряжение ки- слорода в клетке колеблется в диапазоне 20–7 мм рт. ст., конститутивно присутствующие в цитоплазме молекулы HIF подвержены протеолизу. При этом фактор ингибирования HIF, который назвали FIH, отщепляет от фактора, ингибируемого гипоксией, аспарагиновый фрагмент при участии 2-оксиглутарата, аскорбиновой кислоты и Fe++ [8, 9].
В процессе нормоксического протеолиза HIF участвуют также пролилгидроксилаза, белок супрессии опухоли фон Хиппел–Лин-дау и убиквитин. В итоге молекулы фактора, индуцированного гипоксией, попадают в протеосомы, где происходит их окончательная фрагментация [10].
Умеренное уменьшение напряжения кислорода в цитоплазме клетки изменяет катаболизм HIF. Пролилгидроксилаза перестает влиять на исход начального этапа деградации фактора. Промежуточные продукты метаболизма HIF-α и HIF-β теперь не доступны для протеосомальной деструкции [9, 10].
В условиях гипоксии начальные этапы протеолиза HIF становятся невозможными. При этом HIF-α и HIF-β вкупе с коактиватором транскрипции Р300/СВР оказываются в ядре клетки, где включают транскрипцию большого количества генов. Эти гены участвуют в формировании клеточного ответа на гипоксию [9, 10]. Транскрипционный каскад, запускаемый HIF, может активировать до 1500 генов [11, 12].
Скорость вовлечения клеток в реакции на гипоксию с участием HIF не высока. Ранние результаты перестройки внутриклеточного метаболизма в ответ на интрацеллюлярную гипоксию проявляются через час [13]. Максимальное значение экспрессии генов в условиях хронической внутриклеточной гипоксии наблюдается спустя 24 ч [10]. Мыши, нокаутированные по HIF, погибают на десятый день эмбрионального развития. Следовательно, HIF-зависимый механизм реагирования на действие хронической гипоксии востребован уже на пренатальном этапе индивидуального развития [14].
Уменьшение внутриклеточной концентрации кислорода затрагивает метаболизм около 200 кислородчувствительных белков, активирующих каскады посттрансляционных изменений других белков. Среди кислород- чувствительных белков выделяют гидроксилазы, из которых важнейшими являются про-лилгидроксилазы. Последние гидроксилируют аминокислоту пролин в различных белковых молекулах [15].
Часть молекулы пролилгидроксилазы (PHD), ассоциированная с трансляцией молекул HIF в цитоплазме на фоне клеточной нормоксии, перманентно гидроксилирует пролин α-субъединиц данной гетеродимерной молекулы. Это приводит к кислородзави-симой деградации HIF-α [13]. Следовательно, PHD играет роль ближайшего регулятора активности HIF [16]. Очевидно, что означенное распределение ролей между этими молекулами заставляет нас считать цитоплазматическим сенсором на кислород не HIF, а HIF-гидроксилазы, в т.ч. PHD [17].
Следовательно, у высших млекопитающих в цитоплазме клеток имеется кислородчувствительный метаболический пул (HIF-пул), включающий в себя субъединицы HIF-α и HIF-β. HIF-α имеет три вариации: HIF1-α, HIF2-α, HIF3-α. Первая из них экспрессируется во многих, если не во всех клетках млекопитающих, а вторая и третья присутствуют в некоторых видах эндотелия и соединительной ткани [18]. Помимо кислорода на молекулярные взаимоотношения в HIF-пуле влияют активные формы кислорода (АФК), NO, HSP90 и другие молекулы [19].
Таким образом, HIF-пул цитоплазмы клетки способен адекватно кооптировать многокомпонентный генетический ответ на предъявление продолжительного гипоксического стимула. Время реагирования этого пула велико и укладывается в диапазон от десятков минут до десятков часов.
