Evaluation of the docking algorithm based on tensor train global optimization
Автор: Oferkin I.V., Zheltkov D.A., Tyrtyshnikov E.E., Sulimov A.V., Kutov D.C., Sulimov V.B.
Рубрика: Программирование
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.8, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Effectiveness of modern rational new drugs development is connected with accurate modelling of binding between target-proteins responsible for the disease and small molecules (ligands) candidates to become drugs. The main modeling tools are docking programs for positioning of the ligands in the target proteins. Ligand positioning is realized in the frame of the docking paradigm: the ligand binds to the protein in the pose corresponding to the global energy minimum on the complicated multidimensional energy surface of the protein-ligand system. Docking algorithm on the base of the novel method of tensor train global optimization is presented. The respective novel docking program SOL-T is validated on the set of 30 protein-ligand complexes with known 3D structures. The energy of the protein-ligand system is calculated in the frame of MMFF94 force field. SOL-T performance is compared with the results of exhaustive low energy minima search carried out by parallel FLM docking program on the base of Monte Carlo method using large supercomputer resources. It is shown that SOL-T docking program is about 100 times faster than FLM program, and SOL-T is able to find the global minimum (found by FLM docking program) for 50% of investigated protein-ligand complexes. Dependence of SOL-T performance on the rank of tensor train decomposition is investigated, and it is shown that SOL-T with rank 16 has almost the same performance as SOL-T with rank 64. It is shown that the docking paradigm is true not for all investigated complexes in the frame of MMFF94 force field.
Docking, global optimization, tensor train, protein-ligand complex, drug design
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147159347
IDR: 147159347 | УДК: 004.942+519.6+539.6+577.2 | DOI: 10.14529/mmp150407
Текст научной статьи Evaluation of the docking algorithm based on tensor train global optimization
Protein-ligand binding free energy calculation is one of the key problems for molecular modelling in the computer-aided structural based drug design [1-4]. Though the most accurate calculations of the protein-ligand binding free energy can be done with molecular dynamics (MD) simulations [5], the more demanded approach to calculate the proteinligand binding energy is docking that is the molecular modelling method, based on the search of the ligand binding pose in the target protein active site and subsequent calculation of the score, i.e. estimation of the protein- ligand binding free energy. Although appreciable progress in improving accuracy of protein-ligand binding free energy calculations with docking is visible in recent years, e.g. see [6,7], the accuracy of such calculations better than 1 kcal/mol has not been reached yet for a randomly selected target protein [1]. Only with such high accuracy of the protein-ligand binding free energy calculations it is possible to perform the rational inhibitor optimization on the basis of computer modelling. Docking as well as MD simulation accuracy depends on many interrelated factors in a complicated manner. Those factors are: the force field describing inter- and intra-molecular interactions, the solvent (water) model, target protein and ligand models, method and approximations of the free energy calculation, algorithms of calculations and computing resources concentrated on solving of the docking problem for one protein-ligand pair, etc.
In the frame of the docking procedure the ligand binding pose is generally believed to be the global minimum of the protein-ligand potential energy function. It is the docking paradigm. Thus, the ligand positioning is the global minimum search problem for the energy target function, depending on the degrees of freedom of the given protein-ligand system. Due to thermal motion in the thermodynamic equilibrium state the ligand continuously jumps from one binding pose to another and to estimate the binding energy we have to find not only the global energy minimum but at least the low-energy part of the whole local minima spectrum. Certainly, the more accurate description of the molecular interactions and the more adequate models of the target protein and the ligand are used for docking the larger computation resources are demanded. Therefore, development of new effective algorithms for the global minimum search on the multidimensional energy surface is needed for further improvement of docking accuracy. These algorithms must be able to solve the global minimum search problem for the target function of many variables: 10 - 20 degrees of freedom for the rigid target protein and the flexible ligand, but much more variables in the case of the flexible protein and the ligand both.
In this work, we present the novel docking algorithm based on Tensor Train (TT) decomposition of multidimensional arrays (tensors) [8] applied to the global minimum search problem and results of its validation for the protein-ligand energy calculated in the frame of Merck molecular force field (MMFF94) [9] on a set of 30 protein-ligand complexes.
-
1. Methods
For realization of the new docking algorithm we have to choose the target function determining energy of the protein-ligand complex for its every conformation. For this purpose we use MMFF94 force field [9] in vacuum, and during the energy minima search ligands are considered to be fully flexible and target-proteins to be rigid. The latter approximation is needed to reduce dimension of the search space and it is common for many docking programs. MMFF94 force field combines sufficiently good parameterization based on ab initio quantum-chemical calculations of a broad spectrum of organic molecules, flexibility allowing to apply this force field to a wide diversity of compounds, and the well-defined easy-to-use procedure of atom typification. Certainly, this force field is not perfect and it is not able to substitute quantum-chemical methods for description of molecular systems, but MMFF94 is not worse than many other popular force fields such as: AMBER [10], OPLS-AA [11], CHARMM [12] etc. Moreover, MMFF94 force field is implemented in docking SOL program which demonstrated good results in one of CSAR competitions [13] and it was used successfully for new inhibitors development [14,15].
