Activation therapy: theoretical and applied aspects
Автор: Kit Oleg I., Shikhlyarova Alla I., Zhukova Galina V., Maryanovskaya Galina Y., Barsukova Lyudmila P., Korobeinikova Elena P., Sheiko Elena A., Protasova Tatiana P., Evstratova Olga F., Barteneva Tatiana A., Salatov Ruslan N., Sergostiants Gennady Z., Atmachidi Dmitry P.
Журнал: Cardiometry @cardiometry
Рубрика: Review
Статья в выпуске: 7, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The paper presents a brief review on how some concepts on the organism general adaptational reactions developed, including their role in increasing the unspecific resistance in the organism. Demonstrated is periodicity of the patterns of anti-stressor type reactions (training, calm and elevated activation) and stress in a wide range of stimulation values. The concepts on the organism adaptational reactions and reactivity levels have created the theoretical basis for practical applications of the activation therapy aimed at health improvement, prevention and treatment of various diseases, including oncology. Evidence data on the applications of the activation therapy as a promising approach to the organism state control are confirmed by the originators of this scientific discovery, their followers and medical experts.
General unspecific adaptational reaction, resistance, activation therapy
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148308805
IDR: 148308805 | DOI: 10.12710/cardiometry.2015.7.2229
Текст обзорной статьи Activation therapy: theoretical and applied aspects
Imprint
Oleg I. Kit, Alla I. Shikhlyarova, Galina V. Zhukova, Galina Y. Maryanovskaya, Lyudmila P. Barsukova, Elena P. Korobeinikova, Elena A. Sheiko, Tatiana P. Protasova, Olga F. Evstratova, Tatiana A. Barteneva, Ruslan N. Salatov, Gennady Z. Sergostiants, Dmitry P. Atmachidi. Activation therapy: theoretical and applied aspects. Cardiometry; No.7; November 2015; p.22-29; doi:10.12710/cardiometry.2015.7.2229; Available from:
F ormation of the scientific outlook is a complicated multistaged process of accumulation of knowledge treated by the philosophy laws as follows: the law of the negation of the negation, the law of the unity and conflict of opposites, and the law of the passage of quantitative changes into qualitative changes. These simple genuine dialectics approach capable of interpreting all properties, phenomena and complex processes in biological and social life is considered to be the fundamental instrument for science.
The theory of adaptational reactions in an organism that was developed by Russian researches L.Kh. Garkavi, M.A. Ukolova and E.B. Kvakina is a good illustration of the quantitative-qualitative concept of adaptation of an organism to changing factors in the external and internal environments. The elaboration of a justified concept on how to control human organism states was built upon a scientific discovery made by the above researchers (Scientific Discovery Registration Certificate No. 158 issued by the Committee on Inventions and Discoveries at the Council of Ministers of the USSR to L.Kh. Garkavi, M.A. Ukolova and E.B. Kvakina) which describes patterns and regularities in development of adaptational reactions by an organism, including anti-stress reactions, as listed below: the reaction of training (L.Kh. Garkavi, M.A. Ukolova and E.B. Kvak-ina 1969), the reaction of calm activation and the reaction of elevated activation (L.Kh. Garkavi 1968), and, as this takes place, every reaction refers to a certain specific state of the human or- ganism [1, 2-12].
Canadian scientist Hans Selye opened a new chapter in medicine since he pio- neered in overcoming the psychological barrier of the primacy of quality and specifics, suggesting the primacy of quantity in nonspecific response of an organism to a stimulus. Fascinated by the idea of non-specifics, Selye concentrated all his efforts on proving his rather incredible suggestion that there is always a stereotypical response by an or- ganism to stimuli varying in their quality. Selye’s discovery of a stress reaction to strong gross harmful exposures of any nature was a breakthrough in science: he pioneered in developing a theory of pathology by describing stress as a general adaptation syndrome (H. Selye,
