Биологические особенности паренхимы и стромы костного мозга при апластической анемии
Автор: Погодина Н. А., Семенова Н. Ю., Ругаль В. И., Балашова В. А., Шилова Е. Р., Бессмельцев С. С.
Журнал: Вестник гематологии @bulletin-of-hematology
Рубрика: Оригинальные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.15, 2019 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В обзоре литературы описаны последние данные исследований стромального микроокружения костного мозга, мультипотентных имных стромальных клеток, генетические нарушения в клетках гемопоэтического ряда. Приведены данные, свидетельствующие о вовлечении гемопоэтической ниши в патологический процесс при апластической анемии.
Апластическая анемия, костный мозг, стромальное микроокружение
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170172530
IDR: 170172530
Текст обзорной статьи Биологические особенности паренхимы и стромы костного мозга при апластической анемии
анемию Фанкони, врождённый дискератоз, синдром Швахмана-Даймонда и др. Приобретённая АА может быть результатом воздействия токсинов (органофосфаты, хлорированный углеводород, бензол и др.), вирусов (ВИЧ, вирус Эпштейна-Барра, гепатиты А, В, С, D, E и G), лекарств (циклоспорин), аутоиммунных реакций,беременности и др. [4]. Однако в 50 % случаев АА является идиопатической, когда первопричину возникновения заболевания выявить не удаётся [2, 5].
Различают нетяжелую (нАА), тяжёлую (тАА) и сверх-тяжелую АА (стАА) по степени гранулоцитопении, тромбоцитопении и ре-тикулоцитопении: тАА при наличии двух любых из перечисленных критериев (гра-нулоцитопения < 0,5 х 10 9 /л, тромбоцитопения < 20,0 х 10 9 /л, ретикулоцитопения
1 % с коррекцией на гематокритное число) в сочетании с аплазией костного мозга по данным трепанобиопсии (клеточность КМ не более 30 % от нормальных значений) стАА соответствует критериям тяжёлой, но грануло-цитопения < 0,2 х 109/л; нАА— нет критериев тяжёлой [5, 6]. Также принято выделять АА без ПНГ-клона, с ПНГ-клоном и с синдромом ПНГ, когда появляются признаки внутрисосудистого гемолиза.ТипАА необходимоучитывать при выборе дальнейшей терапии. Так для тяжёлой АА первой линией терапии у молодых пациентов (до 45 лет) при наличии HLA-идентичного донора является аллогенная трансплантация КМ (алло-ТКМ), в то время как для пациентов, у которых нет показаний к алло-ТКМ, применяется комбинированная иммуносупрессивная терапия (ИСТ) [5, 7]. Результатом ИСТ является иммуносупрессия, активация пролиферации ГСК, подавление активации Т-клеток.
Припостановке диагнозанеобходимогисто-логическое исследование КМ пациентов. При АА в КМ наблюдается увеличение количества жировых клеток и уменьшение количества гемопоэтических клеток до 20–30 %. Также в трепанобиоптате могут быть представлены лимфоциты, плазматические клетки, макрофаги и тучные клетки, однако мегакариоциты всегда отсутствуют. В целом наблюдается общая гипоклеточность КМ (рис.1). От других заболеваний, для которых также характерна панцитопения, АА отличается уменьшенным количеством ретикулоцитов в мазке крови и трепанобиоптате (от 0,5 до 0 %), отсутствием выраженной аномалии клеток крови и ги-поклеточностью КМ [8]. Также при АА в плазме крови наблюдается высокий уровень гемопоэтических факторов роста,включая эритропоэтин [9], тромбопоэтин [10] и гранулоцитарные колониестимулирующие факторы [11].
