Интеграция IBL и CLIL в подготовке будущих учителей к преподаванию естественных наук в условиях полиязычия
Автор: Бабич Ирина Михайловна, Омарова Вера Константиновна, Баратова Алия Ахатовна, Чуркина Наталья Ивановна
Журнал: Интеграция образования @edumag-mrsu
Рубрика: Академическая интеграция
Статья в выпуске: 2 (103), 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Актуальность проблемы подготовки будущих учителей естественно-научных дисциплин к преподаванию на нескольких языках определяется социальным заказом общества. Недостаточная практическая подготовленность молодых специалистов требует поиска эффективных методов, способствующих решению проблемы. Цель исследования – изучение влияния интеграции методов IBL и CLIL на качество подготовки будущих педагогов естественно-научных дисциплин (на примере химии) к преподаванию на английском языке. Впервые предложена интеграция методов IBL и CLIL для подготовки будущих учителей естественно-научных дисциплин к преподаванию на английском языке как иностранном в условиях полиязычного образования. Материалы и методы. В исследовании приняли участие 63 учащихся III курса направлений «Химия», «Химия и биология». Для изучения показателей качества подготовки – речевых актов будущих учителей естественно-научных дисциплин в период педагогической практики в школе – применялись методы педагогического эксперимента, наблюдения, тестирования, анализа аудиозаписей уроков, описательной и математической статистики. Исследование проводилось до и после обучения студентов с помощью метода CLIL (контрольная группа) и интеграции IBL и CLIL (экспериментальная группа). Результаты исследования. Полученные результаты демонстрируют неслучайный характер изменений между экспериментальной и контрольной группами будущих учителей. Студенты экспериментальной группы издали больше директив. Значительный прирост зафиксирован по вопросам высокого уровня на этапах уроков по организации самостоятельных исследований учащихся. Видовой состав директивных актов стал разнообразнее, чем в контрольной группе. Доказано положительное влияние интеграции методов IBL и CLIL на рост показателей качества подготовки студентов. Обсуждение и заключение. Представленные материалы могут быть использованы для подготовки будущих учителей естественно-научных дисциплин к преподаванию предметов на любом втором языке. Результаты исследований будут актуальными для преподавателей университетов европейских стран и стран СНГ, которые находятся в поиске эффективных способов подготовки полиязычных педагогов.
IBL, CLIL, будущий учитель естественно-научных дисциплин, полиязычие, английский язык, директива
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147231353
IDR: 147231353 | УДК: 378:005.591.6 | DOI: 10.15507/1991-9468.103.026.202102.304-320
Текст научной статьи Интеграция IBL и CLIL в подготовке будущих учителей к преподаванию естественных наук в условиях полиязычия
В полиязычных странах актуальным является вопрос подготовки будущих учителей к преподаванию на одном или нескольких дополнительных языках. Владение как минимум тремя языками считается одной из важнейших базовых образовательных компетенций. Это может быть второй язык страны, обучение на котором позволит сохранить ее культурно-языковое многообразие, а также один или несколько иностранных языков, например, английский как наиболее широко применяемый в международном общении в условиях глобализации.
Настоящее исследование посвящено изучению проблемы подготовки будущих учителей естественно-научных дисциплин к преподаванию в условиях полиязычия. Потребность в таких учителях объясняется постепенным переходом общеобразовательных школ Республики Казахстан к преподаванию на трех языках ‒ казахском, русском, английском ‒ и изучению естественных наук в старших классах на английском языке.
Будущий педагог, преподающий предмет на втором (или иностранном) языке, должен иметь хорошо развитые навыки коммуникации, уметь самостоятельно планировать урок с учетом языковых и предметных целей, преподавать, поддерживая развитие у учащихся знания предмета, академического английского языка, мышления высокого порядка. Необходимость подготовки таких специалистов обуславливает актуальность проведенного исследования.
Как показывает практика, будущие учителя испытывают серьезные затруднения в реализации вышеперечисленных навыков на уроке. Поэтому в настоящее время имеется противоречие между объективно существующей потребностью общества в выпускниках педагогических университетов с высоким уровнем владения вторым и иностранным языком в предметной и педагогической области и недостаточной практической подготовленностью молодых специалистов, приходящих в школы. Устранение указанного противоречия мы видим в поиске и при- менении эффективных методов подготовки студентов к преподаванию предметов естественно-научного цикла в условиях полиязычия. Для решения этой задачи целесообразно исследовать комплексное влияние уже известных методов на формирование ожидаемых навыков будущих учителей.
Перспективным направлением, на наш взгляд, является применение интеграции предметно-языкового интегрированного обучения Content and Language Integrated Learning (CLIL) и обучения на основе запросов Inquiry-based learning (IBL). В научной литературе рассматриваются различные аспекты использования каждого метода в обучении будущих учителей в отдельности. IBL влияет на совершенствование исследовательских навыков студентов, умение формулировать вопросы различного когнитивного уровня, стимулирует к совместной работе, направлен на диалоговое обучение. CLIL применяется для одновременного изучения языка, предмета, развития коммуникативных навыков и навыков высокого мышления.
Идея исследования заключается в интеграции методов IBL и CLIL как эффективного средства подготовки будущих учителей естественно-научных дисциплин к преподаванию в условиях полиязычия. Одновременное применение методов может усилить положительный эффект «полезности» каждого из них в отдельности, оценить который позволяют директивы как самые распространенные речевые действия учителя в классе.
Теоретическая значимость исследования состоит в определении способа подготовки будущих учителей естественных дисциплин (на примере химии) к преподаванию на втором (или иностранном) языке. Практическая – в возможности применения результатов исследования для подготовки будущих учителей естественных дисциплин к преподаванию в условиях полиязычия. Проверка эффективности интеграции методов осуществлялась с помощью английского языка как одного из иностранных языков, изучаемых в странах СНГ и мире.
Целью нашего исследования стало изучение того, как объединение методов
IBL и CLIL оказывает влияние на качество подготовки будущих учителей к преподаванию естественных наук на английском языке. Показателями качества подготовки определены изменения в числе, разнообразии, когнитивном уровне директивных речевых актов, произнесенных студентами в процессе преподавания на уроках химии. Мы предположили, что, если использовать интеграцию IBL и CLIL, то это положительно повлияет на качество подготовки студентов к преподаванию естественно-научных дисциплин на английском языке, которое отразится в повышении числа, разнообразия и когнитивного уровня директивных речевых актов будущих учителей.
