Фундаментальные и клинические аспекты заболеваний щитовидной железы и новые подходы для их лечения (обзор литературы)
Автор: Фокина Е.А., Шпаков А.О.
Журнал: Сибирский журнал клинической и экспериментальной медицины @cardiotomsk
Рубрика: Клинические исследования
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.37, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Распространенность заболеваний щитовидной железы (ЩЖ), в том числе аутоиммунного гипертиреоза (болезни Грейвса), аутоиммунного тиреоидита, различных форм тиреоидного рака, с каждым годом возрастает, в то время как эффективность их лечения по-прежнему остается низкой и ограничивается в основном заместительной терапией тиреоидными гормонами и хирургическими и радиоизотопными методами. В настоящем обзоре представлено современное состояние проблемы фармакологической коррекции заболеваний ЩЖ, рассмотрены новые подходы, направленные на регуляцию функциональной активности компонентов системы синтеза тиреоидных гормонов в фолликулярных клетках ЩЖ, включая его начальный, сенсорный, компонент - рецептор тиреотропного гормона. Среди препаратов, которые разрабатываются в настоящее время, необходимо выделить аллостерические регуляторы рецептора тиреотропного гормона, специфичные к нему антитела, а также селективные агонисты β-изоформы рецепторов тиреоидных гормонов.
Щитовидная железа, рецептор тиреотропного гормона, тиреоидные гормоны, фармакотерапия, антитиреоидные препараты
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149141439
IDR: 149141439 | УДК: 616.441-08(048) | DOI: 10.29001/2073-8552-2022-37-3-90-97
Текст научной статьи Фундаментальные и клинические аспекты заболеваний щитовидной железы и новые подходы для их лечения (обзор литературы)
В последние годы число заболеваний щитовидной железы (ЩЖ) продолжает повышаться, и это во многом обусловлено повышением продолжительности жизни, что приводит к накоплению в человеческой популяции хронических неинфекционных заболеваний, в том числе эндокринных [1]. По данным различных авторов, распространенность дисфункций ЩЖ в мире варьирует от 10 до 30% от общего населения и в значительной степени зависит от условий питания и климатической зоны [2]. По данным когортных исследований, гипертиреоз (включая субклинический) встречается у 0,5–2% женщин, но в среднем в 10 раз реже встречается у мужчин [3]. Распространенность гипотиреоза различной этиологии варьирует в зависимости от региона и колеблется от 1 до 8% от общей популяции, а расчетная частота развития новых случаев гипотиреоза в европейских странах составляет 226 случаев на 100 000 населения в год [4].
Аутоиммунный гипертиреоз (болезнь Грейвса)
В основе болезни Грейвса лежит образование стимулирующих аутоантител к внеклеточному домену рецептора тиреотропного гормона (ТТГ), который локализован в плазматической мембране тироцитов и отвечает за синтез и секрецию тиреоидных гормонов – тироксина (Т4) и трийодтиронина (Т3) [5]. Результатом этого является неконтролируемая активация рецептора ТТГ и гиперпродукция тиреоидных гормонов. Наряду с выработкой аутоантител к рецептору ТТГ у значительной части пациентов с болезнью Грейвса снижается иммунная толерантность к другим компонентам тиреоидной системы. Так, у 50–70% из них обнаруживаются антитела к ферменту тиреопероксидазе (ТПО), ответственному за йодирование остатков тирозина в молекуле тиреоглобулина (ТГ) и за слияние йодированных остатков тирозина при синтезе тиреоидных гормонов, а также антитела к ТГ – продуцируемому фолликулярными клетками щитовидной железы белку, являющемуся источником йодированных остатков тирозина [6].
В настоящее время представлены доказательства того, что имеется множество причин развития болезни Грейвса, среди которых генетические факторы, эпигенетические изменения, нарушения гормонального и метаболического статуса, а также факторы окружающей среды. Наследственные факторы считают определяющими в этиологии болезни Грейвса, что убедительно продемонстрировано в когортных исследованиях случаев семейного аутоиммунного гипертиреоза, а также подтверждается данными об этнических особенностях встречаемости этого заболевания [7, 8]. Болезнь Грейвса, как полагают, является полигенным заболеванием, и на данный момент выявлен целый ряд генов, ответственных за ее развитие. При этом каждый ген по отдельности вносит сравнительно небольшой вклад в развитие болезни Грейвса, поскольку у пациентов с этой патологией, как правило, имеются комбинации мутаций сразу в нескольких генах [6]. Показано, что часть этих генов ответственны за развитие различных аутоиммунных заболеваний, в то время как некоторые ассоциированы исключительно с заболеваниями ЩЖ [8].
Одним из факторов, способствующих развитию болезни Грейвса, является женский пол пациента. Непосредственными причинами здесь являются полиморфизм эстрогенового рецептора 2-го типа (ESR2) [9, 10] и особенности инактивации Х-хромосомы [11, 12]. К неспецифическим факторам окружающей среды, способствующим развитию болезни Грейвса, относят курение, употребление наркотических и психоактивных веществ, стрессовые воздействия, вирусные заболевания, радиационные и химические воздействия [13]. К специфическим факторам относится избыток потребляемого йода, в том числе вместе с пищей [14].
