Learning through games and its impact on the development of student’s knowledge during the pandemic period
Автор: Besa Havziu, Aneta Barakovska, Lulzim Memedi, Teuta Ramadani Rasimi
Журнал: International Journal of Cognitive Research in Science, Engineering and Education @ijcrsee
Рубрика: Review articles
Статья в выпуске: 2 vol.11, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Learning through play in the teaching process is a technique that has received a lot of attention since play itself increases the focus of students, and develops memory, creativity, and creative skills in students. However, the COVID-19 pandemic period was a very challenging period for every character included in the educational system, where many techniques used with physical presence were evaporated, or transformed in another form, as played through gamification. The objective of our research was to analyze the level and form of implementation of games as a teaching technique during COVID-19 in primary schools, among teachers N=120, students N=80 from I do 5th grade, and parents N=100 in Kosovo and North Macedonia. Results showed that there is a strong correlation of the implementation of games as a technique by parents and teachers in the implementation of the pandemic and the students learning and mental health, respectively their learning success has risen and their mental health was improved.
Play, strategy, knowledge, teaching, learning activities, parents, mental health
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170198718
IDR: 170198718 | УДК: 004.92:795]:373.23 | DOI: 10.23947/2334-8496-2023-11-2-311-319
Текст научной статьи Learning through games and its impact on the development of student’s knowledge during the pandemic period
Starting from the fact that play is an inseparable part of children’s lives, the way we can turn it into a technique for learning has shown and shows interest from many different authors who try to introduce innovations in the field of education and children’s education ( Stott and Neustaedter, 2013 ; Chang et al., 2017 ; Yu, 2019 ). Play is believed to be the most effective and motivating method for learning which can be applied in various forms. Therefore, we say that, when the game is well planned and oriented, we can influence in the incorporation of new concepts and students can develop and improve their skills without losing the motivation to learn ( Mubaslat, 20120 ). The COVID-19 pandemic in North Macedonia and Kosovo affected the whole educational system, highlighting the lack of possibilities to use play as a teaching method ( Kyriazis et al., 2021 ). Students were educated through an online form, which was a very unfamiliar form for teachers and s dents as well in North Macedonia and Kosovo. Even though children faced some emotional and social difficulties all over the world, a similar situation is described in the book of Lovatt (2021) “Paper rainbows began to appear in windows, painted as a token of hope by children kept indoors; but of children themselves, there was no sign” was happening in North Macedonia and Kosovo as well. It was evident that teachers and students were trying to find new alternatives of teaching and learning.
As professionals on the field, we were intrigued to analyze and research how much teachers and parents as well have collaborated among themselves during pandemic period in order to introduce different form of play/game as a technique of learning and teaching that can affect the overall success of students during the learning process ( Rogers, 2022 ).

© 2023 by the authors. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license .
The learning process and gaming/play
Learning through play is a continuum that brings together the spheres of children’s lives such as: home, school and the wider world over time. Play is a natural activity of children which helps to understand the development and views of children. As children become mature they are able to represent their needs mentally and use the thinking process to create motivations for play ( Vig, 2007 ). Children should have opportunities to explore with different materials and objects because this opportunity develops children’s creativity. Children’s play is connected to the objects and materials they play with. They contain the meaning, form and technique of the activity through the game. Therefore, the right choice of game affects the good education of children. In order to fulfill this multiple function, the game must fulfill a multitude of pedagogical requirements, must respond to the educational purpose with content and form, must be accessible to children, must stimulate children’s interest, influence the development of creativity, personality etc ( 2010 ).
Through play, the child grows, develops, learns new habits. Play is the best way to put them on a good path in the difficult and long learning process. Gaming as form of play in general and game-based learning in particular have the potential to turn learning into a challenge.In the last decade there is a new term “gamification” which has been defined by some author ( Nieto-Escamez and Roldan-Tapia, 2021 ) as the use of game elements in non-entertainment contexts to promote learning.Through play can be introduced concepts and students can develop and improve their skills without losing motivation. The game creates the foundation of reading and writing. Gamification pursues the use of game design elements to create engaging and motivating experiences ( Lister, 2015 ). There are countless skills that students can develop through play such as critical thinking skills, creativity, teamwork and good sportsmanship. They can also create a positive memory and learning experience for students in the classroom.A game is one of the easiest ways to engage students, capturing their attention and making learning fun ( Havziu, Memedi and Ameti, 2017 ).