Обзор литературы
В аспекте проблематики исследования привлекает внимание точка зрения У. Дахллёф и его соавторов о том, что при поиске методов обучения важно не искать «лучший метод», а использовать методы или их комбинации, более подходящие для конкретных целей, потребностей студентов и среды обучения1. CLIL и IBL основаны на конструктивистской теории обучения [1; 2]. Каждый из методов обеспечивает ориентированное обучение, взаимодействие студентов друг с другом в процессе конструирования новых знаний, развитие навыков решения проблем [3; 4]. Схожая философия обучения создает предпосылки для интеграции методов друг в друга.
IBL определяют как обучение, управляемое вопросами, основанное на процессе поиска знаний, нового понимания [5; 6], состоящее из пяти стадий: ориентации, концептуализации, исследования, заключения, обсуждения [7].
По мнению Р. Брудер, Э. Прескотт, И. Букхобзы, Б. Гюлерр, М. Сахина, IBL является одним из наиболее успешных методов, используемых в естественно-научном образовании [8–10]. Он развивает навыки мышления и дает преимущества в предметной области, улучшая успеваемость и отношение к предмету [11–14].
М. Фут, Б. Де Вефер, Й. Кенсинг, Н. Иноуэ, С. Бучинский рассматривают влияние IBL на обучение будущих педагогов [15; 16]. Несмотря на разные аспекты изучения проблемы, авторы приходят к мнению об эффективности метода в подготовке студентов педагогических специальностей. Обучение с помощью IBL повышает самоэффективность будущих учителей при проведении уроков. Они разрабатывают уроки с большей степенью свободы, особенно в сотрудничестве и общении с коллегами.
Исследования в области подготовки будущих учителей CLIL нашли отражение в публикациях зарубежных, казахстанских и российских авторов [4; 17–21]. Ученые отмечают важность применения данного метода в одновременном изучении содержания предмета и иностранного языка, на совместную и взаимовыгодную роль которых в CLIL указывает Д. Марш2, и рассматривают различные аспекты улучшения подготовки будущих учителей к работе в условиях двух- и полиязычия. Д. Койл, П. Худ, Д. Марш считают, что для успешного урока CLIL учителя должны формировать взаимосвязь между содержанием (предметом), коммуникацией (языком), познанием (мышлением) и культурой3. Данные аспекты позволяют создать среду, в которой учителя и учащиеся постепенно овладевают коммуникативной компетенцией на дополнительном языке.
Для развития навыков коммуникации учителю важно владеть языком обучения (предметная терминология, языковые конструкции, необходимые для изучения предмета), языком для обучения (коммуникация в группах, вопросы, обсуждение) и языком через обучение (непредсказуемый язык, возникающий на уроке в процессе предоставлеия обратной связи, советов, рекомедаций). П. Мехисто, Д. Марш, М. Фриголс полагают, что движущей силой CLIL является познание, направленное на развитие навыков высокого мышления4, важность изучения которых учителями, наряду со знанием языка и содержания, подчеркивают Дж. Камминс, М. Суэйн [22]. В дальнейшем эта мысль получила свое развитие в работе С. Хил-льярд [23]. Она утверждает, что учитель CLIL должен освоить реализацию таксономии Блума на уровне навыков мышления высшего порядка, а также эффективно владеть языком преподавания, управления классом, объяснениями и инструктажами.
Теоретический анализ литературы показал, что исследования, связанные с интеграцией IBL и CLIL для подготовки будущих учителей естественных наук к преподаванию на английском языке, не проводились. Однако имеются исследования, рассматривающие эффективность обучения, основанного на запросе, в изучении английского языка [24]. С другой стороны, О. Мейер и соавторы указывают на то, что без правильного использования академического языка CLIL невозможно достигнуть глубокого академического понимания в предметной области [25]. Б. Мохан, К. Леунг, Т. Слейтер главным свидетельством обучения считают язык [26].
Самыми распространенными речевыми актами в классах CLIL, отражающими способность формулировать знания, понимание, мысли, идеи на английском языке, являются директивы [27–29]. Эр-мавати, Н. Юнус, А. Памму утверждают, что в основе цикла IBL находится директивный запрос [30]. В соответствии с таксономией речевых актов Дж. Серла [31]
директивы направляют слушателя на действия или их прекращение. Примеры директив ‒ команды, запросы, советы, приказы, предупреждения и вопросы различного когнитивного уровня5 [31]. Директивные речевые действия происходят между учителем и учеником, между учениками в регулятивном или учебном регистре, которые рассматриваются как часть педагогического дискурса в классе6 [27]. С. Далтон-Пуффер, Т. Никула обращают внимание на важность понимания, какое педагогическое действие наилучшим образом обеспечит доступ учащихся к максимально богатой языковой среде обучения [27].
Таким образом, анализ ряда исследований позволяет констатировать, что CLIL и IBL оказывают положительное влияние на различные аспекты подготовки будущих педагогов, необходимые для работы в условиях полиязычия: развитие навыков коммуникации, высокого мышления, изучение английского языка, одновременное изучение языка и неязыкового предмета. Вместе с тем вопрос влияния интеграции методов IBL и CLIL на подготовку учителей естественных наук к преподаванию на английском языке требует детального изучения.
Материалы и методы
Методологической основой исследования является системно-деятельностный подход. Для проведения эмпирического исследования были выбраны методы педагогического эксперимента, наблюдения, тестирования, анализа аудиозаписей уроков, описательной и математической статистики. Исследование проводилось в период с февраля 2019 г. по февраль 2020 г. на базе Павлодарского педагогического университета и школ Павлодарской области (Казахстан), в которых преподавание предметов естественно-математического цикла осуществляется на английском языке. В исследовании приняли участие 63 студента третьего курса, обучающихся по образовательным программам «Химия» и «Химия и биология». В выборку респондентов вошли студенты, имеющие уровень английского языка не ниже В1. Определение уровня владения английским языком в соответствии с общеевропейскими стандартами компетенций владения языком Common European Framework of Reference (CEFR)7 осуществлялось с помощью программы онлайн-тестирования General English, разработанной организацией Cambridge Assessment English.
Экспериментальная (31 чел.) и контрольная (32 чел.) группы были сформированы с помощью программы генератора случайных чисел. На констатирующем этапе эксперимента были проанализированы учебные результаты студентов двух групп по английскому языку и общей химии, осуществлено наблюдение уроков в период практики в школе (февраль 2019 г.). На формирующем этапе происходило обучение студентов с помощью элективного курса «Преподавание химии на английском языке» (сентябрь 2019 г. – декабрь 2019 г.) с применением интеграции методов CLIL и IBL в экспериментальной группе. Контрольная группа прошла стандартное обучение только с применением метода CLIL. Повторное наблюдение уроков студентов естественно-научных дисциплин осуществлено в феврале 2020 г.