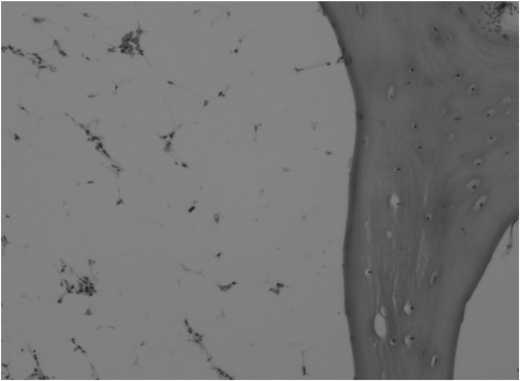
Рисунок 1. Костный мозг при апластической анемии. Гематоксилин-эозин, ув. 200х
АА является гетерогенным заболеванием костного мозга с разной этиологией заболевания. На данный момент выделяют 5 механизмов возникновения АА [4]:
-
1. Дефекты развития гемопоэтических стволовых клеток (ГСК)
-
2. Нарушение продукции и высвобождения важных гемопоэтических факторов роста
-
3. Клеточная или гуморальная иммуносупрессия мультипотентных клеток КМ
-
4. Дефекты стромального микроокружения
-
5. Прогрессивная эрозия теломер хромосом
Все эти нарушения приводят к первичной недостаточности гемопоэтических стволовых клеток (ГСК) и вторичному нарушению баланса деления и дифференцировки ГСК. Самым распространённым механизмом возникновения АА являются патологические аутоиммунные процессы,о чем свидетельствует положительная реакция организма 70 % больных АА на ИСТ [3, 12]. В таких случаях цитотоксические Т-лимфоциты (цТ-лм) разрушают ГСК и прогениторные клетки, которые начинают продуцировать аутоантигены, такие как кинектины,моезин и деазепамсвя-зыващий белок-1 [13].
Индукция апоптоза CD34+ мультипотент-ных предшественников осуществляется за счёт действия цТ-лм и секреции Т-хелперами 1 (Т-х1) ингибиторов цитокинеза — ИФ- γ , TNF- α , ИЛ-17 и ИЛ-27 [3, 14]. Также происходит спонтанное или митоген-индуцирован-ное увеличение продукции мононуклеарами факторов, ингибирующих развитие гемопоэтических клеток: ИФ- γ, ИЛ-2 и фактора некроза опухоли TNF- α [15–17].
ПриААпроисходитуменьшениеколичества регуляторных Т-клеток (CD4+CD25+FoxP3+) (Т-рег), которые необходимы для предотвращения аутоиммунных реакций и подавления иммунного ответа других клеток. Уменьшение Т-рег способствует моно- или олигоклональной экспансии аутореактивных CD8+CD28– T-клеток, которые индуцируют апоптоз ГСК [18–19]. Гиперфункция CD8+ Т-клеточной популяции при тяжёлых формах АА может быть связана и с укорочением их теломер [20]. Помимо уменьшения количества Т-рег пациенты с АА демонстрируют нарушение способности супрессировать эффекторные Т-клетки, в то время как Т-рег здо- ровых доноров успешно выполняют данную функцию [21].
У пациентов с АА также увеличивается количество Т-х1 и Т-х2 и повышается уровень Т-х17 при тАА [21]. Т-х17 продуцируют ИЛ-17 и ассоциированы с аутоиммунными заболеваниями. При АА количество CD3+CD4+ Т-клеток, продуцирующих ИЛ-17, увеличива-ется,по сравнению с контролем и коррелирует с тяжестью заболевания.
В недавнем исследовании показано появление NK-клеток в КМ больных АА, которые, вероятно также участвуют в повреждении КМ [22],в то время как в периферической крови их количество напротив уменьшается [23].
Общими признаками для врождённой и приобретённой АА являются укорочение теломер и дефекты в теломеразе, которые встречаются у 10–20 % пациентов с АА [3]. Теломеры — это гетерохроматиновые структуры с тандемными ДНК повторами на концах хромосом. С каждым клеточным делением теломеры укорачиваются, что приводит к ограничению количества делений соматических клеток (предел Хейфлика). Клетки с короткими теломерами уходят в апоптоз, пока механизмы ДНК репарации не привели к анеуплоидии и опухолевой трансформации. Таким образом, укорочение теломер является важным супрессивным механизмом, который ограничивает способность к клеточной пролиферации и приводит к геномной нестабильности.
Для пациентов с АА было показано укорочение теломер у пациентов, не отвечающих на ИСТ [24–25]. Также была показана ассоциация длины теломер с клональной экспансией, риском рецидива и общей выживаемостью при тяжёлой форме заболевания [26–27]. Однако в данных работах длина теломер не коррелировала с ответом на ИСТ. Несмотря на противоречивость собранных данных, предлагается использование данного признака для прогноза лечения ИСТ [28].
