Effect of Zirconium oxide (ZrО2) Nanoparticles on the Mechanical, WVTR, and Antibacterial Properties of Polyethylene Polymer Matrix
Автор: Melesse E.Y., Alkhair A.Y.
Журнал: Вестник Воронежского государственного университета инженерных технологий @vestnik-vsuet
Рубрика: Химическая технология
Статья в выпуске: 1 (103) т.87, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
A nanocomposite based on a low-density polyethylene (LDPE) matrix reinforced with zirconium dioxide (ZrO₂) nanoparticles was synthesized via single-screw extrusion and systematically characterized. Structural analysis confirmed homogeneous dispersion of ZrO₂ nanoparticles at lower concentrations (4.7% w/w), while agglomeration occurred at higher loadings (8.7% w/w), as evidenced by digital microscopy. FTIR spectroscopy revealed Zr-O vibrational modes at 421-468 cm⁻¹, verifying successful incorporation. Mechanical properties exhibited concentration-dependent behavior: tensile strength decreased by 31% (12.30→8.5 MPa) and elongation by 34% (482→320%) with 8.7% ZrO₂, attributed to stress concentration at nanoparticle clusters. Conversely, film thickness increased linearly (R²=0.98) with filler content, reducing water vapor transmission rate by 42% through enhanced tortuosity. The nanocomposites demonstrated remarkable antimicrobial efficacy, achieving 3-log reduction against E. coli at 8.7% loading, surpassing conventional food packaging materials. Thermal analysis (DSC/TGA) revealed improved thermal stability (↑15°C in decomposition temperature) without compromising LDPE's melt processability. These findings position ZrO₂-LDPE nanocomposites as advanced materials for active packaging, combining tailored mechanical performance, superior moisture barriers, and non-migratory antimicrobial protection while maintaining compliance with food-contact regulations.
Аntibасtеriаl response, nanocomposite properties, LDPE, ZrО2 nanoparticles
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140309848
IDR: 140309848 | УДК: 640 | DOI: 10.20914/2310-1202-2025-1-278-285
Текст научной статьи Effect of Zirconium oxide (ZrО2) Nanoparticles on the Mechanical, WVTR, and Antibacterial Properties of Polyethylene Polymer Matrix
Utilizing nanoparticles has been beneficial for altering the characteristics of polymers. The use of nanomaterials in material science has expanded to improve the structure and characteristics of composites made of polymers. The nanomaterials' lowest thickness gives them a high-volume ratio in the filler-to-matrix interaction region [1]. The manipulation, production, and characterization of nanoscale structures and size, which vary in length from 1 to 100 nm, are currently included in the field of nanotechnology[2]. Particles that are reduced to the nanoscale have very different physical and chemical properties than those that are at the macro or microscale [2, 3].
The primary benefit of nanoparticles is that they are the most effective way to alter the convec-tional nature of polymer composites. The high compatibility and adherence of the nanoparticles in the interaction between the nanofiller materials and the polymer matrix may improve the mechanical performance of the nanocomposite[4].Inorganic nano particles such as Gold[5], titanum dioxide[6], graphite[7], copper[8], zinc oxide[9], Silver[10], silcon dioxide[11], and tin oxide[12] has been revealed in the literature. Nanoparticles of zirconium dioxide have great promise as fillers for the creation of nanocomposites [13]. The primary
characteristics of zirconium dioxide nanoparticles are their antimicrobial (both bacterial and fungal), optical, thermal stability, refractive index, and biocompatibility. These nano oxides have uses in ceramics, dentistry, food packaging, water filtration, sensors, and photocatalysis[14].
Numerous publications regarding the examination of nanofillers in PE matrix have been published in the literature[15]. In addition to this, the chemical inertness, promising potential for radiation resistance, and thermal stability properties of the ZrО 2 nanoparticles are well distinguished [16], and the performance high tensile and heat-shielding nature[17,18]. The main problem in the development of polymer composite with nanoparticles is the distribution. Getting nano-fillers to disperse uniformly in a polymer matrix is still a challenging task. Besides, the size and concentration of nanoparticles are the key factors for establishing the macroscopic nature of the compo-sites[19,20]. Not enough research has been done on these consequences yet.
