Клинико-рентгенологические варианты поражения легких при инфекции, вызванной Staphylococcus aureus
Автор: Винокуров Антон Сергеевич, Смирнова Александра Дмитриевна, Беленькая Ольга Игоревна, Юдин Андрей Леонидович, Юматова Елена Анатольевна
Журнал: Клиническая практика @clinpractice
Рубрика: Обзоры
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.12, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Несмотря на высокий уровень современных технологий в области лабораторных методов и лучевой визуализации органов дыхания, проблема ранней и точной дифференциальной диагностики воспалительных заболеваний легких остается важной в практической медицине. Решение этой проблемы ведет к улучшению результатов лечения и уменьшению числа таких осложнений, как эмпиема плевры, свищи, медиастинит, сепсис и др., а в ряде случаев позволяет заподозрить наличие первичного гнойного источника в организме, как в случае с септической эмболией легких. В обзоре представлены особенности Staphylococcus aureus как возбудителя легочных заболеваний, современная эпидемиология, патогенез и клинико-лучевая диагностика различного вида воспалительных изменений легких с фокусом на их деструкцию.
Пневмония, абсцесс легких, гангрена легких, staphylococcus aureus, септическая эмболия, кт, деструкции
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143178082
IDR: 143178082 | DOI: 10.17816/clinpract71642
Текст обзорной статьи Клинико-рентгенологические варианты поражения легких при инфекции, вызванной Staphylococcus aureus
Submitted 17.05.2021
Revised 23.06.2021
Published 30.07.2021
Лицензия CC BY-NC-ND 4 /
The article can be used under the CC BY-NC-ND 4 license
КТ ГА
О ВОЗБУДИТЕЛЕ
Staphylococcus aureus (золотистый стафилококк) — грамположительная аэробная бактерия. Среди факторов патогенности S. aureus отмечают как структурные компоненты бактериальной клетки (капсула, белки клеточной стенки), так и выделяемые ими вещества (экзотоксины, экзоферменты) [1–3], в частности:
-
1) факторы адгезии (клампинг-фактор, эластин-связывающие белки, фибронектинсвязываю-щие белки, агглютинирующий фактор А):
-
• клампинг-фактор (clumping factor — фактор слипания ) формирует так называемую псевдокапсулу из белковых структур плазмы крови, что способствует персистенции стафилококков и обусловливает длительное или рецидивирующее течение инфекции;
-
• эластинсвязывающие белки принимают участие в бактериальной колонизации посредством связывания с эластином, присутствующим в тканях легких, кожи и стенках кровеносных сосудов;
-
• фибронектинсвязывающие белки способствуют адгезии стафилококков посредством связывания с фибронектином и могут функционировать как фактор инвазии;
-
• агглютинирующий фактор А является медиатором S. aureus -индуцированной агрегации тромбоцитов и формирования фибриновых тромбов, и в теории может быть предрасполагающим фактором в развитии гангренозных изменений;
-
2) факторы, способствующие распространению стафилококков по тканям организма:
-
• стафилокиназа (стафилококковый фибринолизин) разрушает фибрин, соединяющий клетки организма, что способствует распространению бактерий из первичного очага. Фермент разрушает также фибрин, образуемый стафилококковой коагулазой, в результате чего формируются инфицированные микротромбы, которые гематогенно распространяются по организму и могут обусловливать такое осложнение стафилококковой инфекции, как септическая эмболия;
-
• коагулаза вырабатывается стафилококками в виде профермента, активируемого после контакта с плазмой крови. Комплекс коагу-
- низма, функция которой — защита микробной клетки от фагоцитоза и бактерицидного действия компонентов крови. Данный механизм играет важную роль в персистенции стафилококков;
-
3) факторы, инактивирующие защитные системы организма (факторы с антикомплементарной, антиинтерфероновой, антилизоцимной и другой активностью);
-
4) антифагоцитарные факторы (протеин А, полисахаридная капсула):
-
• протеин А проявляет антифагоцитарную активность посредством связывания Fc-домена IgG, является медиатором прикрепления S. aureus к фактору фон Виллебранда, что способствует адгезии бактериальных клеток и развитию сосудистых инфекций.
Основным токсином, вызывающим дегрануляцию и разрушение лейкоцитов, является лейкоцидин Пантона–Валентайна (Panton–Valentine leukocidin, PVL). PVL построен из двух белковых субъединиц, которые интегрированы в хромосому бактерий. Эпидемиологически PVL ассоциируется с тяжелыми инфекциями кожи и некротической пневмонией. PVL синтезируется преимущественно штаммами вне-больничного метициллинрезистентного золотистого стафилококка (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA) [1–3]. PVL приводит к развитию воспалительных и цитотоксических эффектов нейтрофилов и макрофагов. Нейтрофилы являются клетками, которые формируют первую линию защиты против инвазии S. aureus . Происходит массивная неконтролируемая гибель нейтрофилов с выделением агрессивных ферментов, в том числе и протеаз, которые способны вызывать разрушение чувствительных структур альвеолярной ткани и приводить к инфекционной деструкции легких [3, 4].
ЭПИДЕМИОЛОГИЯ
Инфекционная деструкция легких — это большая группа неспецифических воспалительных полиэтио-логичных процессов, основным морфологическим признаком которых является гнойно-некротическое воспаление ткани легких с образованием распадов. Из этой группы исключены гранулематозные, в том числе специфические (туберкулез, бруцеллез, сифилис и др.) инфекционные заболевания. При них деструктивные изменения в легочной ткани соче- лазы с активатором плазмы крови — ста-филотромбин — формирует вокруг клетки фибриновую псевдокапсулу из белков орга- таются с эпителиоидно-клеточными гранулемами [5, 6]. Гранулематозный процесс при инфицировании S. aureus отсутствует. Но не всякое попадание клиническая: 9П91
тактика
стафилококка вызовет деструктивный процесс — возможно развитие обычной пневмонической инфильтрации или даже бронхита.
В последние годы отмечается увеличение числа больных тяжелыми и осложненными формами течения инфекционной деструкции легких [5]. По данным разных авторов, частота развития осложнений при абсцессах легких колеблется от 30 до 70% [7–9]. Европейское респираторное общество (European Respiratory Society, ERS) оценило эпидемиологические данные нескольких исследований: так, распространенность гнойно-деструктивных заболеваний, вызванных S. aureus , составила до 4% среди всех госпитализированных пациентов и до 19% среди поступивших в отделения реанимации и интенсивной терапии, в том числе 7–29% пришлось на госпитализированных пациентов пожилого возраста [10]. Особенно тяжелое клиническое течение имеют пневмонии, вызванные MRSA: у 75% больных выявляется полисегментарное поражение легких, а 72,5% пациентов проходят лечение в отделениях реанимации и интенсивной терапии. В целом показатели смертности, связанной с гнойно-деструктивными заболеваниями легких, вызванными S. aureus , варьируют от 20 до 75% [10]. По данным А.П. Надеева и соавт. [11], при анализе летальных исходов среди пациентов с внебольничными пневмониями S. aureus как этиологический агент был обнаружен в 12,7% случаев в 2017 г. и в 20% — в 2018 г.
Наиболее высокая летальность наблюдается при внутрибольничной пневмонии, вызванной S. aureus (31,8%) и Klebsiella pneumoniae (35,7%) [12]. Многие из авторов решающую роль в развитии инфекционных деструкций легких отводят неспорообразующей анаэробной флоре, однако есть мнение, что в развитии многих гнойно-деструктивных заболеваний легких участвует полиморфная микрофлора [5, 13]. О.О. Ясногородский с соавт. [14] указывают на микробные ассоциации с преобладанием до 70,8% S. aureus , Escherichia coli и Pseudomonas aeruginosa у больных с инфекционными деструкциями легких.
У пациентов с муковисцидозом сниженный клиренс вязкого секрета дыхательных путей приводит к колонизации и инфекции, вызванной S. aureus , путем формирования биопленок в дыхательных путях. При муковисцидозе у больных довольно часто обнаруживают хроническую инфицированность S. aureus , реже — P. aeruginosa [15].
Во время эпидемии гриппа А(H1N1) стафилококк при внебольничных пневмониях обнаруживали в 15,5% случаев (что уступало только Streptococcus pneumoniae — 32,4%); также было отмечено повышение роли ассоциаций этих бактерий (19,8%) у пациентов с тяжелым течением пневмонии [16], на лидирующие позиции которых указывали зарубежные авторы [17, 18]. В 2011 г. во Франции во время пандемии вируса гриппа A(H1N1) среди 103 пациентов, поступивших в отделения реанимации и интенсивной терапии с подтвержденной инфекцией вируса гриппа A(H1N1), у 48 развилась бактериальная коинфекция (из них 54% с S. pneumoniae, 31% — с S. aureus) [19].
Напротив, во время текущей пандемии, вызванной новым SARS-CoV-2, по данным метаанализа B.J. Langford и соавт. [20], бактериальные коинфекции, в том числе S. aureus , встречаются значительно реже, чем при гриппе. Китайские авторы X. Zhu и соавт. [21] обнаружили в своей группе пациентов коинфекцию COVID-19 и S. aureus в 8,2% случаев (наличие бактерии подтверждено методом полимеразной цепной реакции), что значимо уступало S. pneumoniae (59,5%) и другим патогенам ( Klebsiella , Haemophilus influenzae и др.).
Интересным в отношении патогенеза является факт, что при различных путях проникновения S. aureus в легкие (бронхогенный или гематогенный путь, реже — контактный при травмах), а также при разном состоянии организма (реактивность, имму-нозащитные механизмы, микроциркуляция в легких, сохранность местных механизмов элиминации и иммунной компетентности бронхов и альвеол) и ассоциации с другими микроорганизмами морфологические изменения в легких и, соответственно, лучевая картина будут значительно разниться. В меньшей степени это относится к клиническим проявлениям, которые зачастую схожи. Важным является и факт сочетания определенных факторов патогенности у каждого конкретного штамма бактерии [6, 13].
Патогенез острых гнойных деструкций легких определяется наличием одного или нескольких факторов [22]:
-
• острого инфекционного воспалительного процесса в ткани легких;
-
• нарушения проходимости бронхов;
-
• местного нарушения кровотока с некрозом легочной ткани;
-
• состояния иммунной резистентности организма.
Среди состояний, которые ведут к снижению резистентности организма и развитию стафилококковой инфекции, можно отметить вирус иммунодефицита человека (ВИЧ), вирусные гепатиты, сахарный
КТ ГА
диабет, злоупотребление алкоголем, иммуносупрессии различного генеза, системные заболевания, муковисцидоз, наличие хронических источников инфекции различной локализации (в том числе гнойных заболеваний верхних дыхательных путей, ротоглотки, зубов, лимфатических узлов и т.д.) [23, 24].
Сахарный диабет сам по себе является значимым фактором риска развития пневмонии, особенно инфекции S. aureus. При внебольничных пневмониях у больных сахарным диабетом встречаемость стафилококка достигает 30% против 11% у лиц без сопутствующего диабета [25], что связано в том числе с бессимптомной колонизацией (носительством) S. aureus в носоглотке у таких больных с последующей аспирацией содержимого в легкие [26]. Исследователи, кроме того, указывают на высокий уровень антибиотикорезистентности среди больных сахарным диабетом [8, 12, 27].
