Adrenaline heart
Автор: Rudenko M.Y., Berseneva I.А., Deberdeev M.P., Pasikova M.V., Tychinsky A.V., Mitilineo-obukhova A. I., Yuldashev B.А., Murodova M.D.
Журнал: Cardiometry @cardiometry
Рубрика: Editorial
Статья в выпуске: 22, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The role of adrenaline in the body, especially in athletes, is considered. Special attention is paid to the cardiovascular system performance in conditions of the continuous release of adrenaline. The ECG shape and the possible therapy in case of adrenaline heart are discussed.
Adrenaline, cardiovascular, heart, ecg, athlete
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148324411
IDR: 148324411 | DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2022.22.106107
Текст научной статьи Adrenaline heart
Imprint
Mikhail Y. Rudenko, Irina А. Berseneva, Murat P. Deberdeev, Maria V. Pasikova, Alexander V. Tychinsky, Amalia I. Mitilineo-Obuk-hova, Botir А. Yuldashev, Malika D. Murodova. Adrenaline heart. Cardiometry; Issue 22; May 2022; p. 106-107; DOI: 10.18137/ cardiometry.2022.22.106107; Available from:
The excitement an athlete feels when participating in a sport or activity is the release of adrenalin into their circulatory system. Adrenalin is the body’s response to stress. The influx of adrenal surge is a welcomed effect in conditions of stress, for example, when an athlete is about to do battle in the sporting arena. There’s an increase of energy sent to the muscles and the muscles response is to boost their ability to react. There’s an enhanced alertness brought about by an arousal of the central nervous system. The body begins to sweat more, in preparation to cool the muscles and the pupils dilate in an effort to take in more of the surroundings.
When adrenalin is released into the bloodstream, it invariably finds its way to the heart. The heart, upon feeling the increase in adrenalin, immediately boosts the rate and strength of its beating. The result is an increase in blood pressure, which, in turn, allows for an increase in respiratory exchange, making more oxygen available for the working muscles. The more oxygen available, the better the performance.
The rush of adrenalin into the working muscles has a positive effect on athletic performance. Unfortunately, if the person is not able to control the hormonal flow, it could have negative effects on overall health. The production of adrenalin is designed as a survival technique, but far too often the stress hormones are called into action at inappropriate times. If this happens more frequently then it should, the result is a suppressed immune system and a propensity toward a resistance of infections.
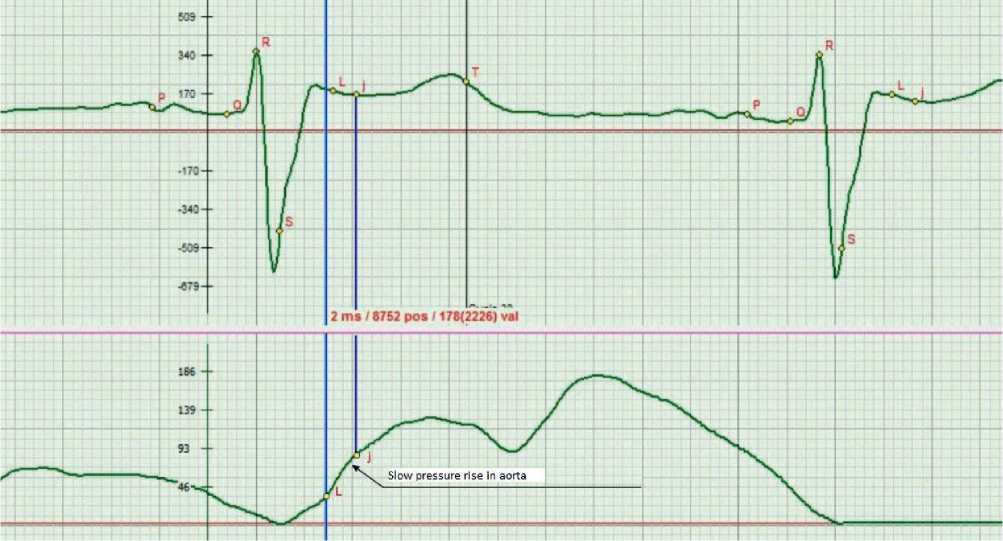
The Ca++ excess in cells destroys mitochondria. The ECG shape in the S-L phase depends on the amount of Ca ++ in the muscle fibers, which is active and activates the process of their contraction. It is important that the intracellular and extracellular Ca++ ions are balanced [1-3]. Adrenaline, especially its constant effect, provides an increased constant penetration of Ca ++ into a cell, resulting in the destruction of mitochondrial membranes. The ECG shape in the S-L phase will be smoothed out, as a result of which the amplitude fluctuations will not appear. This is a dangerous state, expressed in the fact that in the absence of a sufficient accelerating blood flow in the rapid ejection phase (indicated on RHEOgram), the pressure rise will be much smaller (see Figure 1 herein). The consequences will be found soon, and a chain of various problems with hemodynamics will arise [4-7].
Therapy
-
1. It is recommended to reduce constant mental stress that stimulates the continuous release of adrenaline.
-
2. It is advisable to take medical drugs containing Mg, which dramatically reduces the effect of adrenaline.
-
3. The wave resonance therapy with the EZh-2 device is needed [5].
-
4. Administration of L-carnitine (Elkar drug) in case of problems with the mitochondrial performance, it is used as a supportive agent to ensure O2 delivery.
-
5. Administration of ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate (Mexicor) (succinic acid)) for the purpose
-
6. Acupuncture is prescribed: Zhaohai (R6) and Hegu (Gi 4) to maintain vitality; when tactile impact on the points is available, rigid tissue turgor should be observed [5].
Figure 1. The S-L phase curve with excessive constant exposure to adrenaline promotes the entry of Ca ++ into the cell and affects the membranes of mitochondria
Table 1
Cardiometric diagnostics of the adrenaline heart signs
|
Detectable physiological, functional, metabolic and other changes |
ECG signs |
Possible consequences |
Recommendations |
|
Adrenaline heart. Ca++ excess in cells destroying mitochondria |
Smoothing the S-L wave. AP is growing slightly on RHEO |
Danger! Sudden changes in condition and significant changes in hemodynamics are possible |
|
of constant dynamic consumption in energy conversion processes [5].
Список литературы Adrenaline heart
- Rudenko MY, Voronova OK, Zernov VA. Theoretical Principles of Heart Cycle Phase Analysis. Munchen, London, New York: Fouque Literaturverlag.; 2009.
- Rudenko MY, Zernov VA, Voronova OK. Study of Hemodynamic Parameters Using Phase Analysis of the Cardiac Cycle. Biomedical Engineering. July 2009; 43(4): 151-5.
- Rudenko MY, et al. Cardiovascular system of an athlete. Cardiometric characteristics of physical capabilities before, during and after sports activities / ed. by M. Yu. Rudenko. Taganrog, Moscow: IKM, 2020. - 160 p. 978-5-86746-123-8 [in Russian].
- ISBN: 978-5-86746-123-8
- Zernov VA, et al. Application of the computer cardiograph "Cardiocode" in engineering and social psychology. Vysshee obrazovanie segodnya. 2019; 3: 68-75. [in Russian].
- http://cardiocode.net.
- Baevsky RM, Berseneva AP, Bersenev Y, Denisov L, Eshmanova. Problems of monitoring and prognostication of the cardiovascular system performance at bus drivers. Diagnostics and treatment of cardiovascular system regulation. Moscow2008:263.
- Baevsky RM, Berseneva AP. Evaluation of adaptation abilities of organism and pathology development risk. Moscow: Medicina; 1998.