Острая гипоксия. Молекулярные механизмы реагирования клеток на быстрое нарастание гипоксического стимула изучены в меньшей степени. Нобелевскую премию за обоснование роли хеморецепторов, чувствительных к содержанию кислорода и локализующихся в сонных артериях и аорте, Корнелу Хеймансу присудили еще в 1938 г. Однако молекулярные механизмы сенсорной трансдукции динамики напряжения кислорода в управляющие нервные импульсы еще 50 лет оставались неясными.
В 1988 г. Жозе Лопес-Барнео с сотрудниками опубликовал доказательства того, что большие кальцийзависимые калиевые каналы (BKCa) клеточных мембран чувствительны к уменьшению напряжения кислорода (по сравнению со значением внутриклеточной нормы), т.е. чувствительны к гипоксии [20]. Их сообщение тщательно проверялось, и к 1997 г. появился первый обзор данных по кислородной чувствительности мембранных ионных каналов этого класса, цитирующий 73 публикации [21]. Авторы обзора показали, что BK Ca перестают функционировать при понижении напряжения кислорода в около-мембранном пространстве до значений менее 20 мм рт. ст. Этот эффект устойчиво воспроизводился в широком спектре клеточных моделей (нейронов коры гиппокампа и черной субстанции, гладкомышечных клеток артериальных сосудов, клеток нейроэпителиальных тел в бифуркациях бронхов, клеток первого типа каротидных тел). Было сделано предположение, что и другие типы ионных каналов плазматических мембран, возможно, также подвергаются модулирующему влиянию со стороны молекул кислорода. В дальнейшем это подтвердилось.
Последующие попытки найти кислородный сенсор внутри молекулярной структуры калиевых каналов не увенчались успехом [22]. К этому времени была сформулирована система взаимосвязанных вопросов, ответы на которые не удавалось получить в экспериментах с изолированными калиевыми каналами. Как эти каналы могут работать длительное время без митохондриальной поддержки при регистрации их активности в режиме patch clamp? Являются ли BKCa кислородными сенсорами или они только эффекторное звено в реакции на гипоксию? Почему BKCa реагируют на уменьшение напряжения кислорода в околомембранном пространстве клетки очень быстро (за несколько секунд)?
В поисках ответов на эти и другие актуальные вопросы начали складываться зачатки так называемой «мембранной гипотезы» [23–25]. В соответствии с этой гипотезой существуют неизвестные пока белковые ансамбли, прямо или дистантно связанные с BK Ca и другими калиевыми каналами.
В дальнейшем экспериментально на клетках I типа каротидных тел крыс была показана тесная ассоциация молекулярной конструкции BKCa с белками гемоксигеназы-2 [26]. Последняя, преобразуя геминовые молекулы, продуцирует СО, биливердин и Fe++. В условиях внутриклеточной нормоксии в качестве кофакторов участвуют NADP(H) и молекулярный кислород. Монооксид углерода в условиях нормоксии выступает в роли активатора BK Ca [27].
При уменьшении напряжения кислорода в зоне вышеописанных молекулярных агрегатов тоническое влияние СО на ионные каналы ослабевает и их проводимость для ионов К+ снижается. Молекулы гемоксигеназы-2 играют, таким образом, в этом околомем-бранном молекулярном ансамбле роль кислородного сенсора.
Другие группы авторов сумели экспериментально обосновать ингибирующее влияние H 2 S в управлении BK Ca на фоне гипоксии в клетках I типа каротидных тел мышей, крыс и человека [28, 29]. Это привело к необходимости включить в «мембранную гипотезу», объясняющую влияние гипоксии на работу мембранных калиевых каналов, два внутриклеточных газотрансмиттера – СО и H2S [25].
Авторы «мембранной гипотезы» утверждают, что калиевые каналы являются эффекторным звеном сигнальной сети околомем-бранной локализации [22, 24, 25]. Чувствительными же к недостатку кислорода в клетке следует считать процессы взаимодействия ассоциированных с этими каналами белков, таких как гемоксигеназа-2, NADP(H), цистио-нин-гаммалиаза, гуанилатциклаза, циклический гуанозинмонофосфат и протеинкиназа G.
