Магнитно-резонансная томография как инструмент дифференциальной диагностики при поражении ствола головного мозга у детей
Автор: Марченко Наталья Викторовна, Войтенков Владислав Борисович, Скрипченко Наталья Викторовна, Бедова Мария Алексеевна, Курзанцева Ольга Олеговна
Журнал: Клиническая практика @clinpractice
Рубрика: Обзоры
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.11, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В данном обзоре литературных данных мы рассматриваем магнитно-резонансную томографию как инструмент дифференциальной диагностики поражения ствола головного мозга у детей. Показано, что поражение ствола мозга, как изолированное, так и связанное с супратенториальными изменениями, возникает при широком спектре патологических состояний - при острых нарушениях мозгового кровообращения, дисметаболических нарушениях, воспалительных процессах как инфекционной, так и неинфекционной (аутоиммунной, паранеопластической) этиологии, нейродегенеративных заболеваниях, опухолях. Небольшой размер ствола, а также менее четкое различие между серым и белым веществом и определенное ограничение мультипараметрической магнитно-резонансной томографии в случае исследования стволовых структур часто приводят к затруднениям в проведении дифференциальной диагностики. Иногда большое диагностическое значение приобретают топография очага и интенсивность сигнала от него. Для целей дифференциальной диагностики основополагающее значение, тем не менее, играют клинические, эпидемиологические и лабораторные исследования.
Ствол мозга, дети, магнитно-резонансная томография
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143170836
IDR: 143170836 | DOI: 10.17816/clinpract16531
Текст обзорной статьи Магнитно-резонансная томография как инструмент дифференциальной диагностики при поражении ствола головного мозга у детей
Ствол мозга — отдел центральной нервной системы, состоящий из продолговатого мозга, моста, среднего мозга, промежуточного мозга и мозжечка. В стволе мозга сосредоточены ядра и проводящие пути, обеспечивающие жизнедеятельность организма, в частности дыхательный и сосудодвигательный центры, а также ретикулярная формация [1]. Серое и белое вещество ствола мозга обладает комплексной структурой, анатомически тесно переплетенной, что делает его топографию сложной для интерпретации при нейровизуализации.
Высокотесловая магнитно-резонансная томография (МРТ), более 1,5 Тл, дает детализированную визуализацию морфологии, интенсивности сигнала и метаболической составляющей стволовых ядер, равно как и визуализацию серого и белого вещества. Стандартный МРТ-протокол у детей должен быть адаптирован к возрасту пациента: следует визуализировать весь головной мозг вплоть до затылочного отверстия. Т2-взвешенные изображения лучше выявляют гиперинтенсивные очаги в задней мозговой ямке, чем изображения в Flair-режиме [2]. Flair-последовательность у детей младше 12 мес жизни неэффективна [3]. Стандартной характеристикой стволовых очагов является гиперинтенсивность сигнала на турбо-спин-эхо Т2-взвешенных изображениях, очаги могут быть фокальными или диффузными, изолированными или множественными [3, 4].
Базируясь исключительно на интенсивности сигнала, особенно у детей, невозможно дифференцировать острое и хроническое очаговое поражение. Более того, в случаях хронического метаболического заболевания или воспалительного поражения центральной нервной системы новые острые очаги могут возникать на фоне хронического процесса, что дополнительно затрудняет интерпретацию нейровизуализационных находок [5]. С точки зрения морфологии, наличие отека и Т1-га-долиниевого усиления предполагает наличие воспалительного и/или инфекционного или неопластического процесса, в то время как масс-эффект является более типичным для последнего [6].
В оценке стволового поражения большую помощь оказывает знание особенностей васкуляризации ствола, распределения серого и белого вещества и селективной уязвимости мозговой ткани. С точки зрения васкуляризации важно отметить, что из вертебробазилярного бассейна происходят задняя спинальная, задняя нижняя мозжечковая и передняя спинальная артерии. Ишемические и септические эмболы обычно проникают по артериальному кровотоку настолько далеко, насколько это допускает их размер, что часто обусловливает поражение небольших по калибру артерий ствола мозга [5]. Пограничными зонами артериальных терминалей являются покрышка мозга, продолговатый мозг и мост; у новорожденных эти части ствола считаются самыми восприимчивыми к гипоксиче-ски-ишемическому поражению [6, 7]. Венозная система ствола отличается сложностью и большим количеством сосудов, но хорошо визуализируется с применением протокола SWI (Susceptibility Weighted Imaging — изображения, взвешенные по магнитной восприимчивости) [5].
Серое вещество ствола мозга тесно переплетено с проводящими путями (белым веществом). Тем не менее б о льшая часть структур серого вещества глубоко расположена, в то время как белое вещество распределено по периферии ствола. Это связано с тем, что волокна, составляющие пирамидные пути и ножки мозга, расположены в мосту вентролатерально. Вследствие этого поражение белого вещества мозга ожидается преимущественно в периферических зонах ствола без краниокаудальной специфичности [7]. С точки зрения селективной уязвимости мозговой ткани важным является то, что ядра серого вещества более восприимчивы к метаболическим повреждениям. Это связано с тем, что их метаболические потребности выше, чем у структур белого вещества. Поскольку ядра серого вещества, в особенности ретикулярной формации, расположены от среднего до продолговатого мозга, метаболическое поражение центральной нервной системы также не демонстрирует краниокаудальной специфичности [8].
Цель обзора — раскрыть современные представления об МРТ головного мозга как инструменте дифференциальной диагностики при поражении ствола мозга. С этой целью были проанализированы научные статьи и монографии, посвященные вопросам нейровизуализации при поражении ствола мозга различной этиологии. Поиск осуществлялся с использованием баз данных PubMed, Medline, eLibrary. ru. Для поиска использовались ключевые слова MRI+encephalitis, MRI+brainstem, brainstem+MRI.
ПОРАЖЕНИЕ СТВОЛА МОЗГА
ПРИ ОСТРЫХ НАРУШЕНИЯХ МОЗГОВОГО КРОВООБРАЩЕНИЯ У ДЕТЕЙ
Острые нарушения мозгового кровообращения у детей в 5–6% случаев поражают ствол мозга [8, клиническая; 20
Том 121 № 0 1
-
9] . Эмболы попадают в артериальные терминали и приводят к появлению Т2-гиперинтенсивных очаговых поражений (рис. 1). Крупный очаг (более 50% диаметра ствола) является прогностически неблагоприятным признаком [9].
