Digital Islamic Banking Financial Inclusion Mechanism for Digital Financial Empowerment Reading the UAE Experience
Автор: Mekdad Yousra, Benazza Hicham, Belaid Hayat, P. Khatima Bahadji
Журнал: Science, Education and Innovations in the Context of Modern Problems @imcra
Статья в выпуске: 1 vol.8, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Islamic banks have not been immune to the development of financial technology services and start-ups that provide innovative financial solutions; they have experienced a radical transformation over the past years, driven by the growth of digital technologies, the adoption of a digital transformation strategy, as well as the growing demand by the youth for banking products based on the latest innovations, to provide a better customer experience. This highlights the urgent need at the present time for Islamic banking to move towards creating advanced digital services. This study aims to shed light on the reality of digital financial inclusion in the United Arab Emirates, by clarifying the role of digital financial services in financial empowerment through which financial inclusion is achieved. The analytical approach was relied upon to analyze the development of the use of digital technology in the United Arab Emirates and its impact on financial inclusion. This study concluded that the use of digital technology and financial services in the United Arab Emirates has increased as a result of the availability of communications infrastructure and high-speed internet, which has had a positive impact on the levels of financial inclusion in it, through extrapolation of secondary data and statistics issued by the "World Bank", for the period extending from 2017 to 2028 expectations.
Digital transformation, financial technology, Islamic banks, digital banking services, financial inclusion, United Arab Emirates
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/16010346
IDR: 16010346 | DOI: 10.56334/sei/39
Текст научной статьи Digital Islamic Banking Financial Inclusion Mechanism for Digital Financial Empowerment Reading the UAE Experience
Digital transformation is one of the key pillars of the future of the financial and banking sector, as customers are increasingly turning to conducting their banking transactions through electronic applications and smart solutions. In this context, both Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Financial Technology (Fintech) have a real potential to reshape the structure of traditional financial services. Fintech has the capability to make financial services faster, cheaper, safer, more transparent, and more accessible, especially for the large segment of the population that does not engage with the banking sector.
The rapid development of financial technology services and the emergence of startups providing innovative financial solutions have significantly transformed the industry. The integration of AI in financial and banking services reduces operational costs, improves the performance of financial institutions, and enhances profitability. As a result, most institutions seek to invest in modern Fintech applications and tools, as well as in "financial AI."
Financial inclusion is considered a crucial factor in achieving the Millennium Development Goals, particularly those related to poverty eradication. It ensures that financial services are accessible to all segments of society at affordable prices while offering a diverse range of products and services, including lending, saving, and insurance.
Today, financial inclusion plays a vital role in enhancing the accessibility of financial services to individuals wherever they are in a seamless manner. This enables them to utilize their surplus savings or invest their funds in socially beneficial projects without the need for extensive travel and searching, which is a goal that most countries worldwide strive to achieve.
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is among the Arab nations that have made significant efforts to adopt digital transformation strategies to provide necessary financial resources to meet the needs of individuals and institutions, particularly those who are financially excluded. Financial inclusion has become an essential approach to supporting the security and efficiency of payments, given its importance in ensuring the well-being of citizens. It allows unbanked segments of society to transition from cash transactions to digital payments, thereby integrating them into the financial system.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further emphasized the need for financial inclusion. Amid the crisis and its severe social and economic impacts, digital financial services have become increasingly vital in mitigating its negative effects on individuals. Digital technology and the internet have played a crucial role in enabling access to financial services. The pandemic shifted the perception of the information and communications technology (ICT) sector from being merely a tool to an absolute necessity that requires continuous adaptation to keep pace with evolving global trends.
In the UAE, the pandemic has particularly reinforced digital financial inclusion, as the country is among the Arab nations with the highest smartphone penetration rates and widespread internet usage. This has enabled significant progress in financial inclusion, empowering adult women to access financial services, which has contributed to reducing the gender gap.
Based on the above, the following research question arises:
How do digital banking services in the UAE contribute as a mechanism for financial inclusion in empowering individuals financially in the digital realm?
1-1 Importance of the Topic
Both the digital environment and various applications of Islamic financial technology represent a significant breakthrough in the era we live in. Their importance lies in highlighting various applications in the financial industry, encouraging banks to keep pace with them, and their role in stimulating investment activities. Financial inclusion is one of the key criteria that enable low-income segments of society to access digital banking services and facilitate the transition from a traditional economy to a digital economy while managing its associated risks.
1-2 Objectives of the Study
-
- Provide an overview and concepts related to digital transformation and Islamic financial technology.
-
- Highlight various applications of Islamic financial technology and artificial intelligence in Islamic banks.
-
- Understand financial inclusion and digital financial services.
-
- Shed light on the digital infrastructure in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
-
- Examine the state of financial inclusion in the UAE.
-
- Identify how individuals benefit from and are empowered by financial services.
1-3 Literature Review
-
- Kshetri Nir (2021): The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Financial Inclusion in Developing Countries, published in the Journal of Global Information Technology Management. The study aimed to determine how AI contributes to enhancing and activating digital financial inclusion by performing analyses that human workers cannot, leading to improved efficiency of financial institutions and an increase in customer numbers.