Уменьшение проводимости калиевых каналов при умеренной гипоксии и их закрытие по мере развития кислорододефицитных состояний нарушают динамику формирования мембранного потенциала клеток. Это относится и к гломусным клеткам каротидных тел. Как следствие, усиливается импульсация в соответствующей ветви языкоглоточного нерва, что ведет к увеличению вентиляции легких.
В реализации сенсорной трансдукции уровня кислорода в клетках с участием BKCa и некоторых других классов калиевых цито- плазматических каналов участвуют несколько внутриклеточных газовых трансмиттеров. Это монооксид углерода, активирующий функционирование калиевых каналов при нормоксии, сероводород, ингибирующий проводимость этих каналов при гипоксии, и, возможно, монооксид азота, чье действие сходно с влиянием СО [25, 30]. Такой сложный многокомпонентный механизм мембранной и околомембранной локализации обеспечивает оперативную клеточную реакцию на быстрые вариации экстра- и интра-целлюлярных концентраций кислорода. На основании этого механизма эволюционно сложилась система хеморецепции содержания О2 в крови на основе каротидных тел, оперативно обслуживающая многоклеточный организм в плане снабжения кислородом.
Интервальная гипоксия. Курсовая интервальная гипоксическая терапия занимает промежуточное место между хроническим и острым форматом предъявления гипоксического стимула. Поэтому можно ожидать появления попыток объяснить молекулярные внутриклеточные механизмы гипоксического терапевтического действия в интервальной форме как комбинацию активности HIF-пула и околомембранных процессов, связанных с активностью калиевых каналов. Действительно, такой подход намечен в нескольких главах известной монографии под редакцией T.V. Serebrovskaya и Lei Xi [3]. Несмотря на разнообразие исходных аналитических позиций, все авторы этой книги, рискнувшие затронуть вопрос о возможных молекулярных механизмах терапевтического действия недостатка кислорода в прерывистом режиме, сходятся во мнении, что существенную роль при этом играет прооксидантная система клетки на основе сигнальных функций АФК [31–33].
Убедительно доказано, что в условиях гипоксии митохондриями кардиомиоцитов и миоцитов стенок легочной артерии производятся избыточные количества АФК [34, 35]. В частности, ферментативный комплекс цепи окислительного фосфорилирования I генерирует чрезмерное количество супероксид-ани-он-радикалов, а комплекс III продуцирует в этих условиях сверхнормативное количество
Н 2 О 2 [36, 37]. Далее молекулы АФК выходят из митохондрий в цитозоль, где оказывают модулирующее влияние на один из важнейших компонентов HIF-пула – фермент про-лилгидроксилазу-2. По мнению G. Waypa et al. и их единомышленников, избыток АФК в этих условиях успевает частично денатурировать молекулы ферментов HIF-пула, что ведет к уменьшению их активности и прекращению гидролиза фактора, индуцируемого гипоксией [19].
Кроме того, избыток супероксид-анион-радикалов, денатурирующих цитоплазматические белки, может в соединении с оксидом азота генерировать очень активную форму азота – пероксинитрит [38]. И если вредоносное действие активных форм кислорода и азота носит умеренный характер, то клетки активируют цитоплазматический репаративный механизм на основе стрессовых белков или белков теплового шока (БТШ) [32, 39, 40]. Конститутивные БТШ осуществляют перманентную репарацию денатурированных внутриклеточных белковых агрегатов, а индуци-бельные, способные появиться в цитоплазме клеток в течение 30–200 мин после предъявления гипоксического стимула, восстанавливают денатурационные повреждения, нанесенные АФК и пероксинитритом [38, 39].
Таким образом, при умеренной интенсивности гипоксического стимула в рамках протокола интервальной гипоксии клетки способны активизировать конститутивные и индуцибельные репарационные механизмы HSP-пула в цитоплазме. Более интенсивные гипоксические воздействия включают около-мембранный пул калиевых каналов. При длительном курсовом применении интервальной гипоксии клетки используют HIF-пул запуска генетического ответа на гипоксию. Все вышеперечисленные молекулярные механизмы находятся в режиме взаимного влияния.