Вследствие небольших размеров ствола мозга у детей часто регистрируются ложные негативные результаты [10]. Ишемические очаги обычно невелики по размеру и связаны с гиперинтенсивностью на Т2- и Flair-режимах. Ствол мозга обычно рассматривается как резистентный к ишемии отдел центральной нервной системы вследствие высокой плотности васкуляризации [9]. Однако в неонатальном периоде развитие васкуляризации может быть неполным, и дети с гипоксически-ишемической энцефалопатией в перинатальном периоде повышенно восприимчивы к повреждению покрышки мозга [7]. Повреждение покрышки, как правило, конусообразное, билатеральное и обычно симметричное с частым вовлечением каудальной части моста и продолговатого мозга; оно проявляется оральной моторной дисфункцией [7].
Сосудистые мальформации также встречаются в стволе мозга у детей и включают в себя врожденные аномалии вен, кавернозные гемангиомы и капиллярные телеангиоэктазии, а также артериовенозные мальформации. МРТ-паттерн каждого из этих сосудистых образований типичный, и обычно диагностика не вызывает затруднений. Интенсивность МР-сигнала и морфология идентичны наблюдающимся у взрослых пациентов [7].
ДИСМЕТАБОЛИЧЕСКИЕ НАРУШЕНИЯУ ДЕТЕЙ С ПОРАЖЕНИЕМ СТВОЛА МОЗГА
Среди синдромов, связанных с генетическими нарушениями метаболизма, чаще всего поражают ствол митохондриальные энцефалопатии. Митохондриальные заболевания включают широкий спектр клинических синдромов, связанных с дефицитом окислительного фосфорилирования, вызываемым частичным или полным дефицитом одного или более ферментов дыхательной цепи. Наследование может быть аутосомно-рецессивным, аутосомно-доминантным, Х-сцепленным [11, 12]. Дефект митохондриальной дыхательной цепи может быть
Рис. 1. Пациент А., 7 лет. МРТ: поражение ствола мозга в результате острого нарушения мозгового кровообращения по ишемическому типу в бассейне основной артерии, 2-е сут заболевания
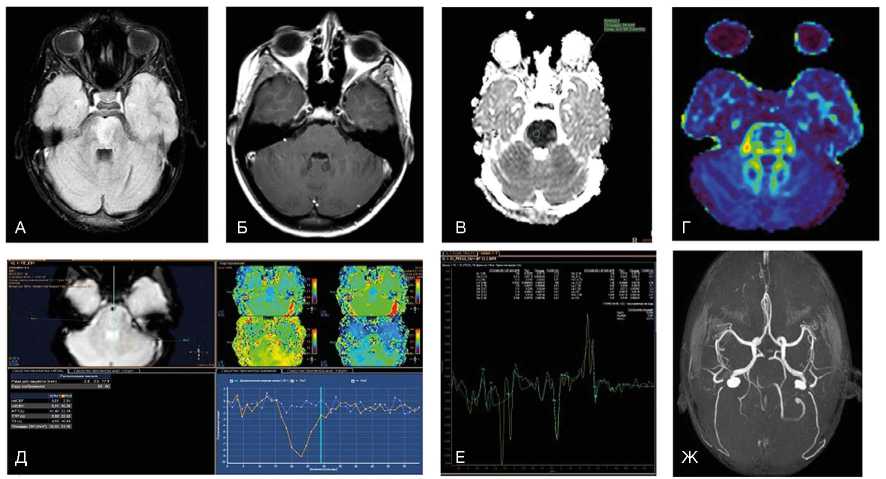
Примечание. При магнитно-резонансной томографии (МРТ) в варолиевом мосту визуализируется зона патологического гиперинтенсивного МР-сигнала на Flair (А) без признаков нарушения гематоэнцефалического барьера при внутривенном контрастировании в зоне поражения (Б). На диффузионных последовательностях (В) визуализируется цитотоксический отек с признаками ограничения диффузии и значениями измеряемого коэффициента диффузии 0,4x10 -3 мм2/с. При выполнении DTI (Г) данная зона демонстрирует снижение значений фракционной анизотропии до 0,25. При контрастной Т2*-перфузии отмечается отсутствие кровотока в зоне поражения (Д), что дополнительно подтверждено на бесконтрастной МР-ангиографии (Ж), где отсутствует визуализация тока крови по базилярной артерии. При МР-спектроскопии (Е) на фоне шума выраженные пики метаболитов в зоне поражения практически отсутствуют (данные Детского научно-клинического центра инфекционных болезней ФМБА, Санкт-Петербург).
вызван генетическими мутациями ядерной или митохондриальной ДНК [13–16]. Метаболическая уязвимость является важной составляющей поражения ствола мозга при этих заболеваниях [17]. Ткани и клетки с высокими метаболическими потребностями более восприимчивы к такого рода повреждению вследствие своей неспособности уменьшить потребление кислорода [18]. Клинически данные заболевания проявляются мультисистемным поражением, постановка диагноза затруднена вследствие широкой генетической и фенотипической гетерогенности.
Синдром Лея может возникать вследствие мутации митохондриальной ДНК, но большая часть случаев обусловлена мутациями ядерной ДНК, поражающей пируват-дегидрогиназный комплекс или любой из комплексов дыхательной цепи [19]. При МРТ ствола мозга регистрируются симметричные, иногда билатеральные очаги [20]. Наиболее часто поражаются черная субстанция, в особенности ее ретикулярная часть, покрышка моста и среднего мозга и нижние бугры четверохолмия. Также часто поражаются нижние ядра олив, но у детей, которые умирают на первом году жизни, такие изменения не описаны [20]. Билатеральная гипертрофическая дегенерация ядер олив была описана в 40% случаев у пациентов с заболеваниями обмена веществ, что заставляет предположить, что нижние ядра олив поражаются при синдроме Лея как из-за первичной метаболической уязвимости, так и от вторичной транссинаптической нейрональной дегенерации [21]. При синдроме Лея поражение ствола может также сопровождаться билатеральными и симметричными очагами в базальных ядрах и диффузной супратенториальной лейкоэнцефалопатией [22]. При синдроме Лея описывается также поражение мозжечка с формированием отека с петехиальным компонентом, что позволяет предполагать наличие микроангиопатии [20]. Гибель клеток Пуркинье и мозжечковая атрофия при синдроме Лея возникает, как предполагается, вследствие эксайтотоксичности. Эти изменения более характерны для других митохондриальных энцефалопатий, таких как миоклоническая эпилепсия с рваными красными волокнами, MERRF, MELAS, синдром Кернса–Сейра [23]. При этих синдромах помощь в дифференциальной диагностике оказывает информация о возрасте дебюта заболевания, клинической картине и особенностях супратенториального поражения. Однако дифференциальная диагностика может быть затруднена, поскольку поражения ствола были описаны при всех этих митохондриальных заболеваниях: напри- мер, при MERRF могут поражаться серое вещество вокруг сильвиевого водопровода и верхние ножки мозжечка, при синдроме Кернса–Сейра описаны билатеральные очаги в покрышке среднего мозга, а при MELAS — инфарктоподобные очаги в различных зонах ствола [24–26]. Кроме того, описывается переход синдрома Лея в MELAS [27].