Классические подходы к лечению аутоиммунного гипертиреоза
Среди основных подходов для лечения аутоиммунного гипертиреоза традиционно рассматривают эра-дикацию избытка тиреоидных гормонов, что позволяет восстановить эутиреоидное состояние у пациентов. Для этого могут быть использованы антитиреоидные препараты (АТП), позволяющие снизить уровни тиреоидных гормонов, а также хирургические методы и радиойодте-рапия (РЙТ), направленные на уменьшение объема ткани ЩЖ, продуцирующей тиреоидные гормоны (рис. 1) [15]. Современные рекомендации по стратегии применения этих подходов приведены в Руководстве Европейской тиреоидной ассоциации по лечению болезни Грейвса [16].
Антитиреоидные препараты
АТП являются терапией первой линии выбора для пациентов с впервые установленным диагнозом аутоиммунного гипертиреоза. Среди них различные производные тионамида, такие как пропилтиоурацил, метамизол и карбимазол, который является проактивным АТП и в организме метаболизируется в метамизол. Механизм действия производных тионамида заключается в ингибировании ряда ферментов, вовлеченных в синтез тиреоидных гормонов. Так, все эти производные способны ингибировать ТПО, в то время как пропилтиоурацил также ингибирует фермент дейодиназу 1-го типа, которая ответственна за превращение Т4 в активную форму Т3 [17]. Среди фармакологических эффектов АТП необходимо обратить внимание на подавление ими окислительного стресса и воспалительных процессов. Однако до сих пор не установлено, являются ли эти эффекты следствием непосредственного воздействия препаратов на ткани-мишени, или они опосредованы достижением эутиреоидного состояния [18].
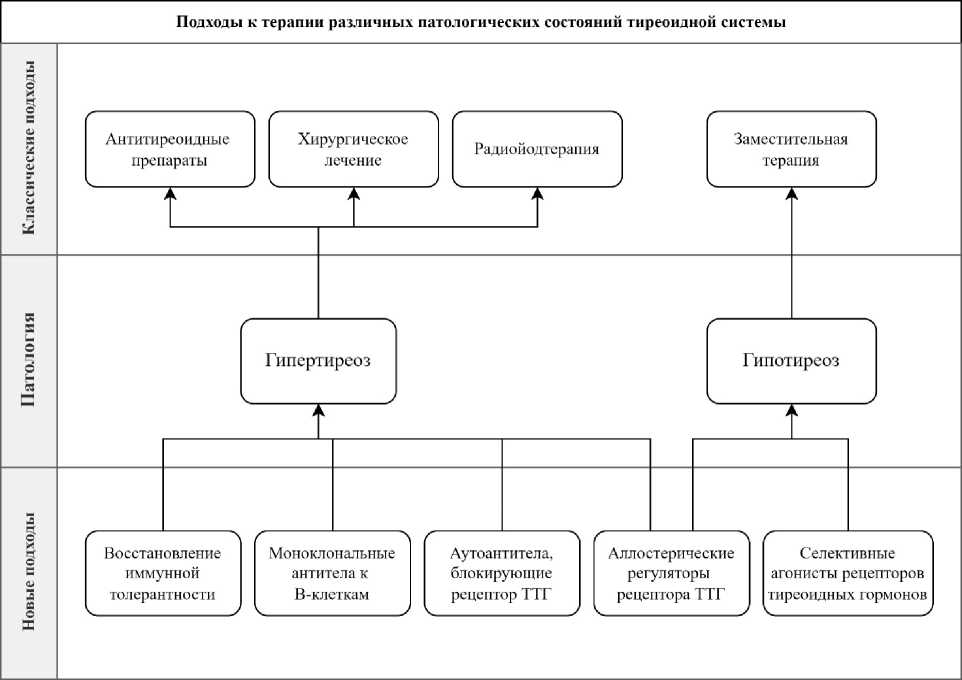
Рис. 1. Соотношение классических и новых подходов к лечению различных патологий щитовидной железы
Fig. 1. The ratio of classical and new approaches to the treatment of various pathologies of the thyroid gland
Лечение АТП считается относительно безопасным, поскольку частота развития нежелательных побочных реакций обычно не превышает 5%. В то же время при развитии серьезных осложнений переход на другой препарат внутри этой лекарственной группы, как правило, затруднен в связи с перекрестной реактивностью. Наиболее распространенными побочными эффектами, вызываемыми производными тионамида, являются кожные реакции, агранулоцитоз, гепатотоксичность, васкулит. Значительным недостатком терапии АТП является высокая частота развития рецидивов, которые в большинстве случаев наступают уже через 12 мес. после завершения лечения. Так, после отмены АТП в течение двух лет рецидивы возникают у 37% пациентов с первично установленным диагнозом болезни Грейвса [19]. Риск их развития индивидуален и зависит от множества факторов, среди которых возраст больного, наличие вредных привычек, размер зоба [15]. Одним из подходов, направленных на снижение риска рецидивов, является пролонгированная терапия метамизолом [20]. Несмотря на это, в настоящее время основной рекомендацией Европейской тиреоидной ассоциации для предотвращения рецидивов болезни Грейвса являются РЙТ и тироидэктомия [16].
Терапия радиоактивным йодом (131I)
РЙТ, впервые использованная еще в 1941 г., позволяет уменьшить объем ткани ЩЖ путем активации в ней процессов цитолиза. Механизм действия радиоактивного изотопа йода 131I состоит в избирательном накоплении в клетках ЩЖ и их облучении изнутри. Основным отличием РЙТ от консервативных методов лечения является позднее проявление ее терапевтического эффекта, поскольку у большинства пациентов нормализация уровней гормонов ЩЖ достигается только через год после обработки радиоактивным йодом [21, 22]. Основными показаниями к назначению РЙТ при лечении пациентов с болезнью Грейвса являются: (1) сохранение или рецидив гипертиреоза после курса АТП, (2) серьезные побочные эффекты, вызванные АТП, (3) низкая чувствительность пациентов к АТП, (4) желание пациента.