-
- Omarini (2017): The Digital Transformation in Banking and the Role of FinTechs in the New Financial Intermediation Scenario. The study examined digital transformation as a major shift in the banking industry, significantly altering banking operations. The findings indicated that digital transformation has substantially changed how banks operate,
requiring them to restructure their processes to adapt to modern technology in terms of products, services, and customer interactions.
-
- Votintseva et al. (2019): Russian Banking Digital Transformation Institutions: Assessments and Prospects. This study evaluated the capabilities of local banks in their digital transformation journey. The findings revealed that digital transformation helps financial institutions focus on providing innovative services, invest in AI technologies, and positively impact banking product markets, services, tools, and customer relations. Additionally, the study emphasized that developing modern banking innovations contributes to improving the efficiency of credit institutions and expanding their digital customer base.
-
- Aziz (2021): Bibliographic Analysis of Studies on Digital Banking and Financial Inclusion from 2014 to 2020. This study explored the relationship between digital banking, financial inclusion, and economic development. It concluded that there is a positive correlation between financial inclusion and digital banking, where the advancement of digital banking services contributes to higher economic development rates. The study also highlighted that mobile banking services significantly enhance financial inclusion for individuals without access to traditional banking services. Although the study primarily focused on general banking, its findings are relevant to Islamic finance as it seeks to establish its role in sustainable development.
Research Outline
The study will cover the following stages:
-
1. Concepts of Financial Inclusion and Digital Transformation
-
2. Theoretical Framework of Digital Banking Services
-
3. Digital Infrastructure Supporting Financial Inclusion in the UAE
2- Concepts of Financial Inclusion and Digital Transformation2-1 Concepts of Financial Inclusion
As of 2021, 76% of adults worldwide had an account at a bank or financial institution, up from 68% in 2017. More importantly, the growth in account ownership was evenly distributed across multiple countries. Over the past decade, Global Findex surveys indicated that most of the growth in financial inclusion was concentrated in India and China.
The COVID-19 pandemic also played a significant role in increasing the use of digital payments. In low- and middle-income countries (excluding China), over 40% of adults who made in-store or online payments for the first time during the pandemic used digital methods such as debit cards, mobile phones, or online banking. This shift underscores the growing importance of digital financial services in enhancing financial inclusion globally.
Figure 01 : Global Account Ownership from 51% to 76% between 2011 and 2021.
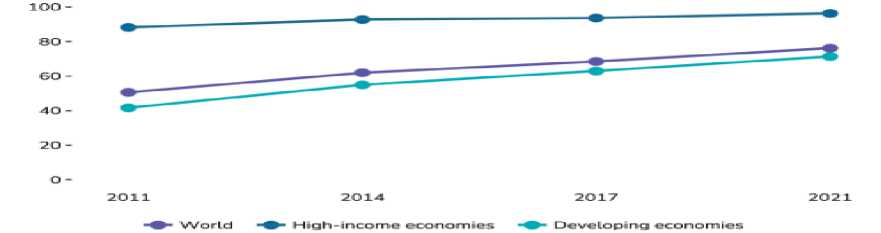
Source :global findex database 2021,
Figure 02 : Contribution of Mobile Money Accounts to an 8 Percentage Point Increase in
Source :global findex database 2021,
Financial inclusion: According to the World Bank's "Global Findex Database" report, there are approximately 1.7 billion people worldwide who do not engage with banks and could be potential customers for banking services. Additionally, more than 200 million small and mediumsized startups and enterprises require financial assistance, guidance, and consulting. This represents an important business opportunity for Islamic fintech companies. The report also mentioned that unbanked populations are predominantly located in Muslim-majority countries or regions, which account for nearly 50% of the unbanked global population. Many of these populations are spread across the poorer regions of North Africa and Asia, so the recent advancements in telecommunications and mobile networks in these areas should help fintech in reaching economically remote populations. (World Bank, 2020).
It is the process of enhancing access to a wide range of regulated formal financial products and services at reasonable times and prices and in sufficient amounts, as per both OECD and the International Financial Education Network. (Council of Arab Banking Governors, 2015)
The process of ensuring the availability and access to financial products and services needed by all segments of society, especially the vulnerable groups, is governed by cost. (Zoheir Mohamed, 2019)
According to the International Monetary Fund, it is the provision of access to all financial products for various segments of society, both institutions and individuals, especially marginalized groups, through official channels, including bank accounts, savings, payment and transfer services, insurance, and credit services. (Bank of Algeria, 2020)
2-1-1 Importance of Digital Financial Inclusion on a Global and Arab Level:
Research shows that countries with deeper levels of financial inclusion experience stronger GDP growth rates and less income inequality, as illustrated in the following figure:
Figure 03 : The Impact of Digital Financial Inclusion on Growth (% of GDP Growth).