1.1. Tensor Train Global Optimization
The Tensor Train (TT) decomposition [8,16] is a representation of multidimensional array (tensor) A G R n 1 xn 2 x"xnd In the form r 1 ,...,r d- 1
A ( i 1 ,i 2 ,...,i d ) = ^^ G 1 ( i 1 ,a 1 ) G 2 ( a 1 ,i 2 ,a 2 ) •••
α 1 =1 ,...,α d- 1 =1
• • • G d - 1 ( a d - 2 , i d - 1 , a d - 1 ) G d ( a d - 1 , i d )
The numbers r 1 ,..., rd- 1 are called TT-ranks of the tensor. For convenience, dummy ranks r 0 = r d = 1 are also Introduced. The 3-dlnienslonal tensors G i G R r i- 1 xnixri are called carriages or cores of the tensor train.
If TT-ranks are reasonably small, then the TT decomposition possesses several very useful properties [8,16]:
-
• Logarithmic storage: only O ( dnr 2 ) memory cells a re used, where r = max r i.
-
• Fast tensor element evaluation: O ( dr 2 ) operations are needed.
-
• Operations on tensors in the TT format are reduced to standard matrix operations.
-
• Fast TT-arithmetic: most of openAlons on tensors are performed In O ( dnr 3 ) arithmetic operations or even faster.
-
• Fast and robust rounding (recompression) procedure: O ( dnr 3 ) operation are needed and accuracy is guaranteed.
-
• Robust method is available when a TT-approximation is sought for a full tensor stored in memory (TT—SVD).
However, we cannot afford computing or storing all the elements for large tensors. It becomes crucial to have a fast approximation method for them which uses only a small number of their elements. Such a method was proposed in [17] and it was named the TT-cross method. It finds a TT-interpolation of tensor evaluating only O ( dnr 2 ) elements and performing just O ( dnr 3 ) arithmetic operations.
The TT-cross approximation method iteratively improves the sets of interpolation points searching for submatrices of larger volume (determinant in modulus) and consequently the elements of larger magnitude. This property allows one to take it as a base for global optimization method [18,19].
Global optimization problem could be either global maximization or global minimization:
x = arg minf (y)(2)
yeQ or x = arg maxf (y)(3)
y e Q
In both cases the problem could be easily transformed to an equivalent problem of the magnitude maximization:
x = arg maxlg(y)|(4)
y e Q
It could be done with the help of some monotonic function, like e 'x оr arcctg( x ) for the minimization problem, e.g. g ( y ) = arcctg( f ( y )). Using the estimates of the range of the function values, one can generally make a better choice.
In this paper Q is a, d -dimeiitional parallelepiped. AVe easily Introduce a, grid on Q. for simplicity let it be a grid with n nodes in each direction. Thus, a discrete version of the problem reads:
i = arg max |G ( j ) |. (5)
j k =1 ...n
If the grid is fine enough then the solutions of continuous and discrete problems are expected to be close.
The discrete problem consists in finding of the maximal in magnitude element of a d -dimensional tensor G E R nx"xn . To solve it, we suggest a technique based on the TT-cross interpolation machinery. It heavily exploits the matrix cross interpolation [20-24] algorithm applied cleverly, although heauristically, to selected submatrices in the unfolding matrices of the given tensor.
The matrix A k E R n xn . A k ( i 1 .. .i k , i k +1 .. .i d ) = A ( i 1 , i 2 ,... ,i d ) Is called the k-tlv unfolding matrix of the tensor A. The TT-rank r k is just the rank of A k. The matrix cross interpolation method [20-24] is a fast approximation method that interpolates B E R mxl using only O (( m + l ) r ) of Its elements and performing only O (( m + l ) r 2) operations.
The TT global optimization method iteratively performs the following steps:
e Previously inspected points P k are used to generate submatrices of corresponding unfolding matrices A k. defined by rows I k and columiis J k.
e These submatrices are approximated by the matrix cross approximation method with rank bounded from above by r max.
e The interpolation points and local minima in their vicinity (projected to the grid) are used to form new sets of "hopefully better" points Pk.
e The sets of points are extended by the points from "neighboring" unfolding matrices and by r max points considered as the best of all inspected values.
A row of the k -th unfolding submatrix of the tensor can Ire described by the first k tensor indices, while a column is specified by the last ( d — k ) indices.
The row Indices I k are constructed from the points P k by taking the first ( k — 1) Indices from each point and appending all possible values for the k -th index (so basically n k P k | row indices are obtained). The column indices J k are constructed in a similar way: to every possible value of ( k + 1)-th Index the last ( d — k — 1) Indices of eac-h point from P k are appended (so we obtain n k +1 |Pk| indices). As soon as this is done, all duplicated rows and columns are excluded.
The complexity of the TT global optimization method is O ( dnr max) functional evaluations, O ( dr max) local optimizations and O ( dnr 3nax) arithmetic operations. It is easy to see that operations for different unfolding matrices could be performed independently, we need synchronization only when constructing the new points at the end of every iteration. Moreover, a parallel implementation of the matrix cross method is also available [25]. In the result, we have a parallel version of the TT global optimization algorithm with parallel complexity O ( r max) functional evaluations. O (1) local optimizations and O ( d + r 2nax) arithmetic operations.
The complexity of our method can be reduced via additional artificial tensorization: we can transform a, d -dimensional tensor with the mode size n = 2 l intо a, dZ -dhnensional tensor with the mode size 2. The complexity of the TT global optimization method is reduced to O ( dr 2nax log2 n ) functional evaluations, O ( dr max log2 n ) local optimizations and O ( dr 3nax log2 n ) arithmetic operations.
On the ouput we get the same result as one without additional tensorization. Although we might need to increase r max and the number of iterations, the practice manifests that the number of evaluations of the functional becomes significantly smaller.