Отложенный эффект РЙТ вызывает необходимость в назначении АТП как до начала такой терапии, так и после нее, что позволяет нормализовать уровни тиреоидных гормонов до наступления антитиреоидного эффекта РЙТ. Однако результатом такого комбинированного лечения является повышение рисков побочных эффектов, которые в этом случае обусловлены как АТП, так и РЙТ [23]. Выявлена положительная корреляция между применением РЙТ и повышением смертности пациентов, причем основной вклад в рост смертности вносили нарушения функций сердечно-сосудистой системы [24]. Однако недавние когортные исследования показали, что риск развития осложнений при РЙТ обусловлен в основном плохо контролируемым гипертиреозом, а не применением радиотерапии [25]. Широко обсуждается вопрос о взаимосвязи между РЙТ и повышением риска развития злокачественных новообразований, в том числе рака молочной железы, желудочно-кишечного тракта и легких. На основе всестороннего анализа, проведенного в 2022 г., L. Bartalena и соавт. заключили, что и в этом случае повышение риска развития онкологических заболеваний в большей степени обусловлено длительным некомпенсированным гипертиреозом, а не применением РЙТ [18]. Вследствие этого при назначении РЙТ и проведении лечения радиоактивным йодом болезни Грейвса особое внимание необходимо уделять постоянному мониторингу уровней тиреоидных гормонов в крови пациентов. Необходимо отметить, что к нежелательным эффектам РЙТ, ассоциированным непосредственно с использованием этого подхода для лечения аутоиммунного гипертиреоза, относят боли в области ЩЖ, сиалоаденит и отеки. РЙТ также может вызывать орбитопатию Грейвса, для профилактики которой могут быть использованы препараты глюкокортикостероидов.
Хирургическое лечение болезни Грейвса
Оперативное вмешательство (тироидэктомия) является наименее предпочтительным способом лечения аутоиммунного гипертиреоза. Показаниями к тироидэк-томии являются: (1) рецидив после однократного курса АТП, 2) большой зоб (более 40–50 мл) с симптомами компрессии соседних органов или без них, (3) ультрасонографически и цитологически подозрительные узлы, (4) отказ или отсутствие условий для проведения РЙТ в качестве радикального лечения, (5) непереносимость АТП при беременности (это исключительная ситуация, требующая хирургического вмешательства во II триместре беременности), (5) низкий уровень поглощения радиоактивного йода тканью ЩЖ, что делает РЙТ мало эффективной, (6) желание пациента.
Преимуществами тироидэктомии являются отсутствие радиационного риска, быстро достижимый контроль над гипертиреозом, отсутствие риска развития офтальмопатии. Однако этот вид лечения характеризуется рядом рисков, одни из которых обусловлены непосредственно хирургическим вмешательством и анестезией (кровотечение, инфекционные осложнения, образование рубца и т. д.), в то время как другие обусловлены локализацией вмешательства (паралич гортанного нерва, гипопаратиреоз). Помимо этого, пациенты, перенесшие тироидэктомию, вынуждены пожизненно принимать тиреоидные препараты (L-тироксин и др.) для поддержания эутиреоидного состояния.
Новые подходы к лечению аутоиммунного гипертиреоза
Все вышесказанное указывает на необходимость разработки новых подходов для лечения болезни Грейвса. Здесь основное внимание сконцентрировано на разработке таргетных препаратов, которые способны воздействовать на определенное звено патогенеза заболевания и, таким образом, могут минимизировать побочные эффекты, характерные для применяемой сейчас антитиреоидной терапии. Все эти подходы в той или иной степени связаны с регуляцией активности рецептора ТТГ, который является мишенью для стимулирующих антител к этому рецептору. К таким подходам относят восстановление иммунной толерантности к рецептору ТТГ [26], ингибирование активности рецептора ТТГ, в том числе с помощью блокирующих рецептор ТТГ антител [27] и с помощью низкомолекулярных аллостерических инверсионных агонистов и антагонистов рецептора ТТГ [28], снижение активности В-лимфоци-тов, ответственных за синтез аутоантител к рецептору ТТГ [18].
Подход, в основе которого лежит восстановление иммунной толерантности к рецептору ТТГ, основан на повторном введении нарастающих количеств антигена. Этот подход активно применяется в аллергологии [29, 30], но до сих пор практически не использовался для лечения аутоиммунных заболеваний, так как введение антигенов может спровоцировать рецидив основного заболевания. Для снижения риска усиления аутоиммунного гипертиреоза в качестве эпитопов выбирали те участки рецептора ТТГ, которые не приводили к генерации аутоантител со стимулирующей активностью [26]. Пациентам с болезнью Грейвса вводили смесь двух синтетических пептидов (5D-K1: KKKKYVSIDVTLQQLESHKKK; 9B-N: GLKMFPDLTKVYSTD), которые соответствуют внеклеточным участкам рецептора ТТГ человека. Введение этой смеси, обозначенной как ATX-GD-59, в течение 18 нед. приводило к улучшению функций ЩЖ у 7 из 10 пациентов с умеренно выраженной болезнью Грейвса. В крови 5 пациентов (50%) отмечали нормализацию концентрации свободного T3, который является наиболее чувствительным маркером гипертиреоидного состояния. Наряду со снижением уровня тиреоидных гормонов снижался уровень аутоантител к рецептору ТТГ, что положительно коррелировало с улучшением состояния пациентов с гипертиреозом. Тем самым получены первые доказательства того, что смесь пептидов ATX-GD-59 может иметь значительный терапевтический эффект при болезни Грейвса [26].