Описано мультисистемное митохондриальное заболевание, специфически поражающее проводящие пути белого вещества, которое называется лейкоэнцефалопатией с поражением ствола головного мозга, спинного мозга и повышенным накоплением лактата (LBSL) [28]. Данное состояние ассоциировано с различными генетическими отклонениями, в частности с мутациями гена DARS2 [29]. При этом синдроме описано билатеральное симметричное поражение белого вещества медиальной петли, тригеминальной петли, пирамидных трактов, задних канатиков спинного мозга, верхних и нижних ножек мозжечка, белого вещества мозжечка; при МР-спектроскопии выявляется увеличение уровня лактата [28, 30].
Среди метаболических синдромов, поражающих ствол, центральный понтинный миелинолиз является МРТ-особенностью синдрома осмотической демиелинизации, метаболического синдрома, развивающегося у пациентов с тяжелыми электролитными нарушениями или быстрой коррекцией гипонатриемии [31, 32]. При этом состоянии в центральной части моста регистрируются Т2-гиперинтенсивные очаги с изменениями сигнала, связанными с поражением миелиновой оболочки, но не аксонов. В некоторых случаях появляется характерный «очаг в форме трезубца», для которого специфично отсутствие поражения кортикоспинальных трактов и вентролатеральной части моста. Такой очаг может распространяться до среднего мозга и средних ножек мозжечка [33]. При экстрапонтинном миелинолизе наблюдаются билатеральные симметричные Т2-ги-перинтенсивные очаги в области базальных ядер [22]. Это состояние является преходящим, и при восстановлении водно-электролитного баланса очаги, как правило, полностью исчезают [34].
У 20–30% младенцев с эпилепсией, получавших вигабатрин, описаны преходящие билатеральные симметричные Т2-гиперинтенсивные очаги в области покрышки, бледного шара и таламуса [35, 36]. Причины развития данного поражения неясны, однако известно, что наиболее выраженные МРТ-из-менения регистрируются через 3–6 мес от начала лечения [35].
клиническая; 20
Том 121 № 0 1
СТВОЛОВОЙ ЭНЦЕФАЛИТ У ДЕТЕЙ
Термины «ромбоэнцефалит» и «стволовой энцефалит» используются для обозначения одного и того же поражения, вовлекающего субтенториальные структуры — ствол мозга и мозжечок [22]. Это состояние воспалительной природы может быть инфекционным, аутоиммунным или пара-неопластическим. Инфекционный ромбоэнцефалит может наблюдаться при любом вирусном или бак- териальном энцефалите; в 50% случаев регистрируется вовлечение супратенториальных структур [37]. Наиболее часто стволовой энцефалит вызывается энтеровирусами 71-го типа, листериями, вирусом простого герпеса [38, 39]. МРТ-находки при этой патологии неспецифичны. Очаги обычно множественные, асимметричные, Т2-гиперинтен-сивные и не всегда накапливающие контрастное вещество в режиме Т1 (рис. 2).
Рис. 2. Пациент М., 9 лет. МРТ: вирусный энцефалит, острый период течения заболевания. Этиология — герпес II типа (IgM с крови)
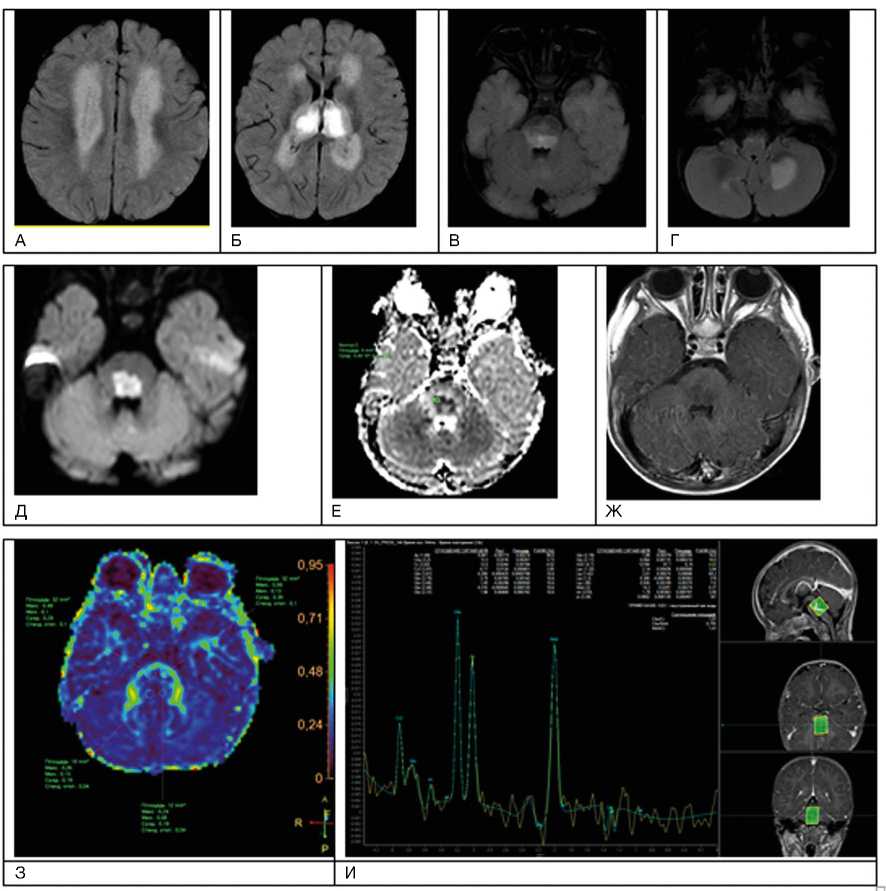
Примечание. А–И — последовательность Т2-flair. Имеется поражение зрительных бугров, глубокого перивентрику-лярного и субкортикального белого вещества лобных и теменных долей, задних отделов моста, глубоких отделов гемисфер мозжечка; Д, Е — с повышением сигнала за счет цитотоксического отека в стволе головного мозга при факторе взвешенности В1000 на диффузионно-взвешенных изображениях и признаками ограничения диффузии (измеряемый коэффициент диффузии снижен до 0,4 x 10 -3 мм2/с);Ж — при внутривенном контрастировании без нарушения гематоэнцефалического барьера в зоне поражения; З — при выполнении DTI МР-трактографии фракционная анизотропия в стволе снижена до 0,19; И — пики NAA и Cho практически одинаковые по высоте, т.е. косвенный признак снижения нейрональной плотности в зоне поражения, пик лактата (маркер анаэробного гликолиза) неубедителен на фоне шума (данные Детского научно-клинического центра инфекционных болезней ФМБА, Санкт-Петербург).