1.2. SOL-T Docking Program
Molecular docking is a problem of potential energy minimization. Thus, one can apply TT global optimization method for solution of the docking problem: to find the low energy local minima spectrum including the global minimum for the rigid protein and fully flexible ligand. The respective novel docking program SOL-T was developed. The docking target function was the protein-ligand energy calculated in the frame of MMFF94 force field. For transformation into magnitude maximization problem the arcctg function was used. Moreover, for better separation of values a shift by currently found minimum is performed. This shift is updated after each iteration of TT global optimization method.
So, TT magnitude maximization was applied to functional g ( y ) = arcctg( f ( y ) — f* ), where f ( y ) is a MMFF94 potential energy value for the ligand position defined by coordinates y, f* is a currently found minimum.
The initial energy grid is generated for each position of the ligand in the conformation space of the active site of the target protein. The conformation space of y coordinates is formed by translations and rotations of the ligand as a whole and also by the ligand torsions (see details in Section 1.3).
The initial grid size was n = 256 = 28 and the TT global optimization with additional tensorization was used. Program has different limitation of maximal rank: SOL-T16 with r max = 16- SOL-T32 with r max = 32 and SOL-T64 with r max = 64.
In order to compute not only a global minimum but also the nearest (by value) local minima the simplest idea to save all obtained local optimization points was used. Finally, energy of each local minimum was additionally optimized with respect to Cartesian coordinates of all ligand atoms (see Section 1.3).
1.3. Program FLM
How to perform validation of the new TT global energy minimum search algorithm and respective docking program SOL-T? Obviously, the best approach to such validation is comparison of the low energy minima spectrum found by SOL-T with the known low energy minima spectrum of a given energy surface. Certainly, this energy surface must be complicated enough to reflect complicacy of real interactions in protein-ligand systems. So, for our validation we decided to use MMFF94 energy surfaces of a set of different protein-ligand complexes with 3D structures taken from Protein Data Bank [26] (see Section 1.4). However, there is only one conformation for each protein-ligand complex in this set, and in general case this conformation does not correspond to any local minimum of the protein-ligand complex energy in the frame of either MMFF94 or any other force field. The respective ligand conformation is usually called as "native" conformation, and after local optimization of the protein-ligand energy with respect to positions of all ligand atoms starting from the ligand native conformation we obtain the locally optimized native ligand conformation. In compliance with the docking paradigm the locally optimized native ligand conformation must correspond to the global minimum of the protein-ligand energy or it must be near the global minimum. So, we have to find the global minimum of the protein-ligand MMFF94 energy and to assure ourselves that it coincides or is close to the locally optimized native ligand conformation. But how is it possible to find the global energy minimum of a protein-ligand complex when the ligand is fully flexible and number of dimensions of the energy surface is more than 10 — 20? The solution of this problem was found in employment of large computing resources available at supercomputer Lomonosov of Moscow State University [27].
The special MPI (message passing interface) based docking program FLM (Find Local Minima) has been developed to perform exhaustive search of low energy local minima of protein-ligand complexes. The energy was calculated in the frame of MMFF94 force field. During the minima search, the protein is considered to be rigid and the ligand is fully flexible. The FLM program finds local energy minima by simple Monte Carlo search algorithm: multiple local optimizations are performed starting from the random initial ligand positions. A random ligand position is obtained by a random continuous ligand deformation and rotation-translation:
-
• The ligand torsions are rota,ted by a random angle from [ —п, п ] (torsion Is a single acyclic bond of the ligand).
-
• The ligand center is moved to a random point of the search area (we used a sphere with the center at the ligand native position center and with the radius of 8A as the search area).
-
• The ligand is rotated as a whole around a random axis passing through the ligand center by a random angle from [ —п, п ].
Not all random system conformations are further optimized. At first, atom-atom distances are checked: atoms from each ligand-ligand or protein-ligand atom pair must be separated by more than 0 , 5A. Otherwise this random system conformation is rejected. Local optimization is performed by L-BFGS (limited-memory Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno) [28, 29] algorithm without any restrictions on the positions of the ligand atoms. All Cartesian coordinates of ligand atoms are moved during optimization. Each local optimization stopped when the maximal component of the optimized target function gradient decreased to the value 10 ~ 5 kcal/mol/A. A set of 1024 computed different local minima with the lowest potential energies is being kept in operative memory during FLM calculations. A new computed local minimum is included into the set, if it differs from any minimum of the set, and the minimum with the highest energy is excluded from this set. Two minima are different if RMSD (root mean square deviation) between them exceeds 0 , 1A. The RMSD is calculated over the ligand heavy atoms without taking into account possible chemical symmetry.
The local minima search is parallelized: independent local optimizations of different initial ligand conformations are continuously performed in parallel by different MPI-processes. The optimization results are collected in the master process to form the low-energy minima set. The current collected minima set is repeatedly sent back from the master process to other processes, so other processes can select only promising minima to send. ELM program performance scales linearly with the increasing number of working processes. The minima search for each protein-ligand complex was conducted during the given time interval of 3 hours. This way of the program halt was used due to some peculiarities of our supercomputer queuing system. Calculations were done on the "Lomonosov" supercomputer in parallel mode of ELM program: 1024 nodes (8192 cores) were utilized for each run of ELM program. About 20 000 CPU*hours per a protein-ligand complex were consumed during these calculations, overall for all 30 complexes it was consumed more than 600 000 CPU*hours. Additional investigation have shown that almost all low energy local minima (1024) have been found for all investigated protein-ligand complexes at the expense of large supercomputer resources employed for these calculations.
