Ways to enhance the economic turnover of fruit and berry production in the region
Автор: Rokhchin Vladimir Efimovich, Uskov Vladimir Sergeevich
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Branch-wise economy
Статья в выпуске: 4 (34) т.7, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Enhancement of the regions' self-sufficiency in handling their socio-economic development issues predetermines their increasing importance in the search for new sources of economic growth and improvement of the quality of life, an important characteristic of which is nutrition, including the consumption of fruit and berries. This issue is particularly relevant for the European North of Russia, where the development of its own fruit and berry production is constrained by climatic conditions. These territories can find a source of economic growth in the formation of the fruit and berry market with a significant potential for development based on the resources of wild fruits and berries that the northern regions are rich in. The article describes the main spheres of functioning of the fruit and berry market in the northern regions through the development of integrated network structures that promote integration of fruit and berry production and processing, as well as support on the part of the authorities in creating appropriate conditions for the normal functioning of the market.
Fruit and berry production, economic growth, region, territorial-industrial complex
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223621
IDR: 147223621 | УДК: 332.1 | DOI: 10.15838/esc/2014.4.34.18
Текст научной статьи Ways to enhance the economic turnover of fruit and berry production in the region
The revival of economic growth and the achievement of the goals of socio-economic development of the territory are the priority tasks for the regional government authorities. Economic growth can be achieved by directing all the available potential toward the enhancement of competitiveness and increase of production of competitive goods, effective and rational use of natural resources [9]. One of such natural resources is fruits and berries, the production of which is important for the regional economy, and for improving the quality of life of the population.
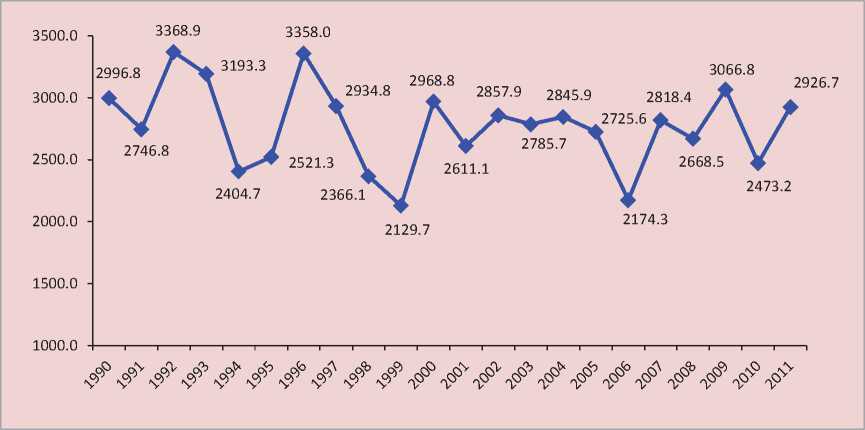
The transition of the Russian economy to market relations in the early 1990s has had adverse effects on the development of the fruit industry within the agro-industrial complex that is the main supplier of cultivated fruits and berries to the market. Their production was unstable during the whole post-reform period (fig. 1) .
In the conditions of market relations, the majority of Russian enterprises specializing in the production of fruit and berry products have become unprofitable. The declining trend in the production is observed at fruit and berry processing enterprises. Only about 20% of gross yield of fruits and berries goes to processing. In the structure of manufactured products more than 90% falls on the processing of fruits and berries for canning, and the production of quick frozen and dried fruit is only 0.5% [2].
Serious problems are observed in the sphere of producing the means of production for all the parts of the fruit-and-berry subsector of agriculture. The domestic machinery lags behind its foreign counterparts in performance (in 2 times), has higher specific consumption of power, water, steam (by 12–18%) and metal consumption (30–40%).
Figure 1. Gross production of fruits and berries in the Russian Federation in all categories of enterprises, thousand tons [6]
The technical level of machines for washing containers, for preparation of raw and auxiliary materials for canning is characterized as extremely low. The situation is especially grave in the fruit-and-berry canning industry: most of the companies have outdated equipment for the packaging of products [2].
The above problems have led to the fact that currently the production does not fully satisfy the demand of the population for fruit and berry products, since it provides only 18–20 kg of fruit and berries a year per person, or 25–30% of the minimum amount required. The shortage of production is covered by its import (fig. 2) .
The basis of import supplies of fruits is citrus fruits, apples, pears, apricots, peaches, cherries, sweet cherries, and bananas (fig. 3) .
But even if we take import into account, the actual consumption of fruits and berries per capita (in terms of fresh fruits and berries, without those processed to make wine) in the Russian Federation is only 40–50% from the rational standard recommended by the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences.