Алкоголизм является фактором, который способствует развитию бактериальной пневмонии, вероятно, из-за прямого токсического воздействия на дыхательную и иммунную систему. Этиловый спирт снижает мукоцилиарный клиренс, ухудшает альвеолярный и клеточный иммунитет, нарушает функцию альвеолярных макрофагов и нейтрофилов [28]. В результате исследования, проведенного с участием 137 496 больных пневмонией в возрасте от 18 лет и старше, госпитализированных в 177 больниц США в период с 27 октября 2017 г. по 20 августа 2018 г., было выявлено, что в 65% случаев у пациентов, злоупотребляющих алкоголем, пневмония, вызванная MRSA, протекала тяжелее [9]. Кроме непосредственного воздействия спирта на иммунную и иные системы организма, у людей с алкогольной зависимостью существуют и банальные проблемы, которые приводят к большей подверженности инфекционным заболеваниям легких — плохие жилищные условия, питание с малым содержанием протеина, частые переохлаждения, эпизоды аспирации желудочного содержимого в состоянии опьянения [29].
Ежегодная заболеваемость бактериальной пневмонией у пациентов с ВИЧ колеблется от 5,5 до 29%. При уровне CD4+-лимфоцитов более 200/мл частыми этиологическими агентами пневмоний являются S. pneumoniaе и S. aureus [4, 30]. Но бактериальная пневмония может развиться на любой стадии ВИЧ-инфекции и чаще встречается у лиц с развитой иммуносупрессией. По данным И.Б. Викторовой и соавт. [31], S. aureus как агент септической пневмонии встречается у лиц с ВИЧ-инфекцией в 16,8% случаев, уступая лишь внебольничным пневмониям с иными возбудителями (38,4%) и туберкулезу легких (27%).
КЛИНИЧЕСКАЯ КАРТИНА, ДИАГНОСТИКА
Почти любая пневмония, вызванная S. aureus , независимо от формы имеет острое начало с выраженным синдромом интоксикации и подъемом температуры выше 38°С (у 87% пациентов). У всех заболевших с первых дней отмечаются слабость и сухой кашель, который затем переходит в продуктивный (объем и характер мокроты будет зависеть от формы изменений) [32]. Одышка присоединяется чаще у больных с обширным деструктивным процессом в легких. При некоторых формах могут возникать неприятные опущения в грудной клетке, боли плеврального типа [33].
Почти у 50% больных насыщение гемоглобина кислородом в артериальной крови (SaО2) снижается менее 92% и наблюдаются нарушения общей гемодинамики. Осложнения в виде сепсиса, отека легких или мозга, гнойного менингита диагностируются в 60,5% случаев. Более того, MRSA связан с повышенной вероятностью эндокардита и повышенным риском летального исхода в сравнении с другими штаммами S. aureus [34].
В целом каждая из форм рассматриваемого варианта поражения легких будет иметь типичные общие и респираторные симптомы, которые встречаются почти при любой легочной инфекции.
Важная роль в диагностике и лечении инфекционной деструкции легких принадлежит лабораторной, особенно микробиологической диагностике, позволяющей провести этиологическую верификацию возбудителя/возбудителей, оценить их чувствительность к антибактериальным препаратам. При большинстве видов стафилококкового поражения сложностей с получением материала не возникает из-за продукции больными различного вида мокроты [35]. Меньшая информативность свойственна очаговым легочным процессам. В случае гематогенного распространения стафилококка целесообразен посев гемокультуры [36].
Лучевая диагностика является непременной частью современного обследования больных с подозрением на инфекционную деструкцию легких на всех стадиях процесса, поскольку помогает определить вид и объем поражения легких, диагностировать осложнения, оценить эффективность терапии, к тому же является важным этапом в принятии решения о необходимости хирургического лечения. В то же время любые виды поражения легких неспе-
<линическая 2021 п эакти keu Том 12 №3
цифичны лишь для конкретного возбудителя, поэтому окончательное слово в этиологической верификации ставит лабораторная диагностика.
В представленном литературном обзоре, посвященном заболеваниям органов дыхания, вызванным S. aureus , рассматриваются следующие варианты поражения:
-
• очаговая пневмония/бронхиолит;
-
• деструктивная пневмония;
-
• септическая эмболия;
-
• абсцесс легкого (острый и хронический);
-
• гангренозный абсцесс;
-
• гангрена легкого.
Очаговая пневмония (бронхопневмония), бронхиолит являются «малыми формами» инфекционного поражения легких, которые возникают при аэрогенном попадании возбудителя в бронхи с последующим формированием небольших воспалительных очагов, которые расположены вокруг мелких дыхательных путей (пневмония) или же непосредственно в просветах мелких бронхов (бронхиолит). Нельзя сказать, что бронхопневмония/ бронхиолит являются распространенным видом поражения легких при S. aureus -инфицировании, но все же данные случаи описаны [37]. Подобные малые изменения при пневмонии чаще ассоциированы с пневмококком. Очаги пневмонии можно наблюдать и в самом начальном периоде поражения легких, а в дальнейшем происходит увеличение и слияние таких бронхопневмонических очагов с формированием уже более крупного инфильтрата. Подтвердить именно стафилококковую природу очаговой пневмонии даже микробиологически удается далеко не всегда, поэтому подбор терапии происходит эмпирически. Заподозрить возбудителя, отличного от пневмококка, может отсутствие клинической/лучевой динамики на фоне приема антибактериальных препаратов первой линии.
По данным компьютерной томографии (КТ) у пациентов с очаговой пневмонией обнаруживают небольшие перибронхиальные очаги, обычно солидного типа или с нечеткими контурами за счет ободка «матового стекла», при бронхиолите — мелкие очажки в виде симптома «дерева с набухшими почками», при этом прилежащие стенки бронхов могут быть утолщены и уплотнены за счет воспалительного процесса. Возможно слияние очагов, которое не принимает характера обширной инфильтрации. При пневмонии контуры очагов менее четкие из-за преобладания экссудативного воспалительного компонента, что отличает ее от бронхиолита [38].
Важным симптомом бронхогенного процесса можно рассматривать наличие патологического содержимого в просвете бронхов, что представлено слизистым или гнойным содержимым (рис. 1). На традиционных рентгенограммах изменения из-за малого размера могут быть вовсе не заметны или представлять собой мелкие очаги/ограниченную диссеминацию; отмечается локальное усиление/ обогащение легочного рисунка, преобладающее в какой-то одной доли легкого.
Клиническая картина очаговых изменений при S. aureus может отличаться от таковой при других рассматриваемых нами формах: симптомы обычно более «мягкие», продукция мокроты не так выражена, на первый план выходят общие проявления и явления интоксикации.
Деструктивная, или некротизирующая, пневмония представляет собой инфильтрацию легочной ткани с формированием распадов и некрозом паренхимы. Патогенез некротизирующей пневмонии связан с продукцией описанных ранее токси-
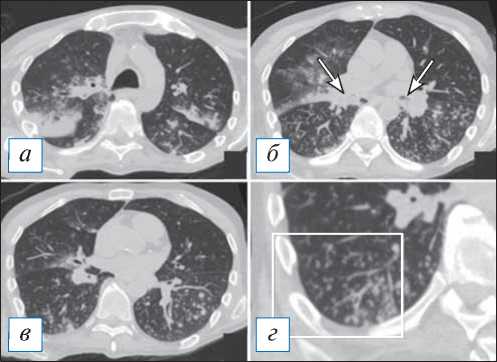
Рис. 1. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки в аксиальной проекции ( а–г ). Двусторонняя сливная бронхопневмония и бронхиолит у пациента с наличием в мокроте S. pneumoniae и S. aureus в значимых титрах. С обеих сторон, больше в нижних долях, на фоне обтурации просветов крупных бронхов патологическим содержимым (стрелки) имеются перибронхиальные разнокалиберные очаги, в том числе по типу симптома «дерева с набухшими почками» (рамка). В верхних отделах данные очаги сливаются в инфильтраты. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 1. Chest CT, axial projection ( а–г ). Bilateral bronchopneumonia and bronchiolitis (with the etiology of S. pneumoniae and S. aureus confirmed by a sputum test). On both sides, more in the lower lobes against the background of bronchial sputum obturation (arrows), there are peribronchial nodules of various sizes, including a “tree in bud” sign (frame). In the upper lungs areas the nodules formed infiltrates. [Images from the authors’ archive].
КТ ГА
нов, выделяемых золотистым стафилококком, которые приводят к поражению сосудистой стенки и венозным тромбозам [39].
Обычно деструктивная пневмония вызывается S. aureus , способным к продукции PVL. Деструктивная, или некротизирующая, пневмония, ассоциированная с PVL, значимо выделяется среди других пневмоний. PVL-негативные штаммы служат возбудителями «классической» пневмонии, которая характеризуется медленным развитием, отмечается у пациентов старшего возраста (>60 лет), часто протекает на фоне хронических заболеваний, сопровождается меньшим уровнем летальности [9, 39].
Отмечено, что вирусная инфекция усиливает адгезию бактерий к респираторным клеткам. Кроме того, вирус способствует усиленной продукции Т-клетками интерферона-γ, который ухудшает устойчивость организма к бактериальной инфекции из-за снижения активности натуральных киллеров и альвеолярных макрофагов. В случае поражения легких вирусом гриппа происходит интенсивная стимуляция образования цитокинов, что приводит к дисрегуляции и неконтролируемому их выделению («цитокиновому шторму»). Некоторые штаммы S. aureus способны выделять протеазы, высвобождающие и активирующие вирусный гемагглюти- более обширных участков; в начале этого процесса в полостях распада можно наблюдать некоторое количество содержимого с горизонтальным уровнем; секвестры нехарактерны (рис. 2). Внутренняя стенка полостей имеет четкий контур, что объясняется дренированием содержимого через бронхи, которые в ряде случаев прослеживаются (рис. 3). Может отмечаться выраженная реакция плевры, с развитием выпота или даже эмпиемы и пиопнев-моторакса, особенно при формировании свища [8, 9, 40]. Негативными последствиями некротизирующей пневмонии может являться формирование фиброза с бронхоэктазами, персистирование полостей распада при отсутствии их спадения, а также облитерация плевральной полости на уровне воспалительного процесса [39].
Септическая эмболия — вторичный инфекционный легочный процесс, при котором инфицированный тромб (эмбол), содержащий микроорганизмы из очагов внелегочной инфекции (инфекционный эндокардит, абсцессы брюшной полости и забрюшинного пространства, паратонзиллярные абсцессы, инфекции кожи, остеомиелит и др.) [41, 42], проникает в системный кровоток и вызывает обтурацию в микроциркуляторном русле легких с последующим развитием инфарктов и их инфицировани- нин; усиливают репликацию, вирулентность и патогенность вирусов. При массивной инфильтрации легких иммунными клетками и суперинфекции PVL-продуцирующими S. aureus лизис иммунных клеток может рассматриваться в качестве причины обширных некрозов [39, 40].