1.4. Validation Set of Protein-Ligand Complexes
The set of 30 protein-ligand complexes with experimentally known structures was chosen from Protein Data Bank (PDB) [26] for low-energy local minima search:
-
• 6 complexes of urokinase protein (PDB ID: 1C5Y, 1F5L, 1O3P, 1SQO, 1VJ9, 1VJA);
-
• 4 complexes of CHK1 (checkpoint kinase 1) protein (4FT0, 4FT9, 4FSW, 4FTA);
-
• 2 complexes of ERK2 (extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2) protein (4FV5, 4FV6);
-
• 2 complexes of thrombin protein (1DWC, 1TOM);
-
• 4 complexes of factor Xa protein (1LQD, 1MQ6, 2P94, 3CEN);
-
• 3 complexes of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase protein (1EFY, 2PAX, 3PAX);
-
• 2 complexes of trypsin protein (1K1J, 1PPC);
-
• 1 complex of neuraminidase protein (1B9V);
-
• 1 complex of ricin protein (1BR5);
-
• 1 complex of HIV-1 protease protein (1HPV);
-
• 1 complex of GNC92H2 antibody (li7Z);
-
• 1 complex of beta-1,4-xylanase protein (1J01);
-
• 1 complex of hen egg-white lysozyme protein (1LZG);
-
• 1 complex of apolipoprotein protein (3KIV).
These protein-ligand complexes were chosen, because they are available in the PDB with good resolution, and the ligands variety covers a wide range from small and rigid ligands (e.g. 1C5Y ligand — 20 atoms including hydrogen atoms, 0 torsions) to big and flexible ones (e.g. 1VJ9 ligand — 74 atoms including hydrogen atoms, 19 torsions). Also, the locally optimized ligand native position has RMSD from the original native pose less than 1 . 5A for all these complexes. Thus the locally optimized ligand native position still can represent the native ligand pose.
Protein structures were prepared by elimination of all the records corresponding to atoms, ions and molecules which are not part of the protein structure from the PDB files of the complexes, and then hydrogen atoms were added by the original APLITE program [13, 30] to the protein structures. The APLITE program adds hydrogen atoms according to the standard amino acid protonation states at pH =7. Optimization of hydrogen atoms positions is performed with MMFF94 force field after the hydrogen atoms pre-placement keeping fixed all heavy atoms. During this optimization all rotation variants of torsionally moveable hydrogen atoms (for example, hydroxyl hydrogen atom from tyrosine) are tested.
Ligands were also taken from the PDB files. Hydrogen atoms were added to the ligands by Avogadro program [31]. The heavy atoms optimization is not performed for the initial ligand conformation.
1.5. Evaluation
We compared local minima found by docking programs FLM, SOL-T16, SOL-T32 and SOL-T64 using several criteria. Firstly, comparing energies of the minima including the minima with the lowest energy found by different docking programs. Secondly, comparing numbers of local minima in a given energy interval from the lowest energy. Thirdly, comparing the ligand poses in the energy minima using RMSD between coordinates of respective ligand heavy atoms. Finally, comparing energies and poses of the found minima with the native and the locally optimized native ligand position. For the latter it is convenient to introduce the following notations. The minima set of the given protein-ligand complex with energies calculated by a given target function can be sorted by their energy in ascending order, i.e. every minimum gets its own index ecpial to its number in this sorted list of minima. The lowest energy minimum has index equal to 1. When we include the energy of the locally optimized native ligand in this sorted list, it also will get a certain index and we will designate it as "Index of Native" or "IN". When we do not include the optimized native ligand in this sorted minima list, some minima from the list might be close in space to the native (non-optimized) ligand position. It is possible even that one minimum found by the FLM program will coincide with the optimized native ligand position. We designate the index of the minimum having RMSD from the non-optimized native ligand position less than 2A as "Index of Near Native" or "INN". If there are several such minima which are close to the native position, we will choose the minimum with the lowest energy (with the lowest index) as "INN". The extreme values of these indices could be interpreted as follows:
-
• IN = 1 and INN = 1: the target function is valid for ligand positioning, and the minima search is thorough; the docking paradigm is true;
-
• IN = 1 and INN » 1: the minima search is most likely to be incomplete. When the optimized native position has the lowest energy, some near-native positions will certainly have also low energies;
-
• IN » 1 and INN = 1: there are likely to be experimental inaccuracies in the native ligand position. The target function is most likely valid for ligand positioning, and the minima search is thorough; the docking paradigm is true;
-
• IN » 1 and INN » 1: the target function is invalid for ligand positioning, the docking paradigm is not true for the energy function.
-
2. Results and Discussion
Comparing spectra of low energy minima got by ELM and different variants of SOL-T programs we conclude that the minimum with lowest energy, i.e. the energy global minimum, was found by ELM program practically for all (for 29 out of 30) investigated complexes. Minima with the lowest energy found by SOL-T programs he above the energy of the global minimum found by ELM program, e.g. for 1DWC complex the minimum with the lowest energy found by SOL-T (rank 16) program is 36 . 905 kcal/mol above the ELM global minimum as it can be seen in Tab. 1. Formally the only one exception occurs for 4FT0 complex where the lowest FLM energy is 0 , 085 kcal/mol above the SOL-T(rank 32) lowest energy. For approximately 50% complexes SOL-T also finds the FLM global energy minimum, and for 9 complexes the FLM global energy minimum was found by all three variants of SOL-T program (see Tab. 1). Numbers of local minima being in the energy interval of 5 kcal/mol above the global minimum are presented in five rightmost columns of Tab. 1. We can see that FLM program finds the largest number of minima being in this energy interval, and as a rule the higher rank of SOL-T program the more minima it can find in this interval. One can see from Tab. 1 that performance of SOL-T64 is not much better than one of SOL-T16, however the latter is much faster (see below).