The main reasons for the insufficient provision of consumers with domestic fruit-and-berry products are seen in the following.
The first reason is an extremely low state support of agriculture and its fruit and berry cultivation. The lack of investment in the industry, in the creation and development of agricultural infrastructure, including high-quality storehouses leads to the fact that Russia imports even apples.
The second reason lies in the immaturity of the market of Russian producers. The system of distribution of domestic products
Figure 2. Resources and the use of fruits and berries in the Russian Federation, thousand tons [6]
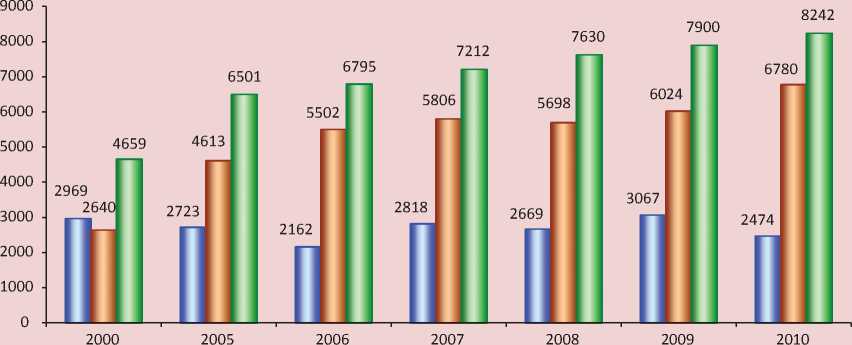
□ Production □ Import □ Private consumption
Figure 3. Commodity structure of fruit and berries import in Russia in 2012,% [8]
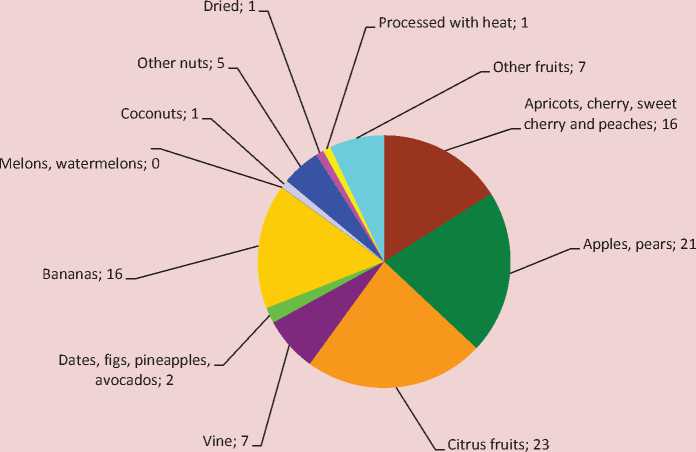
has not been created so far, while the channels for distribution of foreign fruits and berries are working effectively. As a result, substantial reserves for the development of domestic fruit and berry sector remain unused.
The problem of providing the population with fruit-and-berry products is particularly acute for the people, who live in the Northern territories of Russia, including the regions of the Non-Chernozem forest zone. Their climatic conditions are not suitable for cultivating fruit and berry crops dynamically; in this regard, a significant share of fruits and berries is imported from abroad and from the southern regions of the country.
At the same time, even the NonChernozem zone has a significant potential for providing the people with fruit and berry products. A good resource base for this can be found in significant reserves of wild berries: cranberry, cowberry, bilberry, blueberry, which are very important in the food balance of the country.
In recent years three leading centers for the harvesting and processing of wild crops have developed (tab. 1) .
Involvement of wild berries, which are the traditional local natural resources, in the economic turnover should be considered as one of the sources of growth for the economy both in the region and European North of Russia, where the biological reserve of cranberry is 160 thousand tons per year, blueberry – 372 thousand tons, blueberry – 37 thousand tons, cranberry – 214 thousand tons.
