Assessing the structural stability and dynamics of Tinospora Cordifolia alkaloids with AKT1 protein: a molecular dynamics simulation study
Бесплатный доступ
The AKT1 protein is an important signaling kinase that participates in gastric disorderrelated pathways. Phytocompounds from Tinospora cordifolia, such as berberine, have gastroprotective properties, although the atomic details and stability of their interaction with AKT1 remain unknown. The purpose of this study is to use molecular dynamics simulations to analyze the structural stability, flexibility, and dynamic behavior of the AKT1 protein in association with four important T. cordifolia alkaloids (berberine, jatrorrhizine, tembetarine, and tinosporine). Molecular dynamics simulations were carried out for 10 ns using the CABSflex 2.0 and iMODS servers. Key parameters studied included rootmeansquare fluctuation (RMSF), deformability, Bfactor, eigenvalues, covariance, and elastic network models. All complexes shown stability throughout the simulation. The berberineAKT1 complex exhibited the best features, with low eigenvalues, restricted variation at the binding site, with strong correlated movements, indicating a stable and rigid binding mode. The MD simulations show that berberine forms the most stable complex with AKT1, effectively constraining its dynamics in a way that promotes inhibition. These findings provide a molecular basis for T. cordifolia's apparent bioactivity and identify berberine as a promising option for further exploration.
Tinospora cordifolia, alkaloids, berberine, AKT1 protein, molecular dynamics
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147252429
IDR: 147252429 | УДК: 001.891.32 | DOI: 10.14529/food250407
Текст научной статьи Assessing the structural stability and dynamics of Tinospora Cordifolia alkaloids with AKT1 protein: a molecular dynamics simulation study
The search for new therapeutic agents derived from natural products is fundamental to pharmaceutical research, providing a diverse array of chemicals that frequently exhibit favorable safety profiles [1]. Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Miers, known as Giloy or Guduchi, is highly regarded in traditional Ayurvedic medicine. It has been widely prescribed due to its diverse pharmacological properties, which encompass immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-ulcerogenic activities [2, 3]. The historical application of this substance in the management of gastrointestinal disorders, including dyspepsia and gastric ulcers, is significant [4]. T. cordifolia's medicinal potential is largely related to its broad array of bioactive phytoconstituents, with isoquinoline alkaloids such as berberine, jatrorrhizine, tembetarine, and tinosporine being considered primary active components [5].
The protein kinase B (AKT1) signaling pathway is a crucial regulatory mechanism in cellular processes related to gastrointestinal health and disease. AKT1 is a serine/threonine kinase integral to the PI3K-AKT pathway, regulating cell survival, proliferation, metabolism, and inflammation [6]. The dysregulation of this pathway is associated with several pathologies, such as inflammatory bowel disease and gastric cancers [7]. Thus, AKT1 is a prospective therapeutic target. Modulating AKT1 using natural chemicals is a strategy for treating signaling disorders. Our preliminary observations and current literature suggest that T. cordifolia alkaloids, particularly berberine, interact with AKT1 [8]. Instead of capturing the protein-ligand complex's dynamic behaviour and stability in a near-physiological environment, molecular docking merely offers a static snapshot of its binding pose.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation is an essential instrument in structural biology and computer-aided drug design, facilitating temporal resolution of structural predictions [9]. MD simulations, on the other hand, show how atoms and molecules move over time, giving us a far deeper understanding of how stable, flexible, and conformational changed biomolecular complexes are [10]. MD measures such as rootmean-square fluctuation (RMSF) and B-factor evaluate residual flexibility, whereas normal mode analysis (NMA) elucidates collective motions and the complex's energy landscape using eigenvalues and covariance matrices [11]. These investigations are critical in determining whether a docked position represents a sustained, biologically relevant interaction or a fleeting, unstable encounter.
Hence, this in silico study aims to go beyond initial binding affinity predictions and rigorously compare the dynamic stability of four key T. cordifolia alkaloids namely berberine, jatrorrhiz-ine, tembetarine, and tinosporine in complex with the AKT1 protein. We use MD simulations and NMA to assess these complexes' structural fidelity, flexibility, and interaction mechanics. Providing atomistic-level proof of the stability of these interactions provides a molecular justification for the traditional usage of T. cordifolia in GI problems and identifies the most potential ligand for future experimental research.