This regularity takes place for most of the complexes and for an arbitrary energy interval above the global minimum as it can be seen in Fig. 1 where the local minimum energy is plotted as a function of the local minimum index. The complex 1VJA shown as an example.
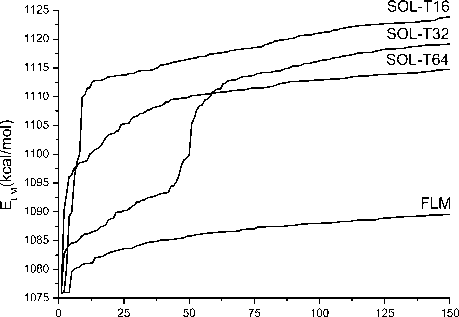
However, there are exceptions: sometimes SOL-T32 finds more local minima than SOL-T64 in a given energy interval as in Fig. 2 a) or SOL-T16 finds more minima than FLM as in Fig. 2 b). By the way, the latter shows that FLM program sometimes finds not all low energy local minima. Most of the local minima found by SOL-T programs coincide with minima found by FLM program. Nevertheless, there are rare occurrences when some low energy minima found by SOL-T programs are cpiite different in their poses from ones found by FLM program. These rare examples show that FLM program does not find all low energy minima for some complexes, i.e. there are low energy minima that were missed during performance of FLM program.
Comparison of low energy minima found by FLM and SOL-T programs with the native and the locally optimized native ligand poses and energies results in values of indices IN and INN (see Section 1.5) presented in Tab. 2.
First of all, we can see in Tab. 2 that the protein-ligand MMFF94 energy in vacuo is the valid docking target function for ligand positioning strictly speaking only for several protein-ligand complexes (column FLM): 1C5Y, 1F5L, 1I7Z, 1J01, 1LQD, and 1PPC. Only for these six complexes (20% out of 30 complexes) the docking paradigm is true: the optimized native ligand position has the lowest energy among all energy minima found by the FLM program (IN=1), and the position of the minimum with the lowest energy (the global minimum of the energy function) found by the FLM program is close to the ligand native pose (INN=1).
Generally speaking one can say that the docking paradigm is true for many other complexes where numbers of IN and INN are small as for the complex 1MQ6 (IN=7, INN=3). Practically the same pattern is found for low energy minima by all three versions
Table 1
Relative energies of respective global energy minima found by ELM program and by three different versions of SOL-T program for 30 tested protein-ligand complexes. Four rightmost columns contain numbers of low energy local minima found by different docking programs in the range of 5 kcal/mol from the respective global minimum. N gb is the number of complexes for which the global energy minimum have been found by the respective docking program
|
Complex id |
Difference between lowest minima found by different docking programs, kcal/mol |
The number of local minima in the range of 5 kcal/mol from the global minimum |
||||||
|
FLM |
SOL-T rank 16 |
SOL-T rank 32 |
SOL-T rank 64 |
FLM |
SOL-T rank 16 |
SOL-T rank 32 |
SOL-T rank 64 |
|
|
1B9V |
0 |
2,326 |
1,267 |
1,212 |
212 |
7 |
18 |
40 |
|
1BR5 |
0 |
3,687 |
2,726 |
2,726 |
11 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
|
1C5Y |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
1DWC |
0 |
36,905 |
26,053 |
5,734 |
11 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
1EFY |
0 |
3,547 |
0 |
0 |
30 |
8 |
14 |
28 |
|
1F5L |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1,467 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
1HPV |
0 |
7,108 |
6,465 |
2,912 |
4 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
1I7Z |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
1J01 |
0 |
0 |
10,074 |
8,342 |
4 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
1K1J |
0 |
0 |
0,056 |
0 |
9 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
|
1LQD |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
11 |
9 |
13 |
17 |
|
1LZG |
0 |
19,460 |
9,946 |
13.594 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
1MQ6 |
0 |
7,007 |
0,968 |
2,701 |
19 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
1O3P |
0 |
1,513 |
0,349 |
0 |
12 |
5 |
6 |
9 |
|
1PPC |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
12 |
9 |
6 |
11 |
|
1SQ0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
1TOM |
0 |
2,202 |
2,202 |
2,202 |
22 |
8 |
10 |
9 |
|
1VJ9 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0,173 |
17 |
7 |
11 |
15 |
|
1VJA |
0 |
1,888 |
0 |