При некоторых вирусных энцефалитах (энцефалит Святого Луиса, японский энцефалит) регистрируется селективная уязвимость черной субстанции [40, 41]. Формирование абсцесса с кольцевым усилением сигнала после введения контрастного вещества наблюдается при поражении всех уровней ствола мозга, при инфекции, обусловленной Listeria monocytogenes [42]. При туберкулезе регистрируется милиарный паттерн [43]. Для обеих этих форм стволового энцефалита характерно формирование абсцессов, которые обычно расположены в мосту и выглядят как очаги с легкой Т2-гиперинтенсивно-стью сигнала вследствие формирования вазогенного отека. Центральная часть этих очагов может выглядеть изо- или гиперинтенсивной в Т2-режиме [44]. В случае формирования туберкуломы сигнал от центральной части очага — Т2-гипоинтенсивный [45]. Из-за гематогенного распространения распределение абсцессов обычно напоминает артериальную эмболию. Поражение ствола при энцефалите может быть ассоциированным с супратенториальными нарушениями, в некоторых случаях со специфическими симметричными билатеральными очагами в области базальных ядер.
Существует «только стволовой энцефалит», известный также как энцефалит Бикерстаффа, который, как предполагается, имеет воспалительную неинфекционную природу и в большинстве случаев аутоиммунную этиологию [46]. После того как была продемонстрирована патогенетическая роль антиганглиозидных антител, пациенты, у которых клинически наблюдался широкий спектр симптомов — от офтальмоплегии и атаксии до нарушения сознания и арефлексии, и которые ранее описывались как случаи симптома Миллера–Фишера, синдрома Гийена–Барре или энцефалита Бикерстаффа, стали расцениваться как больные синдромом анти-GQ1B антител [47–49]. В случае этих синдромов иммунная кросс-реакция, видимо, запускается предшествующим инфицированием Campylobacter jejuni и Mycoplasma pneumoniae [49, 50]. Энцефалит Бикерстаффа может имитировать глиому: для дифференциальной диагностики применяются исследование профиля метаболитов при МР-спектроскопии, повторная МРТ после терапии глюкокортикостероидами и анализ ликвора на ан-ти-GQ1B-антитела [48].
После обычных вирусных инфекций, таких как грипп А и В, парагрипп II, герпес-вирус VI типа, Коксаки вирус или энтеровирус, у иммунокомпетентных детей может развиться быстропрогрес- сирующая энцефалопатия, известная как острая некротизирующая энцефалопатия [51]. Она начинается в течение первых 4 сут от развития симптомов вирусной инфекции с летаргического состояния, которое затем в 50% случаев сменяется комой и судорогами. Среди пациентов, перенесших первый эпизод, у 50% развивается хотя бы одно обострение. Как семейные, так и спорадические формы развиваются у пациентов с миссенс-мутацией гена RAN-binding 2 [52]. Острая некротизирующая энцефалопатия считается другой нозологической формой, чем острый диссеминированный энцефаломиелит.
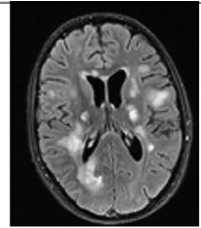
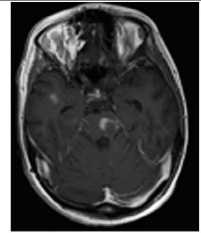
Острый диссеминированный энцефаломиелит в большинстве случаев — монофазное и мультифокальное воспалительное заболевание [38, 53, 54]. Стволовые очаги по данным МРТ невозможно дифференцировать от таковых при рассеянном склерозе, однако у таких пациентов чаще выявляются повреждения на уровне среднего мозга, кроме того, они более симметричны, билатеральны, чем при рассеянном склерозе [38, 55]. Билатеральное симметричное вовлечение мозжечка, базальных ядер, таламуса и относительная сохранность мозолистого тела подтверждают диагноз острого диссеминированного энцефаломиелита (рис. 3).
Кроме того, при повторных МРТ в периоде ре-конвалесценции очаги при остром диссеминированном энцефаломиелите уменьшаются в количестве, размерах, а также наблюдается ослабление интенсивности в режиме Т2. В 50% случаев очаги полностью исчезают [56]. При рассеянном склерозе часто происходит вовлечение ствола мозга. Очаги чаще расположены на дне 4-го желудочка, в периферических частях ствола, в особенности в мосту [57]. Субтенториальное расположение очагов считается специфичным для рассеянного склероза (пересмотренные критерии Мак-Дональда, 2017) [58]. Рассеянный склероз у детей наблюдается редко [59], тем не менее в дебюте заболевания вовлечение ствола и мозжечка, особенно у мальчиков, встречается чаще, чем у пациентов с дебютом в молодом возрасте [60, 61]. Это послужило основой для гипотезы, что при рассеянном склерозе преимущественно в иммунный процесс вовлечен более зрелый миелин [62]. Кроме того, необходимо отметить, что ствол мозга вовлекается в патологический процесс также при заболеваниях нейрооп-тикомиелитного спектра, что связано с образованием аутоантител к аквапорину-4 и в некоторых случаях в отсутствии этих антител [63].