Одним из подходов для ингибирования активности рецептора ТТГ может быть применение аутоантител, блокирующих эти рецепторы [27]. Наибольший интерес представляют антитела К1-70ТМ, которые являются высокоспецифичными моноклональными аутоантителами к рецептору ТТГ человека и блокируют связывание гормона с рецептором и стимуляцию рецептора. Их активность оценивали у пациентов с болезнью Грейвса в рамках первой фазы клинических исследований. Было показано, что однократное внутримышечное введение (25 мг) антител K1-70TM или их однократное внутривенное введение (50 или 150 мг) снижали повышенные уровни свободного Т3, свободного Т4 и ТТГ до их значений в контроле и даже ниже. Также у пациентов были отмечены клинически значимые улучшения симптомов болезни Грейвса, что выражалось в уменьшении тремора, нормализации сна, улучшении ментальных способностей, улучшении функций желудочно-кишечного тракта. В пользу ослабления симптомов орбитопатии Грейвса свидетельствовали уменьшение показателей экзофтальма и снижение светочувствительности. Ни у одного из 18 пациентов, получивших антитела K1-70TM, не было выявлено заметных побочных эффектов, не наблюдалось значительного иммуногенного ответа [27]. Таким образом, на примере антител K1-70TM продемонстрирована перспективность применения блокирующих аутоантител к рецептору ТТГ для коррекции аутоиммунного гипертиреоза и орбитопа-тии Грейвса.
Воздействие на В-клетки, продуцирующие аутоантитела
Моноклональные антитела, направленные на CD-20 положительные В-лимфоциты, первоначально применялись для лечения неходжкинских лимфом, однако впоследствии были зарегистрированы как препараты для лечения других аутоиммунных заболеваний, включая рассеянный склероз и системную красную волчанку. Препараты этой группы проходят различные фазы клинических исследований и в связи с множеством ограничений демонстрируют неоднозначные результаты, хотя эта группа лекарственных средств, безусловно, считается весьма перспективной [18].
Наиболее известным препаратом этой группы является ритуксимаб, который имеет сложный, не до конца выясненный механизм действия, обусловленный стимуляцией апоптотической и цитотоксической гибели В-лим-фоцитов [31]. Истощение пула лимфоцитов происходит в течение нескольких часов после инфузии и сохраняется в течение 8 мес. [18, 32]. Терапия ритуксимабом сопровождается развитием ряда нежелательных явлений, таких как зуд в горле и заложенность носа, которые могут быть скорректированы скоростью инфузии препарата, а также суставной синдром и неспецифические воспалительные заболевания желудочно-кишечного тракта, связанные с образованием иммунных комплексов после введения препарата [33]. Препараты нового поколения, такие как окрелизумаб и офатумумаб, характеризующиеся лучшей переносимостью и более широким профилем безопасности, в перспективе могут заменить ритуксимаб и стать потенциальными препаратами для лечения болезни Грейвса.
Аллостерические антагонисты и инверсионные агонисты рецептора тиреотропного гормона
Наряду с аллостерическими агонистами рецептора ТТГ имеются лиганды расположенного в трансмембранном домене рецептора аллостерического сайта, наделенные активностью нейтральных антагонистов, способных подавлять стимуляцию рецептора его агонистами, или инверсионных агонистов, способных снижать собственную базальную активность рецептора ТТГ. В первом случае снижаются стимулирующие эффекты ТТГ и стимулирующих аутоантител к рецептору ТТГ, что важно при лечении болезни Грейвса. Во втором случае снижается не только гиперактивация рецептора ТТГ, вызванная различными по природе его агонистами, но также и активность рецептора, повышенная вследствие активирующих мутаций в кодирующем его гене, что может быть использовано при лечении обусловленного такими мутациями рака ЩЖ [34]. В настоящее время разработано несколько низкомолекулярных аллостерических антагонистов и инверсионных агонистов рецептора ТТГ, но они пока находятся на различных этапах доклинических испытаний [35, 36]. Нами созданы и изучены два тиено[2,3-d]-пиримиди-новых производных с активностью антагониста (TPY1) и инверсионного агониста (TP48) рецептора ТТГ, которые были активны в условиях in vitro , подавляя стимулирующие эффекты ТТГ на систему тиреоидогенеза в тироци-тах FRTL-5, а также, что особенно ценно, в условиях in vivo при введении крысам, снижая уровень тиреоидных гормонов в крови и экспрессию генов тиреоидогенеза в ЩЖ, стимулированные интраназально вводимым тиро-либерином, рилизинг-фактором ТТГ [37, 38]. Важно, что
TP48 также, хотя и в незначительной степени, снижал базовые уровни тиреоидных гормонов.
Гипотиреоз, в том числе аутоиммунный тиреоидит
Распространенность в мире субклинической формы гипотиреоза, который характеризуется повышенным уровнем ТТГ и уровнем Т4 в пределах нормы, составляет 4,3%, в то время как манифестный гипотиреоз, для которого характерно снижение уровня тироксина на фоне повышенного уровня ТТГ, выявляется у 0,3% населения. Установленным фактом является более высокая встречаемость гипотиреоза среди женщин в сравнении с мужчинами [39]. Выявлены этнические особенности распространения этого заболевания. Так, в ретроспективном обсервационном исследовании канадских ученых [40] показано, что частота врожденного гипотиреоза ниже среди темнокожего населения и выше у народов Кавказа, что, по мнению авторов, является свидетельством генетической природы заболевания. В метаанализе полногеномных ассоциативных исследований показан значимый вклад вариабельности гена тиреопероксидазы в риск развития гипотиреоза [41]. Однако не только генетические факторы вовлечены в развитие этого заболевания, о чем свидетельствует наличие взаимосвязи между риском развития гипотиреоза, с одной стороны, и курением, гестационным возрастом на момент рождения (недоношенностью), алиментарной дистрофией, употреблением алкоголя и наркотических препаратов, с другой [4].