Learning through play creates the possibility of a comprehensive approach to the learning process as the student seeks to learn independently and consciously ( Glenn, Cousins and Helps, 2006 ). The game attracts even shy children, who in other situations would not participate in the tasks assigned by the teacher, because most of them prefer to use mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets ( Krouska, Troussas and Sgouropoulou, 2021 ). Equally important for the learning process is the definition and clarification of rules of the game/play. They should be simple, clear, accepted by students and should not become an obstacle to the progress and flow of the game. We must be very careful to respect the age of the students and the level of skills in the selection of the game, because otherwise, the students would lose interest and the game would have no effect. The literature ( Toda et al., 2019 ) show that there are three main concerns regarding this topic: (a) instructors and teachers does not have the resources to plan and develop gamification strategies into their classes; (b) gamification needs a systematic approach to achieve the desired positive results; (c) inexistence of systematic approaches that connect and help in the design of gamification and social network tasks within these contexts. The game focuses on solving problems. The search for a solution to the problem stimulates the diversity of teachers’ perspectives and pushes the student towards productive, creative and not merely reproductive thinking ( Adachi and Willoughby, 2013) . According to Manzano-Leo et al. (2022) among the most used elements in educational gamifications are PBL (Points, Badges and Leaderboard), avatars and narratives.
The role of teachers in the process of gamification
COVID 19 pandemic era changed the carriers of educational system, the teachers. In developed countries the burden of online teaching cannot be compared with the burden of teachers from developing countries. During the first wave of the pandemic, the governments of the included countries (North Macedonia and Kosovo) supported the educational system in different ways, like broadcasting on national television or national education information network (Korez, et al., 2021). If in some developed countries researches showed that the online teaching process with the process of gamification has elevated stress and anxiety in teaching staff, and made pressure to change approaches to teaching and assessment to achieve the highest score (Lakeman, et al., 2022), there are little evidence (Miftari, Dzogovic and Zdravkovska-Adamova, 2021; World Bank, 2020) how teachers in North Macedonia and Kosovo have experienced these, except for higher education (Krasniqi and Shabani, 2022; Leskova, 2021). In addition, even though social distancing has been accompanied by online interaction thanks to continuous advances in digital technologies, it requires educator to work to find ways of increasing students’ motivation and engagements (Nieto-Escamez and Roldan-Tapia, 2021), which is why the teachers attitudes toward it is very important. There are some research (Marti-Parreno, Segui-Mas and Segui-Mas, 2016) that have shown a difference of attitudes between teachers from public settlements and private settlements, respectively they found that there is a significant more positive attitude towards gamification for teachers serving in private universities then in public universities. We can speculate from reviewing different literature that teachers negative attitude could be as a result of lack of recourses, and it has been underlined in several researchers (Asifayanti, Weda and Abduh, 2020).
The importance of implementing the strategy through the game lies in the fact that the information must be given in an appropriate way. Activities through play in order to be more effective in learning and teaching must be structured according to pedagogical rules and processes. Each activity must meet these criteria: activities through play should be well balanced with fun in learning, the activity must be planned with dedication and care in order to involve teachers and students in the activities, the content of the activity should be an integral part of the game, teachers must give the necessary instructions, ensure that the activity through the game develops according to the rules and that there is tolerance and cooperation among the students, also, the teacher must provide the conditions for all students to be an active part in the organized activity ( Xhajkovska, 2016 ). There is some consideration that teachers should consider before presenting an activity through game, respectively the teacher must know the baggage of knowledge of the students choosing the game, they must decide the purpose of the game in order to make them useful. When choosing the game, a basic aspect that teachers should consider before explaining is that students must understand exactly how to play the game, because they may need to adapt it to the level and age of the students and this will be more difficult if the rules are not clear ( Bodrova and Leong, 2003 ). Interruption of the game should be as rare as possible, so as not to reduce the interest of the students in the game.