1,888 |
46 |
1 |
6 |
7 |
|
2P94 |
0 |
0,915 |
3,204 |
1,897 |
7 |
5 |
1 |
3 |
|
2 PAX |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
3CEN |
0 |
12,940 |
2,433 |
2,433 |
7 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
3KIV |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
7 |
7 |
7 |
|
3PAX |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
|
4FSW |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
4FT0 |
0,085 |
26,523 |
0 |
18,248 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
4FT9 |
0 |
14,482 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
0 |
3 |
5 |
|
4FTA |
0 |
15,872 |
15,872 |
6,304 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
4FV5 |
0 |
15.871 |
17.214 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
4FV6 |
0 |
11,117 |
16,004 |
10,310 |
4 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
N gb |
29 |
13 |
15 |
14 |
||||
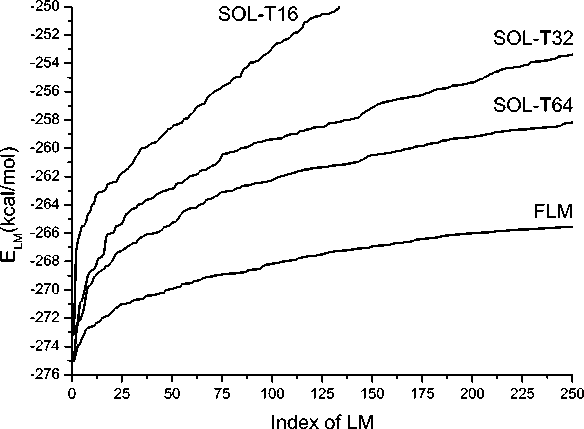
Fig 1. Local minimum energy ( E LM) as a function of its index for the complex 1VJA
Index of LM
a)
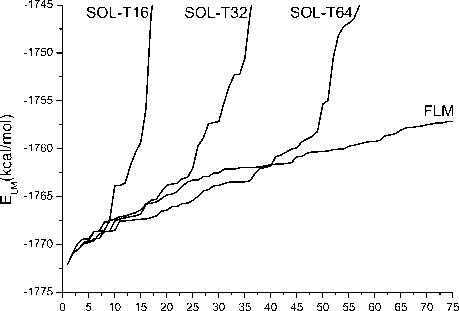
Index of LM
b)
Fig 2. Local minimum energy (ELM) as a function of its index: a) for the complex 1K1J and b) for the complex 1LQD of SOL-T. It is also worth to note that FLM and SOL-T programs demonstrate cases IN«1 and INN«1 almost for the same complexes, and for them the energy global minimum is found by all these programs (see Tab. 1). Indices IN and INN for SOL-T program are smaller or equal than indices for FLM program, as it can be seen in Tab. 2. This means that SOL-T program as a rule finds less minima in a given energy interval than FLM program, and it is also demonstrated in Tab. 1, Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 a). There are some exceptions. For example for 4FV6 complex SOL-T works better than FLM: FLM did not find the energy minimum corresponding to the native ligand pose (INN=inf) and the energy of the optimized native ligand position is higher than energies of all found by FLM 1024 low energy minima (IN=inf). On the other hand, the minima indices found by SOL-T16 for this complex are IN=7, INN=13.
Table 2
IN/INN values for all tested 30 protein-ligand complexes for ELM program and three different versions of SOL-T program. "Inf" for IN means that all found low-energy minima have energy below the energy of the optimized native ligand. "Inf" for INN means that all found low-energy minima have RMSD from the native position above 2A
|
Complex id |
FLM |
SOL-T rank 16 |
SOL-T rank 32 |
SOL-T rank 64 |
|
1B9V |
inf/inf |
216/308 |
467/242 |
872/872 |
|
1BR5 |
inf/121 |
76/25 |
155/24 |
258/149 |
|
1C5Y |
1/1 |
1/1 |
1/1 |
1/1 |
|
1DWC |
inf/629 |
2/inf |
56/7 |
70/18 |
|
IFFY |
192/88 |
33/27 |
84/inf |
140/127 |
|
1F5L |
1/1 |
1/1 |
1/1 |
1/1 |
|
1HPV |
97/1 |
4/1 |
9/1 |
10/1 |
|
1I7Z |
1/1 |
1/1 |
1/1 |
1/1 |
|
1J01 |
1/1 |
1/1 |
1/inf |
1/inf |
|
1K1J |
5/1 |
3/1 |
2/1 |
2/1 |
|
1LQD |
1/1 |
1/1 |
1/1 |
1/1 |
|
1LZG |
inf/inf |
196/inf |
480/inf |
999/1111 |
|
1MQ6 |
7/3 |
1/1 |
2/1 |
1/1 |
|
1O3P |
15/13 |
6/6 |
9/7 |
12/10 |
|
1PPC |
1/1 |
1/1 |
1/1 |
1/1 |
|
1SQO |
2/1 |
2/1 |
2/1 |
2/1 |
|
1TOM |
inf/inf |
115/inf |
296/284 |
480/471 |
|
1VJ9 |
32/1 |
13/1 |
23/1 |
34/1 |
|
1VJA |
40/4 |
2/inf |
6/5 |
8/5 |
|
2P94 |
36/2 |
8/1 |
5/inf |
7/inf |
|
2PAX |
2/1 |
2/1 |
2/1 |
2/1 |
|
3CEN |
92/1 |
2/inf |
7/inf |
15/inf |
|
3KIV |
12/1 |
И/1 |
12/1 |
12/1 |
|
3PAX |
2/1 |
2/1 |
2/1 |
2/1 |
|
4FSW |
8/7 |
3/3 |
4/4 |
6/6 |
|
4FT0 |
26/12 |
3/10 |
8/4 |
6/inf |
|
4FT9 |
43/27 |
2/inf |
19/inf |
31/31 |
|
4FTA |
inf/inf |
12/inf |
35/35 |
73/73 |
|
4FV5 |
186/120 |
11/11 |
14/12 |
25/inf |
|
4FV6 |
inf/inf |
7/13 |
3/inf |
14/261 |
The obtained results show that there are two different types of protein-ligand complexes with different complexities of their MMFF94 energy surfaces among our validation set of 30 complexes. First, "simple" complexes for which the docking paradigm is true for MMFF94 energy as the docking target function (IN~1, INN~1), the global energy minimum is found by FLM and SOL-T programs both. Second, complexes with "complicated" MMFF94 protein-ligand energy surfaces for which the docking paradigm is not true (IN»1 or INN»1), the lowest energy minima found by FLM and SOL-T programs are different.