Основной причиной гипотиреоидных состояний является дефицит алиментарного йода. В регионах, эндемичных по дефициту йода, повышена заболеваемость аутоиммунным тиреоидитом (болезнью Хашимото), который обусловлен выработкой антител к ТГ, ТПО и рецептору ТТГ [42]. Эти антитела образуются в ходе деструкции Щ через посредство активации T- и B-клеточного иммунитета. Гипотиреоз может быть классифицирован на первичный, то есть вызванный уменьшением количества функционирующей ткани (например, в результате тиреоидэктомии) или нарушением синтеза тиреоидных гормонов (например, на фоне дефицита алиментарного йода), и на центральный или вторичный, то есть обусловленный патологией на уровне центральных отделов гипоталамо-гипофизарно-тиреоидной оси (в частности, к центральному гипотиреозу относят опухоли гипофиза, синдром Шихана). Отличительной особенностью вторичного гипотиреоза является снижение уровня ТТГ в крови, в то время как при других клинических формах гипотиреоидных состояний уровень этого гормона в различной степени повышается. Сравнительно редкой формой гипотиреоза является состояние, в основе которого лежит повышение продукции дейодиназы 3-го типа гемангиомами или другими опухолями, что приводит к ускоренной деградации тиреоидных гормонов, являющихся субстратами для этой дейодиназы [43, 44].
Фармакологические подходы для лечения гипотиреоза
Поскольку гипотиреоидные состояния вне зависимости от вызывающих их причин являются классическими гормонодефицитными эндокринопатиями, то стандартным подходом для их лечения является заместительная терапия, для чего используют различные препараты тиреоидных гормонов – L-тироксин [4]. Терапия тиреоидными гормонами и их аналогами призвана возместить возникший в организме дефицит тиреоидных гормонов, в первую очередь Т3, снизить уровень ТТГ в крови до такового, находящегося в пределах референсного интервала, и тем самым купировать патологические проявления основного заболевания с минимальными побочными эффектами.
К основным побочным эффектам терапии тиреоидных гормонов относят фибрилляцию предсердий и остеопороз, что во многом связано с ятрогенным избытком тироксина. Для предотвращения этих эффектов при терапии пациентов с помощью L-тироксина рекомендуется постоянный мониторинг уровней Т3, Т4 и ТТГ в крови [45]. Помимо этого, эффект от лечения, видимо, зависит от полиморфизма гена дейодиназы 2-го типа, которая ответственна за превращение проактивного тироксина в активную форму Т3 [46, 47].
Селективные агонисты рецепторов тиреоидных гормонов
Перспективным подходом к лечению гипотиреоза и сопутствующих ему метаболических расстройств является создание селективных агонистов рецепторов тиреоидных гормонов [48]. Эти рецепторы локализованы внутри ядра, будучи связаны с промоторными участками тирео-ид-специфичных генов, и выполняют тем самым функции транскрипционных факторов [49, 50]. Имеются различные изоформы этих рецепторов – α и β, причем в функционально активном состоянии рецепторы тироидных гормонов образуют гетеродимерный комплекс с рецептором ретиноида X. Показано, что β-изоформа рецептора, в отличие от α-изоформы, отвечает преимущественно за метаболические эффекты Т3 и Т4, в связи с чем основное внимание исследователей направлено на разработку селективных агонистов β-изоформы. Механизм действия тиромиметиков состоит в селективном связывании с рецептором тиреоидных гормонов в области лиганд-связы-вающего домена, следствием чего является потенцирование физиологических эффектов Т3 и Т4 [51].
На начальном этапе были разработаны два препарата – собетиром и эпротиром, которые показали высокую эффективность in vitro, однако во время их доклинических испытаний обнаружились значительные токсические эффекты этих препаратов на хрящевую ткань, в связи с чем дальнейшие их клинические исследования были прекращены [52]. Более перспективным, в том числе с точки зрения безопасности, оказался препарат ресметиром, который не оказывает влияния на частоту сердечного ритма (наиболее распространенный побочный эффект тиромиметиков), не нарушает процесса костеобразования и по механизму отрицательной обратной связи не подавляет центральные звенья регуляции гипоталамо-гипофизарно-тиреоидной оси [53]. В настоящее время ресметиром проходит уже третью фазу многоцентрового двойного слепого плацебо-контролируемо-го исследования.