Внутриклеточная сигнализация при адаптации к гипоксии. Цитоплазматические, околомембранные и митохондриальные механизмы обеспечения кислородного гомеостазиса клетки, являясь активными сторонами цел-люлярного энергетического метаболизма, состоят в тесной сигнальной кооперации.
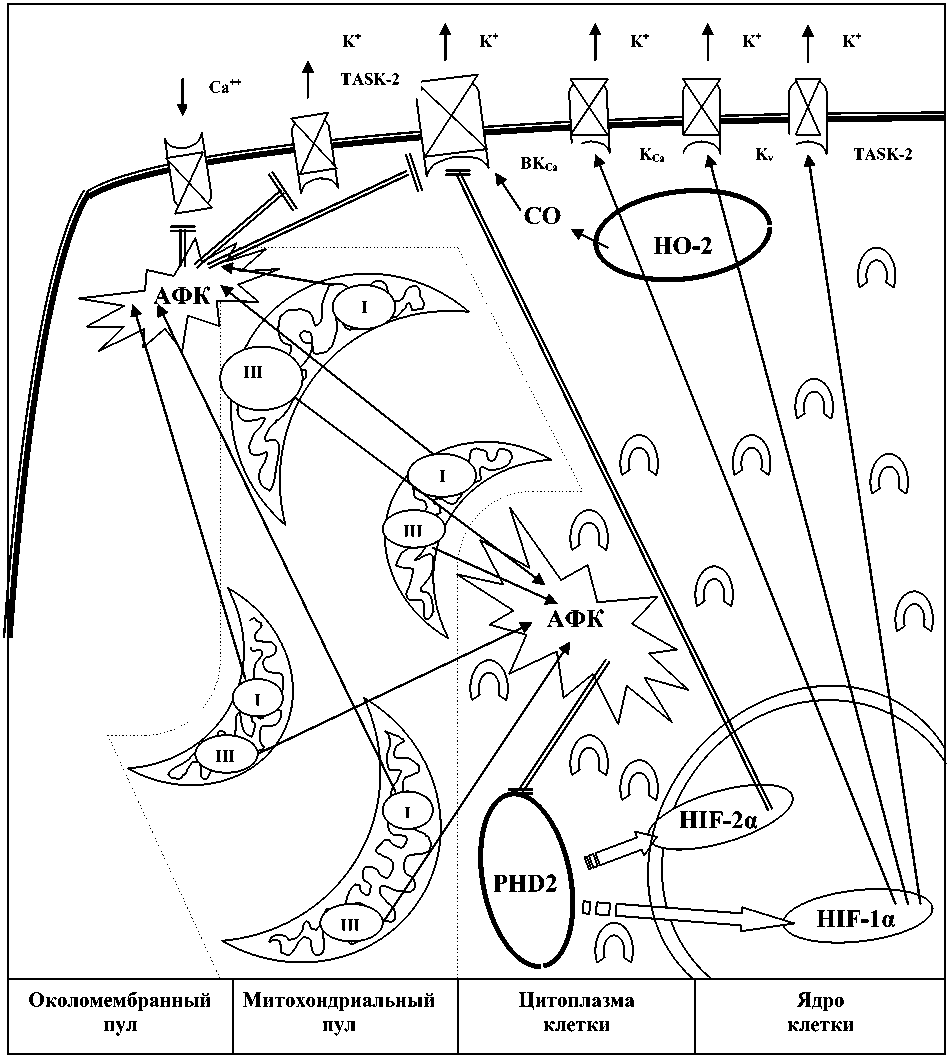
Рис. 1. Сигнальные отношения компонентов клеточного энергетического метаболизма: – мембранные ионные каналы;
и III – ферментативные комплексы I и III в цепи окислительного фосфорилирования митохондрий;
PHD2 – домен пролилгидроксилазы-2 (внутриклеточный сенсор на кислород);
НО-2 – домен гемоксигеназы-2 (внутриклеточный сенсор на кислород);
→ – активация; h – супрессия
Метаболический кластер цитоплазматических процессов, в которых мастером-регулятором является HIF, представлен на рис. 1. АФК, продуцируемые на фоне нормоксии, выходят из митохондрий, перемещаются в цитоплазме и оказывают умеренное супрессирующее влияние на активность PHD2 [41]. На фоне предъявления клетке гипоксического стимула этот процесс усиливается, что заметным образом тормозит протеолитическую деградацию HIF. Как следствие, разновидности α и β индуцированного гипоксией фактора перемещаются в ядро клетки. Запускается транскрипция семейства «гипоксических» генов. В течение суток формируется клеточный гипоксический ответ, что может служить руководством для выбора интервала времени между сеансами при проведении гипокситерапии [42].