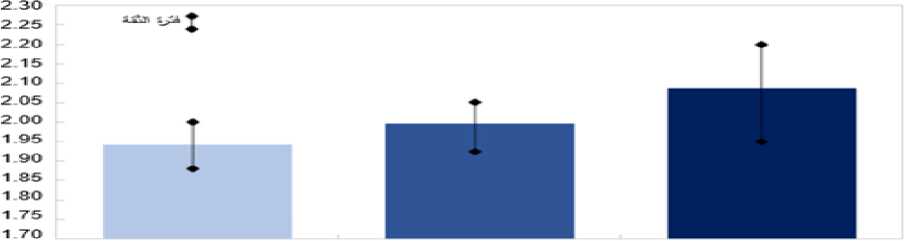
Source: International Monetary Fund.
It is the result of digital access to formal financial services and their use by previously excluded or deprived individuals. These services must be designed according to customer needs, according to CGAP. (CGAP, 2021)
2-1-2 Principles of Digital Financial Inclusion:
-
- In 2020, the G20 issued high-level guidelines on digital financial inclusion policies for youth, women, and small businesses. The principles are distributed as follows:
-
- Support the development of a secure and responsible digital infrastructure that is widely accessible.
-
- Encourage the provision of digital financial products that meet needs and are affordable, while ensuring compliance with international requirements for anti-money laundering, customer due diligence, and digital identity systems.
-
- Improve the availability and accuracy of data regarding access to digital financial products.
-
- Do not adopt policies that aim to increase financial inclusion levels in national strategies.
-
- Support regulatory and legal reforms that reduce inequalities in access to digital financial services, which result in social and economic inequalities.
-
- Promote financial, business, and digital literacy and build capacity through interventions that support digital financial inclusion by leveraging the spread of technology.
-
- Support financial customer protection measures, including data protection, that meet the needs of youth, women, and small and medium-sized enterprises.
-
- Consider developing a regulatory framework that supports digital innovation in both the public and private sectors. (Arab Monetary Fund, 2021)
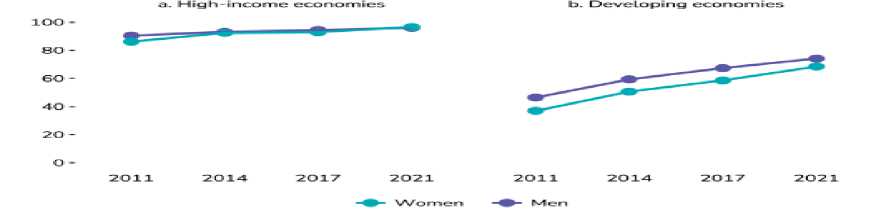
Figure 04: Efforts to Narrow the Gender Gap and Their Results Since 2017.
Source :global findex database 2021,
The report noted that the Middle East and North Africa region made progress in narrowing the gender gap in account ownership, reducing it from 17% in 2017 to 13%. In the Sub-Saharan Africa region, for example, the lack of an identity document remains one of the main obstacles preventing 30% of people without bank accounts from owning a mobile money account. (World Bank, 2020)
The shift towards formal saving methods also represents another opportunity, as around 14 million adults in the region, including 7 million women, saved using semi-formal methods, despite not having a bank account.
For the first time since the creation of the Global Findex Database in 2011, the survey found that the gender gap in account ownership had decreased, helping women gain more privacy, security, and control over their money. The gap reduced from 7 percentage points to 4 percentage points globally, and from 9 to 6 percentage points in low- and middle-income countries. (CGAP, 2021)
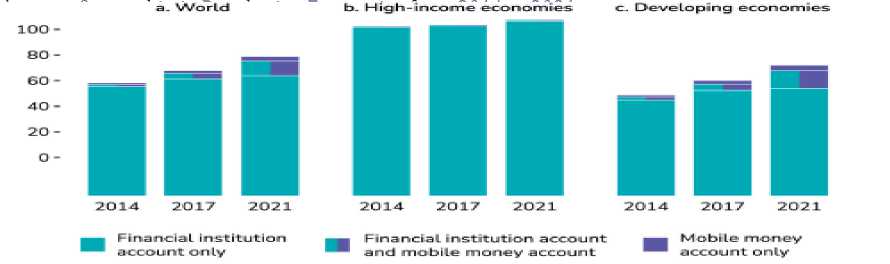
Figur e 05: In Developing Economies, Rapid Growth in the Percentage of Account Holders Using Digital Payments.
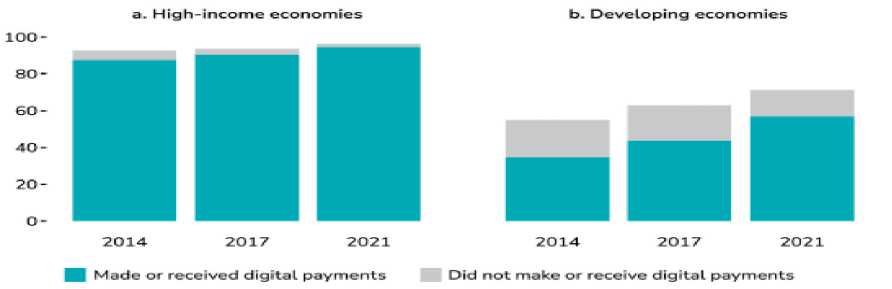
Source :global findex database 2021,
Figure 06: Adults Who Received Government Transfers or Pension Payments in the Last Year (%) in 2017 and 2021.