Аллостерические агонисты рецептора тиреотропного гормона
Использование ТТГ для стимуляции рецептора ТТГ в условиях клиники не применяется, что обусловлено как мощным онкогенным потенциалом препаратов ТТГ, так и высокой иммуногенностью гормона. В то же время в рецепторе ТТГ, наряду с расположенным в его эктодомене высокоаффинным (ортостерическим) сайтом, с которым взаимодействует ТТГ, имеются еще и аллостерические сайты. Они локализованы в трансмембранном и цитоплазматическом доменах рецептора и также могут быть вовлечены в регуляцию активности рецептора ТТГ и модуляцию его ответа на ТТГ [34]. Наиболее перспективными кандидатами на роль аллостерических агонистов рецептора ТТГ являются низкомолекулярные соединения, способные проникать в аллостерический сайт, расположенный внутри трансмембранного канала рецептора, и переводить его в активированное состояние (см. рис. 1). Поскольку этот сайт не перекрывается с ортостерическим сайтом, то связывание таких аллостерических агонистов не препятствует эффективному взаимодействию ТТГ с гормоном, то есть не приводит к ТТГ-резистентности [35, 36]. Нами разработаны препараты, являющиеся производными тиено[2,3-d]-пиримидина, которые способны в условиях in vitro при действии на культуру тироцитов крысы FRTL-5 повышать экспрессию генов, вовлеченных в синтез тиреоидных гормонов. В условиях in vivo при введении крысам данные препараты повышают у них уровень тиреоидных гормонов в крови, а также усиливают экспрессию тиреопероксидазы и дейодиназы 2-го типа в ткани ЩЖ, как это продемонстрировано для наиболее активного из них – соединения TPY3m [54]. Важно, что производные тиено[2,3-d]-пиримидина сохраняют свою активность не только при внутрибрюшинном, но и при пероральном введении, что делает их прототипами препаратов для стимуляции тиреоидогенеза. Определенный интерес представляют и пептиды, соответствующие третьей цитоплазматической петле рецептора ТТГ, которые, взаимодействуя с аллостерическим сайтом, локализованным в цитоплазматических петлях, активируют рецептор ТТГ и повышают уровень тиреоидных гормонов как в условиях in vitro, так и in vivo [55, 56]. Следует, однако, отметить, что пептидные регуляторы не устойчивы в кровотоке, и эффективным в случае их применения являлось только интраназальное введение.
Заключение
Несмотря на то, что заболевания ЩЖ известны с древних времен, терапевтические подходы к коррекции гипертиреоза и гипотиреоза разработаны в недостаточной степени и имеют ряд серьезных ограничений, связанных как с вариабельностью этиологических факторов заболеваний ЩЖ, так и с несовершенством самих подходов с точки зрения патогенеза этих заболеваний. Многочисленные нежелательные эффекты классических методов лечения патологии ЩЖ снижают качество жизни пациентов и иногда могут стать причиной вынужденного отказа от терапии. Поэтому непрерывно ведется поиск новых, в том числе фармакологических, подходов для лечения гипо- и гипертиреоидных состояний. Полученные в последние годы данные о молекулярных причинах таких патологий ЩЖ, как болезнь Грейвса и аутоиммунный тиреоидит, позволяют разрабатывать принципиально новые таргетные препараты, мишенью которых являются различные звенья системы тиреоидогенеза, в том числе рецептор ТТГ. Среди них аллостерические регуляторы рецептора ТТГ, антитела, способные специфично взаимодействовать с этими рецепторами, селективные агонисты внутриклеточных рецепторов тиреоидных гормонов. Все эти препараты в перспективе смогут стать более безопасной альтернативой существующим терапевтическим подходам.
Список литературы Фундаментальные и клинические аспекты заболеваний щитовидной железы и новые подходы для их лечения (обзор литературы)
- GBD 2017 Mortality Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality and life expectancy, 1950-2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1684-1735. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31891-9.
- Vanderpump M.P.J. Epidemiology of thyroid disorders. In: Luster M., Duntas L., Wartofsky L. (eds.). The thyroid and its diseases. Springer International Publishing AG; 2019:75-85. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-72102-6_6.
- Vanderpump M.P. The epidemiology of thyroid disease. Br. Med. Bull. 2011;99:39-51. DOI: 10.1093/bmb/ldr030.
- Chaker L., Razvi S., Bensenor I.M., Azizi F., Pearce E.N., Peeters R.P. Hypothyroidism Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2022;8(1):30. DOI: 10.1038/ s41572-022-00357-7.
- Burch H.B., Cooper D.S. Management of Graves Disease: A Review. JAMA. 2015;314(23):2544-2554. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2015.16535.
- Wemeau J.L., Klein M., Sadoul J.L., Briet C., Velayoudom-Cephise F.L. Graves' disease: Introduction, epidemiology, endogenous and environmental pathogenic factors. Ann. Endocrinol. (Paris). 2018;79(6):599-607. DOI: 10.1016/j.ando.2018.09.002.
- Brix T.H., Kyvik K.O., Christensen K., Hegedüs L. Evidence for a major role of heredity in Graves' disease: a population-based study of two Danish twin cohorts. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001;86(2):930-934. DOI: 10.1210/jcem.86.2.7242.
- Antonelli A., Ferrari S.M., Ragusa F., Elia G., Paparo S.R., Ruffil-li I. et al. Graves' disease: Epidemiology, genetic and environmental risk factors and viruses. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020;34(1):101387. DOI: 10.1016/j.beem.2020.101387.
- Kisiel B., Bednarczuk T., Kostrzewa G., Kosinska J., Miskiewicz P., Ptazinska M.T. et al. Polymorphism of the oestrogen receptor beta gene (ESR2) is associated with susceptibility to Graves' disease. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.). 2008;68(3):429-434. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.03060.x.
- Cury S.S., Oliveira M., Sibio M.T., Clara S., Luvizotto Rd. A., Conde S. et al. Gene expression of estrogen receptor-alpha in orbital fibroblasts in Graves' ophthalmopathy. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015;59(3):273-276. DOI: 10.1590/2359-3997000000050.