клиническая; 20
тактика ™
в рассеянный склероз
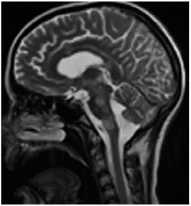
А. Т2-ВИ сагиттально
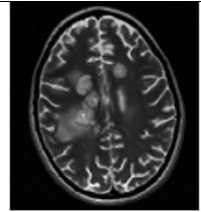
В. Т2-ВИ аксиально
Д. FLAIR аксиально
Ж. Т1-ВИ с контрастированием аксиально
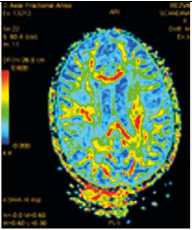
И. Карта фракционной анизотропии
Рис. 3. Пациентка Р., 15 лет. МРТ: острый диссеминированный энцефаломиелит с трансформацией
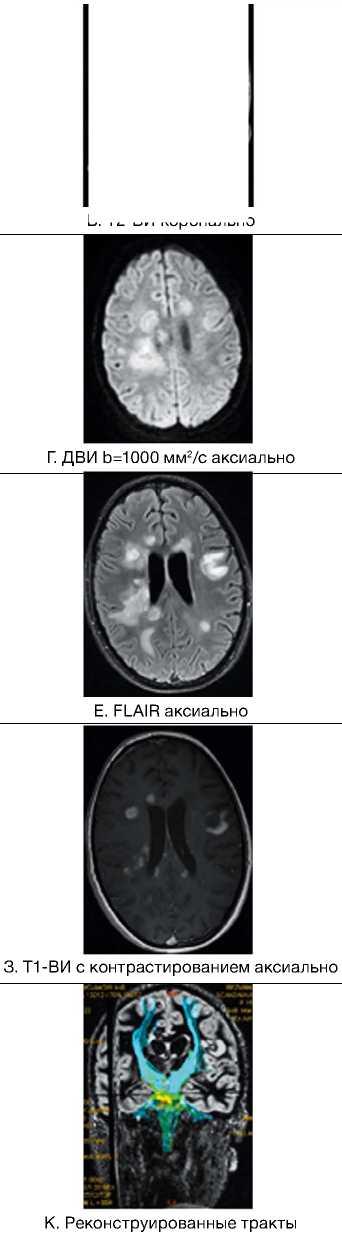
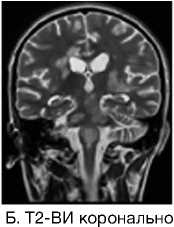
Примечание. Множественные перивентрикулярные, субкортикальные крупные очаги с нечеткими и неровными контурами, накапливающие контрастное вещество фрагментарно, преимущественно по краям (нарушение гематоэнцефалического барьера), с незначительным повышением МР-сигнала на ДВИ 1000 с/мм2 (отечные изменения). Внутренняя структура очагов неоднородная. Визуализируется поражение ствола мозга, спинного мозга и мозжечка. Ограничение фракционной анизотропии на уровне очагов (до 0,2) и снижение плотности реконструируемых трактов на этом уровне (данные Детского научно-клинического центра инфекционных болезней ФМБА России, Санкт-Петербург).
НЕЙРОДЕГЕНЕРАТИВНЫЕЗАБОЛЕВАНИЯ У ДЕТЕЙ
Дефицит кофактора молибдена является редким аутосомно-рецессивным нейродегенератив-ным заболеванием. Возможно, данная патология является не столько редкой, сколько трудно диагностируемой. При данном поражении развивается энцефалопатия с ранним дебютом или с поздним дебютом в атипичных случаях в виде общей задержки развития. Структурная МРТ и диффузионно-взвешенная МР-картина напоминает таковую при диффузном гипоксически-ишемическом поражении [64]. Тем не менее, в случае если наблюдается преимущественное вовлечение ножек мозга, бледного шара и субталамической области, это может заставить предположить описываемое состояние. Ранняя диагностика дефицита кофактора молибдена является критической для начала ранней поддерживающей и заместительной терапии, что позволяет предотвратить атрофию мозга [65].
Гипертрофическая дегенерация ядер оливы считается специфической формой транссинаптической гипертрофической дегенерации и развивается вследствие неспецифического повреждения денто-рубро-оливарного пути [66]. Хотя это состояние у детей считается редким, сообщается о его превалировании у пациентов с метаболическими заболеваниями, а также после операции по поводу опухолей задней черепной ямки [67, 68]. На МРТ выявляются Т2-гиперинтенсивные очаги, часто с билатеральным и симметричным увеличением оли-варных ядер. Они начинают появляться в течение месяца после острого события и в течение 3–4 лет имеют тенденцию к разрешению [69].
ОПУХОЛИ СТВОЛА МОЗГА У ДЕТЕЙ
МРТ-признаками глиомы ствола мозга являются Т2-гиперинтенсивные очаги с масс-эффектом, окружающие цистерны, 4-й желудочек, сильвиев водопровод и/или мозжечок. Чаще всего у детей развиваются отличающиеся по анатомии и клиническому течению 3 группы глиом ствола — это диффузная внутренняя понтинная глиома, экзофитиче-ская среднемозговая глиома и тектальная глиома [70]. Первый вариант имеет наихудший прогноз выживаемости (около 1 года) [71]. На МРТ отличительными особенностями являются перифокальный отек, отсутствие накопления контраста и масс-эф-фекта. Чаще всего возникает в возрасте 5–10 лет с развитием клинической триады — атаксии, поражения черепно-мозговых нервов и длинных трак- тов. В типичном случае поражение тотальное или субтотальное, чаще всего в мосту. Хотя отсутствие накопления контраста является характерной особенностью, в некоторых случаях наблюдается негомогенное частичное или периферическое накопление парамагнетика [72].