1968) [13-16].
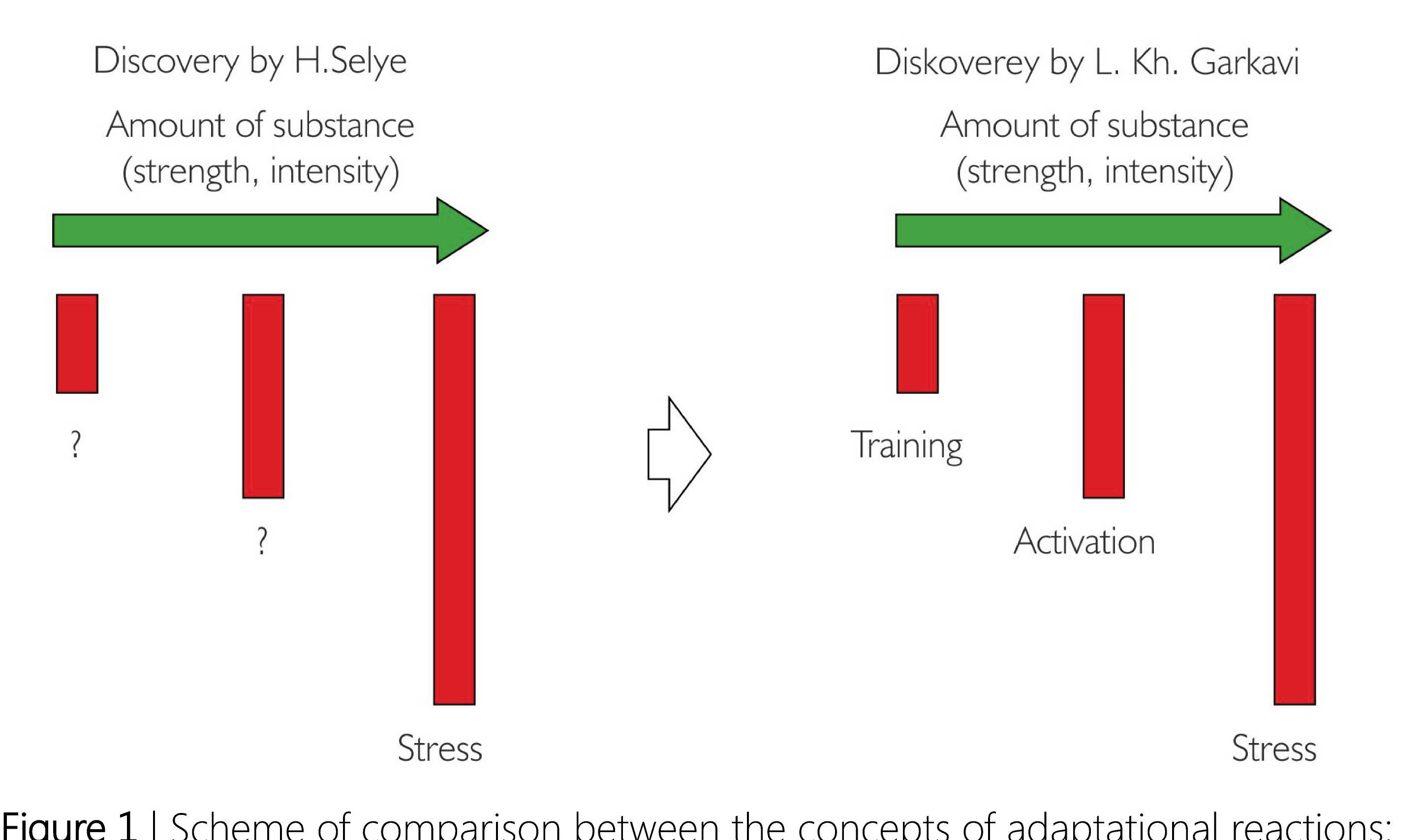
But at the same time, it should be noted that stress cannot be treated to be the only form of the reaction of an organism within a wide range of influence intensities. A subdivision of nonspecific response by the organism in terms of quantity parameters led to a detection of other archetypes of reactions, i.e. the reactions of a category identical to stress (general, unspecific and adaptation reactions), but which should be considered to be alternative, as to the essence of changes occurring in the nervous, the endocrine, the thymus lymphatic and other systems in an organism. Whereas stress is a high-price protection by the organism due to eventual pathological damages and high-level energy consumption, the anti-stress reactions of training, calm and elevated elevation result in physiological enhancement of the natural resistance of the organism by optimizing the regulatory mechanisms at all hierarchical levels: from the central systemic levels up to molecular cell ones (see Figure 1).
Thus the above proposed structure, covering the four general unspecific reactions, namely, the reaction of training (to a weak stimulus), the reactions of calm and elevated activation (to a middlescale stimulus) and the reaction of stress (to a strong stimulus), demonstrates that, firstly, a response to a stimulus is
Activation
Discovery by H.Selye
Amount of substance (strength, intensity)
Diskoverey by L. Kh. Gari Amount of substance (strength, intensity)
H. Selye vs. Lyubov Kh. Garkavi.
formed by an organism in a discrete way and that, secondly, each reaction makes its own specific contribution to the regulation of homeostasis and elevation of the resistance level, namely, control of the functional state of the organism as a whole.
Using a scale with relative units to indicate intensity values of exposure or influence factors: “greater” (as compared to the stressor one) – “less even less
than less”, it is possible to characterize the sequence of the adaptational reactions within a certain small range according to the said stimulus intensity scale. If the reactions are graduated in a broad range of absolute values of exposure factors, and in this case we deal with a really wide range, that is equivalent to a sensitivity, when “it is necessary to detect the sound of the slightest rustling __________A of a moving snake and at the same time to be capable of seeing a flash of lightning without going blind“
(A.M. Molchanov. I ‘ solute value scale of influence intensities. When analyzing an organism at the different levels of reactivity, revealed has been a periodical system of repetitive occurrence of the adaptational reaction tetrad (Fig. 2).
The dialectical principle of periodicity is common both to organic and inorganic nature. To illustrate this fact, the famous periodic table by Mendeleev should be mentioned, where the structure of the table reflects the particular arrangement of the electrons in each type of atom and where elements with similar chemical properties appear at regular intervals. The same is applicable to the periodicity of adaptational reactions detected by us: the reactivity levels in our periodic table correspond to the periods in Mendeleev’s periodic table, and the op- posite reactions can be compared to the Mendeleev’s table rows, where the far right column exhibits noble gases, and in our case it is the state of the so-called areactivity, or a “silence area”.
So, the periodic system of adaptational reactions represents a differentiated, biologically expedient system of responses of an organism to stimuli of variable values, including absolute values (the levels of reactivity) and relative values (reactions and areactivity at each level), i.e. it is instrumental for regulation of homeostasis (Fig. 3).