Table 1. Russia’s leading regions in the harvesting and processing of wild berries
|
Region |
Specifics |
|
Northwestern |
The impetus for the development of gathering in the Republic of Karelia, in the Pskov, Arkhangelsk and other oblasts can be found in direct investment from interested Swedish, Finnish and Norwegian companies. The reasons for the interest on the part of foreigners are clear: this Russian region is very close to the borders of the countries, where the consumption of wild plants (primarily berries) is at a very high level. In fact, the companies engaged in berry processing are now working with the relatively cheap Russian market of raw materials. Today in Karelia there are already up to 40 companies involved in the gathering and delivery of wild crops to Northern Europe. They all have full funding from Western partners. But the processing of wild raw materials in the region is not being developed: the vast majority of participants in this market gather berries and deliver them for export “as they are”. There emerged a fairly developed system of procurement centers; and the local population is actively involved in the procurement process as well. |
|
Central |
Procurers from the Ivanovo, Vladimir and other oblasts focus on the Moscow market. Several large companies such as Ecoproduct, Bogorodskaya Trapeza, Wimm-Bill-Dann engaged in the canning of mushrooms, berries and juices have formed their own procurement base. According to the available data, the Ivanovo Oblast-based company Cantarella that specializes in the production of frozen berries and mushrooms remains the leader in the region. |
|
Siberian |
So far the dominant position belongs to the Tomsk Oblast: local procurement companies are successfully working in the Altai and Krasnoyarsk Krai. In addition, the region has developed a range of companies that position themselves not only as producers but also as the raw material processing enterprises: the remoteness from the boundaries naturally stimulates the development of deeper processing in order to minimize costs of the products’ delivery to foreign markets. This factor urges the Siberian companies to work more seriously in the domestic market. |
Table 2. Forecast revenues of the Vologda Oblast budget system from harvesting berries by forestries [3]
|
Indicator |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
Total for 2014 – 2017 |
|
Planned volume of procurement of berries in forestry sections, tons |
499.2 |
504.3 |
509.2 |
514.3 |
2027.0 |
|
Average pay for harvesting berries, rub. |
4.84 |
4.84 |
4.84 |
4.84 |
– |
|
Inflow of revenues to the budget from the harvesting and collection of non-timber resources, thousand rub. |
300 |
304 |
307 |
310 |
1221 |
|
Inflow of revenues to the budget, from harvesting of forest food resources and medicinal plants, thousand rub. |
3651 |
3691 |
3725.1 |
3765.3 |
14832.4 |
|
Total budget revenues from harvesting and collection of non-timber resources, forest food resources and medicinal plants, thousand rub. |
3951 |
3995 |
4032.1 |
4075.3 |
16053.4 |
It should be emphasized that the development of these resources requires an efficient communications system that makes it possible to purchase fresh berries in all the territories of the region.
Consumer cooperatives and forest industry enterprises remained the main gatherers of wild berries for a long time [4]. However, their plans for gathering berries are very small.
One of the main reasons why forestry lost its position in the market of wild forest foodstuffs can be found in the collapse of the former distribution system.
It should be noted that, according to forecasts, the implementation of estimated procurement of berry resources by forestry sections will allow the Vologda Oblast budget system to earn additional revenue. On average it will be about 4000 thousand rubles per year (tab. 2) . Total inflow into the budget for the period from 2014 to 2017 will reach nearly 16 million rubles.
However, one should bear in mind that we are talking only about the revenues of the region’s budget system that come from harvesting activities of forestry sections, i.e. from organized collectors. At the same time, more significant amounts of wild berries are gathered by the local population and are taken to the reception stations under district departments of consumer cooperatives, and in most cases – to the buyers-up of berries; therefore, the regional budget loses quite a substantial sum of money.
These data show that at present the issue associated with the development of market infrastructure that ensures the sales of fruit-and-berry products, is rather acute in the region. The years of market transformation resulted in actual destruction of the system of berry products distribution. This caused a decrease in the volume of sales to the state, the emergence of unregulated food markets, the formation of new, mainly market, distribution channels and the increase in the share of such sales.
Studies show that in modern economic conditions the innovativeness of fruit-and- berry cultivation and the enhancement of production efficiency can be facilitated through the application of new effective forms of cooperation by combining the production and processing of fruit-and-berry raw materials, logistics and other services on the basis of the development of integration processes.
A motive stimulating the integration processes is the effect received through the increase of the scale of production, the connection of separate stages of a single technological process and the opportunity to have a complete cycle of production, processing and distribution of diverse and competitive products, as well as the achievement of resources’ savings in the joint sphere of activity, coordinated actions and a more effective distribution of products on the market.