У детей младше 3 лет могут возникать солидные примитивные нейроэктодермальные опухоли. Они фокально, экзофитно расположены обычно в мосту, умеренно накапливают контраст и часто распространяются субарахноидально [73–75]. Опухоли ствола у детей также могут развиваться при неврофиброматозе 1-го типа [76, 77]. Чаще всего возникает астроцитома, которая растет менее агрессивно, чем у детей без неврофиброматоза [78]. У таких пациентов выявляются яркие Т2-гиперинтенсивные очаги, которые остаются стабильными и иногда исчезают у пациентов старше 12 лет [79]. Интракраниальное поражение ствола мозга может развиваться при гистиоцитозе клеток Лангерганса [80, 81]. Это редкое гранулематозное заболевание системы моноцит-макрофаг. Типичные клинические проявления при этом — литические очаги краниофациального скелета, вовлечение гипоталами-чески-питуитарной области, несахарный диабет. Интракраниально выявляются симметричные Т2-гиперинтенсивные очаги нейродегенерации и реже регистрируются массивные туморозные очаги [82].
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Поражение ствола мозга, изолированное или связанное с супратенториальными изменениями, возникает при широком спектре патологических состояний. Небольшой размер ствола, менее четкое различие между серым и белым веществом и определенное ограничение мультипараметри-ческой МРТ в случае исследования стволовых структур часто приводят к затруднениям в дифференциальной диагностике. Иногда большое диагностическое значение приобретают топография очага и интенсивность сигнала от него. Для целей дифференциальной диагностики основополагающее значение, тем не менее, играют клинические, эпидемиологические и лабораторные исследования.
ИСТОЧНИК ФИНАНСИРОВАНИЯ
Поисково-аналитическая работа проведена на личные средства авторского коллектива.
клиническая; 20
Том 121 № 0 1
Список литературы Магнитно-резонансная томография как инструмент дифференциальной диагностики при поражении ствола головного мозга у детей
- Ишков С.В., Левошко Л.И. Новые данные о проекционной анатомии отделов ствола головного мозга на основе компьютерно-томографических исследований // Морфология. - 2017. - Т.152. - №5. - С. 25-28.
- Bastianello S, Bozzao A, Paolillo A, et al. Fast spin-echo and fast fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery versus conventional spin-echo sequences for MR quantification of multiple sclerosis lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997;18(4):699-704.
- Li C, Yan JL, Torheim T, et al. Low perfusion compartments in glioblastoma quantified by advanced magnetic resonance imaging and correlated with patient survival. Radiother Oncol. 2019;134:17-24. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.01.008
- Kawanaka Y, Ando K, Ishikura R, et al. Delayed appearance of transient hyperintensity foci on T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Jpn J Radiol. 2019;37(4):277-282. DOI: 10.1007/s11604-018-00808-w
- Cai M, Zhang XF, Qiao HH, et al. Susceptibility-weighted imaging of the venous networks around the brain stem. Neuroradiology. 2015;57(2):163-169. DOI: 10.1007/s00234-014-1450-z
- Beller E, Keeser D, Wehn A, et al. T1-MPRAGE and T2-FLAIR segmentation of cortical and subcortical brain regions-an MRI evaluation study. Neuroradiology. 2019;61(2):129-136.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00234-018-2121-2
- Quattrocchi CC, Errante Y, Rossi Espagnet MC, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging differential diagnosis of brainstem lesions in children. World J Radiol. 2016;8(1):1-20.
- DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i1.1
- Войтенков В.Б., Карташев А.В. Ретикулярная формация головного мозга в норме и патологии. - СПб.: Реноме, 2013. - 115 с.
- Lagman-Bartolome AM, Pontigon AM, Moharir M, et al. Basilar artery strokes in children: good outcomes with conservative medical treatment. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2013;55(5):434-439.
- DOI: 10.1111/dmcn.12092
- Toi H, Uno M, Harada M. et al. Diagnosis of acute brain-stem infarcts using diffusion-weighed MRI. Neuroradiology. 2003;45(6):352-356.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00234-002-0897-5
- Uziel G, Ghezzi D, Zeviani M. Infantile mitochondrial encephalopathy. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011;16(4):205-215.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.siny.2011.04.003
- Wong LJ. Mitochondrial syndromes with leukoencephalopathies. Semin Neurol. 2012;32(1):55-61.
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0032-1306387
- Nishino I, Spinazzola A, Hirano M. Thymidine phosphorylase gene mutations in MNGIE, a human mitochondrial disorder. Science. 1999;283(5402):689-692.
- DOI: 10.1126/science.283.5402.689
- Tang S, Wang J, Lee NC, et al. Mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma mutations: an ever expanding molecular and clinical spectrum. J Med Genet. 2011;48(10):669-681.
- DOI: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100222
- Scheper GC, van der Klok T, van Andel RJ, et al. Mitochondrial aspartylt-RNA synthetase deficiency causes leukoencephalopathy with brain stem and spinal cord involvement and lactate elevation. Nat Genet. 2007;39(4):534-539.
- DOI: 10.1038/ng2013
- Uluc K, Baskan O, Yildirim KA, et al. Leukoencephalopathy with brain stem and spinal cord involvement and high lactate: a genetically proven case with distinct MRI findings. J Neurol Sci. 2008;273(1-2):118-122.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jns.2008.06.002
- Cavanagh JB. Selective vulnerability in acute energy deprivation syndromes. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1993;19(6):461-470.
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1993.tb00474.x
- Nagai T, Goto Y, Matsuoka T, et al. Leigh encephalopathy: histologic and biochemical analyses of muscle biopsies. Pediatr Neurol. 1992;8(5):328-332.
- DOI: 10.1016/0887-8994(92)90084-c
- Chen L, Cui Y, Jiang D, et al. Management of Leigh syndrome: Current status and new insights. Clin Genet. 2018;93(6):1131-1140.
- DOI: 10.1111/cge.13139
- Veiga MG, Marecos C, Duarte ST, et al. Leigh syndrome with atypical cerebellar lesions. eNeurological Sci. 2019;16:100-107.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ensci.2019.100197
- Bindu PS, Taly AB, Sonam K, et al. Bilateral hypertrophic olivary nucleus degeneration on magnetic resonance imaging in children with Leigh and Leigh-like syndrome. Br J Radiol. 2014;87:2013047.
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20130478
- Quattrocchi CC, Longo D, Delfino LN, et al. MR differential diagnosis of acute deep grey matter pathology in paediatric patients. Pediatr Radiol. 2013;43(6):743-761.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00247-012-2491-2
- Sparaco M, Bonilla E, Di Mauro S, Powers J.M. Neuropathology of mitochondrial encephalomyopathies due to mitochondrial DNA defects. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993;52(1):1-10.