Помимо укорочения теломер в монону-клеарах у пациентов с АА наблюдаются соматические мутации в ГСК, которые приводят к клональной пролиферации гемопоэтических клеток. В связи с этим АА считается пре-опухолевым заболеванием с высоким риском развития таких клональных заболеваний, как пароксизмальная ночная гемоглобинурия (ПНГ), миелодиспластический синдром (МДС) и приобретённая миелоидная лейке- мия [29], и до сих пор неизвестна причина, которая к этому приводит. Было предположено, что причиной развития клональных заболеваний при АА может быть добавление ростовых факторов при иммуносупрессивной терапии, однако это не подтвердилось [30].
У более чем 50 % пациентов с АА появляется минорный клон ПНГ [31] и в 11–17 % случаев развивается синдром ПНГ. Для ПНГ-клона показана преимущественная стабильность на протяжении 1,5–3-х лет [32], однако риск развития синдрома ПНГ у пациентов с минорным клоном всё-таки есть [33]. Согласно некоторым данным наличие минорного ПНГ-клона является хорошим прогностическим признаком успешности прохождения ИСТ [34–35], в то время как проведение ИСТ увеличивает риск развития клональных заболеваний [36]. Так как ПНГ-статус может меняться,в течение заболевания необходимо постоянно проводить оценку наличия ПНГ-клона у больных АА [13].
Помимо формирования ПНГ-клона, у 20– 25 % пациентов с АА появляются другие соматические мутации (например, ASXL1, DN T3A), которые могут привести к мие-лодиспластическому синдрому (МДС) или острому миелоидному лейкозу (ОМЛ). В отличие от ПНГ, когда наличие клона является положительным прогностическим признаком, эти мутации ассоциированы с плохой выживаемости после ИСТ [37].
Генетические нарушения в клетках гемопоэтического ряда являются одними из ключевых в развитии заболевания, однако на судьбу клеток влияет не только генетическая программа, но и то микроокружение, в котором они находятся. В 1978 году была предложена концепция ниши ГСК [38] и с тех пор для ряда гематологических заболеваний было показано участие микроокружения в патогенезе. На данный момент показана вовлеченность микроокружения КМ в патогенез таких заболеваний, как острый миелоидный лейкоз, миелодиспластический синдром, множественная миелома [39], а также хронический лимфолейкоз [40] и др. Однако для АА основная роль отводится аутоиммунным процессам, а роль микроокружения изучена слабо.
На сегодняшний день гемопоэтическую нишу КМ разделяют на две ниши: эндостальную и сосудистую (периваскулярную). Эндостальная ниша представлена остеобластами, нервными клетками, сосудами, остеокластами и макрофагами,однако долгое время основную роль в поддержании ГСК отдавали остеобластам, которые, как считалось, осуществляютрегуляциюза счёт прямыхкон-тактов с ГСК через N-кадгерины [41] и за счёт секреции факторов SCF и CXCL12 [42]. Однако это не подтвердилось экспериментально [42, 43] и на данный момент остеобласты в эндо-стальнойнишерассматривают сточкизрения прямого влияния на более дифференцированные гемопоэтические клетки и опосредованного влияния на ГСК [44]. Кость является васкуляризированной тканью и предполагается, что ГСК в эндостальной нише располагаются не столько рядом с остеобластами, сколько рядом с эндотелием [45].
Помимо того, что сосуды пронизывают кость,они также представлены в строме КМ, где являются нишей для ГСК. Периваскулярная ниша образована эндотелиальными и периваскулярными клетками, которые представляют собой гетерогенную груп- пу мезенхимных стволовых клеток (МСК) [46]. Предполагалось, что в периваскулярной нише располагаются ГСК на стадии деления, а эндост является нишей для покоящихся ГСК [47]. Однако исследование локализации покоящихся и активно пролиферирующих ГСК показало, что 85 % клеток располагаются в области синусоидов и только небольшойпроцентклеток былобнаружен на эндосте [48].