Преподавателями языка и предмета было проанализировано 252 аудиозаписи: по 126 уроков в экспериментальной и контрольной группах до начала проведения эксперимента и после него.
Для определения директив применялась классификация, предложенная Дж. Серлом [31] и дополненная Я. Мейем8 и Ф. Кристи9 (табл. 1).
Т а б л и ц а 1. Характеристика директивных речевых актов
T a b l e 1. Characteristics of directive speech acts
Вид директив / Types of directives
Определение речевого акта / Definition of a speech act
Директива / Directive
Учебная / Instructional
Запрос на информацию / Requests for information
Вопросы низкого уровня / Low order thinking questions
Вопросы высокого уровня / Higher order thinking questions
Другие директивы / Other directives
Запрос на действие / Requests for action
Регулятивная / Regulative
Полученные результаты анализировались с помощью программы статистической обработки информации IBM SPSS Statistics 26. Были использованы критерии Колмогорова – Смирнова, Манна – Уитни, Уилкоксона.
Для определения центральной тенденции данных числа директив применяли медиану как устойчивую к аномальным отклонениям альтернативу среднему арифметическому. Соотношение числа вопросов высокого уровня на различных этапах урока осуществлялось посредством средних арифметических значений. Анализ изменений абсолютных величин проводился с помощью относительной величины сравнения и процента прироста.
Результаты исследования
В процессе проведения исследования влияния интеграции IBL и CLIL на подготовку будущих учителей естественно-научных дисциплин к преподаванию на английском языке изучались директивы как самые распространенные речевые акты педагогов в классе. Выбор непараметрических критериев связан с тем, что данные, полученные в экспериментальной и контрольной группах, не подчиняются закону нормального распределения.
На основе критерия Манна – Уитни осуществлены проверка статистически значимых различий и сравнение показателей между двумя группами будущих учителей до начала и после окончания эксперимента.
Для определения однородности экспериментальной и контрольной групп по признакам, которые могут влиять на количество издаваемых директив в классе, был проведен анализ предметных и языковых знаний будущих учителей естественно-научных дисциплин до формирующего эксперимента.
Согласно данным, представленным в таблице 2, не обнаружены статистически значимые различия ( p < 0,05) между двумя группами студентов по интересующим нас признакам. Это указывает на однородность контрольной и экспериментальной групп на начало проведения эксперимента.
Отсутствие статистически значимых различий ( p < 0,05) между двумя группами также обнаружено по показателям количества директив, произнесенных будущими учителями естественно-научных дисциплин до педагогического вмешательства (табл. 3).
Как показывают данные таблицы 3, статистически значимые различия проявляются по всем видам учебных директив между двумя группами студентов после проведения обучения ( U = 85 при р < 0,05). Не обнаружены значимые различия ( p > 0,05) по показателям регулятивных директив как до начала, так и после проведения формирующего эксперимента.
Для сопоставления значений медиан экспериментальной и контрольной групп после проведения обучения использовали относительную величину сравнения.
Т а б л и ц а 2. Определение однородности контрольной и экспериментальной групп до проведения формирующего эксперимента с помощью критерия Манна – Уитни
T a b l e 2. Determination of the homogeneity of the control and experimental groups before carrying out the forming experiment using the Mann – Whitney test
|
Показатель / Indicator |
Медиана / Median |
U |
Значимость / Value, p < 0,05 |
|
|
Экспериментальная группа / Experimental group |
Контрольная группа / Control group |
|||
|
Английский язык / English language |
B1* |
B1 |
519 |
0,713 |
|
Общая химия / General Сhemistry |
3,33** |
3,33 |
520 |
0,730 |
Примечание : * – показатель шкалы Общеевропейских компетенций владения языком CEFR (Common European Framework of Reference); ** – показатель по шкале Среднего балла аттестата GPA (Grade Point Average).
Note : * – an indicator of the Common European Framework of Reference scale (CEFR); ** – an indicator of the scale of GPA certificate (Grade Point Average).
Т а б л и ц а 3. Сравнение показателей учебных и регулятивных директив между контрольной и экспериментальной группами до и после формирующего эксперимента
T a b l e 3. Comparison of indicators of educational and regulatory directives between the control and experimental groups before and after the forming experiment
|
Директивы / Directives |
Пре-тест / Pre-test |
Пост-тест / Post-test |
|||||||
|
Медиана / Median |
U |
Значимость / Value p < 0,05 |
Медиана / Median |
U |
Значимость / Value p < 0,05 |
Относительная величина сравнения, % / Relative comparison value, % |
|||
|
Экс / Exp |
Контр / Contr |
Экс / Exp |
Контр / Contr |
||||||
|
Учебные директивы / Instructional directives |
35 |
41 |
617 |
0,094 |
82 |
47 |
85 |
0,000 |
174 |
|
Запрос на информацию / Requests for information |
30 |
36 |
588 |
0,201 |
65 |
41 |
277 |
0,003 |
159 |
|
Вопросы низкого уровня / Low order thinking questions |
25 |
28 |
641 |
0,44 |
42 |
33 |
74 |
0,000 |
127 |
|
Вопросы высокого уровня / Higher order thinking questions |
5 |
5 |
517 |
0,751 |
11 |
7 |
38 |
0,000 |
157 |
|
Другие директивы / Other directives |
0 |
0 |
77 |
1 |
5 |
0 |
0,0 |
0,000 |
– |
|
Запрос на действие / Requests for action |
5 |
5 |
396 |
0,13 |
8 |
7 |
100 |
0,000 |
125 |
|
Регулятивные директивы / Regulative directives |
28 |
27 |
420 |
0,287 |
42 |
42 |
537 |
0,572 |
– |
Примечание : Экс – экспериментальная группа. Контр – контрольная группа. Note : Exp – Experimental group. Contr – Control group.
За базу сравнения были приняты результаты контрольной группы. Студенты экспериментальной группы произнесли на 74 % больше учебных директив, чем студенты контрольной группы. Наибольшее различие в числе директив наблюдалось по запросу на информацию. Будущие учителя, обучающиеся с помощью интеграции CLIL и IBL, произнесли на 59 % больше запросов на информацию и на 25 % больше запросов на действие. Таким образом, самым распространенным видом учебных директив на уроках в контрольной и экспериментальной группах были вопросы. Будущие учителя экспериментальной группы задали на 57 % больше вопросов высокого уровня и на 27 % больше вопросов низкого уровня по сравнению с будущими учителями контрольной группы.