В свою очередь метаболический HIF-пул через активацию «гипоксических» генов способен по принципу положительной обратной связи уменьшать прооксидантный потенциал путем регулирования активности ацетилкоэн-зима-А [43, 44].
В условиях быстро развивающейся гипоксии ферментативный комплекс I цепи окислительного фосфорилирования митохондрий увеличивает продукцию молекул супер-оксид-анион-радикалов [45, 46]. А они ингибируют проводимость кальциевых каналов, встроенных в плазматические мембраны клеток [45]. Избыток молекул супероксид-анион-радикалов вблизи внутренней поверхности оболочки клетки блокирует проводимость калиевых каналов семейства TASK-2 [47]. Эта же причина ведет к закрытию кальцийзависи-мых калиевых каналов высокой проводимости BK Ca [19]. Таким образом, побочные продукты процесса окислительного фосфорилирования – АФК – в условиях гипоксии способствуют деполяризации плазматической мембраны клетки за счет ингибирования нескольких семейств калиевых каналов.
Особенности изменений в мембраносвязанных микродоменах, объединяющих каналы и митохондрии, активно исследуются в настоящее время. Вместе с тем не меньший интерес у специалистов вызывают внутриклеточные сигнальные отношения чувствительных к гипоксии околомембранных механиз- мов и HIF-пула цитоплазмы клетки. Однако пока количество экспериментальных исследований в этой узкой области невелико. Нам не удалось найти ни одного обзора на эту тему.
Еще в 2006 г. появились данные о влияния HIF-пула клеток культуры меланомы человека в ходе длительной гипоксии на увеличение проводимости кальцийзависимых калиевых каналов (K Ca ). Это происходило под действием избыточной экспрессии HIF-1α в ответ на недостаток кислорода в среде культивирования [48]. Позднее аналогичный эффект был получен на культурах гладкомышечных клеток легочной артерии крыс для семейства потенциалзависимых калиевых каналов (К v ) [49] и WEHI-231B-клеток мыши для TASK-2-калиевых каналов [50].
В доступной нам литературе имеются отдельные сведения о роли HIF-2α в условиях хронической гипоксии. Этот сигнальный фактор блокирует активность генов, ответственных за синтез β 1 -субъединицы BK Ca , и тем самым обедняет вклад этих каналов в стабилизацию мембранного потенциала [51].
Данных о нисходящем влиянии около-мембранного кластера с участием калиевых каналов на HIF-пул цитоплазмы клеток найти не удалось. Отсутствие таких сведений объясняется многократной разницей скоростей реагирования ионных каналов (несколько секунд) и метаболических ответов в HIF-пуле (десятки минут) на гипоксический стимул. При таком сочетании лабильностей сравниваемых систем медленные процессы могут оказывать эффективное влияние на быстрые, но не наоборот.