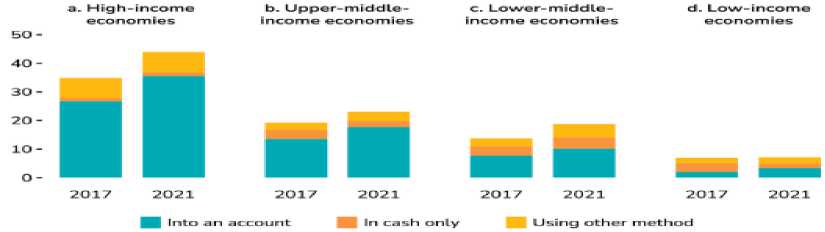
Source :global findex database 2021,
2-2 Digital Transformation
2-2-1 What is Digital Transformation?
Before discussing the importance of digital transformation in Qatar and Saudi Arabia, we must first have a quick look at its definition. Digital transformation is the process in which companies use digital technology to improve and develop all aspects of their operations, resulting in a fundamental change in the way the organization works and delivers value to customers by adopting modern technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and others. This helps companies grow, become more efficient and innovative, and respond better to changing market demands and customer needs.
2-2-2 Importance of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is crucial for improving efficiency, fostering innovation, and enhancing the customer experience. It helps companies stay competitive by integrating digital technologies into their processes, automating operations, and adapting to changing market demands. The importance of digital transformation is highlighted in the following areas:
-
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: It contributes to improving the efficiency of production processes within companies by speeding up performance and reducing dependence on human intervention. This reduces human errors, helps manage resources more effectively, reduces waste, and increases operational effectiveness.
-
- Improved Customer Experience: It allows companies to offer personalized services that meet customer needs precisely and helps customers access and interact with services
online, enhancing the customer experience and increasing satisfaction. This builds strong, long-term relationships with clients.
-
- Enhanced Competitiveness: It assists companies in developing new products and services that meet the rapidly changing market needs. Technology strengthens a company's ability to adapt and respond quickly to changes in the competitive environment, giving them a significant competitive edge.
-
- Data Analysis and Decision Making: It enables the collection and analysis of large volumes of data quickly and accurately, providing valuable insights into operations, market requirements, and customer needs. This contributes to informed decision-making and future planning to achieve business objectives.
-
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: It enhances collaboration among teams within the company, allowing employees to work together efficiently, whether in the office or remotely. Improved internal and external communication boosts teamwork effectiveness and increases productivity.
-
- Supporting Innovation: Digital transformation encourages creative thinking and continuous development within companies. The adoption of modern technologies helps discover new opportunities and develop innovative solutions. A work environment that fosters innovation contributes to achieving sustainable growth and excellence in the market.
-
- Cost Reduction: Digital transformation helps reduce operational costs, including maintenance and updating expenses, enabling companies to use their resources more effectively and boosting profitability.
In summary, the importance of digital transformation lies in enhancing companies' ability to achieve sustainable growth and continuous innovation, making it essential for any organization aiming for success in the digital age.
3- Theoretical Framework of Digital Banking Services
Digital banking services are defined as: "Managing digital banking services for customers through a variety of dedicated and available channels, such as ATMs, smartphones, and online platforms. These channels provide opportunities for banks worldwide to offer banking services to their clients through digital banking, enabling customers to meet their banking needs easily without the need to visit physical bank branches." (Egala, 2021)
3-1 Types of Digital Banking Services:
Digital banking services often include the following operations and activities:
-
- Bank Cards: Debit cards, credit cards, and gift cards.
-
- Point of Sale (PoS) Devices: Portable PoS devices that read bank cards for payment approval and completion.
-
- Mobile Wallets: Google Pay, Apple Pay, Samsung Pay.
-
- Mobile Payment Applications: Zelle, Venmo, PayPal.
-
- Online Electronic Payment Systems: Bank transfers, electronic checks, and buynow-pay-later solutions. (Kazim, 2023)
3-2 Difference Between Digital Banking and Traditional Banking:
The main difference between digital and traditional banking lies in the fact that traditional services require customers to visit bank branches or ATMs in person to conduct banking transactions, and fees are usually charged for those transactions. On the other hand, digital banking relies on modern technologies such as cloud computing, providing an easily accessible platform for all customers, and these services are typically available for free. (Washija Kazim, 2023)
The number of digital banking service users has been growing globally, and the digital banking market is expected to generate benefits exceeding $800 billion, considering the increasing demand for its services. (Digital Banks, 2023)
Figure 07: Evolution of Digital Bank Membership from 2020 to 2024.