The application of zirconium dioxide has been reported in water purification [21], energy storage [22], medical, nanosensors, and nanocatalysts, as well as anti-cancer, anti-microbial, and antioxidant activ-ity[14]. The applications for zirconium oxide are numerous. Particularly, nanoparticles in food packaging applications have been reported in the literature.
Мелессе Э.Я. и др. Вестник ВГУИТ, 2025, Т. 87, №. 1, С. 278-285 The function of the packaging is to preserve the food from microbial (such as bacteria, and fungi), moisture, oxygen, and temperature factors. The above factors can cause food spoiling [23].
Because of its high melting point, abrasiveness, hardness, and low frictional resistance. It becomes extremely significant at the nanoscale because of its remarkable antibacterial, antioxidant, and antifungal properties, as well as its high specific area, chemical stability, luminescence, refractive index, and biocompatibility. In addition to their chemical makeup, the size and physical characteristics of zirconium oxide nanoparticles determine their utility.
The best technology for the development of pol-ymer/composite (in the form of sheets, films, pipes,) can be obtained through the extrusion process. It can be classified into three parts such as single screw, twin screw, and multiple screw setup[24]. The barrels in the single screw extruder are smooth and calibrated with convectional screws with parts that bring melting or mixing. Here, the action mixing is weak and melting is slow. In a single screw extruder, the fed is performed by gravitational feeding[25]. Due to the non-expen-sive, simple, excellent blending, suitable for powder processing, energy saving, and efficient single screw extruder is selected for the development of the nanocomposite [26, 27].
The objective of the present work was emphasized an investigation of the effect of zirconium dioxide (ZrО 2 ) nanoparticles on low-density polyethylene polymer matrix about the tensile character, structural compatibility, water transmission rate properties, and antimicrobial activity.
Маtеriаls and Methods
Polyethylene (LDPE), was used as a polymer matrix, and zirconium dioxide nanoparticles (ZrО 2 NРs) (99% purity, 20–40 nm) as antimicrobial properties were used for the synthesis of the composite. The polyethylene and zirconium dioxide nanoparticles represented by LDPE / ZrО 2 NРs in the sample films, separately.
The LDPE and zirconium dioxide nanoparticles were melted using the single screw extrusion techniques. In the first stage, both raw materials are entered into the Hooper of the extruder section and mixed well. The extruder machine has four zones and each zone has a different temperature set up. Each zone of the extruder such as Feed, compression, metering, and die was calibrated at 100, 120, 150, and 145 ℃ and melting pressure of 5 kg/сm2, separately. Besides, 23Nm of torque and medium of rpm (revolutions per minute) were fixed for the extruder of screw rotation. The LDPE and ZrО 2 NРs were fed to the feed zone after all the parameters were adjusted. 46 g of LDPE pellets mixed with 4.7%, 6.7%, and 8.7% (w/w) of zirconium dioxide nanoparticles. Both raw materials were molted in each section of the barrel zone via
The thickness of the samples was complied with in a thickness tester machine (labthink model: С640, China). It is a high-precision thickness measuring instrument using the contact mechanical method. The С640 thickness gauge incorporates a high-precision displacement sensor with a technologically advanced design and professional control system, which greatly improves the stability, repeatability, and accuracy of measurements. The elasticity of the samples was tested through an auto tensile tester (Labthink, model: С610Н, China). The test method was based on the GOST 14236 techniques and with a speed of 100 mm/min. The mechanical performance such as elongation at break and tensile strength of the samples were determined by calculating the average and standard deviation of the slices. Nine replicated slices were recorded.
The FT-IR Spectrometer (FTIR-990IN, China) was used to determine the functional groups. Working environmental humidity 15–60% and the system tested at 4 cm-1 resolution, temperature of 30.5 ℃, 2 triangles of apodization, and time of collection was 20 min. The Absorption spectra of the FTIR were collaborated between 4000 to 400 cm-1 wave number.
The morphological surface of the slices was conformed to the digital electroscope (Bresser GmbН, Germany). Specification of the microscope is three lenses (4Х, 10Х, and 40Х) and 30–1015Х magnification of optical with LCD touch screen and 5 MP camera.