Material and Methods
System Preparation
The initial three-dimensional structures of the protein-ligand complexes between the AKT1 protein (PDB ID: 3O96) and four bioactive alkaloids from T. cordifolia- berberine, jatrorrhizine, tembetarine, and tinosporine were obtained from a molecular docking study conducted by our group. These pre-docked complexes represented the most favorable binding pose for each ligand, as determined by binding affinity scores.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation
AKT1 complex structural flexibility and residue-level fluctuations were assessed using molecular dynamics simulations on the CABS-flex 2.0 web service CABSflex2) [12]. CABS-flex efficiently simulates near-native dynamics with a coarse-grained protein model. Docked PDB files of each complex were submitted to the server. Simulation lasted 10 nanoseconds. All other simulation parameters, including temperature and simulation cycles, were kept at server defaults. CABS-flex's main output was the RMSF profile for each protein chain residue, which measures the average departure from its mean position over the simulation trajectory.
Normal Mode Analysis (NMA)
The iMODS server was used to perform Normal Mode Analysis (NMA) to assess protein-ligand complex dynamics, stability, and collective movements [11]. NMA is effective for studying biomolecules' large-scale conformational flexibility. The iMODS server received the same docked PDB files as CABS-flex. The server's default parameters utilized an internal coordinate’s mechanics (ICM) technique and a coarse-grained elastic network model for the investigation. The following properties were extracted from the iMODS output for each complex:
-
1. Deformability: To identify the most flexible regions in the protein backbone.
-
2. B-factor: Correlated with the RMSF to validate residue mobility.
-
3. Eigenvalues: The energy required to deform the structure along each normal mode; lower values indicate higher complex flexibility and stability.
-
4. Variance Map: Illustrating the individual and cumulative variance per normal mode.
-
5. Covariance Matrix: Representing the correlated (red), uncorrelated (white), and anticorrelated (blue) motions between residue pairs.
-
6. Elastic Network Model: Depicting the interconnected pairs of atoms, with darker regions indicating stiffer areas within the protein structure.
Data Analysis and Visualization
The graphical outputs and numerical data generated by the CABS-flex and iMODS servers were compiled and analyzed comparatively across the four AKT1-ligand complexes to rank their relative stability and dynamic behavior.
Results and Discussion
The current study employed MD simulations and NMA to evaluate the comparative assessment of the stability, flexibility and dynamic behaviour of the AKT1 protein in complex with four T. cordifolia bioactive alkaloids namely berberine, jatrorrhizine, tembetarine, and tinosporine.
Comparative Assessment of Residual Flexibility and Local Dynamics
The intrinsic flexibility of the AKT1 complexes was evaluated by analyzing the RootMean-Square Fluctuation (RMSF) and B-factor profiles. These metrics are critical for identifying regions of high mobility and understanding the local structural impact of ligand binding.
Root-Mean-Square Fluctuation (RMSF) Analysis
The CABS-flex RMSF profiles showed unique fluctuation patterns for each complex (Fig. 1). A noteworthy discovery was limited mobility in the berberine-AKT1 complex. For instance, Chain A's residue 80 in this complex showed minimal fluctuations (0.5260 Å), indicating a stable interaction. However, the tembetarine-AKT1 complex showed the largest fluctuation of 6.0360 Å at residue 392, indicating a more flexible and potentially unstable binding mechanism. Low RMSF values indicate little departures from the average position, indicating that the berberine complex imposes more struc-
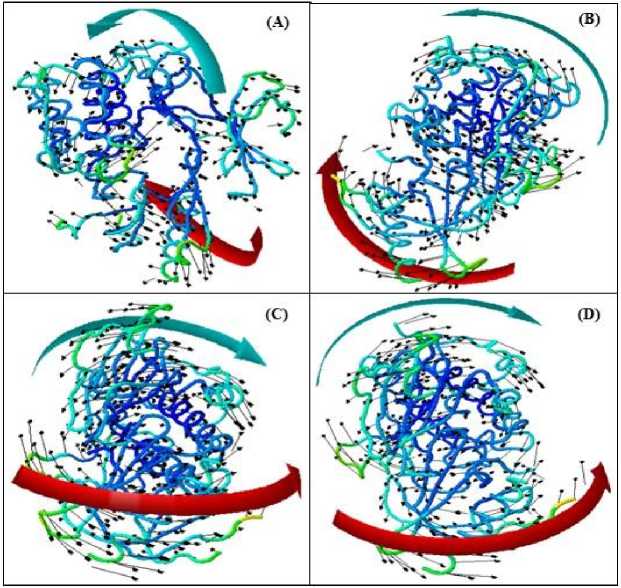
Fig 1. NMA of docked complexes evaluated molecular mobility of (A) AKT1-berberine;
(B) AKT1-Jatrorrhizine; (C) AKT1-Tembetarine and (D) AKT1-Tinosporine. The mobility or direction of motion is shown by the two colored affine arrows; longer arrows denote greater motion
tural rigidity on AKT1 than the other alkaloids, which is ideal for an inhibitor [13]. The tembetarine-AKT1 complex showed the highest peak fluctuation (6.0360 Å at residue 392), suggesting a more elastic and unstable binding mechanism. Jatrorrhizine and tinosporine complexes had moderate RMSF patterns. Example: Tinosporine lowest fluctuation was at residue 253 (0.3990 Å) and a considerable peak at 394 (3.9710 Å), indicating a binding pose that stabilizes one region while allowing flexibility in another.