After many years of extensive research, completed by L.Kh. Garkavi, M.A. Ukolova, E.B. Kvakina and their scientific school, supported by the staff of experimental study labs, clinical division of the Rostov-on-Don Oncology Research Institute and other large-scale health care institutions in Rostov-on-Don and some other cities in Russia, they have demonstrated the role of different reactions and areactivity in an organism in development of a disease, for premorbidity and the healthy state. The above mentioned researchers succeeded in describing the dependence of the physical and psychological state in human on the type and the nature of the adaptational reactions. Based on their new concepts, they identified new ways and methods of control (harmonization) of the functional state of an organism by inducing development of harmonious physiological reactions of calm and elevated activation that laid the
Non-linearity in biology. Pushchino, 1992, p. 55),it turns out that a regular pattern of development of the adaptational reactions is periodically repeated at different levels of reactivity, i.e. in different segments (ranges) of the ab-
I—
Stress
Elevated activation
Calm activation
Figure 2 | Scheme of the evolution of concepts of the general adaptational syndrome on different reactivity levels.
A Lymphocytes (%)
foundation of the activation prevention and the activation therapy (L.Kh. Garkavi, M.A. Ukolova and E.B. Kvakina, 1979; L.Kh. Garkavi, M.A. Ukolova and T.S. Kuz’menko, 1990; L.Kh. Garkavi, E.B. Kvakina, T.S. Kuz’menko and A.I. Shikhlyarova, 2002; 2003).
Our scientific team uses always various feedback options in order to trace efficacy of applications of the activation therapy concept in practice: analyzed are mass media sources, letters received by us from medical staff and researchers and personal communication with our patients. We maintain contacts with medical experts who have been trained at workshops dedicated to the application of the activation therapy, and we believe that it is of great importance that many health
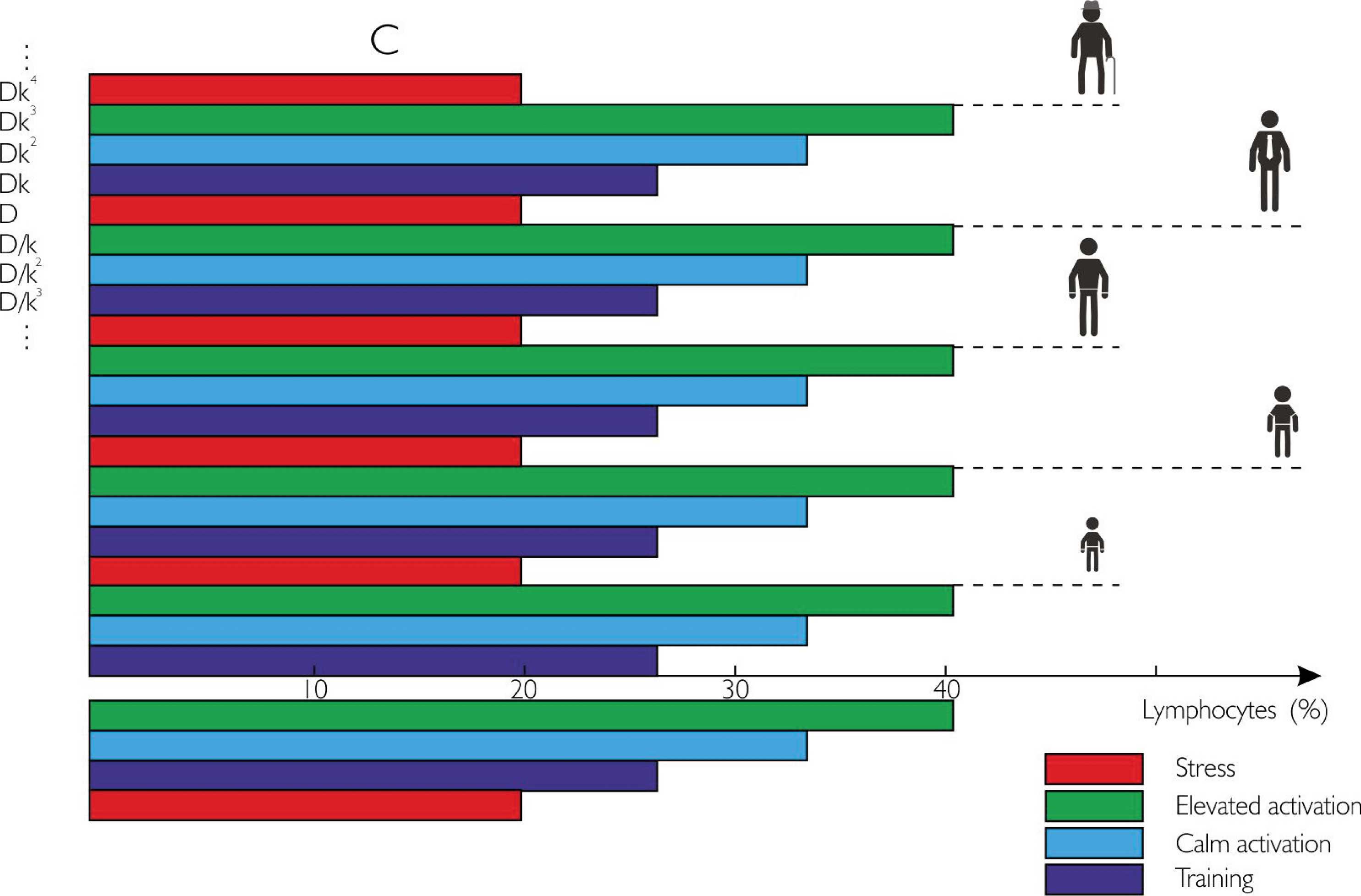
Figure 3 | Interrelation between the reactivity levels and the human age groups for the differential approach to the homeostasis regulation.
care experts share our opinion the most effective way of therapy is to initiate functioning of all the protection capabilities in the organism.