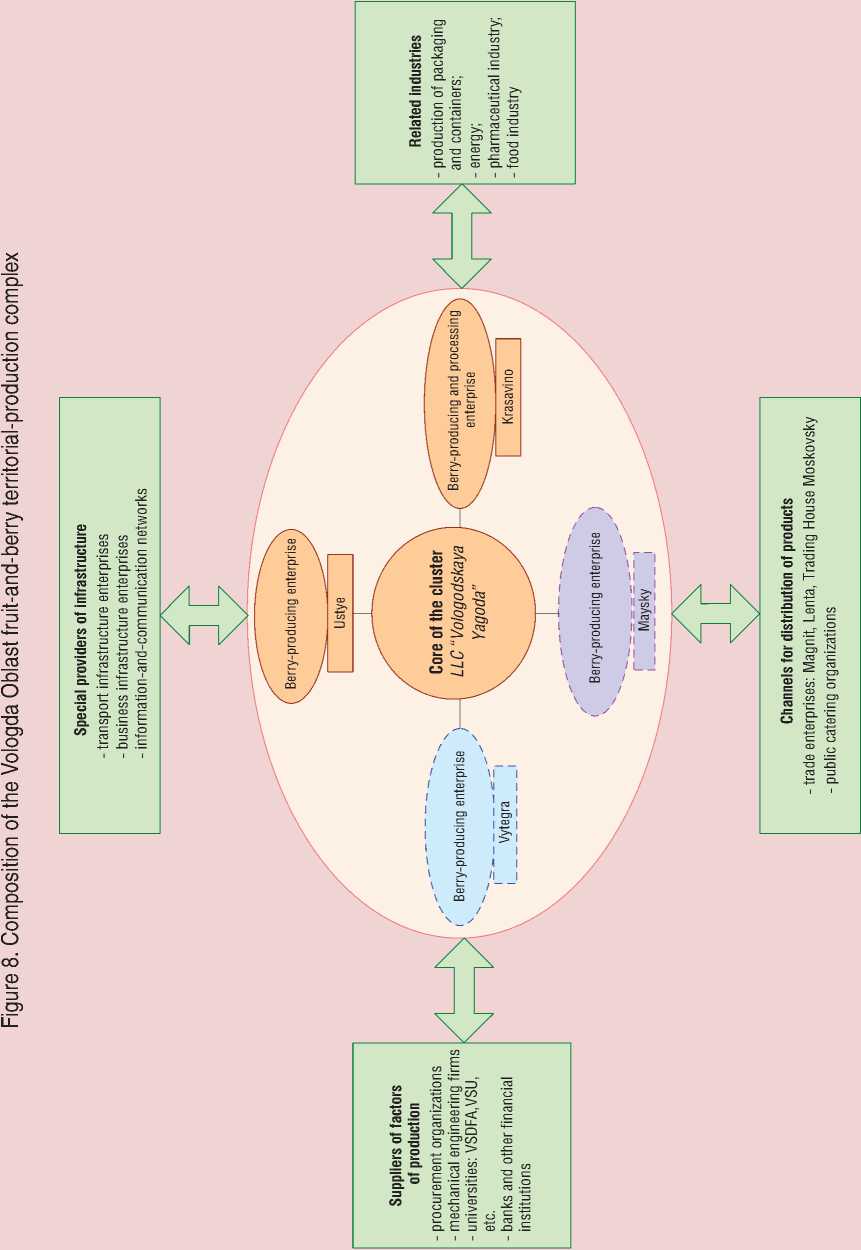
In our opinion, the promotion of innovation activity and involvement of wild fruit and berry resources in the economic turnover in the Vologda Oblast requires the formation of the territorial-production complex as a special integrated structure based on the regional non-profit partnership – an association of individuals and legal entities for the purpose of mutual cooperation while preserving their autonomy and independence.
This integrated structure can combine different economic entities, including investors, intermediaries, leasing organizations, customers, information and advisory organizations, government authorities, investment-innovation institutions, financial and credit institutions, insurance and research organizations, etc.
The creation of a territorial-production complex is a priority in the development of the region (the point of economic growth), contributing to the concentration of the necessary resources in those areas that bring maximum return and increase the efficiency and competitiveness of the products of agriculture and processing enterprises [1].
In our opinion, an important principle of the formation of the territorial-production complex consists in the competitiveness of the products and the demand on foreign and domestic markets. At present, the analyzed market is in a stage of gradual growth and has a significant potential.
There has been a steady demand for berry products on the Russian market. For instance, in 2008–2012 the sales of frozen fruits and berries increased by 37%. 76 thousand tons of frozen fruits and berries were sold in 2012. According to the forecast, the sales of these products will have reached 87.5 tons by 2015.
We add that during this period the retail price of frozen fruits and berries increased by more than 50% (196.38 rubles per kg in 2012 against 128.96 rubles in 2008), and it will have risen up to 268.87 rubles per kg by 2015 (fig. 4) .
Fruit and berry products are in great demand abroad. For the period between 2007 and the first half of 2012 the Russian enterprises exported 35 847.4 tons of frozen fruits and berries, which is equal to 132252 thousand dollars (fig. 5) .