Overall, one can conclude that FLM program finds low energy local minima much better than any variant of SOL-T program. However, this better behavior of FLM program is at the expense of employment of much larger computational resources: FLM uses ~ 108 s - cores (about 5 x 105 local optimizations). 1 rut SOL-T16 use only 105 — 106 s - cores. Relative performance of SOL-T with ranks 16, 32 and 64 is 1:3:9 for many complexes. However sometimes there are exceptions when performance of SOL-T32 and SOL-T64 programs is almost the same. The latter can be connected with non-optimized SOL-T code for Lomonosov supercomputer [27].
Conclusions
Novel docking algorithm on the base of the Tensor Train global optimization method is described. The performance of the respective docking program SOL-T is investigated for a set of different protein-ligand complexes with experimentally defined atomic structures and having flexible ligand of different sizes. The protein-ligand energy (the docking target function) is calculated in the frame of MMFF94 force field. Dimension of the global minimum search space is up to several dozen depending on the ligand size and flexibility. Performance of SOL-T program is compared with one of FLM docking program developed on the base of Monte Carlo local minima search algorithm covering almost whole search space at the expense of large supercomputer resources employed. The conclusions of the present investigation are as follows.
-
1. FLM docking program finds the lowest energy minimum of each protein-ligand system. SOL-T docking program finds the global energy minimum (found by FLM program) only for 50% of the investigated protein-ligand complexes.
-
2. Ability to find low energy minima is almost the same for different investigated variants of SOL-T programs on the base of rank 16, rank 32 and rank 64 tensor train representations, but SOL-T rank 16 program is much faster.
-
3. As a rule the number of low energy local minima in a given energy interval from the global minimum, say 5 kcal/mol, found by FLM program is larger than one found by SOL-T programs, and the higher rank of SOL-T program the more low energy minima are found in the given energy interval. Nevertheless, SOL-T finds little number of minima which are different in their conformations from ones found by FLM program for about 30% of complexes.
-
4. SOL-T16 program is faster about 100 times than FLM program and about 10 times than SOL-T64.
-
5. FLM and SOL-T performance demonstrates that the docking paradigm is true for energy calculated in the frame of MMFF94 force field for many of investigated proteinligand complexes. As a rule the energy global minimum for such complexes is found by FLM and SOL-T programs both.
The Tensor Train global optimization method is perspective for application to the docking problem with up to several dozen degrees of freedom of flexible ligand — dimension of the search space.
The reported work was financially supported by the Russian Scientific Fund, Agreement # 15-11-00025 in the part of FLM and SOL-T docking programs development using MMFF9f force field, investigation of the low energy minima of the protein-ligand complexes, validation of TT-docking effectiveness. The result obtained in the frame of work according to the grants RFBR # 13-01-12061 ofi_m (E.E.Tyrtyshnikov) and # If-OI-31239 mol_a (D.A. Zheltkov) are used in the part of development of theoretical foundation of the tensor train global optimization.
Список литературы Evaluation of the docking algorithm based on tensor train global optimization
- Mobley D.L., Dill K.A. The Binding of Small-Molecule Ligands to Proteins: "What You See" is not Always "What You Get". Structure, 2009, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 489-498. DOI: DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2009.02.010
- Sadovnichii V.A., Sulimov V.B. Supercomputing Technologies in Medicine. Supercomputing Technologies in Science, Education, and Industry, Moscow, Moscow University Publishing, 2009, pp. 16-23.
- Merz K.M., Ringe D., Reynolds C.H., eds. Drug Design: Structure and Ligand-Based Approaches. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 2010. DOI: DOI: 10.1017/CBO9780511730412
- Plewczynski D., Lazniewski M., Augustyniak R., Ginalski K. Can We Trust Docking Results? Evaluation of Seven Commonly Used Programs on PDBbind Database. Journal of Computational Chemistry 2011, vol. 32, pp. 742-755. DOI: DOI: 10.1002/jcc.21643
- Klimovich P.V., Shirts M.R., Mobley D.L. Guidelines for the Analysis of Free Energy Calculations. Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design, 2015, vol. 29, no. 5, pp. 397-411. DOI: DOI: 10.1007/s10822-015-9840-9
- Chen W., Gilson M.K., Webb S.P., Potter M.J. Modeling Protein-Ligand Binding by Mining Minima. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2010, vol. 6, no. 11, pp. 3540-3557. DOI: DOI: 10.1021/ct100245n
- Allen W.J., Balius T.E., Mukherjee S., Brozell S.R., Moustakas D.T., Lang P.T., Case D.A., Kuntz I.D., Rizzo R.C. DOCK6: Impact of New Features and Current Docking Performance. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2015, vol. 36, no. 15, pp. 1132-1156. DOI: DOI: 10.1002/jcc.23905