Наиболее типичной для деструктивной пневмонии является следующая клиническая картина: заболевание первоначально напоминает грипп; общими симптомами являются персистирующая лихорадка (>39°C), тахикардия, тахипноэ, выделение обильного количества гнойной мокроты, кровохарканье, а также снижение оксигенации артериальной крови. PVL-положительная деструктивная пневмония может стать причиной возникновения тромбоцитопенической пурпуры [39, 40].
При проведении КТ органов грудной клетки отмечается уплотнение, чаще в виде консолидации или по смешанному типу, в сочетании с «матовым стеклом» пораженной части легкого, которая может быть несколько увеличена в размерах (рис. 2, Б), что объясняется скоплением экссудата и отеком легочной паренхимы по типу «выбухающей борозды». На фоне уплотнения быстро происходит деструкция легочной ткани в виде множественных очагов или
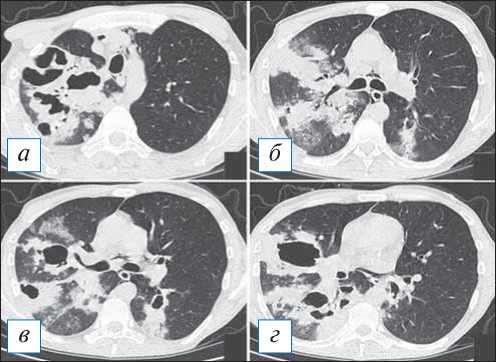
Рис. 2. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки в аксиальной проекции ( а–г ). Двусторонняя по-лисегментарная пневмония. С обеих сторон в легких, больше справа, имеются инфильтраты, на фоне которых просматриваются полости различного размера без жидкостного содержимого. Незначительный пневмомедиа-стинум. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 2. Chest CT, axial projection ( а–г ). Bilateral polysegmen-tal pneumonia. On both sides in the lungs, more to the right, there are infiltrates and cavities of various sizes without liquid content. Minor pneumomediastinum. [Images from the authors’ archive].
<линическая 2021 п эакти keu Том 12 №3
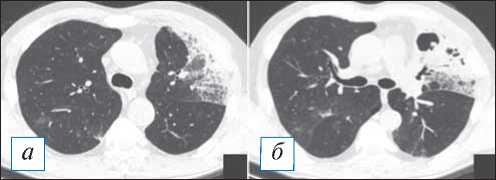
Рис. 3. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки в аксиальной проекции ( а, б ). Пневмоническая инфильтрация в верхней доле слева с деструкциями. Имеются участки по типу «шальной исчерченности» в сочетании с консолидацией, на фоне которой обнаруживаются разнокалиберные полости распада без содержимого, наружный их контур не прослеживается. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 3. Chest CT, axial projection ( а, б ). Pneumonic infiltration in the upper lobe on the left with destructions. There are areas of a «crazy paving» sign in combination with consolidation, against the background of which one can see destructive cavities of various sizes without content, their outer contour is not traced. [Images from the authors’ archive].
ем. Септическая эмболия ассоциируется с высоким уровнем смертности и остается диагностической проблемой в клинической практике из-за неспецифических клинических проявлений и опасных для жизни осложнений, таких как массивная тромбоэмболия легочных артерий, абсцесс легкого, эмпиема, аневризмы легочных артерий [43, 44]. S. aureus — один из наиболее частых патогенов, вызывающих септическую эмболию. За счет вышеописанных свойств патогенности формируется сильная местная неспецифическая воспалительная реакция с дисфункцией эндотелия цитотоксинами, а также запускается прямое изменение реологических свойств крови в виде гиперкоагуляции и формирования тромбов за счет продукции коагулазы [45].
Патогенез септической эмболии состоит из следующих этапов:
-
• формирование инфицированных тромбов в месте первичного гнойного очага;
-
• отрыв и миграция эмболов с микроорганизмами по венозному руслу в правые отделы сердца и попадание в мелкие ветви легочной артерии;
-
• обтурация сосуда в месте эмболии и возникновение инфаркта легкого;
-
• инфильтрация стенок сосуда и переход воспаления на легочную ткань с образованием очага или инфильтрата различных размеров и последующим распадом (абсцедирование) из-за действия бактериальных токсинов и регионарных дефектов гемоциркуляции;
-
• сообщение полости абсцесса через бронхи/ бронхиолы в связи с расплавлением их стенки и возможность дренирования гнойного содержимого.
Клинические проявления септической эмболии: начало заболевания чаще острое; возникают кашель, боли в грудной клетке, отхождение гнойной мокроты. Одышка и кровохарканье могут быть проявлением самих инфильтративных изменений, следствием деструкции эмболических очагов, а также признаком тромбоэмболии достаточно крупных ветвей легочной артерии с формированием инфарктов легкого. Практически у всех больных имеется высокая лихорадка с ознобом (38°С и выше) [5, 9]. Для поиска «материнского» очага инфекции используют инструментальные исследования: например, эхокардиографию, если предполагается инфекционный эндокардит, реже — позитронно-эмиссионную томографию, совмещенную с КТ [46]. Ультразвуковые методы, КТ и магнитно-резонансную томографию применяют при поиске гнойных скоплений в брюшной полости и забрюшинном пространстве (в том числе абсцессы паренхиматозных органов), инфильтратов в мягких тканях, костях и головном мозге. Важным этапом диагностики при подозрении на септическую эмболию любой этиологии является также посев крови [47], что при остальных формах стафилококковой инвазии применяется редко.
Чувствительность традиционной рентгенографии при септической эмболии невысока — 22–40% [48, 49]. На снимках обнаруживают сочетание синдромов — очаги и круглые тени, кольцевидные тени и усиление легочного рисунка с двух сторон.
Септическая эмболия по данным КТ наиболее часто представлена округлыми очагами различной плотности и размера (от милиарных до крупных, 12– 15 мм), которые располагаются с двух сторон, преимущественно в периферических зонах легких или перибронховаскулярно, где и происходит обтурация сосудов малого калибра эмболами. Очаги гематогенного типа (не имеют четкой связи со структурами интерстиция, часть очагов можно наблюдать вдоль висцеральной плевры) [27] (рис. 4). Поражение одного легкого практически не наблюдается [43].
В то же время наряду с очагами в легких появляются участки инфильтрации с четкими контурами (по типу консолидации), различных размеров, также преимущественно в периферической зоне. В ряде случаев эти участки могут быть окружены

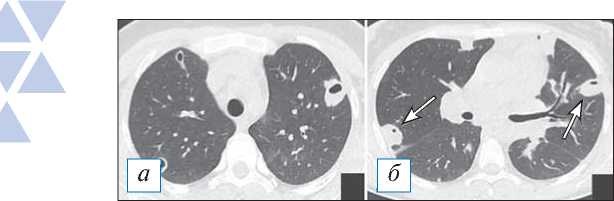
Рис. 4. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки в аксиальной проекции ( а, б ). Септическая эмболия легких у пациентки с инфекционным эндокардитом трикуспидального клапана. В картине поражения легких преобладают как уже сформированные округлые полости, так и формирующиеся из субплевральных уплотнений с четкими контурами (стрелки). [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 4. Chest CT, axial projection ( а, б ). Septic embolism in a patient with infectious endocarditis of the tricuspid valve. In the picture of the lung damage, one can see predominance of both completely formed rounded cavities and those formed from subpleural opacities with clear contours (arrows). [Images from the authors’ archive].
зоной «матового стекла» (симптом «венца», «halo» sign) или по типу «обратного венца» («reversed halo» sign) — зоны «матового стекла», окруженной по периферии полоской консолидацией различной толщины [50]. Данные КТ-симптомы главным образом представляют сформированные участки инфарктов легкого в сочетании с воспалительной инфильтрацией (рис. 5).
По ходу течения инфекционного процесса начинается преобразование очагов и инфильтратов с образованием в них участков распада, гнойные массы из очагов и полостей дренируются через бронхи и бронхиолы, оставляя на своем месте тонкостенные полости. Полости распада при септической эмболии чаще имеют правильную округлую, как бы штампованную форму и преимущественное периферическое расположение. В полостях можно наблюдать перегородки, наличие небольшого количества жидкости [43]. Важный дифференциальный признак септической эмболии — быстрое течение с отрицательной динамикой и преобразование очагов и уплотнений в характерные полости.
Абсцесс легких — гнойное расплавление легочной ткани, чаще всего в пределах одного сегмента с формированием одной или нескольких полостей, заполненных гноем и окруженных областью перифокальной воспалительной инфильтрации легочной ткани [51], при этом от интактных участков легкого гнойная полость отграничена капсулой. Обычно абсцесс развивается на фоне предшествующего пневмонического инфильтрата (пневмонио- генный абсцесс; пневмонии осложняются абсцессом в 2–5% случаев) [52], однако данную стадию развития не всегда удается зафиксировать методами лучевой диагностики, и часто больной попадает в лечебное учреждение уже с «классической» картиной абсцесса.
Основной механизм развития острых абсцессов — аспирационный. Предрасполагающими факторами к аспирации являются нарушение сознания из-за употребления алкоголя, употребление наркотиков, дисфагия (в результате заболевания верхних отделов пищеварительного тракта или нервной системы). Для начала формирования абсцесса необходима как аспирация инфицированного материала, так и фиксация его в воздушных путях в условиях снижения или отсутствия их очистительной функции и кашлевых движений, являющихся важным защитным механизмом. Стойкое нарушение бронхиальной проходимости приводит к ателектазу, в зоне которого создаются благоприятные условия для развития воспаления, некроза и последующего гнойного расплавления участка легкого, поэтому острые абсцессы нередко форми-
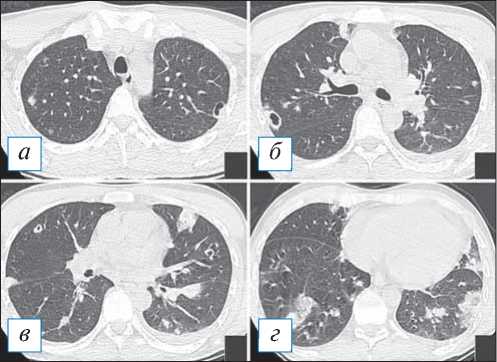
Рис. 5. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки в аксиальной проекции ( а–г ). Септическая эмболия легких у пациента с инфекционным эндокардитом. В обоих легких с преобладанием в периферических отделах определяются очаги, небольшие полости, а также уплотнения смешанного типа (консолидация в сочетании с «матовым стеклом»), отображающие участки инфарктов. Малый плевральный выпот слева. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 5. Chest CT, axial projection ( а–г ). Septic embolism in a patient with infectious endocarditis. In both lungs, with a predominance in the peripheral parts, foci, small cavities, as well as opacities of a mixed type (consolidation in combination with «ground glass») are determined, reflecting the areas of infarcts. Minor pleural effusion on the left. [Images from the authors’ archive].