Figure 4. Sales of frozen fruits and berries and their retail price
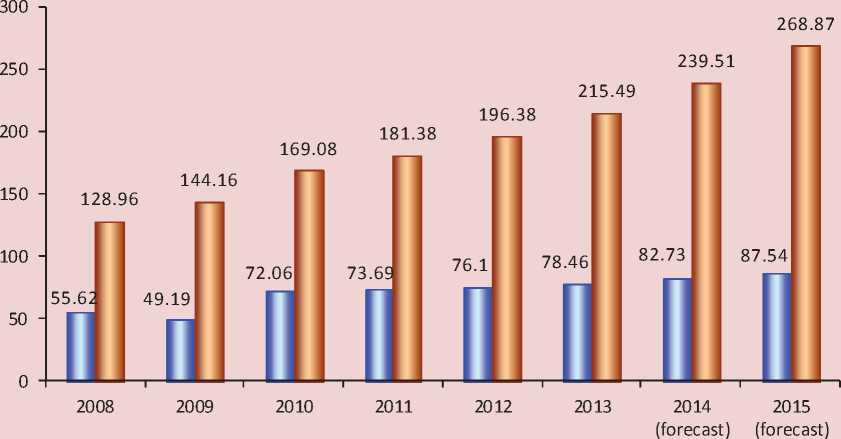
□Volume of sales of fruits and berries (frozen), thousand tons
□ Retail price of frozen fruits and berries, rubles/kg
Figure 5. Volume of export of frozen fruits and berries and their retail price
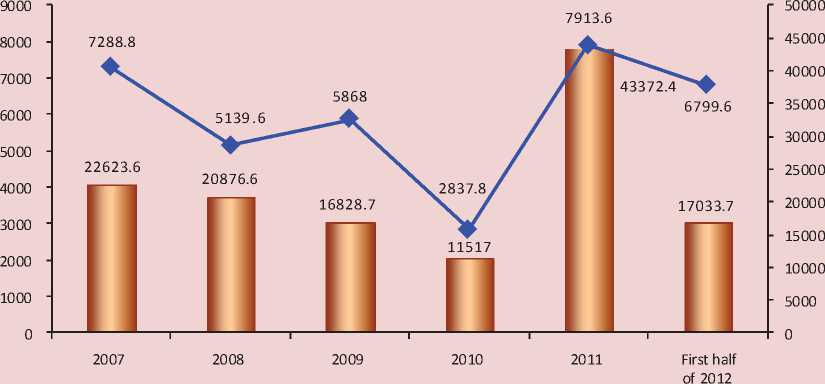
I—I Frozen fruits and berries, tons
— ♦ — Price of frozen fruits and berries, thousand U.S. Dollars
The presence of the prime company that produces ready-made (non-primary) products is essential for the formation of the territorial-production complex. In our opinion, LLC Vologodskaya Yagoda (Vologda berry) that is engaged in the processing of berries, can be considered the main enterprise of the fruit-and-berry territorialproduction complex in the Vologda Oblast; the company has facilities in Ust-Kubinsky and Velikoustyugsky districts of the oblast.
The current turnover of LLC Vologodskaya Yagoda has reached 8 billion rubles; the company has a network of procurement centers – stationary points, to which anyone can bring berries. It has its own bank in order to effect prompt payments to the people for the berries delivered, its own logistics – warehouses and vehicles. For 2006–2012
LLC Vologodskaya Yagoda has increased its turnover from 2.2 to 8 billion rubles (fig. 6) .
Currently, LLC Vologodskaya Yagoda is the leader in the Russian market of berry products. The company’s share in the market of frozen berries, berry puree, and berries in modified-atmosphere packaging varies from 85 to 100% (tab. 3) .
In general, the volume of production and sales of fruit-and-berry products of LLC Vologodskaya Yagoda is growing continuously. The revenues from sales increase every year; the only exception was 2010, when the sales declined due to adverse weather conditions caused by the unusually hot summer and, as a consequence, a sharp decline in yield and berrying.