The theory of the adaptational reactions enables us to utilize new criteria of an assessment of health states of an organism and evaluation of efficacy of therapy tools. Moreover, it makes possible to substantiate the necessity of an intense formation of a favorable non-specific background, considering every pathology case individually treated by the responsible medicine expert and taking into account the actual sensitivity of various systems in the patient’s organism. It has been established that the most sensitive structures in the human organism are the nervous, the endocrine, the immune and the cardiovascular systems.
Actually, some study reports have shown that severity of a pathological process and the prediction of potential health improvement should be considered to be in a close correlation to the determined type of the adaptational reaction. In this connection, a retrospective analysis by Dr. Med. Sc. M.L. Kolomievsky, Chair for Propedeutics in Internal Medicine at the Pirogov Medical University, Moscow, Russia, furnishes an excellent example thereof (Assessment, prediction and treatment of cardiovascular diseases based on adaptational reactions).
His studies were carried out in 308 patients with ischemic heart disease treated in a cardiology unit, including a modern cardiovascular intensive care unit, versus 27 healthy individuals as a reference group (M.L. Kolomievsky Clinical Medicine, 1982, No. 7). During the studies, it has been demonstrated that the high incidence of ischemic heart disease can be usually attributed to the background of stress or tensioned reactions of training
In those cases, when a discrepancy between the blood test data and the respective ECG evidence was observed (in some individual cases for lethal outcome patients), it might be stated the following: the ECG evidence indicated that there was a positive coronary activity dynamics available, but the respective blood test data marked a deep stress condition. That demonstrated a higher informative value of the blood signal indicators of the adaptational reaction for predicting efficacy of a treatment strategy. Besides, other lethal outcomes were reported for some patients with normalized ECG upon their release from the hospital, when stress was identified according to the blood test data. The researcher thereon concluded that the respective signal indicator of the adap-tational reactions of stress, tensioned reactions of training and activation are instrumental for a complex assessment of the health state in a patient and dynamics of a cardiovascular system disease.
According to experimental data obtained by Ryazan Medical Higher
School’s scientists L.P. Afrikanov, M.A. Butov and A.I. Denisov (1985), the correlation between the MI severity and the nature of the adaptational reaction in the patients has been retained even during their physiological rehabilitation.
Further studies on the adaptational reactions in MI patients in the process of their rehabilitation under sanatorium conditions (L.I. Dodis et al., 1983) have shown that the patients in that group reported no signs or syndromes of their disease and were more tolerable to physical exercises, when they were in the state of the reaction of activation. The number of patients with ECG positive dynamics in that group was three times higher than that in the “stressor” group (Rostov-on-Don, data obtained by Cardiology Division, Sanatorium “Rostovsky”).
Investigations on adaptational reactions in the late post-MI periods revealed that the development of the reaction of activation favors an early recovery of the conventional individual sex behavior (V.G. Smirnov, 1983). So, in an examination of 98 patients, it has been established that the positive emotional state and the conventional sexual activity are restored under the conditions of the reaction of activation, and under the tensioned reactions of over-activation or stress formed are somatic and sexual neurotic-like symptom complexes destabilizing the main process in the patients (G.V. Smirnov and T.G. Smirnova, 1990, Pedagogical Institute, Saratov). To summarize, our cardiology experts note in the above cases that there is a complex positive resetting in the human organism. This very important factual evidence provides support for the view that we deal with a systemic nature of changes under dominance of the above mentioned standard-type reactions, especially the reaction of activation.
It should be emphasized that the up-to-date level of medical equipment and technologies, particularly in cardiology, results not only in the most accurate diagnostics of cardiovascular diseases, but they also are capable of discovering integrative mechanisms of the real-time adaptation of an organism and predicting most probable outcome for a patient [17-20].
Russian researchers M. Rudenko, V. Zernov and O. Voronova are the originators of a new fundamental scientific field: it is cardiometry. This new science is based on integrated concepts which include theory of measuring of hemodynamic, bio-physical and biochemical parameters as components of the cardiovascular performance in human. This approach offers a unique possibility to trace an influence of any factor on the heart performance, including medication, or any other influences, or exposures [21, 22]. The above researchers are the first who have succeeded in designing and developing the medical PC-assisted device CARDIOCODE which is capable of non-invasively recording and evaluating of the actual multi-parameter performance of the heart and the blood vessel system as the key acceptor mechanism of the adaptation ability of the entire human organism. This scientific achievement confirms the factual evidence that there is a clear-cut correlation between the nature of the changes in cardiometric parameters, delivered by the CARDIOCODE device, and the integral adaptational reaction of the organism under examination, that is decisive for reliability and accuracy both in diagnostics and an adequately specified treatment.
In regard to therapy of cardiovascular diseases, we should treat the known examples of the successful application of the activation therapy for this purpose. Experience of many cardiologists who have introduced the activation therapy in practice provides support to the view that the activation therapy significantly increases efficacy of the treatment. Just one illustration: cardiologist N.N. Naumcheva (Hospital No.1, Shchelkovo, Moscow Region) has involved into the classical treatment of acute MI patients an EHF therapy as an accompanying treatment option. An analysis of more than 300 disease case records made by the cardiologist has made it possible to prepare some recommendations on how to determine the type of the adaptational reaction in a patient in order to provide an unbiased assessment of the curing effects of EHF exposures. The analyzed data form the basis for the proper selection of the most favorable exposure parameters (e.g., exposure durations, number of exposure sessions etc.) to optimize the treatment effects. It is also offered to monitor the status of the respective adaptational reactions in post-treatment periods that makes possible to administer in time further prevention-type activation therapy courses that might be required as soon as stress signs are detected; the activation therapy should be aimed at development and maintenance of the reaction of calm activation (N.N. Naumcheva, 1994, 1995).