Deformability and B-factor Correlations
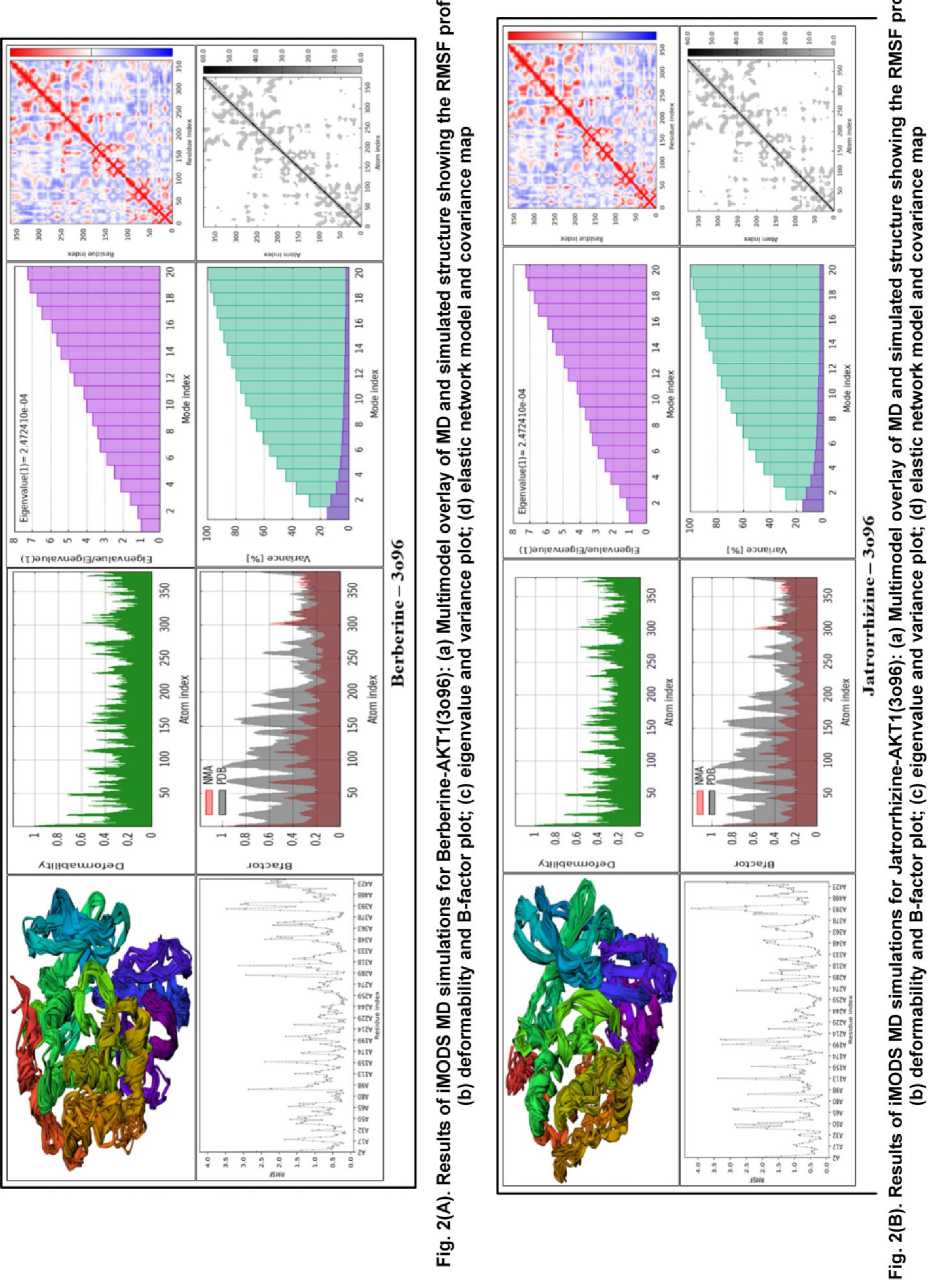
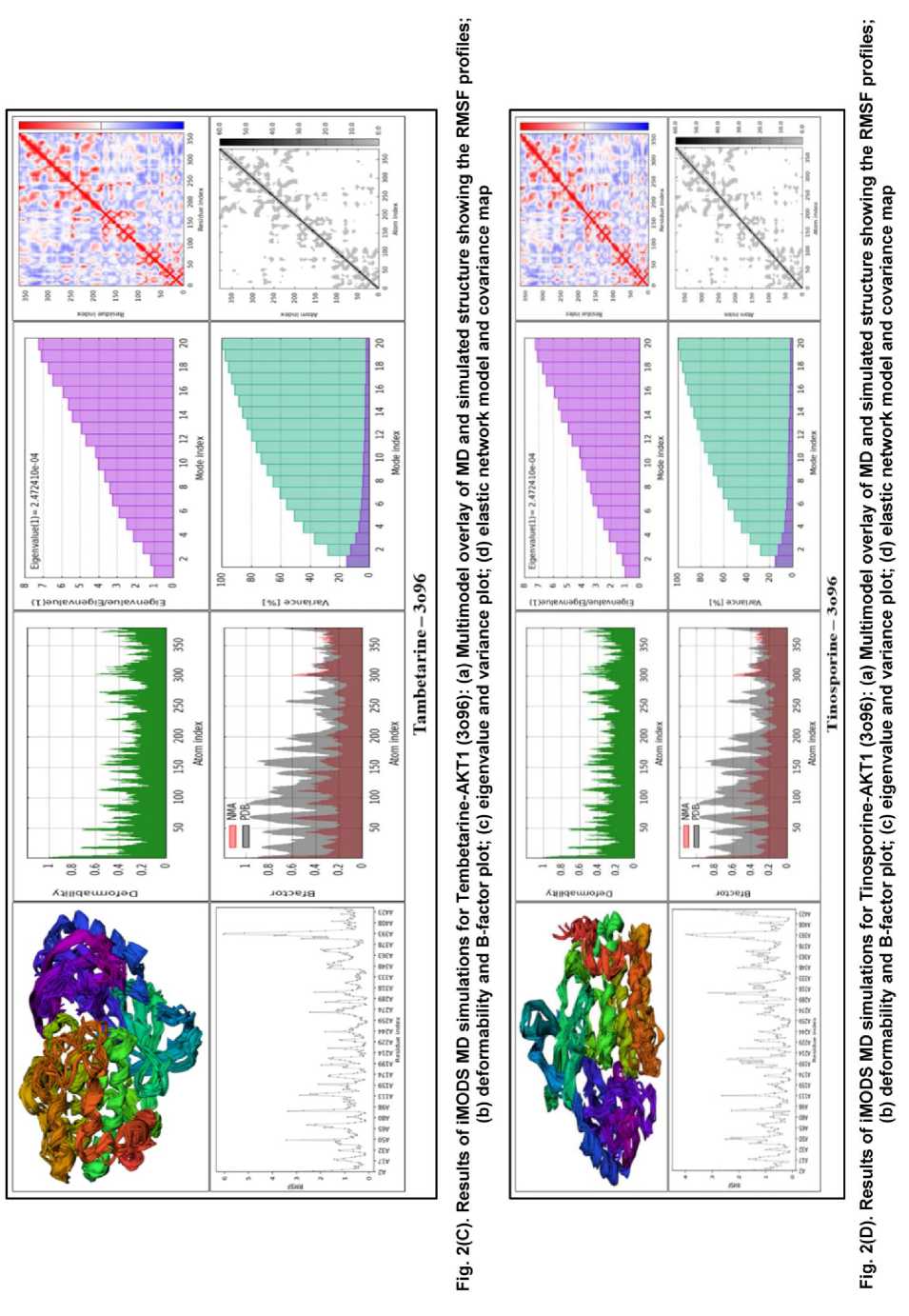
The deformability and B-factor graphs confirmed the stability of the complexes (Fig. 2A-D, panel b). The peaks in these figures represent the most malleable portions of the protein backbone. While all complexes had predicted patterns of flexibility, the berberine-AKT1 complex had a profile with substantial peaks indicating deformable portions, but the overall RMSF was lower. This shows that berberine binding promotes biological flexibility while efficiently stabilizing the global structure and, most importantly, the binding site region. The B-factor analysis yielded approximately average RMS and substantial hinges for all complexes, with the berberine complex demonstrating a favorable balance of stability and natural protein dynamics.