На втором этапе исследования у студентов экспериментальной группы появился новый вид учебных директив, от- сутствующий во время констатирующего эксперимента. Будущие учителя, обучившиеся с помощью интеграции методик IBL и CLIL, произнесли 73 учебных совета и рекомендаций на английском языке (медиана = 5). Данный вид директив не обнаружен у студентов контрольной группы.
Для проверки значимых различий показателей внутри каждой группы до формирующего эксперимента и после него использован критерий Уилкоксона. Результаты сравнения представлены в таблице 4.
Данные таблицы 4 демонстрируют наличие статистически значимых различий ( p < 0,05) между показателями директив до начала эксперимента и после его проведения в контрольной и экспериментальной группах отдельно.
Таким образом, анализируемые изменения внутри и между группами будущих учителей неслучайны.
Т а б л и ц а 4. Сравнение показателей учебных и регулятивных директив в контрольной и экспериментальной группах до и после формирующего эксперимента с помощью критерия Уилкоксона
T a b l e 4. Comparison of indicators of educational and regulatory directives in the control and experimental groups before and after the forming experiment using the Wilcoxon test
|
Директивы / Directives |
Группа / Group |
Медиана / Median |
Z |
Значимость / Value p < 0, 05 |
|
|
Пре-тест / Pre-test |
Пост-тест / Post-test |
||||
|
Учебные директивы / |
Экспериментальная / |
35 |
82 |
4,747 |
0,000 |
|
Instructional directives |
Experimental Контрольная / Сontrol |
41 |
47 |
3,447 |
0,001 |
|
Запрос на информацию / |
Экспериментальная / |
30 |
65 |
4,747 |
0,000 |
|
Requests for information |
Experimental Контрольная / Сontrol |
36 |
41 |
3,447 |
0,001 |
|
Вопросы низкого уровня / |
Экспериментальная / |
25 |
42 |
4,864 |
0,000 |
|
Low-order thinking questions |
Experimental Контрольная / Сontrol |
28 |
33 |
3,445 |
0,001 |
|
Вопросы высокого уровня / |
Экспериментальная / |
5 |
11 |
4,883 |
0,000 |
|
Higher-order thinking questions |
Experimental Контрольная / Сontrol |
5 |
7 |
4,981 |
0,000 |
|
Другие директивы / |
Экспериментальная / |
0 |
5 |
3,140 |
0,001 |
|
Other directives |
Experimental Контрольная / Сontrol |
0 |
0 |
0,000 |
– |
|
Запрос на действие / |
Экспериментальная / |
5 |
8 |
4,0923 |
0,000 |
|
Requests for action |
Experimental Контрольная / Сontrol |
5 |
7 |
5,000 |
0,000 |
|
Регулятивные директивы / |
Экспериментальная / |
28 |
42 |
4,870 |
0,000 |
|
Regulative directives |
Experimental Контрольная / Сontrol |
27 |
42 |
4,942 |
0,000 |
За один и тот же промежуток времени (252 урока) будущие учителя контрольной группы произнесли 2 087 директив до и 2 836 – после эксперимента. Студенты экспериментальной группы, обучающиеся с помощью интеграции методик IBL и CLIL, произнесли 2 009 директив до и 3 302 директивы после формирующего эксперимента. На основе сравнения меди- ан был рассчитан процент прироста числа директив в контрольной и экспериментальной группах.
Студенты, обучающиеся с применением интеграции методик IBL и CLIL, показали значительное увеличение по числу всех видов директив. Прирост учебных директив был больше регулятивных (табл. 5).
Т а б л и ц а 5. Прирост директив в экспериментальной и контрольной группах
T a b l e 5. Increase in directives in the experimental and control groups
|
Директивы / Directives |
Прирост, % / Increase, % |
|
|
Экс / Exp |
Контр / Contr |
|
|
Учебные директивы / Instructional directives |
134 |
15 |
|
Запрос на информацию / Requests for information |
117 |
14 |
|
Вопросы низкого уровня / Low order thinking questions |
68 |
18 |
|
Вопросы высокого уровня / Higher order thinking questions |
120 |
40 |
|
Запрос на действие / Requests for action |
60 |
40 |
|
Регулятивные директивы / Regulative directives |
50 |
56 |
Максимальный процент прироста среди учебных директив был зафиксирован по запросу на информацию. Наибольший рост показали вопросы высокого уровня. Прирост советов и рекомендаций («Другие директивы») не определялся, так как до проведения эксперимента они не были обнаружены в речи будущих учителей.
У студентов контрольной группы обнаружено незначительное увеличение по учебным директивам, запросам на информацию, вопросам низкого уровня.
Прирост регулятивных директив, побуждающих к организационным действиям в классе, оказался выше, чем учебных, направленных на работу с предметным контентом. Среди учебных директив наибольший рост показали запросы на действие, предполагающие ответ в виде действия или объяснения действий в учебном регистре, и вопросы высокого уровня.
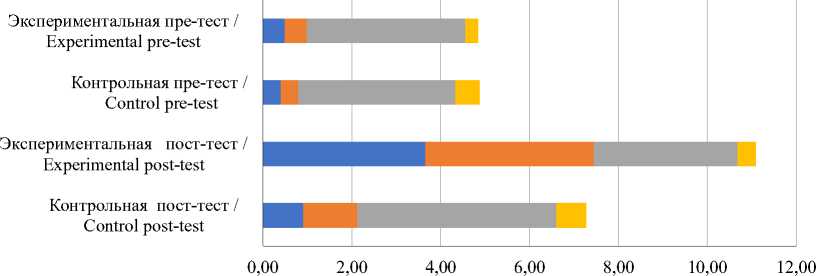
Анализ аудиозаписей позволил нам зафиксировать изменение числа вопросов высокого уровня на разных этапах уроков до и после формирующего эксперимента. На рисунке представлены сравнения средних арифметических значений показателей количества вопросов, требующих навыков высокого мышления и произнесенных студентами обеих групп.
На начало эксперимента студенты контрольной и экспериментальной групп задали в среднем приблизительно одинаковое число вопросов высокого уровня (4,88 и 4,8 соответственно). Чаще всего они использовали этот вид учебных директив на этапе применения новых знаний. После проведения эксперимента значения средних показателей вопросов высокого уровня в контрольной и экспериментальной группах изменились до 7,28 и 11,1 соответственно.