Активация конститутивно присутствующих в цитоплазме стрессовых белков, прежде всего семейств HSP70 и HSP90, происходит на начальных этапах развития гипоксии. В ходе эскалации гипоксического состояния к конститутивным стрессовым белкам добавляются индуцибельные за счет экспрессии соответствующих генов. Последнее характерно для продолжительных гипоксических экспозиций, когда длительный курс интервальной гипоксии переходит в хронический формат.
Таким образом, на сегодняшний день можно выделить три точки приложения действия гипоксического стимула внутри клеток
Metazoa. Во-первых, это гемоксигеназа-2 (HO-2) в ассоциированном с плазматической мембраной комплексе белков, центральным эффекторным звеном которых являются калиевые каналы различных семейств. Данный комплекс обеспечивает реакции клетки на быстро развивающуюся гипоксию.
Во-вторых, это пролилгидроксилаза-2 (PHD2) – сенсор на кислород в пуле метаболических реакций, где мастером-регулятором является HIF. Этот комплекс обеспечивает реакции клетки на хроническое гипоксическое воздействие.
В-третьих, это хорошо изученный митохондриальный пул генерации активных форм кислорода и азота, который наряду с проок-сидантным потенциалом имеет и регуляторную миссию. В гипоксических условиях этот пул оказывает модулирующие влияния на первые два кластера внутриклеточного энергетического метаболизма. АФК также тесно взаимодействуют с репарационным потенциалом стрессовых белков.
Эти три полюса энергетического метаболизма клетки тесно взаимосвязаны и дополняют друг друга.
Список литературы Взаимодействие кислородчувствительных механизмов в клетке
- Малкин И.Б., Гиппенрейтер Е.Б. Острая и хроническая гипоксия. Т. 35. Москва: Наука; 1977. 319.
- Колчинская А.З., Цыганова Т.Н., Остапенко Л.А. Нормобарическая интервальная гипоксическая тренировка в медицине и спорте. Москва: Медицина; 2003. 406.
- Lei Xi, Serebrovskaya T.V., eds. Intermittent Hypoxia. N.Y.: Nova Science Publishers, Inc; 2009. 615.
- Semenza G. Oxygen homeostasis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2010; 2 (3): 336-361.
- Lin F., Suggs S., Lin C., Browne J., Smalling R., Egrie J., Chen K., Fox G., Martin F., Stabinsky Z. Cloning and expression of the human erythropoietin gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1985; 82 (22): 7580-7584.
- Semenza G., Wang G. A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol. Cell Biol. 1992; 12 (12): 5447-5454.
- Bishop T., Ratcliffe P. Signaling hypoxia by hypoxia-inducible factor protein hydroxylases: a historical overview and future perspectives. Hypoxia (Auckl.). 2014; 2: 197-213.
- Masson N., Willam C., Maxwell P., Pugh C., Ratcliffe P. Independent function of two destruction domains in hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha chains activated by prolyl hydroxylation. EMBO J. 2001; 20 (18): 5197-5206.
- Анохина Е.Б., Буравкова Л.Б. Механизмы регуляции транскрипционного фактора при гипоксии (обзор). Биохимия. 2010; 75 (2): 185-195.
- Samanta D., Prabhakar N., Semenza G. Systems biology of oxygen homeostasis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2017; 9 (4): 1-15.
- Semenza G. Dynamic regulation of stem cell specification and maintenance by hypoxia-inducible factors. Mol. Aspects Med. 2016; 47-48: 15-23.
- Prabhakar N., Semenza G. Regulation of carotid body oxygen sensing by hypoxia-inducible factors. Pflugers Arch. 2016; 468 (1): 71-75.
- Hirsi M. M., Koivunen P., Gunzler V., Kivirikko K., Myllyharju J. Characterization of the human prolyl 4-hydroxylases that modify the hypoxia-inducible factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2003; 278 (33): 30772-30780.
- Maltepe E., Schmidt J., Baunoch D., Bradfield C., Simon M. Abnormal Angiogenesis and responses to glucose and oxygen deprivation in mice lacking the protein ARNT. Nature. 1997; 386 (6623): 403-407.