The role of parents in the child’s play/gaming
Parents play an important role in a child’s life. Parents who play with their children form a stronger bond with them. These interactions provide positive life experiences that stimulate children’s brain development. Happy, enjoyable moments are some of the most precious gifts parents can give their children. Therefore, it is important to prepare daily activities through play with children, get involved in family activities and create a corner for the child to play ( Balaj, 2019 ). When parents are active in children’s learning and development, the role of play will be more effective ( Havziu and Rasimi, 2015 ). Primary caregivers are their children’s first teachers. They should be an integral part of school because they can contribute and also learn and apply key strategies at home – so it is important to support parents and provide them with safe tools to implement learning through play at home.
There are many ways parents can stimulate children’s development through nurturing care, conversation and storytelling, and by teaching life skills and providing time and materials for enriched play (UNICEF, 2018). Parents should provide a safe environment and plenty of opportunities for play and learning. The more play and learning activities that take place in the home environment - such as reading books, stories, singing, playing, learning letters and numbers and other activities - the more advanced the child’s development and learning. Through play activities at home, parents help children develop self-confidence and life skills, encouraging their creativity through various games. It is better for the child to choose the game he wants to play, where through it he creates a sense of emotional security which enables growth and development (Kraja, 2012). As can be seen, parents have an important influence on the growth and development of children, and yet when we talk about play, the role of the parent is somewhat more passive. We must not forget that the game is an activity created and that belongs only to children, so they are the only ones who will guide us in their game (Xhemali and Çeça, 2019). However, the pandemic period encountered many unprepared parents to meet the challenge of digitalization, and therefore gamification (Amzalog, 2021). There has been increase of researchers that have investigated the beliefs of parents towards these processes (Hanghoj and Brund, 2010; Bourgonjon et al., 2011; Hidayat, 2022), and according to Hidayat (2022), there is a contradictory attitudes of parents regarding the digitalization and gamification, respectively many parents allow their children to have screen time and even facilitate their children with gadgets but main concern for the children’s game-time is the lack of social interaction, health issues, and digital addiction.
Materials and Methods
The literature review raised many questions towards the situation in North Macedonia and Kosovo, which intrigued us to carry a research were the main objective was analyze the level of cooperation of parents and teacher during the pandemic period while incorporatinggamification as a technique that affects the overall success of students during the learning process and its correlation to students learning and their mental health. To answer this objective, we defined one general hypothesis:implementation of the game by parents and teachers in the period of the pandemic has had a positive impact on the students’ learning and their mental health.The main variable was the use of gamification as predictor, and criterion variable were the involvement of teachers, of parents and students metal health related to their learning success.
To carry the research, it was used a different approach of research, starting with the theoretical analysis of literature review and comparative method, since the results were compared between Kosovo and North Macedonia, and statistical methodwith descriptive and inferential statistic, as Pearson correlation and t-test.
Techniques and instruments needed for this research included a questionnaire as a measuring instrument for teachers and parents, as well as an interview dedicated to students of the lower cycle in primary education.
Sample/population - The research was focused on eight primary schools in Kosovo and Macedonia, which comprise two groups of teachers, parents and students, overal N=300.This sample was comprised by 120 teachers (60 from RNM and 60 from Kosovo) and 100 parents from 16 schools, as well as 80 students. This research involved teachers who work with students from class I to class V and the parents of these students.
Results
In this mini chapter we present the results regarding the main hypothesis “ The implementation of the game by parents and teachers in the period of the pandemic, has had a positive effect on the students’ learning and their mental health “ by using correlation analysis with Pearson’s assess the correlation of use of gamification with student’s success.
Table 1. Pearson correlation
|
Kosovo 1 2 |
North Macedonia 1 2 |
|||
|
1. Game strategy by teachers during the pandemic |
- |
- |
||
|
2. Student success during the pandemic |
.695" |
- |
.528" |
- |
Based on the table nr.1, the results show that there is a significant positive strong relationship between “Teachers’ Game Learning Strategy during the Pandemic” and “Students’ Success during the Pandemic” (r=.695**, p<0.01) for Kosovo, and there is a significant moderate positive relationship between “Learning strategy through play by teachers” and “Success of students during the pandemic” (r=.528**, p<0.01) for Macedonia. This means that when teachers have used game strategies during the pandemic, student success has also increased in both states.