Иммуногистохимический анализ эндостальной и периваскулярной ниш при АА показал снижение количества эндостальных клеток (антитела к остеопонтину), эндотелиальных (антитела к CD34) и периваскулярных (антитела к CD146) [49, 50]. После алло-ТКМ клеточность периваскулярной ниши восстанавливается. Также при АА наблюдается уменьшение плотности сосудов (рис. 2), в то же время данный показатель ниже у пациентов с тАА и стАА, чем у пациентов с нетяжелой формой данного заболевания [51].
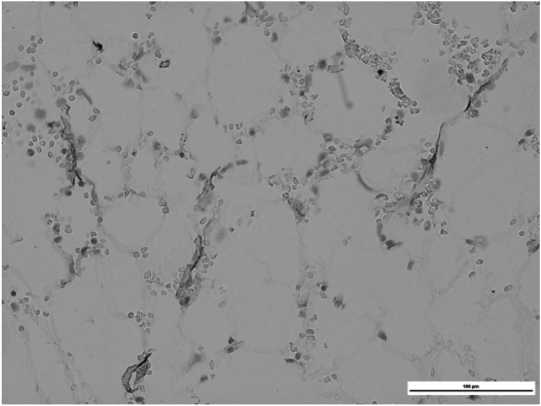
Рисунок 2. Костный мозг при апластической анемии.
Главным фактором, регулирующим ангиогенез, является VEGF (фактор роста эндотелия сосудов), который экспрессируется мегакариоцитами и незрелыми миелоидными клетками [52]. Помимо его основной роли в пролиферации эндотелиальных клеток,он также принимает участие и в регуляции роста и дифференцировки ранних гемопоэтических предшественников [53]. При анализе экспрессии VEGF у пациентов с АА были получены разные результаты в двух группах: повышенная [54] и пониженная экспрессия
-
[13]. В исследованиях с пониженным уровнем VEGF также было показано повышение экспрессии данного белка после ИСТ [54], и алло-ТКМ [50].
Отмечено снижение уровня Ang-1, отвечающего за поддержание ГСК в состоянии покоя, и VCA -1 (CD106), необходимого для адгезии зрелых ГСК к сосудистому компоненту [13]. В работе Park et al. показано уменьшение количества остеонектин+ клеток в КМ, что вероятно сказывается на способности ткани восстанавливаться и ремоделироваться. В то же время различий в экспрессии остеопонти-на, остеокальцина, нестина и SDF-1 у больных АА и контрольной группы найдено не было [22]. Иммунофенотипический анализ эндостальных клеток показал, что при тАА происходит окрашивание антителами к CD51, CD56 и тенасцину, в то время как связывания АТ с CD15, CD34, CD43 и CD117 не происходит, что согласуется с картиной нормального КМ [55].
Одним из важных компонентов микроокружения являются МСК и ММСК (мультипо-тентные мезенхимные стромальные клетки), которые необходимы для регуляции и поддержания гемопоэза. В связи с отсутствием методов работы с МСК, объектом изучения обычно выступают ММСК [46]. ММСК могут дифференцироваться в стромальные клет-ки,составляющие ниши ГСК, и изменение их функционирования может привести к серьёзным нарушениям гемопоэза. В связи с этим особое внимание уделяется изучению ММСК при АА, однако полученные данные достаточно противоречивы, и сделать однозначные выводы о роли ММСК в патогенезе данного заболевания пока нельзя.
В большинстве исследований ММСК выделенные из КМ больных АА (АА-ММСК) имеют нормальный иммунофенотип и морфологию [56–58], и только в одной работе было показано нарушение морфологической структуры АА-ММСК [59]. Также в некоторых работах было отмечено нарушение пролиферативной активности [56,59,60], клоногенного потенциала [59,60], адипогенной [56] и остеогенной дифференцировки [56,59], а также способности поддерживать CD34+ клетки [60]. В одной из работ был проведён анализ профиля экспрессии генов ММСК здоровых людей и АА-ММСК, который показал, что АА-ММСК в большей степени экспрессируют гены,свя-занные с апоптозом,адипогенезом и иммунными реакциями, в то время как в ММСК здоровых людей экспрессируется большое количество генов,вовлечённых в клеточный цикл, пролиферацию и хемотаксис [59].