- Townley-Tilson W., Pi X., Xie L. The Role of Oxygen Sensors, Hydroxylases, and HIF in Cardiac Function and Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longey. 2015; 2015: 676893.
- Bell E., Chandel N. Mitochondrial Oxygen sensing: regulation of Hypoxia-inducible factor by mitochondrial generated reactive oxygen species. Essays Biochem. 2007; 43: 17-27.
- Coleman M., Ratcliffe P.J. Oxygen sensing and Hypoxia-induced responses. Essays in Biochemistry. 2007; 43: 1-16.
- Погодина М.В., Буравкова Л.Б. Особенности экспрессии HIF-1A в мультипотентных мезенхимных стромальных клетках при гипоксии (обзор). Бюллетень экспериментальной биологии и медицины. 2015;159: 333-335.
- Waypa G., Smith K., Schumacher P. O2 sensing, mitochondria and ROS signaling: The fog is lifting. Mol. Aspects Med. 2016; 47-48: 76-89.
- Lopez-Barneo J., Lopez-Lopez J., Urena J., Gonzalez C. Chemotransduction in the carotid body: K current modulated by PO2 in type I chemoreceptor cells. Science. 1988; 241 (4865): 580-582.
- Haddad G., Jiang C. O2-sensing mechanisms in excitable cells: role of plasma membrane K channels. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 1997; 59: 23-42.
- Prabhakar N., Peers C. Gasotransmitter regulation of ion channels: a key step in O2 sensing by the carotid body. Physiology (Bethesda). 2014; 29 (1): 49-57.
- Hoshi T., Lahiri S. Cell biology. Oxygen sensing: it's a gas! Cell biol. 2004; 306 (5704): 2050-2051.
- Kemp P., Peers C. Oxygen sensing by ion channels. Essays Biochem. 2007; 43: 77-90.
- Peers C., Wyatt C., Evans A. Mechanisms for acute oxygen sensing in the carotid body. Respiratory Physiology
- Williams S., Wootton P., Mason H., Bould J., Iles D., Riccardi D., Peers C., Kemp P. Hemoxygenase-2 is an oxygen sensor for a calcium-sensitive potassium channel. Science. 2004; 306 (5704): 2093-2097.
- Hou S., Heinemann S., Hoshi T. Modulation of BKCa channel gating by endogenous signaling molecules. Physiology (Bethesda). 2009; 24: 26-35.
- Peng Y., Nanduri J., Raghuraman G., Souvannakitti D., Gadalla M., Kumar G., Snyder S., Prabhakar N. H2S mediates O2 sensing in the carotid body. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010; 107 (23): 1071910724.
- Li Q., Sun B., Wang X., Jin Z., Zhou Y., Dong L., Jiang L., Rong W. A crucial role for hydrogen sulfide in oxygen sensing via modulating large conductance calcium-activated potassium channels. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010; 12 (10): 1179-1189.
- Li Y., Zheng H., Ding Y., Schultz H. Expression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in rabbit carotid body glomus cells regulates large-conductance Ca2 -activated potassium currents. J. Neurophysiol. 2010; 103 (6): 3027-3033.
- Lukyanova L.D., Dudchenko A. V., Germanova E.L. Mitochondrial signaling in formation of body resistance to hypoxia. In: Lei Xi, Serebrovskaya T.V. (Eds.), Intermittent Hypoxia. N.Y.: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.; 2009: 391-417.
- Sazontova T.G., Arkhipenko Y.V. Intermittent hypoxia in resistance of cardiac membrane structures: role of reactive oxygen species and redox signaling. In: Lei Xi, Serebrovskaya T.V. (Eds.), Intermittent Hypoxia. N.Y.: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.; 2009: 113-150.
- Manukhina E.B., Vanin A.F., Malyshev I.Yu. Intermittent hypoxia-Induced cardio- and vasoprotection: role of NO stores. In: Lei Xi, Serebrovskaya T.V. eds.), Intermittent Hypoxia. N.Y.: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.; 2009: 79-112.