клиническая: 9П91 Том 122 №13
руются на фоне хронических заболеваний органов дыхания (бронхиальная астма, бронхит, эмфизема), системных заболеваний (пороки сердца, болезни крови, сахарный диабет), а также у пожилых больных [5, 51, 53]. Отдельно выделяют группу абсцессов, возникающих на фоне проникающих травматических повреждений грудной стенки [54].
В 60% случаев поражено правое и в 34% — левое легкое; в 6% определяется билатеральный процесс. Б о льшая частота поражения правого легкого связана с особенностями строения бронхиального дерева: широкий правый главный бронх является как бы продолжением трахеи, что обусловливает более частое попадание инфицированного материала в правое легкое [51, 53]. По данным современных авторов, острые абсцессы занимают существенное место среди легочных деструкций — от 40,1 до 81,1% [14, 55].
Клинически заболевание начинается обычно внезапно, состояние больного сразу становится тяжелым: возникают озноб, повышение температуры тела до 38–39°С, недомогание, тупые боли в грудной клетке, тахикардия и тахипноэ, гиперемия кожных покровов лица. Может появиться сухой, реже продуктивный кашель. В анализах крови характерны нейтрофильный лейкоцитоз, сдвиг лейкоцитарной формулы влево, увеличение скорости оседания эритроцитов и С-реактивно-го белка. Появление неприятного характерного запаха изо рта при дыхании больного — важный ранний симптом формирования острого абсцесса [56]. Сформировавшийся, но не дренирующийся абсцесс в легком проявляется признаками интоксикации: нарастающей слабостью, потливостью, появлением и нарастанием анемии, сохранением лейкоцитоза, тахикардией, высокой температурой. При вовлечении в воспалительный процесс плевры усиливаются болевые ощущения при глубоком дыхании. В типичных случаях первая фаза гнойно-некротического расплавления легкого продолжается до 6–8 дней, затем происходит прорыв в бронхи [51], сопровождающийся выделением гнойной гнилостной мокроты с примесью крови. После того как абсцесс начинает опорожняться через дренирующий бронх, состояние больного улучшается: снижаются температура тела, лейкоцитоз; восстанавливается аппетит [51]. Уменьшение количества мокроты с одновременным повышением температуры тела и признаками интоксикации свидетельствуют об ухудшении бронхиального дренирования, образовании се- квестров и скоплении гнойного содержимого в полости распада легкого.
Диагностика острого абсцесса легкого по данным рентгенографии после его частичного опорожнения не представляет сложности: это кольцевидная тень с уровнем жидкости, контуры «кольца», обычно достаточно четкие (рис. 6). При рентгеноскопии или повороте тела можно наблюдать и изменение уровня жидкости в абсцессе (рис. 7). Сложнее с диагностикой абсцесса при его формировании, когда затенение не имеет типичных черт и может быть неправильной формы: оно представлено чаще круглой тенью или отграниченным затенением, центральные отделы которого могут быть несколько неоднородными, однако этот признак очень непостоянный.
При КТ во время формирования абсцесса выявляют участок уплотнения легочной ткани без четких контуров. В дальнейшем за счет формирования капсулы и рассасывания перикавитарной инфильтрации контуры абсцесса становятся более четкими. Некротический инфильтрат имеет мягкотканную плотность, однородную структуру, просветы бронхов в нем не видны, при этом просвет соответствующего долевого бронха не изменяется. Часто можно увидеть типичный обрыв сегментарных бронхов или их ветвей внутри гнойного инфильтрата. Форма абсцесса при небольших его
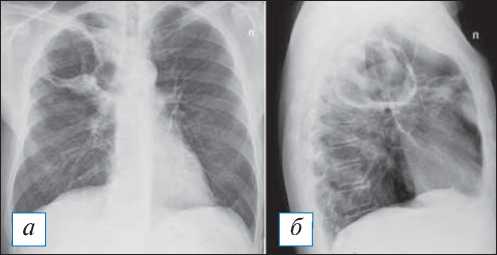
Рис. 6. Рентгенография органов грудной клетки в прямой и правой боковой проекциях. Острый абсцесс в верхней доле правого легкого. В верхней доле справа имеется кольцевидная тень с небольшим горизонтальным уровнем жидкости, что свидетельствует о почти полном дренаже абсцесса. В S3 рядом с полостью — неоднородное затенение и сгущение легочного рисунка. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 6. Chest X-ray. Acute abscess in the upper lobe of the right lung. In the upper lobe on the right there is a ring-shaped shadow with a small horizontal level of fluid, which indicates almost complete drainage of the abscess. In S3, next to the cavity, there is a non — uniform shading and thickening of the pulmonary pattern. [Images from the authors’ archive].



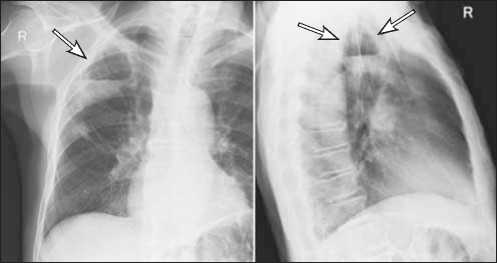
Рис. 7. Рентгенография органов грудной клетки в прямой и правой боковой проекциях. Острый абсцесс в верхней доле правого легкого. Полость в верхней доле справа на 1/3 заполнена жидкостью с горизонтальным уровнем, который соответствует положению пациента во время снимка (стрелки). [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 7. Chest X-ray. Acute abscess in the upper lobe of the right lung. The cavity in the upper lobe on the right is filled with liquid by 1/3 with a horizontal level that corresponds to the position of the patient during the image acquisition (arrows). [Images from the authors’ archive].
размерах округлая или овальная. В случае расположения абсцесса над междолевой плеврой
ферии может выявляться полоса окружающей инфильтрации, в которой обычно видны просветы мелких бронхов. После внутривенного введения контрастного препарата плотность центральной зоны некроза не изменяется (остается гиподенс-ной), а плотность окружающей ткани, представленной пневмоническим инфильтратом и ателектази-рованной тканью легкого, повышается на 10–30 HU (см. рис. 8) [5, 53]. Эта разница в плотности иногда бывает видна и при нативном сканировании, что является важным дифференциальным моментом, который позволяет судить о формировании абсцесса еще до его дренирования в бронхиальную систему и появления там газа.
После частичного дренирования гноя из полости абсцесса формируется хорошо известная лучевая картина — полость с горизонтальным уровнем жидкости, толщина стенок которой зависит от стадии процесса (рис. 9, 10). После начала отхождения гноя через бронхи их стенки рядом с абсцессом могут быть утолщены (как проявление бронхита). При полной санации острого абсцесса возможно определяется симптом ее «провисания» в зоне наибольших некротических изменений (рис. 8, б). Возможно наличие реактивного плеврального выпота.
Нередко в зоне некроза и гнойного расплавления видны мелкие пузырьки воздуха. По пери- постепенное уменьшение в размерах и полное спадение стенок полости в дальнейшем под действием эластических сил легкого с формированием рубцово-фиброзных изменений.
В ряде случаев абсцесс легкого прорывается в плевральную полость (эмпиема) с формирова-
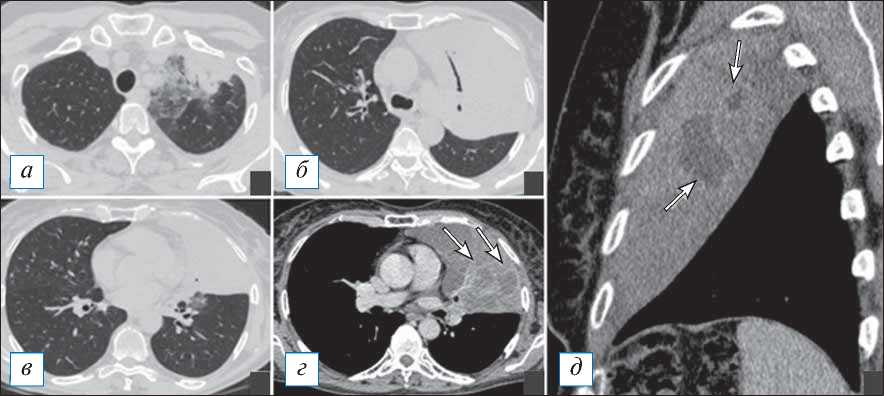
Рис. 8. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки в аксиальной ( а–г ) и сагиттальной проекциях ( д ). Формирующиеся абсцессы в обширном инфильтрате верхней доли левого легкого. После внутривенного контрастирования имеются участки пониженной плотности (стрелки), представляющие собой гнойные отграниченные фокусы, которые в дальнейшем с большой вероятностью превратятся в абсцессы. По границе данных фокусов контрастирование несколько усилено, что может говорить о формировании пиогенной мембраны. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 8. Axial ( а–г ) and sagittal ( д ) chest CT images. Forming abscesses in the extensive infiltrate of the upper lobe of the left lung. After an intravenous contrast enhancement, there are areas of reduced density (arrows), which correspond to purulent delimited foci, likely to turn into abscesses. Along the border of these areas, the contrast is somewhat enhanced, which may indicate the formation of a pyogenic membrane. [Images from the authors’ archive].
<линическая 2021 п эакти keu Том 12 №3
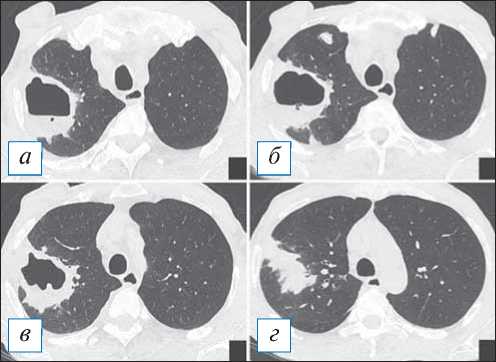
Рис. 9. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки в аксиальной проекции ( а–г ). Типичная картина острого абсцесса. В верхней доле справа имеется полость с содержимым, при этом наружная и внутренняя стенка полости с достаточно четкими контурами, пери-кавитарная инфильтрация выражена слабо. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 9. Chest CT, axial projection ( а–г ). A typical picture of an acute abscess. In the upper lobe on the right there is a filled cavity the outer and inner wall of the cavity having fairly clear contours, pericavitic infiltration is poorly expressed. [Images from the authors’ archive].
нием достаточно крупного соустья и представлен единым пространством (рис. 11, 12).
Причины, способствующие формированию хронического абсцесса (встречается в торакальных отделениях в 18% случаев) [14], — слабое дренирование гнойной полости в легком через бронхи, наличие секвестров в полости, отсутствие терапии или неадекватное лечение (короткий курс антибиотикотерапии, монотерапия, нечувствительность микроорганизма) и различная сочетанная патология. Одной из анатомических предпосылок хронизации абсцесса может быть его расположение в нижних отделах легких, что связано со слабым естественным бронхиальным дренажом этих областей.