Evaluation of Global Dynamics and Complex Stability
To understand the collective motions and energetic stability of the complexes, NMA was performed using the iMODS server.
Eigenvalue Analysis and Energetic Favorability
The eigenvalue, which measures the energy required to alter the protein structure, is an important predictor of global stability. A lower eigenvalue indicates a more stable compound that is more easily deformed, a property frequently related with functional ligand binding [14]. The eigenvalue analysis (Fig 2A-D, panel c) revealed critical insights, with the AKT1 complex having the lowest eigenvalue of the proteins investigated. This suggests that berberine binding produces the most energy-efficient and stable complex. The jatrorrhizine and tinosporine complexes had reasonably low eigenvalues, whereas the tembetarine complex required significantly more energy to deform, indicating a less stable connection.
СО Я»
ф с
Variance and Collective Motions
The variance maps, which display the individual and cumulative variation per normal mode, demonstrated the berberine complex's stability. The cumulative variance (green-shade bars) increased more gradually for berberine-AKT1 than for the others, demonstrating that the majority of large-scale collective motions are caught in the first few low-frequency modes, indicating a stable complex [15]. The other complexes, especially tembetarine, had a steeper cumulative variance, indicating a stronger contribution from higher-frequency, more disruptive modes.
Analysis of Residue Correlations and Mechanical Rigidity
The collective behavior and internal mechanics of the complexes were investigated through covariance matrices and elastic network models.
Covariance Matrix Reveals Correlated Motions
The covariance matrices (Fig 2A-D, panel d) visualized the correlated (red), uncorrelated (white), and anti-correlated (blue) motions between residue pairs. The berberine-AKT1 and jatrorrhizine-AKT1 complexes have the most widespread areas of correlated motion (red) compared to the other complexes. A higher degree of correlation frequently indicates a more cooperative and functionally integrated structure, and such correlated motions have been shown to improve complex quality. The tembetarine complex exhibited less correlated motion and more areas of uncorrelated and anticorrelated motion, indicating a less harmonious dynamic pattern.
Elastic Network Model Identifies Stiff Regions
The elastic network models (Fig. 2A-D, panel d) show a network of interconnected atoms, with darker-gray portions representing stiffer, more rigid sections of the protein structure. All four AKT1 complexes generated believable and plausible elastic maps, indicating a well-connected network. Berberine and jatrorrhizine complexes had larger and darker areas around their binding sites, indicating that these ligands improved AKT1's mechanical stability and stiffness more than tembetarine or tinosporine.
Comparative Stability of the AKT1 Complexes
Integrating the results of all analyses enables a comprehensive ranking of the four AKT1-alkaloid complexes based on their dynamic stability:
-
• Berberine-AKT1: This complex was the most stable, with the fewest residue fluctuations (low RMSF), the most favorable energetic profile (lowest eigenvalues), the strongest correlated motions, and a reinforced mechanical network. This makes it the prime candidate for therapeutic targeting.
-
• Jatrorrhizine-AKT1: This complex demonstrated very good stability, with strong correlated motions and favorable eigenvalues, positioning it as a promising secondary candidate.
-
• Tinosporine-AKT1: This complex showed a mixed profile, stabilizing some regions while allowing significant flexibility in others, resulting in intermediate stability.
-
• Tembetarine-AKT1: This complex exhibited the highest flexibility (high RMSF), less favorable energy requirements, and weaker correlated motions, suggesting it forms the least stable complex with AKT1.
Berberine and jatrorrhizine complexes have strong molecular motion stability due to their low eigenvalues and high correlation. A stable ligandprotein combination is more likely to remain and have a biological effect, making it essential for effective inhibition. The gastro-protective properties of T. cordifolia may be due to the persistent binding of berberine and, to a lesser extent, jatrorrhizine to AKT1, which modulates the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Thus, while berberine is the leading option, jatrorrhizine is promising and merits additional study.
Conclusion
This MD simulation study confirms atomistically that T. cordifolia's principal alkaloid, berberine, forms the most stable and stiff complex with AKT1. High stability, low residual fluctuations, favorable eigenvalues, and strong correlated movements indicate a strong and prolonged connection that inhibits targets. These findings explain berberine's traditional use in GI diseases and make it the best option for further experimental development as a nutraceutical or therapeutic agent targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway.