Однако в 2014 году, а затем в 2016 были опубликованы 2 работы, в которых не были найдены нарушения функционирования
АА-ММСК, описанные другими авторами [57,58]. Стоит отметить, что выборка в работе ichelozzi et al. была ограничена пациентами, успешно прошедшими ИСТ, и результаты работы не могут быть распространены на все случаи АА.
Помимо роли в формировании микроокружения, ММСК также могут выполнять иммуносупрессивную функцию, подавляя пролиферацию Т-клеток и высвобождение цитокинов,а для пациентов с АА показано нарушение данной функции у ММСК [61].
Исследование профиля экспрессии генов АА-ММСК и ММСК здоровых пациентов выявило различие в синтезе FGF2 фактора, который необходим для клеточного роста и гемопоэза. Было показано, что экспрессия данного фактора понижена в АА-ММСК, а также снижено количество FGF2 в экстраклеточ-ной жидкости, что, вероятно, может вносить вклад в патогенез заболевания [62]. Также было предположено, что в АА-ММСК нарушена экспрессия нестина,что приводит к истощению пула ГСК, однако различий в экспрессии нестина при АА и у контрольной группы отмечено не было [22], но было обнаружено нарушение экспрессии CD106, CXCL12, CCL2 и ИЛ-6 ММСК при АА [63]. Наравне с уменьшением экспрессии CD106 падает и количество NF-kb — транскрипционного фактора, регулирующего экспрессию данного белка [64].
На сегодняшний день в литературе представлены недостаточные и во многом противоречивые данные о вовлечении структур микроокружения в патогенез апластической анемии. Однако исследования в этой области продолжаются, так как твёрдо установлено значение дефектов ниши в расстройствах гемолимфопоэза.
В заключение хотелось бы отметить, что сочетанный морфологический, иммуномор-фологический, молекулярно-генетический анализ нишеобразующих структур необходим для обнаружения причинно-следственных связей, определяющих развитие и прогрессию многих заболеваний системы крови, а также для поиска новых мишеней терапии этих заболеваний.
Список литературы Биологические особенности паренхимы и стромы костного мозга при апластической анемии
- Boddu PC, Kadia TM. Updates on the pathophysiology and treatment of aplastic anemia: a comprehensive review // Expert Rev. Hematol.— 2017.—Vol.10, N5.— P. 433-448.
- Mukherjee S, Sekeres MA. What's all the fuss about facts and figures about bone marrow failure and conditions // Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep.— 2012.—Vol. 7, N4.— P. 300-309.
- Dolberg OJ, LevyY. Idiopathic aplastic anemia: diagnosis and classification // Autoimmun. Rev.— 2014.— Vol. 13, N4-5.—P. 569-573.
- Segel GB, Lichtman MA. Aplastic anemia: acquired and inherited // Williams Hematol.— 2010.— P. 463-484.
- Бессмельцев С. С. Диагностика и дифференциальная диагностика апластической анемии // Клин мёд.— 1997.— № 9.— С. 20-25.
- Савченко В. Г. Алгоритмы диагностики и протоколы лечения заболеваний системы крови // М.: Практика.— 2018.— 1008 c.
- Scheinberg P, Young NS. How I treat acquired aplastic anemia // Blood.— 2015.— Vol. 120, N6.— P. 11851197.
- Бессмельцев С. С., Романенко Н. А. Анемия при опухолевых заболеваниях системы крови // Москва: СИМК.— 2017.— 228 с.
- Kojima S, Takaharu M, Yoshihisa K. Circulating erythropoietin in patients with acquired aplastic anaemia // Acta Haematol.— 1995.—Vol. 94.—P. 117-122.
- Emmons R V, Reid DM, Cohen RL, et al. Human thrombopoietin levels are high when thrombocytopenia is due to megakaryocyte deficiency and low when due to increased platelet destruction // Blood.— 1996.— Vol. 87, N10.— P. 4068-4071.
- Kojima S, Matsuyama T, Kodera Y, et al. Measurement of endogenous plasma granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with acquired aplastic anemia by a sensitive chemiluminescent immunoassay // Blood. — 1996.— Vol. 87, N4.— P. 1303-1308.