Не всегда хронический абсцесс является прямым переходом из острого абсцесса без клинического улучшения, хотя такой сценарий возможен. Встречаются варианты постепенной хронизации процесса на фоне повторных пневмонических инфильтратов в тех же долях легких, а также активация ранее перенесенного острого процесса при его неполном обратном развитии во время эпизодов иммуносупрессии (в том числе сезонных вирусных заболеваний) через некоторое время после клинического выздоровления [54]. Профилактика хронического абсцесса заключается в своевременном и адекватном лечении острой бактериальной деструкции легких в условиях специализированных стационаров, а также в квалифицированном наблюдении и лечении пациентов с «сухими» остаточными полостями в легких в условиях терапевтического стационара [5, 7, 10, 13].
Наиболее часто хронические абсцессы развиваются в задних сегментах легких. Основной морфологический признак хронического абсцесса легкого — формирование соединительнотканной капсулы к концу 6–8-й недели от начала болезни. Пиогенная капсула утолщается за счет разрастающейся соединительной ткани, становится ригидной и уже не способна к самостоятельному спадению под действием эластических сил легких. Вокруг полости деструкции легочная ткань также уплотняется. На внутреннюю стенку полости постепенно распространяется эпителий дренирующего бронха, который в ряде случаев подвергается плоскоклеточной метаплазии [57]. Усиление процессов
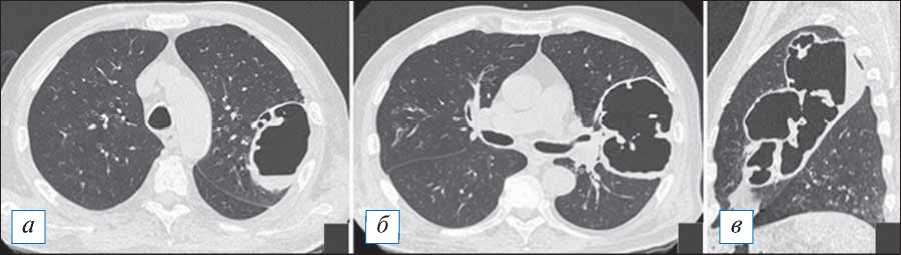
Рис. 10. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки в аксиальной ( а, б ) и сагиттальной ( в ) проекциях. Многокамерный «лестничный» острый абсцесс в верхней доле левого легкого. В абсцессе имеется незначительное количество содержимого, инфильтрация вокруг полости отсутствует. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 10. Axial ( а, б ) and sagittal ( в ) chest CT images. Multi-chamber «ladder» acute abscess in the upper lobe of the left lung. There is a small amount of fluid in the abscess, and there is no infiltration around the cavity. [Images from the authors’ archive].
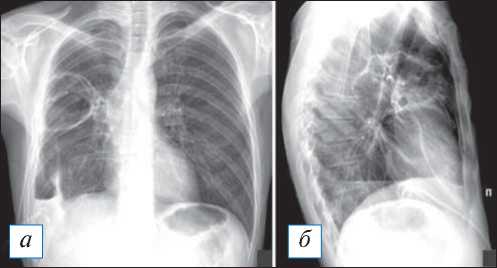
Рис. 11. Рентгенография органов грудной клетки в прямой и правой боковой проекциях. Абсцесс в верхней доле правого легкого, сообщающийся с плевральной полостью справа с формированием единого пространства (подтверждено данными компьютерной томографии). Как в полости абсцесса, так и в полости эмпиемы имеются дренажи. В плевральной полости — некоторое количество жидкости. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 11. Chest X-ray. Abscess in the upper lobe of the right lung, communicating with the pleural cavity on the right with the formation of a single combined space (confirmed by CT). There are drains both in the cavity of the abscess and in the cavity of the empyema. In the pleural cavity — a certain amount of fluid. [Images from the authors’ archive].
пневмосклероза приводит к нарушению трофики легочной ткани, что ухудшает течение заболевания, способствует волнообразному воспалительному процессу, который, в свою очередь, является причиной развития и распространения деструктивных изменений.
Клинические проявления связаны с фазой течения хронического абсцесса — ремиссией или обострением. Во время ремиссии проявления заболевания выражены слабо. Пациенты могут жаловаться на кашель с умеренным количеством слизисто-гнойной вязкой мокроты, сохраняющуюся слабость, потливость и похудание. Постепенно из-за фиброзного процесса и уменьшения объема легкого на стороне поражения могут сужаться межреберные промежутки, деформироваться грудная клетка. При длительном течении заболевания и частых обострениях развивается гипопротеинемия, появляются признаки хронической гипоксии и интоксикации (утолщение ногтевых фаланг в виде «барабанных палочек», ногти в виде «часовых стекол»).
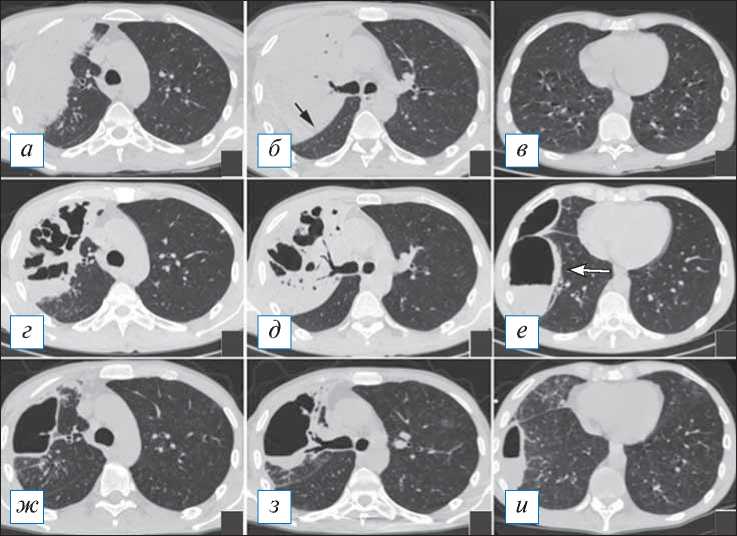
Рис. 12. Тот же пациент. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки пациента (см. рис. 11) в аксиальной проекции от 14.12.2020 ( а–в ), 23.12.2020 ( г–е ) и 18.01.2021 ( ж–и ) на соответствующих уровнях. Характерное течение стафилококковой пневмонии. На фоне массивного инфильтрата в верхней доле справа (с «провисанием» плевры; стрелка) образовались множественные деструкции, которые в дальнейшем объединились в единую полость абсцесса, также осложненную эмпиемой плевры (головка стрелки). [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 12. The same patient one presented in Fig. 11. Chest CT, axial projection from 14.12.2020 ( а–в ), 23.12.2020 ( г– е ) and 18.01.2021 ( ж–и ) at the corresponding levels. A typical course of staphylococcal pneumonia. Against the background of a massive infiltrate in the upper lobe on the right (with «sagging» of the pleura; arrow), multiple destructions were formed, which later merged into a single abscess cavity, also complicated by pleural empyema (arrow head). [Images from the authors’ archive].
<линическая 2021 п эакти keu Том 12 №3
Обострение может быть спровоцировано любой бактериальной и вирусной инфекцией. У больных поднимается температура тела, усиливается кашель, появляются одышка, боли в груди, увеличивается количество мокроты, которая приобретает неприятный запах. Нередко присоединяется кровохарканье.
По данным лучевых методов исследования, хронический абсцесс представляет собой полость с толстой неровной стенкой, которая, в отличие от острого абсцесса, часто имеет неправильную форму (рис. 13). Жидкостное содержимое в полости наблюдается, как правило, только во время обострений.
По ряду причин не всегда удается проследить развитие абсцесса анамнестически и установить истинное время его существования. Отличить острый абсцесс от обострения хронического абсцесса поможет состояние окружающей ткани вокруг полости, где формируются тяжи, деформируется интерстиций, появляются бронхоэктазы и эмфизематозные изменения, а плевра локально может утолщаться. Сама доля, где располагается абсцесс, постепенно уменьшается в объеме, фиброзные тяжи подтягивают сосудистый пучок ворот легкого в свою сторону. С течением времени возможна грибковая колонизация хронического абсцесса (появление в полости грибкового тела), что характерно для любой длительно существующей полости в легком.
В качестве осложнения хронического абсцесса рассматривают возникновение легочных крово-
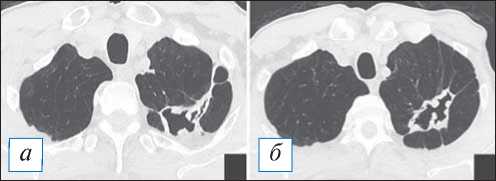
Рис. 13. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки в аксиальной проекции ( а, б ). Хронический абсцесс верхней доли левого легкого вне обострения. Имеется полость неправильной формы с четкими наружными и внутренними краями, при этом внутренний контур бухтообразный. Содержимое в полости отсутствует, вокруг легочная ткань деформирована тяжами и фиброзными участками. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 13. Chest CT, axial projection ( а, б ). Chronic abscess of the upper lobe of the left lung in the period without exacerbation. There is an irregular cavity with clear outer and inner edges, the inner contour is bay-shaped. The contents in the cavity are absent, the lung tissue around it is deformed by strands and fibrous areas. [Images from the authors’ archive].
течений, появление новых абсцессов как на стороне поражения, так и в противоположном легком, реже эмпиему плевры [54].
При неоднократных обострениях абсцесса, отсутствии положительной динамики в отношении размеров полости, при развитии гемоптоэ, а также при присоединении грибковой инфекции необходима консультация торакального хирурга для решения вопроса о хирургическом лечении, особенно в случае рефрактерности к проводимой консервативной терапии.
Гангрена легкого — некроз значительного участка легочной ткани (доли, двух долей или всего легкого) без демаркации, имеющий тенденцию к дальнейшему распространению. Характерно наличие секвестров в полости распадов. Гангрена легкого занимает по тяжести клинического течения и неудовлетворительным результатам лечения ведущее место среди гнойно-некротических заболеваний легких [58]. К счастью, в настоящее время встречаемость заболевания среди госпитализированных по поводу инфекционных деструкций не превышает, по данным О.О. Ясногородского и соавт., 1% [14].
Попадание любого этиологического фактора гнойных заболеваний легких вызывает развитие острой пневмонии. При неблагоприятных обстоятельствах даже на фоне своевременной терапии в большинстве наблюдений острого воспалительного процесса развивается некроз легочной ткани с последующим формированием полостей деструкции [58–60]. К факторам, способствующим развитию гангрены легкого, можно отнести алкоголизм, наркоманию, курение, иммунодефициты различной этиологии. Этиологическую значимость имеют бессознательное состояние; приступы эпилепсии; черепно-мозговые травмы, при которых происходит аспирация содержимого ротоглотки и, возможно, инородных тел; аспирация желудочного содержимого; длительное пребывание в условиях низких температур в легкой одежде [29, 40, 58]. Как правило, гангрена легкого возникает у достаточно истощенных больных, имеющих сопутствующие хронические заболевания, а также при плохом или скудном рационе питания, что обусловливает невозможность нормального иммунного ответа и отграничение патологического участка, в связи с чем является медико-социальной проблемой [61].