- DOI: 10.1097/00005072-199301000-00001
- Ito S, Shirai W, Asahina M, Hattori T. Clinical and brain MR imaging features focusing on the brain stem and cerebellum in patients with myoclonic epilepsy with ragged-red fibers due to mitochondrial A8344G mutation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29(2):392-395
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A0865
- Valanne L, Ketonen L, Majander A, et al. Neuroradiologic findings in children with mitochondrial disorders. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998;19(2):369-377.
- Castillo M, Kwock L, Green C. MELAS syndrome: imaging and proton MR spectroscopic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1995;16(2):233-239.
- Kori A, Hori I, Tanaka T, et al. Transition from Leigh syndrome to MELAS syndrome in a patient with heteroplasmic MT-ND3 m.10158T>C. Brain Dev. 2019;41(9):803-807.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.braindev.2019.05.006
- Schicks J, Schöls L, van der Knaap MS, Synofzik M. Teaching NeuroImages: MRI guides genetics: leukoencephalopathy with brainstem and spinal cord involvement (LBSL). Neurology. 2013;80(16):e176-e177.
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31828cf846
- Yelam A, Nagarajan E, Chuquilin M, Govindarajan R. Leucoencephalopathy with brain stem and spinal cord involvement and lactate elevation: a novel mutation in the DARS2 gene. BMJ Case Rep. 2019;12(1):32-35.
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-227755
- Lan MY, Chang YY, Yeh TH, et al. Leukoencephalopathy with brainstem and spinal cord involvement and lactate elevation (LBSL) with a novel DARS2 mutation and isolated progressive spastic paraparesis. J Neurol Sci. 2017;372:229-231.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jns.2016.11.058
- Chinoy A, Wright NB, Bone M, Padidela R. Severe hypokalaemia in diabetic ketoacidosis: a contributor to central pontinemyelinolysis? Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2019;2019(1):30-35.
- DOI: 10.1530/EDM-19-0034
- Bansal LR, Zinkus T. Osmotic demyelination syndrome in children. Pediatr Neurol. 2019;97:12-17.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2019.03.018
- Alleman AM. Osmotic demyelination syndrome: central pontine myelinolysis and extrapontine myelinolysis. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2014;35(2):153-159.
- DOI: 10.1053/j.sult.2013.09.009
- Fuller K, Guerrero C, Kyin M, et al. The role of the interdisciplinary team in subacute rehabilitation for central pontine myelinolysis. Disabil Rehabil. 2019;1:1-7.
- DOI: 10.1080/09638288.2019.1579261
- Milh M, Villeneuve N, Chapon F, et al. Transient brain magnetic resonance imaging hyperintensity in basal ganglia and brain stem of epileptic infants treated with vigabatrin. J Child Neurol. 2009;24(3):305-315.
- DOI: 10.1177/0883073808324219
- Dracopoulos A, Widjaja E, Raybaud C, et al. Vigabatrin-associated reversible MRI signal changes in patients with infantile spasms. Epilepsia. 2010;51(7):1297-1304.
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2010.02564.x
- Skripchenko NV, Ivanova GP, Skripchenko EY, Murina EA. Panencephalitis in children in modern conditions: clinical, etiological and MRI-aspects. Zh Nevrol PsikhiatrIm S S Korsakova. 2019;119(6):20-31.
- DOI: 10.17116/jnevro201911906120
- Skripchenko EY, Ivanova GP, Karev VE, Skripchenko NV. [Difficulties of differential diagnosis of organic injury of the nervous system in children. (In Russ).]. Zh Nevrol PsikhiatrIm S S Korsakova. 2018;118(5):25-30.
- DOI: 10.17116/jnevro20181185225
- Jubelt B, Mihai C, Li TM, Veerapaneni P. Rhombencephalitis / brainstem encephalitis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2011;11(6):543-552.
- DOI: 10.1007/s11910-011-0228-5
- Wasay M, Diaz-Arrastia R, Suss RA, et al. St Louis encephalitis: a review of 11 cases in a 1995 Dallas, Tex, epidemic. Arch Neurol. 2000;57(1):114-118.
- DOI: 10.1001/archneur.57.1.114
- Kalita J, Misra UK. The substantianigra is also involved in Japanese encephalitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000;21(10):1978-1980.
- Reynaud L, Graf M, Gentile I, et al. A rare case of brainstem encephalitis by Listeria monocytogenes with isolated mesencephalic localization. Case report and review. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007;58(1):121-123.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2006.11.001
- Nogueira Delfino L, Fariello G, Lancella L, et al. Central nervous system tuberculosis in non-HIV-positive children: a singlecenter, 6 year experience. Radiol Med. 2012;117(4):669-678.
- DOI: 10.1007/s11547-011-0743-0
- Ramalho J, Castillo M. Case of the season: brainstem abscess. Semin Roentgenol. 2008;43(3):168-170.
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ro.2008.03.001
- Akhaddar A, Mahi M, Harket A, et al. Brainstem tuberculoma in a postpartum patient. J Neuroradiol. 2007;34(5):345-346.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurad.2007.09.001
- Tan IL, Mowry EM, Steele SU, et al. Brainstem encephalitis: etiologies, treatment, and predictors of outcome. J Neurol. 2013;260(9):2312-2319.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-013-6986-z
- Odaka M, Yuki N, Hirata K. Anti-GQ1b IgG antibody syndrome: clinical and immunological range. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001;70(1):50-55.
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.70.1.50
- Shahrizaila N, Yuki N. Bickerstaff brainstem encephalitis and Fisher syndrome: anti-GQ1b antibody syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013;84(5):576-583.
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2012-302824
- Ito M, Kuwabara S, Odaka M, et al. Bickerstaff's brainstem encephalitis and Fisher syndrome form a continuous spectrum: clinical analysis of 581 cases. J Neurol. 2008;255(5):674-682.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-008-0775-0
- Steer AC, Starr M, Kornberg AJ. Bickerstaff brainstem encephalitis associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. J Child Neurol. 2006;21(6):533-534.
- DOI: 10.1177/08830738060210061401
- Wang GF, Li W, Li K. Acute encephalopathy and encephalitis caused by influenza virus infection. Curr Opin Neurol. 2010;23(3):305-311.