The finished products of the company go to distributor networks such as “Auchan”,
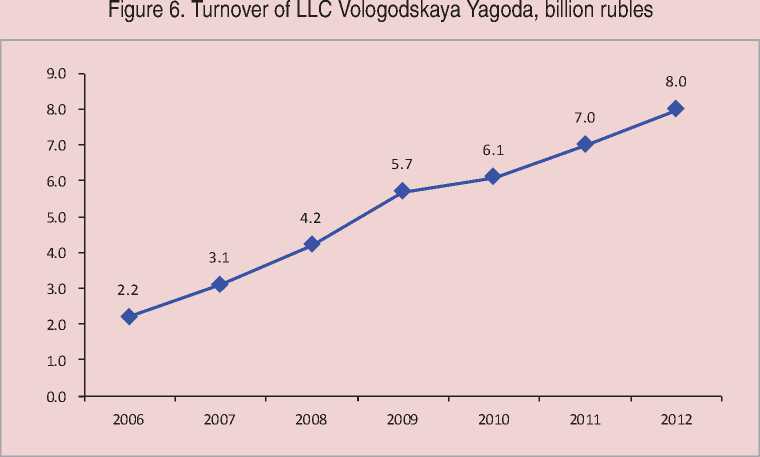
Table 3. Some performance indicators of LLC Vologodskaya Yagoda
|
Goods |
Current production output, tons/year |
Share of LLC Vologodskaya Yagoda in the Russian market, % |
|
|
wild berries |
cultivated berries |
||
|
Frozen berry |
35000 |
85 |
10 |
|
Berry puree |
4000 |
85 |
10 |
|
Concentrated berry puree |
4000 |
- |
- |
|
Berries in modified-atmosphere packaging |
0.5 |
100 |
|
|
Juice concentrate of cultivated fruit and berries |
0.5 |
1 |
|
|
Bilberry (pharmacy) |
4000 |
5 |
|
“Metro”, “Dixie”, “Lenta”, “Globus Gourmet”, etc.; semi-finished products and berry concentrates are sold to the juice, milk, confectionery and pharmaceutical companies. The major consumers of the products of LLC Vologodskaya Yagoda are OJSC Lebedyansky, OJSC Wimm-Bill-Dann Beverages, LLC Agrana Fruit – Danone, LLC SKFruit and others. These companies are the largest buyers of finished products such as fresh and frozen berries, concentrated juices and purees, and they intend to continue their cooperation with the enterprise; besides, due to the steady growth of the Russian market of juices and baby food (in 2009 consumption growth amounted to 18.5%), they are planning to increase purchases of raw fruit and berries for the production of juice and juice products.
Thus, LLC Vologodskaya Yagoda has a chance to become the parent company of a future fruit-and-berry territorial-production complex. Its participants may include specialized horticultural and small processing enterprises of the region, such as LLC Vologda Plant of Forest Foods, and Integrated
Agricultural Production Company Plemzavod Maysky, the largest producer of cultivated fruits and berries.
Small enterprises act as participants of the network structures. At present, those enterprises located in small towns and rural areas and engaged in the processing of agricultural products from locally available fruits, berries and herbs are becoming especially important. These facilities play a key role in the solution of social issues such as the increase in employment, creation of new jobs, and improvement of the quality of life. Besides, they solve the problem of stable supply of products at prices that are affordable for different social groups. The importance of this role of small businesses is evidenced by the fact that the production of canned mushrooms, vegetables and fruit by these enterprises reaches 45–50% of the total production [7].
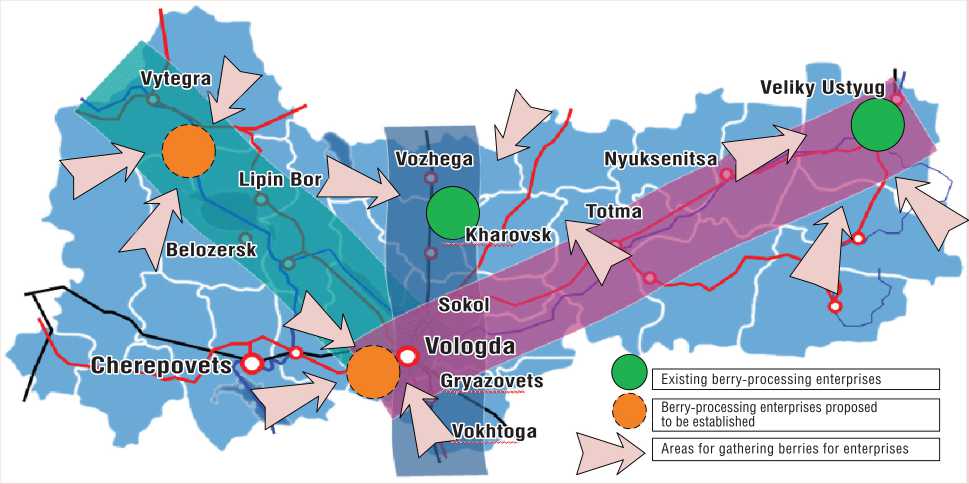
The presence of substantial reserves of wild berries in almost all the districts of the Vologda Oblast makes it possible to create a network of small enterprises for processing fresh berries, in particular, in the towns Vytegra, Krasavino and rural settlement Maysky.