The activation therapy has a wide application in many other fields in medicine. So, in treatment of different types of inflammatory and internal diseases, the maintenance of the anti-stress reactions of calm and elevated activation with the use of pantocrin solution and eleuthe-rococcum extract (proportion 1:10) has resulted in stable remission both of main and accompanying diseases for 35 years. The activation therapy with the utilization of the EHF exposures has been recognized to be most contributing factor to the greatest therapeutic effects in patients with recurrent pyelonephritis and genitourinary fistulas, provided that the reaction of activation in them is kept up (D.L. Perepechai, D.V. Kan, T.B. Rebrova et al., 1994; Moscow).
Of great concern is also the role of the activation theory in surgery and traumatology. It is well known that the surgery-related stress can be treated as a classical stress model. It has been established that under the targeted stimulation of the reaction of activation, a clear-cut increase in the resistance to the surgery-related stress takes place (S.Z. Keltskin. 1983, 1984, Moscow). This effect has been experimentally substantiated on the basis of nociception simulation and eleuthe-rococcum extract dosing in rats that has been reported to reliably promote a decrease in deviations of the cardiac rhythm indicators, subject to the condition that the anti-stress reactions develop.
Of special note is the significance of the activation therapy in neurosurgery. Yu.V. Seregin (1983, 1986, Rovno) has offered methods and equipment designed for restoration of motor function in pediatric patients with cerebral palsy, cere- brovascular diseases and post-traumatic brain disorders. The most favorable effect has been detected in the patients upon development of the reaction of activation: the motor function has been fully restored in those children who had been subjected to the conventional therapy with no positive outcome before. In order to specify the required exposure parameters, Seregin has elaborated a mathematical model of inducing the development of the adaptational reactions in case when the head is under exposures.
The dependence of the traumatic injury dystrophy complications on the nature of the adaptational reaction has been studied by the Traumatology Department at the Rostov-on-Don State Medical Institute (Golubev G.Sh., Lokshina Y.G., 1983; Golubev G.Sh., 1985). Professor Lokshina Y.G., the research project leader, the Head of the Department, conducted the activation therapy with local influence on a compound fracture area with magnetic field that allowed reducing by more than two times the period required for the normal healing of such fractures.
The studies on the adaptational reactions in patients with schizophrenia, manic-depressive psychosis, involutional psychosis and secondary encephalitis have demonstrated the prevalence of stress for the majority of the patients. To relieve the stress condition in a patient and carry out the activation therapy, applied was an individual administration of antidepressants, hormones and adaptogen doses, which were 7-20 times lower than those to be conventionally indicated (Shevelev A.I. et al; 1984). Besides, the doses of symptomatic psychotropic drugs were 3-10 times lower than those to be conventionally used. The clinical efficacy and cost-effectiveness of the accompanying activation therapy has been recorded to be twice what the conventional treatment delivers that has been confirmed by the State Inventor Certificate (I.C. No. 995792 dated 1981).
Y.I. Makeeva (1981) and M.Y. Litvak (1993) presented some data on their method for an intensive activation psychotherapy of lingering neuroses that was applied within the disease specific treatment complex. The developers thereof believe that some opiate systems, which keep stress from being developed, participate in the development of the reactions of activation and training. The mechanism of analgesic and calming effects of endorphins and enkephalins represents blocking release of dopamine, noradrenaline and adrenaline that corresponds to the changes in a mediator link under the activation reaction induced by low doses of eleuthe-rococcus or insulin(Kalinkin L.A., Litvak M.Y., 1987; Rostov-on-Don State Medical Institute).
The activation therapy has been carried out with the use of low doses of adrenaline, lev-amisole, ultrasound or UHF eddy current devices to provide the thy-

Like this article?
You can share it with your colleagues at issues/no7-november-2015/ activation-therapy
mus area exposure, i.e. the influences with a great variety of quality. At the Military Medical Academy in St. Petersburg, a targeted pathogenetic therapy of infiltrative and destructive forms of tuberculosis has been conducted (Patent Certificate No. 1367963 issued to Brazhenko N.A.; Rybalko V.V., Brazhenko N.A., Khavinson V.Kh., 1986; Denisova L.V., 1990). Established was a direct statistically reliable dependence between the adaptational reaction type and the distribution of tuberculous process, its phase state and duration of treatment with tuberculostatic remedies [24]. Besides, the normalization of the hormonal status and the inflammatory potential has made it possible to avoid administration of glucocorticoids [25]. In general, in opinion of the originators of this method, the pathogenetic therapy, conducted under the adaptational reaction monitoring, becomes controllable and manageable.
Y.A. Gorgolyuk (Moscow, 1983) shares their opinion when reporting on his successful application of the activation therapy in dermatology. R.P. Kikut, M.E. Liyepa, S.R. Kikute et al. (Riga, 1981) state high efficacy of the activation therapy of optochiasmatic leptomeningitis, and M.A. Butov (1994) notes the regulatory effect of the anti-stressor reactions in the period of climacteric disorders.
Highlighting the diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of the adaptational reactions in research in the last decade it is impossible to ignore one of the most important medical disciplines: it is sure oncology.
At the Rostov-on-Don Oncology Research Institute, “alma mater” of the scientific discovery of the law of development of the adaptational reactions associated with the names of researchers L.Kh. Garkavi, I.A. Ukolova, E.B. Kvakina (1975, 1998, 2001, 2003) and their followers, under the auspice and strong support by RAS Academi- cian, Professor Y.S. Sidorenko, Director of FSBI RORI, Professor O.I. Kit and clinical department staff, an extensive experimental and clinical basis for de- velopment and substantiation of the activation therapy applications in oncology has been created.