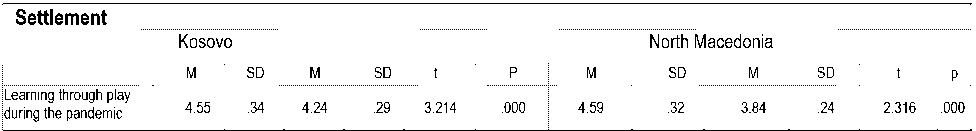
To see if there are differences of level of use of gamification related to the place of residence, we calculated the t-test for differences of means, and the results presented on table 2 show that there are significant differences on the level of use of gamification between teachers of North Macedonia and Kosovo, respectively the t (58)= 3.214, p=.000, where M for Kosovian is 4,24 while North Macedonia M is 3.84. These results highlighted the higher level of gamification used among students by teachers in the teaching and learning process in Kosovo schools, compared to North Macedonia.
Table 2. t- test analysis
We continued with in-depth analysis for parent’s involvement on gamification of teaching process correlated to student’s success, and again we used Pearson correlation to assess the level of correlation between the two variables on table 3.
Table 3. Pearson correlation
|
Kosovo |
North Macedonia |
|||
|
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
1. Involvement of parents during the pandemic period |
- |
- |
||
|
2. Children's success during the pandemic period |
.557" |
- |
.668” |
- |
Based on the table 3 above, the results show that there is a significant moderate positive relationship between “ Parental engagement during the pandemic period” and “Children’s success “ (r=.557**, p<0.01) for Kosovo and a strong positive relationship between “ Parents’ engagement during the pandemic period” and “Children’s success “ (r=668**, p<0.01) for Macedonia.
We continued with calculation of differences of level of parental involvement on gamification related to their settlement, respectively between North Macedonia and Kosovo, by using t-test for differences of means. The results presented on table 4 show that there are significant differences on parental involvement because t (38)= 3.595, p=.000 is for Kosovo with M 3.21, while t (38)= 4.112, p=.000 for North Macedonia with M 3.61. These results highlighted the higher level of gamification used among parents in North Macedonia compared to Kosovo.
Table 4. T-test analysis
|
Settlement |
||||||||||||
|
Kosovo |
North Macedonia |
|||||||||||
|
M |
SD |
M |
SD |
t |
P |
M |
SD |
M |
SD |
t |
P |
|
|
Parent engagement during the pandemic |
3.62 |
.24 |
3.21 |
.33 |
3.595 |
.000 |
4.28 |
.25 |
3.61 |
.52 |
4.112 |
.000 |
In the main hypothesis we underlined as well as the mental health of students related to gamification of the learning process. In order to test this variable as well, we calculated Pearson coefficient for correlation of level of gamification and student’s mental health, which is presented in table 5.
Table 5. Pearson correlation
|
Kosovo |
Macedonia |
|||
|
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
1. Implementation of the game by students during the pandemic |
- |
- |
||
|
2. Mental health |
,668м |
- |
,557м |
- |
Based on the table above, the results show that there is a strong positive significant relationship between “Implementation of the game by students during the pandemic” and “Mental health” (r=.668**, p<0.01) for Kosovo and there is also a significant moderate positive relationship between “Implementation of the game by students during the pandemic” and “Mental health (r=.557**, p<0.01) for Macedonia.
Qualitative data
To ensure more subjective data of the research, we carried on an interview with students from Kosovo and North Macedonian schools, and to follow up the results we present most common statements, starting with the mental health of the students, where they were asked to discuss how the implementation of gamification had affected their wellbeing, and most of the respondents underlined that in general use game in their spare time, thus using games just made them very happy.
-
- During distance learning when teachers used activities through games such as quizzes, competitions between groups, imaginary games, etc. How did you feel about these activities?
-
- The most frequent statement was that during the pandemic period the activities and games that their teachers have prepared to facilitate distance learning have had a positive impact on their mental health as well as the development of knowledge and skills.
The second theme of the interview was regarding the learning process, and how much gamification have helped or hampered this process, and in general by using games during online classes increased their motivation and simplified the tasks for them, which enabled them to overcome learning difficulties.
-
- What games did your teachers organize with you during the pandemic period and did they help you overcome difficulties in learning?
-
- Most of them stated that their teachers have organized various games during the pandemic, such as quizzes, activities related to learning units, association games, and physical activities through the projector, and this has helped them a lot in overcoming any difficulties they had.
The third theme was regarding the involvement of parents in the process of gamification and how this collaboration has affected them, and the vast of the respondents addressed as positive points the involvement of parents and the biggest supporters. However, there were a considerable number of parents that were working online as well during the online classes, and they pointed out the mismanagement in that time with the parents.