Наибольшее количество запросов на информацию высокого когнитивного уровня в экспериментальной группе после формирующего эксперимента было произнесено на этапах актуализации знаний, целеполагания (3,65) и при изучения нового материала (3,79).
Студенты контрольной группы задали больше вопросов высокого уровня на этапе применения знаний (4,47), по сравнению со студентами экспериментальной группы (3,23). Незначительное увеличение количества директив, направленных на развитие навыков высокого мышления, были отмечены в контрольной группе на рефлексивном этапе уроков (0,68), по сравнению с экспериментальной группой (0,42).
■ Начало урока (целеполагание) / The beginning of the lesson (setting the objectives of the lesson)
■ Изучение нового материала / New material acguisition
■ Применение нового материала / New material application
■ Рефлексия / Reflection
Р и с у н о к. Распределение вопросов высокого уровня сложности на различных этапах урока F i g u r e. Distribution of questions of a high level of complexity at different stages of the lesson
Все наблюдаемые изменения в когнитивном уровне задаваемых вопросов происходили у студентов в период практики в школе на третьем (пре-тест) и четвертом курсах (пост-тест) в процессе преподавания одного и того же раздела курса химии Analytical techniques . Выдержки из уроков иллюстрируют изменение уровня формулируемых вопросов конкретными студентами по окончании формирующего эксперимента (табл. 6).
На этапе целеполагания будущий учитель А экспериментальной группы совместно с учениками формулировал вопросы исследования урока по теме Application of analytical techniques. Эти вопросы до и после проведения формирующего эксперимента обеспечивали развитие мыслительных умений учащихся различного уровня сложности: от воспроизведения знаний (пре-тест) до умения выражать суждения и оценивать (пост-тест). При изучении нового материала NMR spectroscopy студент B экспериментальной группы использовал вопросы для организации самостоятельной работы учащихся с предлагаемыми ресурсами. Изменения в когнитивном уровне издаваемых учебных директив были обнаружены после обучения с применением интеграции CLIL и IBL. Вопросы на этапе пре-теста соответствовали мыслительным уровням «Знание» и «Понимание». Вопросы на этапе пост-теста направлены на развитие навыков оценки и анализа у учащихся.
Увеличение среднего значения вопросов высокого уровня (от 3,54 до 4,47) наблюдалось у будущих учителей контрольной группы на этапе применения знаний. Выдержки аудиозаписей фрагментов урока Mass spectrometry студента С демонстрируют изменение когнитивного уровня задаваемых им вопросов на различных стадиях исследования. На этапе констатирующего эксперимента вопросы способствуют развитию навыков применения знаний учащимися. После проведения эксперимента студент формулирует вопросы, требующие мыслительных умений высокого уровня и направленные на развитие навыков оценки у учащихся.
Т а б л и ц а 6. Изменение когнитивного уровня задаваемых вопросов у студентов на разных этапах урока
T a b l e 6. Changes in the cognitive level of the questions asked by students at different stages of the lesson
|
Этап урока / |
Пре-тест / |
Пост-тест / |
|
Lesson stage |
Pre-test |
Post test |
Начало урока (целеполагание) / The beginning of the lesson (setting the objectives of the lesson)
Студент A (экспериментальная группа) / Student A (experimental group)
Where are the Mass spectrometry, Rate the value of integration of Mass spectrometry gas-liquid chromatography, NMR and Gas-liquid chromatography, Mass spectrome-spectroscopy used?* try and NMR spectroscopy to support research in the field of medicine, space exploration, archeology, environmental protection?**
Изучение нового ма- Студент B (экспериментальная группа) / Student B (experimental group) териала / New material acuisition What solvents are used in Nucle- Why do you think tetrachloromethane is used as q ar magnetic resonance?* List the a solvent in Nuclear magnetic resonance?** Why properties of Tetramethyl silane as would the deuterated solvent CDCl3 be used instead a standard in NMR spectroscopy? * of CHCl3? **
Describe Low-resolution NMR and Compare the common things and differences between
High-resolution NMR *
Low-resolution NMR and High-resolution NMR? **
Применение нового материала / New material application
Студент C (контрольная группа) / Student C (control group)
What charge does the molecular ion Estimate the probability of the location of the mo-of ethanol have on its mass spec- lecular ion of ethanol at the origin of the axis Mass-trum? * to-charge ratio? Justify your answer **
Identify a fragment of an ethanol Predict the possible structural formula of a sub-
molecule with a molecular weight stance presented on its mass spectrum, if we know of 15? * that it belongs to the class of alcohols? **
Примечание : * - вопросы низкого уровня, ** - вопросы высокого уровня. Note : * – low-order thinking questions; **– higher-order thinking questions.
Студенты контрольной и экспериментальной групп произнесли разное количество видов учебных директив. Советы и рекомендации, появившиеся у будущих учителей химии экспериментальной группы после проведения обучения с применением IBL и CLIL, были использованы для оказания поддержки ученикам, испытывающим затруднения при выполнении самостоятельных работ.
В таблице 7 представлено сравнение аудиозаписей диалогов учащихся и студентов обеих групп на уроках по теме NMR spectroscopy . Учебные ситуации предполагали предоставление совета (рекомендации) ученикам для решения практического вопроса.
Студент D экспериментальной группы реагировал на запрос учащегося и представлял рекомендацию на английском языке. Студент E контрольной группы после непродолжительной паузы перешел на первый язык (русский). Поэтому данный совет не был учтен при подсчете числа директив.
Обсуждение и заключение
В ходе исследования установлено, что студенты экспериментальной группы произнесли большее количество директивных актов, чем учащиеся контрольной группы. Значительный прирост наблюдался как по учебным, так и по регулятивным директивам. Видовой состав директивных актов в экспериментальной группе студентов стал разнообразнее. Среди всех учебных директив наибольший при- рост зафиксирован по вопросам высокого уровня, входящих в состав запроса на информацию.