- Brix T.H., Knudsen G.P., Kristiansen M., Kyvik K.O., Orstavik K.H., Hegedüs L. High frequency of skewed X-chromosome inactivation in females with autoimmune thyroid disease: A possible explanation for the female predisposition to thyroid autoimmunity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005;90(11):5949-5953. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2005-1366.
- Simmonds M.J., Kavvoura F.K., Brand O.J., Newby P.R., Jackson L.E., Hargreaves C.E. et al. Skewed X chromosome inactivation and female preponderance in autoimmune thyroid disease: An association study and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014;99(1):E127-E131. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2013-2667.
- Ferrari S.M., Fallahi P., Antonelli A., Benvenga S. Environmental issues in thyroid diseases. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2017;8:50. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00050.
- Bürgi H. Iodine excess. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010;24(1):107-115. DOI: 10.1016/j.beem.2009.08.010.
- Kahaly G.J., Bartalena L., Hegedüs L. The American Thyroid Association/American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists guidelines for hy-perthyroidism and other causes of thyrotoxicosis: A European perspective. Thyroid. 2011;21(6):585-591. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2011.2106.ed3.
- Kahaly G.J., Bartalena L., Hegedüs L., Leenhardt L., Poppe K., Pearce S.H. 2018 European Thyroid Association Guideline for the Management of Graves' Hyperthyroidism. Eur. Thyroid J. 2018;7(4):167-186. DOI: 10.1159/000490384.
- Burch H.B., Cooper D.S. Antithyroid drug therapy: 70 years later. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018;179(5):R261-R274. DOI: 10.1530/EJE-18-0678.
- Bartalena L., Piantanida E., Gallo D., Ippolito S., Tanda M.L. Management of Graves' hyperthyroidism: Present and future. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022;17(2):153-166. DOI: 10.1080/17446651.2022.2052044.
- Vos X.G., Endert E., Zwinderman A.H., Tijssen J.G., Wiersinga W.M. Predicting the risk of recurrence before the start of antithyroid drug therapy in patients with graves' hyperthyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016;101(4):1381-1389. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2015-3644.
- Azizi F., Ataie L., Hedayati M., Mehrabi Y., Sheikholeslami F. Effect of long-term continuous methimazole treatment of hyperthyroidism: comparison with radioiodine. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2005;152(5):695-701. DOI: 10.1530/eje.1.01904.
- Aung E.T., Zammitt N.N., Dover A.R., Strachan M.W.J., Seckl J.R., Gibb F.W. Predicting outcomes and complications following radioiodine therapy in Graves' thyrotoxicosis. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.). 2019;90(1):192-199. DOI: 10.1111/cen.13873.
- Bonnema S.J., Hegedus L. Radioiodine therapy in benign thyroid diseases: Effects, side effects, and factors affecting therapeutic outcome. En-docr. Rev. 2012;33(6):920-980. DOI: 10.1210/er.2012-1030.
- Walter M.A., Briel M., Christ-Crain M., Bonnema S.J., Connell J., Cooper D.S. et al. Effects of antithyroid drugs on radioiodine treatment: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2007;334(7592):514. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39114.670150.BE.
- Metso S., Jaatinen P., Huhtala H., Auvinen A., Oksala H., Salmi J. Increased cardiovascular and cancer mortality after radioiodine treatment for. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007;92(6):2190-2196. DOI: 10.1210/ jc.2006-2321.
- Bartalena L., Piantanida E., Tanda M.L. Can a patient-tailored treatment approach for Graves' disease reduce mortality? Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(4):245-246. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30057-9.
- Pearce S.H.S., Dayan C., Wraith D.C., Barrell K., Olive N., Jansson L. et al. Antigen-pecific Immunotherapy with Thyrotropin Receptor Peptides in Graves' Hyperthyroidism: A Phase I Study. Thyroid. 2019;29(7):1003-1011. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2019.0036.
- Furmaniak J., Sanders J., Sanders P., Li Y., Rees Smith B. TSH receptor specific monoclonal autoantibody K1-70™ targeting of the TSH receptor in subjects with Graves> disease and Graves> orbitopathy - Results from a phase I clinical trial. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.). 2022;96(6):878-887. DOI: 10.1111/cen.14681.
- Krause G., Eckstein A., Schulein R. Modulating TSH receptor signaling for therapeutic benefit. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2020;9(1):66-77. DOI: 10.1159/000511871.
- Kang S.Y., Seo J., Kang H.R. Desensitization for the prevention of drug hypersensitivity reactions. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2022;37(2):261-270. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2021.438.
- Cox L. Grand challenges in allergen immunotherapy. Front. Allergy. 2021;2:710345. DOI: 10.3389/falgy.2021.710345.
- Pavanello F., Zucca E., Ghielmini M. Rituximab: 13 open questions after 20-years of clinical use. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017;53:38-46. DOI: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.11.015.
- Lane L.C., Cheetham T.D., Perros P., Pearce S.H.S. New therapeutic horizons for Graves' hyperthyroidism. Endocr. Rev. 2020;41(6):873-884. DOI: 10.1210/endrev/bnaa022.
- El Fassi D., Nielsen C.H., Junker P., Hasselbalch H.C., Hegedus L. Systemic adverse events following rituximab therapy in patients with Graves' disease. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2011;34(7):e163-e167. DOI: 10.3275/7411.
- Shpakov A.O. Endogenous and synthetic regulators of the peripheral components of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal-gonadal and - thyroid axes. Neurosci. Behav. Physi. 2021;51:332-345. DOI: 10.1007/s11055-021-01076-4.