- DOI: 10.1097/wco.0b013e328338f6c9
- Gika AD, Rich P, Gupta S, et al. Recurrent acute necrotizing encephalopathy following influenza A in a genetically predisposed family. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2010;52(1):99-102.
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03405.x
- Caldemeyer KS, Smith RR, Harris TM, Edwards MK. MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Neuroradiology. 1994;36(3):216-220.
- DOI: 10.1007/bf00588134
- Rossi A. Imaging of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2008;18(1):149-161.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nic.2007.12.007
- Lu Z, Zhang B, Qiu W, et al. Comparative brain stem lesions on MRI of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, and multiple sclerosis. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e22766.
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022766
- Atzori M, Battistella PA, Perini P, et al. Clinical and diagnostic aspects of multiple sclerosis and acute monophasic encephalomyelitis in pediatric patients: a single centre prospective study. Mult Scler. 2009;15(3):363-370.
- DOI: 10.1177/1352458508098562
- Yousry TA, Grossman RI, Filippi M. Assessment of posterior fossa damage in MS using MRI. J Neurol Sci. 2000;172(Suppl 1):S50-S53.
- DOI: 10.1016/s0022-510x(99)00279-8
- Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B, et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol. 2011;69(2):292-302.
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.22366
- Лобзин Ю.В., Скрипченко Н.В., Иванова Г.П., Команцев В.Н. Диссеминированный лейкоэнцефалит и рассеянный склероз: причинно-следственная взаимосвязь // Саратовский научно-медицинский журнал. - 2013. - Т.9. - №2. - С. 170-178.
- Chabas D, Strober J, Waubant E. Pediatric multiple sclerosis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2008;8(5):434-441.
- DOI: 10.1007/s11910-008-0067-1
- Ghassemi R, Antel SB, Narayanan S, et al. Lesion distribution in children with clinically isolated syndromes. Ann Neurol. 2008;63(3):401-405.
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.21322
- Ghassemi R, Narayanan S, Banwell B, et al. Quantitative determination of regional lesion volume and distribution in children and adults with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e85741.
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085741
- Wingerchuk DM, Banwell B, Bennett JL, et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitisoptica spectrum disorders. Neurology. 2015;85(2):177-189.
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001729
- Екушева Е.В., Данилов А.Б. Наследственная спастическая параплегия (обзор) // Журнал неврологии и психиатрии им. С.С. Корсакова. - 2002. - Т.102. - №8. - С. 44-52.
- Vijayakumar K, Gunny R, Grunewald S, et al. Clinical neuroimaging features and outcome in molybdenum cofactor deficiency. Pediatr Neurol. 2011;45(4):246-252.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2011.06.006
- Екушева Е.В. Сенсомоторная интеграция при поражении центральной нервной системы: клинические и патогенетические аспекты: Автореф. дис.... докт. мед. наук. - М., 2016. - 48 с. Доступно https://search.rsl.ru/ru/record/01006661768. Ссылка активна на 14.12.2019.
- Sonam K, Khan NA, Bindu PS, et al. Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with Leigh syndrome and SURF1 mutations. Brain Dev. 2014;36(9):807-812.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.braindev.2013.10.012
- Mirabelli-Badenier M, Morana G, Bruno C, et al. Inferior olivary nucleus involvement in pediatric neurodegenerative disorders: does it play a role in neuroimaging pattern-recognition approach? Neuropediatrics. 2015;46(2):104-109.
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1544185
- Tartaglione T, Izzo G, Alexandre A, et al. MRI findings of olivary degeneration.after surgery for posterior fossa tumours in children: incidence, time course and correlation with tumour grading. Radiol Med. 2015;120(5):474-482.
- DOI: 10.1007/s11547-014-0477-x
- Grimm SA, Chamberlain MC. Brainstem glioma: a review. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2013;13(5):346.
- DOI: 10.1007/s11910-013-0346-3
- Garzón M, García-Fructuoso G, Guillén A, et al. Brain stem tumors in children and adolescents: single institutional experience. Childs Nerv Syst. 2013;29(8):1321-1331.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00381-013-2137-1
- Guillamo JS, Doz F, Delattre JY. Brain stem gliomas. Curr Opin Neurol. 2001;14(6):711-715.
- DOI: 10.1097/00019052-200112000-00006
- Nowak J, Seidel C, Pietsch T, et al. Ependymoblastoma of the brainstem: MRI findings and differential diagnosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2014;61(6):1132-1134.
- DOI: 10.1002/pbc.24915
- Zagzag D, Miller DC, Knopp E, et al. Primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the brainstem: investigation of seven cases. Pediatrics. 2000;106(5):1045-1053.
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.106.5.1045
- Екушева Е.В., Данилов А.Б., Вейн А.М. Синдром гемипареза: клинико-патофизиологический анализ // Журнал неврологии и психиатрии им. С.С. Корсакова. - 2002. - Т.102. - №11. - С. 18-28.
- Bilaniuk LT, Molloy PT, Zimmerman RA, et al. Neurofibromatosis type 1: brain stem tumours. Neuroradiology. 1997;39(9):642-653.
- DOI: 10.1007/s002340050484
- Guillamo JS, Créange A, Kalifa C, et al. Prognostic factors of CNS tumours in Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1): a retrospective study of 104 patients. Brain. 2003;126(Pt 1):152-160.
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awg016
- Ullrich NJ, Raja AI, Irons MB, et al. Brainstem lesions in neurofibromatosis type 1. Neurosurgery. 2007;61(4):762-766; discussion 766-767.
- DOI: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000298904.63635.2D
- Hervey-Jumper SL, Singla N, Gebarski SS, et al. Diffuse pontine lesions in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: making a case for unidentified bright objects. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2013;49(1):55-59.
- DOI: 10.1159/000355417
- Grois N, Fahrner B, Arceci RJ, et al. Central nervous system disease in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. J Pediatr. 2010;156(6):873-881.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.03.001
- Savardekar A, Tripathi M, Bansal D, et al. Isolated tumorous Langerhans cell histiocytosis of the brainstem: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2013;12(3):258-261.
- DOI: 10.3171/2013.6.PEDS13132
- Prosch H, Grois N, Wnorowski M, et al. Longterm MR imaging course of neurodegenerative Langerhans cell histiocytosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28(6):1022-1028.
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A0509