Эти изменения в экспериментальной группе произошли после обучения будущих учителей с применением двух инновационных методов. Роль CLIL в интеграции с IBL заключалась в обеспечении взаимосвязи между целями изучения химии, методики ее преподавания и языковыми задачами. CLIL обеспечивал усвоение содержания в трех предметных областях посредством развития языка обучения (Language of learning). Планировалось, что развитие языка через обучение (Language through learning) будет способствовать повышению разнообразия видов директив, появлению в речи студентов рекомендаций, советов, т. е. речевых актов, которые возникают в классах в ходе предоставления обратной связи и не могут быть запланированы будущими учителями. Такие директивные акты отсутствовали у студентов контрольной группы, обучающихся с применением CLIL. Появление рекомендаций и советов на уроках студентов экспериментальной группы, вероятно, связано с развитием разнообразия речи будущих педагогов на английском языке, которую обеспечивал IBL в интеграции с CLIL. Эта позиция согласуется с выводом, О. Амарал, Л. Гаррисон, М. Кленчи [32]. Они утверждают, что применение IBL способствует не только повышению уровня естественно-научных знаний студентов, но и уровня владения академическим английским языком.
Т а б л и ц а 7. Выбор языка советов (рекомендаций) в контрольной и экспериментальной группах
T a b l e 7. Choosing the Language of advice (recommendations) in the control and experimental groups
Экспериментальная группа / Experimental group
Контрольная группа / Control group
Ученик 1 / I am having difficulty identifying Ученик 2 /
Learner 1 a substance by its spectrum Learner 2
Студент D / I suggest you apply rule (n + 1) to the Студент E / Student D splitting pattern. Then you will see Student E what protons are on the neighboring carbon atoms
It is difficult for me to determine the structure of a substance by its spectrum
Пауза / Pause.
Попробуй применить правило (n + 1). Оно даст возможность понять, сколько атомов водорода в окружении / Try to apply the rule. It will make it possible to understand how many hydrogen atoms are in the environment
Обучение будущих учителей с помощью интеграции IBL и CLIL было сфокусировано на организации сотрудничества и общения студентов в группах. Участие в групповых коммуникациях по конструированию уроков способствовало развитию разговорных навыков студентов и, как следствие, быстроте и разнообразию ответов на поступающие запросы. Установленный факт не противоречит точке рения Р. Фахрия [33]. Он утверждает, что улучшение речевых навыков учащихся неотделимо от их участия в речевой деятельности на английском языке.
Реакцией студентов контрольной группы на запросы учащихся были рекомендации и советы, которые они задавали на русском языке. Наблюдаемое отсутствие словарного запаса CLIL у преподавателей ‒ не носителей английского языка также описывали Т. Никула [34], Э. Дафуз, Б. Нуньес [35]. С отсутствием разнообразия речи студентов контрольной группы, по всей видимости, связано и меньшее количество произнесенных ими запросов на действие в учебном регистре по сравнению со студентами экспериментальной группы. Таким образом, IBL усиливает влияние CLIL на способность студентов к разнообразной устной речи.
Одной из функций языка для обучения (Language for learning) в CLIL является умение формулировать вопросы и управлять работой учащихся в классе. Преобладающим видом учебных директив на уроках в контрольной и экспериментальной группах были вопросы. Этот вывод подтверждают результаты исследования, которые получили С. Далтон-Пуф-фер [27], Х. Харьянто, Х. Мубарок [36] и Т. Септианингсих, У. Уорсон [37].
Однако у будущих учителей экспериментальной группы наблюдался значительный прирост в числе вопросов высокого и низкого уровня после проведения эксперимента, по сравнению с будущими учителями контрольной группы. Данный факт позволяет сформулировать предположение о положительном влиянии интеграции IBL и CLIL на навыки задавания вопросов. CLIL обеспечивал умение правильно формулировать вопросы, а IBL соз- давал среду, в которой вопросы были необходимы для осуществления совместного исследования. Такая позиция о среде IBL, в которой студенты приобретают умение задавать вопросы высокого уровня, планировать и исследовать, подтверждена результатами работы А. Гофштейна, Р. Шор, М. Кипнис [38].
Когнитивный уровень задаваемого вопроса может указывать на уровень мышления человека. Увеличение количества вопросов высокого уровня в группе студентов, обучающихся с помощью интеграции IBL и CLIL, вероятно, связано с влиянием IBL на развитие навыков высокого мышления. Этот вывод подтверждается С. Психа-рисом [39], Г. Мадхури и др. [40].
Студенты контрольной группы чаще задавали вопросы высокого уровня на этапе применения знаний, а у студентов экспериментальной группы наблюдалось изменение средних показателей количества вопросов высокого уровня на различных этапах урока до и после проведения эксперимента. После проведения обучения с помощью интеграции IBL и CLIL они произнесли больше вопросов высокого уровня на начальном этапе урока и в ходе изучения нового материала. Формулировка вопросов высокого уровня на этих этапах урока была связана с организацией ими групповых исследований в классе, т. е. будущие учителя химии экспериментальной группы использовали методику IBL в процессе преподавания. Этот факт согласуется с выводом Дж. Кале, Дж. Су-повица, Д. Майер [41]. Они обнаружили положительную взаимосвязь между профессиональным развитием учителей в области IBL и применением стратегий обучения IBL в классе.
Результаты исследования показали отсутствие значимых различий в числе регулятивных директив, побуждающих к организационным действиям в классе, в контрольной и экспериментальной группах. Вероятно, это связано с тем, что в большей степени данный вид директивных актов регулировался и развивался с помощью CLIL посредством языка для обучения (Language for learning). Изучение языка управления классом (Classroom
Language), составляющего основу регулятивных речевых актов, было обязательной частью обучения студентов двух групп в рамках элективного курса «Преподавание химии на английском языке».
По мнению К. Долтон-Пуффер, У. Смит, CLIL осуществляет роль катализатора в изучении языка, переключая внимание студентов с языковых форм на выполнение конкретных задач, связанных с содержанием предметов [42]. IBL в контакте с CLIL является своеобразным «надкатализатором» среды изучения языка и предмета. Если CLIL направляет внимание студентов от языковой формы к реализации задач контента, то IBL связан со способом решения этих задач. Он направляет внимание студентов к последовательному выполнению цикла запроса, в котором происходит решение поставленных предметных задач с использованием необходимых языковых конструкций.
Таким образом, в ходе эмпирического исследования получены факты, подтверждающие не случайный характер изменений между двумя группами студентов, которые обучались с применением только методики CLIL и с интеграцией методик IBL и CLIL. Выявлены значимые различия между студентами двух анализируемых групп по количеству произнесенных учебных директив на английском языке в ходе проведения уроков химии. Установлено, что будущие учителя естественно-научных дисциплин, обучающиеся с помощью интеграции CLIL и IBL, имели наибольший прирост в числе учебных директив, задали больше вопросов высокого уровня и произнесли больше директивных актов в целом. Они использовали свой опыт обучения с применением IBL для организации исследований в классе. Их речь на уроке была более разнообразной за счет появления нового вида директивных актов – советов и рекомендаций, не характерных для студентов, обучающихся только с использованием CLIL.