The on-site processing of berries will reduce the cost of production by reducing transport costs. The feasibility of establishing small enterprises for processing berries is point out in the Strategy for socio-economic development of the Vologda Oblast for the period up to 2020. These enterprises should be created in the region’s development corridors (fig. 7) : the Western corridor – “Kirillov – Belozersk – Lipin Bor – Vytegra”; the Northern corridor – “Vokhtoga – Gryazovets – Sokol – Kharovsk – Vozhega”; the
Eastern corridor – “Totma –Nyuksenitsa – Veliky Ustyug”. Development corridors are located along major highways that provide access to the regional (local) market for all the members of business entities and maximum coverage of all the districts of the oblast. In addition, such a scheme of location of companies will give an impetus to the development of consumer cooperation as one of the key elements of the infrastructure of berry products market. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct systematic work in the corridors of development aimed to form engineering, transport, information, social and administrative infrastructures.
Taking into account the specifics of the economy of the territories, the structure of the regional fruit-and-berry territorialproduction complex should contain private subsidiary plots, which are the main producers of cultivated berries and the main collectors of wild berries. Despite the fact that they cannot form the basis of the progress in the industry due to small-scale production and limited resources for modernization, they are distinguished by the maximum efficient use of available resources and a high level of personal interest in the results of the work. The support of private subsidiary plots is social, rather than economic, in nature, and it implies the gradual evolution of the more successful of them into small and medium enterprises.
Transport-and-distribution centers can promote the integration of the subjects of the fruit market most efficiently. These centers make it possible to carry out the analysis, accumulation and redistribution of the flows of goods and materials within the region, between separate business entities within the
Figure 7. Possible locations of small enterprises for processing berries within the existing development corridors of the Vologda Oblast
territorial-production complex. The creation of a network of transport-and-distribution centers through the implementation of public-private partnership will provide a synergistic effect due to cost savings of business structures with the joint use of infrastructure and special equipment, and will lead to the growth and transformation of potential network integration structures into strong and stable ones [5].
The Vologda State Dairy Farming Academy named after N.V. Vereshchagin, the Vologda State University and other educational institutions can supply the enterprise of the territorial-production complex with skilled employees. It can be said that these universities will contribute to scientific and technological support of the production and processing of fruit-and-berry products in the proposed complex. This interaction is particularly important in the context of the necessity to create an innovation system and infrastructure for the production of competitive fruit-and-berry products.
The material and technological base and production technologies can be upgraded through the participation of engineering firms and research institutes in this complex.
Public authorities of different levels, innovation infrastructure, and the system of higher professional education are external partners of the fruit-and-berry territorialproduction complex. Regional and municipal authorities, in particular, should establish a favorable external environment for its creation. At the regional level it is necessary to make appropriate adjustments to the Vologda Oblast socio-economic development strategy, to determine the place of the fruit-and-berry territorial-industrial complex as a landmark of priority development.
At the same time it is necessary to develop an adequate system of state regulation and support of the industry. The organizing role of public authorities is very important at the initial stage of formation of the fruit-and-berry territorial-production complex.
In general terms, the structure of the fruit-and-berry territorial-production complex in the Vologda Oblast can be represented as follows (fig. 8) .
The development of the fruit-and-berry territorial-production complex by 2020, according to our calculations, will be characterized by the following indicators (tab. 4) . In addition, by 2020, the processing enterprises that will join the complex will contribute about 430–450 million rubles to the budget.
The increase in the economic turnover of wild berries in the Northern territories will be promoted by assistance from the authorities in the formation of the infrastructure of the local fruit-and-berry market by creating conditions to ensure the proper functioning of the market.
These conditions include:
– coordination of current and future directions in the development of regional and national economy;
– maintenance of the budget and commodity-money balance;
– development of legislation to provide a legal framework and protection of interests of all the participants in the local market of fruit and berries;
– creation of necessary conditions and control in order to ensure free and fair competition in the market;
– provision of rational and legitimate distribution of goods.
Due to the fact that the methods of state regulation in the formation of the fruit-and-berry market infrastructure are multi-dimensional in nature, their implementation should be effected by competent legislative, executive, supervisory and other public authorities.
In our opinion, this will contribute to the formation and sustainable development of the local fruit-and-berry market, turning it into a source of growth in the regional economy.