-
- How much do you think the game has affected you and who has helped you during the pandemic?
-
- The answers received were that the game and the activities through it have had a positive effect on them and have helped them to remove stress and negative thoughts, and they emphasized the role of parents as well in this process and their collaboration with teachers.
The last theme was regarding the use of gamification during their leisure time, which was their favorite topic to talk about, since the whole world was using the pandemic time for online promotion. The majority have used different online educational games that have discovered during this period, and their attitudes were positive.
-
- Have you implemented any games at home?
-
- They have implemented various games with parents, sisters or brother, such as the bowling game where they have placed some bottles and a ball and through hitting the bottles they learned how to subtract numbers.
Conclusion
After extracting the results, we can confirm the raised hypothesis, that implementation of the game by parents and teachers in the period of the pandemic is strongly correlated with students’ learning and their mental health, since there were two significant correlation with the process of gamification, teachers involvement and parents involvement. Even though, we must underline the difference among teacher’s involvement, that were higher for Kosovian, in other side parents from North Macedonia showed higher preparedness for involving in the process of gamification. Nevertheless, both variables were strongly correlated to student’s success like it has been documented in many other research ( Adachi and Willoughby, 2013 ; Amzalog, 2021 ; Mubaslat, 2012 ; Ye et al., 2022 ), respectively as more teachers have used gamification in the teaching process, the learning success of students has risen. Most likely that through play, children connect more with parents, so the time spent with them brings positive effects both physical and psychological, as has been shown in some research ( Calandri, Cattelino and Graziano, 2022 ). In addition, students spend 1/3 of the day in school, so by using gamification teachers contribute to students’wellbeing as well, which is why the qualitative data from the interview of our research with the students was positive regarding the gamification during the teaching process, and its positive effect on overcoming the learning difficulties, as well the involvement of parents in this process, which can be found in on other researches ( Almusharraf, 2021 ; Mariano and Cordova, 2022 ). In North Macedonia and Kosovo the pandemic era was a changing era of digitalization of the educational system, even though teachers and parents weren’t prepare, it has had highly positive effect on changing the mindset of teachers. By learning new techniuques and apps they were able to to be up to date with the western system of schooling. Thus, we strongly hope that these results will intrigue other researchers from North Macedonia and Kosovo to widen their scope of research in the bigger sample and draw recommendations that can make policymakers change the educational system, a system that will seek to apply research based techniques of teaching.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratittue to everyone who participated on this research, for their invaluable input and support throughout the research process. Everyones insights and expertise were instrumental in shaping the direction of this project.
Author Contributions
Список литературы Learning through games and its impact on the development of student’s knowledge during the pandemic period
- Adachi, P. J., & Willoughby, T. (2013). More than just fun and games: the longitudinal relationships between strategic video games, self-reported problem solving skills, and academic grades. Journal of youth and adolescence, 42, 1041-1052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-013-9913-9
- Almusharraf, N. (2021). Incorporation of a game-based approach into the EFL online classrooms: students’ perceptions. Interactive Learning Environments, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2021.1969953
- Amzalag, M. (2021). Parent attitudes towards the integration of digital learning games as an alternative to traditional homework. International Journal of Information and Communication Technology Education (IJICTE), 17(3), 151-167. https://doi. org/10.4018/IJICTE.20210701.oa10
- Asifayanti, A., Weda, S., & Abduh, A. (2020). Exploring Teachers’ Perception on Gamification in Online Grammar Teaching. Pinisi Journal of Art, Humanity and Social Studies, 1(4), 1-11. Retreived from https://ojs.unm.ac.id/PJAHSS/article/ view/24113
- Balaj, B. (2019). Çdo ditë mësoj përmes lojës [Every day I learn through play.]. Prishtinë, Kosova: Save the Children. Retrieved from https://kosovo.savethechildren.net/sites/kosovo.savethechildren.net/files/library/ALB_Final_Loja.pdf