Не установлены значимые различия между группами студентов по количеству регулятивных речевых актов. Данный вид директив являлся «компетенцией» CLIL и развивался с помощью этого метода посредством языка для обучения (Language for learning) в экспериментальной и контрольной группах студентов.
Результаты исследования подтверждают сформулированную нами гипотезу о положительном влиянии интеграции методов CLIL и IBL на качество подготовки студентов к преподаванию естественно-научных дисциплин на английском языке, которое отразилось в повышении числа, разнообразия и когнитивного уровня директивных речевых актов будущих педагогов экспериментальной группы. Полученные результаты позволяют продолжить начатое исследование в следующих перспективных направлениях:
-
1) изучение влияния методов преподавания будущих учителей на развитие коммуникативных и когнитивных навыков учеников в условиях полиязычного обучения;
-
2) изучение влияния интеграции IBL и CLIL на отношение будущих учителей к преподаванию предметов естественно-научного цикла на дополнительном (втором или иностранном) языке;
-
3) исследование влияния интеграции IBL и CLIL на подготовку будущих учителей общественно-гуманитарных дисциплин в условиях полиязычия.
Практическую значимость исследования мы видим в использовании интеграции IBL и CLIL для подготовки будущих учителей естественных наук к преподаванию на дополнительном (втором или иностранном) языке в условиях полиязычного образования. Материалы статьи будут актуальными для преподавателей педагогических университетов европейских стран и стран СНГ, которые находятся в поиске эффективных подходов к подготовке будущих полиязычных учителей.
Список литературы Интеграция IBL и CLIL в подготовке будущих учителей к преподаванию естественных наук в условиях полиязычия
- Sirotova A. [Reflection of the Ideas of Social Constructivism within the Framework of the Principle of Sub¬ject-Language Integration]. Nizhegorodskoye obrazovaniye = Nizhny Novgorod Education. 2019; (1):112-118. Available at: https://clck.ru/TYvJj (accessed 09.11.2020). (In Russ.)
- Saif Husam M., Laszlo K. The Role of Constructivism in the Enhancement of Social Studies Education. Journal of Critical Reviews. 2020; 7(7):249-256. (In Eng.) DOI: http://doi.org/10.31838/jcr.07.07.41
- Mieg H.A. Introduction: Inquiry-Based Learning – Initial Assessment. In: Inquiry-Based Learning – Un-dergraduate Research: The German Multidisciplinary Experience. H.A. Mieg (ed.). 2019. p. 1-16. (In Eng.) DOI: http://doi.org/10.1007/9783030142230
- Byrdina O.G., Yurinova E.A., Dolzhenko S.G. Developing Foreign Language Professional-Communica¬tive Competence of Pedagogical University Students by Means of CLIL. The Education and Science Journal. 2020; 22(7):77-100. (In Russ., abstract in Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.17853/1994-5639-2020-7-77-100
- Spronken-Smith R., Angelo T., Matthews H., O’Steen B., Robertson J. How Effective is Inquiry-Based Learning in Linking Teaching and Research? An International Colloquium on International Policies and Prac¬tices for Academic Enquiry. 2007; 7(4):1-7. Available at: https://clck.ru/TUkA9 (accessed 09.11.2020). (In Eng.)
- Kim S.L., Kim D. English Learners’ Science-Literacy Practice through Explicit Writing Instruction in In-vention-Based Learning. International Journal of Educational Research Open. 2021; 2-2:100029. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedro.2020.100029
- Pedaste M., Mäeots M., Siiman L.A., de Jong T., van Riesen S.A.N., Kamp E.T., et al. Phases of Inqui¬ry-Based Learning: Definitions and the Inquiry Cycle. Educational Research Review. 2015; 14:47-61. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2015.02.003
- Bruder R., Prescott A. Research Evidence on the Benefits of IBL. ZDM Mathematics Education. 2013; 45:811-822. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-013-0542-2
- Boukhobza I. Is IBL (Inquiry based learning) Helping Zayed University Students Acquire Scientific Skills in a General Science Course? The Online Journal of Science and Technology. 2015; 5(4):57-63. Available at: https://www.tojsat.net/journals/tojsat/articles/v05i04/v05i04-07.pdf (acesses 22.02.2021). (In Eng.)
- Güler B., Şahin M. Using Inquiry-Based Experiments to Improve Pre-Service Science Teachers’ Scien¬ce Process Skills. International Journal of Progressive Education. 2019; 15(5):1-18. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi. org/10.29329/ijpe.2019.212.1
- Hattie J. Visible Learning: A Synthesis of over 800 Meta-Analyses Relating to Achievement. Taylor & Francis; 2008. 392 p. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203887332
- Santana-Vega L.E., Suárez-Perdomo A., Feliciano-García L. El aprendizaje basado en la investigación en el contexto universitario: una revisión sistemática. Revista Española de Pedagogía. 2020; 78(277):519-538. (In Span) DOI: https://doi.org/10.22550/REP78-3-2020-08
- Romero-Ariza M., Quesada A., Abril A.M., Sorensen P., Oliver M.C. Highly Recommended and Poor¬ly Used: English and Spanish Science Teachers’ Views of Inquiry-based Learning (IBL) and Its Enactment. EURASIA J Math Sci Technol Educ. 2019; 16(1):1-16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/109658
- Eltanahy M., Forawi S. Science Teachers’ and Students’ Perceptions of the Implementation of Inqui¬ry-Based Learning Instruction in a Middle School in Dubai. Journal of Education. 2019; 199(1):13-23. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0022057419835791
- Voet M., De Wever B. Preparing Pre-Service History Teachers for Organizing Inquiry-Based Learning: The Effects of an Introductory Training Program. Teaching and Teacher Education. 2017; 63:206-217. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2016.12.019
- Ketsing J., Inoue N., Buczynski S. Enhancing Pre-service Teachers’ Reflective Quality on Inquiry-based Teaching through a Community of Practice. Science Education International. 2020; 31(4):367-378. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.33828/sei.v31.i4.5
- Pérez Cañado M.L. Innovations and Challenges in CLIL Teacher Training. Theory into Practice. 2018; 57(3):1-10. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00405841.2018.1492238
- Zhorabekova A.N., Sagdullaev I.I. [Mastering by Future Teachers the Methodology of Subject-Language In¬tegration in the Process of Special and Methodological Training]. Zhurnal obshchestvennogo obedineniya uchenykh i pedagogov respubliki Kazakhstan Kazakhskoy akademii obrazovaniya = Journal of the Public Association of Sci¬entists and Teachers of the Republic of Kazakhstan of the Kazakh Academy of Education. 2020; (1):40-45. Avai¬lable at: https://egi.kz/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/KAO-2020-1.pdf#page=40 (accessed 23.01.2021). (In Russ.)