Tens of PhD’s and doctoral theses present the materials supporting expediency and efficacy of the applications of the activation therapy as an additional treatment in cancer therapy as well as a suitable instrument in investigations of complex changes in the neuroendocrine and immune status, including signal criteria of the general unspecific adaptation reactions in the organism [26-30]. Studies on applications of the activation magnetotherapy in the conventional treatment of inflammatory processes and malignant neoplasms of the skin, the lower lip, organs of the small pelvis, the mammary glands and other localizations are also pioneering (Salatov R.N., 2001) [31].
S.G. Chilingaryants’ doctoral thesis (2006) was devoted to the issue of improvement of some methods of postoperative lung cancer therapy. The researcher treated therein his new method of the postoperative magnetotherapy under low-frequency variable magnetic field exposure of the brain occipital region that was implemented for the first time in practice, and the protective anti-stressor effect of the method has been clinically verified.
Adjuvant chemo- and radiation therapy with exposure of the brain to magnetic field, when treating malignant glioma brain tumors, promoted a decrease in the cytostatic medication toxicity and a reduction in undesirable side effects of ionizing radiation and allowed obtaining the greater efficacy of treatment as compared to the conventional chemotherapy (Atmachidi D.P., 2009).
It stands to reason that the fundamental mechanisms of producing such effects on the tumor and the organism should be revealed in order to provide the proper clinical application of the magnetic field central exposure. These aspects were carefully studied in the doctoral thesis by E.B. Kvakina (1974), the PhD theses by G.Y. Maryanovskaya (1976) and Y.S. Kotlyarevskaya (1976). Y.P. Korobeinikova has determined the role of the brain emotionogenic structures in the anti-stressor reactions formation (1992), and Y.A. Sheiko has identified the molecular and cellular criteria of increase in the unspecific antitumor resistance. In this regard, research on defining the role of the electromagnetic field biotropic parameters in an increase of the organism anti-tumor resistance, was presented by A.I. Shikhlyarova in her doctoral thesis (2001), which is of great theoretical and practical significance. G.V. Zhukova has developed strategy and tactics of the activation therapy in her doctoral thesis (2006) by demonstrating applications of the activation therapy principles in order to increase the anti-tumor efficacy of the electromagnetic influences in her experiment.
Besides, the characterization of the EEG features of the brain functional state in oncological patients, when applying low-frequency electromagnetic field, was presented and an analysis of the adaptational reaction structure was conducted (Protasova T.P., 2007). It was established that the anti-stressor reac- tion formation contributes to the brain bioelectric activity normalization, inten- sifies the spatial synchronization of cortical biopotentials and lowers the asymmetry of the skin resistance at hypothalamus points.
The role of the experimental activation magneto- and SCENAR-therapy in normalization of the brain structures meta- bolic markers (including those of the hypophysis) has been demonstrated by Y.F. Komarova in her doctoral thesis (2011) and Y.A. Pogorelova’s PhD thesis (2012). Their data bear witness to the fact that there are reliable markers indi- cating elevation of the organism stress resistance level by the important criteria of free radical, hydrolytic and hormonal processes.
The biochemical examination results correlate to the markers of the immune system morphofunctional status in ani-mals-tumor bearers both at the central and peripheral component level. Besides, identified has been a high correlative relationship between the immune organs state and the degree of the antitumor impact due to electromagnetic exposure, when applying some activation therapy algorithms (Barteneva T.A., 2011).
An increase in efficacy of the anti-tumor therapy, when applying the electromagnetic influence of some other spectral ranges (optical, optical magnetic, ultrasound) has been shown in local cancer treatment, e.g., in the mammary glands, (Kechedziev S.M., 2011), in the lung (Belan O.S., 2009) and in the mucous oral cavity (Krokhmal’ Y.N., 2014).
The application of the adaptational reaction theory for evaluation of the antitumor therapy efficacy in case of cancer of various localizations allowed identifying the relations between the shortterm, the immediate and long-term follow-up results and the type of the prevailing adaptational reaction. It has been demonstrated that in case of the most pronounced effect, i.e. in case of full or partial regression of the mam- mary gland cancer tumor, the physiolog- ical reactions of training and activation prevail (Vladimirova L.Y., 2000, 2005;
Starzhetskaya M.V., 2002; Soldatkina
N.V., 2006; Luganskaya R.G., 2009; Svetitskaya Y.V., 2010). The features of the adaptational reaction formation in surgery, medication and radiation treatment of the lung cancer have been discussed in detail by G.Z. Sergost’yants (2005) and by S.A. Zin’kovitch (2005) in their doctoral theses as well as by A.V. Spitchenkova (2005) and Y.A. Karnaukhova (2010) in their PhD theses.
Studies on the integral mechanism of the anti-tumor effect realization were conducted considering different variants of the genital malignant tumors treatment (Moiseenko T.I., 2003; Rodionova O.G., 2004; Men’shenina A.P., 2009; Mkrtchyan E.T., 2015).
The development of criteria for an assessment of the organism adaptational capability allowed creating a computer version of numerical scale to classify the reactions and the reactivity levels. L.Kh. Garkavi, E.B. Kvakina and N.M. Maschenko (2003) developed the AntiStress program which includes the modes of selection of the activation therapy doses, the system of the quantitative identification of the adaptational reactions and the reactivity level, supported by the questionnaire for the patients’ health state self-evaluation. The improvement of the adaptational reactions pattern aided by the AntiStress program is useful to achieve anti-recur- rent and anti-metastatic effects. At the same time reported is an improvement in life quality that is favorable to oncology patients’ rehabilitation.