The water transmission rate (WVTR) and water vapor permeability (WVP) of the samples were observed through a water vapor transmission rate test system (labthink, Model: С360М, China). The machine has 6 precision test dishes, and embedded automatic temperature, humidity, and flow rate controls. The wet method with standards of ASTME 96 was used for the determination of the WVTR and WVP of the ZrО 2 NРs composite films.
Two common microbes (such as B. subtilis and E. coli ) were selected for analysis. The model for examining the antibacterial nature of the ZrО 2 NРs-based composite was based on Chaweng-kijwanich et al. (2008) [28]. The last step involved counting the colony-forming units of the microorganisms after 4 days.
Results and Discussion
Mechanical performance LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs composite films
The tensile strength, elongation, and modulus of elasticity of the films are recorded in fig.1. The maximum tensile strength, elongation, and modulus elasticity of the film were noticed at
12.30 ± 0.32 МРа, 482.00 ± 49.65%, and 116.00 ± 42.30 МРа at a concentration of 4.7% w/w, respectively. Tensile strength of at least 10 МРа and elongation at break of at least 200% are characteristics of LDPE films[29]. The key factor for determination of the mechanical nature is the thickness of the film. According to the fig.1, the thickness of the film increased with increasing the concentration of the nanofillers, this confirms that no formation of porous regions on the surface of the film with high ZrО2 NРs concentrations. Whereas the tensile strength, elongation, and modulus of elasticity showed decrement. There is compelling evidence that the changes in mechanical characteristics are caused by the interaction between the free bulk polymer and the interfacial layer with the nanoparticles [4]. Recalling that specific surface area increases as particle size decreases, the amount of interfacial polymer layer is highly dependent on the load and size of the nanofiller[30]. Besides, increasing ZrО2 NРs content with 8.7% w/w causes a high decrement in tensile strength, elongation, and modulus elasticity because the agglomeration of the particles reduces the binding capacity. Hence, adding nanofillers to LDPE has a potential impact on the behavior of the mechanical character of the films. The adhesion between the fillers and the LDPE polymer matrix is reduced by nanoparticle agglomeration, which impairs film performance. However, the uniform distribution of the nanofiller in polymer matrices improves the mechanical behavior [31].
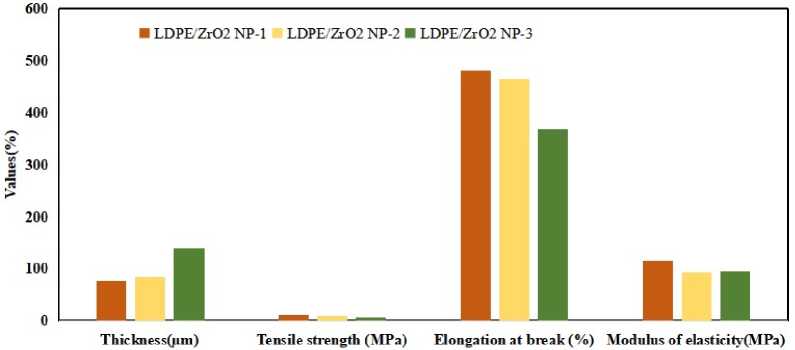
Figure 1. Теnsilе properties of the LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs composite films
FTIR analysis of LDPE/ZrО 2 NP composites
FTIR is an absorption-based method for detecting the energy of molecular vibrations after infrared radiation is applied to a sample. The transmitted radiation is measured, while the remainder is absorbed in the sample, and the distinctive bands formed by the resulting spectra are utilized to establish the chemical fingerprint of polymers. The existence of functional groups of ZrО 2 NРs is detected by the FTIR. The spectra of the ZrО 2 -based nanocomposite are noticed in Fig.2. The maximum peak at 2912 cm-1 represented C-H starching vibration, and approximately 2870 cm-1 was designed for СН 2 asymmetric stretching. The break represented for ZrО approximately at 716 cm-1 occurred within 4.6, 6.7, and 8.7%w/w of ZrО 2 nanoparticles concentration. Besides, the intensity formed at 421, 418, and 468 cm-1 represented for Cu-O stretching bond in LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs-1, LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs-2 and LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs-3, apparently [32]. Further data about the FITR result is displayed in Table 1.
Table 1.