- Oseledets I.V., Tyrtyshnikov E.E. Breaking the Curse of Dimensionality, or How to Use SVD in Many Dimensions. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2009, vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 3744-3759. DOI: DOI: 10.1137/090748330
- Halgren T.A. Merck Molecular Force Field. 1. Basis, Form, Scope, Parameterization and Performance of MMFF94. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 1996, vol. 17, pp. 490-519. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(199604)17:5/63.0.CO;2-P
- Cornell W.D., Cieplak P., Bayly C.I., Gould I.R., Merz K.M. Jr., Ferguson D.M., Spellmeyer D.C., Fox T., Caldwell J.W., Kollman P.A. A Second Generation Force Field for the Simulation of Proteins, Nucleic Acids, and Organic Molecules. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1995, vol. 117, pp. 5179-5197. DOI: DOI: 10.1021/ja00124a002
- Jorgensen W.L., Maxwell D.S., Tirado-Rives J. Development and Testing of the OPLS All-Atom Force Field on Conformational Energetics and Properties of Organic Liquids. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1996, vol. 118, no. 45, pp. 11225-11236. DOI: DOI: 10.1021/ja9621760
- Vanommeslaeghe K., Hatcher E., Acharya C., Kundu S., Zhong S., Shim J., Darian E., Guvench O., Lopes P., Vorobyov I., Mackerell A.D. Jr. CHARMM General Force Field: A Force Field for Drug-Like Molecules Compatible with the CHARMM All-Atom Additive Biological Force Fields. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2010, vol. 31, no. 4, pp. 671-690. DOI: DOI: 10.1002/jcc.21367
- Sulimov A.V., Kutov D.C., Oferkin I.V., Katkova E.V., Sulimov V.B. Application of the Docking Program SOL for CSAR Benchmark. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2013, vol. 53, no. 8, pp. 1946-1956. DOI: DOI: 10.1021/ci400094h
- Sinauridze E.I., Romanov A.N., Gribkova I.V., Kondakova O.A., Surov S.S., Gorbatenko A.S., Butylin A.A., Monakov M.Yu., Bogolyubov A.A., Kuznetsov Yu.V., Sulimov V.B., Ataullakhanov F.I. New Synthetic Thrombin Inhibitors: Molecular Design and Experimental Verification. PLoS ONE, 2011, vol. 6, no. 5, e19969. DOI: DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019969
- Sulimov V.B., Katkova E.V., Oferkin I.V., Sulimov A.V., Romanov A.N., Roschin A.I., Beloglazova I.B., Plekhanova O.S., Tkachuk V.A., Sadovnichiy V.A. Application of Molecular Modeling to Urokinase Inhibitors Development. BioMed Research International, 2014, vol. 2014, Article ID 625176, 15 p. DOI: DOI: 10.1155/2014/625176
- Oseledets I.V. Tensor-Train Decomposition. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2011, vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 2295-2317. DOI: DOI: 10.1137/090752286
- Oseledets I.V., Tyrtyshnikov E.E. TT-Cross Approximation for Multidimensional Arrays. Linear Algebra and its Applications, 2010, vol. 432, no. 1, pp. 70-88. DOI: DOI: 10.1016/j.laa.2009.07.024
- TTDock: метод докинга на основе тензорных поездов/Д.А. Желтков, И.В. Оферкин, Е.В. Каткова, А.В. Сулимов, В.Б. Сулимов, Е.Е. Тыртышников//Вычислительные методы и программирование. -2013. -Т. 14. -С. 279-291.
- Желтков, Д.А. Увеличение размерности в методе докинга на основе тензорных поездов/Д.А. Желтков, Е.Е. Тыртышников//Вычислительные методы и программирование. -2013. -Т. 14. -С. 292-293.
- Goreinov S.A., Tyrtyshnikov E.E., Zamarashkin N.L. Pseudo-Skeleton Approximations of Matrices. Reports of Russian Academy of Sciences, 1995, vol. 342, no. 2, pp. 151-152.
- Goreinov S.A., Tyrtyshnikov E.E., Zamarashkin N.L. A Theory of Pseudo-Skeleton Approximations. Linear Algebra Appl., 1997, vol. 261, pp. 1-21. DOI: DOI: 10.1016/S0024-3795(96)00301-1
- Tyrtyshnikov E.E. Incomplete Cross Approximation in the Mosaic-Skeleton Method. Computing, 2000, vol. 64, no. 4, pp. 367-380. DOI: DOI: 10.1007/s006070070031
- Goreinov S.A., Tyrtyshnikov E.E. The Maximal-Volume Concept in Approximation by Low-Rank Matrices. Contemporary Mathematics, 2001, vol. 208, pp. 47-51. DOI: DOI: 10.1090/conm/280/4620
- Goreinov S.A., Oseledets I.V., Savostyanov D.V., Tyrtyshnikov E.E., Zamarashkin N.L. How to Find a Good Submatrix. Research Report 08-10, ICM HKBU, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong, 2008.
- Желтков, Д.А. Параллельная реализация матричного крестового метода/Д.А. Желтков, Е.Е. Тыртышников//Вычислительные методы и программирование. -2015. -Т. 16. -С. 369-375.
- Protein Data Bank. Available at: http://www.rcsb.org/(accessed September 21, 2015).
- Moscow University Supercomputing Center. URL: http://hpc.msu.ru/(accessed September 21, 2015).
- Byrd R.H., Lu P., Nocedal J., Zhu C. A Limited Memory Algorithm for Bound Constrained Optimization. SIAM J. Sci. Comput., 1995, vol. 16, no. 5, pp. 1190-1208. DOI: DOI: 10.1137/0916069
- Zhu C., Byrd R.H., Lu P., Nocedal J. Algorithm 778: L-BFGS-B: Fortran Subroutines for Large-Scale Bound-Constrained Optimization. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 1997, vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 550-560. DOI: DOI: 10.1145/279232.279236
- APLITE Program, Dimonta. Available at: http://dimonta2.1gb.ru/en/node/55 (accessed September 21, 2015).
- Avogadro: an Open-Source Molecular Builder and Visualization Tool. Version 1. XX. Available at: http://avogadro.openmolecules.net/(accessed September 21, 2015).