- Young NS. Pathophysiologic mechanisms in acquired aplastic anemia // Hematology.— 2006.— P. 72-77.
- Петрова Т. В. Этиология и возможные механизмы патогенеза апластической анемии // Онкогема-тология.— 2007.—Т 4.—С. 91-95.
- Sloand E, Kim S, Maciejewski JP, et al. Intracellular interferon-gamma in circulating and marrow T cells detected by flow cytometry and the response to immunosuppressive therapy in patients with aplastic anemia // Blood.— 2002.— Vol. 100, N4.— P. 1185-1191.
- Laver J, Castro-Malaspina H, Kernan NA, et al. In vitro interferon-gamma production by cultured T-cells in severe aplastic anaemia: correlation with granulomonopoietic inhibition in patients who respond to anti-thymocyte globulin // Br. J. Haematol.— 1988.— Vol. 69, N4.— P. 545-550.
- Gascon P, Zoumbos NC, Scala G, et al. Lymphokine abnormalities in aplastic anemia: implications for the mechanism of action of antithymocyte globulin // Blood.— 1985.—Vol. 65, N2.— P. 407-413.
- Shinohara K, Ayame H, Tanaka M, et al. Increased production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in the patients with aplastic anemia // Am. J. Hematol.— 1991.—Vol. 37, N2.— P. 75-79.
- Risitano AM, Maciejewski JP, Green S, et al. In-vivo dominant immune responses in aplastic anaemia: Molecular tracking of putatively pathogenetic T-cell clones by TCR (3-CDR3 sequencing // Lancet.— 2004.— Vol. 364.— P. 355-364.
- Solomou EE, Rezvani K, Mielke S, et al. Deficient CD4+ CD25+ FOXP3+ T regulatory cells in acquired aplastic anemia // Blood.— 2007.— Vol. 110, N5.— P. 1603-1606.
- Wang C, Zhang T, Wang Y, et al. The shortening telomere length of T lymphocytes may be associated with hyper-function in severe aplastic anemia // Mol. Med. Rep.— 2017.—Vol. 17.— P. 1015-1021.
- Kordasti S, Marsh JCW, Al-khan S, et al. Functional characterization of CD4 + T cells in aplastic anemia // Blood.— 2012.—Vol. 119, N9.— P. 2033-2043.
- Park M, Park C, Jang S, Kim D. Reduced expression of osteonectin and increased natural killer cells may contribute to the pathophysiology of aplastic anemia // Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol.— 2015.— Vol. 23, N2.—P. 139-145.
- Li Z, Shao Z, Fu R, et al. [Percentages and functions of natural killer cell subsets in peripheral blood of patients with severe aplastic anemia] // Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.— 2011.— Vol. 91, N16, P. 1084-1087.
- Brummendorf TH, Maciejewski JP, Mak J, Young NS, Lansdorp PM. Telomere length in leukocyte subpopulations of patients with aplastic anemia // Blood.— 2001.— Vol. 97, N4.— P. 895-900.
- Lee JJ, Kook H, Chung IJ, et al. Telomere length changes in patients with aplastic anaemia // Br. J. Haematol. — 2001.— Vol. 112, N4.— P. 1025-1030.
- Cooper JN, Calado R, Wu C, Scheinberg P, Young N. Telomere length of peripheral blood leukocytes predicts relapse and clonal evolution after immunosuppressive therapy in severe aplastic anemia // Blood.— 2008.— Vol. 112, N11.— 442 p.
- Scheinberg P, Cooper JN, Sloand EM, et al. Association of telomere length of peripheral blood leukocytes with hematopoietic relapse, malignant transformation, and survival in severe aplastic anemia // JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc.— 2010.—Vol. 304, N12.— P. 1358-1364.
- Park HS, Park SN, Im K, et al. Telomere length and somatic mutations in correlation with response to immunosuppressive treatment in aplastic anaemia // Br. J. Haematol.— 2017.—Vol. 178, N4.— P. 603615.
- OgawaS.Clonal hematopoiesis in acquired aplastic anemia // Blood.— 2016.—Vol. 128, N3.— P. 337348.