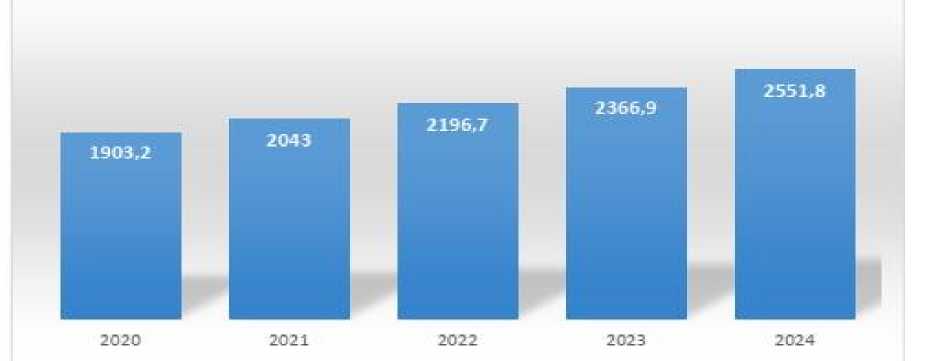
:source :Statista2023
3-3 Opportunities for Expansion in the Use of Islamic Financial Technology:
Approximately 93 Islamic fintech companies primarily operate in financing services, with 65% of them being funded by Peer-to-Peer (P2P) platforms. It is no surprise that P2P platforms are the most common in Islamic fintech due to their embodiment of the essence of Islamic finance. This industry is expected to grow and surpass $3.472 trillion by 2024. (ICD, 2019)
Figure 08: Distribution of Islamic Financial Technology Worldwide.
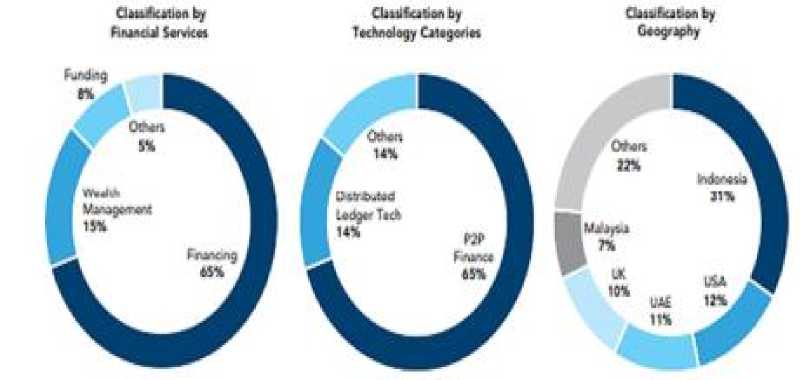
Source: (World Bank Group, 2020, p. 29)
3-3 Distribution of the Use of Islamic Financial Technology Worldwide by Main Area:
We find that Islamic financial technology primarily relies on business and consumer financing, as well as international money transfers, with 62 companies in this field. This is a result of the digital economic trends in the economies of Islamic countries.
Table 01: Distribution of Islamic Financial Technology Usage Worldwide by Main Area.
|
Sector |
Number of Companies |
|
1. Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies |
22 |
|
2. Payments, Money Transfers, and Forex |
20 |
|
3. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Financing |
20 |
|
4. Trading and Investment |
18 |
|
5. Crowdfunding Platforms |
17 |
|
6. Digital Challenger Banks |
10 |
|
7. Alternative Financing |
9 |
|
8. Personal Finance Management |
7 |
|
9. Knowledge Infrastructure for the Islamic Economy |
7 |
|
10. Data |
6 |
|
Analytics |
|
|
11. Robo- Advisors |
5 |
|
12. Takaful (Islamic Insurance) Technology |
2 |
|
Total Number of Islamic FinTech Companies Worldwide |
142 |
Source: (IFN Fintech Landscape, 2020
It is expected that the banking sector will benefit even more from artificial intelligence systems, as specialized reports indicate its anticipated role in enabling the banking community to achieve savings exceeding 1 trillion dollars by 2030. The global AI market was valued at approximately 7.91 billion USD in 2020, and it is expected to reach 26.67 billion USD by 2026. The market is also expected to witness a compound annual growth rate of 23.17% during the forecast period (2021-2026). (IfnFintech, 2019)
Figure 09: Market Value of Assets Managed by Robo-Advisors from 2018 to 2023 (Trillion USD).
Hr- шпй1йг<1 Pur&cUc. Service IRobot Shlpirentc, in Milkin Un:15, Global 2016 3023
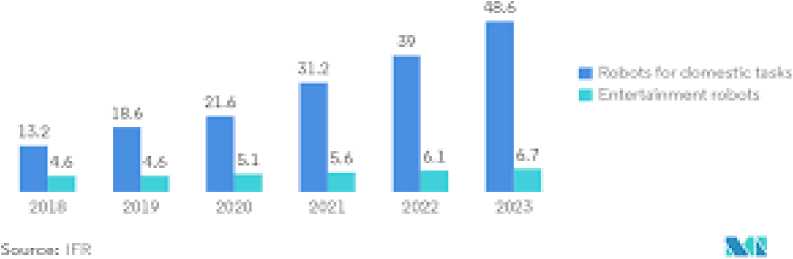
source :business insider
Artificial intelligence is used in the finance industry to examine cash accounts, credit accounts, and investment accounts to assess an individual's overall financial health, keep up with real-time changes, and generate customized advice based on incoming new data. AI and machine learning have benefited banks and fintech by allowing them to process vast amounts of information about customers. This data and information are then compared to obtain results regarding the appropriate services/products customers want, which has greatly helped in developing relationships with clients.