Table 4. Main indicators of the development of the Vologda Oblast fruit-and-berry territorial-production complex (calculations made by the author)
|
Share in the market |
Type of market |
|||||
|
Global |
Russian |
Regional (NWFD) |
||||
|
Fact 2012 |
Plan 2020 |
Fact 2012 |
Plan 2020 |
Fact 2012 |
Plan 2020 |
|
|
Fast-frozen berries, vegetables and mushrooms, % |
1,5 |
2,2 |
9 |
14 |
73 |
91 |
|
Concentrated berry juices and puree, % |
3 |
5 |
53 |
71 |
62 |
89 |
|
Concentrated vegetable juices and puree, % |
0 |
1 |
0 |
11 |
0 |
24 |
|
Production output of frozen berries, tons |
Fact 2012 |
Plan 2020 |
||||
|
39 000 |
94 200 |
|||||
|
Number of employees at the berry processing enterprises, including: |
||||||
|
– regular |
210 |
580 |
||||
|
– temporary |
1700 |
4000 |
||||
Cited works
-
1. Glotko A.V. Formation and Development of Horticulture Cluster in the Regional Agroindustrial Complex . Available at: http://oldvak.ed.gov.ru/common/img/uploaded/files/vak/2010/announcements/economich/12-04/ GlotkoAV.doc
-
2. Kulikov I.M., Medvedev S.M., Urusov V.F. Optimization of the Placement of Companies of Fruit and Berry Complex of AIC in the Central Federal District of the Russian Federation for the Period of 2009–2012. Horticulture and Viticulture , 2009, no.3, pp. 25-32.
-
3. The Forest Plan of the Vologda Oblast . Available at: http://www.forestvologda.ru/page/ wood_plan
-
4. Miloserdov V.V., Miloserdov K.V. Stages of Development of Russian Cooperation: the Ups and Downs. Economics of Agriculture and Processing Enterprises , 2012, no.4, pp. 10-16.
-
5. Morozov N.M., Konakov M.A. Small Agroindustrial Clusters. Economics of Agricultural and Processing Enterprises , 2009, no.2, pp. 30-33.
-
6. Agriculture, Hunting and Hunting Sector, Forestry in Russia: Statistical Digest . Rosstat. Moscow, 2011. 446 p.
-
7. Seregin S.N., Kashirina O.N., Kolonchin K.V. Principles and Specifics of Spatial Location of the Production Base of the Food Industry. Economics of Agricultural and Processing Enterprises, 2012, no.5, pp. 12-19.
-
8. Customs Statistics of Russia’s Foreign Trade . Available at: http://www.ved-stat.ru/pub/81-fruitimport
-
9. Tsibul’nikova M.R. Development of the Methodology for Accounting and Valuation of Natural Resources at the Regional Level (Case Study of the Tomsk Oblast) . Available at: http://www.lib.tsu.ru/mminfo/000063105/341/ image/341-243.pdf
Список литературы Ways to enhance the economic turnover of fruit and berry production in the region
- Glotko A.V. Formirovanie i razvitiya klastera sadovodstva v regional'nom APK . Available at: http://oldvak.ed.gov.ru/common/img/uploaded/files/vak/2010/announcements/economich/12-04/GlotkoAV.doc
- Kulikov I.M., Medvedev S.M., Urusov V.F. Optimizatsiya razmeshcheniya predpriyatii plodovo-yagodnogo podkompleksa APK v Tsentral'nom federal'nom okruge RF na period 2009-2012 gg. . Sadovodstvo i vinogradarstvo , 2009, no.3, pp. 25-32.
- Lesnoi plan Vologodskoi oblasti . Available at: http://www.forestvologda.ru/page/wood_plan
- Miloserdov V.V., Miloserdov K.V. Etapy razvitiya Rossiiskoi kooperatsii: vzlety i padeniya . Ekonomika sel'skogo khozyaistva i pererabatyvayushchikh predpriyatii , 2012, no.4, pp. 10-16.
- Morozov N.M., Konakov M.A. Agropromyshlennye klastery maloi formy . Ekonomika sel'skokhozyaistvennykh i pererabatyvayushchikh predpriyatii , 2009, no.2, pp. 30-33.
- Sel'skoe khozyaistvo, okhota i okhotnich'e khozyaistvo, lesovodstvo v Rossii. 2011: stat. sb. . Rosstat. Moscow, 2011. 446 p.
- Seregin S.N., Kashirina O.N., Kolonchin K.V. Printsipy i osobennosti territorial'nogo razmeshcheniya proizvodstvennoi bazy pishchevoi promyshlennosti Rossii . Ekonomika sel'skokhozyaistvennykh i pererabatyvayushchikh predpriyatii , 2012, no.5, pp. 12-19.
- Tamozhennaya statistika vneshnei torgovli Rossii . Available at: http://www.ved-stat.ru/pub/81-fruitimport
- Tsibul'nikova M.R. Razvitie metodologii ucheta i otsenki prirodnykh resursov na regional'nom urovne (na primere Tomskoi oblasti) . Available at: http://www.lib.tsu.ru/mminfo/000063105/341/image/341-243.pdf