При гангрене легкого, в отличие от остальных форм деструкций, в большинстве случаев наблюдают микробные ассоциации: неспорообразующие анаэробы сочетаются с аэробными госпитальными
КТ ГА
штаммами; S. aureus часто ассоциирован с Bac-teroides spp., P. aeruginosa, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, Enterococcus spp. [29].
В патогенезе большое значение придают нарушению проходимости бронхиального дерева, обусловленному диффузным гнойно-некротическим панбронхитом, формированием ателектазов, дезорганизацией кровообращения по бронхиальным и легочным сосудам (за счет васкулита и тромбозов с развитием ишемии бронхолегочных структур и последующим некрозом) [29, 58]. Предшествующие гангрене воспалительные процессы проявляются лейкоцитарными инфильтратами в зонах некроза и в зонах, пограничных с некрозом.
Гангрена отличается от остальных видов легочных деструкций преобладанием некробиотических изменений тканей. В легочных артериях выявляются тромбы, признаки васкулита [58–60]. Лизис гангре-низированной ткани легкого осуществляется лизосомальными энзимами, бактериальными протеиназами, гиалуронидазой, коллагеназой, лецитиназой, фибринолизином и другими биологически активными субстанциями, продуцируемыми анаэробноаэробной микрофлорой. Морфологически лизис проявляется некрозом межальвеолярных перегородок, отеком и кровоизлияниями, патологическим изменением сосудисто-бронхиальных структур.
При гангрене легкого происходит отторжение от основной массы органа больших участков легочной паренхимы (секвестрирование), что обнаруживается в процессе операции или при лучевых методах исследования [58]. Секвестрированные ткани легкого могут находиться в его паренхиме или отторгаться в плевральную полость [59, 60]. Именно легочные секвестры являются благоприятной средой для вегетации анаэробных организмов [29], которые присутствуют при гангрене наряду с S. aureus .
Гангрена характеризуется обширным поражением одной или нескольких долей легкого, прогрессирующим увеличением размеров полостей деструкции, вовлечением в патологический процесс новых участков легочной ткани и появлением новых крупных секвестров на фоне сохранения существующих. Жидкости в полостях распада немного. Формируется пиопневмоторакс в результате прорыва гнойника в плевральную полость [5, 58].
Клинические проявления гангрены легкого демонстрируют признаки воспаления и интоксикации, дыхательной недостаточности. Течение заболевания крайне тяжелое. Возможно развитие бактериально-токсического шока с прогрессирующим снижением артериального давления, тахикардией, олигурией. Характерны высокая лихорадка гектического характера с ознобами и проливным потом, головная боль, слабость, похудание, отсутствие аппетита, бессонница. Иногда возникают делириозные состояния и нарушения сознания. Болевой синдром в соответствующей половине грудной клетки при гангрене легкого свидетельствует о вовлечении в патологический процесс плевры. На фоне выраженного иммунодефицита общие симптомы могут быть подострыми, преобладают респираторные жалобы.
Через несколько дней после появления общих симптомов присоединяется кашель, сопровождающийся выделением мокроты, которая при гангрене легкого имеет грязно-серый или бурый цвет [54], резко зловонный гнилостный запах. При микроскопии мокроты выявляют большое количество лейкоцитов, эритроцитов, некротизированных элементов легочной ткани; эластические волокна отсутствуют.
В качестве осложнений гангрены легкого выделяют пиопневмоторакс, эмпиему, профузное легочное кровотечение, полиорганную недостаточность, септикопиемию, которые являются причинами смерти больных в 40–80% случаев [58–60].
При рентгенографии на стороне поражения имеется интенсивное затенение пораженного отдела легкого (обширное, субтотальное или тотальное), границы между ним и средостением, диафрагмой стерты. На фоне затенения наблюдаются просветления различного размера, отображающие распады, которые могут иметь горизонтальный уровень. В случае крупных полостей распада на фоне просветления можно отметить неправильной формы небольшие тени — секвестры. Средостение не смещено или смещается в сторону от поражения, что в том числе зависит от сочетанных плевральных изменений.
На КТ органов грудной клетки воспалительная инфильтрация легочной ткани при гангрене легкого не имеет четких границ и захватывает большое пространство — обычно больше одной доли, нередко все легкое (рис. 14). В начале процесса на КТ гангрена проявляется обширным участком консолидации (где частично прослеживаются просветы бронхов) или сочетанием консолидации с «матовым стеклом» (рис. 15). Далее, в динамике, на этом фоне появляются в большом количестве полости, обычно малого и среднего размера, в просвете которых обнаруживаются отдельно лежащие фрагменты
<линическая 2021 п эакти keu Том 12 №3
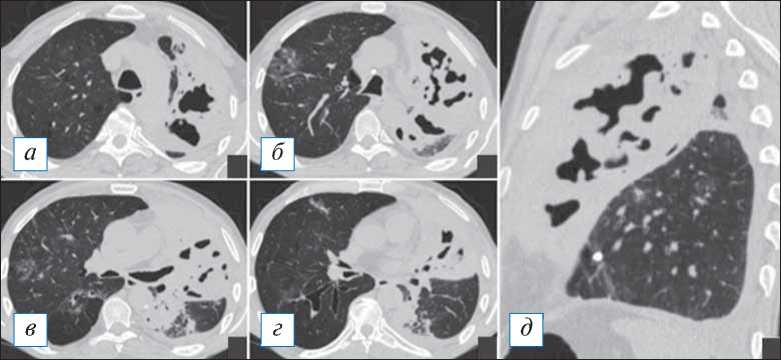
Рис. 14. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки в аксиальной ( а–г ) и сагиттальной ( д ) проекциях. Гангрена верхней доли левого легкого. Имеется тотальная инфильтрация верхней доли с наличием множественных полостей распада неправильной формы, а также фокусы инфильтрации в иных отделах легких. Небольшой выпот слева. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 14. Axial ( а–г ) and sagittal ( д ) chest CT images. Gangrene of the upper lobe of the left lung. There is a total infiltration of the upper lobe with the presence of multiple irregular-shaped destructive cavities, as well as little areas of infiltration in other parts of the lungs. A small pleural effusion is seen on the left. [Images from the authors’ archive].
легкого — секвестры (аваскулярные при контрастировании); могут быть видны сосудистые балки в виде тяжей, которые некротизируются обычно в последнюю очередь (рис. 16).
В полостях имеется гной, который визуализируется в виде участков жидкости с горизонтальным уровнем (лучше различим от ткани легкого при контрастном усилении). В подавляющем большинстве случаев гангрена легкого сочетается с плевральным выпотом и эмпиемой при расплавлении стенок полостей и висцерального плевраль- ного листка. Переход выпота в эмпиему можно определить по появлению газовых пузырьков на фоне жидкости, более крупного скопления газа в плевре с горизонтальной границей раздела сред, неоднородности жидкостного содержимого. При контрастном усилении плевра обычно утолщена, накапливает контрастный препарат. В тяжелых случаях секвестрированные участки легкого могут попадать в плевральную полость.
Гангренозный абсцесс представляет собой гнойно-гнилостный распад участка некроза сегмен-
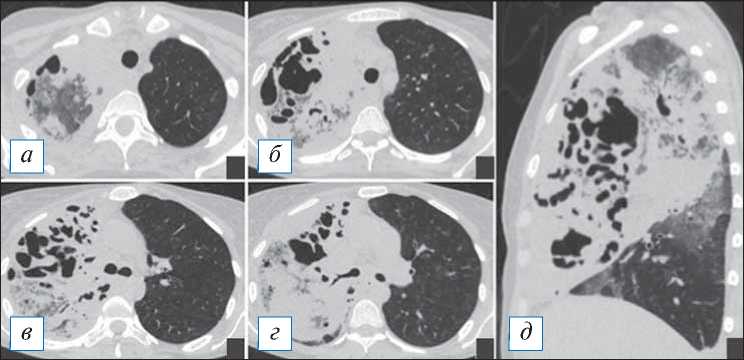
Рис. 15. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки в аксиальной ( а–г ) и сагиттальной ( д ) проекциях. Гангрена верхней и средней доли правого легкого в начальной стадии. Наблюдается тотальная инфильтрация долей в виде «матового стекла» и консолидации, на фоне которой имеются полости причудливой формы, склонные к слиянию. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 15. Axial ( а–г ) and sagittal ( д ) chest CT images. Gangrene of the upper and middle lobes of the right lung at its initial stage. There is a total infiltration of the lobes in the form of ground glass opacity and consolidation, against which there are oddly shaped cavities that tend to merge. [Images from the authors’ archive].
КТ ГА
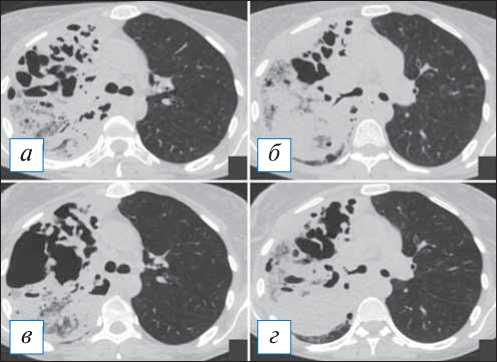
Рис. 16. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки в аксиальной проекции от 14.09.2020 ( а, б ) и 22.09.2020 ( в, г ). Отрицательная динамика гангрены легкого. Наблюдается слияние мелких полостей в более крупные, неправильной формы; содержимое в полостях отсутствует. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 16. Chest CT, axial projection from 14.09.2020 ( а, б ) and 22.09.2020 ( в, г ). Negative dynamics of lung gangrene. Small cavities confluence into larger ones, irregular shapes, the contents in the cavities are absent. [Images from the authors’ archive].
та или доли легкого со склонностью к секвестрации и отграничению от непораженных участков. Это можно считать признаком более благоприятного, чем при гангрене, течения заболевания [51, 61]. В отношении гангренозного абсцесса можно встретить формулировки: «абсцесс легкого с секвестрацией», «отграниченная гангрена» [62]. Морфологиче- ски при гангренозном абсцессе выявляют полости в пределах доли легкого с «бухтообразным» внутренним контуром из-за некротических секвестров легочной ткани [51, 61]. Иногда гангрена легкого трансформируется в гангренозный абсцесс, что можно считать благоприятным течением заболевания при успешной антибиотикотерапии [54].