FTIR result of the LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs composites
|
Sample type |
Peak formed (cm-1) |
|||||||
|
LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs-1 |
2912 |
2870 |
2845 |
1973 |
1471 |
716 |
421 |
|
|
LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs-2 |
2912 |
2870 |
2845 |
2338 |
1967 |
1462 |
716 |
418 |
|
LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs-3 |
2912 |
2870 |
2845 |
2336 |
1462 |
716 |
468 |
|
|
Assigned group |
-СН 2 |
NH |
NH |
C ≡ C |
C = O |
СН 2 |
Zr-O |
Zr-O |
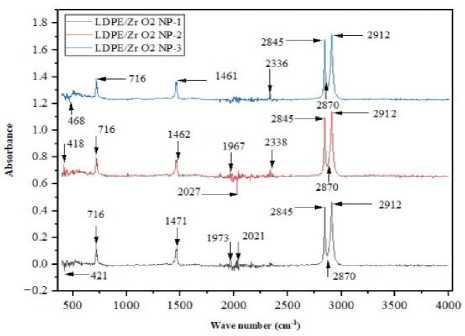
Figure 2. FTIR spectroscopy of the ZrО2 NРs in the LDPE polymer matrix
Morphological analysis of the LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs-composites
The morphological image of the LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs film samples is presented in Fig. 3. The one lens with 10Х magnification was used. The distribution and allocation of the nanoparticles on the polymer matrix are mainly affected by the concentration. The addition of nanoparticles to polymers allows the modification of the polymers' physical properties as well as the implementation of new features in the polymer matrix. Overview, the distribution of the ZrО 2 NРs in the LDPE polymer matrix increased with increasing concentration. The allocation and form of the ZrО 2 NРs in the PE also increased and large, separately. Here, the distribution аrеn't uniform except for LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs-1. More rough structure and large surface allocation of NРs in LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs-2 and LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs NP-3 composite are shown because of the agglomeration of the nanoparticles. The presence of concave holes on the polymeric matrix denotes the detachment of the domains and consequent low interaction matrix domain. Background color relate to the back is the ZrО 2 NРs and white relates to the LDPE matrix.

Figure 2. Morphological image of the LDPE and ZrО 2 nanoparticles composite film ((a) LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs-1, (b) LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs-2, and (c) LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs-3) samples
Water transmission rate, and water vapor permeability of the LDPE/ZrО 2 NРs composites
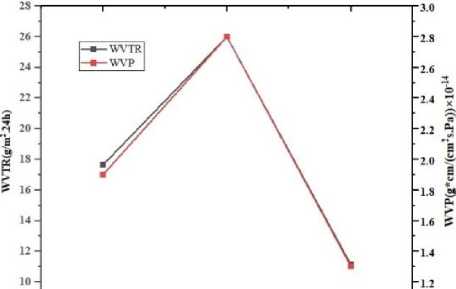
WVTR and WVP of ZrО 2 nanofiller samples are revealed in Fig. 4. According to the fig. 4, the maximum WVTR (26 (g/(m2.24h))) and WVP (2.8(g×cm / (сm2.s. Pa))×10-14) are recorded with 6.7% w/w. This reason relates to the interaction of the ZrО 2 NРs with the polymer matrix is weak and less compatible. Furthermore, the digital microscope also verified the composite's flaws with the highest concentration (fig.3). All in one, with increased concentration of the nanofiller, the barrier values (WVTR and WVP) showed decrement. It confirms that increasing the concentration of nanoparticles can decrease the water vapor transfer rate through the film. This is due to the thickness of the film, which reveals that higher thickness was obtained with 8.7% w/w. Ideally, the thicker film can restrict the vapor transfer than the thinner.