Figure 09: Share of Investment Banks Worldwide Using AI by Application Types.
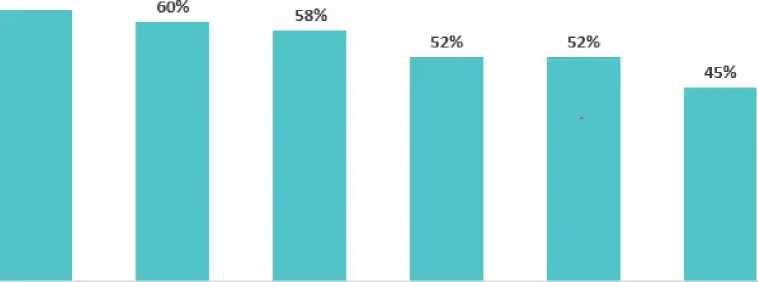
Ma chine learning Predictive analytics Virtual assistant Image analysis Natural language Robotic process (e.g. chatbots) processing automation
Source :worldwide ;
Process automation is one of the key drivers of artificial intelligence in financial institutions. However, it is further evolving into cognitive process automation, where AI systems can perform more complex automation processes. For example, in May 2020, Traydstream, a FinTech company that scans commercial documents using artificial intelligence (AI), partnered with Infosys Finacle to implement blockchain technology and increase automation in trade finance. This partnership may allow Finacle’s blockchain technology, called Finacle TradeConnect, to integrate with the Traydstream platform, which uses AI to scan documents and reduce the time required for verifying rules or regulations in trade.
4- Digital Infrastructure Supporting Financial Inclusion in the UAE4-1: Strengthening the Digital Financial System
One of the main trends in the digital banking market in the United Arab Emirates is the focus on personalized and seamless customer experiences. Digital banks are leveraging advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to offer customized financial solutions and enhance customer engagement. Furthermore, partnerships between traditional banking institutions and fintech companies have become more common, leading to the introduction of innovative digital banking products and services in the market. The following figure illustrates the percentages of certain digital banking services in the UAE for 2023.
In 1971, the UAE adopted continuous modernization and development by considering the latest technological updates and developments. It was one of the first Arab countries to launch the e-government project and continued to lead in all stages, eventually reaching the digital government, which aligns with the Fourth Industrial Revolution and the era of data and technologies based on artificial intelligence. The different stages it has gone through are outlined below:
Table 02: Stages of Digital Transformation in the United Arab Emirates.
|
ear |
Strategies |
|
982 |
Establishment of the General Information Authority. |
|
985 |
Introduction of internet access in the UAE. |
|
995 |
Establishment of Dubai Internet City. |
|
999 |
Launch of the first e-Government initiative in the region ( Dubai eGovernment ). |
|
000 |
Introduction of the first electronic payment service ( eDirham ). |
|
001 |
Establishment of the Telecommunications Regulatory Authority (TRA). |
|
003 |
TRA assigned to oversee digital transformation. |
|
009 |
Launch of the UAE government portal ( uae.gov ). |
|
010 |
Launch of the Mohammed bin Rashid Smart Learning Program. |
|
011 |
Launch of the Smart Government Initiative ( Mobile Government ). |
|
013 |
Launch of the Federal Electronic Network ( Fed Net ). |
|
015 |
Introduction of the Smart ID system. |
|
016 |
Launch of the Digital Identity System ( UAE Pass ). |
|
018 |
Launch of the Digital Wallet on the Blockchain platform. |
|
019 |
Preparation for the next 50 years of the UAE Union. |
|
020 |
Decree announcing the Telecommunications and Digital Government Regulatory Authority ( TDRA ), marking the Digital Government era. |
|
021 |
Official transition to Digital Government Strategy. |
Source: (Telecommunications Regulatory Authority and Digital Government, 2021,
Page 7)
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has the requirements for digital transformation, ranking 21st globally in 2021 across three pillars: smart services, telecommunications and information technology infrastructure, and human capital. This represents an improvement of eight places compared to 2016. Regarding the Smart Services Index within the e-Government Development Index (United Nations, 2020), the UAE ranked 8th globally. In the broadband wireless index, it ranked first globally, and in cybersecurity, it ranked 4th globally, according to the Global Digital Competitiveness rankings. The UAE was also ranked first in the Arab world across all of the above indicators.
The digital banking market in the UAE is experiencing significant growth and development, driven by various factors that shape the financial landscape in the region. These factors can be explained in the following points: (Statista, 2024)
Figure 10: Evolution of Digital Banking Deposits in the UAE from 2017 to 2028.