- Latif R., Realubit R.B., Karan C., Mezei M., Davies T.F. TSH receptor signaling abrogation by a novel small molecule. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2016;7:130. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00130.
- Marcinkowski P., Kreuchwig A., Mendieta S., Hoyer I., Witte F., Furkert J. et al. Thyrotropin receptor: Allosteric modulators illuminate intramolecular signaling mechanisms at the interface of ecto- and transmembrane domain. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019;96(4):452-462. DOI: 10.1124/ mol.119.116947.
- Derkach K.V., Bakhtyukov A.A., Sorokoumov V.N., Shpakov A.O. New Thieno-[2,3-d]pyrimidine-based functional antagonist for the receptor of thyroid stimulating hormone. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2020;491(1):77-80. DOI: 10.1134/S1607672920020064.
- Bakhtyukov A., Derkach K., Sorokoumov V., Fokina E., Shpakov A.O. The development of new low-molecular-weight allosteric antagonists of thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor and their effect on the basal and thyroliberin-stimulated production of thyroid hormones. FEBS Open Bio. 2021;11(1):87-88. DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.13205.
- Hollowell J.G., Staehling N.W., Flanders W.D., Hannon W.H., Gunter E.W., Spencer C.A. et al. Serum TSH, T(4), and thyroid antibodies in the United States population (1988 to 1994): National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002;87(2):489-499. DOI: 10.1210/jcem.87.2.8182.
- Stoppa-Vaucher S., Van Vliet G., Deladoey J. Variation by ethnicity in the prevalence of congenital hypothyroidism due to thyroid dysgenesis. Thyroid. 2011;21(1):13-18. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2010.0205.
- Teumer A., Chaker L., Groeneweg S., Li Y., Di Munno C., Barbieri C. et al. Genome-wide analyses identify a role for SLC17A4 and AADAT in thyroid hormone regulation. Nat. Commun. 2018;9(1):4455. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06356-1.
- Garber J.R., Cobin R.H., Gharib H., Hennessey J.V., Klein I., Mechanick J.I. et al. Clinical practice guidelines for hypothyroidism in adults: co-sponsored by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American Thyroid Association. Endocr. Pract. 2012;18(6):988-1028. DOI: 10.4158/EP12280.GL.
- Huang S.A., Fish S.A., Dorfman D.M., Salvatore D., Kozakewich H.P., Mandel S.J. et al. A 21-year-old woman with consumptive hypothyroidism due to a vascular tumor expressing type 3 iodothyronine deiodinase. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002;87(10):4457-4461. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2002-020627.
- Mouat F., Evans H.M., Cutfield W.S., Hofman P.L., Jefferies C. Massive hepatic hemangioendothelioma and consumptive hypothyroidism. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008;21(7):701-703. DOI: 10.1515/ jpem.2008.21.7.701.
- Jonklaas J., Bianco A.C., Bauer A.J., Burman K.D., Cappola A.R., Celi F.S. et al. Guidelines for the treatment of hypothyroidism: Prepared by the american thyroid association task force on thyroid hormone replacement. Thyroid. 2014;24(12):1670-1751. DOI: 10.1089/ thy.2014.0028.
- Ettleson M.D., Bianco A.C. Individualized therapy for Hypothyroidism: Is T4 enough for everyone? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020;105(9):e3090-e3104. DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa430.
- McAninch E.A., Bianco A.C. The history and future of treatment of hypothyroidism. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016;164(1):50-56. DOI: 10.7326/M15-1799.
- Grover G.J., Mellstrom K., Malm J. Therapeutic potential for thyroid hormone receptor-beta selective agonists for treating obesity, hyperlip-idemia and diabetes. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2007;5(2):141-154. DOI: 10.2174/157016107780368271.
- Brent G.A. Mechanisms of thyroid hormone action. J. Clin. Invest. 2012;122(9):3035-3043. DOI: 10.1172/JCI60047.
- Mendoza A., Hollenberg A.N. New insights into thyroid hormone action. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017;173:135-145. DOI: 10.1016/j. pharmthera.2017.02.012.
- Saponaro F., Sestito S., Runfola M., Rapposelli S., Chiellini G. Selective thyroid hormone receptor-beta (TRp) agonists: New perspectives for the treatment of metabolic and neurodegenerative disorders. Front. Med. (Lausanne). 2020;7:331. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00331.
- Meruvu S., Ayers S.D., Winnier G., Webb P. Thyroid hormone analogues: where do we stand in 2013? Thyroid. 2013;23(11):1333-1344. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2012.0458.
- Jeong S.W. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A drug revolution is coming. Diabetes Metab. J. 2020;44(5):640-657. DOI: 10.4093/ dmj.2020.0115.
- Bakhtyukov A.A., Derkach K.V., Fokina E.A., Sorokoumov V.N., Zakharova I.O., Bayunova L.V. et al. Development of low-molecular-weight allosteric agonist of thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor with thyroidogenic activity. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2022;503(1):67-70. DOI: 10.1134/S1607672922020016.
- Shpakov A.O., Shpakova E.A., Derkach K.V. The sensitivity of the adenylyl cyclase system in rat thyroidal and extrathyroidal tissues to peptides corresponding to the third intracellular loop of thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor. Current Topics in Peptide & Protein Research. 2012;13:61-73.
- Derkach K.V., Shpakova E.A., Titov A.K. et al. Intranasal and intramuscular administration of lysine-palmitoylated peptide 612-627 of thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor increases the level of thyroid hormones in rats. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2015;21:249-260. DOI: 10.1007/ s10989-014-9452-6.