To analyze relatively large samples, a system of calculation of a coefficient of the correlation between the anti-stressor reactions and stress has been proposed (Shikhlyarova A.I., 2005). This algorithm is formed by stages, basing on the individual identification of the adapta-tional reaction type in the studied group of patients. The chaotic structure is ordered by forming a separate cluster for each reaction. The cluster consists of the reactions under the same names, and the respective cluster volume should be calculated (i.e. frequent occurrence of the specified type of reaction in the studied group). The formed, oppositely located, clusters of chronic and acute stress, training, calm and elevated activation present actually the pattern of the adaptational reactions which is common to the respective group. It is just the stage, where and when the coefficient of the correlation between the anti-stressor reactions and stress (К АС/С) can be identified. Its integrated value defines the dynamics of an increase or a decrease in the adaptational potential and demonstrates objective efficacy of the anti-tumor treatment at an integrated system level.
Our 10 years experience in the АС/С coefficient utilization allows demonstrating efficacy of various, especially pioneering, methods for treatment as mentioned in a great number of theses in statistical and graphical way. The list of these methods may be completed with the data on the organism adaptation status evaluation in case of onco-urologic diseases (Zhloba A.N., 2009; Khomutenko I.A., 2010), skin melanoma (Gusareva M.A., 2006), colon, rectum and lung cancer unresectable processes (Dzhabarov F.R., 2008; Solntseva A.A., 2009; Emel’yanovaL. E., 2006) and soft tissue sarcoma (Mashurova S.A., 2012).
The theory of the adaptational reactions played a great part in sports (Glukhman N.V., Stupin G.K., 1979). It was demonstrated that the activation therapy method is reliable and informative, and it allows taking into account the athletes’ individual features and correcting the training process in due time in different kinds of sports (Sautkin M.F., Polyakov A.P., Iononva T.V., 1984, Ryazan’, Medical University). Ulyanov V.I. (1981, 1997) and Ulyanov N.V. (1984) came to the same conclusions when conducting their sports medicine studies in Pyatigorsk. The activation therapy application in sanatorium-resort therapy is one of the key prerequisite for obtaining a high therapy effect. A system of the organism state evaluation, including the adap-tational reaction criteria, was developed to predict the adaptation condition and indicate eventual failures therein (Kly-achkin L.M., 1991).
Doctors of the Russian Air Forces sanatorium “Chemitokvadze” studied the adaptational reactions behavior in patients suffering from cardiovascular, respiratory and locomotor system diseases. It was reported that the application of the dosed functional loading according to the activation therapy principles contributed to the formation of the most favorable adaptational reactions of high reactivity levels that led to an increase in sanatorium-resort therapy efficacy (Maryanovskaya A.A., Bondarenko R.A., Tatkov O.V., Romasyuk S.I., Otkidatch S.A., 1997). The similar effects were noted by the doctors of the Krainka (Tula region) and the Khmel’nik (Vinitsa) resorts. Currently, the regional sanatoria of Kislovodsk, Pyatigorsk, Maikop (Lagonaki) and Anapa show a great interest in the application of the scientifically based activation therapy approach. The most illustrative is an experience of the activation therapy application in children in radiation contaminated areas (216 individuals), Arctic regions (2324 individuals), in ischemic heart disease and chronic bronchitis patients (450 individuals) and Chernobyl nuclear power plant accident emergency workers (44 individuals).
Finalizing the above data, we can conclude the following:
-
1. The clinical progression and prediction of an outcome of a disease correlate to the respective adaptational reactions in an organism. The most severe progression and unfavorable outcome are observed under stress, over-activation and at low levels of re-
- activity.
-
2. The activation therapy increases the efficacy of the generally accepted conventional treatment methods, reduces
-
3. The adaptational reaction theory may become a methodological basis for health improvement and rehabilitation system offered by special medical institutions and resorts, and it may deliver effective instruments for health status
their side effects and makes possible to lower specific medication doses. It is unspecific pathogenetic therapy for various diseases.
assessment.
Statement on ethical issues
Research involving people and/or animals is in full compliance with current national and interna-tional ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author contributions
All authors read the ICMJE criteria for authorship and approved the final manuscript.
Список литературы Activation therapy: theoretical and applied aspects
- Garkavi LK, Zhukova GV, Shikhliarova AI, et al. Anti-tumor action and other regulatory effects of low intensity electromagnetic and chemical factors in experiment. Biofizika. Nov-Dec 2014;59(6):1161-72.
- Garkavi LK, Tatkov OV. Nonspecific adaptation reactions in patients with cardiovascular pathology and vertebral osteochondrosis during rehabilitation in a sanatorium. Voenno-meditsinskii zhurnal.2003;324(4):36-42.
- Garkavi LK, Shepelev AP, Tatkov OV, Marianovskii AA.The efficacy of Eleutherococcus and cralonin in the sanatoriumhealth resort treatment of patients with ischemic heart disease and neurocirculatory dystonia. Voenno-meditsinskii zhurnal. Sep 2000;321(9):42-7.
- Garkavi LK, Kvakina EB, Shikchlyarova AI, et al. Magnetic fields, adaptational reactions and self-organization of living systems. Biofizika. 1996;41(4):904-5.