- Mansfield K., Guzy R., Pan Y., Young R., Cash T., Schumacker P., Simon M. Mitochondrial dysfunction resulting from loss of cytochrome c impairs cellular oxygen sensing and hypoxic HIF-alpha activation. Cell Metab. 2005; 1 (6): 393-399.
- Guzy R., Mack M., Schumacker P. Mitochondrial complex III is required for hypoxia-induced ROS production and gene transcription in yeast. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007; 9 (9): 1317-1328.
- Finkel T. Signal transduction by mitochondrial oxidants. J. Biol. Chem. 2012; 287 (7): 4434-4440.
- Brand M. Mitochondrial generation of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide as the source of mitochondrial redox signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016; 100: 14-31.
- Ветош А.Н. Биологическое действие азота. Санкт-Петербург; 2003. 231.
- Алексеева О.С., Ветош А.Н., Коржевский Д.Э., Косткин В.Б. Влияние кверцитина на развитие азотного наркоза и накопление белков теплового шока в клетках коры головного мозга крыс. Доклады академии наук. 2010; 430 (3): 421-423.
- Zhong N., Zhang Y., Fang Q.Z., Zhou Z.N. Intermittent hypoxia exposure-induced heat-shock protein 70 expression increases resistance of rat heart to ischemic injury. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2000; 21 (5): 467-472.
- Murphy M., Holmgren A., Larsson N., Halliwell B., Chang C., Kalyanaraman B., Rhee S., Thornalley P., Partridge L., Gem, D., Nystrom T., Belousov V., Schumacker P., Winterbourn C. Unraveling the biological roles of reactive oxygen Species. Cell Metab. 2011; 13 (4): 361-366.
- Semenza G. Hypoxia-inducible factors in physiology and medicine. Cell. 2012; 148 (3): 399-408.
- Ivan M., Kaelin Jr. The EGLN-HIF O2-Sensing System: Multiple Inputs and Feedbacks. Mol. Cell. 2017; 66 (6): 772-779.
- Kim J., Tchernyshyov I., Semenza G., Dang C. HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: a metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Metab. 2006; (3): 177-185.
- McElroy G., Chandel N. Mitochondria control acute and chronic responses to hypoxia. Exp. Cell Res. 2017; 356 (2): 217-222.
- Fernandez-Aguera M., Gao L., Gonzalez-Rodriguez P., Pintado C., Arias-Mayenco I., Garda-Flores P., Garda-Perganeda A., Pascual A., Ortega-Saenz P., Lopez-Barneo J. Oxygen Sensing by Arterial Chemoreceptors Depends on Mitochondrial Complex I Signaling. Cell Metab. 2015; 22 (5): 825-837.
- Ward J. Oxygen sensors in context. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2008; 1777 (1): 1-14.
- Tajima N., Schonherr K., Niedling S., Kaatz M., Kanno H., Schonherr R., Heinemann S. Ca2 -activated K channels in human melanoma cells are up-regulated by hypoxia involving hypoxia-inducible factor-1-alpha and the von Hippel-Lindau protein. J. Physiol. 2006; 571 (Pt 2): 349-359.
- Don Q., Zhao N., Xia C., Fu X., Du Y. Hypoxia induces voltage-gated K (Kv) channel expression in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells through hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). Bosn. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2012; 12 (3): 158-163.
- Shin D., Lin H., Zheng H., Kim K., Kim J., Chun Y., Park J., Nam J., Kim W., Zhang Y., Kim S. HIF-1a-mediated upregulation of TASK-2 K channels augments Ca2 signaling in mouse B cells under hypoxia. J. Immunol. 2014; 193 (10): 4924-4933.
- Bautista L., Castro M., Lopez-Barneo J., Castellano A. Hypoxia inducible Factor-2alpha stabilization and maxi-K channel beta1-subunit gene repression by hypoxia in cardiac myocytes: role in preconditioning. Circ. Res. 2009; 10 (12): 1364-1372.