- Bodrova, E., & Leong, D. J. (2003). Chopsticks and Counting Chips: Do Play and Foundational Skills Need To Compete for the Teacher’s Attention in an Early Childhood Classroom?. Young Children, 58(3), 10-17. Retrieved September 6, 2021, from http://www.journal.naeyc.org/btj/200305/Chopsticks_Bodrova.pdf
- Bourgonjon, J., Valcke, M., Soetaert, R., DeWever, B., & Schellens, T. (2011). Parental acceptance of digital game-based learning. Computers & Education, 57(1), 1344-1444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2010.12.012
- Calandri, E., Cattelino, E., & Graziano, F. (2023). Is playing video games during COVID-19 lockdown related to adolescent well-being? The role of emotional self-efficacy and positive coping. European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 20(3), 533-549. https://doi.org/10.1080/17405629.2022.2148651
- Chang, C. C., Liang, C., Chou, P. N., & Lin, G. Y. (2017). Is game-based learning better in flow experience and various types of cognitive load than non-game-based learning? Perspective from multimedia and media richness. Computers in Human Behavior, 71, 218-227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.01.031
- Glenn, A., Cousins, J., & Helps, A. (2006). Strategji të Provuara dhe Tesuara: Loja dhe të Nxënët në Moshën e Hershme [Tried and Tested Strategies: Play and Early Learning]. David Fulton Publishers. Retrieved from https://albania. savethechildren.net/sites/albania.savethechildren.net/files/library/Playing%20%26%20Learning%20in%20the%20 Early%20Years.pdf
- Hanghøj, T., & Brund, C. E. (2010, October). Teacher roles and positionings in relation to educational games. In Proceedings of the 4th European conference on games based learning (pp. 116-122). Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/ publication/290673816_Teacher_roles_and_positionings_in_relation_to_educational_games
- Havziu, B., & Rasimi, T. R. (2015). Leisure time for secondary school students. International Journal of Cognitive Research in Science, Engineering and Education:(IJCRSEE), 3(1), 51-55. https://doi.org/10.23947/2334-8496-2015-3-1-51-55
- Havziu, B., Mehmedi, D. D. L., & Ameti, M. (2017). The Influence of Socio-Educational Factors in the Selection of Contents for Fullfilling Free Time of High School Students. European Journal of Social Science Education and Research, 4(2), 21-27. https://doi.org/10.26417/ejser.v9i2.p22-28
- Hidayat, I. K. (2022). Teachers’ and Parents’ Viewpoints of Game-Based Learning: An Exploratory Study. KnE Social Sciences, 77-84. https://doi.org/10.18502/kss.v7i13.11647
- Korcz, A., Krzysztoszek, J., Łopatka, M., Popeska, B., Podnar, H., Filiz, B., ... & Bronikowski, M. (2021). Physical education teachers’ opinion about online teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic—Comparative study of European countries. Sustainability, 13(21), 11730. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132111730
- Kraja, M. (2012). Personaliteti i mësuesit dhe pedagogut [The personality of the teacher and lecturer]. Tiranë: Vllamasi.
- Krasniqi, R., & Shabani, A. (2022). Hybrid Teaching during Covid-19—A Case Study of Public Universities in Kosovo. Open Journal of Social Sciences, 10(13), 72-80. https://doi.org/10.4236/jss.2022.1013007
- Krouska, A., Troussas, C., & Sgouropoulou, C. (2021). Mobile game-based learning as a solution in COVID-19 era: Modeling the pedagogical affordance and student interactions. Education and Information Technologies, 27(2), 229–241 https:// doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10672-3
- Kyriazis, A., Mews, G., Belpaire, E., Aerts, J., & Malik, S. A. (2021). Physical distancing, children and urban health: The COVID-19 crisis’ impact on children and how this could affect future urban planning and design policies. Cities & health, 5(sup1), S83-S88. https://doi.org/10.1080/23748834.2020.1809787
- Lakeman, R., Coutts, R., Hutchinson, M., Massey, D., Nasrawi, D., Fielden, J., & Lee, M. (2022). Playing the SET game: how teachers view the impact of student evaluation on the experience of teaching and learning. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2022.2126430
- UNICEF. (2018). Learning through play Strengthening learning through play in early childhood education programmes in support of 2 Learning through play. Retrieved 12 17, 2021, from https://www.unicef.org/sites/default/files/2018-12/ UNICEF-Lego-Foundation-Learning-through-Play.pdf
- Leskova, G. (June, 2021). Youth Choose: Adapting to Online Learning. Retrieved from RYCO: Regional Youth Cooperation Office. Retrieved from https://www.rycowb.org/?p=10418
- Lister, M. (2015). Gamification: The effect on student motivation and performance at the post-secondary level. Issues and Trends in Educational Technology, 3(2). Retrieved from https://journals.librarypublishing.arizona.edu/itlt/article/id/1487/
- (2010). Loja në mendimin pedagogjik [Loja në mendimin pedagogjik.]. Tiranë: Qendra e trajnimit “Kardinal Mikel Koliqi”. Retrieved 10 12, 2021, from https://www.shisalbania.org/media/5acbade18d7fa.pdf
- Lovatt, S. (2021). Birdsong in a Time of Silence. Penguin UK.