- Gurion R, Gafter-Gvili A, Paul M, et al. Hematopoietic growth factors in aplastic anemia patients treated with immunosuppressive therapy-systematic review and meta-analysis // Hematologica.— 2009.— Vol. 94, N5.—P. 712-719.
- Pu JJ, Mukhina G, Wang H, Savage WJ, Brodsky RA. Natural history of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clones in patients presenting as aplastic anemia // Eur. J. Haematol.— 2011.— Vol. 87, N1.— P. 37-45.
- Глазанова Т. В., Шилова Е.Р, ЧубукинаЖ.В, и др. Динамика ПНГ-клона у больных апластической анемией // Гематол. и трансфузиол.— 2014.—Т. 59, № 1.— С. 38-39.
- Narita A, Muramatsu H, Sekiya Y, et al. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and telomere length predicts response to immunosuppressive therapy in pediatric aplastic anemia // Hematologica.— 2015.— Vol. 100, N12.—P. 1546-1552.
- Sugimori C, Chuhjo T, FengX, et al. Minor population of CD55- CD59- blood cells predicts response to immunosuppressive therapy and prognosis in patients with aplastic anemia // Blood.— 2006.—Vol. 107, N4.—P. 1308-1315.
- Kulagin A, Lisukov I, Ivanova M, et al. Prognostic value of paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria clone presence in aplastic anaemia patients treated with combined immunosuppression: results of two-centre prospective study // Br. J. Haematology.— 2014.—Vol. 164.— P. 546-554.
- Tichelli A, Gratwohl A, Nissen C, SpeckB. Late clonal complications in severe aplastic anemia // Leuk. Lymphoma.— 1994.—Vol. 12, N3-4.—P. 167-175.
- Marsh JCW, Mufti GJ. Clinical significance of acquired somatic mutations in aplastic anaemia // Int. J. Hematol.— 2016.—Vol. 104, N2.— P. 159-167.
- SchofieldR.The relationship between the spleen colony-forming cell and the haemopoietic stem cell // Blood Cells.— 1978.—Vol. 4, N1-2.— P. 7-25.
- Вартанян Н. Л., Бессмельцев С. С., Семенова Н. Ю., Ругаль В. И. Мезенхимальные стромальные клетки при апластической анемии, гемобластозах и негематологических опухолях // Бюллетень Сибирского отделения РАМН.— 2014.—Т. 34, № 6.— С. 17-26.
- Семенова Н. Ю., Бессмельцев С. С., Ругаль В. И. Сочетанный анализ стромальных структур костного мозга и лимфатических узлов при хроническом лимфолейкозе // Клиническая онкогематология. Фундаментальные исследования и клиническая практика.— 2016.—Т. 9, № 3.— С. 363.
- Zhang J, Niu C, Ye L, et al. Identification of the haematopoietic stem cell niche and control of the niche size // Nature.— 2003.— Vol. 425.— P. 836-841.
- Kiel MJ, Radice GL, Morrison SJ. Lack of evidence that hematopoietic stem cells depend on N-cadherin-mediated adhesion to osteoblasts for their maintenance // Cell Stem Cell.— 2007.—Vol. 1, N2.— P. 204-217.
- Kiel MJ, Acar M, Radice GL, Morrison SJ. Hematopoietic stem cells do not depend on N-cadherin to regulate their maintenance // Cell Stem Cell.— 2009.— Vol. 4, N2.— P. 170-179.
- Ding L, Morrison SJ. Haematopoietic stem cells and early lymphoid progenitors occupy distinct bone marrow niches // Nature.— 2013.—Vol. 495, N7440.— P. 231-235.
- Nombela-Arrieta C, Pivarnik G, Winkel B, et al. Quantitative imaging of haematopoietic stem and progenitor cell localization and hypoxic status in the bone marrow microenvironment // Nat. Cell Biol.— 2013.—Vol. 15, N5.—P. 533-543.
- Шипунова И. Н. Иерархическая структура стромального микроокружения кроветворной ткани в норме и при заболеваниях системы крови: дис. ... д-ра биол. наук: 14.01.21.— М., 2018.— 50 с.