По данным лучевых методов диагностики выявляют отграниченную полость или полость с небольшим количеством перикавитарной инфильтрации. Полость имеет «бухтообразные» внутренние контуры, в ее просвете можно наблюдать жидкость с горизонтальным уровнем и отдельно лежащие секвестрированные фрагменты легкого (рис. 17, 18). При динамическом наблюдении может отмечаться формирование секвестров из краевых отделов полости. Отграниченность процесса по данным рентгенографии или КТ — важнейший дифференциальный признак отличия гангрены от гангренозного абсцесса. Во всех случаях при подозрении на гангрену легкого или гангренозный абсцесс необходимы госпитализация больного, энергичная антибио-тикотерапия и наблюдение торакальным хирургом из-за большой вероятности развития легочных кровотечений в данной группе больных.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Золотистый стафилококк, различными способами проникающий в организм на фоне различных отклонений иммунного статуса в текущий момент может вызывать различные виды поражения лег-
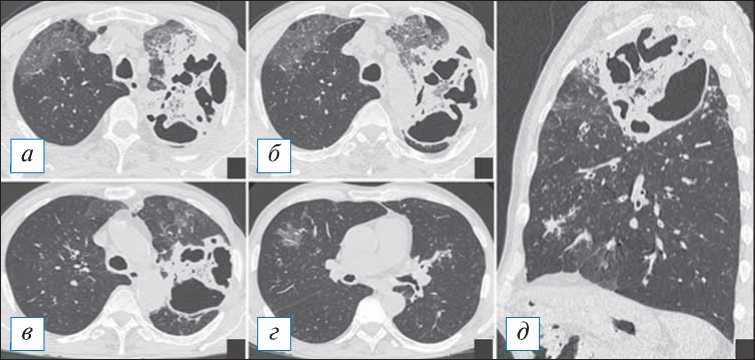
Рис. 17. Компьютерная томография органов грудной клетки в аксиальной ( а–г ) и сагиттальной ( д ) проекциях. Гангренозный абсцесс в верхней доле левого легкого. С двух сторон в верхних долях наблюдается инфильтрация, на фоне которой слева имеется крупная полость с четкими контурами, внутри — формирующийся секвестр. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 17. Axial ( а–г ) and sagittal ( д ) chest CT images. Gangrenous abscess in the upper lobe of the left lung. On both sides, there is infiltration in the upper lobes, against the background of which there is a large cavity with clear contours on the left, and a sequester is forming inside. [Images from the authors’ archive].
<линическая 2021 п эакти keu Том 12 №3
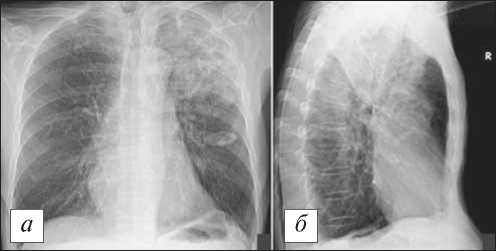
Рис. 18. Рентгенограмма органов грудной клетки в прямой ( а ) и правой боковой ( б ) проекции того же больного, что и на рис. 17. В верхней доле слева хорошо видно неоднородное отграниченное затенение, однако достоверно судить о формировании на этом фоне секвестра затруднительно. [Изображения из архива авторов].
Fig. 18. Chest X-ray of the same patient one presented as in Fig. 17. In the upper lobe on the left, a non-uniform limited opacity is clearly visible, however, it is difficult to reliably judge the formation of the sequester against this background. [Images from the authors’ archive].
ких — от малой бронхопневмонии до неконтролируемой деструкции в виде гангрены.
Лучевые методы диагностики, особенно КТ, вносят значимый вклад в комплексное обследование больных позволяя на ранней стадии выявить вид изменений в легких, отметить появления деструкций, абсцессов, что определяет дальнейшую терапевтическую и хирургическую стратегию при необходимости.
ДОПОЛНИТЕЛЬНАЯ ИНФОРМАЦИЯ
Вклад авторов. Винокуров А.С., Смирнова А.Д. — концепция и план исследования, написание текста, подготовка иллюстраций, анализ литературы; Беленькая О.И. — подготовка иллюстраций, анализ литературы; Юдин А.Л., Юматова Е.А. — концепция и план исследования, редактирование текста. Авторы подтверждают соответствие своего авторства международным критериям ICMJE (все авторы внесли существенный вклад в разработку концепции и подготовку статьи, прочли и одобрили финальную версию перед публикацией).
Author contribution. Vinokurov A.S., Smirnova A.D. — concept and research plan, manuscript writing, preparation of illustrations, analysis of literature; Belenkaya O.I. — illustrations, analysis of literature; Yudin A.L., Yumatova E.A. — concept and research plan, manuscript editing. The author made a substantial contribution to the conception of the work, acquisition, analysis, interpretation of data for the work, draft- ing and revising the work, final approval of the version to be published and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Источник финансирования. Авторы заявляют об отсутствии внешнего финансирования при проведении исследования.
Funding source. This study was not supported by any external sources of funding.
Список литературы Клинико-рентгенологические варианты поражения легких при инфекции, вызванной Staphylococcus aureus
- Okesola A. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-a review of literature. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2011;40(2):97-107.
- Белькова Ю.А. Пиодермии в амбулаторной практике // Клиническая микробиология и антимикробная химиотерапия. 2005. № 2. С. 255-270. [Belkova YuA. Pyoderma in outpatients. Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2005;(2):255-270. (In Russ).]
- Morgan MS. Diagnosis and treatment of Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) associated staphylococcal pneumonia. J Antimicrob Agents. 2007;3(4):289-296. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2007.04.019
- Crum-Cianflone N, Weekes J, Bavaro M. Recurrent community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections among HIV-infected persons: incidence and risk factors. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2009;23(7):499-502. doi: 0.1089/apc.2008.0240
- Тюрин И.Е. Лучевая диагностика инфекционных де-струкций легких // Пульмонология и аллергология. 2009. № 2. С. 8-14. [Tyurin IE. Radiation diagnosis of infectious lung destruction. Pulmonology and Allergology. 2009;(2):8-14. (In Russ).]
- Sicot N, Khanafer N, Meyssonnier V, et al. Methicillin resistance is not a predictor of severity in community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus necrotizing pneumonia-results of a prospective observational study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013;19(3):E142-148. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12022
- Охунов А.О, Хамдамов Ш.А, Охунова Д.А. Гнойно-деструктивные заболевания легких, патогенез и современные принципы их лечения // Проблемы современной науки и образования. 2018. № 4. С. 3-8. [Okhunov AO, Khamdamov ShA, Okhunova DA. Purulent-destructive lung diseases, pathogenesis and modern principles of their treatment. Problems of Modern Science and Education. 2018;(4):3-8. (In Russ).]
- Yi H, Huang J, Guo L, et al. Increased antimicrobial resistance among sputum pathogens from patients with hyperglycemia. Infect Drug Resist. 2020;13:1723-1733. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S243732
- Self WH, Wunderink RG, Williams DJ, et al. Staphylococcus aureus community-acquired pneumonia: prevalence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63(3):300-309. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw300
- Woodhead M, Blasi M, Ewig F, et al. Guidelines for the management of adult lower respiratory tract infections -summary. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17(Suppl 6):1-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03602.x
- Надеев А.П., Козяев М.А., Абышев А.А., и др. Вне-больничная пневмония: эпидемиология, этиология, и клини-ко-морфологические параллели // Сибирский научный медицинский журнал. 2019. № 4. С. 20-29. [Nadeev AP, Kozyayev MA, Abyshev AA, et al. Community-acquired pneumonia: epidemiology, etiology, and clinical and morphological parallels. Siberian Scientific Medical J. 2019;(4):20-29. (In Russ).] doi: 10.31549/2542-1174-2019-4-20-29
- Юренев Г.Л., Юренева-Тхоржевская Т.В. Антибактериальная терапия инфекционных поражений нижних дыхательных путей — место современных макролидов // Consilium Medicum. 2014. № 2. С. 33-41. [Yurenev GL, Yureneva-Tkhorzhevskaya TV. Antibacterial therapy of lower respiratory tract infections - the place of modern macrolides. Consilium Medicum. 2014;(2):33-41. (In Russ).]
- Chalmers SJ, Wylam ME. Methicillin-Resistant staphylo-coccus aureus infection and treatment options. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2069:229-251. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9849-4_16
- Ясногородский О.О., Гостищев В.К., Шулутко А.М., и др. Абсцесс и гангрена легкого: эволюция методов лечения // Новости хирургии. 2020. Т. 28, № 2. С. 150-158. [Yasnogorodsky OO, Gostishchev VK, Shulutko AM, et al. Abscess and gangrene of the lung: the evolution of therapies. Surgery News. 2020;28(2):150-158. (In Russ).] doi: 10.18484/2305-0047.2020.2.150
- Ашерова К.И., Фейжельсон Ж., Амелина Е.Л., и др. Му-ковисцидоз и туберкулез // Пульмонология. 2012. № 4. С. 34-39. [Asherova KI, Feizhelson J, Amelina EL, et al. Cystic fibrosis and tuberculosis. Pulmonology. 2012;(4):34-39. (In Russ).]
- Сергеева И.В., Демко И.В., Корчагин Е.Е. Клинико-ла-бораторная характеристика больных с внебольничными пневмониями на фоне гриппа A(H1N1)PDM09 // Сибирское медицинское обозрение. 2017. № 5. С. 47-53. [Sergeeva IV, Demko IV, Korchagin EE. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of patients with community-acquired pneumonia associated with influenza A(H1N1) PDM09. Siberian Medical Review. 2017;(5):47-53. (In Russ).] doi: 10.20333/2500136-2017-5-47-53
- Rice TW, Rubinson L, Uyeki TM, et al. Critical illness from 2009 pandemic influenza A virus and bacterial coinfection in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2012;40(5):1487-1498 doi: 10.1097/ccm.0b013e3182416f23
- MacIntyre CR, Chughtai AA, Barnes M, et al. The role of pneumonia and secondary bacterial infection in fatal and serious outcomes of pandemic influenza A(H1N1)pdm09. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):637. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3548-0
- Steven YC, Joshua S, Emily E, et al. Staphylococcus aureus infections: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015;28(3):603-661. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00134-14
- Langford BJ, So M, Raybardhan S, et al. Bacterial co-infection and secondary infection in patients with COVID-19: a living rapid review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26(12):1622-1629. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi. 2020.07.016
- Zhu X, Ge Y, Wu T, et al. Co-infection with respiratory pathogens among C0VID-2019 cases. Virus Res. 2020;285:198005. doi: 10.1016/j.viruses.2020.198005
- De la Calle C, Morata L, Cobos-Trigueros N, et al. Staphy-lococcus aureus bacteremic pneumonia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016;35(3):497-502. doi: 10.1007/s10096-015-2566-8
- Tran VG, Venkatasubramaniam A, Adhikari RP, et al. Efficacy of active immunization with attenuated alpha-hemolysin and panton-valentine leukocidin in a rabbit model of staphylococcus aureus necrotizing pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 2020;221(2):267-275. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz437
- Zhang QR, Chen H, Liu B, Zhou M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia in diabetics: a single-center, retrospective analysis. Chin Med J. 2019;132(12):1429-1434. doi: 10.1097/C M9.0000000000000270
- Байсултанова Р., Рачина С.А., Сухорукова М.В., Иван-чик Н.В. Внебольничная пневмония у лиц с сахарным диабетом: эпидемиология, этиология, диагностика, лечение и профилактика // Практическая пульмонология. 2020. № 1. С. 38-47. [Baysultanova R, Rachina SA, Sukhorukova MV, Ivanchik NV. Community-acquired pneumonia in persons with diabetes mellitus: epidemiology, etiology, diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Practical Pulmonology. 2020;(1):38-47. (In Russ).]