- Manzano-León, A., Aguilar-Parra, J. M., Rodríguez-Moreno, J., & Ortiz-Colón, A. M. (2022). Gamification in initial teacher training to promote inclusive practices: a qualitative study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(13), 8000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19138000
- Mariano, J. S., & Cordova, S. G. V. (2022). E-Sports online learning module amidst COVID-19 Pandemic. Interactive Learning Environments, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2022.2137529
- Martí-Parreño, J., Seguí-Mas, D., & Seguí-Mas, E. (2016). Teachers’ attitude towards and actual use of gamification. Procedia- Social and Behavioral Sciences, 228, 682-688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.07.104
- Miftari, V., Dzogovic, S. A., Dzogovic, A., & Zdravkovska-Adamova, B. (2021). The efficiency of online learning during the covid-19 pandemic: Comparative analysis of southeast european countries as participants in the new path of education. Human Research in Rehabilitation, 11, 133-142. Retrieved
- Mubaslat, M. M. (2012). The Effect of Using Educational Games on the Students’ Achievement in English Language for the Primary Stage. Online Submission. Retrieved from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED529467.pdf
- Nieto-Escamez, F. A., & Roldán-Tapia, M. D. (2021). Gamification as online teaching strategy during COVID-19: A mini-review. Frontiers in psychology, 12, 648552. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.648552
- Rogers, S. (2022). Play in the time of pandemic: Children’s agency and lost learning. Education 3-13, 50(4), 494-505. https:// doi.org/10.1080/03004279.2022.2052235
- Stott, A., & Neustaedter, C. (2013). Analysis of gamification in education. Surrey, BC, Canada, 8(1), 36. Retrieved from http:// clab.iat.sfu.ca/pubs/Stott-Gamification.pdf
- Toda, A. M., do Carmo, R. M., da Silva, A. P., Bittencourt, I. I., & Isotani, S. (2019). An approach for planning and deploying gamification concepts with social networks within educational contexts. International Journal of Information Management, 46, 294-303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2018.10.001
- Vig, S. (2007). Young children’s object play: A window on development. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 19, 201-215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10882-007-9048-6
- World Bank. (2020). The ecenomic and Social Impact of COVID-10. Western Balkans regular repost. Retrieved from https:// documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/590751590682058272/pdf/The-Economic-and-Social-Impact-of-COVID-19- Education.pdf
- Xhajkovska, B. E. (2016). Matematika nëpërmjet lojës : 50 aktivitete për përvetësimin e aftësive matematikore [Mathematics through play: 50 activities for acquiring mathematical skills]. Shkup: Fondacioni për iniciativa arsimore dhe kulturore “Hap pas hapi” – Maqedoni. Retrieved from http://www.stepbystep.org.mk/WEBprostor/toolbox/ Matematika_n%C3%ABp%C3%ABrmjet_loj%C3%ABs.pdf
- Xhemali, A., & Çeça, J. (2019). “Fëmijët dhe loja. Si të luani me fëmijën tuaj që ai/ajo të mësojë?”[ “Children and play. How to play with your child so that he/she learns?”]. Tiranë: Qendra Ekonomike e Zhvillimit dhe Edukimit të Fëmijëve (QEZHEF). Retrieved 12 16, 2021, from http://femijetetiranes.al/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/F%C3%ABmij%C3%ABt-dhe-loja. pdf
- Ye, L., Zhou, X., Yang, S., & Hang, Y. (2022). Serious game design and learning effect verification supporting traditional pattern learning. Interactive Learning Environments, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2022.2042032
- Yu, Z. (2019). A meta-analysis of use of serious games in education over a decade. International Journal of Computer Games Technology, 1, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4797032