- Banegas D.L., del Pozo Beamud M. Content and Language Integrated Learning: A Duoethnographic Study about CLIL Pre-Service Teacher Education in Argentina and Spain. RELC Journal. 2020. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0033688220930442
- Kordíková B., Brestenská B. Bilingual Science Education: Perceptions of Slovak in-Service and Pre-Service Teachers. International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism. 2020. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/13670050.2020.1718590
- Custodio Espinar M. CLIL Teacher Education in Spain. In: Tsuchiya K., Pérez Murillo M. (eds). Con¬tent and Language Integrated Learning in Spanish and Japanese Contexts. Cham: Springer International Publi¬shing; 2019. p. 313-337. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-27443-6_13
- Cummins J., Swain M. Bilingualism in Education: Aspects of Theory, Research and Practice. Routledge; 2014. 254 p. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315835877
- Hillyard S. First Steps in CLIL: Training the Teachers. Latin American Journal of Content & Language Integrated Learning. 2011; 4(2):1-13. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.5294/laclil.2011.4.2.1
- Irawan Y., Syahrial S., Sofyan D. The Effect of Using Inquiry Based Learning Strategy on Students Speaking Ability (a Case Study at Sman 7 Bengkulu Selatan). JOALL (Journal of Applied Linguistics and Litera¬ture). 2019; 3(2):59-79. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.33369/joall.v3i2.6848
- Meyer O., Coyle D., Halbach A., Schuck K., Ting T. A Pluriliteracies Approach to Content and Lan¬guage Integrated Learning – Mapping Learner Progressions in Knowledge Construction and Meaning-Making. Language, Culture and Curriculum. 2015; 28(1):41-57. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/07908318.2 014.1000924
- Mohan B., Leung C., Slater T. Assessing Language and Content: A Functional Perspective. In: Paran A., Sercu L., ed. Testing the Untestable in Language Education. Bristol, Blue Ridge Summit: Multilingual Matters; 2010. p. 217-240. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.21832/9781847692672-013
- Dalton-Puffer C., Nikula T. Pragmatics of Content-based Instruction: Teacher and Student Directives in Finnish and Austrian Classrooms. Applied Linguistics. 2006; 27(2):241-267. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/applin/aml007
- Dalton-Puffer C. Discourse in Content and Language Integrated Learning (CLIL) Classrooms. Amster-dam: John Benjamins Publishing Company; 2007. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1075/lllt.20
- Faturrochman R.G., Darmawan A.A., Hadi F. Teacher Talk in Scientific Approach in EFL Classroom: A Speech Acts Perspective. SAGA: Journal of English Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics. 2021; 2(1):35-46. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.21460/saga.2020.21.66
- Ermawati, Yunus N., Pammu A. The Implementation of Inquiry-Based Learning to Reading Comprehen-sion of EFL Students. International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR). 2017; 6(3):1067-1071. Available at: https://www.ijsr.net/archive/v6i3/ART20171521.pdf (accessed 28.01.2021). (In Eng.)
- Searle J.R. Speech Acts. An Essay in the Philosophy of Language. 1969. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi. org/10.1017/CBO9781139173438
- Amaral O.M., Garrison L., Klentschy M. Helping English Learners Increase Achievement through Inqui-ry-Based Science Instruction. Bilingual Research Journal. 2002; 26(2):213-219. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/1 0.1080/15235882.2002.10668709
- Fatkhriyah R.Y. Inquiry-Based Learning: An Attempt to Enhance Students Speaking Perfor¬mance. Jurnal Pendidikan. 2019; 4(7):912-922. Available at: http://journal.um.ac.id/index.php/jptpp/article/ download/12633/5849 (accessed 28.12.2020). (In Eng.)
- Nikula T. Effects of CLIL on a Teacher’s Classroom Language Use. In: Language Use and Language Learning in CLIL Classrooms. John Benjamins Amsterdam; 2010. p. 105-124. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi. org/10.1075/aals.7.06nik
- Dafouz E., Núñez Perucha B. Metadiscursive Devices in University Lectures. In: Language Use and Language Learning in CLIL Classrooms. 2010. p. 213-232. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1075/aals.7.11daf
- Haryanto H., Mubarok H. Teacher’s Directive Expressions Analysis in English Teaching Classes. Len¬sa Kaji Kebahasaan, Kesusastraan, dan Budaya. 2018; 8(1):22-42. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.26714/ lensa.8.1.2018.22-42
- Septianingsih T., Warsono W. Language Use and Language Learning. English Education Journal. 2017; 7(1):26-33. Available at: https://journal.unnes.ac.id/sju/index.php/eej/article/view/14682 (accessed 11.02.2021). (In Eng.)
- Hofstein A., Shore R., Kipnis M. Providing High School Chemistry Students with Opportunities to De-velop Learning Skills in an Inquiry-Type Laboratory: A Case Study. International Journal of Science Education. 2004; 26(1):47-62. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/0950069032000070342
- Psycharis S. Inquiry Based-Computational Experiment, Acquisition of Threshold Concepts and Argu-mentation in Science and Mathematics Education. Educational Technology & Society. 2016; 19(3):282-293. Available at: https://www.jstor.org/stable/jeductechsoci.19.3.282?seq=1#metadata_info_tab_contents (accessed 02.02.2021). (In Eng.)
- Madhuri G., Kantamreddi V., Prakash Goteti L. Promoting Higher Order Thinking Skills Using Inqui¬ry-Based Learning. European Journal of Engineering Education. 2012; 37(2):117-123. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi. org/10.1080/03043797.2012.661701
- Kahle J.B., Supovitz J.A., Mayer D.P. Promoting Inquiry-Based Instructional Practice: The Longitu¬dinal Impact of Professional Development in the Context of Systemic Reform. Educational Policy. 2000; 14(3):331-356. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0895904800014003001
- Dalton-Puffer C., Smit U. Content and Language Integrated Learning: A Research Agenda. Language Teaching. 2013; 46(4):545-559. (In Eng.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0261444813000256