- Ljubic S, Balachandran A, Pavliae-Renar I, Metelko Z. Pulmonary infections in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia Croatica. 2005;33(4):115-124.
- Голоднова С.О. Совершенствование эпидемиологического надзора и контроля за внебольничными пневмококковыми пневмониями // Медиаль. 2016. № 11. С. 129-134.
- [Golodnova SO. Improvement of epidemiological surveillance and control over community-acquired pneumococcal pneumonia. Medial. 2016;(11):129-134. (In Russ).]
- Krumpe PE, Cummiskey JM, Lillington GA. Alcohol and the respiratory tract. Med Clin North Am. 1984;68(1):201-219. doi: 10.1016/S0025-7125(16)31250-0
- Григорьев Е.Г, Коган А.С., Гольдберг О.А., и др. Ключевые этиотропные и патогенетические механизмы гангрены легкого // Бюллетень ВСНЦ СО РАМН. 2006. № 5. С. 63-68. [Grig-oriev EG, Kogan AS, Goldberg OA, et al. Key etiotropic and pathogenetic mechanisms of lung gangrene. Bulletin VSNTS SB RAMS. 2006;(5):63-68. (In Russ).]
- Зверев С.Я., Иванова Э.С., Лузин П.М., и др. Вопросы эпидемиологии, диагностики, клиники и профилактики ВИЧ-инфекции в Прикамье // Вопросы вирусологии. 2014. № 3. С. 18-21. [Zverev SYa, Ivanova ES, Luzin PM, et al. Issues of epidemiology, diagnostics, clinic and prevention of HIV infection in the Kama region. Virology Issues. 2014;(3):18-21. (In Russ).]
- Викторова И.Б., Зимина В.Н., Дадыка И.В., и др. Внеболь-ничные пневмонии у больных ВИЧ-инфекцией // Туберкулез и болезни легких. 2021. Т. 99, № 4. С. 22-28. [Viktorova IB, Zimina VN, Dadyka IV, et al. Community-acquired pneumonia in patients with HIV infection. Tuberculosis and Lung Disease. 2021;99(4):22-28. (In Russ).] doi: 10.21292/2075-1230-2021-99-4-22-28
- He H, Wunderink RG. Staphylococcus aureus Pneumonia in the Community. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;41(4):470-479. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1709992
- Jean SS, Chang LW, Hsueh P. Tentative clinical breakpoints and epidemiological cut-off values of nemonoxacin for Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus isolates associated with community-acquired pneumonia. Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020;23:388-393. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2020.10.017
- Everett CK, Subramanian A, Jarisberg LG, et al. Characteristics of drug-susceptible and drug-resistant staphylococcus aureus pneumonia in patients with HIV. Epidemiology. 2013;3(1):122. doi: 10.4172/2161-1165.1000122
- Zhou H, Cai J, Du L, Wang C. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of polymicrobial Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infectbns. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2020;9(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13756-020-00741-6
- Чипигина Н.С., Куличенко В.П., Виноградова Т.Л., Большакова М.А. Поражение легких при инфекционном эндокардите // Клиницист. 2008. № 2. С. 28-33 [Chipigina NS, Kuli-chenko VP, Vinogradova TL, Bolshakova MA. Lung damage with infective endocarditis. Clinician. 2008;(2):28-33. (In Russ).]
- Rossi SE, Franquet T, Volpacchio M, Aguilar G. Tree-in-bud pattern at thin-section CT of the lungs: radiologic-pathologic overview. Radiographics. 2005;25(3):789-801. doi: 10.1148/rg.253045115
- Im JG, Itoh H. Tree-in-bud pattern of pulmonary tuberculosis on thin-section CT: pathological implication. Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(5):859-865. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.5.859
- Nicolaou EV, Bartlett AH. Necrotizing Pneumonia. Pediatric Annals. 2017;46(2):е65-е68. doi: 10.3928/19382359-20170120-02
- Белобородов В.Б. Некротизирующая пневмония, вызванная Staphylococcus aureus // Эпидемиология и инфекционные болезни. 2014. Т. 21, № 3. С. 4-10. [Beloborodov VB. Necrotizing pneumonia caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Epidemiology and Infectious Diseases. 2014;21(3):4-10. (In Russ).] doi: 10.17816/EID40758
- Ye R, Zhao L, Wang C, et al. Clinical characteristics of septic pulmonary embolism in adults: a systematic review. Respir Med. 2014;108(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2013.10.012
- Jing J, Qiuli L, Lihua L. et al. Septic pulmonary embolism in China: clinical features and analysis of prognostic factors for mortality in 98 cases. BMC Infectious Diseases. 2019;19(1):1082. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4672-1
- Винокуров А.С., Юдин А.Л., Беленькая О.И. КТ-семио-тика септической эмболии легких и ее осложнений // Медицинская визуализация. 2018. Т. 22, № 6. С. 23-32. [Vinokurov AS, Yudin AL, Belenkaya OI. CT semiotics of septic pulmonary embolism and its complications. Medical Imaging. 2018;22(6):23-32. (In Russ).] doi: 10.24835/1607-0763-2018-6-23-32
- Latorre CC, Agosto MR, Hernandez IL, et al. Embolic septic emboli with MRSA: a different source. J Clin Int Care Med. 2019;4(1):44-47. doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001026
- Brenes JA, Goswami U, Williams DN. The association of septic thrombophlebitis with septic pulmonary embolism in adults. Open Respir Med J. 2012;6:14-19. doi: 10.2174/1874306401206010014
- Сазонова С.И., Илюшенкова Ю.Н., Лишманов Ю.Б. Современные возможности однофотонной эмиссионной компьютерной томографии в диагностике инфекционного эндокардита // Российский электронный журнал лучевой диагностики. 2020. Т. 10, № 1. С. 178-190. [Sazonova SI, Ilyushen-kova YuN, Lishmanov YuB. Modern possibilities of single-photon emission computed tomography in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Russian Electronic Journal of Radiology. 2020;10(1):178-190. (In Russ).] DOI: 10.21569/2222-7415-2020-10-1-178-190
- Habib G, Lancellotti P, Antunes MJ, et al.; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis: The Task Force for the Management of Infective Endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Endorsed by: European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS), the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM). Eur Heart J. 2015;36(44):3075-3128. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv319
- Королева И.М., Соколина И.А., Лемешко З.А., и др. Лучевая диагностика септической эмболии легких у пациентов с гнойными заболеваниями челюстно-лицевой области // Медицинская визуализация. 2007. № 1. С. 69-73. [Koroleva IM, Soko-ina IA, Lemeshko ZA, et al. Radiation diagnosis of septic pulmonary embolism in patients with purulent diseases of the maxillofacial region. Medical Imaging. 2007;(1) 69-73. (In Russ).]
- Mendez-Echevarria A, Coronado-Poggio M, Baquero-Artigao F, et al. Septic pulmonary emboli detected by 18F-FDG PET/ CT in children with S. aureus catheter-related bacteremia. Infection. 2017;45(5):691-696. doi: 10.1007/s15010-017-0992-5
- Almeida RR, Marchiori E, Flores EJ. Frequency and reliabil-ty of the reversed halo sign in patients with septic pulmonary embolism due to IV substance use disorder. AJR. 2020;214(1):59-67. doi: 10.2214/AJR.19.21659
- Скворцов В.В, Байманкулов С.С. Острый абсцесс и гангрена легких // Медицинская сестра. 2015. № 6. С. 19-22. [Skvortsov VV, Baimankulov SS. Acute abscess and gangrene of the lungs. Medical Nurse. 2015;(6):19-22. (In Russ).]
- Бисенков Л.Н., Бебия Н.В., Гришаков С.В. Торакальная хирургия: руководство для врачей. Санкт-Петербург, 2004. 928 с. [Bisenkov LN, Bebiya NV, Grishakov SV. Thoracic surgery: a guide for doctors. Saint-Petersburg; 2004. 928 p. (In Russ).]
- Marra A, Hilleja L, Ukena D. [Management of lung abscess. (In German)]. Zentralbl Chir. 2015;140(Suppl 1):47-53. doi: 10.1055/S-0035-1557883
- Гнойные заболевания плевры и легких / под ред. П.А. Куприянова. Ленинград: Медгиз, 1955. 506 с. [Purulent diseases of the pleura and lungs. Ed. by P.A. Kupriyanov. Leningrad: Medgiz; 1955. 506 p. (In Russ).]
- Дунаев А. П. Современная лучевая диагностика деструктивной пневмонии и острого абсцесса легкого: Автореф. дис. ... канд. мед. наук. Москва, 2014. 25 с. [Dunaev AP. Modern radiation diagnostics of destructive pneumonia and acute lung abscess [dissertation abstract]. Moscow; 2014 .25 p. (In Russ).]
- Yang L, Liu T, Liu B. Severe pneumonia advanced to lung abscess and empyema due to rothia mucilaginosa in an immunocompetent patient. Am J Med Sci. 2020;359(1):54-56. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2019.10.015
- Клеточная биология легких в норме и при патологии: руководство для врачей / под ред. В.В. Ерохина, Л.К. Романовой. Москва: Медицина, 2000. 496 с. [Cell biology of the lungs in health and disease: A guide for physicians. Ed. by V.V. Erokhin, L.K. Romanova. Moscow: Medicine; 2000. 496 p. (In Russ).]
- Растомпахов С.В., Коган А.С., Григорьев Е.Г Этиопато-генез и лечение гангрены легкого // Сибирский научный медицинский журнал. 2008. № 4. С. 30-34. [Rastompakhov SV, Kogan AS, Grigoriev EG. Etiopathogenesis and treatment of lung gangrene. Siberian Scientific Medical Journal. 2008;(4):30-34. (In Russ).]
- Moon WK, Im G, Yeon KM, Han M. Complications of Klebsiella pneumonia: CT evaluation. J Comput Assist To-mogr.1995;19(2): 176-181. doi:10.1097/00004728-199503000-00002
- Chatha N, Fortin D, Bosma KJ. Management of necrotizing pneumonia and pulmonary gangrene: a case series and review of the literature. Can Respir J. 2014;21(4):239-245. doi: 10.1155/2014/864159
- Григорьев Е.Г Острый абсцесс и гангрена легкого // Сибирский медицинский журнал. 2013. № 8. С. 123-130. [Grigoriev EG. Acute abscess and gangrene of the lung. Siberian Medical Journal. 2013;(8):123-130. (In Russ).]
- Ионов П.М., Елькин А.В., Дейнега И.В., Яковлев Г.А. Клиника, диагностика, лечение и исходы острых абсцессов легких у больных с ВИЧ-инфекцией // Вестник хирургии имени И.И. Грекова. 2020. Т. 179, № 3. С. 69-74. [Ionov PM, Elkin AV, Deynega IV, Yakovlev GA. Clinic, diagnosis, treatment and outcomes of acute lung abscesses in patients with HIV infection. Herald of Surgery named after I.I. Grekov. 2020;179(3):69-74. (In Russ).] doi: 10.24884/0042-4625-2020-179-3-69-74