- Семенова Н. Ю., Бессмельцев С. Е., Ругаль В. И. Биология ниши гемопоэтических стволовых клеток // Клиническая онкогематология. Фундаментальные исследования и клиническая практика.— 2014.— Т. 7, № 4.— С. 501-510.
- Acar M, Kocherlakota KS, Murphy MM, et al. Deep imaging of bone marrow shows non-dividing stem cells are mainly perisinusoidal // Nature.— 2015.—Vol. 526, N7571.— P. 126-130.
- Wu L, Mo W, Zhang Y, et al. Impairment of hematopoietic stem cell niches in patients with aplastic anemia // Int. J. Hematol.— 2015.— Vol. 102, N6.— P. 645-653.
- Ругаль В. И., Семенова Н. Ю., Шилова Е. Р. Структурные особенности губчатой кости и интрамеду-лярныой микроциркуляции при апластической анемии // Вестник гематологии.— 2014.—Т. 10, № 2.—С. 59.
- Somasundaram V, Tevatia MS, Purohit A, et al. Evaluation of bone marrow microvessel density in patients with aplastic anemia // Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus.— 2017.—Vol. 33, N2.— P. 169-174.
- Möhle R, Green D, Moore MA, Nachman RL, Rafii S. Constitutive production and thrombin-induced release of vascular endothelial growth factor by human megakaryocytes and platelets // Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.— 1997.—Vol. 94, N2.— P. 663-668.
- Gerber HP, Malik AK, Solar GP, et al. VEGF regulates haematopoietic stem cell survival by an internal autocrine loop mechanism // Nature.— 2002.— Vol. 417, N6892.— P. 954-958.
- Füreder W, Krauth MT, Sperr WR, et al. Evaluation of angiogenesis and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in the bone marrow of patients with aplastic anemia // Am. J. Pathol.— 2006.—Vol. 168, N1.— P. 123-130.
- Sillaber C, Walchshofer S, Mosberger I, et al. Immunophenotypic characterization of normal bone marrow stem cells // Tissue Antigens.— 1999.—Vol. 53.— P. 559-568.
- Chao Y-H, Peng C-T, Harn H-J, Chan C-K, Wu K-H. Poor potential of proliferation and differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells derived from children with severe aplastic anemia // Ann. Hematol.— 2010.— Vol. 89, N7.— P. 715-723.
- Bueno C, Roldan M, Anguita E, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from patients with aplastic anemia maintain functional and immune properties and do not contribute to the pathogenesis of the disease // Haematologica.— 2014.—Vol. 99, N7.—P. 1168-1175.
- Michelozzi IM, Pievani A, Pagni F, et al. Human aplastic anaemia-derived mesenchymal stromal cells form functional haematopoietic stem cell niche in vivo // Br. J. Haematol.— 2016.
- Li J, Yang S, Lu S, et al. Differential gene expression profile associated with the abnormality of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in aplastic anemia // PLoS One.— 2012.— Vol. 7, N11.— P. 1-10.
- Hamzic E, Whiting K, Gordon Smith E, Pettengell R. Characterization of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells in aplastic anaemia // Br. J. Haematol.— 2015.—Vol. 169, N6.— P. 804-813.
- Bacigalupo A, Valle M, Podestä M, et al. T-cell suppression mediated by mesenchymal stem cells is deficient in patients with severe aplastic anemia // Exp. Hematol.— 2005.— Vol. 33, N7.— P. 819-827.
- Jiang SY, Xie XT, Jiang H, et al. Low expression of basic fibroblastic growth factor in mesenchymal stem cells and bone marrow of children with aplastic anemia // Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol.— 2014.—Vol. 31, N1.— P. 11-19.
- Shipounova IN, Petrova TV., Svinareva DA, et al. Alterations in hematopoietic microenvironment in patients with aplastic anemia // Clin. Transl. Sci.— 2009.—Vol. 2, N1.— P. 67-74.
- Lu S, Ge M, Zheng Y, et al. CD106 is a novel mediator of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via NF-kB in the bone marrow failure of acquired aplastic anemia // Stem Cell Res. Ther.— 2017.—Vol. 8, N1.— 178 p.