- Garkavi LK, Kvakina EB, Sheiko EA. AMP-induced enhancement of thio-tepa anti-tumor effect in the rats with transplantable ovarian tumor. Experimental Oncology. March 1996;18(1):87-9.
- Garkavi LK, Kvakina EB. The outlook for combining anti-tumor and activation therapies. Voprosy Onkologii. 1995;41(2):47-8.
- Garkavi LK, Kvakina EB, Mulatova AK, Sheiko EI, Shikhlyarova AI. Morphological and physiological characteristics of lymph nodes, thyroid gland, and testes of rats during stress-induced adaptation and activation. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. November 1989;108(5):1669-73.
- Sheiko YA, Shikhlyarova AI. Effect of monochromatic red lighting potentiating anti-tumor action of cyclophosphamide injected with autoblood. Voprosy Onkologii. 2011;57(4):493-6.
- Garkavi Lkh, Ukolova MA, Kvakina EB. Pattern of development of qualitatively differing general unspecific adaptational reactions of the organism. Scientific Discovery Registration Certificate No.158 issued by the Committee on Inventions and Discoveries at the Council of Ministers of the USSR. Scientific discoveries in the USSR. 1975;3:56-61.
- Garkavi Lkh, Kvakina EB, Kuz’menko TS, Shikchlyarova AI. Anti-stressor reactions and activation therapy. Yekaterinburg: Filantrop; 2003. 336 p.
- Kletskin SZ. Surgical stress and regulation of physiological functions. Moscow: Nauka; 1983.85p.
- Gudtskova TN, Zhukova GV, Bragina MI, Garkavi LK, Mikholap AI, Barteneva TA. Signs of cell-cell interactions in sarcoma 45 tissue under conditions of anti-tumor effect caused by injection of magnetite nanoparticles. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. October 2013;155(6):793-7.
- Mikhailov NI, Garkavi LK, Mashchenko NM, Zhukova GV. High-frequency oscillations in a pulse wave signal and their relation to differential blood count leucocytes. Biofizika. January 2012;57(1):99-104.
- Selye H. The evolution of the stress concept. American Scientist. 1973;62(6):642-9.
- Tachè J, Selye H. On stress and coping mechanisms. Issues in Mental Health Nursing. 1985;7(1-4):3-24.
- Selye H. The nature of stress. Basal facts. 1985;7(1):3-11.
- Kolomievsky ML. Adaptation reactions in ischemic heart disease patients. Clinical medicine. 1982;7:32-5.
- Mar'ianovskii AA, Bondarenko RA, Tatkov OV, et al. Concept of complex therapy of cardiovascular system with the biological remedies by Heel Co.. Biological medicine. 1997;1:51-6.
- Naumcheva NN. Effect of the millimeter-length waves on ischemic heart disease patients. Millimeter-length waves in biology and medicine. 1994;3:62-7.
- Naumcheva NN. Application of electromagnetic waves MM-range in cardiology. Millimeter-length waves in biology and medicine.1995;6:26-30.
- Rudenko MY, Zernov VA, Voronova OK. Study of hemodynamic parameters using phase analysis of the cardiac cycle. Biomedical Engineering. 2009;43(4):151-5.
- Rudenko MY, Zernov VA, Voronova OK. Fundamental research on the mechanism of cardiovascular system hemodynamics self-regulation and determination of the norm-pathology boundary for the basic hemodynamic parameters and analysis of the compensation mechanism as a method of revealing the underlying causes of disease. Heart Rhythm. 2012;9(11):1909-10 DOI: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2012.09.091
- Chovatiya R, Medzhitov R. Stress, inflammation and defense of homeostasis. Molecular Cell. 24 April 2014;54(2):281-8.
- Rybalko VV, Brazhenko NA, Khavinson VK. Influence of Thymalin on unspecific resistance in respiratory organs tuberculosis patients. Voenno-meditsinskii zhurnal. 1986;5:34-6.
- Oitzl MS, Champagne DL, van der Veen R, de Kloet ER. Brain development under stress: Hypotheses of glucocorticoid actions revisited. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. May 2010;34(6):853-66.
- Krohmal’ YN. Modified chemo-and radiation therapy of patients with locally advanced oral cavity cancer. Thesis abstract by Krohmal’ YN, Master of Biology. Rostov-on-Don, 2014. 25 pages.
- Pogorelova YA. Changes in metabolic state of rats’ hypothesis and brain structures in dynamics of experimental malignant lung neoplasms. Thesis abstract by Pogorelova YA, Master of Biology. Rostov-on-Don, 2012. 27 pages.
- Svetitskaya YV. Neoadjuvant polychemotherapy on protein concentrate autoplasma in complex treatment of locally advanced mammary gland cancer. Thesis abstract by Svetitskaya YV, Master of Biology. Rostov-on-Don, 2010. 27 pages.
- Starzhetskaya MV. Clinical and experimental ground of autohemochemotherapy application in mammary gland cancer treatment. Thesis abstract by Starzhetskaya MV, Doctor of Biology. Rostov-on-Don, 2002. 27 pages.
- Sheiko EA. Increase in the organism unspecific anti-tumor resistance and criteria of its evaluation. Thesis abstract by Sheiko EA, Master of Biology. Saint Petersburg, 1992. 23pages.
- Perepechai DL, Kan DV, Rebrova TB, et al. Application of electromagnetic radiation of low intensity in treatment of chronic pyelonephritis and urogenital fistulas. Millimeter-length waves in biology and medicine. 1991;1:125-34.
- Kikut RP, Liepa ME, et al. Application of magneto-biological effects in neurosurgery. Issues of balneology, physio-exercise therapy. 1981;4:18-24.