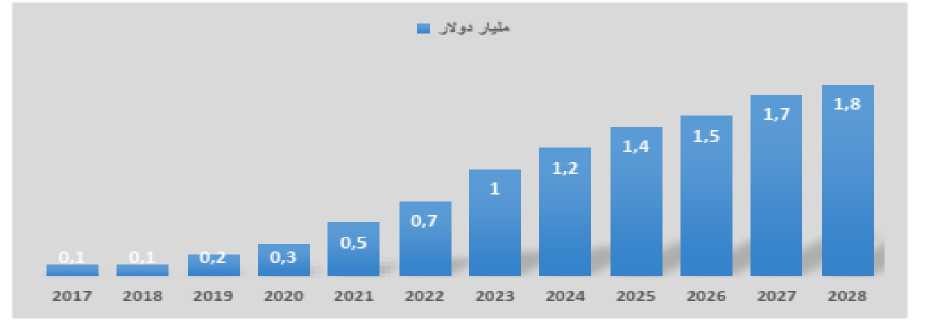
Source: Statista, 2024
4-2 Market Trends:
One of the main trends in the digital banking market in the United Arab Emirates is the focus on personalized and seamless customer experiences. Digital banks are leveraging advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to offer customized financial solutions and enhance customer engagement.
Furthermore, partnerships between traditional banking institutions and fintech companies have become more common, leading to the introduction of innovative digital banking products and services in the market.
The following figure illustrates the percentage distribution of various digital banking services in the UAE for 2023.
Figure 11: Percentage of Digital Banking Services in the UAE for 2023.
Money Transfer via
Mobile
Mobile Payment
Payment via Internet
Ownership о f Digit a 1
Currencies
Percentage
Source: (Telecommunications Regulatory Authority and Digital Government, 2023, Pages 18-36)
4-3 The State of the Internet in the UAE
The following table illustrates the development of the percentage of internet users in the UAE in 2023.
Table 03: Evolution of Internet User Percentage in the UAE (2023).
|
Individual monthly share internet volume (gigabit) |
Download speed on smart phones (MB/s) |
The percentage of internet users |
|
19.6 |
179.6 |
100 % |
Source: (World Bank, 2023, p. 173)
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has a high smartphone penetration rate, allowing a significant portion of the population to access mobile devices. This widespread smartphone adoption has created a favorable environment for the growth of digital banking services. Additionally, government initiatives aimed at promoting a cashless economy and digital transformation have accelerated the adoption of digital banking solutions in the country.
Figure 12: Evolution of the Number of ATMs in the UAE from 2017 to 2028.
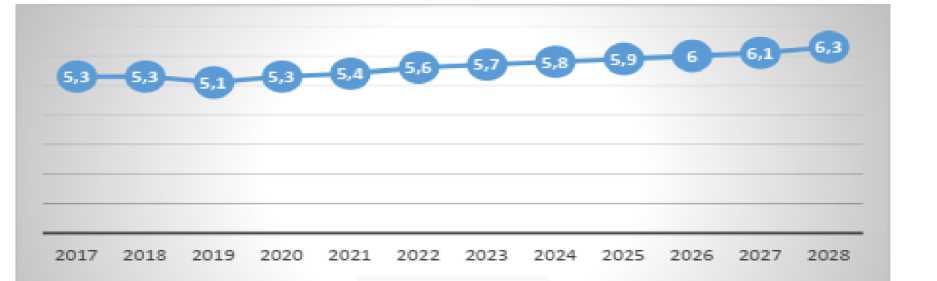
Source: (Statista, 2024)
The expansion of digital banking services in the UAE has led to a gradual increase in the number of ATMs, as part of the country's efforts to improve access to financial services and enhance financial inclusion.
The following figure represents the actual and projected evolution of the number of ATMs in the United Arab Emirates from 2017 to 2028.
Figure 13: Value of Granted and Projected Loans from UAE Digital Banks Between 2017 and 2028.
2.5
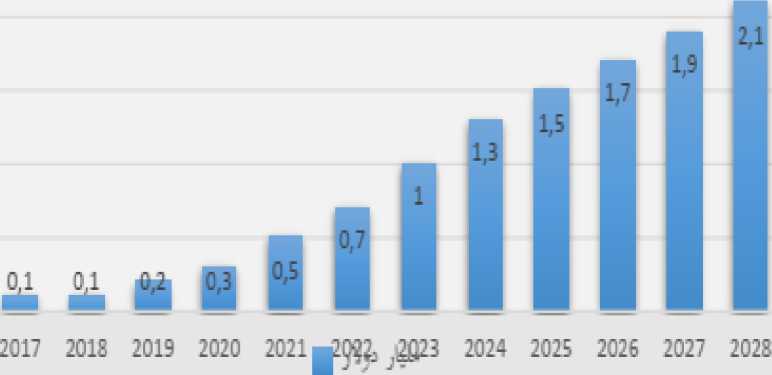
Source: (Statista, 2024)
Regarding the value of loans provided by UAE digital banks, it reached $1 billion in 2023, marking a 30% increase compared to the previous year. It is expected to reach $2.1 billion by 2028.
Figure 14: Actual and Projected Profits of UAE Digital Banks Between 2017 and 2028.