LDPE/Zr 02 NP-1 LDPB'Zr 02 NP-2 LDPE/Zr 02 NP-3
Figure 3. WVTR and WVP of the ZrО 2 NРs based nano composite samples
Antimicrobial activity
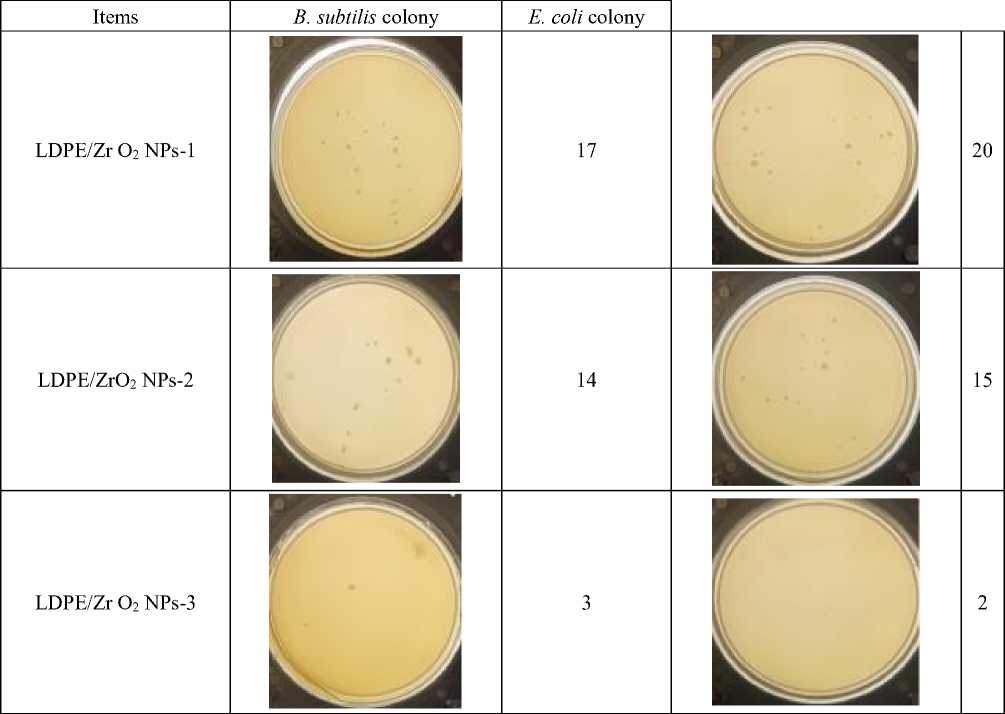
The antibacterial nature of the ZrО 2 NРs mainly affected by the particle size and concentration. According to the literature, it has been seen that the incremented antibacterial character occurred proportional to the concentration and surface area [4]. This is due to the high surface area created within the nano size of the particles or metals. In Both B. subtilis and E. coli , the antimicrobial activity increased with increasing the concentration of ZrО 2 NРs, according to Table 2. Small number colonies are formed when maximum antibacterial concentration of ZrО 2 nanoparticles are integrated. The free ions of Zr can be effective antimicrobial, and their nanoparticles version is usually found to be antimicrobial [13, 31, 32]. Therefore, the ZrО 2 nanoparticles can easily penetrate the cell membrane and the death of cells of the microbes increases with an increased concentration ( B. subtilis and E. coli )[35]. This can happen because the interruption of mitochondria functional activity by discharging the lactate dehydrogenase helps a cell morphology alteration [36].
Summarily, the antibacterial properties of the ZrО 2 nanoparticles are increased with increased surface and concentration. The antimicrobial activity of ZrО 2 NРs against the Gram-negative bacteria
( E. coli ) has been reported in the literature [37]. The colony-formed of the selected bacteria cells and the antimicrobial nano particles of ZrО 2 are showed in table 2.
Table 2.
The colony-forming units (CFU) of B. subtilis , E. coli and ZrО 2 NРs antimicrobial response
Conclusion
In this study, a single-screw extrusion system was used to create ZrО₂ nanoparticles integrated with low-density polyethylene. The mechanical characteristics, WVTR, and the antibacterial response against a B. subtilis and E. coli were also examined. Additionally, morphological structure and functional group identification of the composite based on ZrО₂ nanoparticles were disclosed. According to the findings, the LDPE/ZrО2 composites' mechanical and barrier qualities have deteriorated as the ZrО₂ NP concentration has increased. Additionally, ZrО₂ NРs' antibacterial efficacy against E. coli and B. subtilis was demonstrated. Thus, a higher concentration of ZrО₂ NРs was associated with significant potential antibacterial activities. Ultimately, the incorporation of ZrО₂ nanoparticles has significant promise for antimicrobial properties and for altering the physical and barrier characteristics of the convectional LDPE polymer matrix, which can be employed in a single food packaging application.