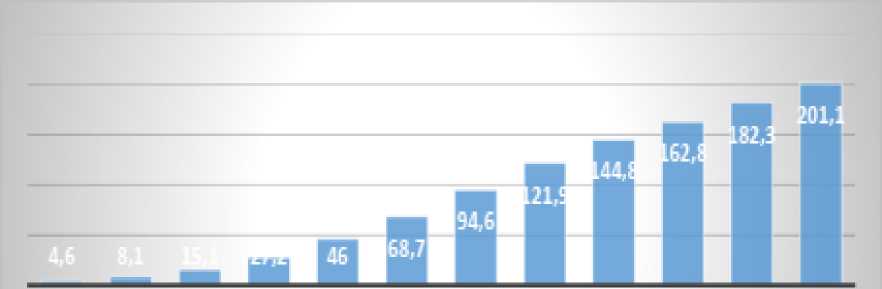
2017 201В 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 2026 2027 2028
Source: (Statista, 2024)
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has achieved significant profits following the digitization of its banking sector. In 2023, its profits reached $94.6 million, and they are expected to exceed $200 million by the end of 2028. The following figure illustrates the growth of UAE digital banks' profits between 2017 and 2028.
The UAE ranked first in the Arab world and 24th globally in the 2023 Global Financial Inclusion Index issued by Principal Financial Group, surpassing several countries, including France, Japan, and Spain. (Al Khaleej, 2023)
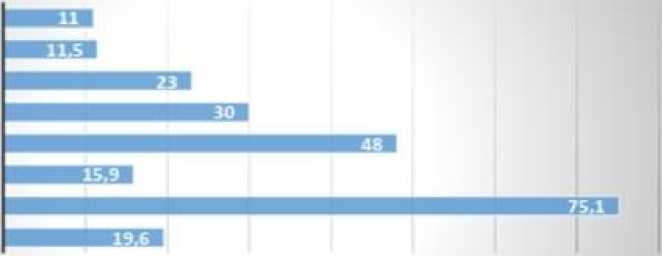
Figure 15: Financial Inclusion Rate of Adults in the UAE as of January 2023.
Trans fer of money via mobile phone or internet (2022).
Mobile phone money account.
Use of mobile phone or internet to pay bills (2022)
Making a purchase using a mobile phone or internet
Ownership of a credit card
Ownership of a debit card
Digital payment
Ownership of an account with a financial institution
Women (15 years)
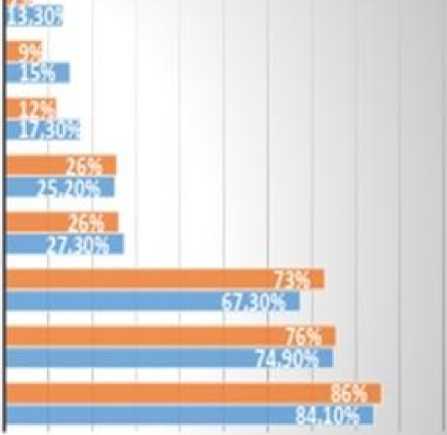
Men (15 years)
Source: (Statista, 2023)
The increasing awareness of the importance of financial services, the adoption of financial technology, and the shift towards cashless transactions reflect a growing trend. Additionally, data indicates an opportunity to further increase the use of credit cards and mobile or online purchases (Statista, 2023), suggesting room for growth in these segments of the financial market. Given the progress the UAE is making in financial inclusion, these rates are expected to rise over time with increasing awareness and improved access to these services.
5- Conclusion
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has achieved an advanced status in financial inclusion indicators, making it a leader in this field within the Arab world. The country has taken significant steps that have demonstrated the benefits and opportunities of digital technologies in enhancing access to secure, transparent, and low-cost financial services. As part of its strategy to strengthen financial inclusion, the UAE has seen improvements in financial accessibility.
The Central Bank of the UAE’s 2022 strategy supports this leadership by focusing on the security and efficiency of digital payment systems and the integration of technology in the banking sector. This expands the range of banking services and provides individuals with more diverse, secure, and transparent financial products, making the UAE a model for achieving financial inclusion through digital banking. This brings us to a set of key findings and recommendations.
Findings:
-
- The UAE has recorded significant growth in financial inclusion indicators through the use of advanced digital technologies.
-
- The country has a highly developed internet network, enabling
institutions and individuals to easily access financial services.
-
- Mobile phone ownership in the UAE has reached 97.6%, while
smartphone penetration is nearly 98%.
-
- The use of artificial intelligence and cloud computing in UAE digital banks has driven innovation in digital banking services.
-
- Digital banking services have contributed to increased profits for UAE digital banks.
Recommendations:
Based on our study, we propose the following:
-
- Develop regulations and policies to improve the expansion of digital financial services.
-
- Enhance transparency in digital financial transactions by leveraging the expertise of leading global economies in this field.
-
- Strengthen digital and technological competencies to ensure the effective use of financial software.
-
- Provide incentives for digital payment users to encourage widespread adoption.
-
- The UAE authorities should increase investment in financial sector infrastructure.
-
- Revise educational curricula to incorporate skills required for new financial technologies.
-
- Innovate new financial products to expand access to digital insurance services.


